physical methods in forensic science exam 2
1/211
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
212 Terms
trace evidence
small, often microscopic, objects that are readily transferred between people and places
BLANK are normally the first examinations performed at the first FBI lab
microscopic comparison of fibers and hairs
earliest and simplest microscope was the single lens commonly referred to as a BLANK
magnifying glass
refraction
an abrupt change in direction of the beam is observed as a consequence of the difference in the velocity of light in the two media
visual image
can be seen only by looking through the lens
real image
can be seen directly (naked eye)
types of microscopes
compound microscope
comparison microscope
stereoscopic microscope
polarizing microscope
microspectrophotometer
scanning electron microscope (SEM)
compound microscope
constructed of two lenses mounted at each end of a hollow tube
for compound microscope, object to be magnified is placed under the BLANK
lower lens (objective lens)
for compound microscope, the magnified image is viewed through the BLANK
upper lens (eyepiece lens)
objective lens forms BLANK
real, inverted, magnified image of the object
eyepiece further magnifies the image into the BLANK
virtual image, which can be seen the eye
parts of compound microscope
base
arm
stage
body tube
coarse adjustment
fine adjustment
illuminator/light source
condensor
objective lens
eye piece or ocular lens
stage
a horizontal plate where the samples are placed to be examined
fine focus adjustment
focuses the microscope lenses (raises and lowers stage) on the specimen at a smaller magnitude
arm
supports the microscope and acts as a handle for carrying
light source
illuminates the specimen that is being examined
eyepiece/ocular lens
magnifies the image produced by the microscope’s objective
course focus adjuustment
focuses the microscope lenses on the specimen by raising and lowering the body tube or stage by larger magnitudes
diaphragm, iris, condenser
adjust the brightness and contrast on the specimen
nosepiece/turret
hold objective lenses in place
base
the support on which the instrument rests and assists in transporting
body tube
serves as a corridor through which light passes from one lens to another, the objective and eyepiece lenses are mounted on opposite lenses
objective lenses
to capture light emitted or reflected by specimen
stage clip
to securely hold the specimen in place
the compound microscope uses BLANK
transmitted illumination
transmitted illumination
light passes up from the condenser and through the specimen (bottom to top)
vertical or reflected illumination
illumination of a specimen from above; in microscopy it is used to examine opaque specimens (top to bottom)
compound microscopes can view
glass, body fluids, cells (transparent & translucent samples)
compound microscope has up to BLANK
1500x magnification
the magnifying power of a microscope is determined by BLANK
multiplying the power of the objective lens by the power of the ocular lens
ocular lens =
10x
field of view
what the examiner sees when looking through the eyepiece
depth of focus can be BLANK
adjusted
lower magnification =
higher depth of focus
higher magnification =
lower depth of focus
comparison microscope can be used to BLANK
compare two specimens
comparison microscope is essentially BLANK
two microscopes connected by an optical bridge
comparison microscope uses BLANK
vertical illumination (top to bottom)
comparison microscopes can compare these specimens side by side
bullet, cartridges, hairs, fibers (translucent & opaque evidence)
when looking through the eyepiece lenses of a comparison microscope, a circulare field, BLANK, is observed
equally divided into two parts by a fine line
stereomicroscope is the ideal instrument for location BLANK
trace evidence in debris, garments, weapons, or tools
a stereomicroscope has BLANK
a wide field of view
long working distance
great depth of focus
the most frequently used and versatile microscope in crime lab
stereomicroscope
stereomicroscope provides BLANK
10x to 125x magnifying power
stereomicroscope presents BLANK
distinctive 3D image of object
polarizing microscope uses BLANK
the difference in how light travels through minerals if different directions
polarizing microscope can distinguish between BLANK
isotropic and anisotropic materials
pleochroism
the property that causes a substance viewed under a polarizing microscope to show different absorption colors when it is exposed to polarized light coming from different directions
amorphous materials
minerals whose atoms are arranged in random order
crystalline materials
minerals whose atoms are arranged in a distinct order
examples of isotropic materials
gasses, liquids, cubic crystals
isotropic materials
same optical properties observed from any direction
examples of anisotropic (or birefringent) materials
quartz, calcite, asbestos
anisotropic (or birefringent) materials
arrangement of atoms is not the same in all directions and thus the arrangement of atoms in the substance appears to change as the direction of observation chances
microspectrophotometer combines BLANK
the capabilities of a spectrophotometer with those of a microscope
with a microspectrophotometer, the microscope BLANK
magnifies the image of the specimen
with a microspectrophotometer, the spectrophotometer BLANK
measures the intensity of light at each wavelegnth
scanning electron microscope (SEM) is used when BLANK
evidence is extremely small and more magnification is needed
SEM can magnify an image BLANK
100,000x
SEM has a depth of focus more than BLANK of an optical microscope
300x
SEM sends BLANK
beams of electron
SEM can view
fine details
hair is strong corroborative evidence for placing an individual at the scene of a crime when:
it is properly collected at crime scene
enough reference samples have been submitted to lab
hair is primarily made of BLANK
keratin
3 layers of hair shaft
medulla
cortex
cuticle
cuticle
outside layer, overlapping keratin cells
cortex
middle layer
medulla
innermost layer
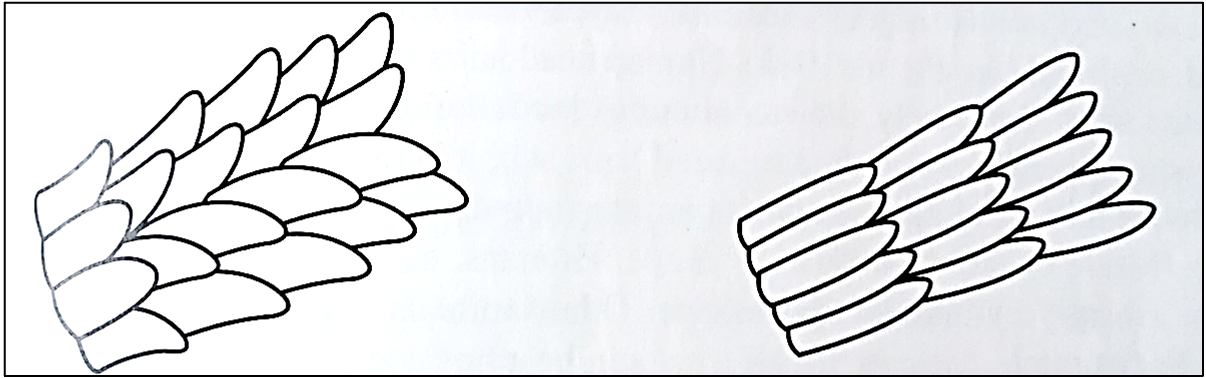
types of cuticle patters
coronal
spinous
imbricate
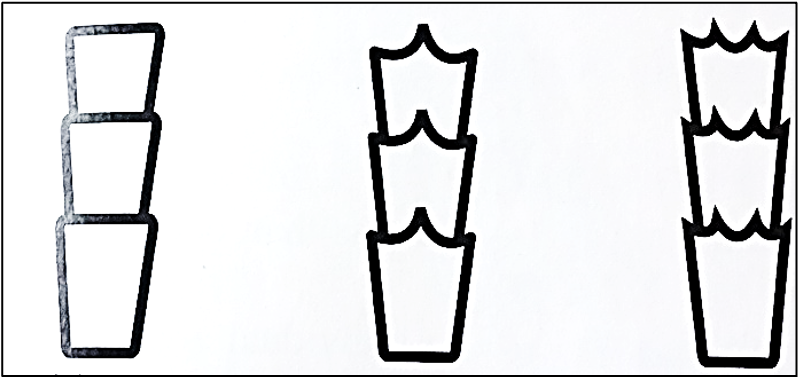
what pattern is this
coronal (crown-like)
what pattern is this
spinous (petal-like)
what pattern is this
imbricate (flattened-scale)
example of imbricate pattern
human
example of coronal pattern type
rodents and bats
example of spinous pattern type
cats
ways to study scale patterns
viewing under scanning electron microscope (SEM)
make a cast of the scale surface
how to make cast of scale surface
embed hair in soft medium (clear nail polish or softened vinyl)
when medium harden, remove hair
clear, distinct impression of cuticle is left
can now be examined by compound microscope
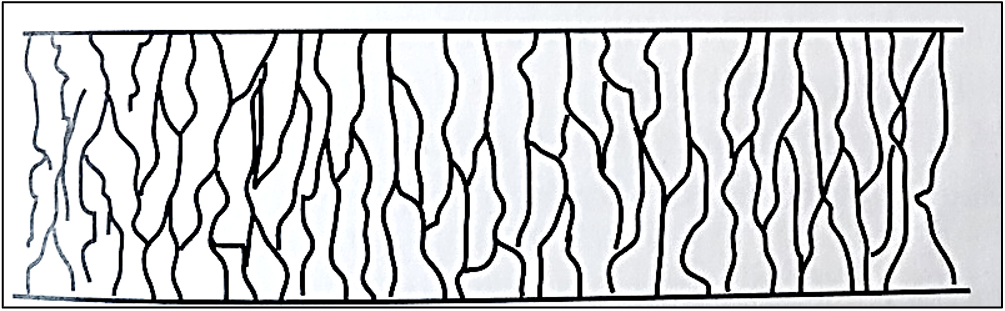
cortex is made of BLANK aligned in a regular array, parallel to the length of the hiar
spindle-shaped cells
cortex is embedded with pigment granules giving hair its BLANK
color
the color, shape, and distribution of granules of the cortex provide points for BLANK
forensic comparison
steps for forensic comparison of cortex
hair mounted in liquid medium with RI close to that of hair
structural features examined under microscope
amount of light reflected off hair’s surface is minimized
amount of light getting through hair is optiminized
the medulla is a BLANK
concentration of cells resembling a central canal running through center of cortex
types of medulla
continuous, interrupted, fragmented
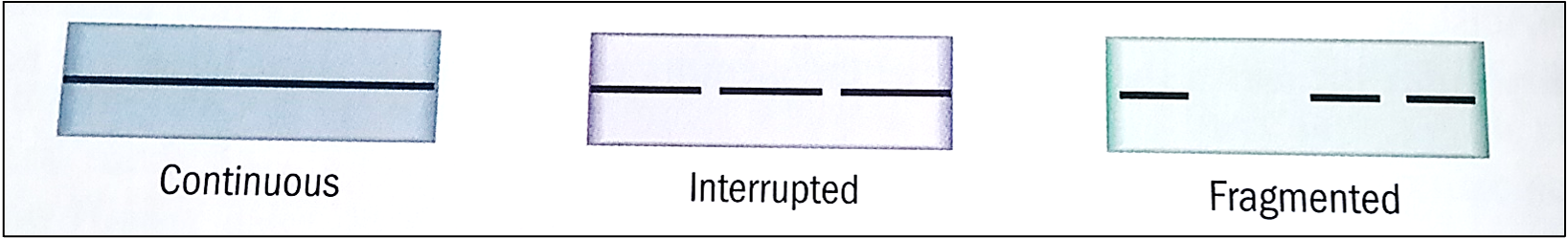
most animals have BLANK or BLANK medulla
continuous or interrupted
presence of medulla BLANK even from hair to hair
varies
human head hairs generally have BLANK or BLANK
no medulla or it may be fragmented

humans and most animals have what shaped medulla
cylindrical
cats have what shaped medulla
string of pearls
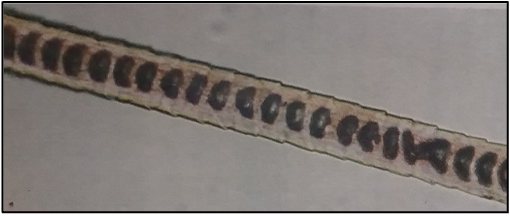
deers have what shaped medulla
spherical cells occupying entire hair shaft

medullary index
measures diameter of the medulla relative to diameter of the hair shaft
equation for medullary index
diameter of medulla / diameter of hair shaft
humans’ medullary index is BLANK
< 1/3
most other animals medullar index is BLANK
> 1/2
hair growth phases
anagen
catagen
telogen
anagen
actively growing phase
may last up to 6 years
when pulled from root, some hairs have follicular tag
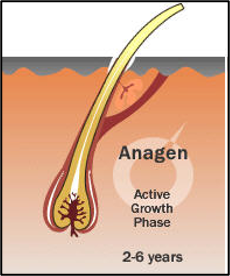
we need the BLANK in hair
follicular tag
follicular tag contains BLANK
richest source of DNA associated with hair
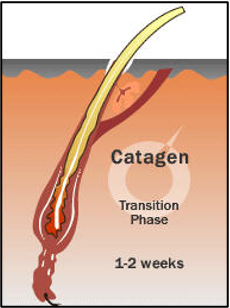
catagen
transition stage between anagen and telogen
lasts only 2-3 weeks
hair continues to grow at decreasing rate
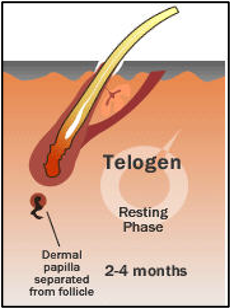
telogen
final growth phase
lasts 2-6 months
hair pushed out follicle
hair shedding