Brain's Lobes, Diencephalon (Interbrain), Brain stem and Cerebellum
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms

The Frontal Lobe
Decision making, problem solving, deliberate movements, consciousness, emotions
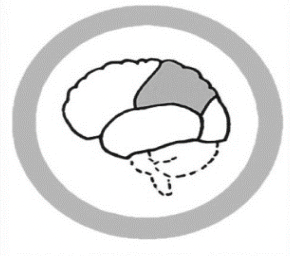
The Parietal Lobe
Processing sensory information, body orientation, attention
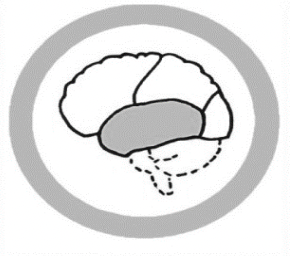
The Temporal Lobe
Auditory processing, language comprehension, speech
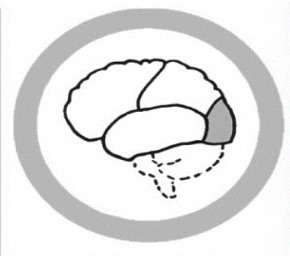
The Occipital Lobe
Visual processing, object recognition
Diencephalon (Interbrain)sits atop ____________, is enclosed by ____________
brain stem, cerebral hemispheres
Thalamus: Relay station for ____________ passing upward to sensory cortex
sensory impulses
Thalamus: Gives crude idea if we are expecting something ____________
pleasant or unpleasant
Hypothalamus: Regulates ____________________________________
body temperature, water balance, and metabolism
Hypothalamus: Called the “_________________” brain
emotional- visceral
________________________________________________ centers are in the hypothalamus
Thirst, appetite, sex, pain, and pleasure
Epithalamus includes ____________ and ____________
pineal gland; choroid plexus
Choroid plexus makes ____________
cerebrospinal fluid
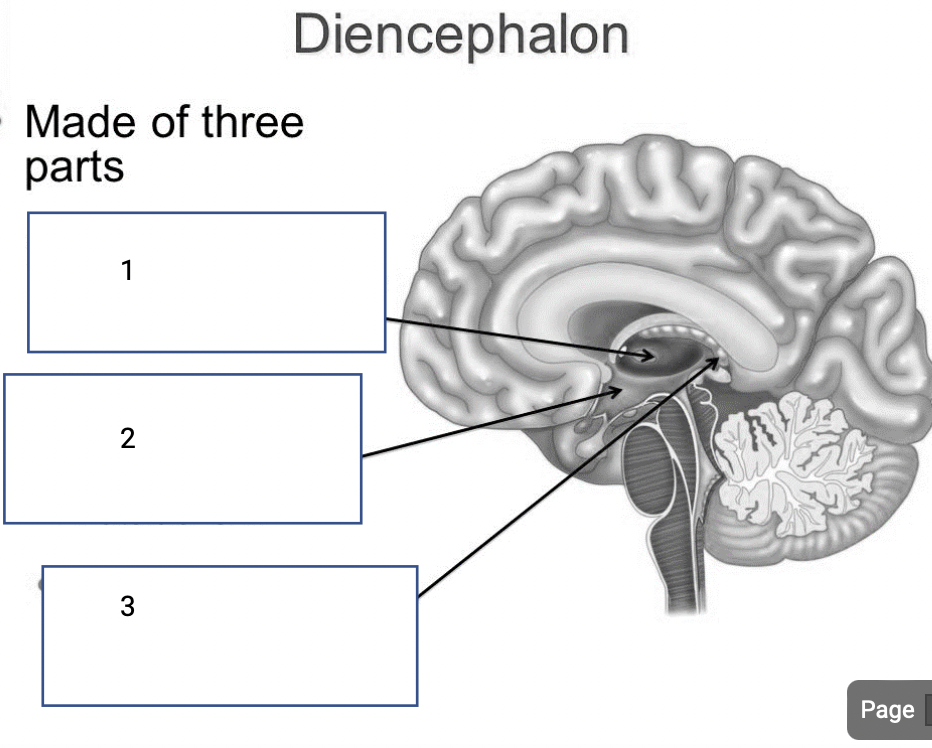
1
Thalamus- relay station for sensory input
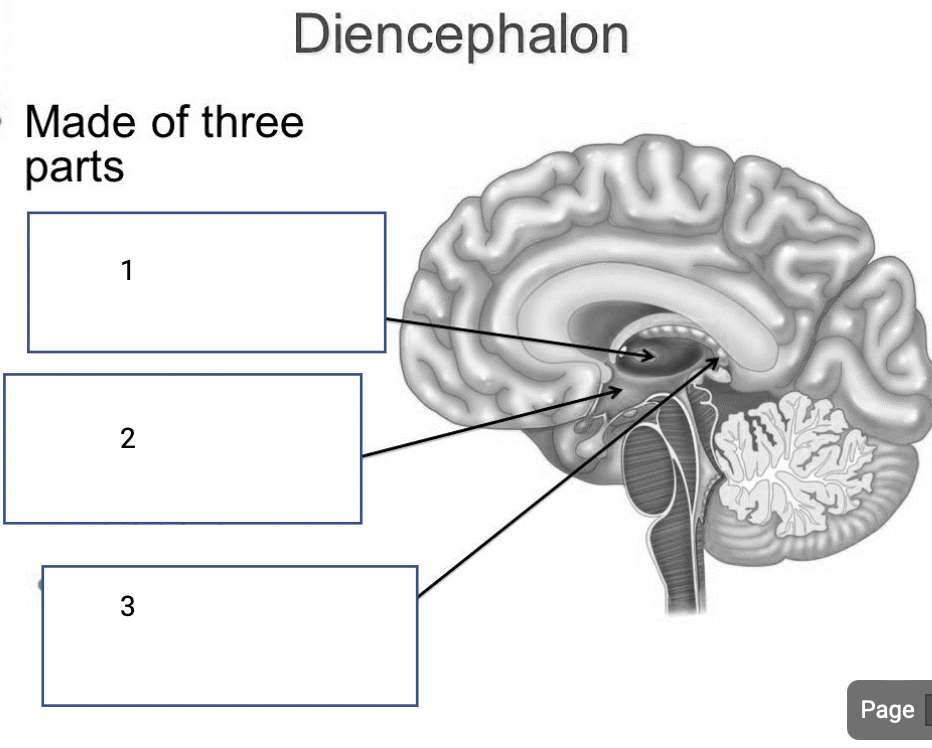
2
Hypothalamus- controls body temp and metabolism
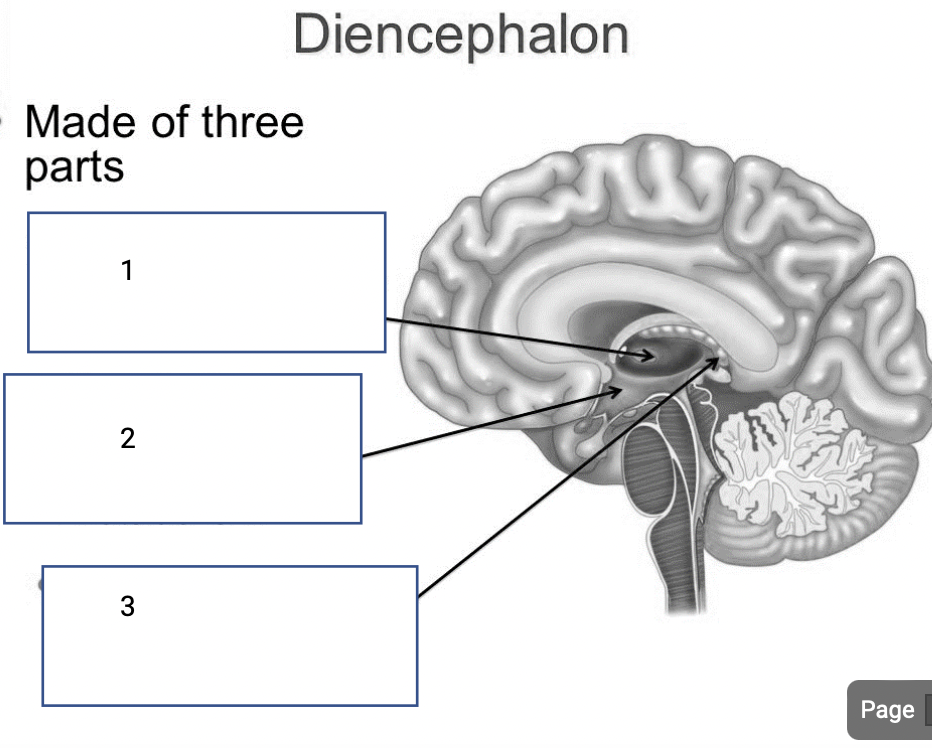
3
Epithalamus- creates brain and spinal fluid
Brain stem: The size of your ____________
thumb
Brain stem 3 main structures:
Midbrain, Pons, medulla oblongata
Pons: Mostly ____________ and has nuclei that control ____________
fiber tracts; breathing
Medulla oblongata: Merges into ____________
spinal cord
Medulla oblongata: Contains centers that control ____________
heart rate, blood pressure,breathing, swallowing and vomiting
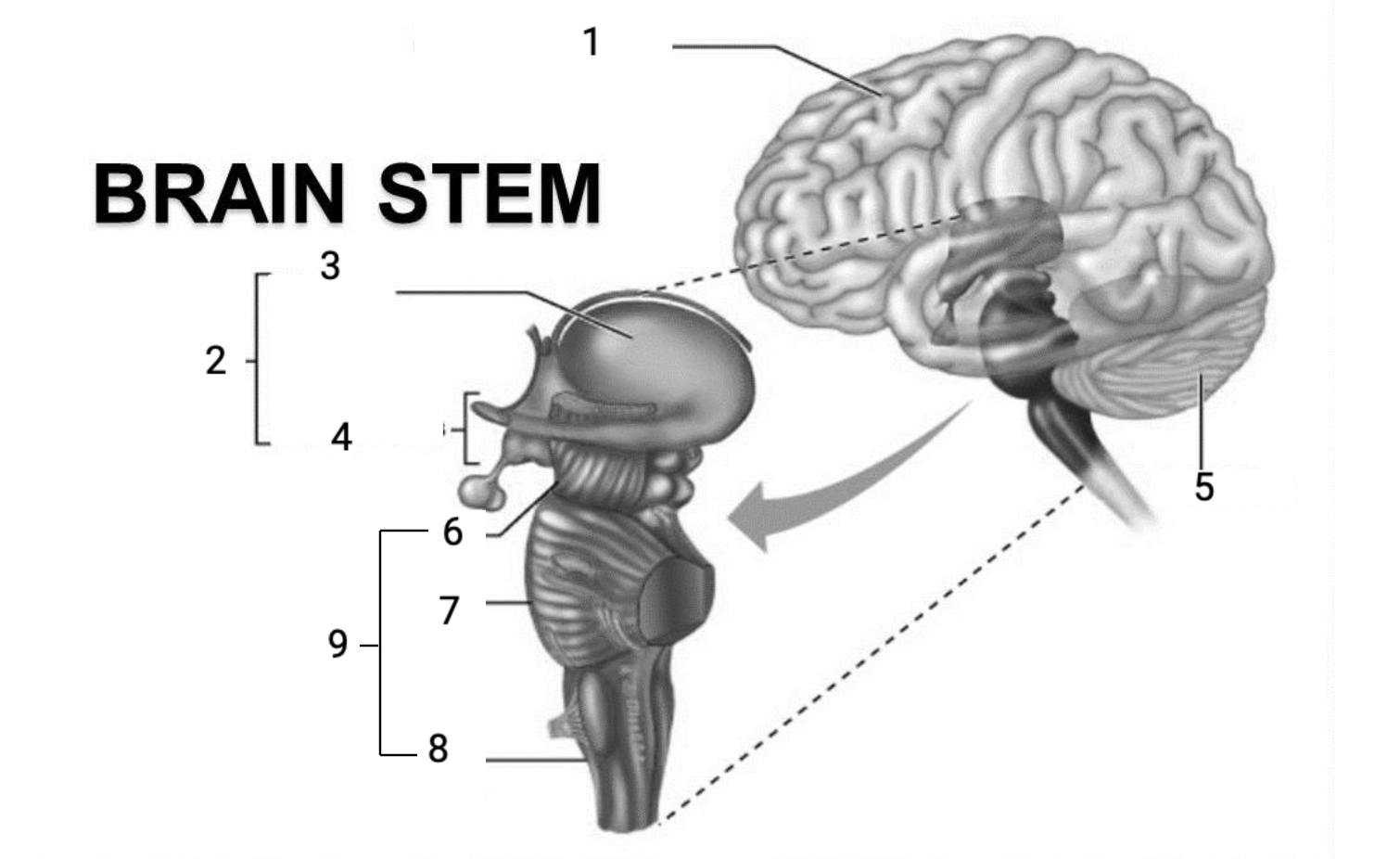
1
Cerebral hemispheres
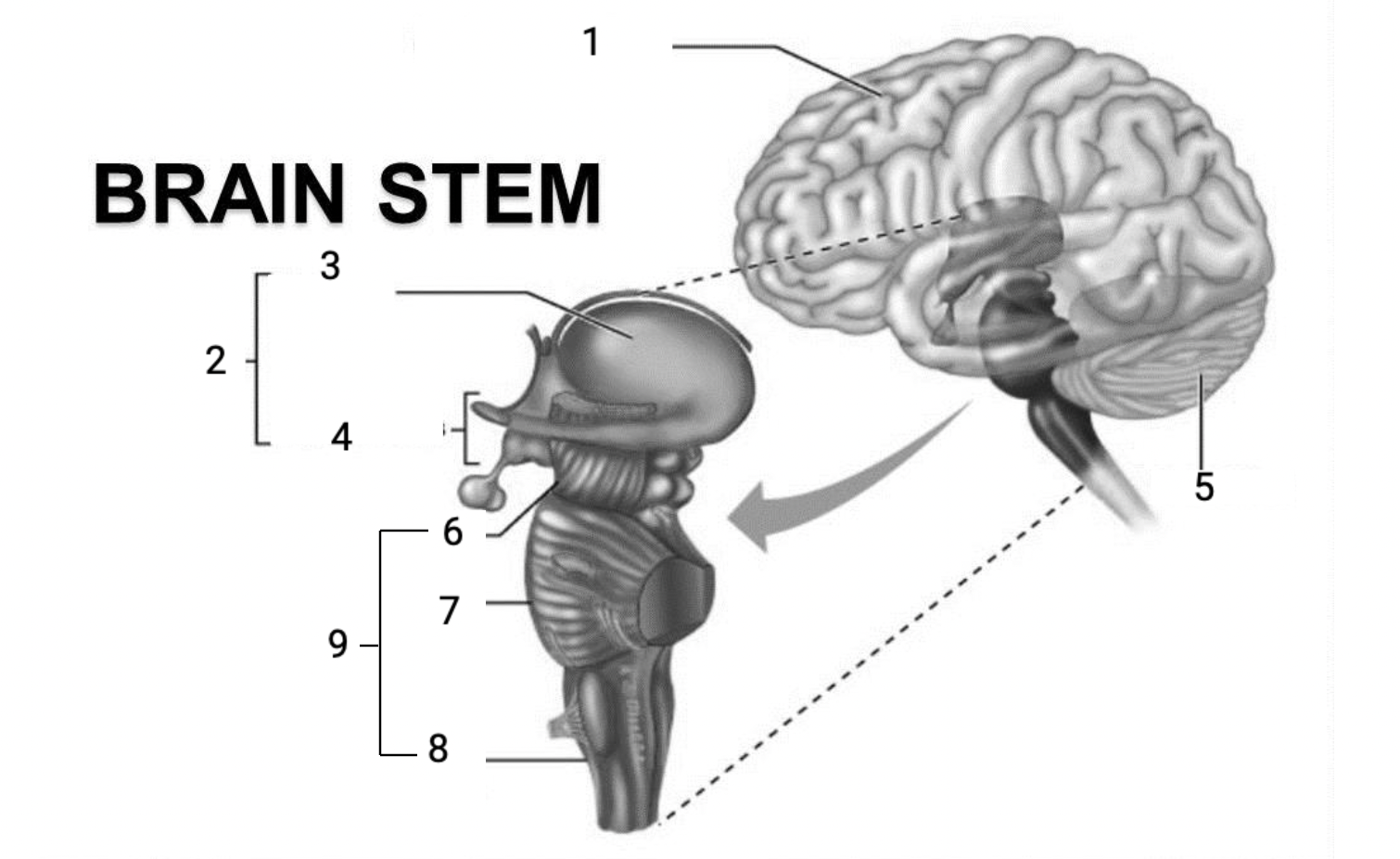
2
Diencephalon
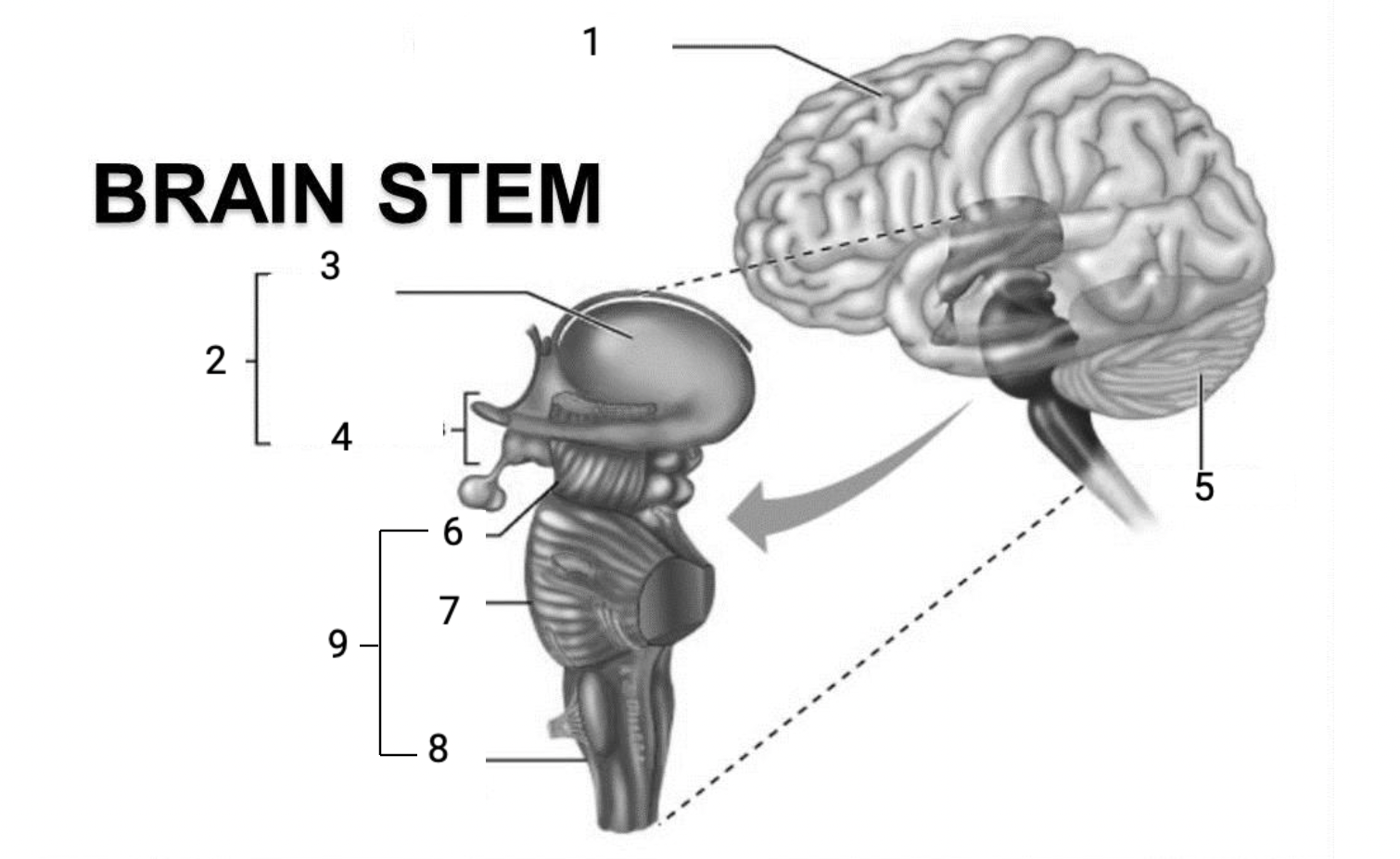
3
Thalamus
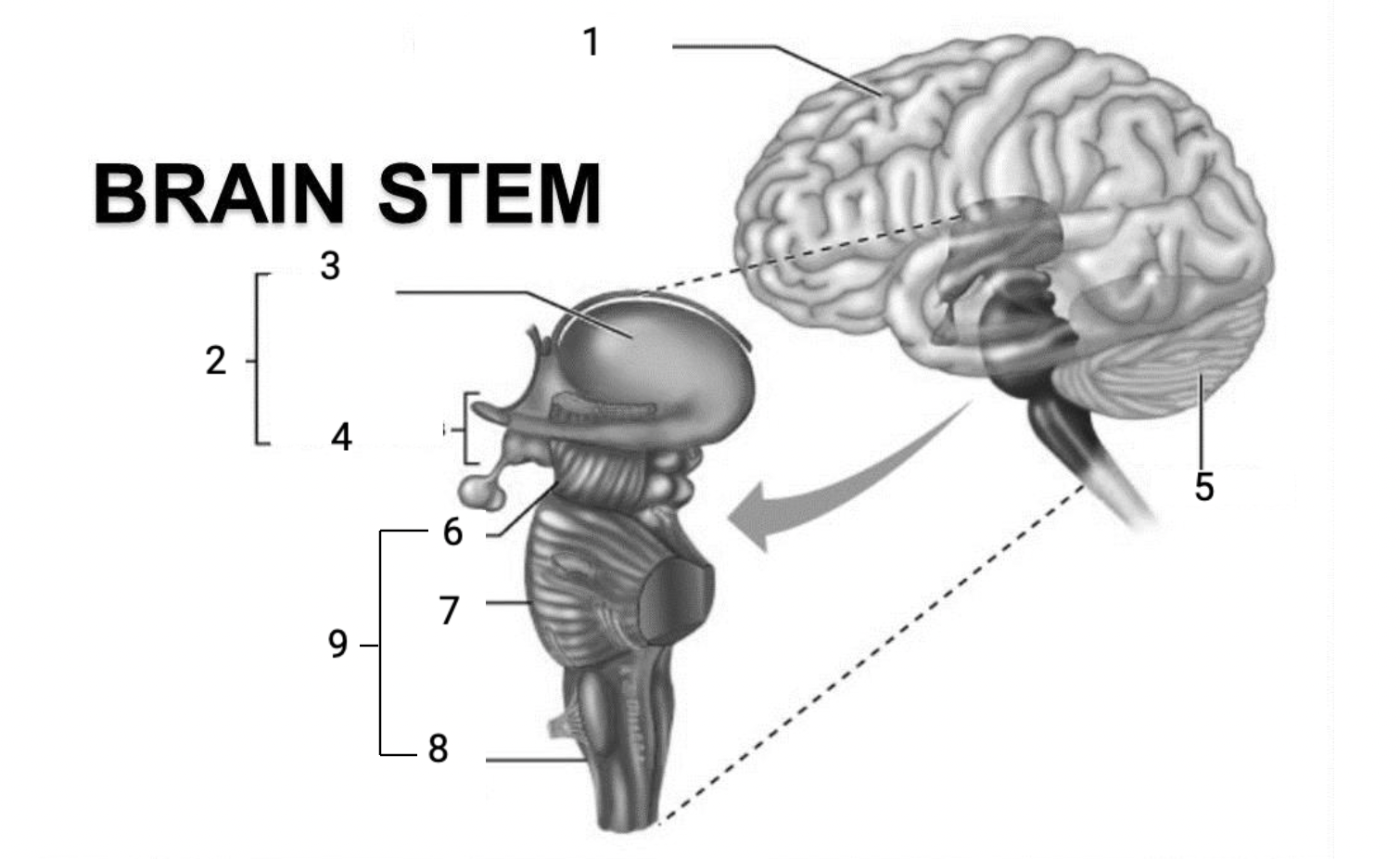
4
Hypothalamus
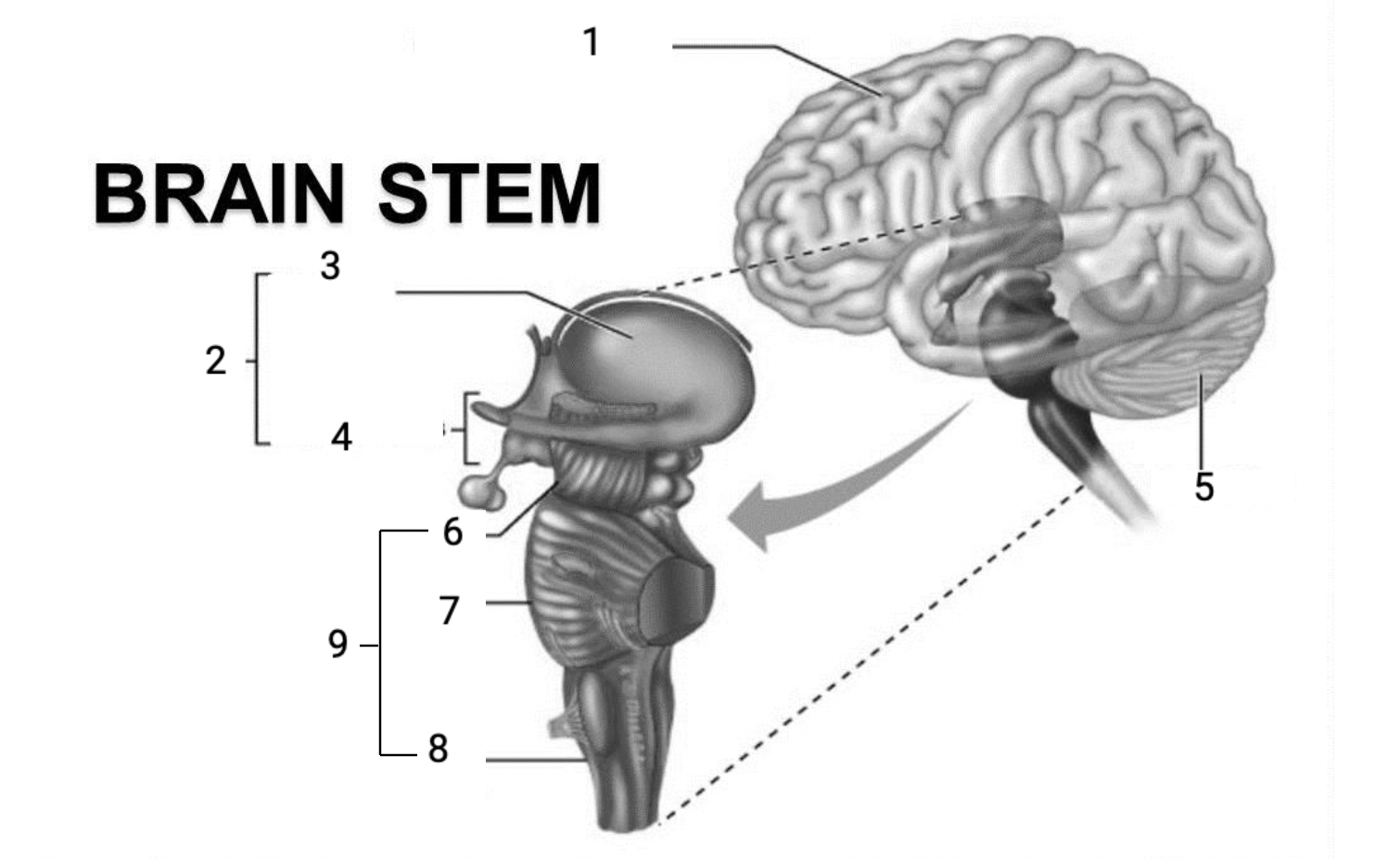
5
Cerebellum
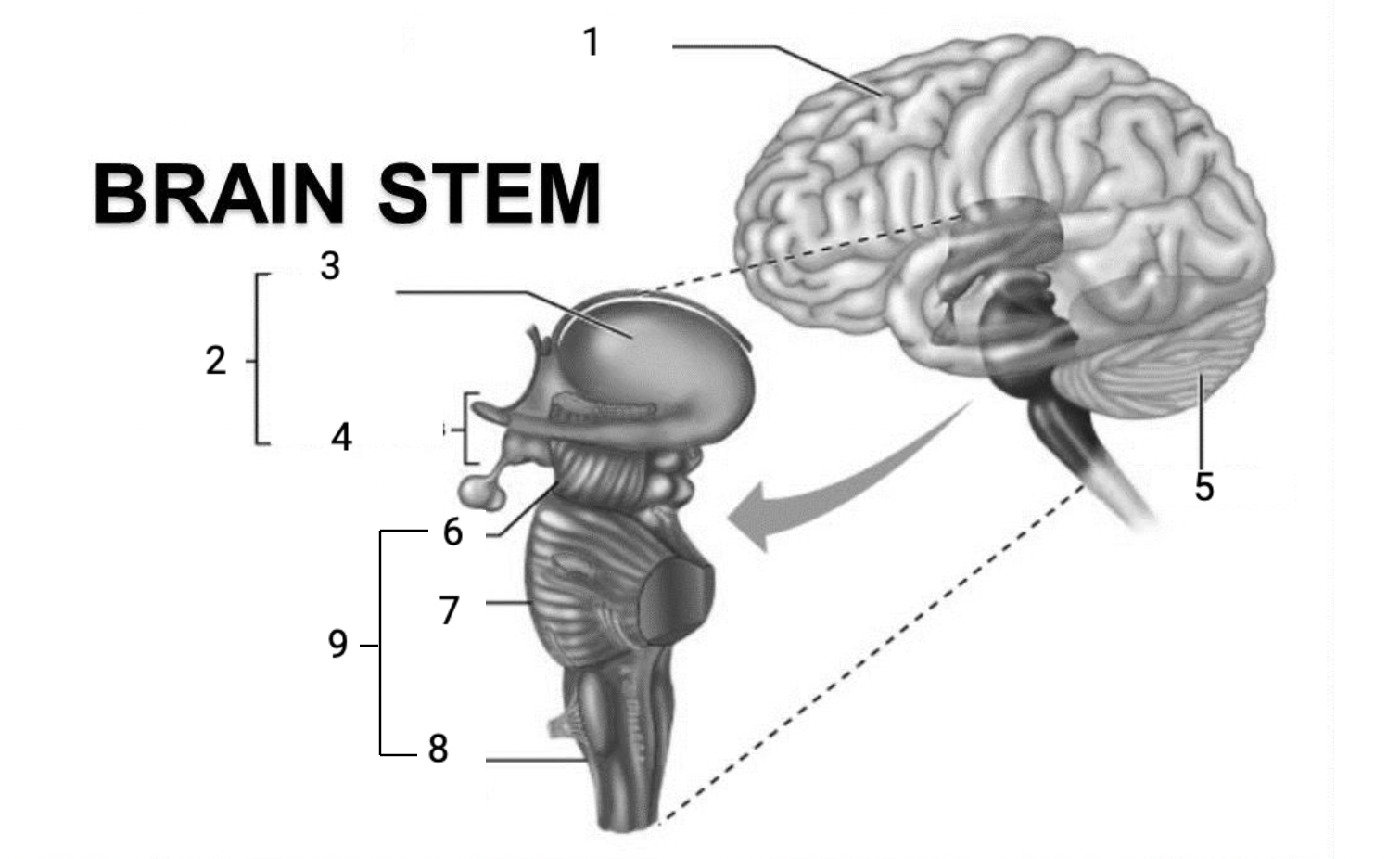
6
Midbrain
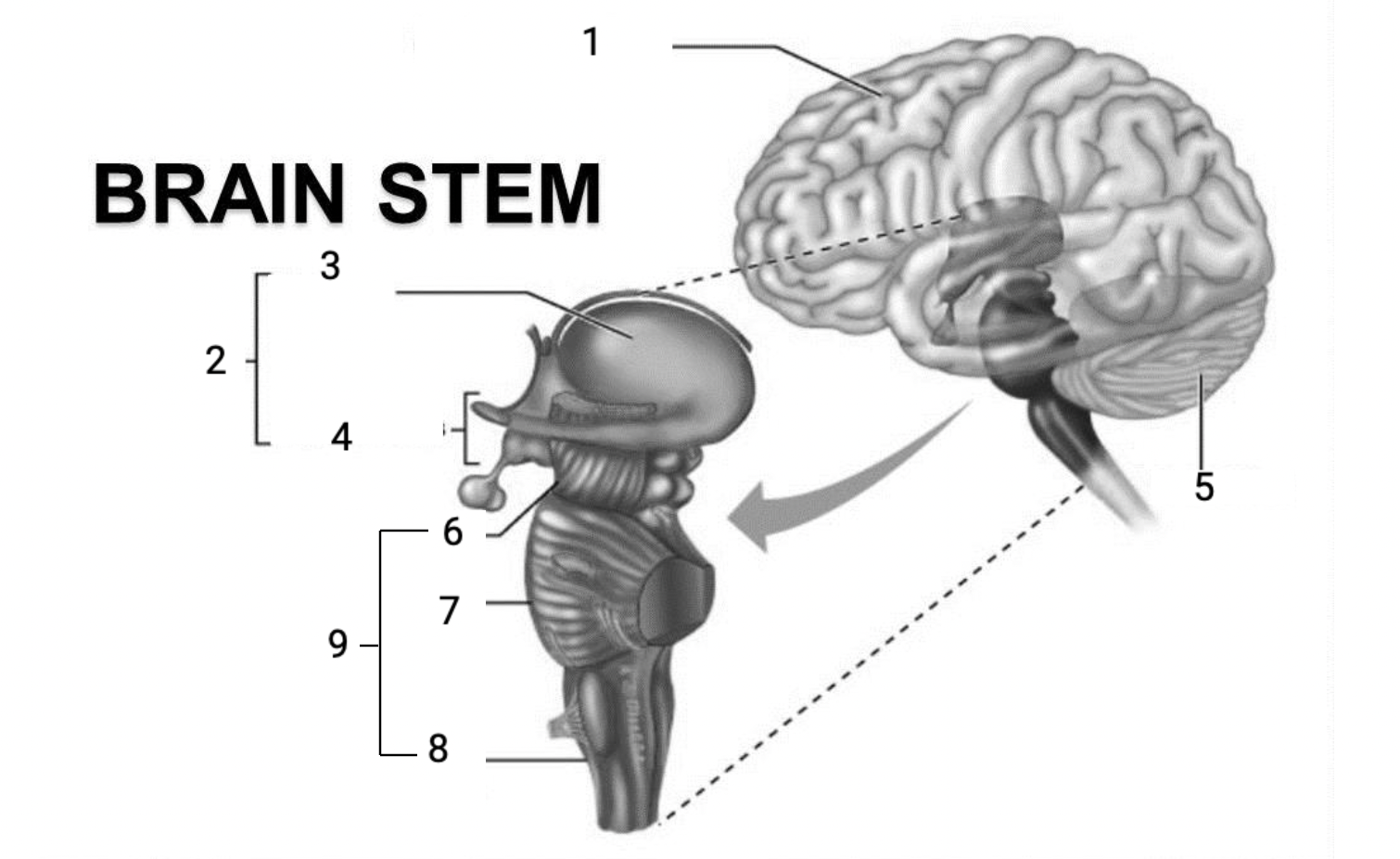
7
Pons
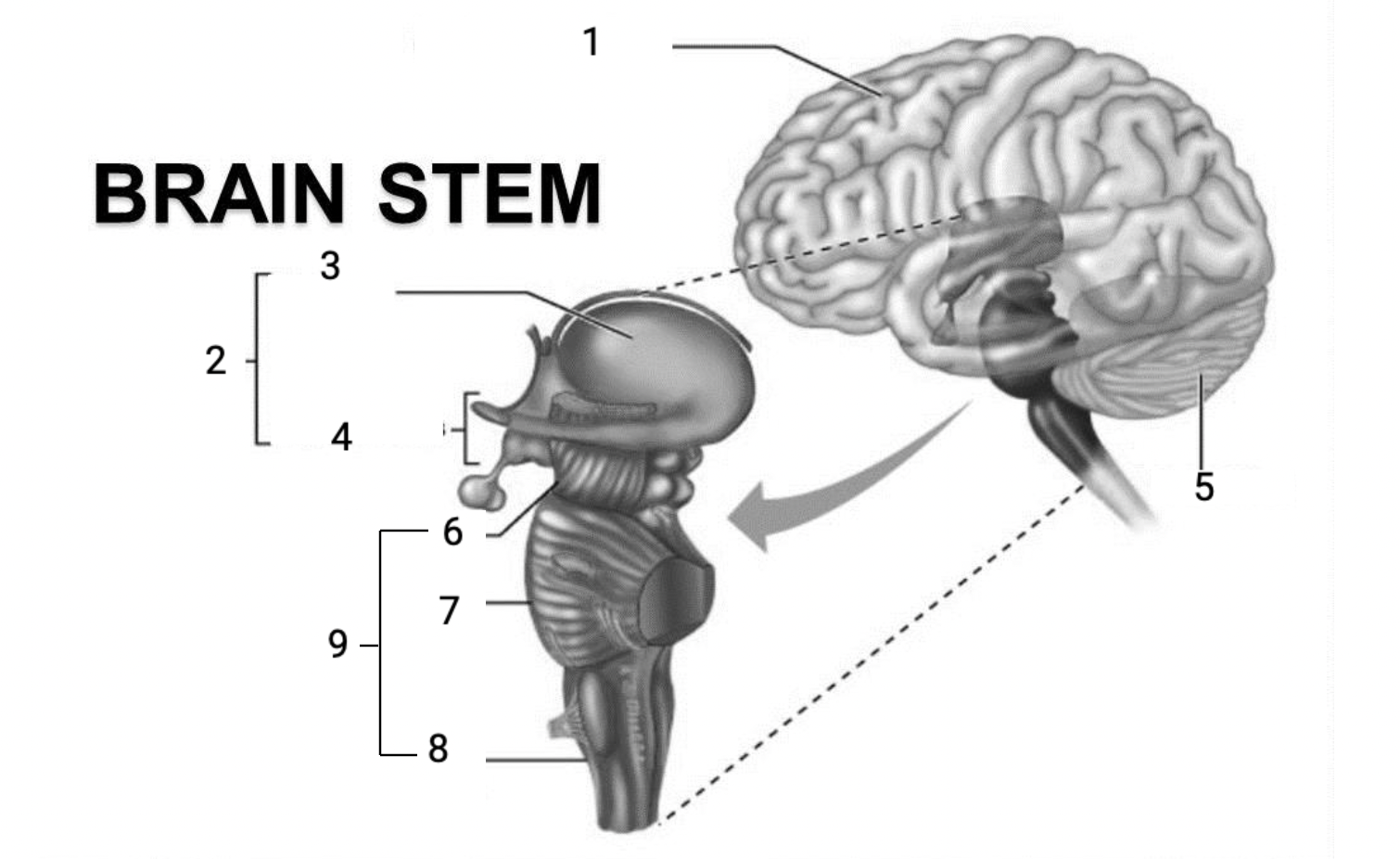
8
Medulla Oblongata
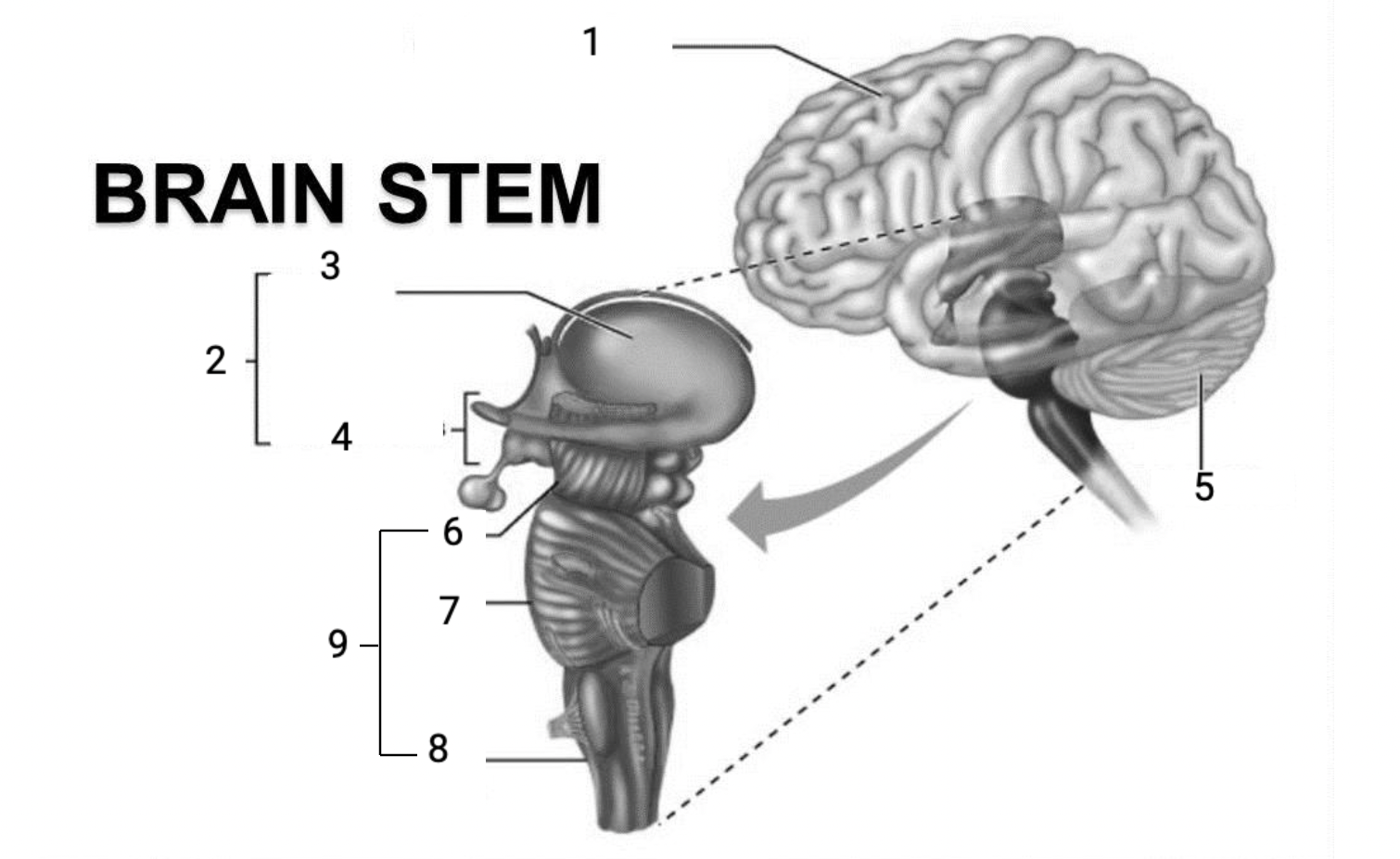
9
Brain stem
Cerebellum: Also has:
____________________________________
____________________________________
____________________________________
____________________________________
2 hemispheres, a convoluted surface, outer cortex of grey matter, inner region of white matter
Cerebellum: Provides precise timing of ____________
skeletal muscle activity
Cerebellum: Controls ____________ and equilibrium
balance
Cerebellum: Can be compared to ____________
autopilot