IOA2 Exam 2 - Retinal Anatomy Clinical Applications
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Separation between RPE and photoreceptors (no intercellular junctions)
Retina detachment
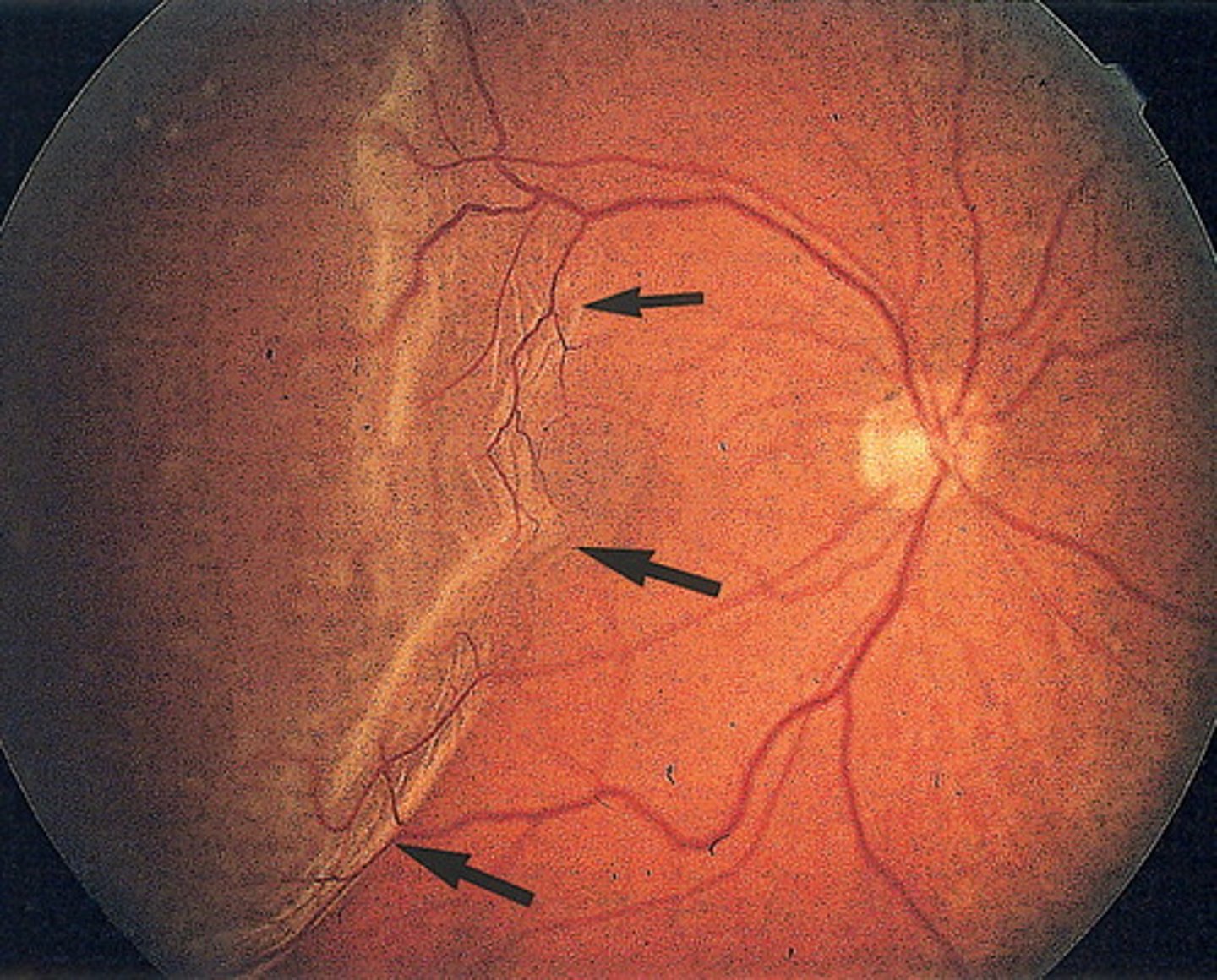
Bruch's membrane contains _________ and ________, which maintain the adherence of RPE cells to it
fibronectin and laminin (adhesive glycoproteins)
Where does fluid accumulate during retinal detachment and what occurs as a result?
Fluid accumulates in the subretinal space
-Photoreceptors DONT receive nutrients from choroid
Tx for retinal detachment
Aragon laser
Cryopexy
Scleral buckle surgery
Pneumatic retinopexy
Vitrectomy
Rupture of superficial pre-capillary arterioles (superficial capillary network)
Flame-shaped hemorrhages
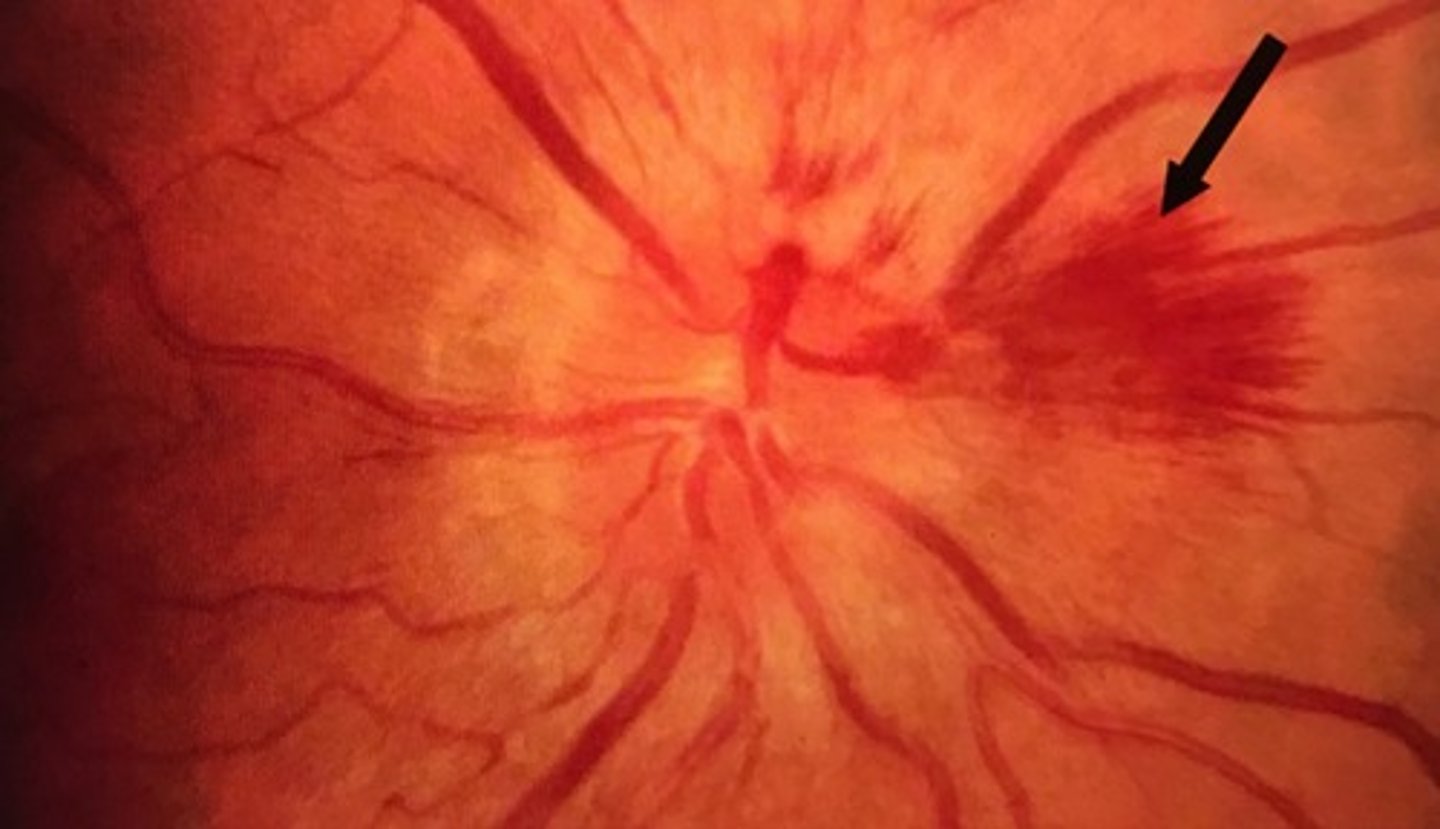
Flame shaped hemorrhages occur in which retinal layer?
Nerve Fiber layer
Flame shaped hemorrhages occur in small or big veins?
Small
During flame shaped hemorrhages, arrangement of the nerve fibers give a ______ pattern.
feathered
Rupture of deep capillaries
Dot or blot hemorrhages
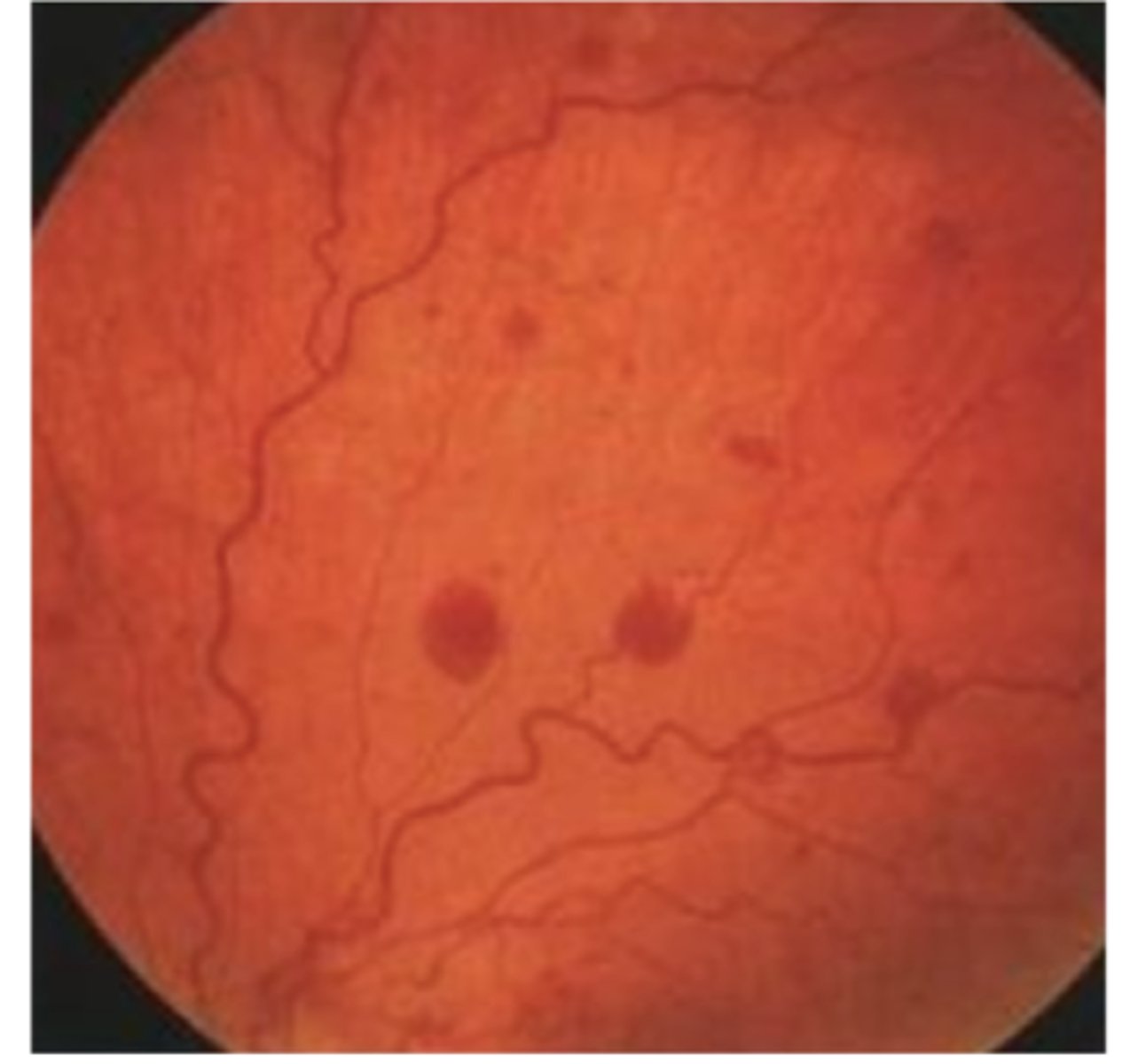
Dot or blot hemorrhages occur in which retinal layer?
Inner nuclear layer
Dot or blot hemorrhages are _______ in shape.
rounded
Common cause of dot or blot hemorrhage
Diabetes
Rupture of large superficial retinal veins into the space between the retina and vitreous
Boat hemorrhages
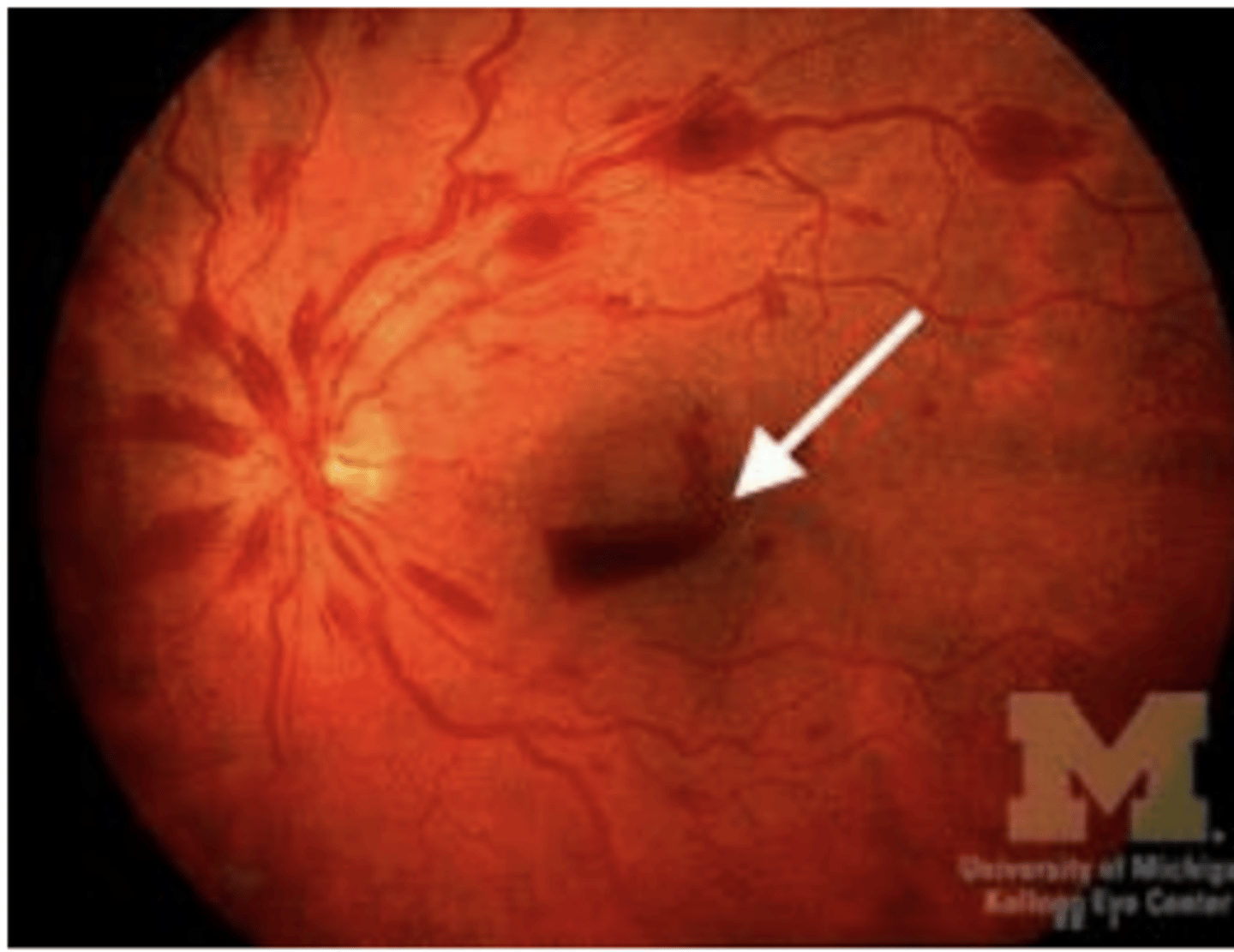
Sometimes boat hemorrhages bleed into the _______.
vitreous cavity
Common causes of boat hemorrhage
-Sudden increase in intracranial pressure
-Anemia
-Thrombocytopenia
-Trauma
Are lipid residues of serous leakage from damaged capillaries, with deep yellow appearance and sharp margins, often circinate
Retinal hard exudates
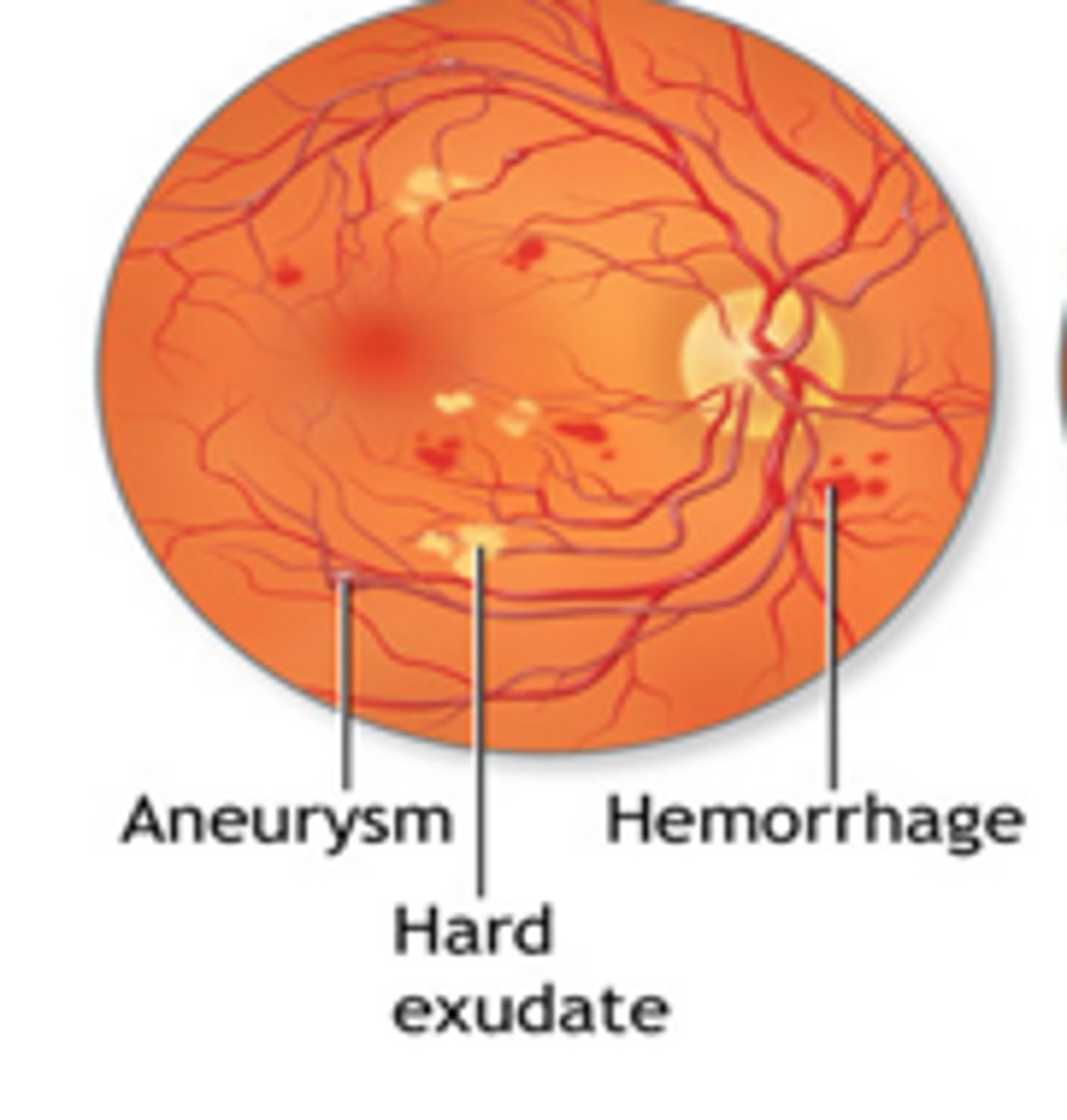
Retinal hard exudates are usually located in which retinal layer?
Outer plexiform layer
Common cause of retinal hard exudates
Diabetes
Other causes of retinal hard exudates
-Retinal vein occlusion
-Angiomas (Von Hippel Lindau disease)
-Vascular dysplasias
-Radiation-induced retinal vasculopathy
Appear fluffy gray-white and are usually near the optic disc
Cotton wool spots
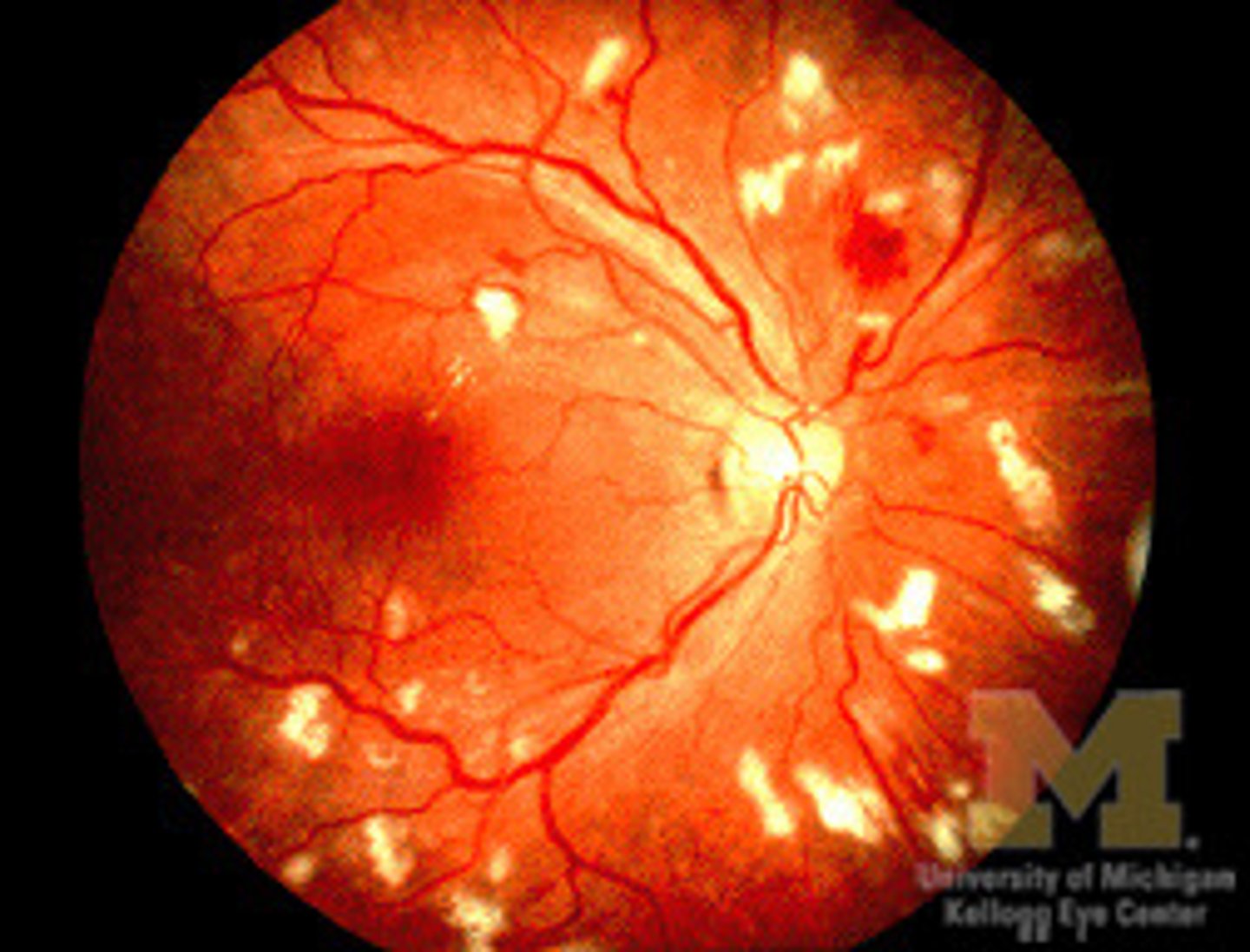
Cotton wool spots are usually located in which retinal layer?
Retinal Nerve Fiber layer
Associated conditions of cotton wool spots
-HTN
-Diabetes
-Connective tissue disease
-HIV
Clusters of yellow-orange spots usually centered around fovea
Retinal drusen
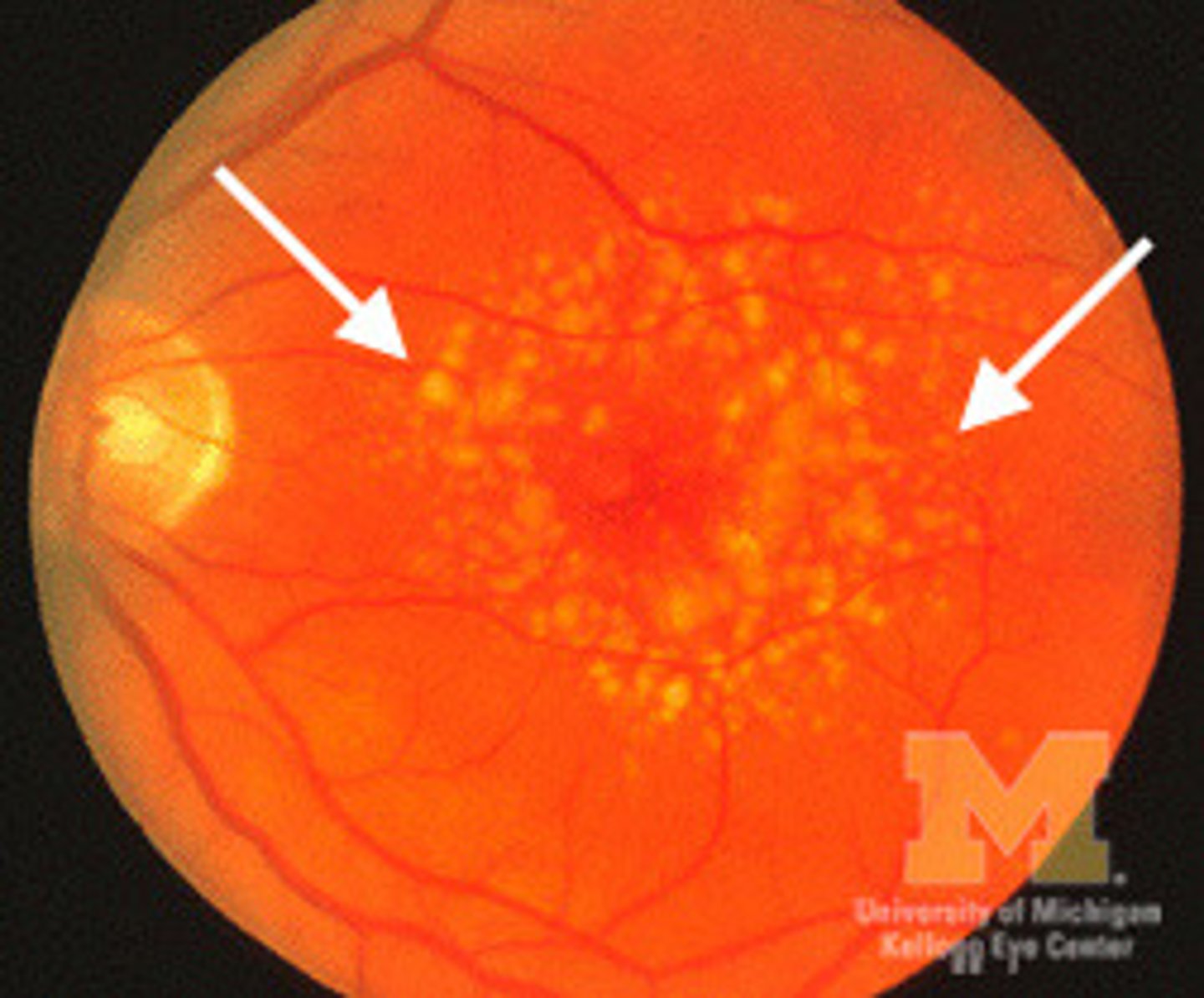
In retinal drusens, where is the metabolic debris from?
retinal pigment epithelium (lipids)
Retinal drusens are located btwn the ______ and ______.
RPE and Bruch's memb
Retinal drusens are associated with this condition:
ARMD
Where are intraluminal plaques usually found?
at bifurcations
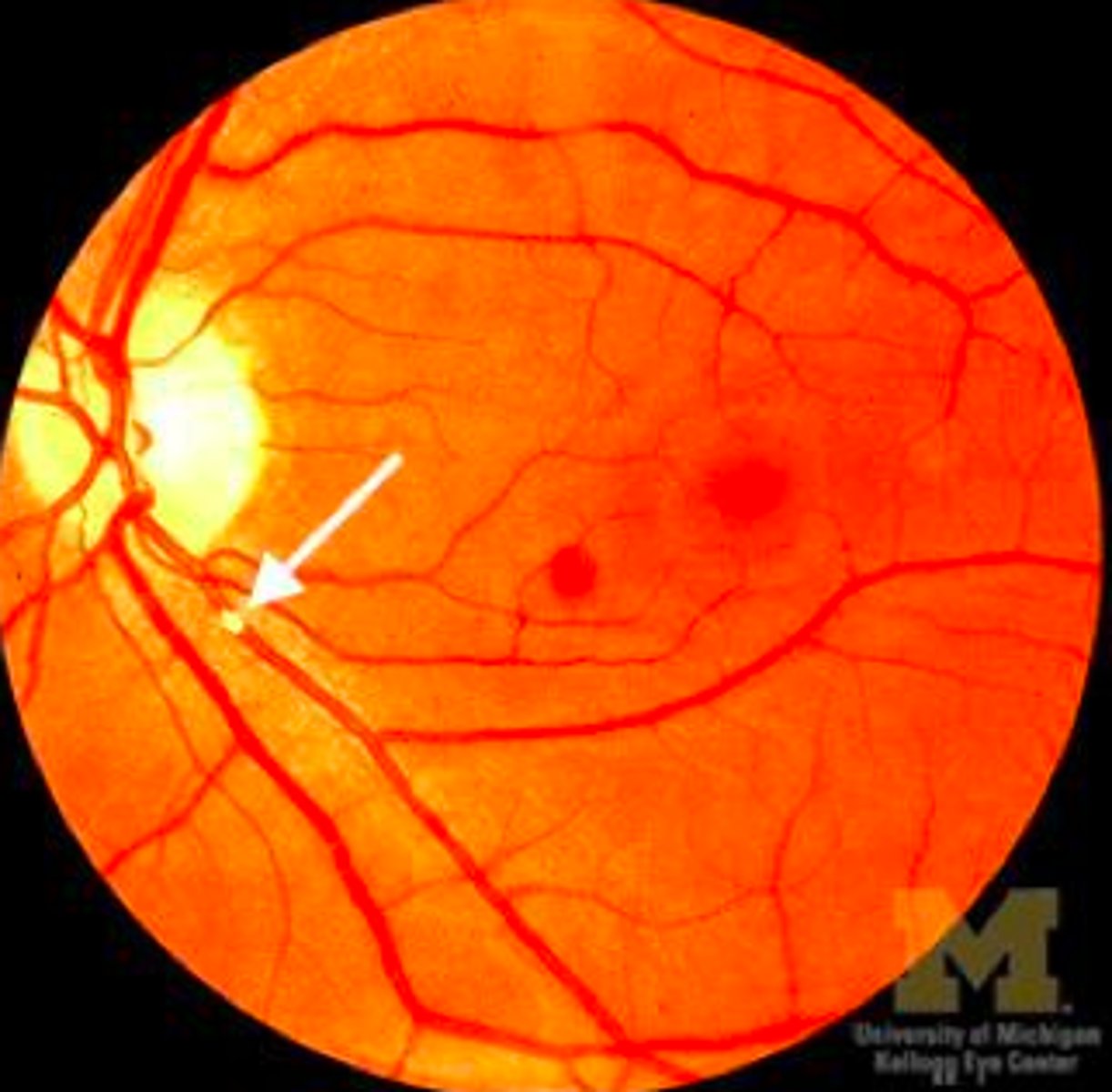
What are intraluminal plaques composed of?
Cholesterol-fibrin
What is a Hollenhorst plaque?
a cholesterol embolism seen in the retinal arteries
Associated causes of intraluminal plaque
-Cervical carotid atherosclerosis
-Calcified cardiac valve
-IV drug abuse
Presents as a feathery white clump usually connected to the optic disc;
Myelinated Nerve Fibers
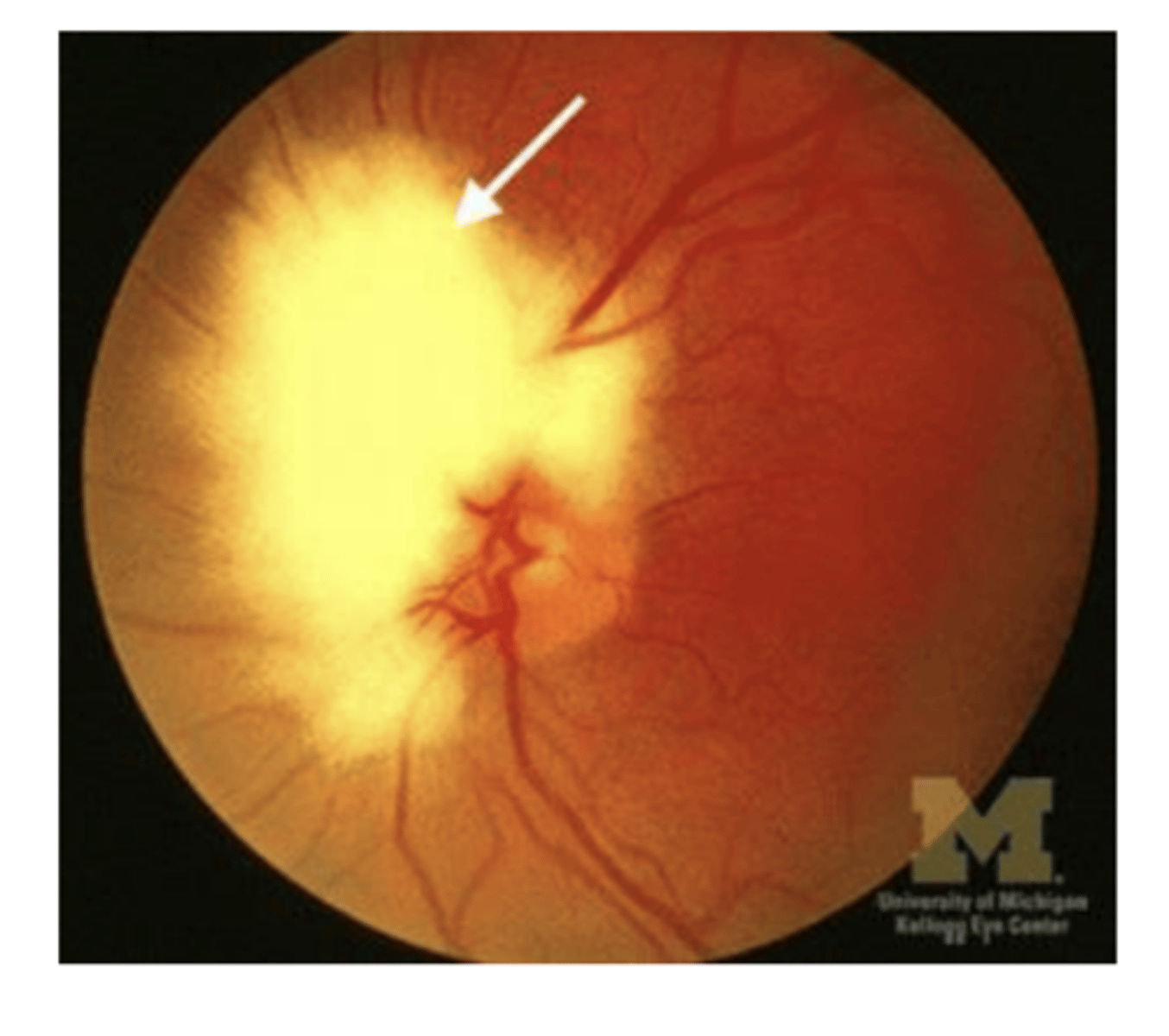
Myelinated Nerve Fibers are an extension of _______ onto retinal ganglion cell axons.
myelin
Conditions associated with myelinated nerve fibers
NONE
The cilioretinal artery is a branch of which artery?
SPCA
What is the significance of the cilioretinal artery in central retinal artery occlusion (CRAO)?
If the cilioretinal artery is present, it can partially preserve central vision in a CRAO because it supplies part of the macula independently of the central retinal artery
Appearance is a white cuff that looks like frosting along the vessels; is sometimes called "sheathing"
Retinal Vasculitis
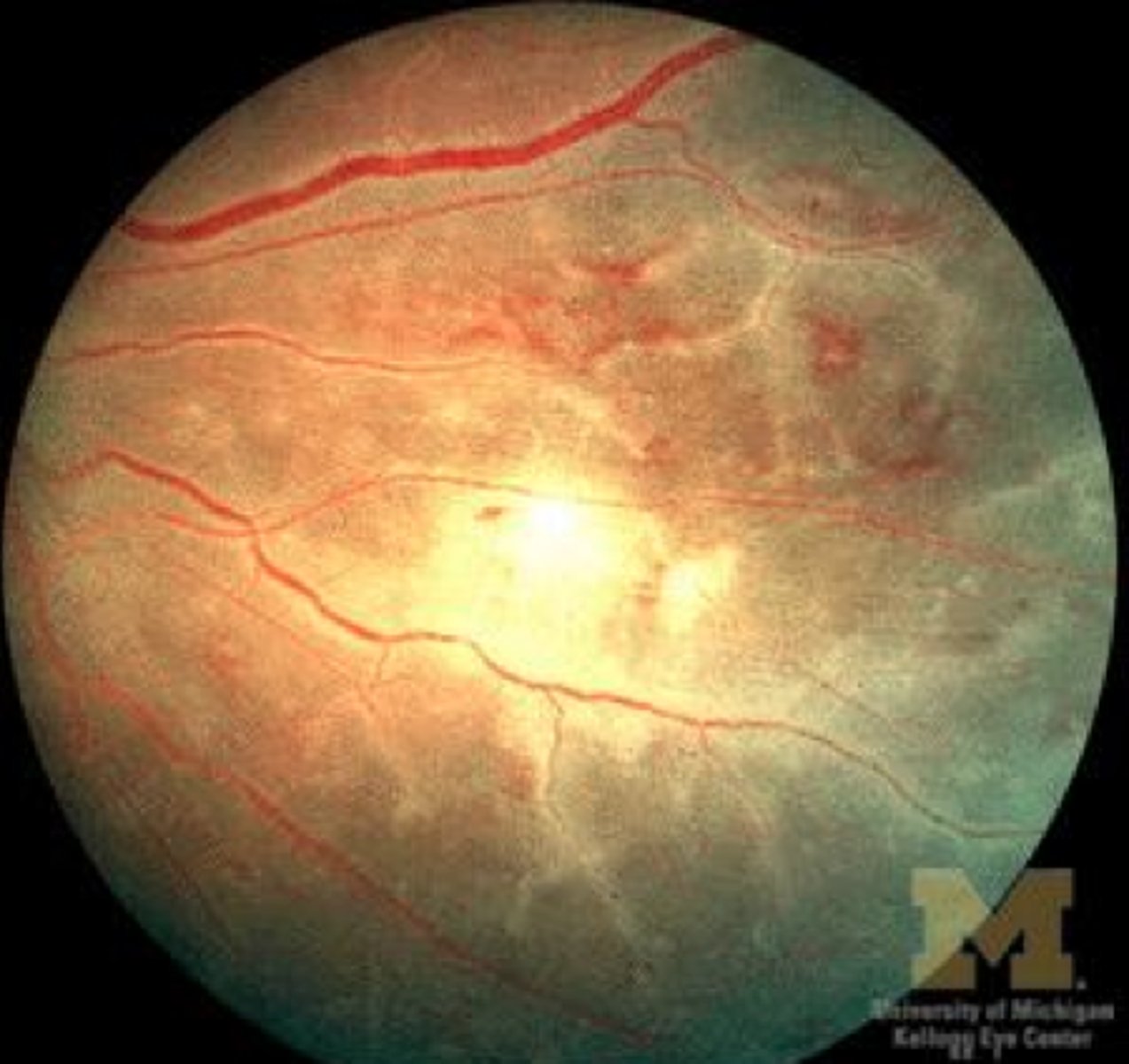
What causes the white "frosting" appearance in retinal vasculitis?
Perivenous lymphocytic infiltration
Conditions associated with retinal vasculitis.
-Sarcoidosis
-Behcet's disease
-Multiple sclerosis
-Idiopathic condt's
Swelling of the optic disc due to increased intracranial pressure, causing fluid accumulation within the fibers and elevation of the disc
Acute optic disc edema
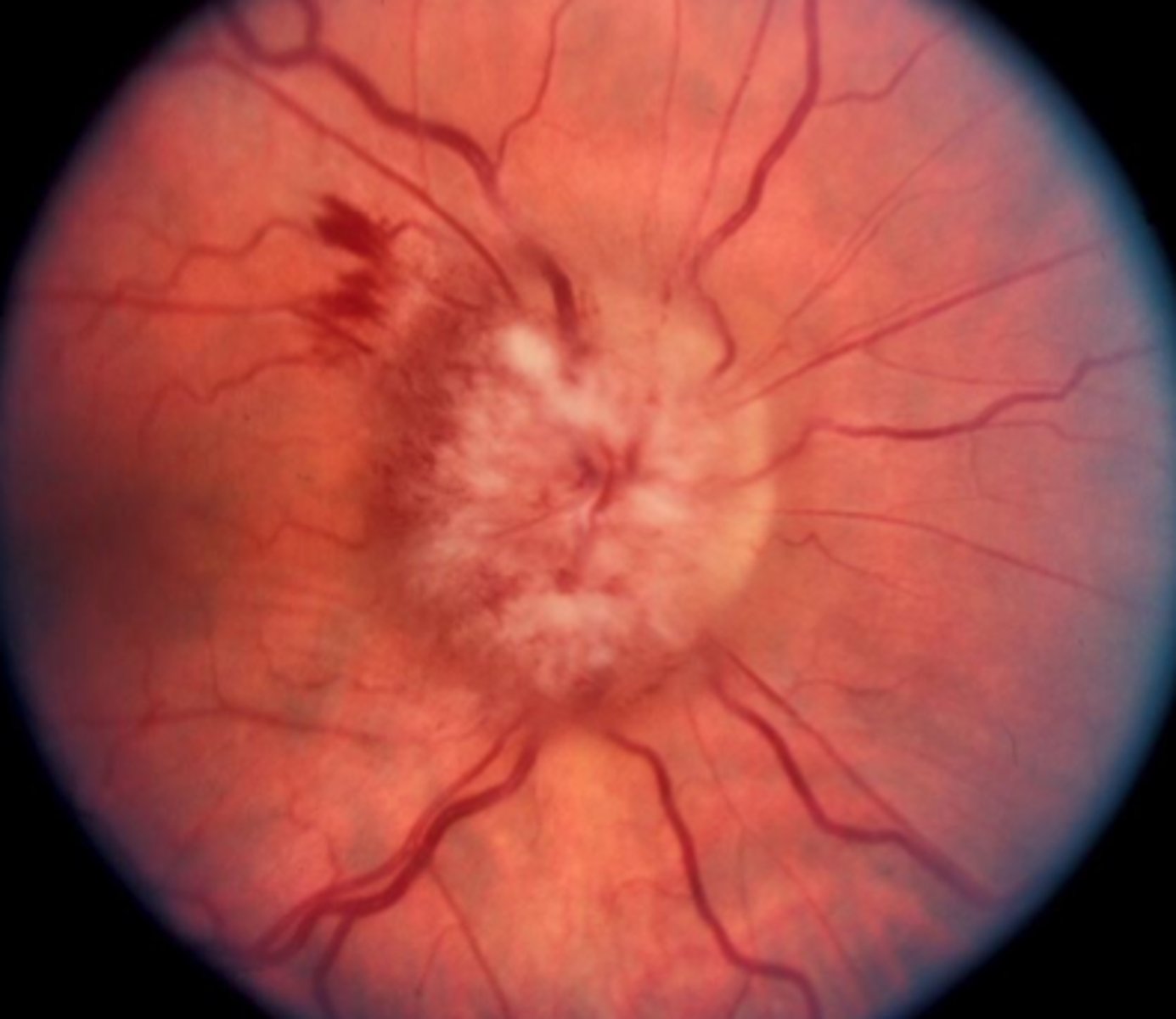
What are the key features of acute optic disc edema?
-Blurred disc margins
-Cotton wool spots (damaged axons)
-Flame hemorrhages (ruptured vessels under pressure)
-Bilateral involvement
Common causes of acute optic disc edema
-Increased intracranial pressure (papilledema)
-Infarction
-Inflammation
-Infiltration (cancer)
2 types of ARMD
1) Dry or non-neovascular or atrophic
2) Wet or neovascular or exudative
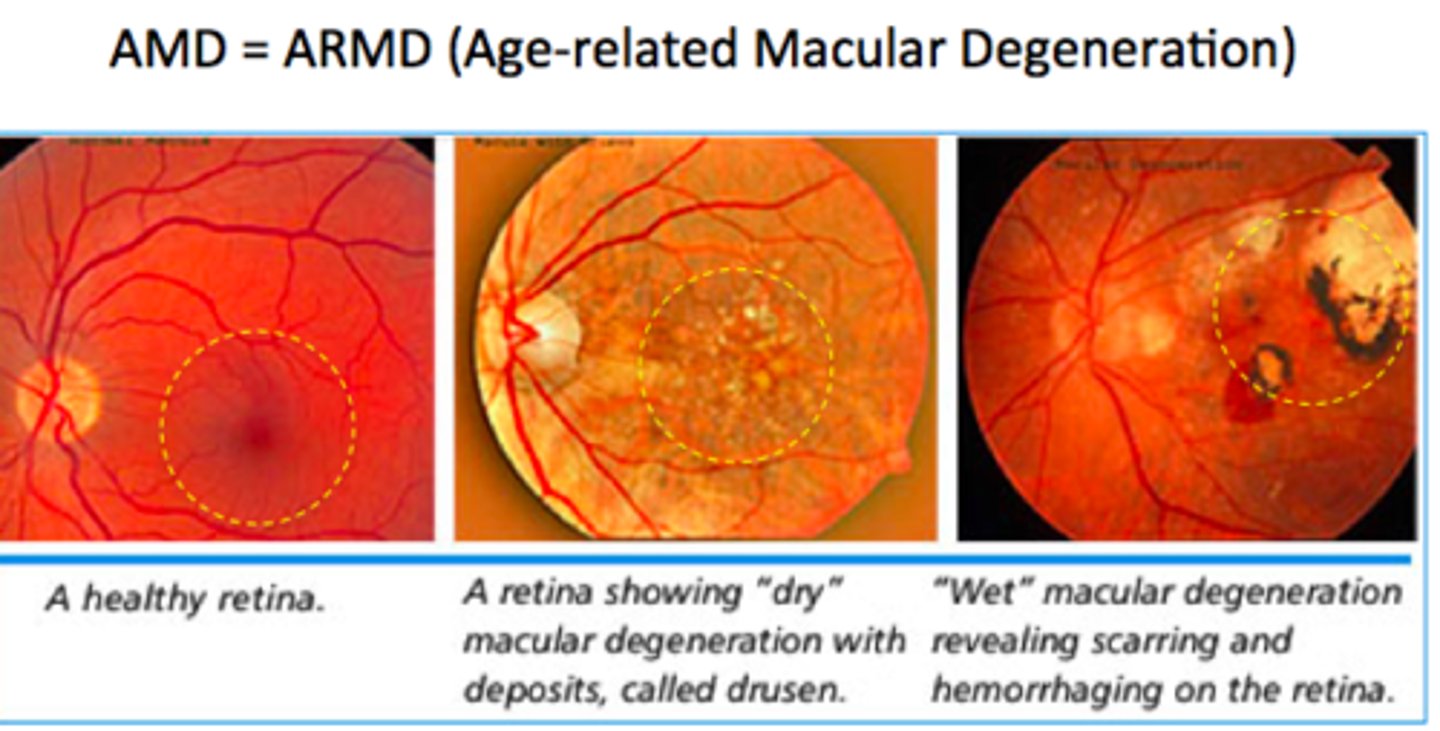
ARMD causes ________.
severe visual loss
ARMD is characterized by
drusen and neovascularization
Degenerative changes of RPE is believed to be a consequence of:
abnormal digestive mechanisms resulting in accommodation of abnormal material in the RPE