Membrane Structure & Function Ch. 7
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
the plasma membrane
is the boundary that separates the living cell from its surroundings
selectively permeable
the plasma membrane is __________ ___________
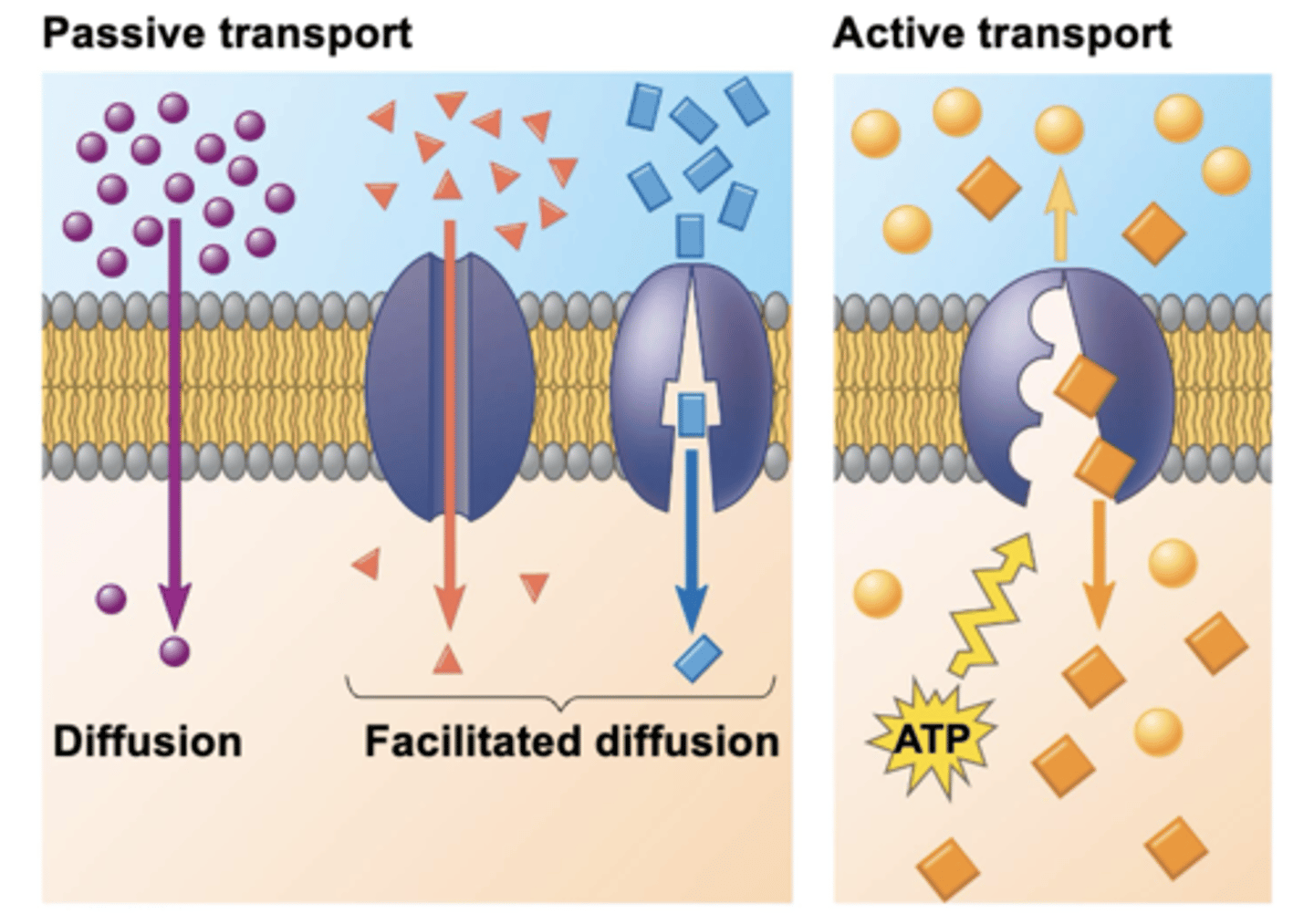
passive transport
(of small molecules) doesn't require energy; it may involve transport proteins
active transport
(of small molecules) requires energy and a transport protein
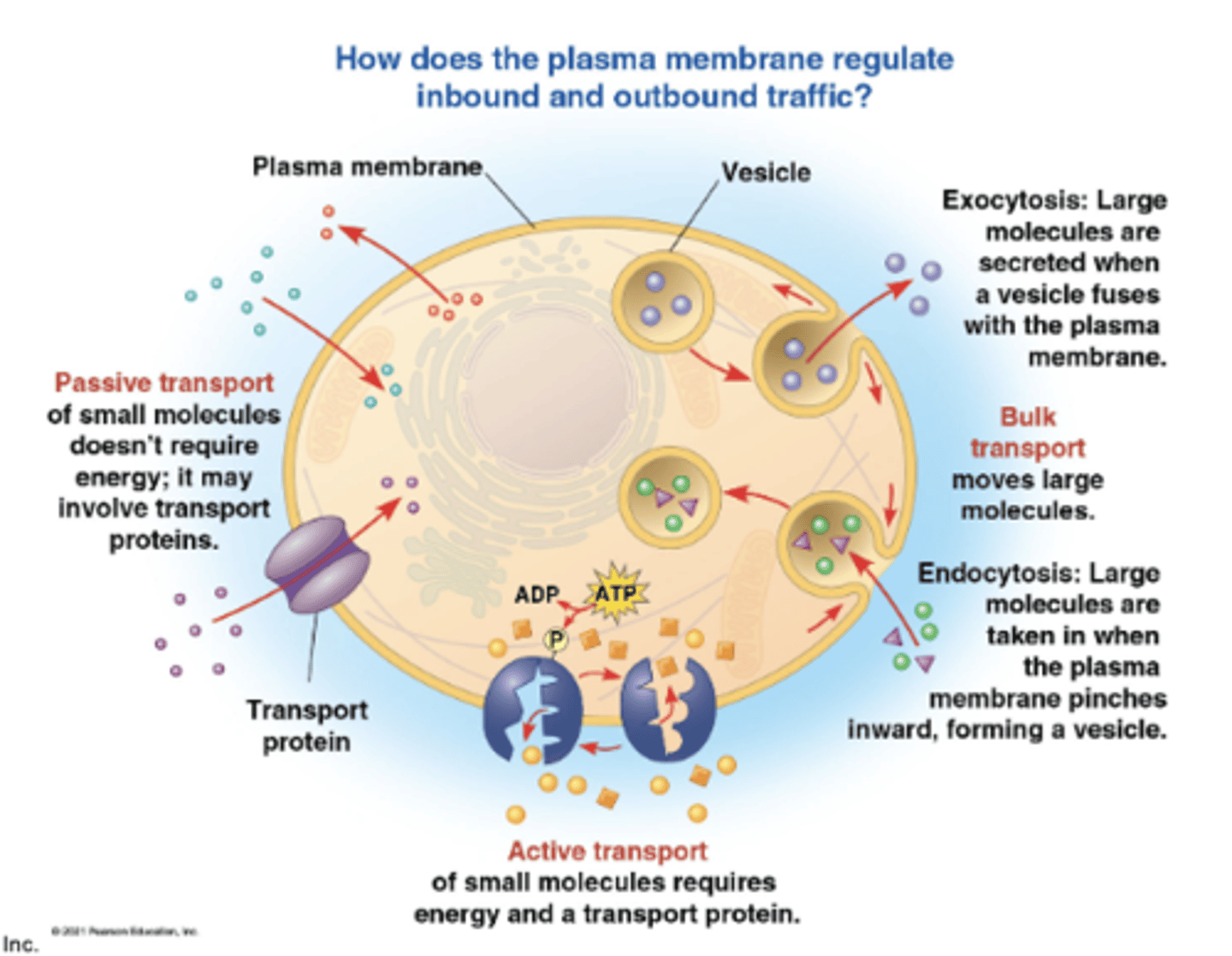
exocytosis
molecules are secreted when a vesicle fuses with the plasma membrane
bulk transport
moves large molecules
endocytosis
large molecules are taken in when the plasma membrane pinches inward, forming a vesicle
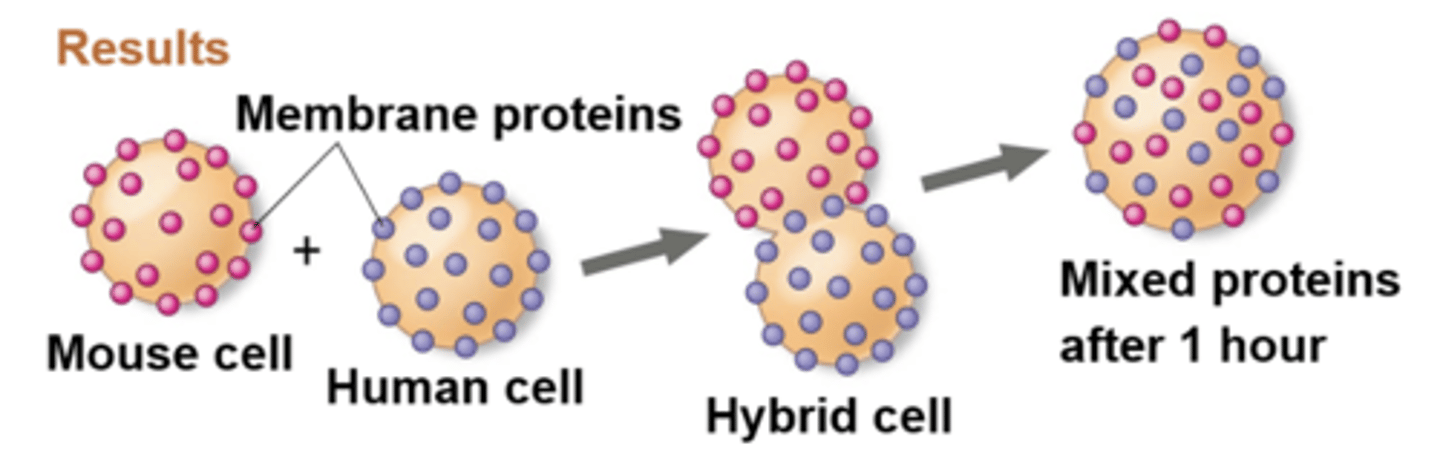
fluid mosaic model
the membrane is a mosaic of protein molecules bobbing in a fluid bilayer of phospholipids
hydrophobic interactions
membranes are held together mainly by weak __________ __________
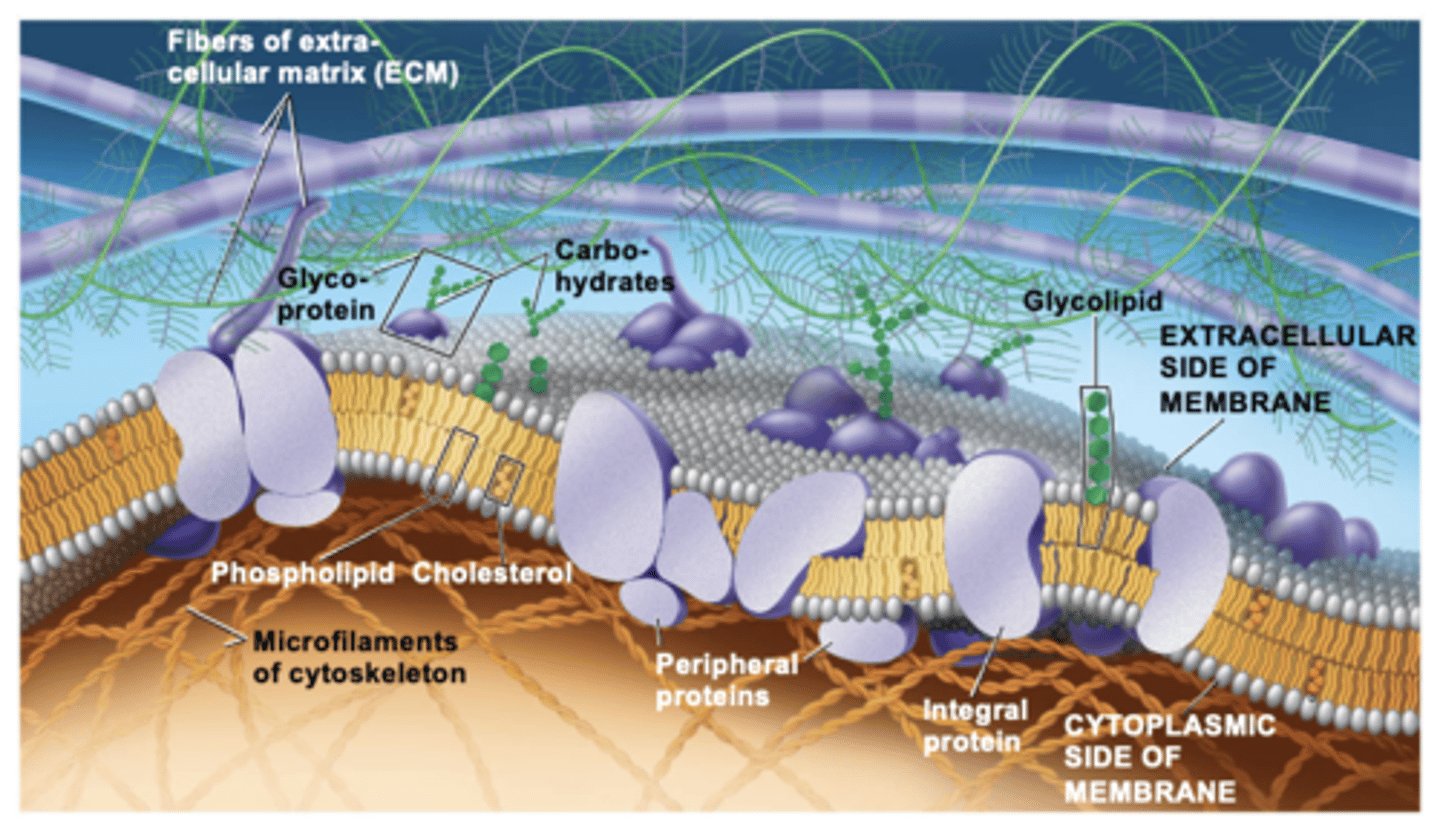
lipids
proteins
most of the _______ and some ______ can move sideways within the membrane
peripheral proteins
are bound to the surface of the membrane
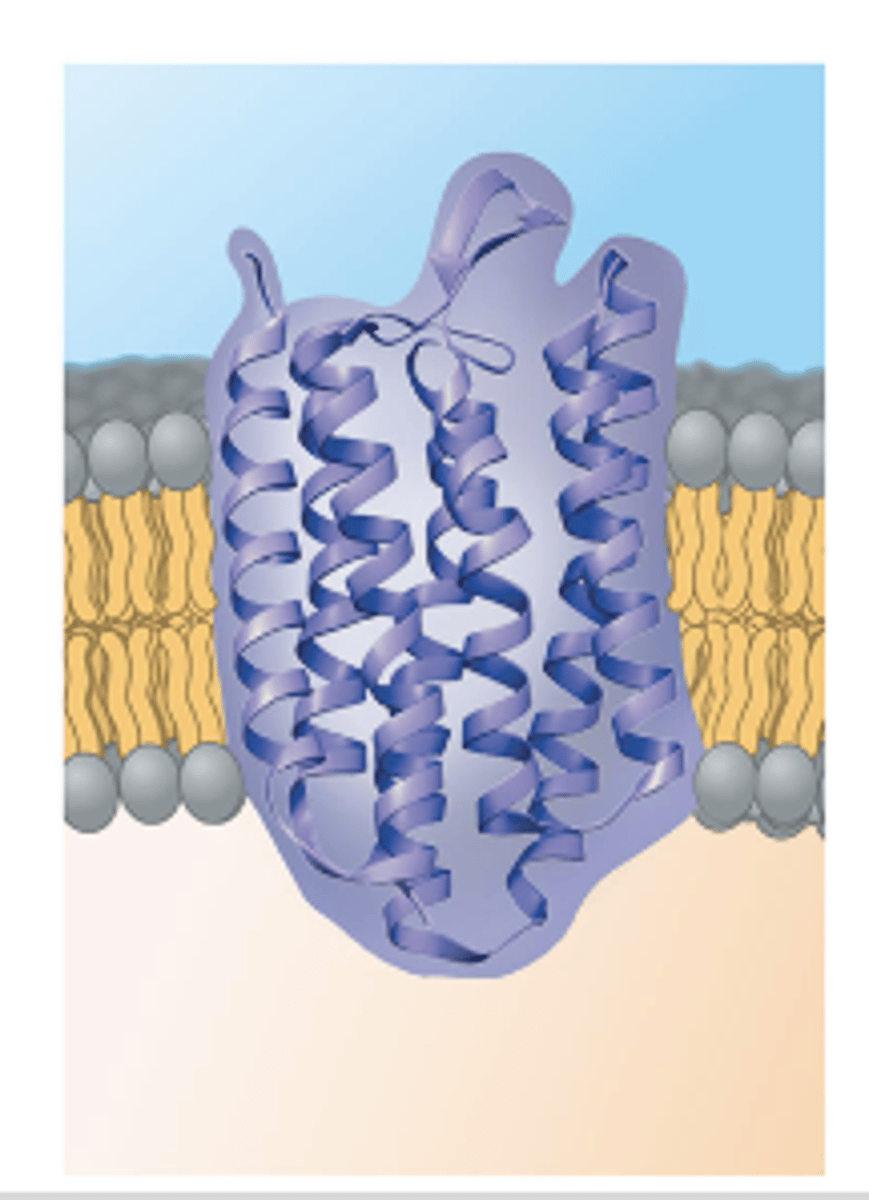
integral proteins
penetrate the hydrophobic core
transmembrane proteins
integral proteins that span the membrane are called __________ __________
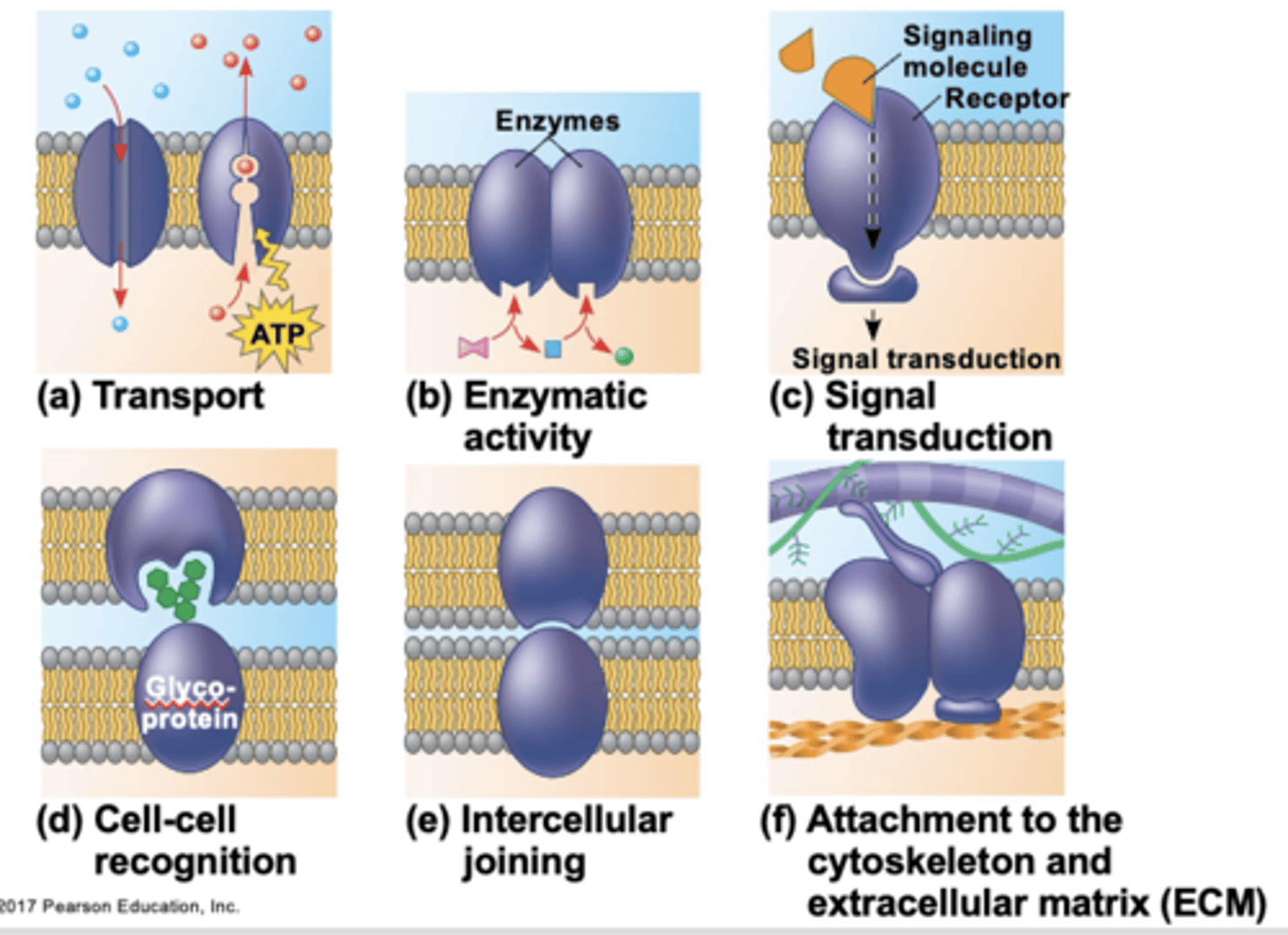
transport, enzymatic activity, signal transduction, cell-cell recognition, intercellular joining, attachment to the cytoskeleton and extracellular matrix (ECM)
cell-surface proteins can carry out several functions (list all 6)
plasma membrane
a cell must exchange materials with its surroundings, a process controlled by the _________ __________
molecular traffic
plasma membranes are selectively permeable, regulating the cell's _________ _________
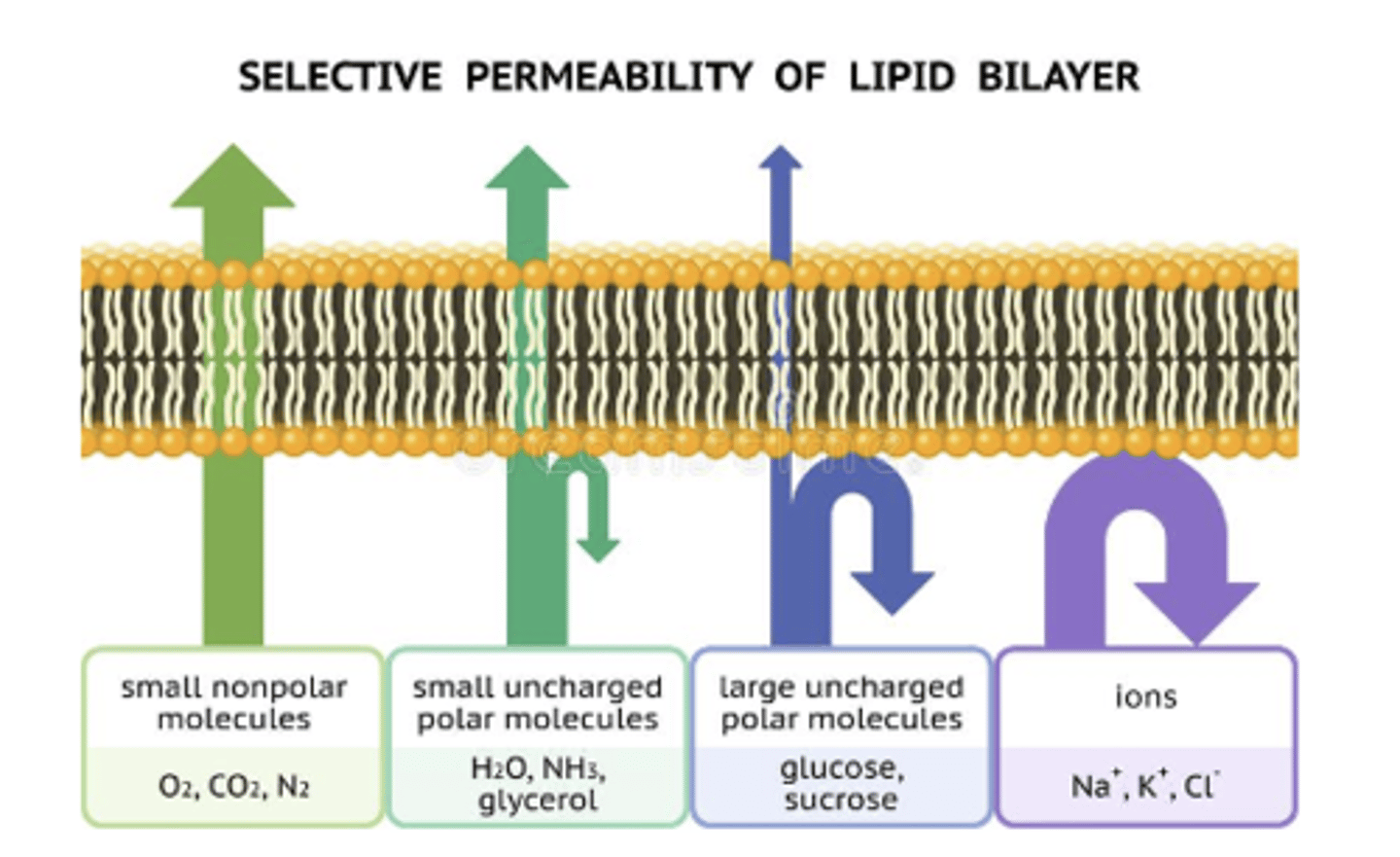
hydrophobic (non polar)
molecules, such as hydrocarbons, can dissolve in the lipid bilayer and pass through the membrane rapidly
hydrophilic (polar)
molecules including ions and polar molecules do not cross the membrane easily
small non polar molecules
O2, CO2, N2
small uncharged polar molecules
H2O, NH3, glycerol
large uncharged polar molecules
glucose, sucrose
ions
Na+, K+, Cl-
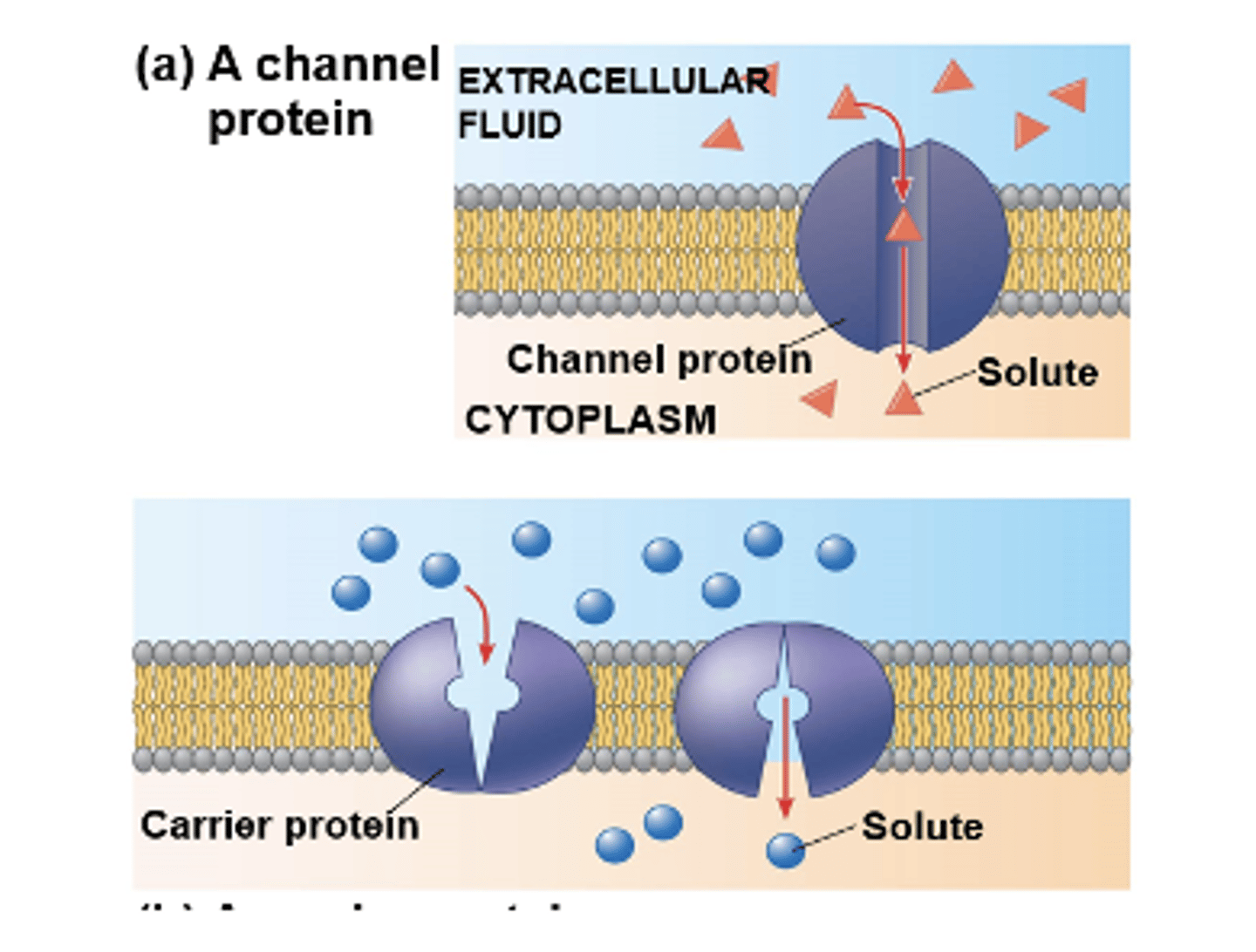
transport proteins
allow passage of hydrophilic substances across the membrane; is specific for the substance it moves
carrier proteins
other transport proteins, called _______ _______, bind to molecules and change shape to shuttle them across the membrane
passive transport
is diffusion of a substance across a membrane with no energy investment
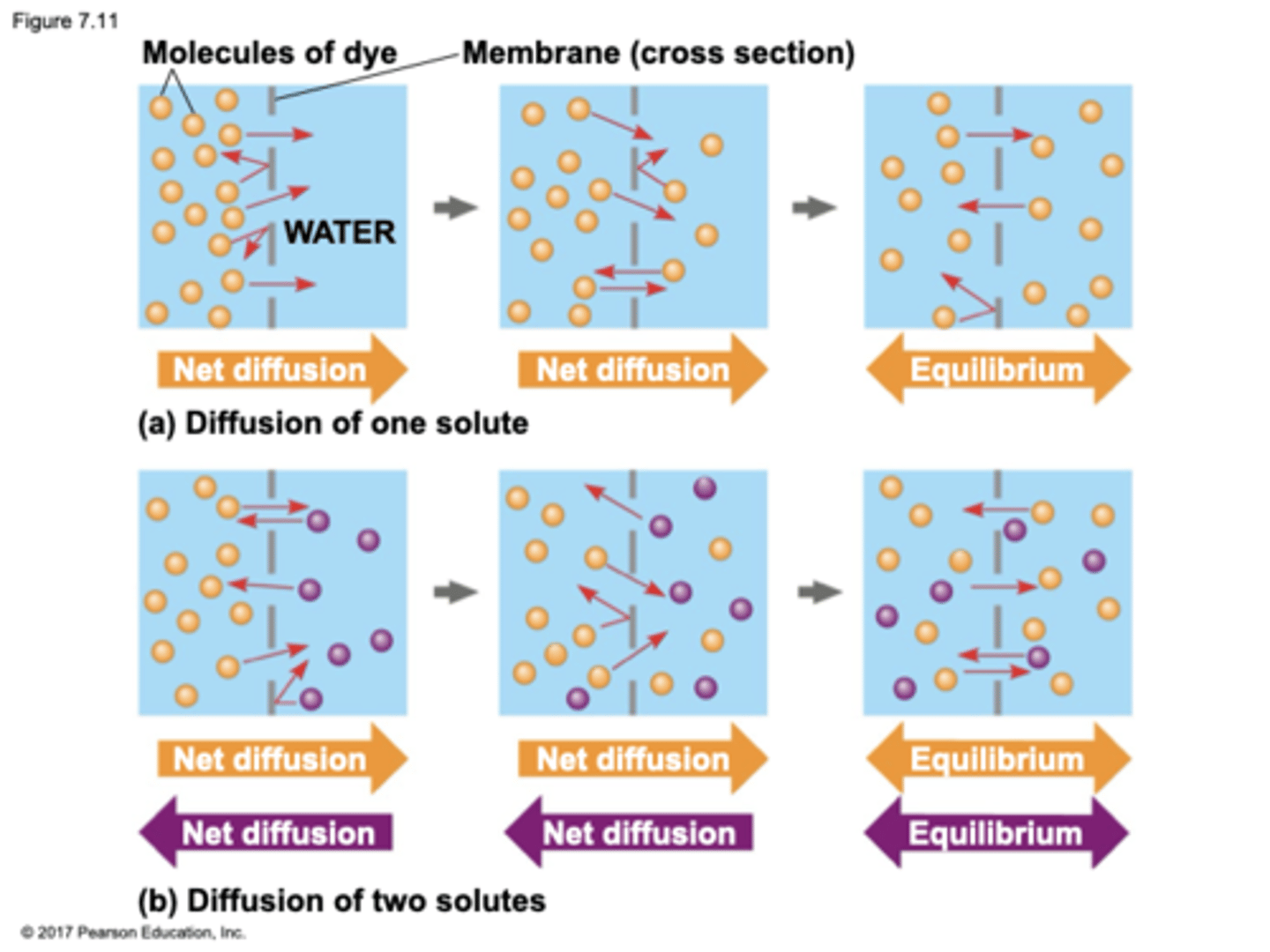
diffusion
is the tendency for molecules to spread out evenly into the available space
directional
although each molecule moves randomly, diffusion of a population of molecules may be ___________
concentration gradient (from high concentration to low concentration)
substances diffuse down their ___________ ___________
passive transport
the diffusion of a substance across a biological membrane is ________ ________ because no energy is expended by the cell to make it happen
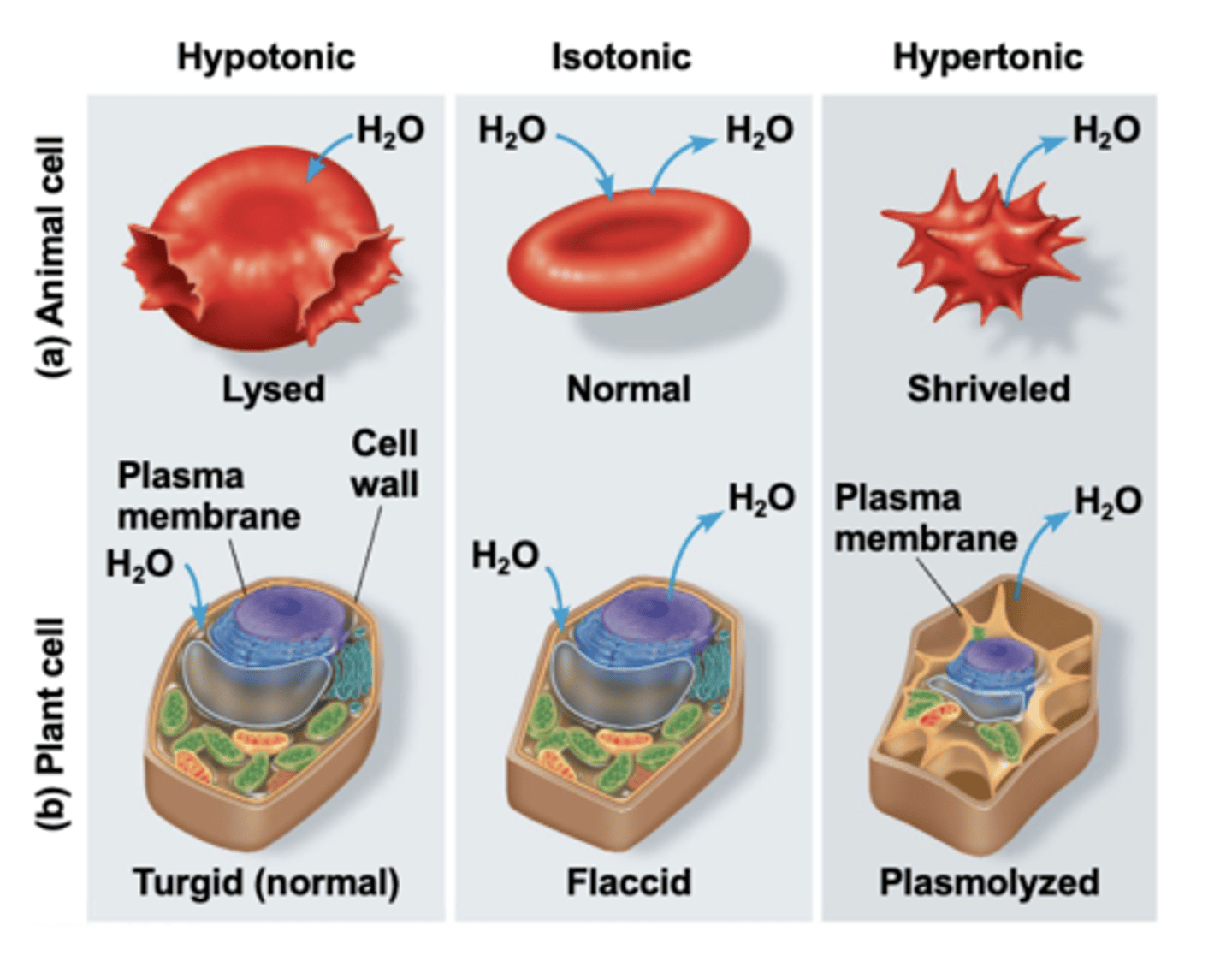
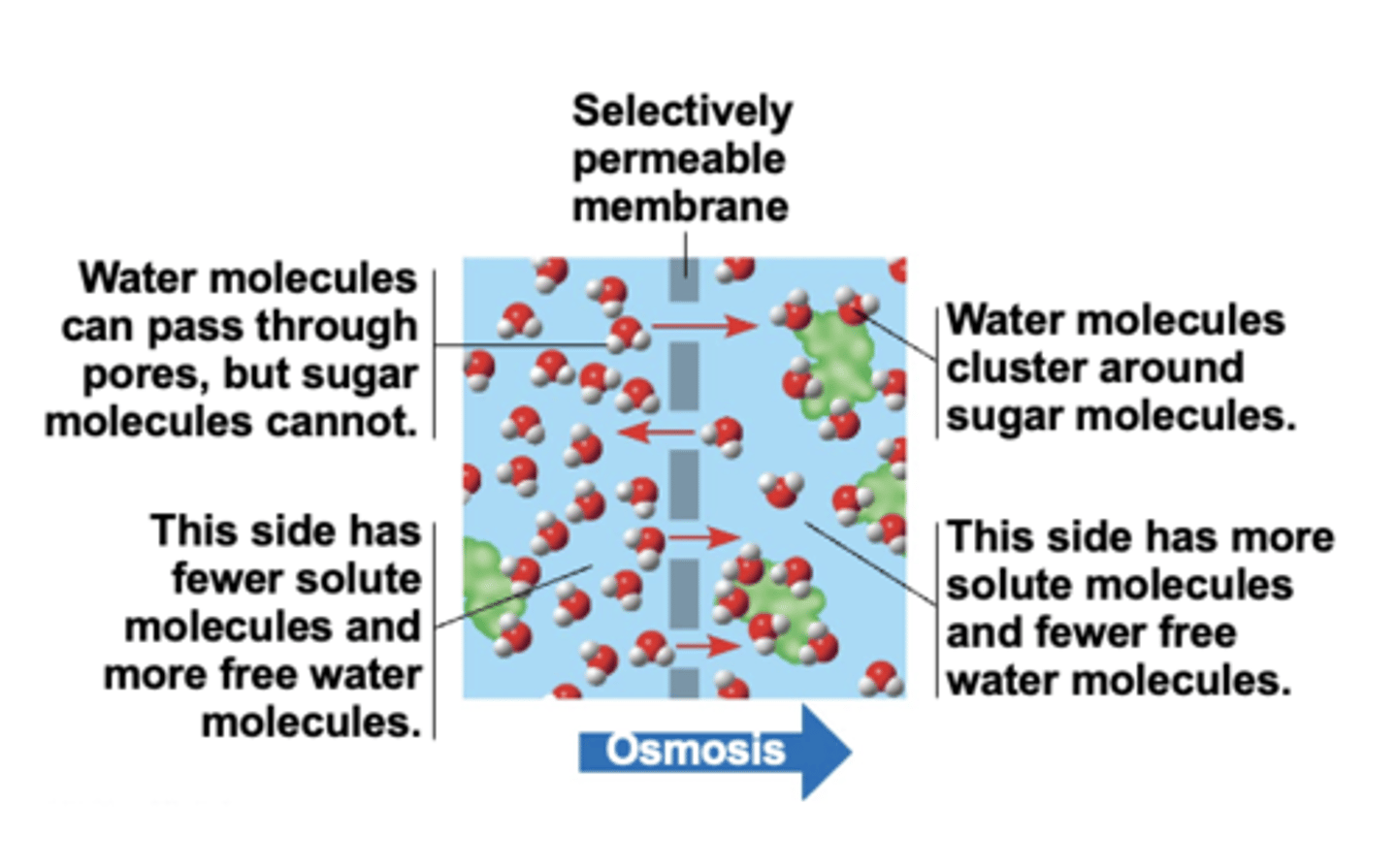
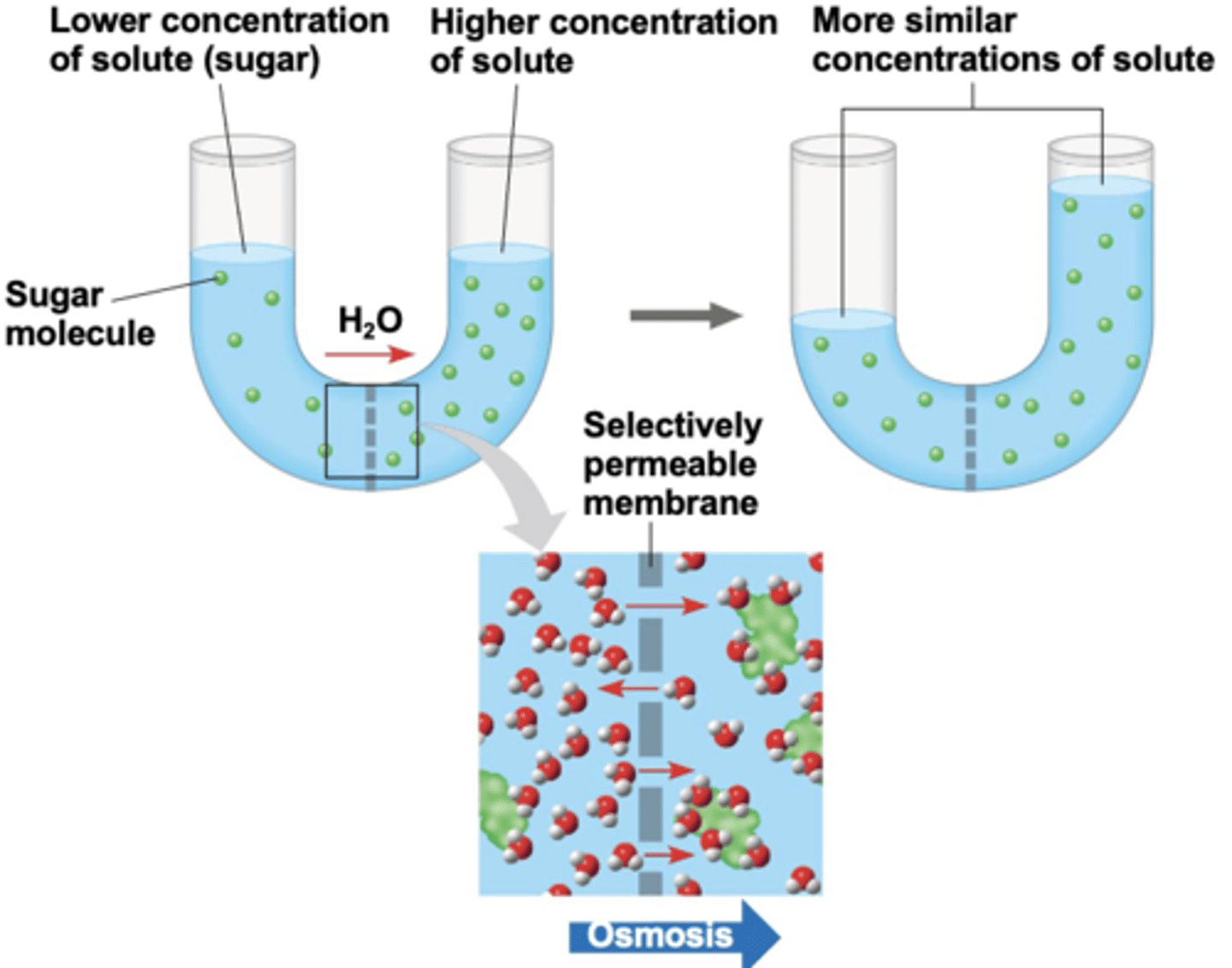
osmosis
is the diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane
lower solute concentration
higher solute concentration
equal
water diffuses across a membrane from the region of ______ _______ _________ to the region of _________ __________ ___________ until the solute is ________ on both sides
ion channels
facilitate the transport of ions
gated channels
some ion channels, called _________ _________, open or close in response to stimulus
facilitated diffusion
is still passive because the solute moves down its concentration gradient, and the transport requires no energy
against
some transport proteins, however, can move solutes ________ their concentration gradients
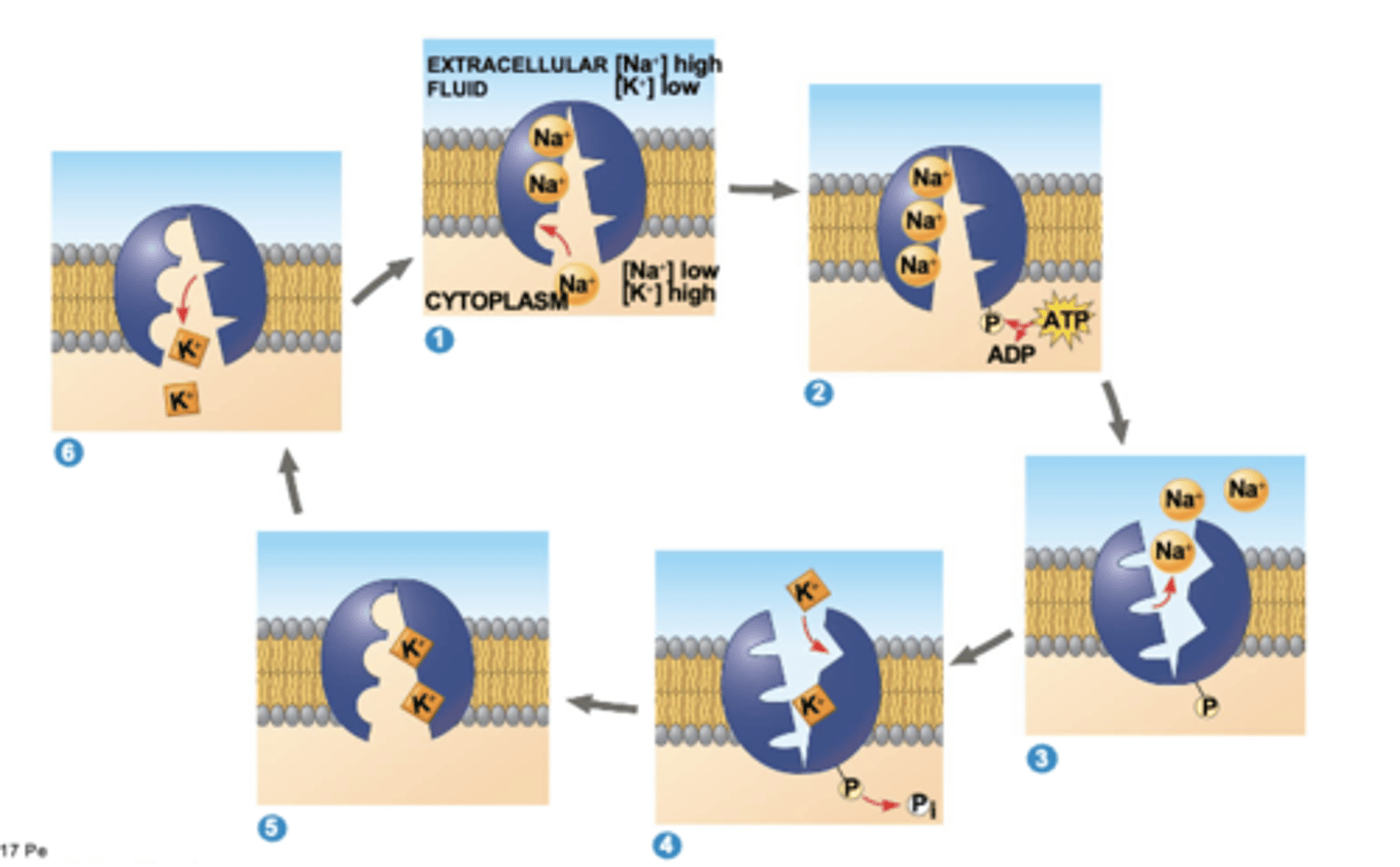
active transport
requires energy, from ATP hydrolysis, to move substances against their concentration gradient
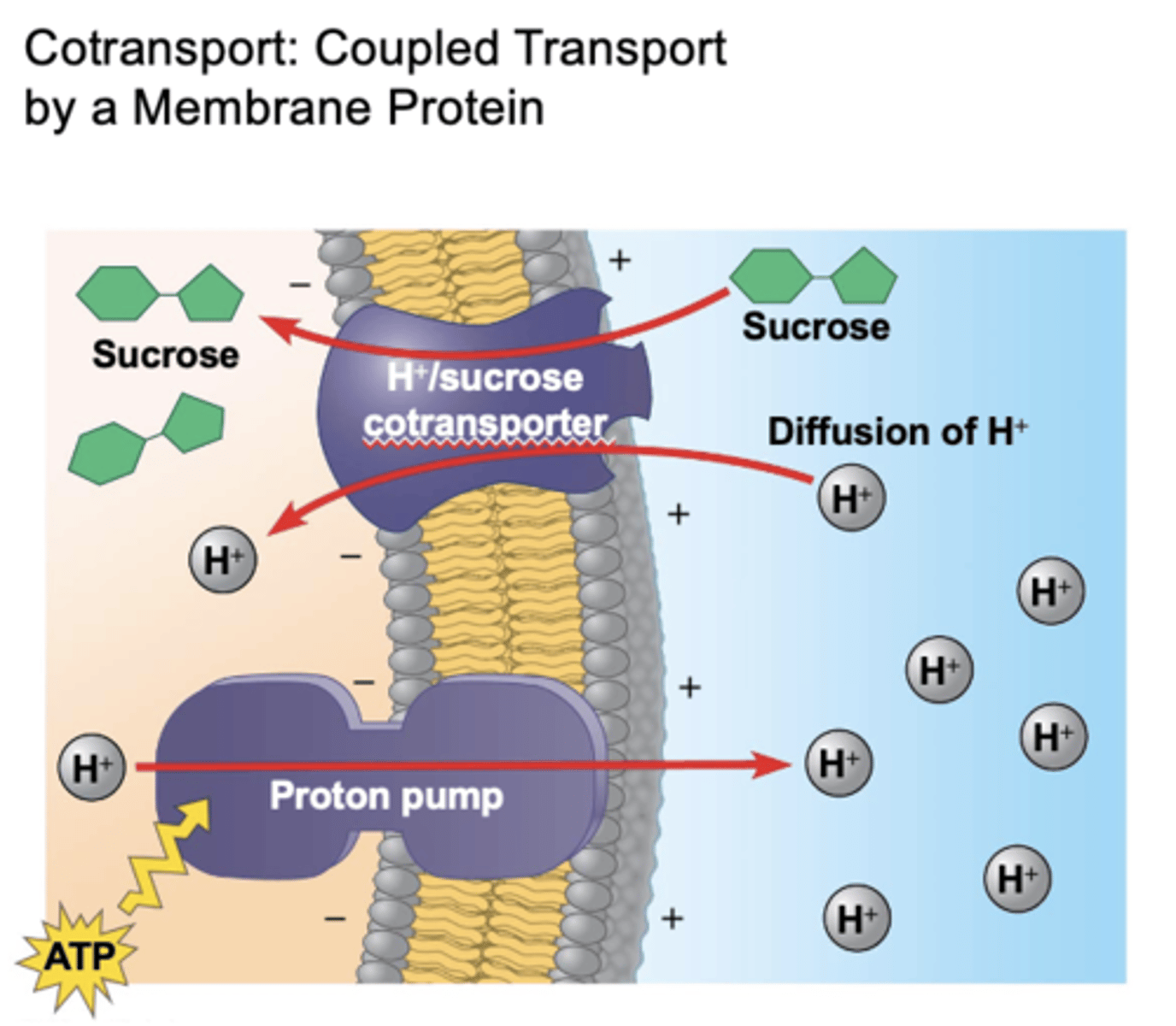
cotransport
coupled transport by a membrane protein; active transport driven by a concentration gradient
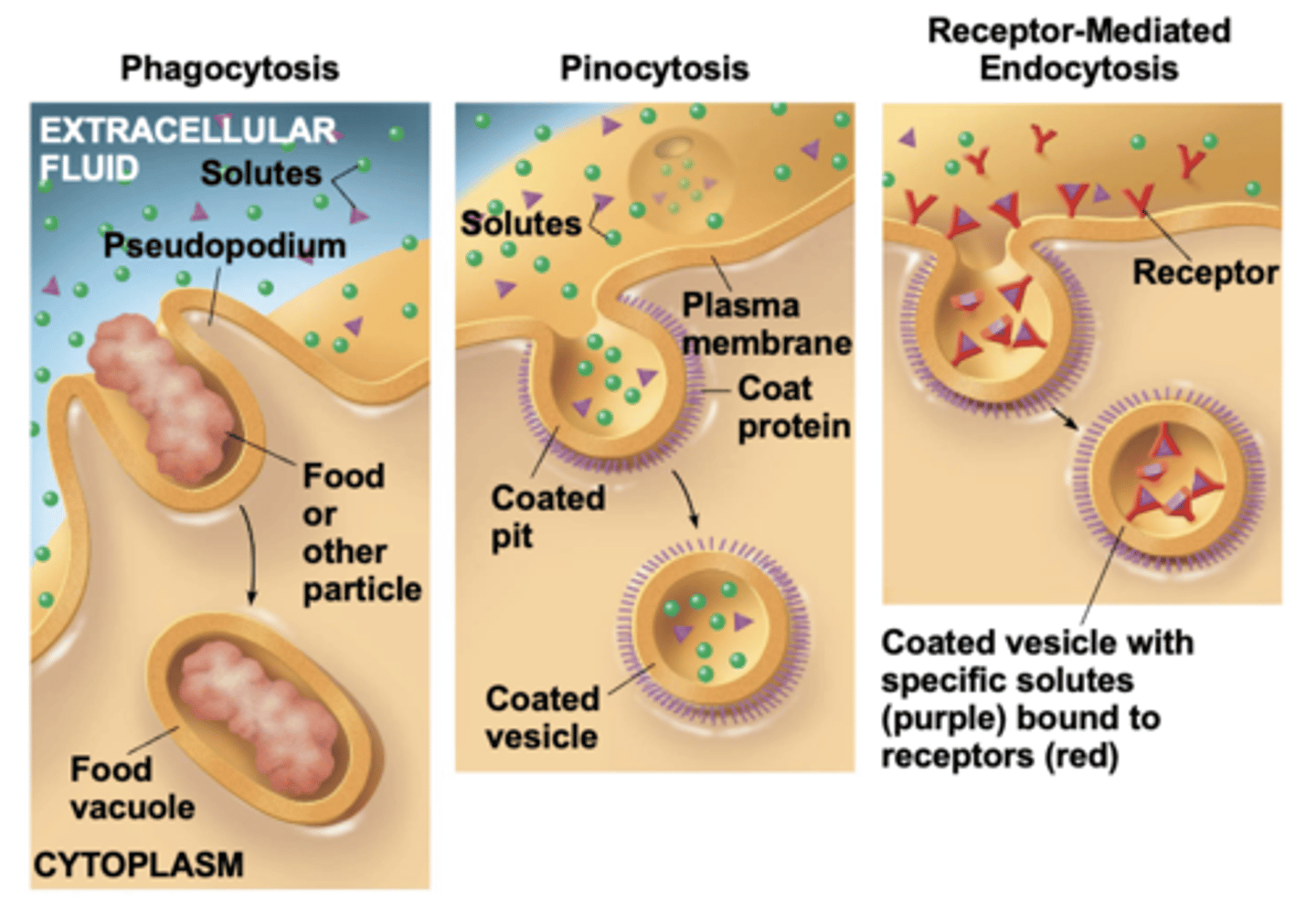
exocytosis and endocytosis
bulk transport across the plasma membrane occurs by __________ and __________
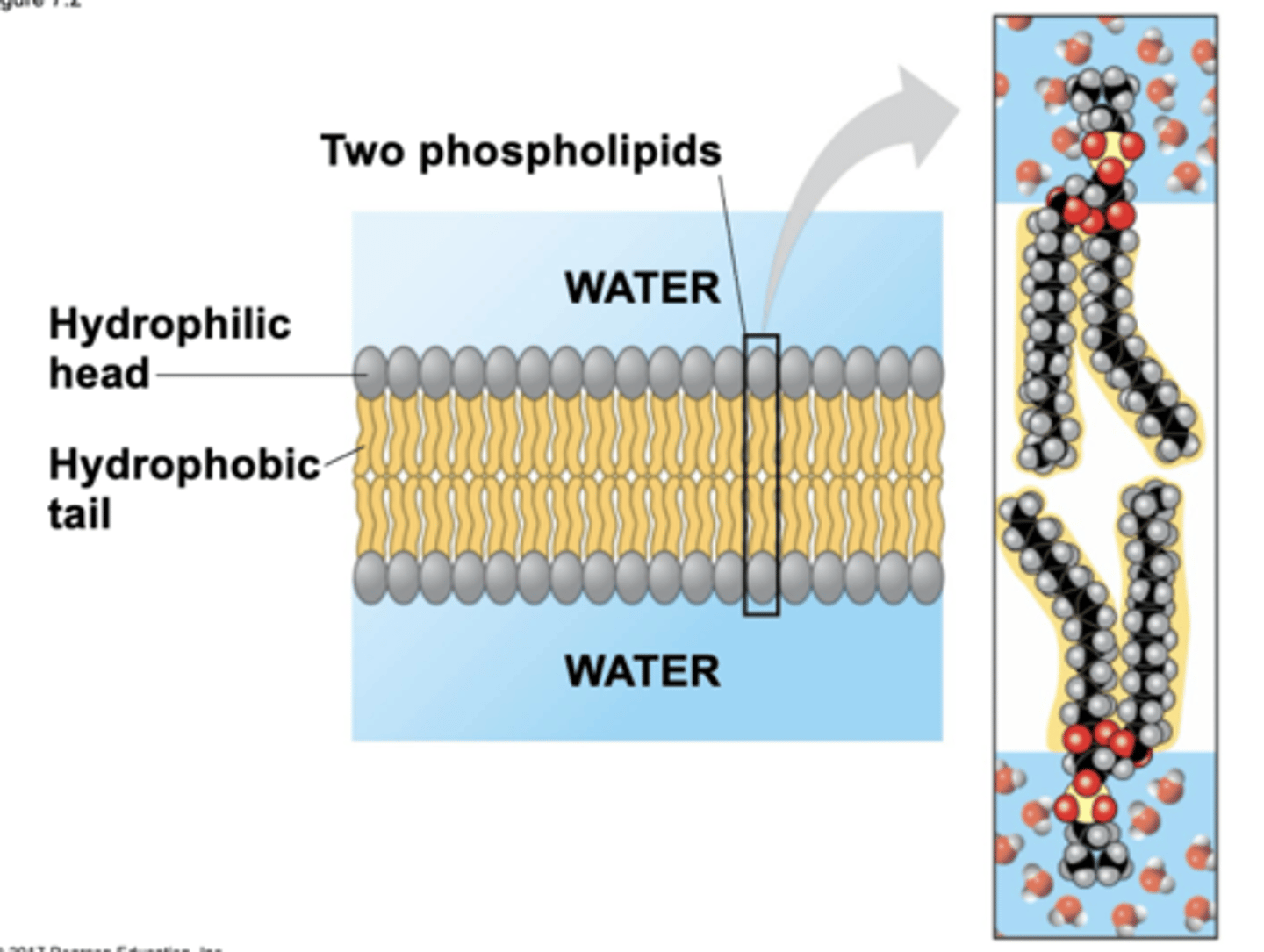
lipid bilayer
transport proteins
small molecules and water enter or leave the cell through the _________ ________ or via _________ _________
vesicles
large molecules, such as polysaccharides and proteins, cross the membranes in bulk via __________
energy
bulk transport requires _________
review this visual
review this visual
review this visual
review this visual
review this visual
review this visual
review this visual
review this visual
review this visual
review this visual (there is a flashcard for this picture)
review this visual (there is a flashcard for this picture)
review this visual
review this visual
review this visual
review this visual
review this visual