uark exercise physiology exam 3
1/202
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
203 Terms
roles of the cardiovascular system:
-a pump that provides continuous linkage with the other three components
-a high-pressure distribution circuit
-exchange vessels
-a low-pressure collection and return circuit
are arteries oxygenated or deoxygenated?
oxygenated
are veins oxygenated or deoxygenated?
deoxygenated
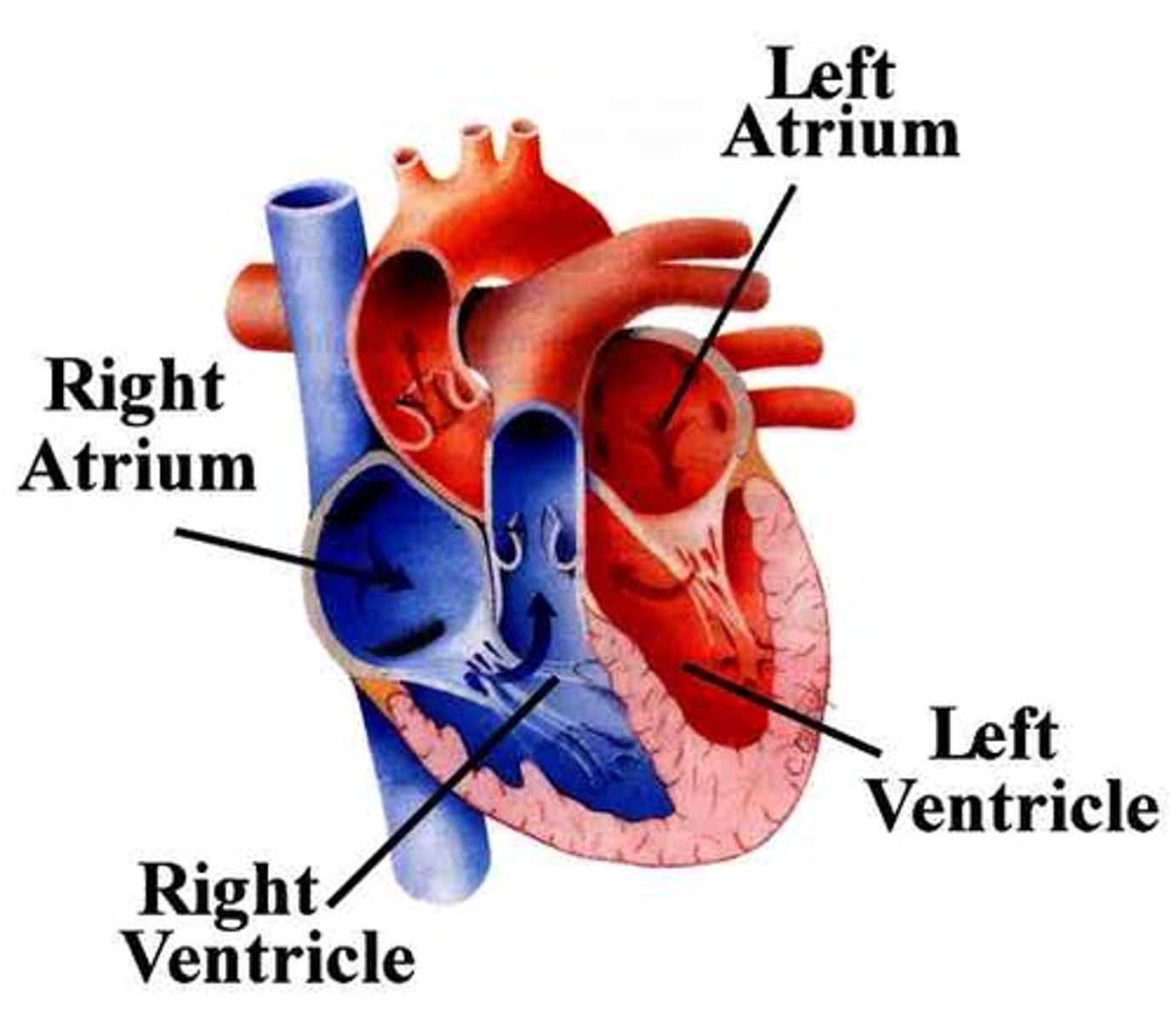
left and right ventricles
where blood leaves the heart
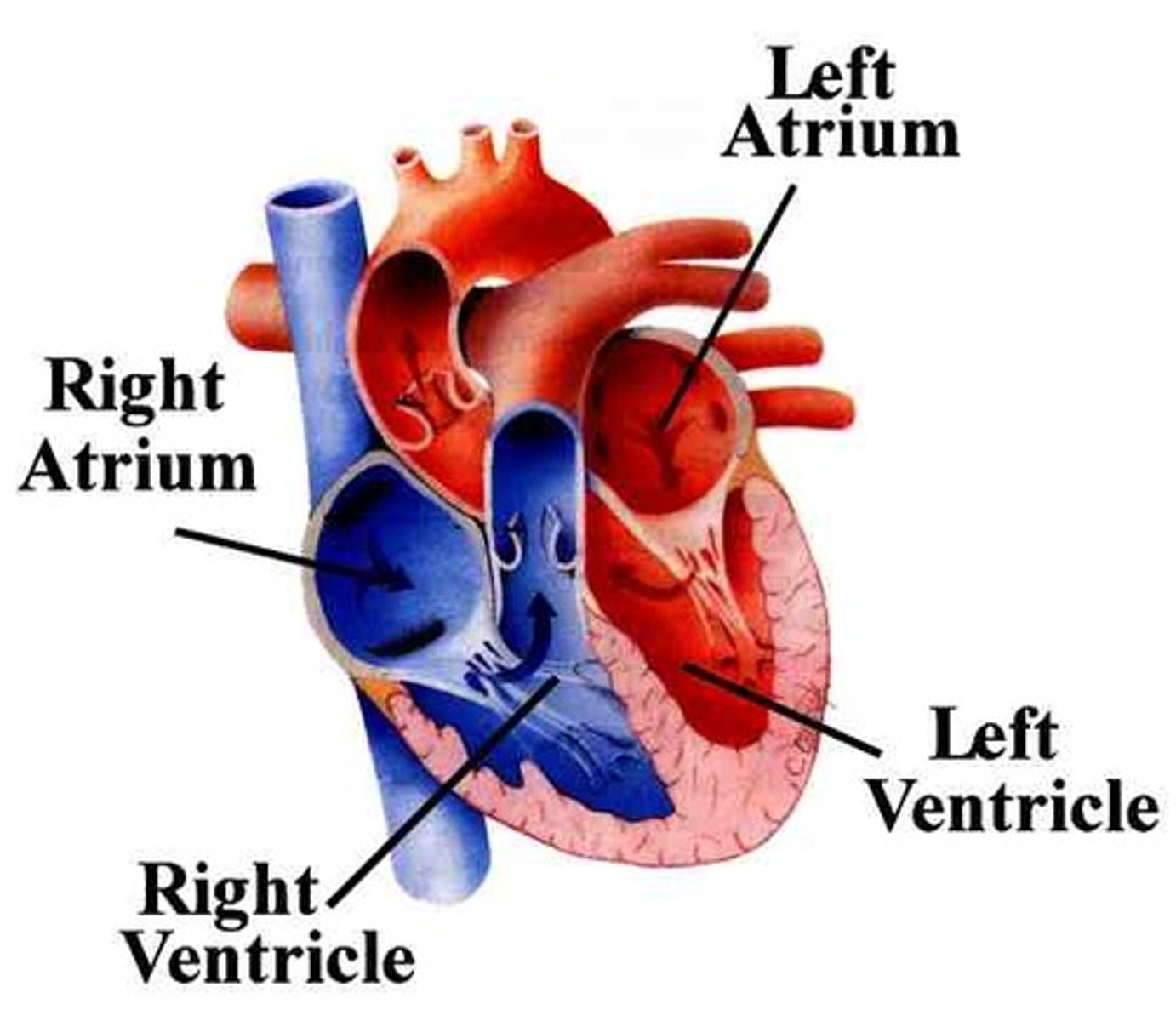
left and right atria
-where blood enters the heart
-right atria is deoxygenated
what is the average stroke volume?
70 ml/beat
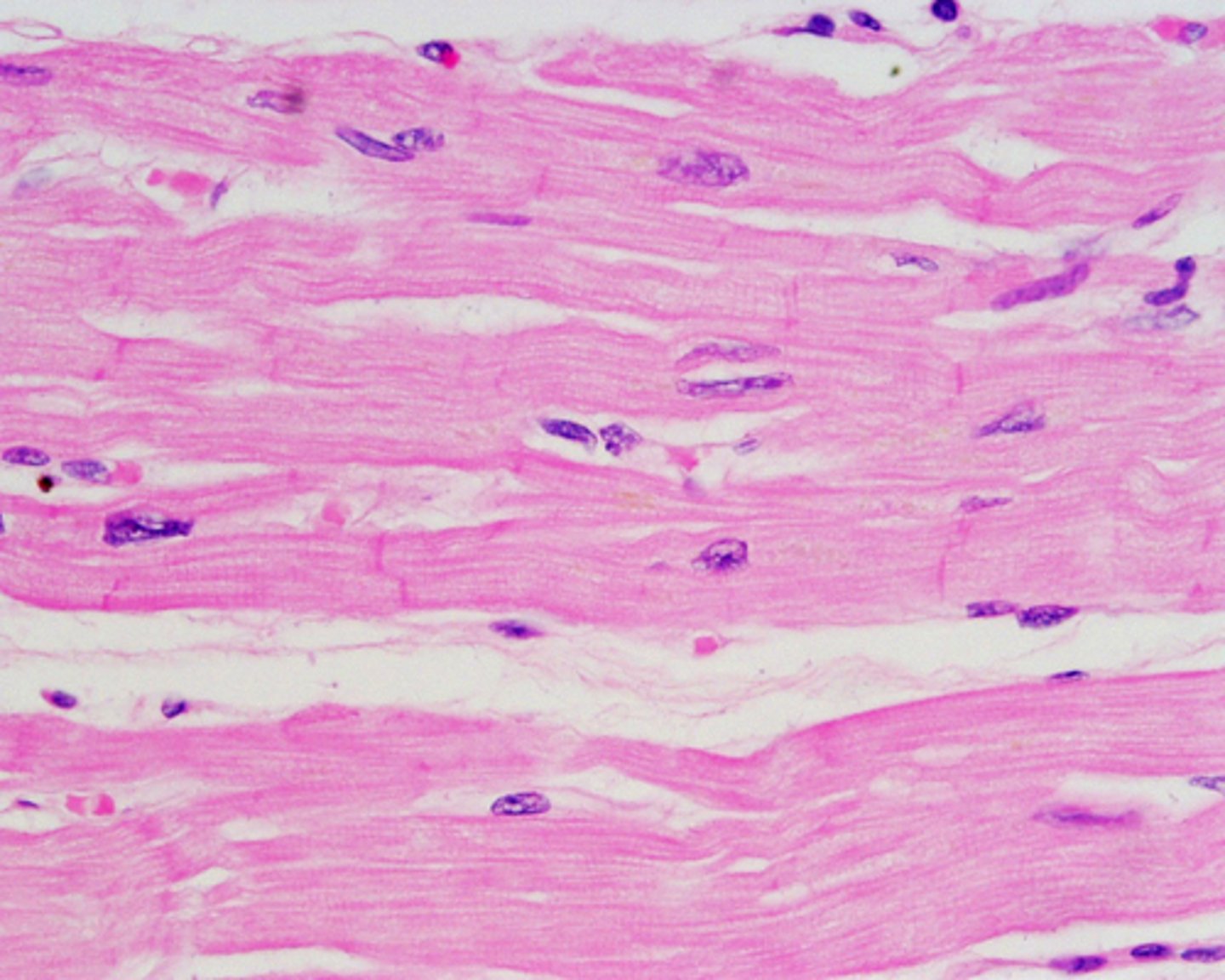
how is cardiac muscle organized?
intercalated discs
what happens to average stroke volume with training?
the heart can enlarge with training, which increases how much blood beats per minute
skeletal
what type of muscle is this

cardiac
what type of muscle is this
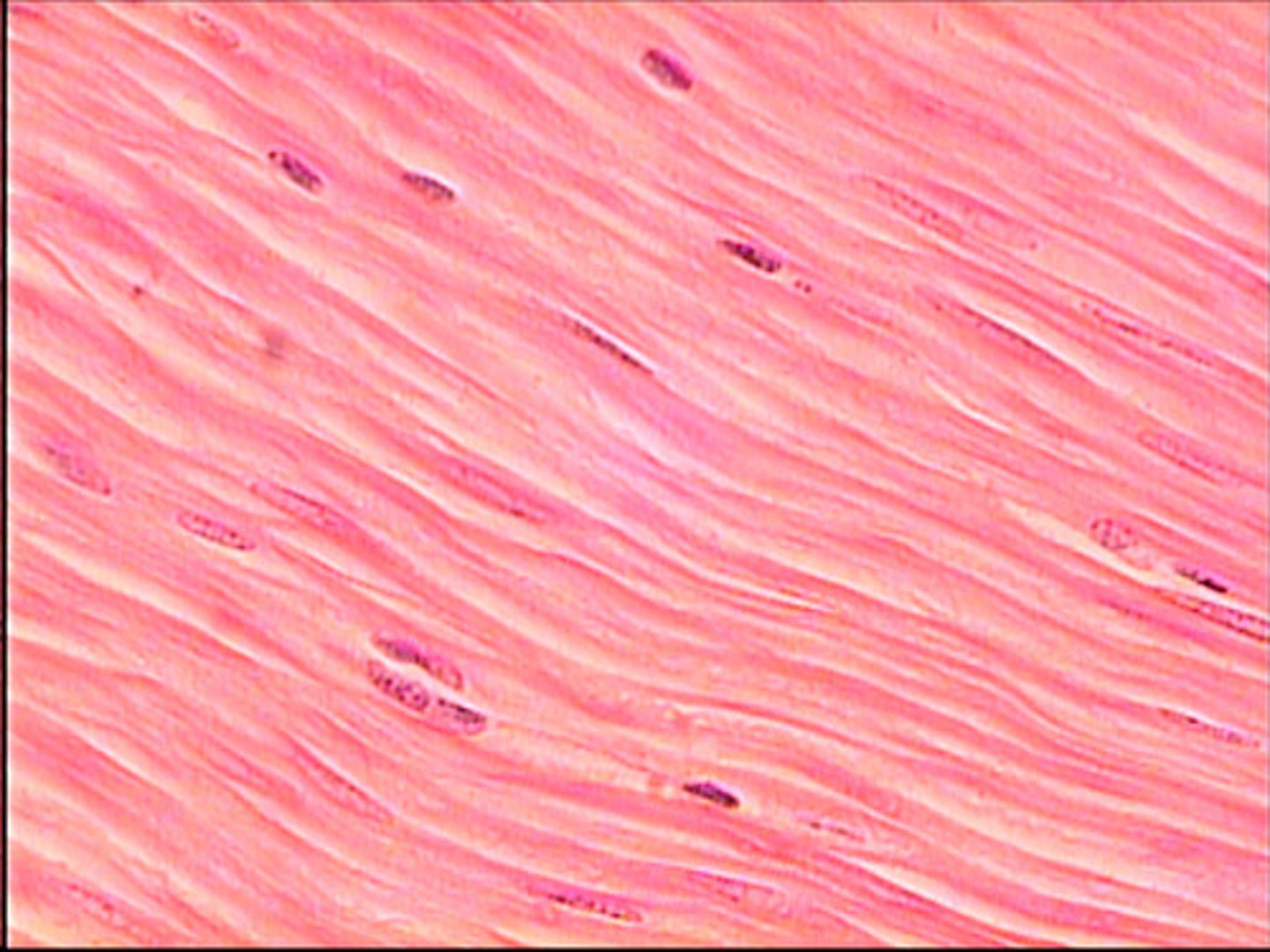
smooth
what type of muscle is this
location/activity/stimulation of skeletal muscle
muscles (biceps)/ strong, quick, intermittent/voluntary
location/activity/stimulation of cardiac muscle
muscle of heart/ strong, quick, rhythmic/involuntary
location/activity/stimulation of smooth muscle
hollow places, blood vessels/ weak, slow, rhythmic/ involuntary
diastole
-relaxation of the heart
-mitral and tricuspid valves open
-pulmonary and aortic valves close
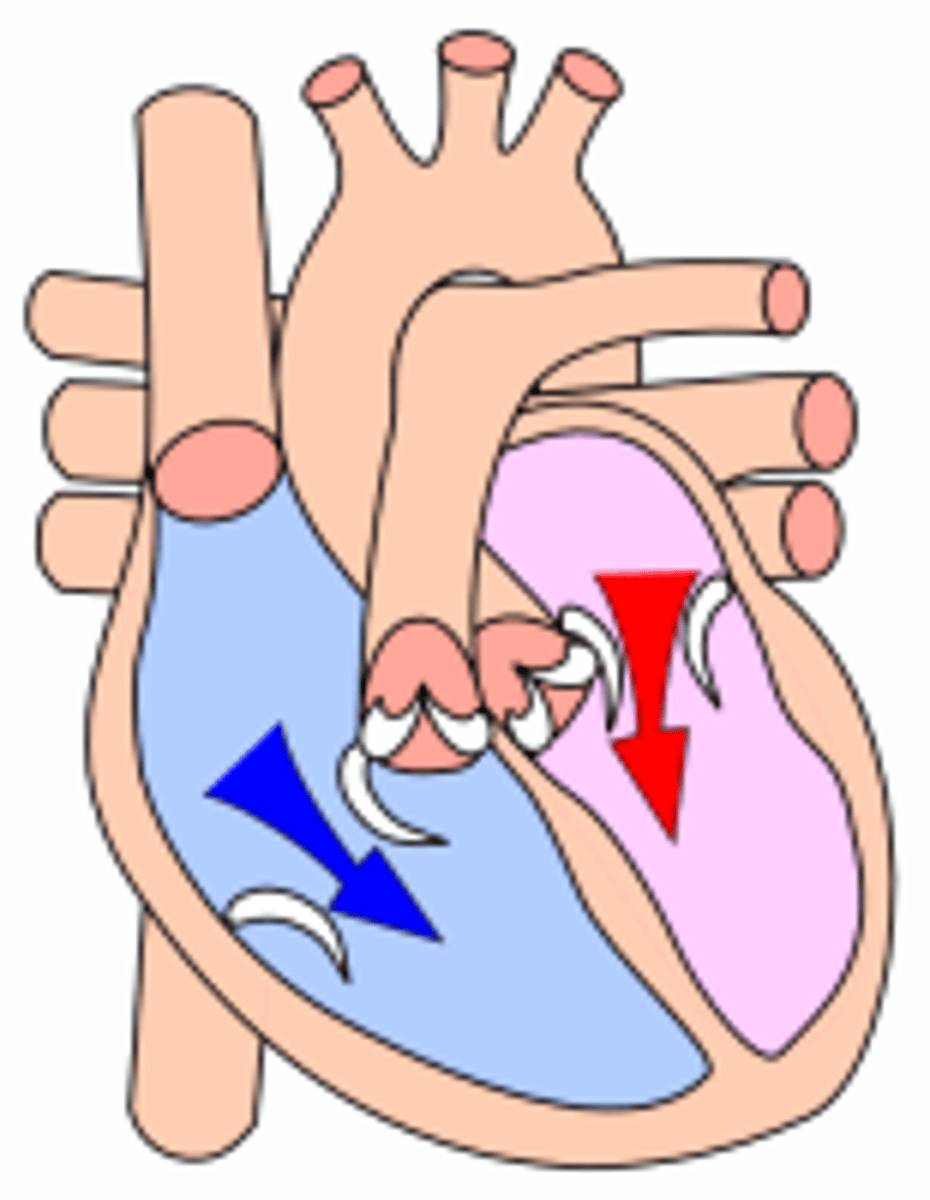
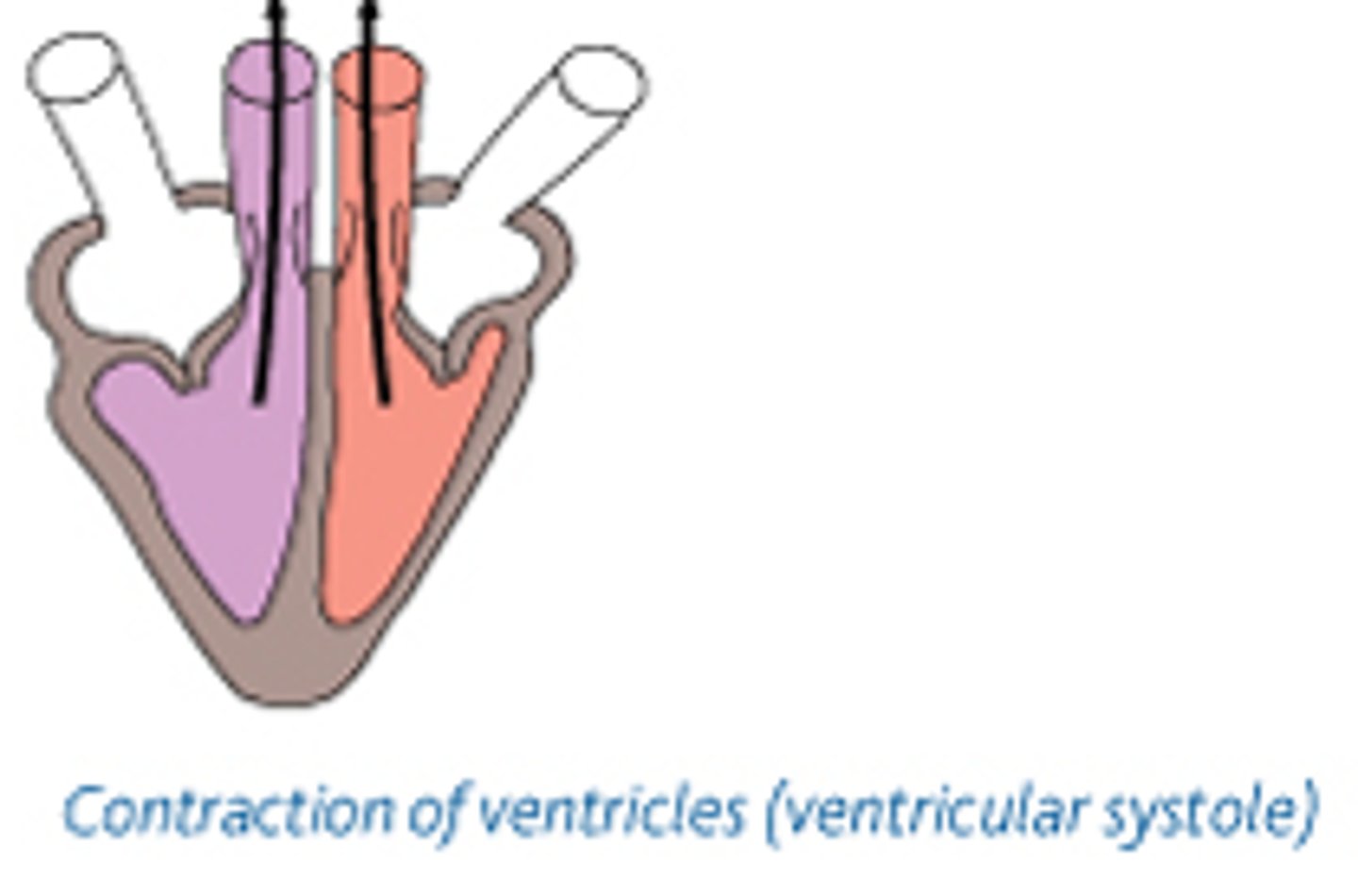
systole
-contraction of the heart
-pulmonary and aortic valves open
-mitral and tricuspid valves close
tricuspid valve
right atrium to right ventricle
mitral/bicuspid valve
left atrium to left ventricle
semilunar valves
prevents blood back wash
what can happen (2) when there is blood back wash
stroke, heart attack
what is the difference for heart attacks between no oxygen and obstructed artery
obstructed artery- recoverable; no oxygen in the arteries- fatal
what are coronary arteries?
any artery that provides blood to the heart
steps of blood flow
1) right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from body's tissues
2) blood passes through the tricuspid (AV valve) to the right ventricle
3) right ventricle pumps blood into the pulmonary artery
4) oxygenated blood from pulmonary vein returns to the left atrium
5) blood passes through the bicuspid (mitral) valve to the left ventricle
6) left ventricle ejects blood through the aortic (semilunar) valve into the aorta for transport in the systemic circuit
the bigger the tubule, the (less/more) pressure, and (lower/higher) velocity of blood travel
the bigger the tubule, the less pressure, and higher velocity of blood travel
do we spend more time in systolic or diastolic?
we spend 33% more time in diastolic
blood pressure =
cardiac output * total peripheral resistance (mmHg)
what is blood pressure?
-the pressure being placed on vasculature
-changes depending on where you measure
-typically measured at brachial artery (easy access + consistency)
what is cardiac output?
how much the heart beats in 1 minute
MAP (mean arteriole pressure) =
diastolic BP +[0.333 (systolic - diastolic)]
What is systolic pressure?
Top number in blood pressure. Amount of pressure heart generates when pumping blood throughout arteries.
What is diastolic pressure?
Bottom number, amount of pressure in arteries when heart is at rest between beats.
which is weighted more heavily, diastolic or systolic?
diastolic
too much/high blood pressure
-sign of cardiovascular disease
-above 140 mmHg systolic + 90 mmHg diastolic
what is considered too high for blood pressure
140+
what is considered too low for blood pressure
90
too little/low blood pressure
-passing out (more common in women)
-orthostatic hypotension
-internal bleeding
hypertension effects on:
-blood vessels
-brain
-heart
-kidneys
-blood vessels: vascular hypertrophy
-brain: blood clot-> aneurysm-> stroke
-heart: left ventricular hypertrophy
-kidneys: kidney failure
how do muscles help blood flow?
muscles can help blood flow into the right directions
how long should you keep your body moving after exercise to give the heart time to calm down?
5 mins
cardiac output =
HR * stroke volume
what happens when we max out C.O.
we have to rely on heart rate
units of C.O.
L/min
what are the 2 sympols for cardiac output
Q (older), and CO (newer)
cardiac output is proportional to what
the metabolic rate of intensity
Fick's law -->
VO2 = ( A-V O2 difference) * cardiac output
A-V O2 difference
oxygen transport from circulation to muscles
when starting exercise, what increases first/second?
stroke volume and then HR
what is preload?
ventricular filling (left ventricle)
end diastolic volume
amount of blood in ventricle before ventricular contraction
Frank Starling Principle
Within normal physiological limits, the force of contraction is directly proportional to the initial length of the muscle fiber"
aka the more blood goes into the heart, the more blood comes out of the heart
what is the frank starling principle explaining
the length tension relationship to the heart; stretch heart-> more blood-> more stroke volume
to increase arterial O2 capacity, what must happen?
increase exercise intensity
how does diastolic and systolic blood pressure change during exercise?
-systolic blood pressure increases -> cardiovascular responses
-diastolic blood pressure is not expected to change/will go down a little
cardiovascular responses to exercise in order:
-increase stroke volume + greater left ventricle
-increase heart rate
-increase in CO2
-increased systolic blood pressure and MAP
-increased arterial compliance
-increased blood pressure
where does blood move when exercising?
to the muscles
the left ventricle becoming larger, increases the _________________
stroke volume
overall effects of exercise on heart
increased systole, HR and SV
cardiovascular adaptations to excerise are designed to maximaze ____
the amount of oxygenated blood delivered to the muscle
what are the 5 CV adaptations to exercise
-more gas exchange-> more capillaries
-more blood to heart-> more SV-> larger left ventricle
-more time for blood to fill the heart-> lower HR
-when SV increases, CO stays the same then HR decreases
-increased circulation-> decreases BP
what are the 3 training adaptations to the heart
-larger left ventricle -> larger SV
-angiogensis-> more capillaries
-more mitochondria-> more oxygen
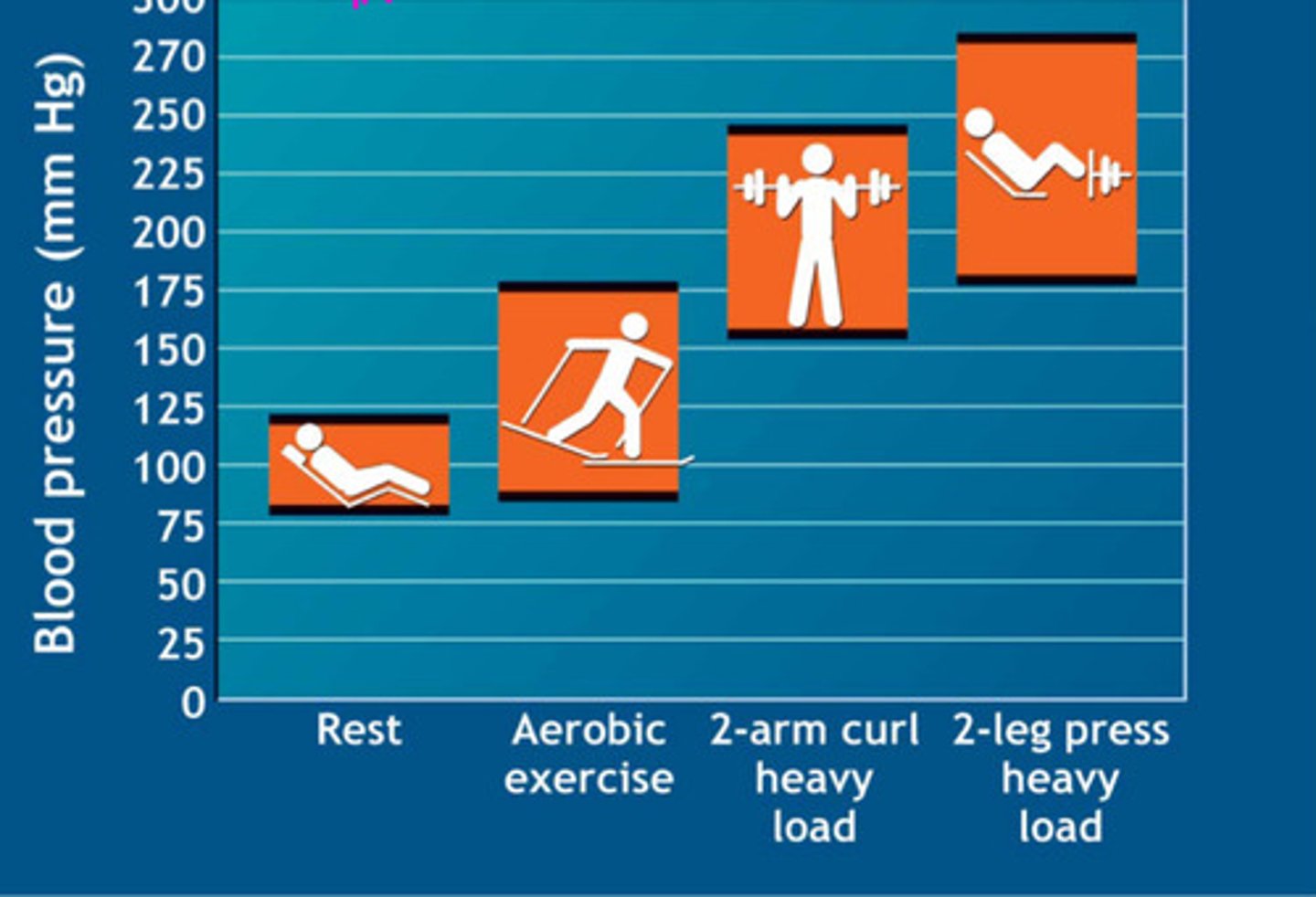
blood pressure increases with increased exercise intensity
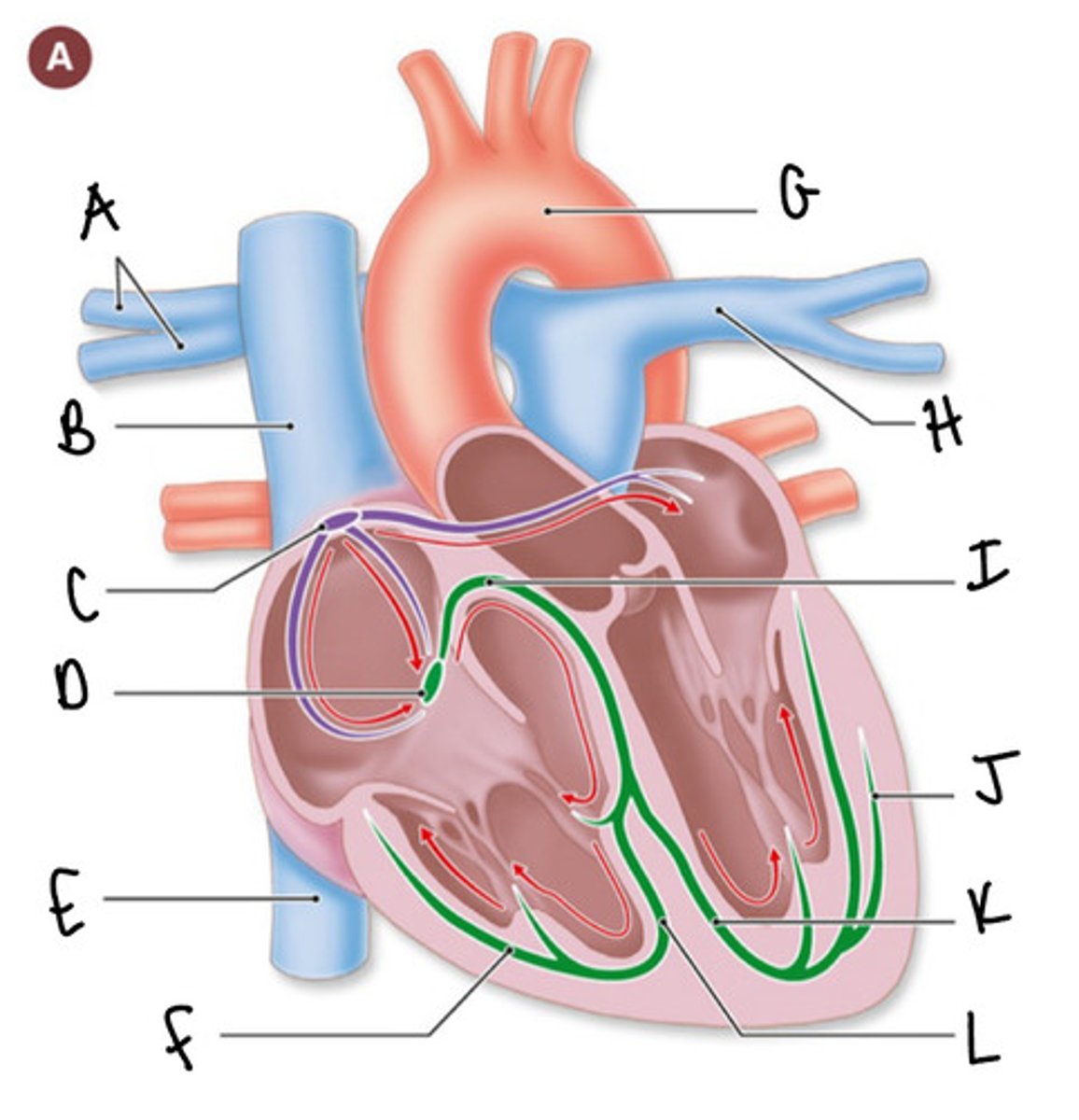
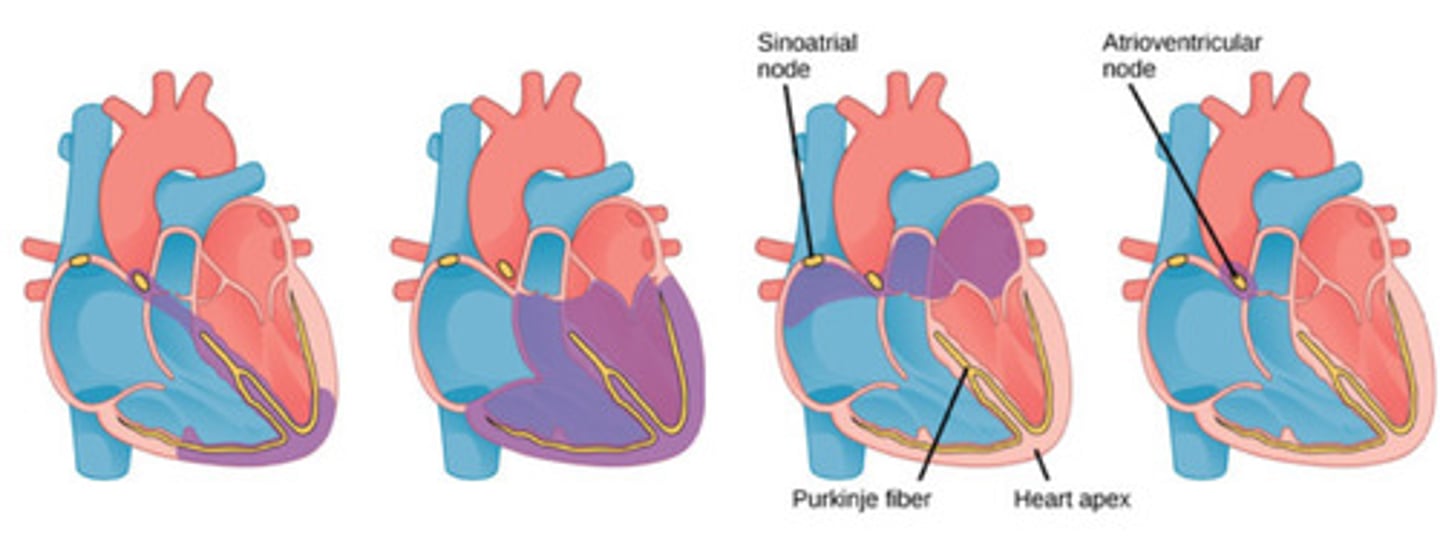
what is happening in this image
A- right pulmonary arteries
B- superior vena cava
C- SA node
D- AV node
E- inferior vena cava
F- Purkinje fibers
G- aorta
H- left pulmonary artery
I- AV bundle (bundle of His)
J- Purkinje fibers
K- left bundle branch
L- right bundle branch
label this diagram
Q; QRS; P; PR interval
label each complex left to right
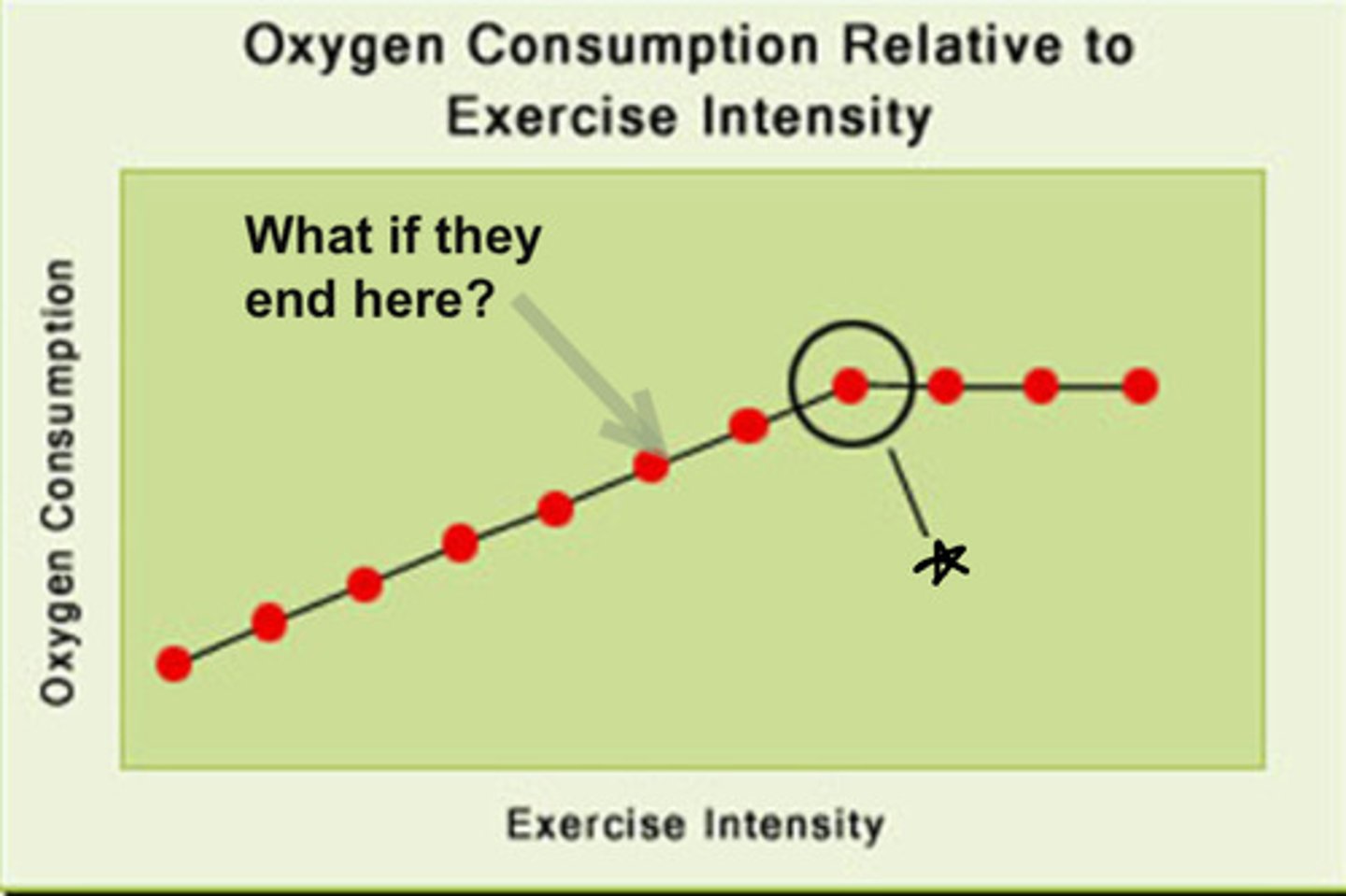
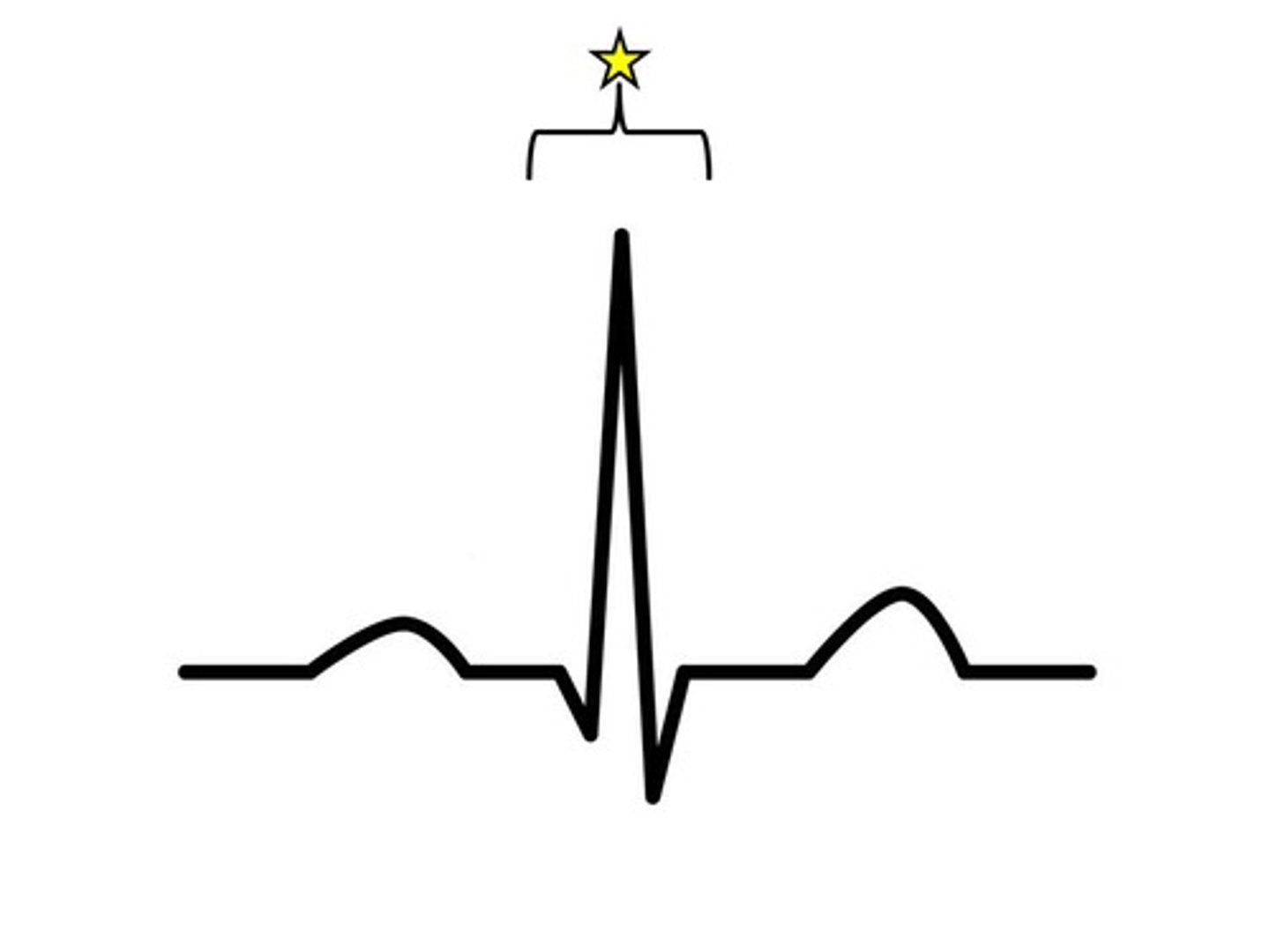
VO2 max
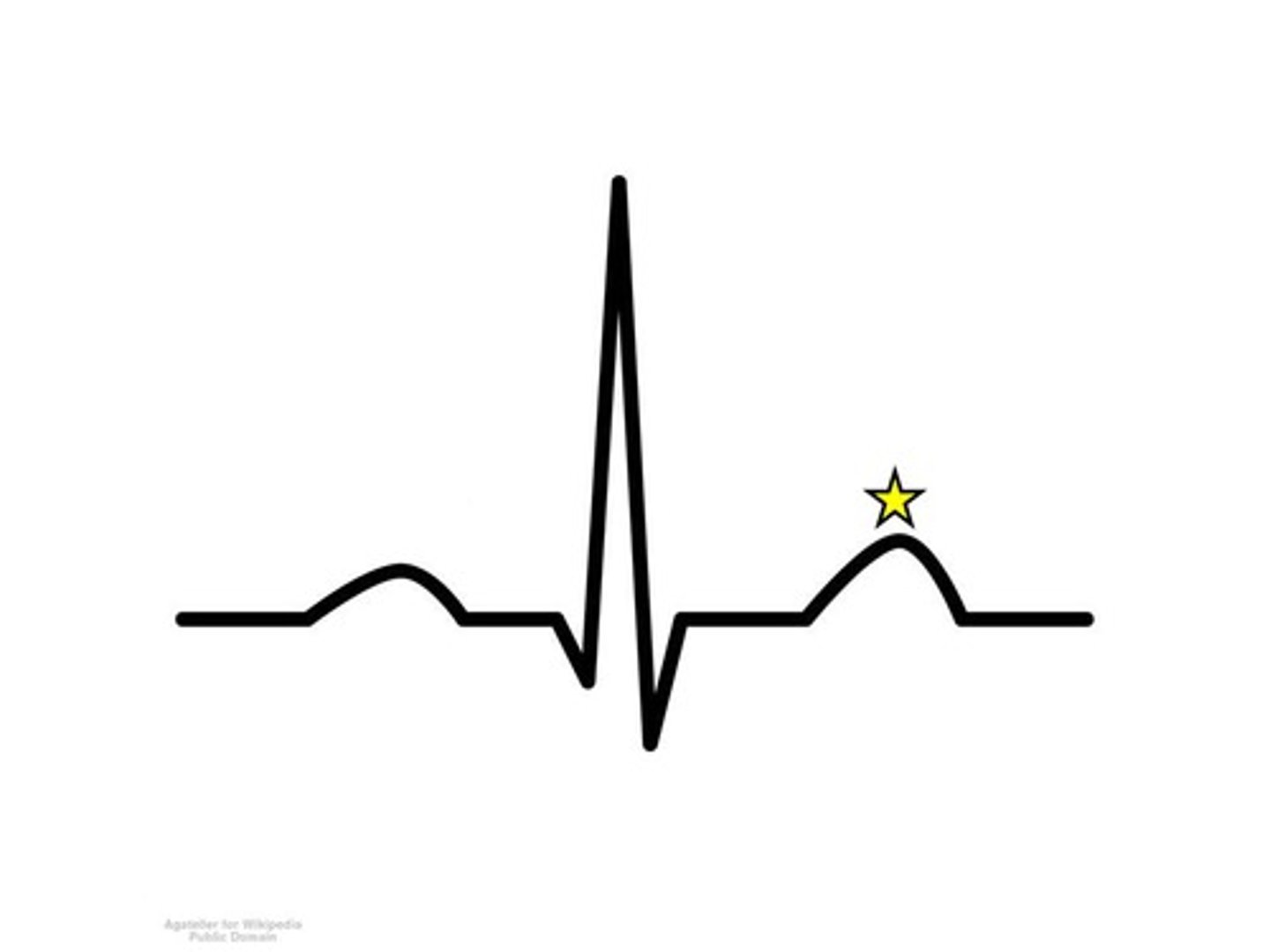
what happens at the star
A- Y
B- 1
C- 2
D- 3
E- X
label the diagram
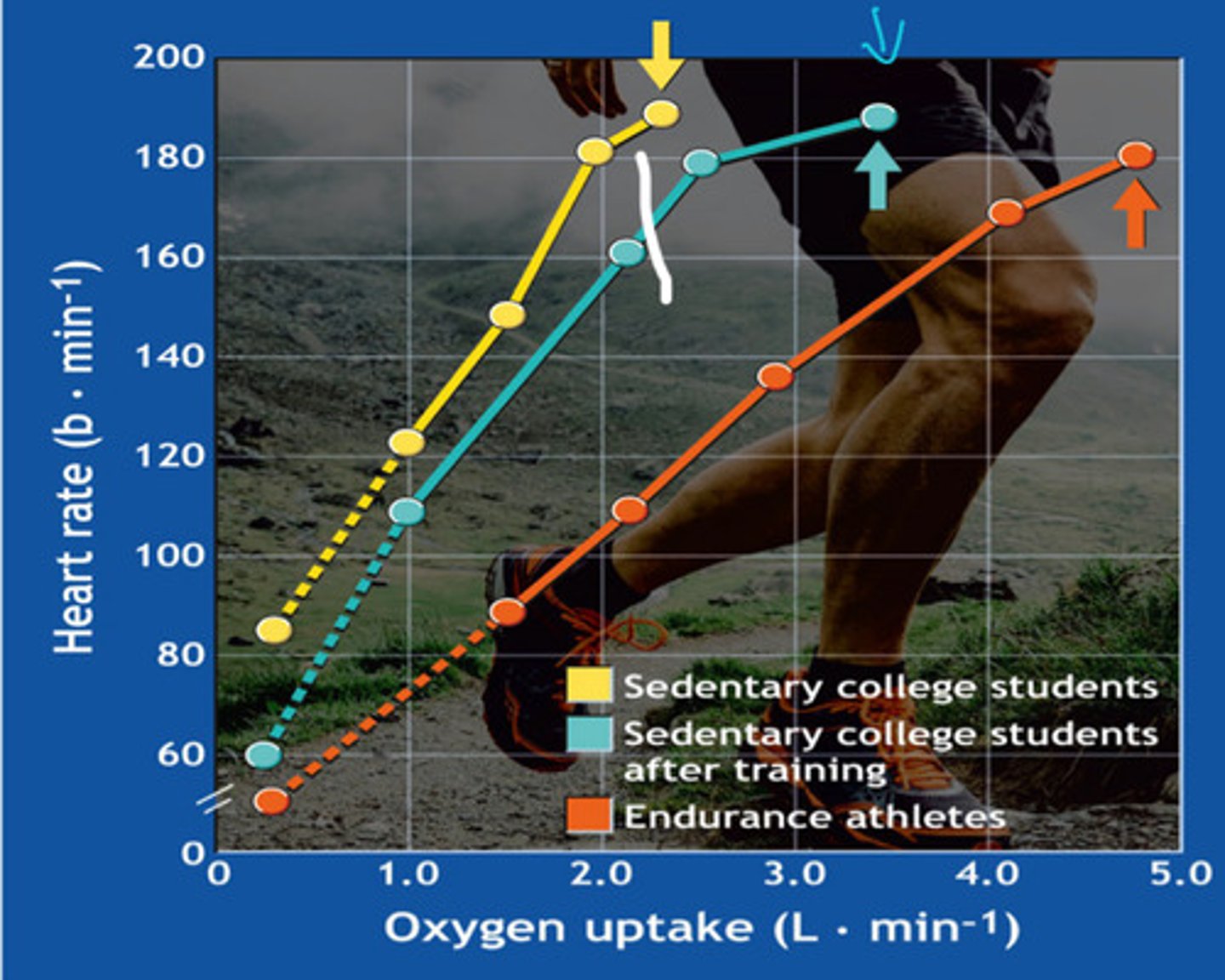
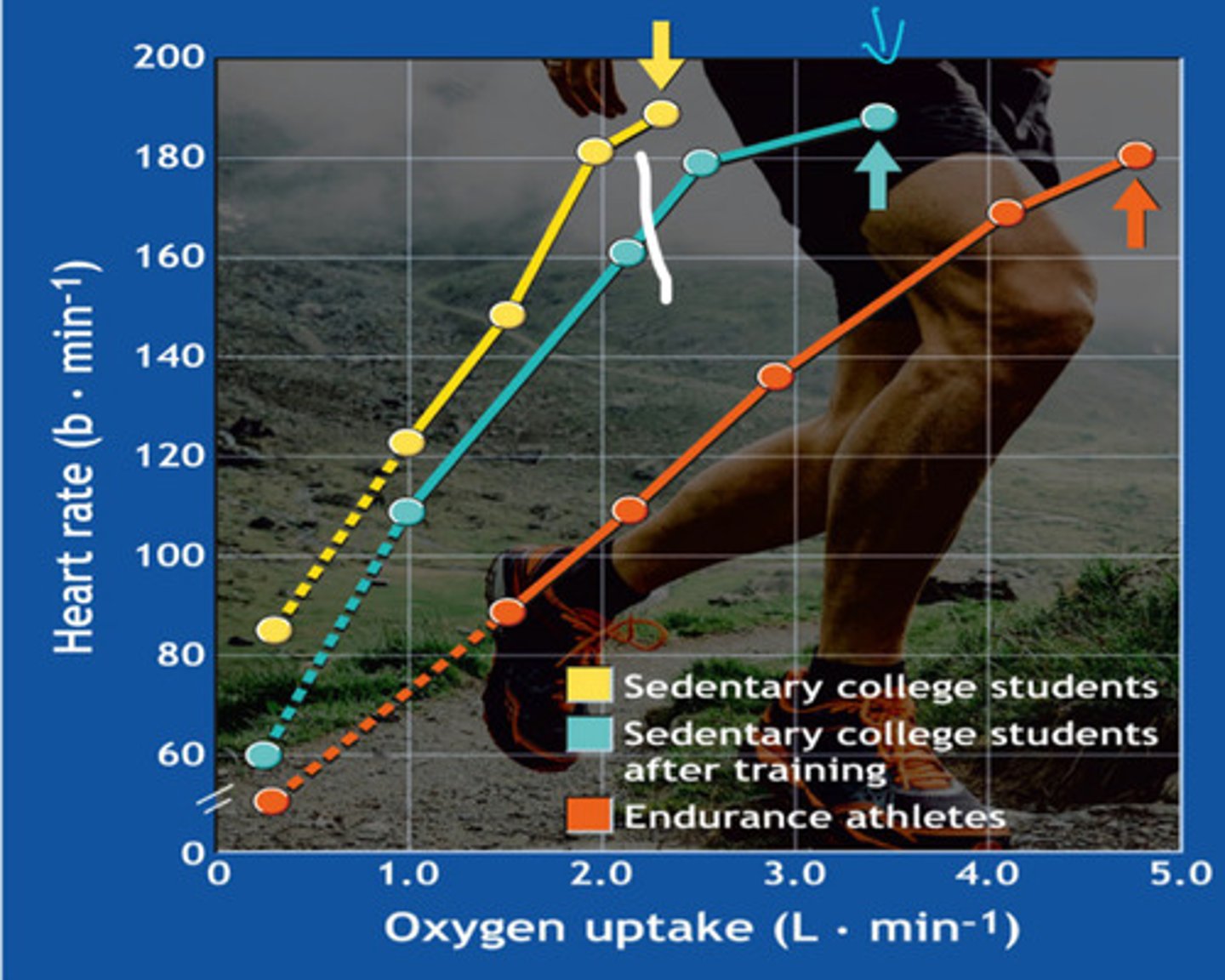
why are there differences in resting heart rate?
-Fitness, age, genetics, and autonomic tone differ between people.
-Medications, stress, or illness can raise or lower baseline HR.
Why are there differences in HR at the same intensity?
- Fitter individuals need a lower HR to meet the same workload (higher stroke volume).
- Environmental factors or individual efficiency change HR response.
-Each person reaches a different max HR and max workload.
-Test stops when the individual reaches their personal limit.
Why do the lines end at different places?
- Lines would be more similar because intensity is normalized (%VO₂max).
- They would all end at 100% VO₂ max instead of at different absolute values.
How may this graph look different if the oxygen consumption were relative to the overall VO2 max?
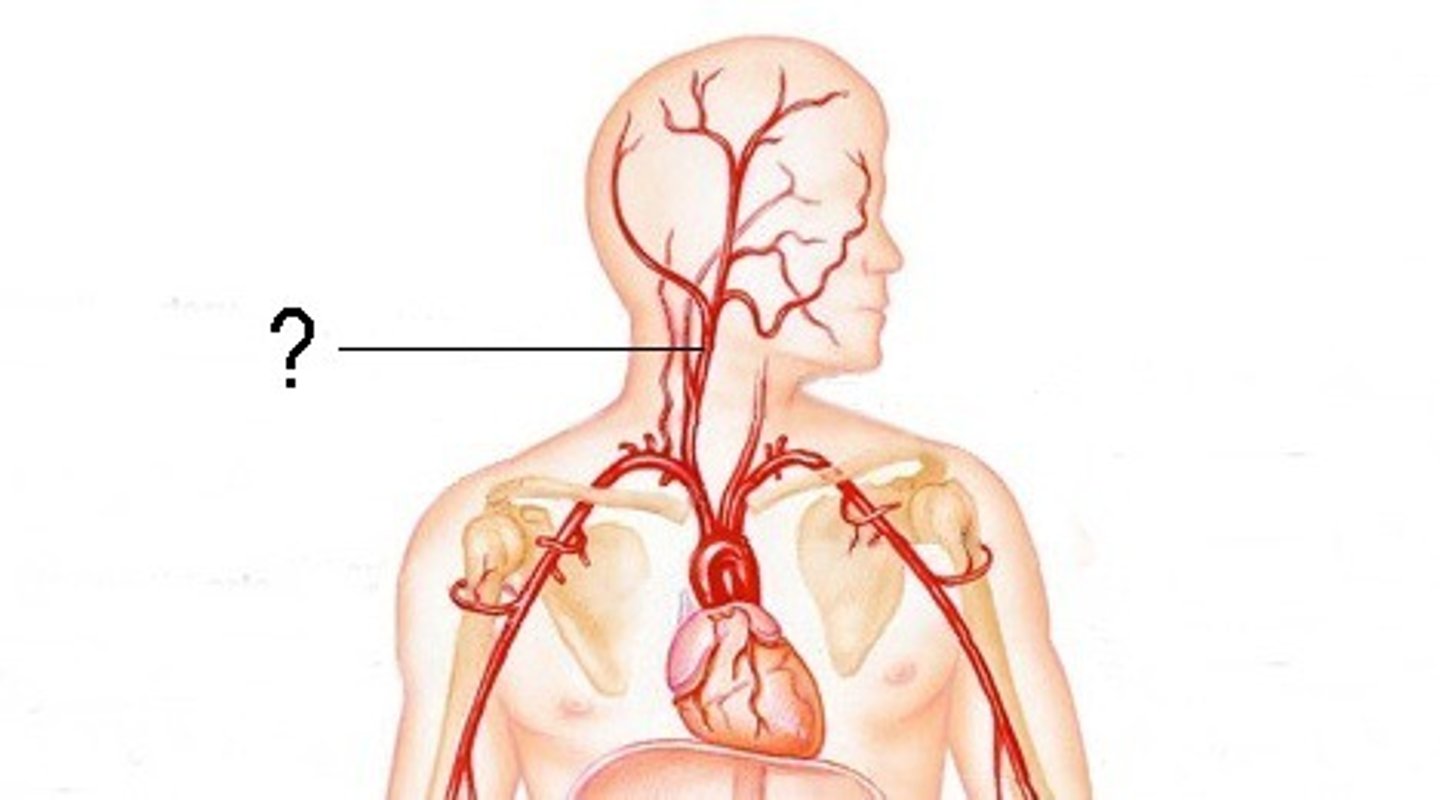
baroreceptors
-get activated with tiny alterations in pressure
-when activated, they decrease heart rate
-one of the main blood supplies to the head
carotid artery
-one of the biggest tubes that delivers blood to the brain
-don't take a persons heart rate here!!!
sympathetic nervous system
fight or flight
catecholamines
-epinephrine and norepinephrine
-what caffeine releases in the body
-increases SA node activation
-increases vasoconstriction
parasympathetic nervous system
rest and digest
when acetylcholine is released in cardiac tissue, what happens? everywhere else?
chill down factor, excitatory factor
during exercise what system is taking over?
sympathetic nervous system (fight or flight)
after exercise what system takes over?
parasympathetic nervous system (rest and digest)
electrocardiogram
measures the electricity of the heart to determine heart health
p-wave; atrial depolarization
name and what is happening
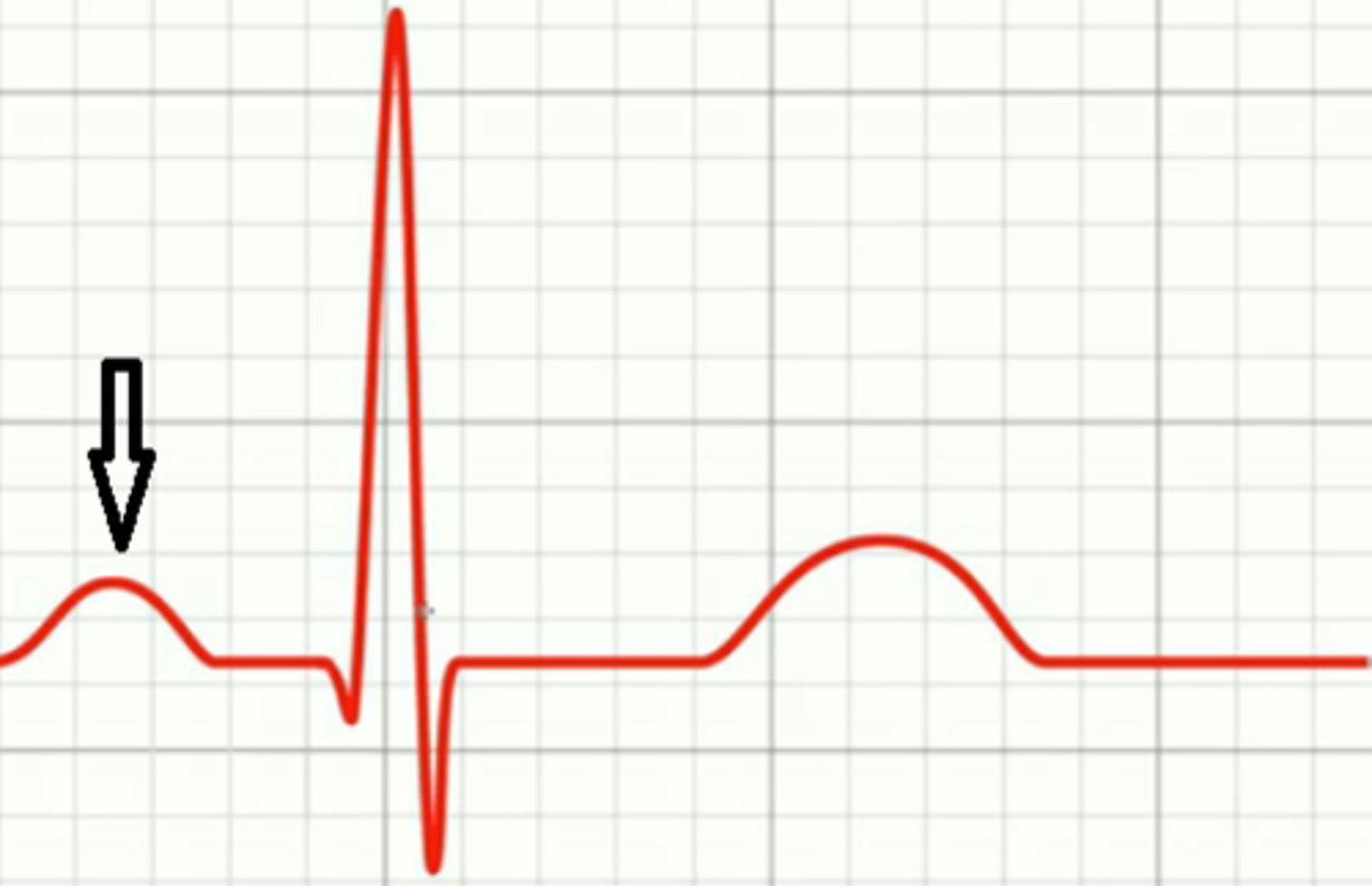
PR interval; conduction delay at AV node
name and what is happening

QRS complex; ventricular depolarization
name and what is happening
T-wave; ventricular repolarization
name and what is happening
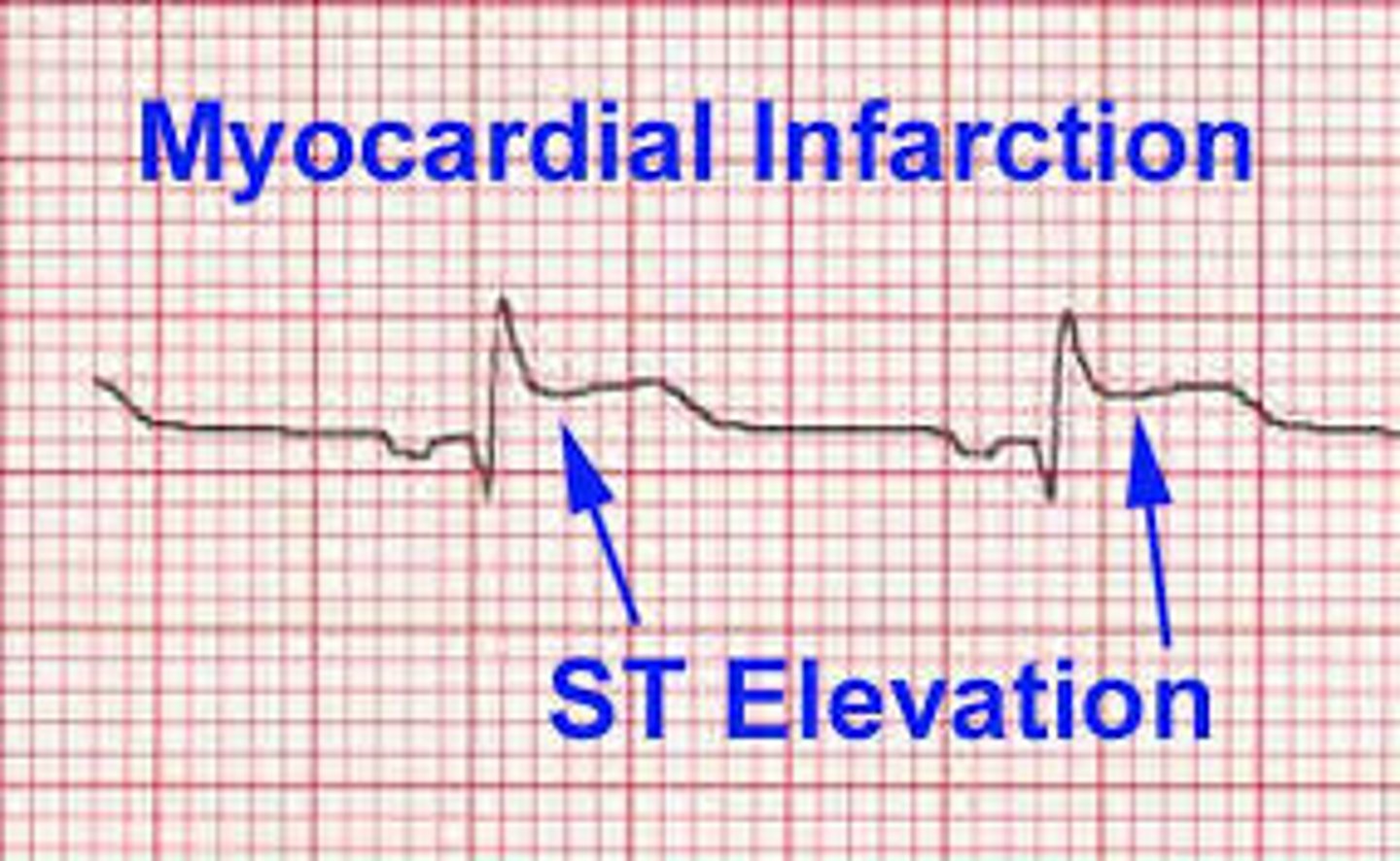
myocardial infarction
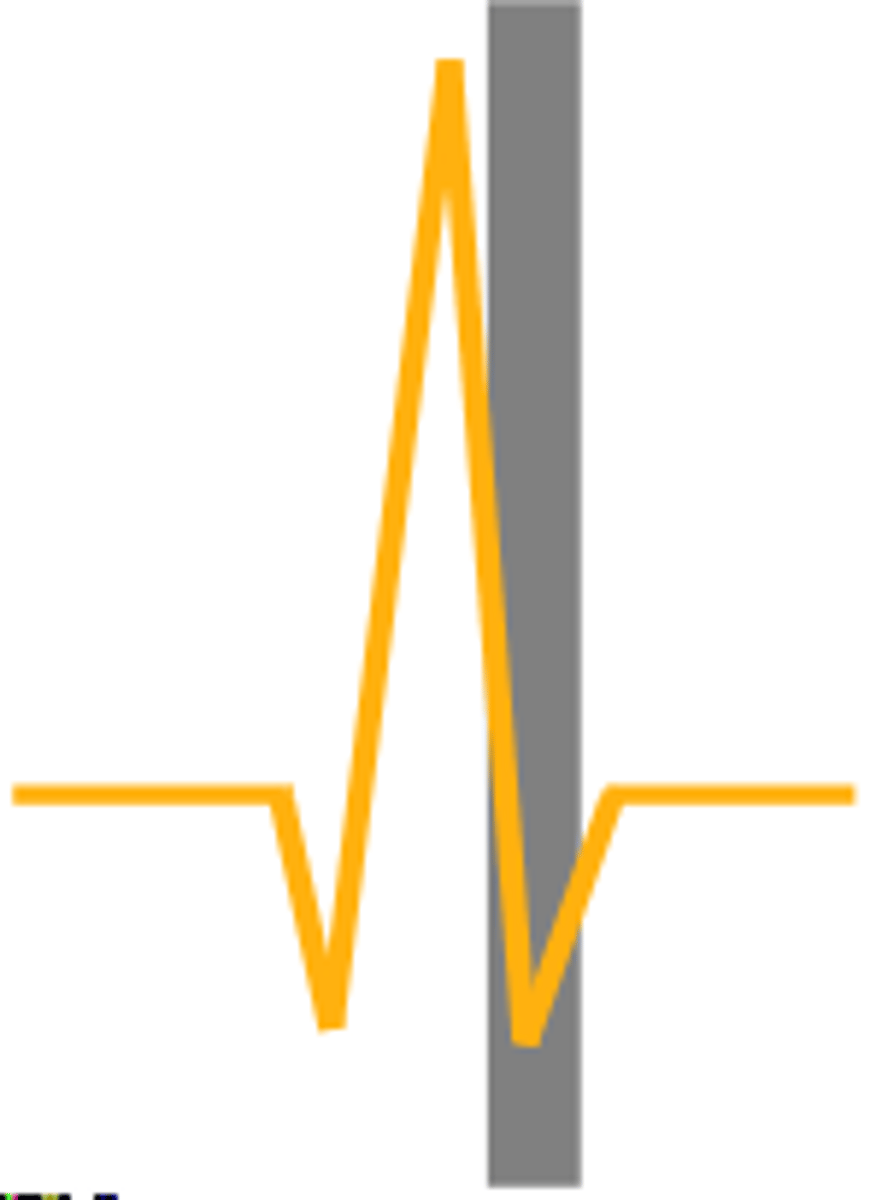
what happens when there is no S or T wave
S-wave; isoelectric ventricle segment
name and what is happening

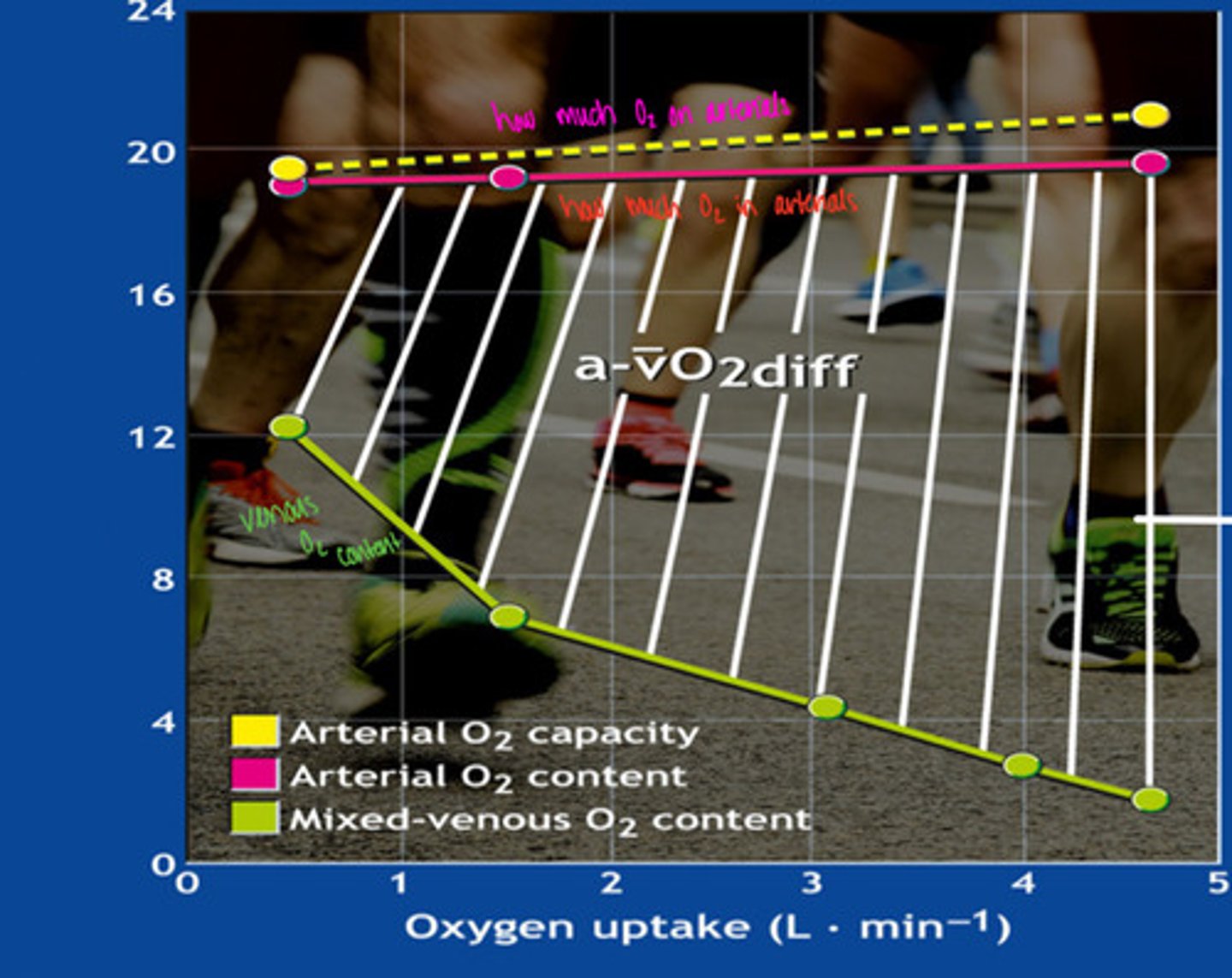
A-VO2 difference
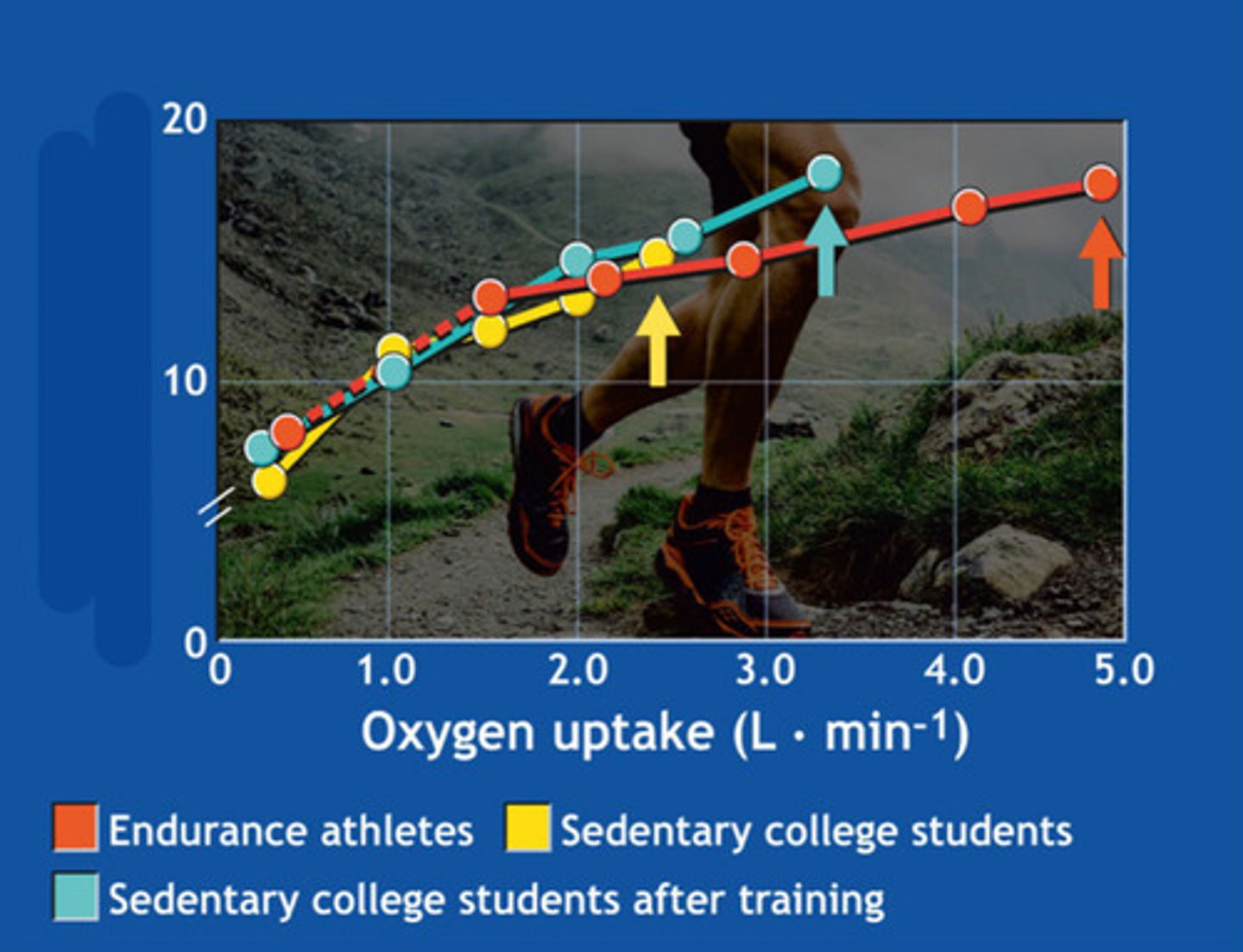
what is this graph showing
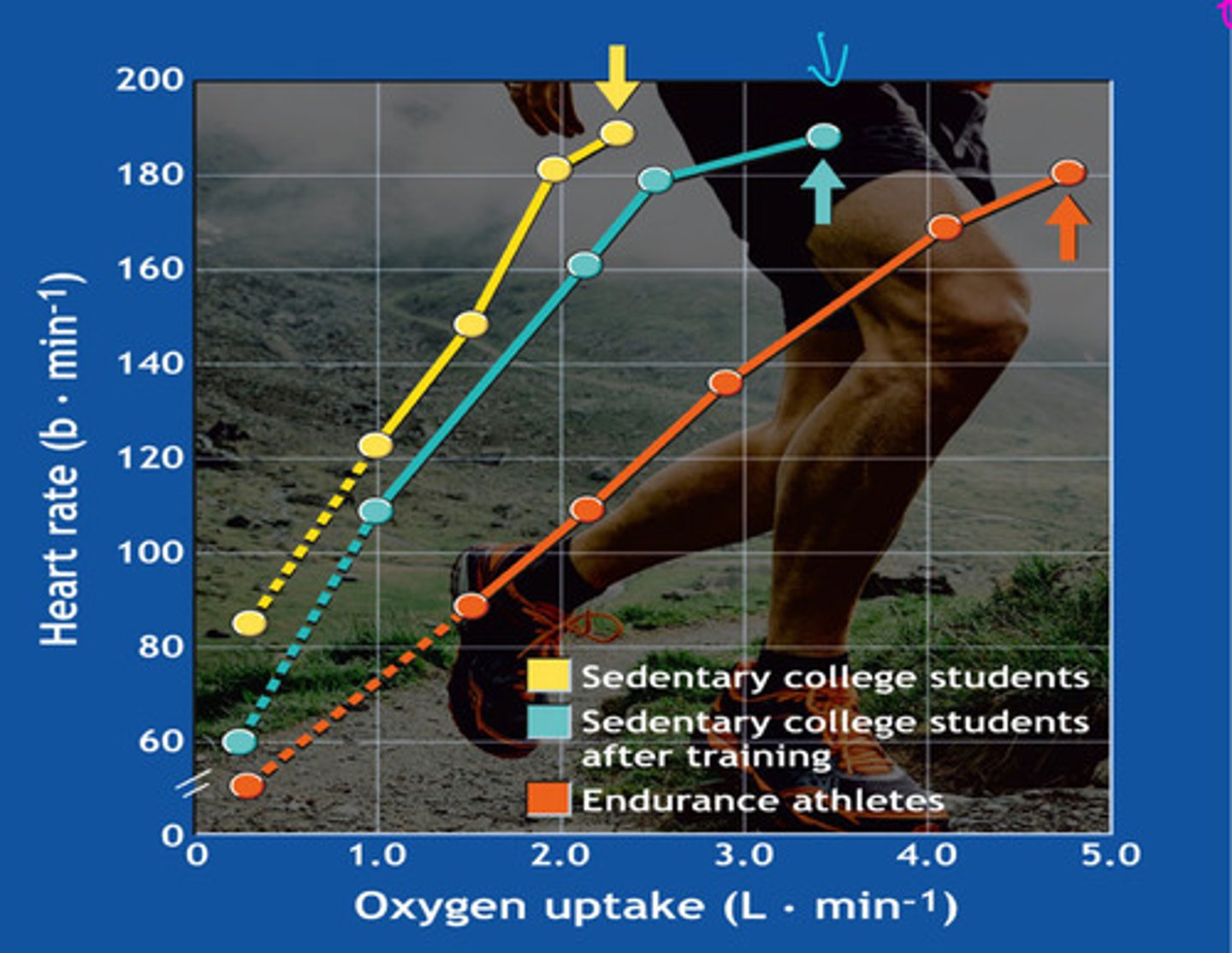
heart rate
what is this graph showing
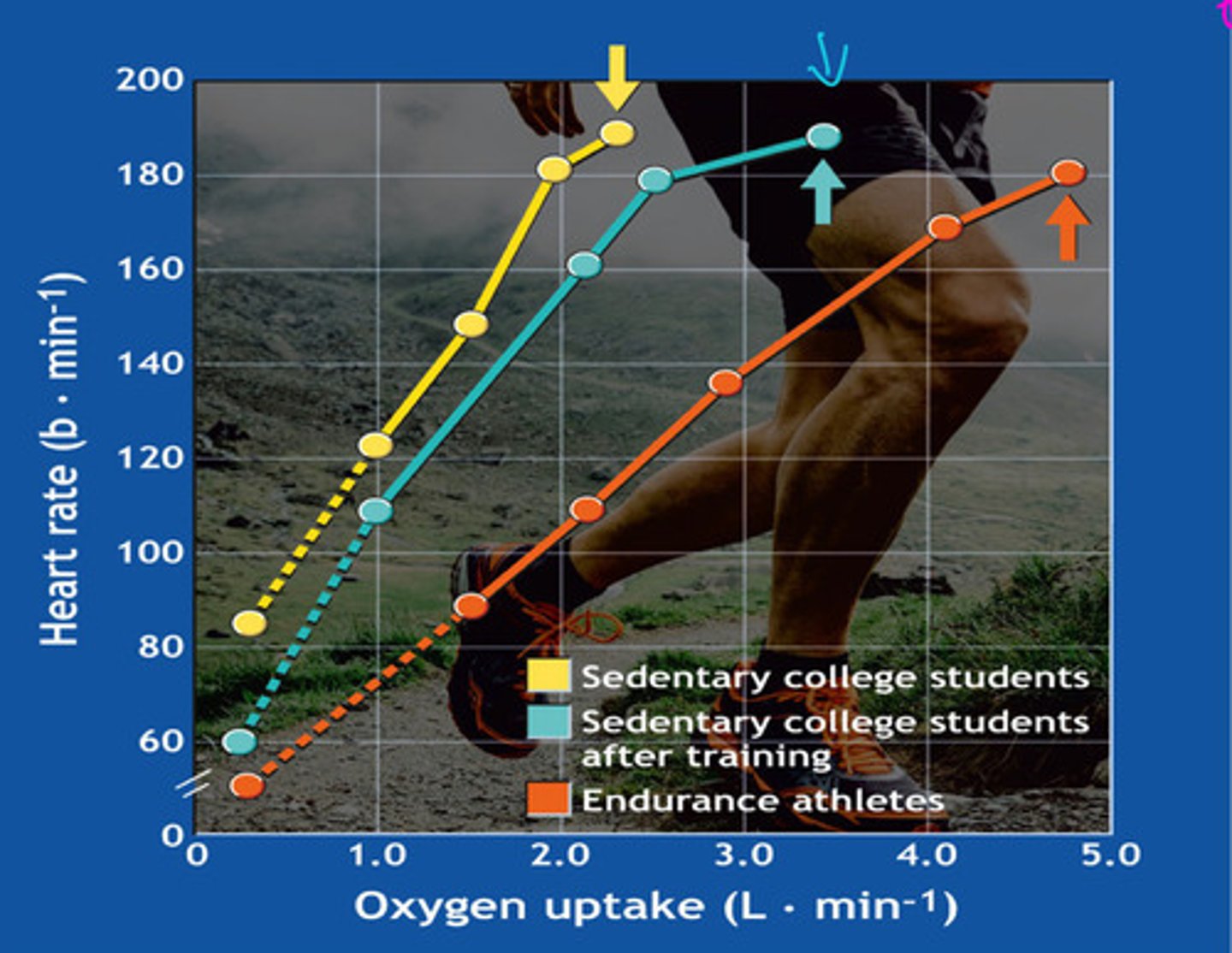
Endurance athletes have the lowest because they have a stronger stroke volume
who has the lower heart rate and why
VO2 max
-maximal volume of oxygen an individual can uptake and utilize
-aerobic capacity
-key indicator of aerobic fitness/health
-units: mL/kg/min or L/min
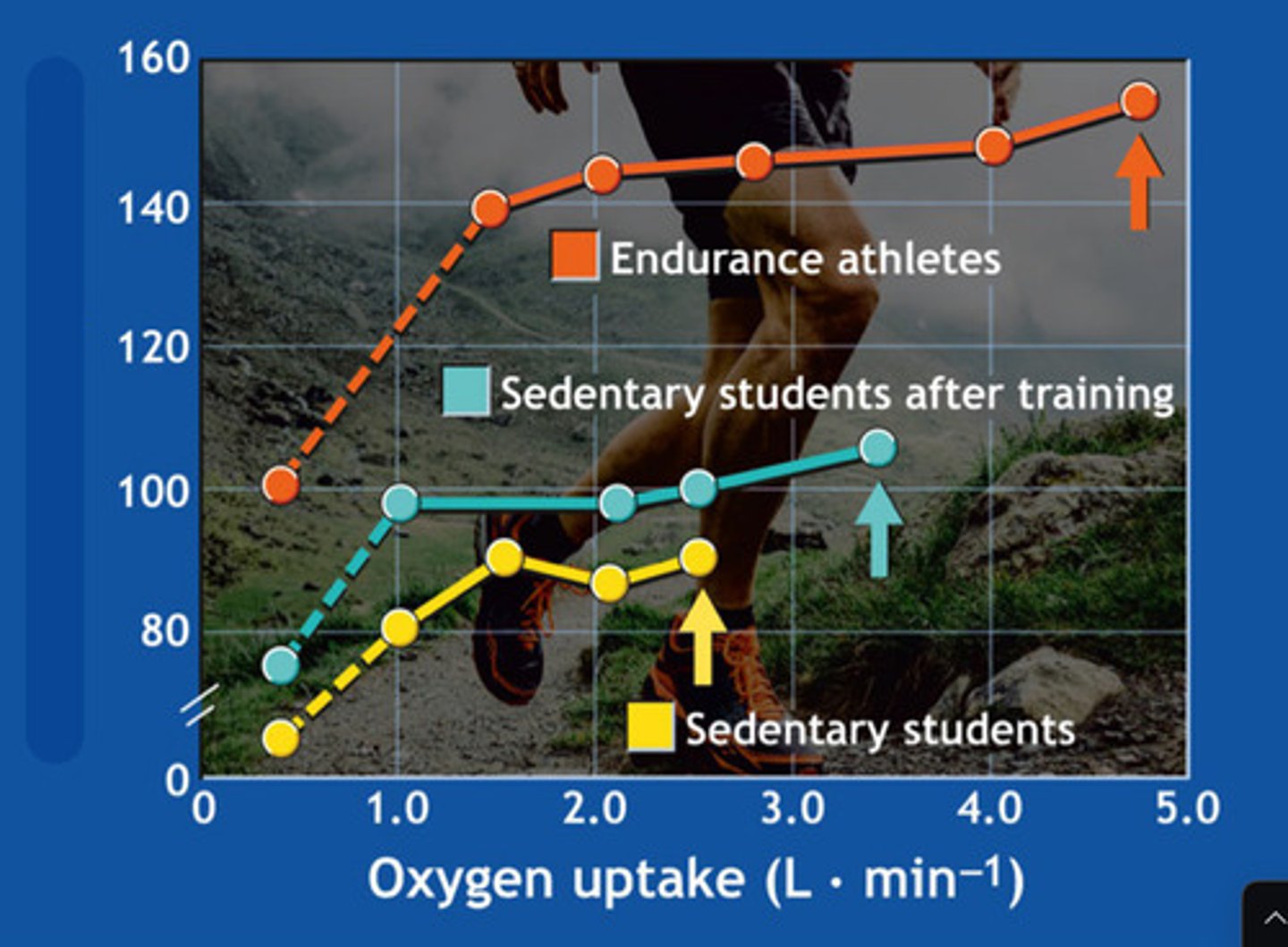
stroke volume
what is this graph showing
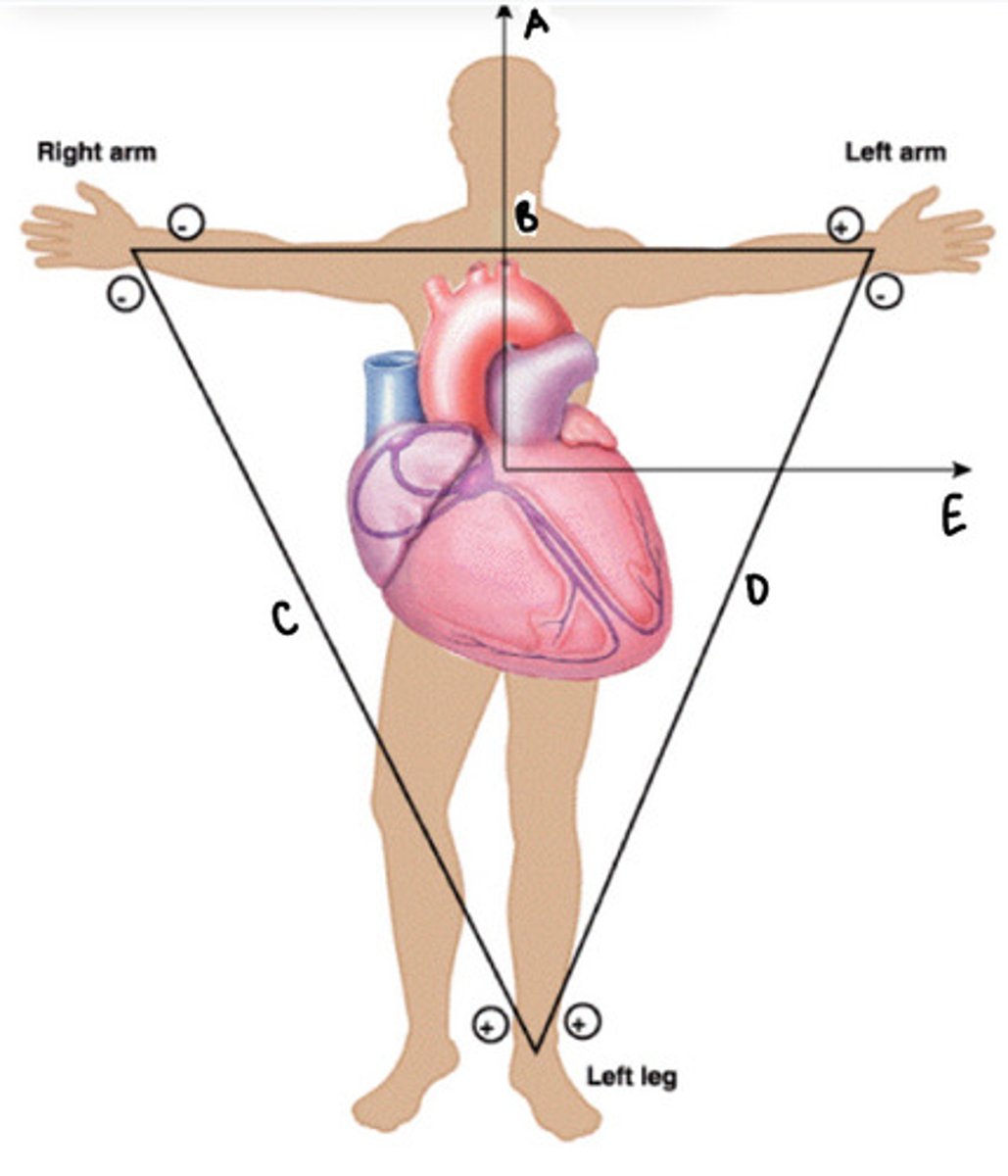
in an ECG, a lead is what and an axis is what
lead: connection between 2 electrodes
axis: imaginary line connecting 2 electrodes
blood oxygen content
what is this graph showing
what are limb leads
measures voltage difference at limb electrodes; right leg is the grounding electrode
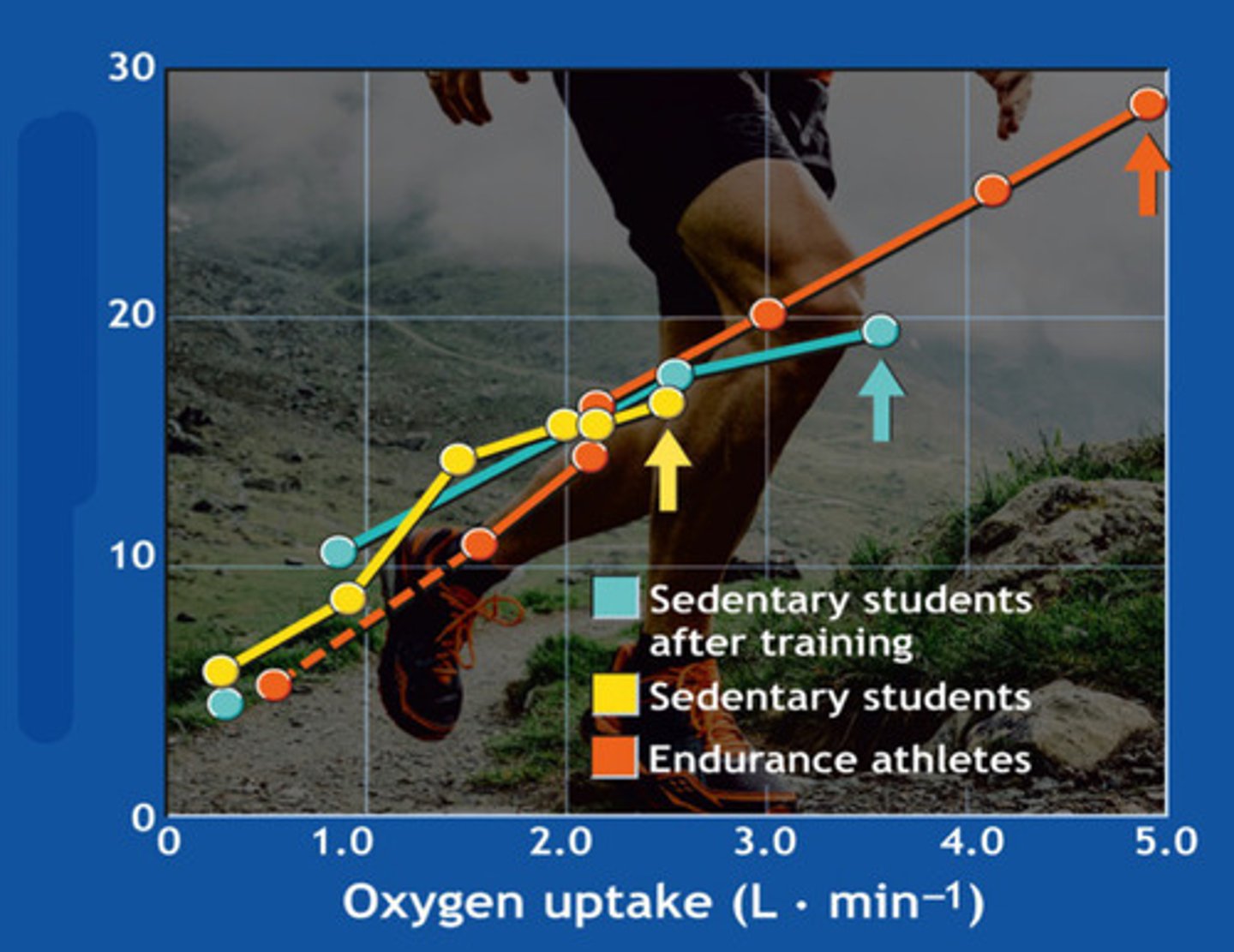
cardiac output
what is this graph showing
what are the chest leads and what do they measure
V1-V6; measure voltage in individual chest leads compared to limb leads
what is VO2 max and its units
maximal oxygen consumption; mL/kg/min
determinants of VO2 max
-sex
-training
-genetics
VO2 max: sex
-muscle mass (greater in men)
-lung size (greater in men)
-heart size (greater in men)
-hemoglobin (men contain more than women)
VO2 man: training
-larger left ventricle -> larger SV
-angiogensis-> more capillaries
-more mitochondria-> more oxygen
VO2 max: genetics
-fiber type
-mitochondria
-vascular content
-size (heart, lungs, etc.)
VO2 peak
highest amount of oxygen consumed during a specific exercise session