VSEPR Theory and Molecular Geometry Overview
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
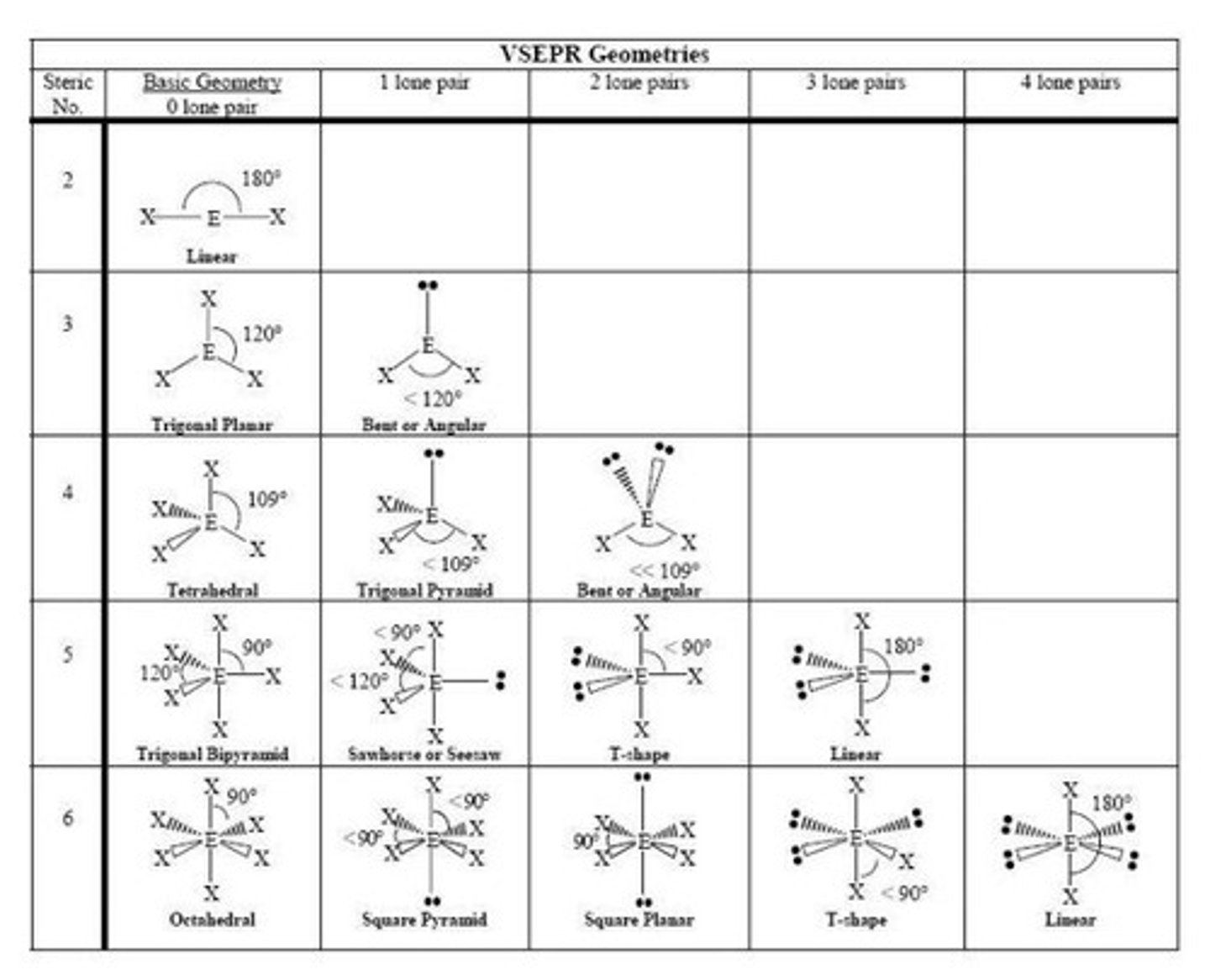
VSEPR Model
Predicts molecular shape by minimizing electron repulsion.
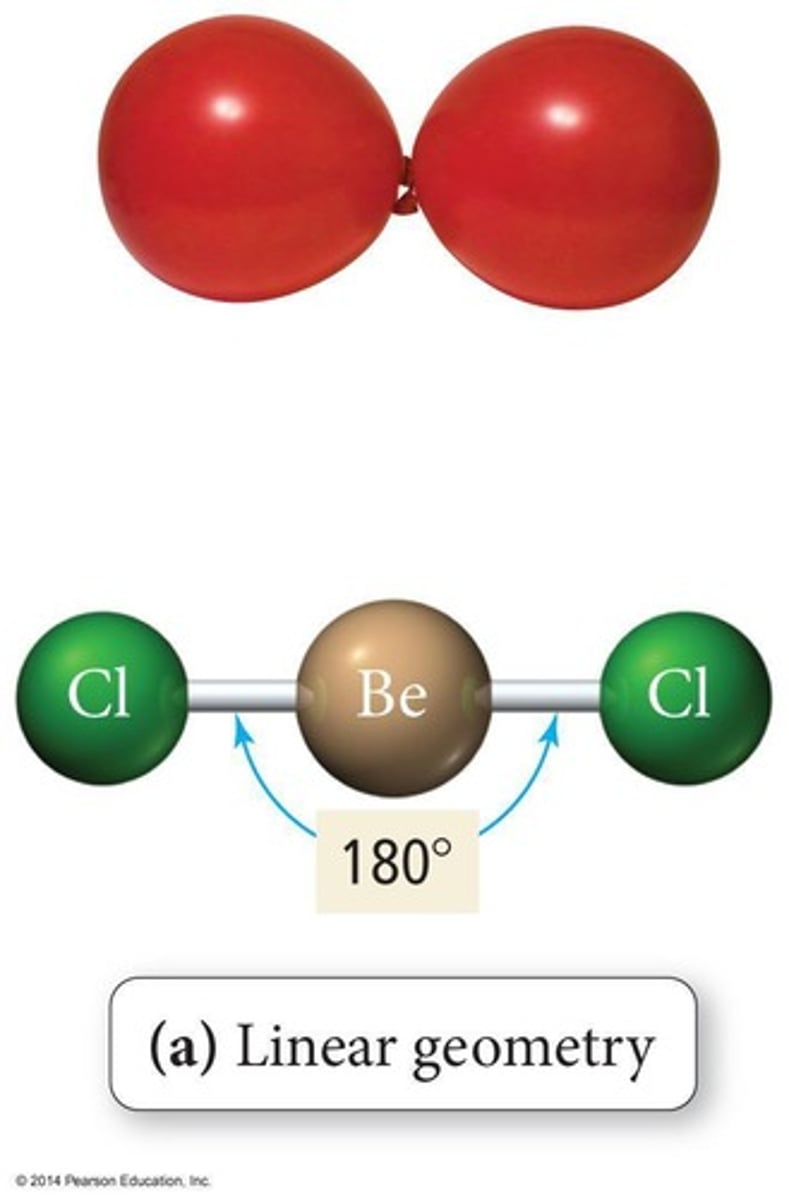
Linear Geometry
Molecule shape with two bonded atoms, 180° angle.
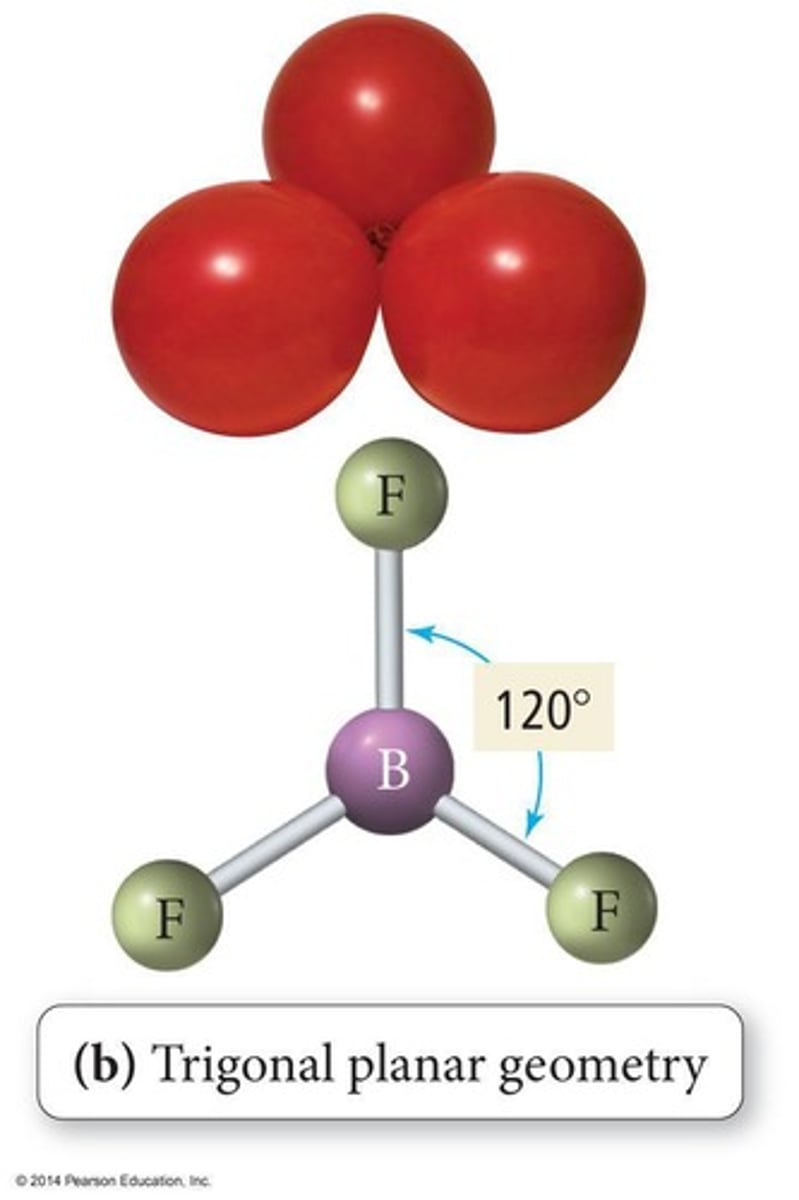
Trigonal Planar Geometry
Three bonded atoms, 120° bond angles.
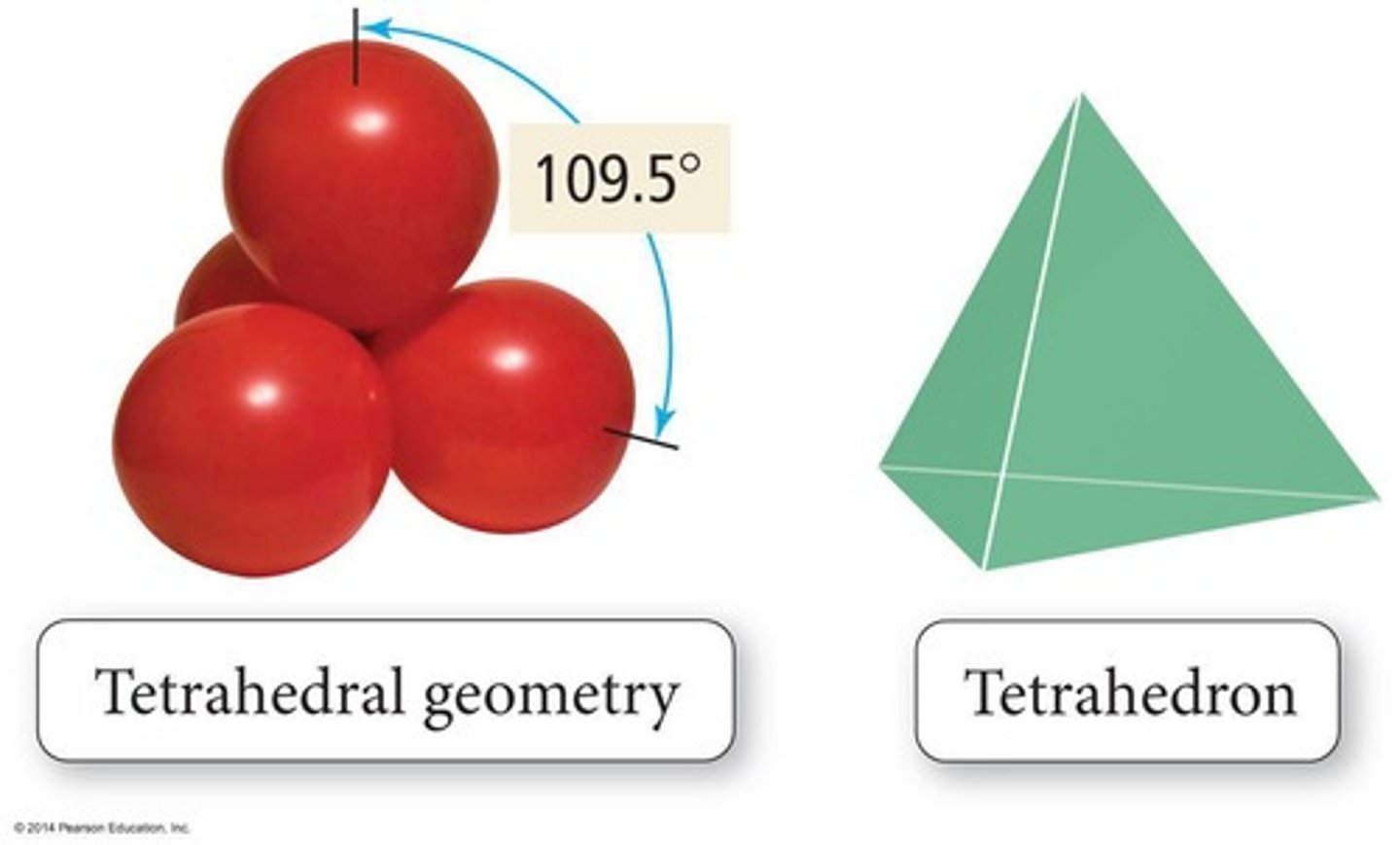
Tetrahedral Geometry
Four bonded atoms, 109.5° bond angles.
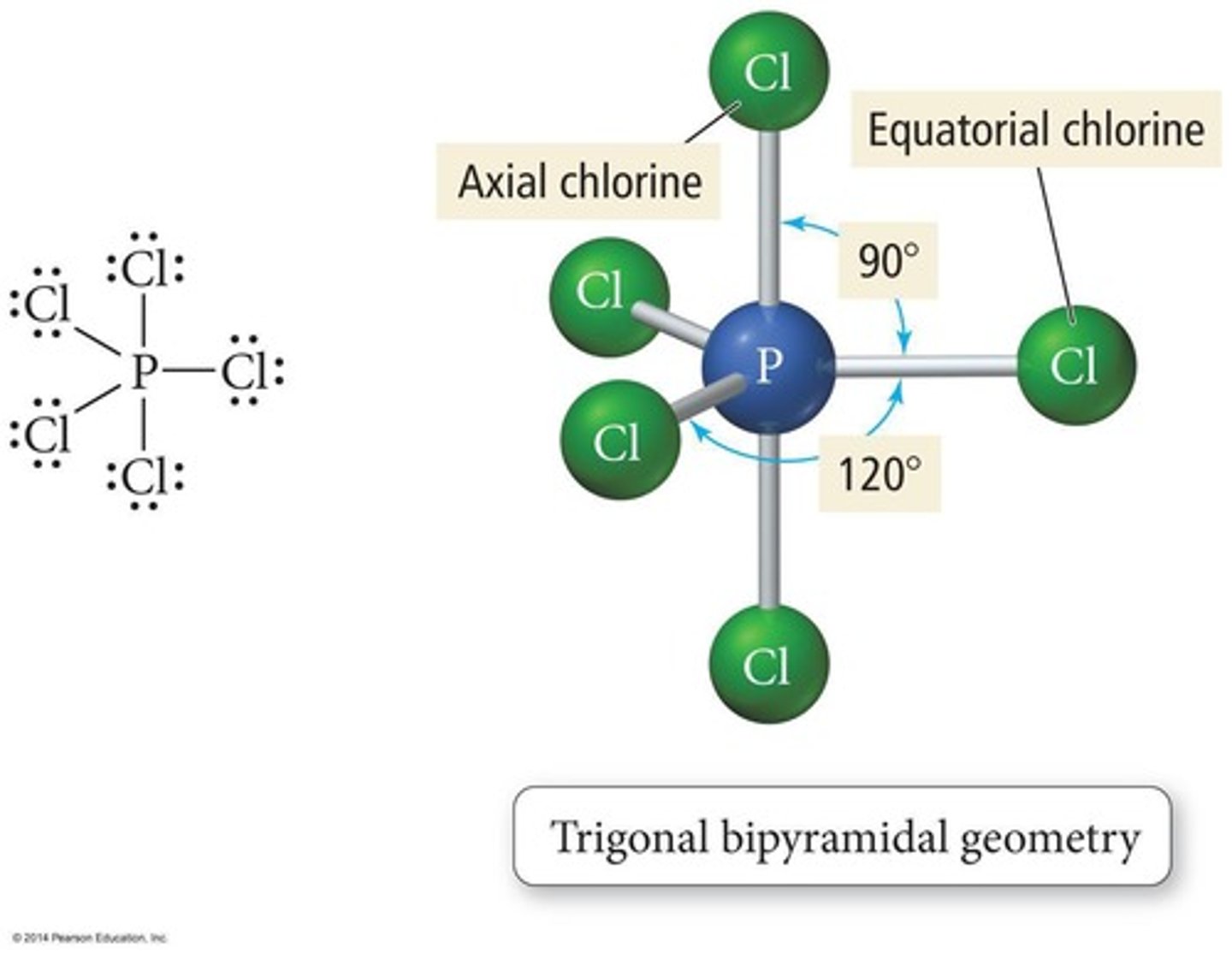
Trigonal Bipyramidal
Five bonded atoms, 90° and 120° angles.
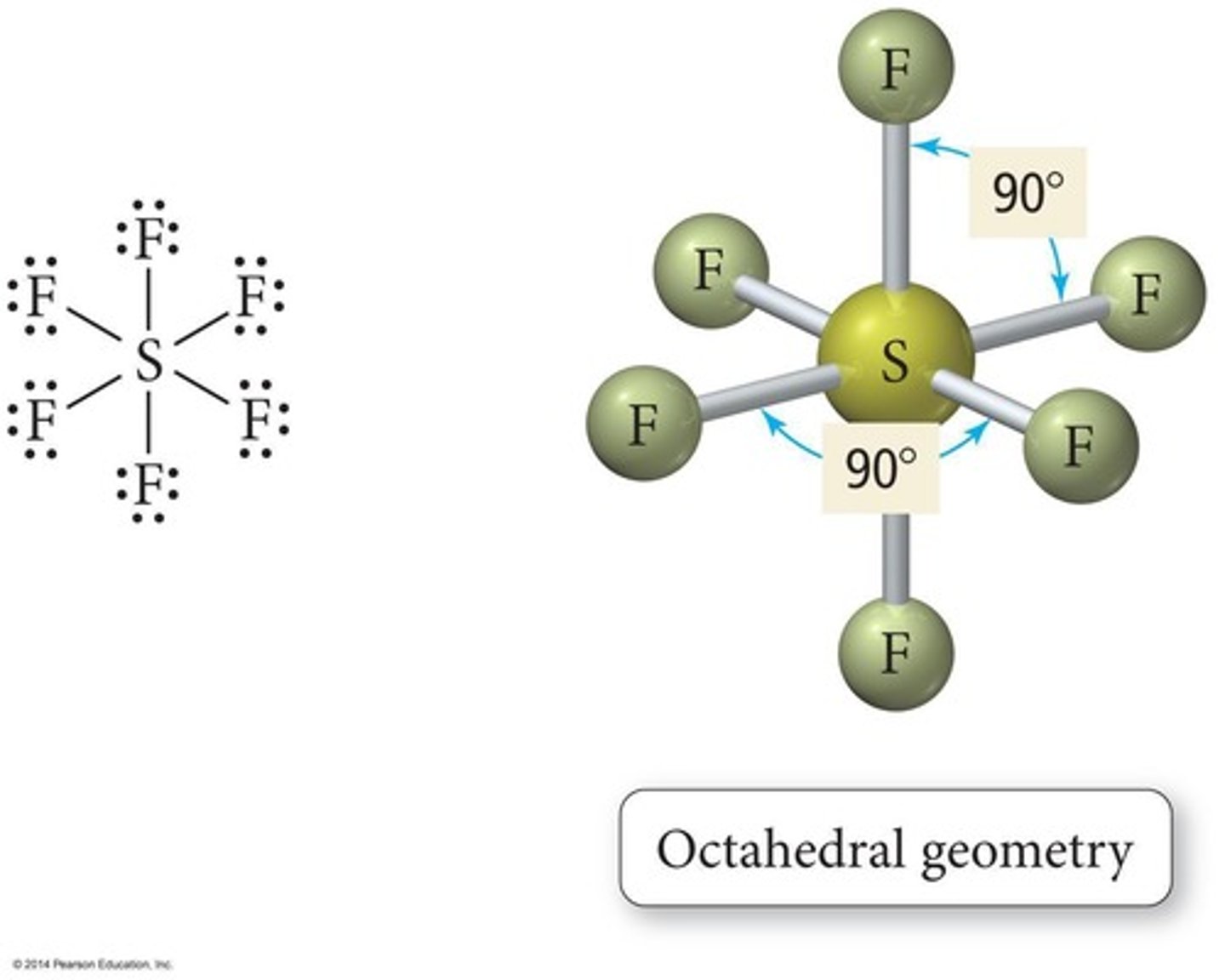
Octahedral Geometry
Six bonded atoms, 90° bond angles.
Lone Pair
Non-bonding electrons affecting molecular shape.
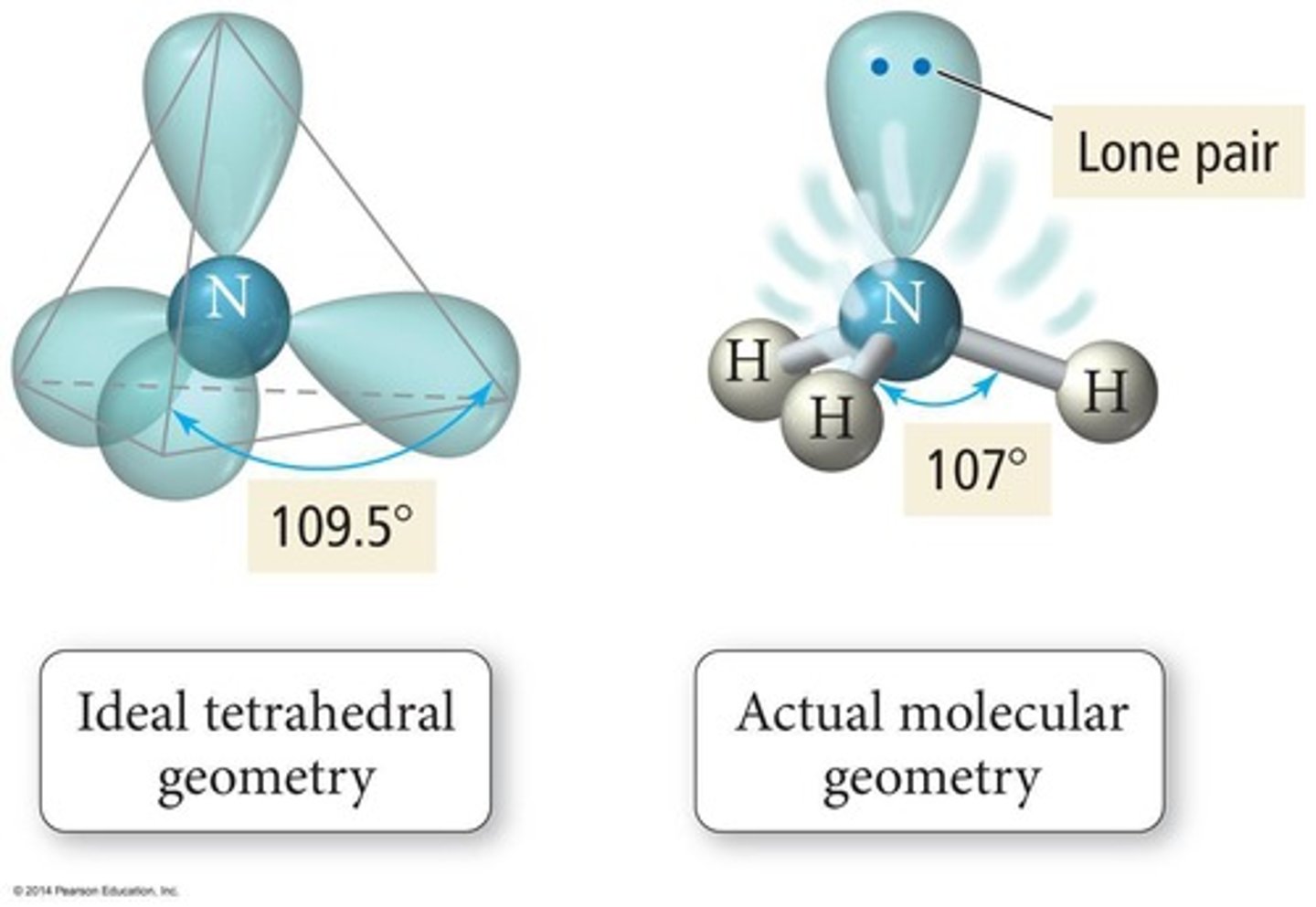
Bond Angle Distortion
Lone pairs reduce bond angles between atoms.
Hybridization
Mixing orbitals to form new hybrid orbitals.
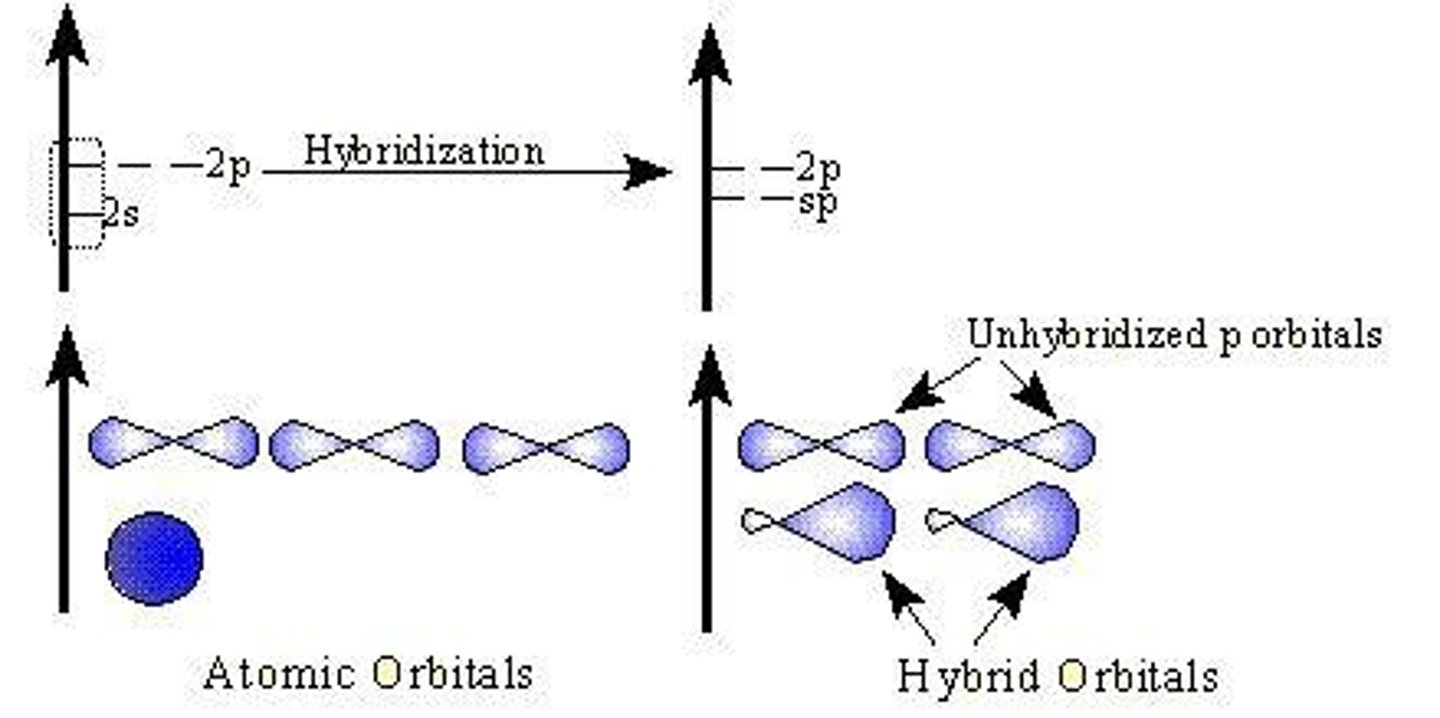
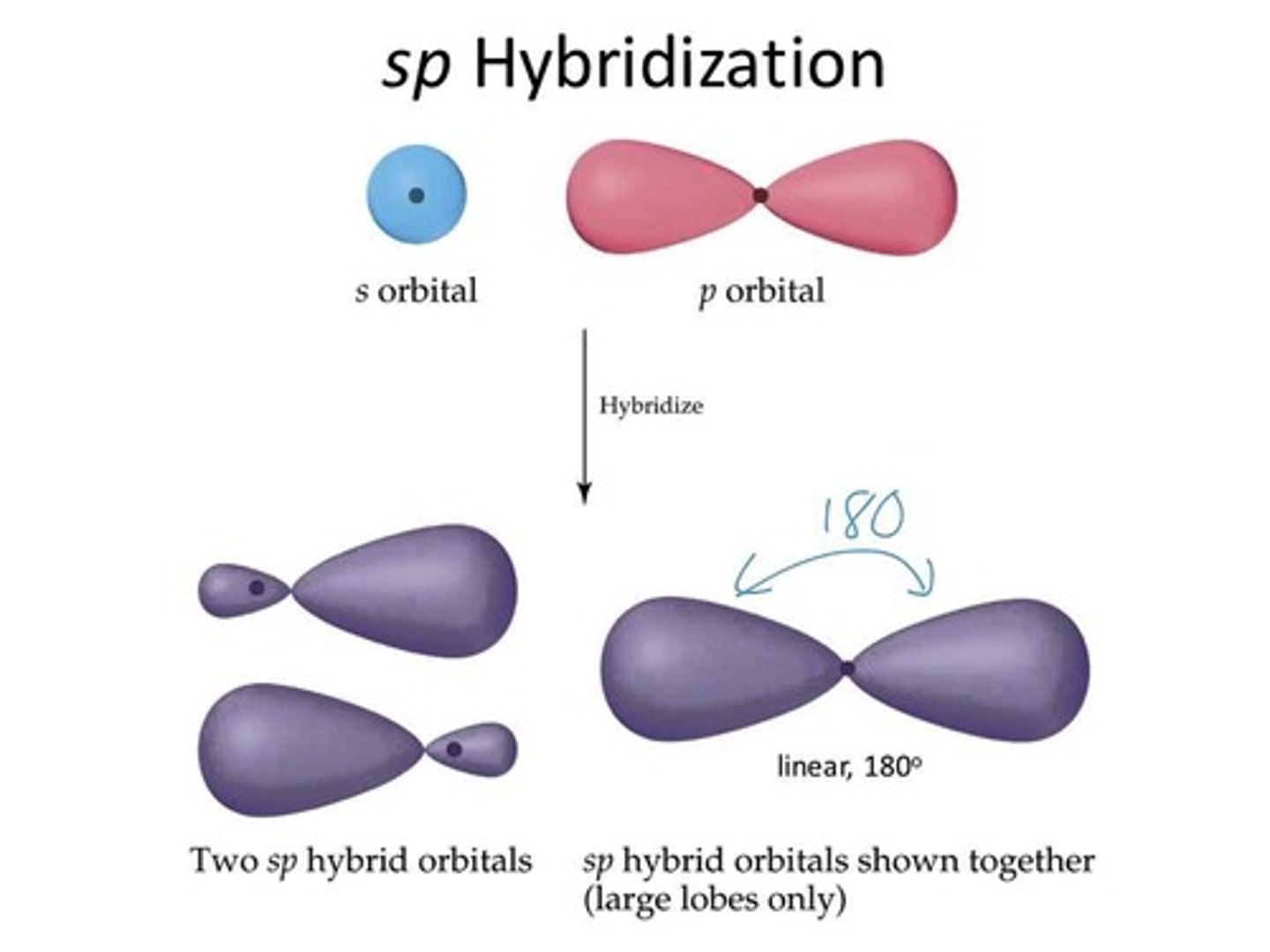
sp Hybrid Orbitals
One s and one p orbital hybridize.
sp2 Hybrid Orbitals
One s and two p orbitals hybridize.
sp3 Hybrid Orbitals
One s and three p orbitals hybridize.
VSEPR - AXE Method
A: central atom, X: bonded atoms, E: lone pairs.
Steric Number
Sum of bonded atoms and lone pairs.
Valence Electrons
Electrons in the outer shell available for bonding.
Octet Rule
Atoms prefer to have eight electrons in outer shell.
Expanded Octet
More than eight electrons in the valence shell.
Ionic Compounds
Formed by the attraction of cations and anions.
Covalent Molecules
Atoms share electrons to achieve full outer shells.
Cation
Positively charged ion from lost electrons.
Anion
Negatively charged ion from gained electrons.
Placement Rules
Guidelines for arranging atoms in molecular structures.
Symmetry in Molecules
Balanced arrangement of atoms for stability.
Lewis Structures
Diagrams showing valence electrons and bonds.