W1, Ch 1 The Study of Human Development
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
What is human development?
Scientific study of systematic processes of change and stability in people
What is life-span development?
Concept of human development as a lifelong process that can be studied scientifically
From what ages do researchers study human development?
From conception to death (“"from womb to tomb”)
What are the 4 goals of scientific field of human development?
To describe, to explain, to predict, to intervene
True/False: The 4 goals of scientific field of human development include to analyze, to assess, to plan, to predict
False; the 4 goals of scientific field of human development include to describe, to explain, to predict, to intervene
What are 3 major domains that developmental scientists study?
Physical development, cognitive development, psychosocial development
What is physical development (1 of the 3 major domains that developmental scientists study)?
Involves changes in body and brain, including senses, motor skills, and health
What is cognitive development (1 of the 3 major domains that developmental scientists study)?
Change in learning, attention, memory, language, thinking, reasoning, and creativity
What is psychosocial development (1 of the 3 major domains that developmental scientists study)?
Change in emotions, personality, and social relationships
What are 8 periods of development (in order)?
Prenatal period, infancy and toddlerhood, early childhood, middle childhood, adolescence, middle adulthood, late adulthood
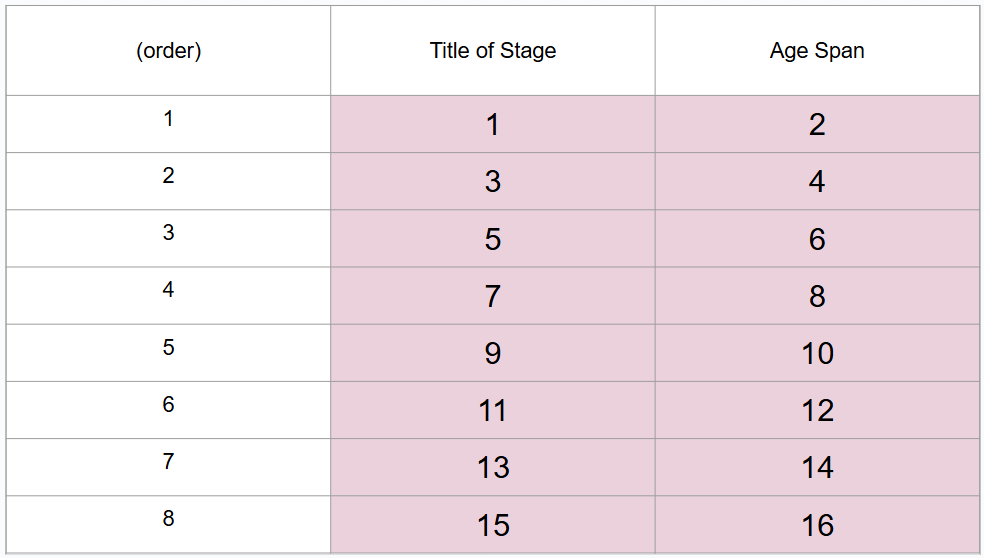
What is this?
8 periods of development
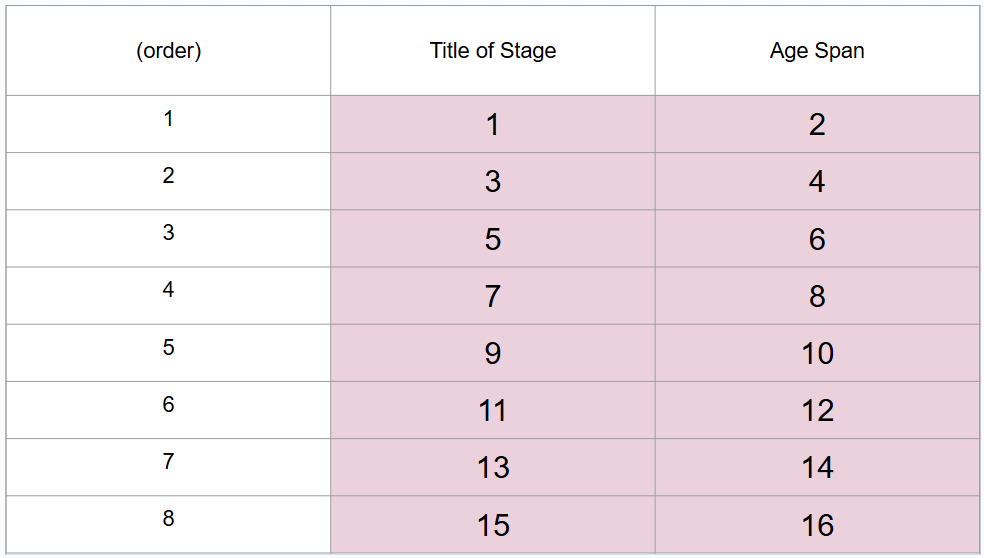
What is #1?
Prenatal period
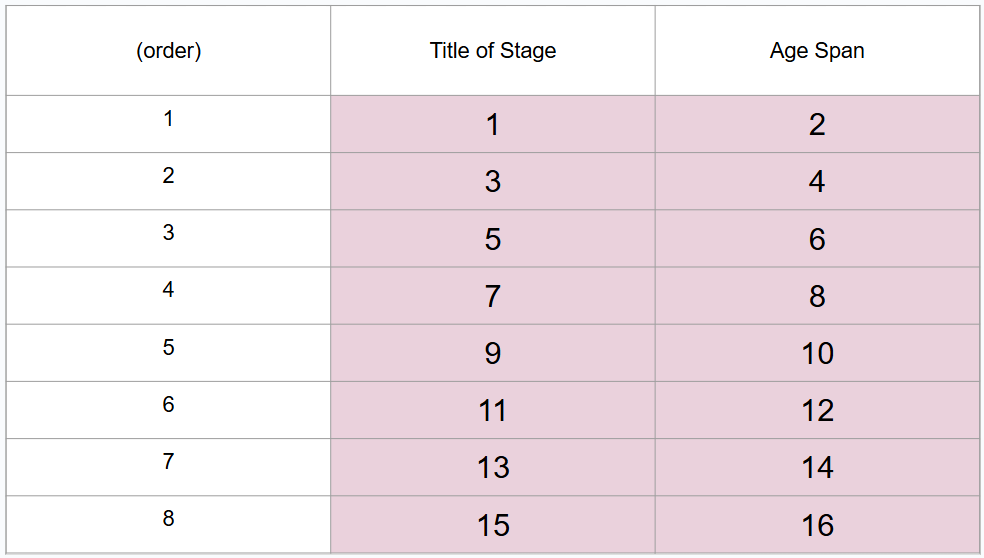
What is #2?
Conception to birth
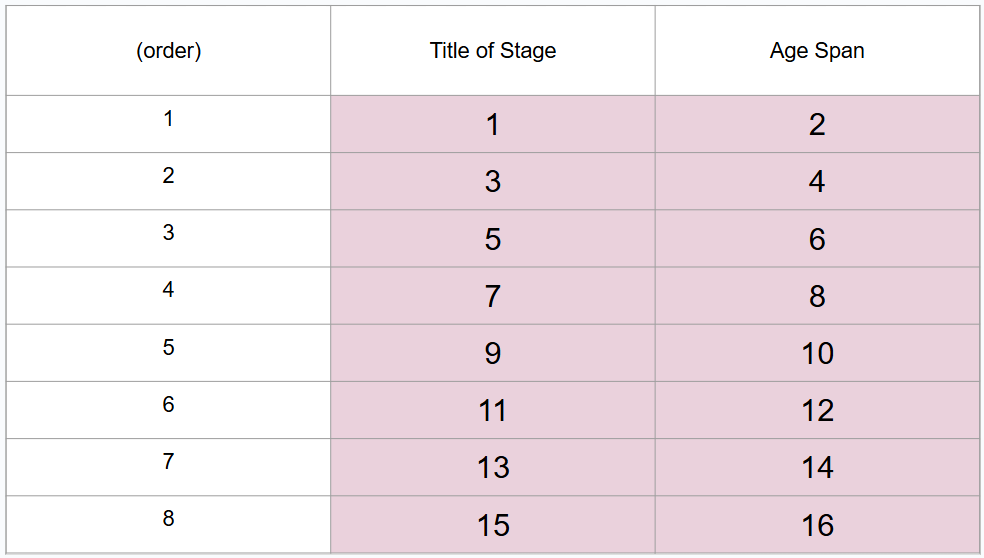
What is #3?
Infancy and toddlerhood
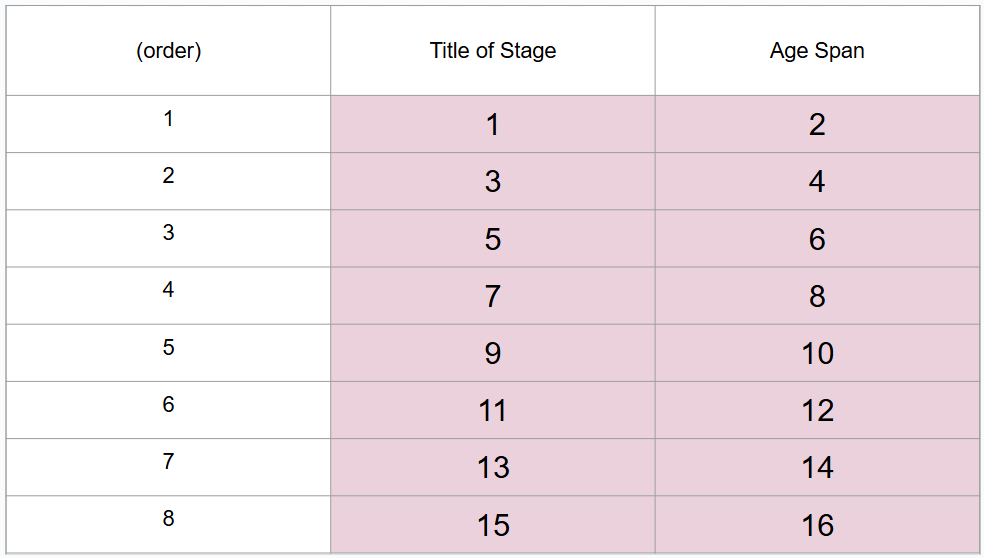
What is #4?
Birth to 3 years
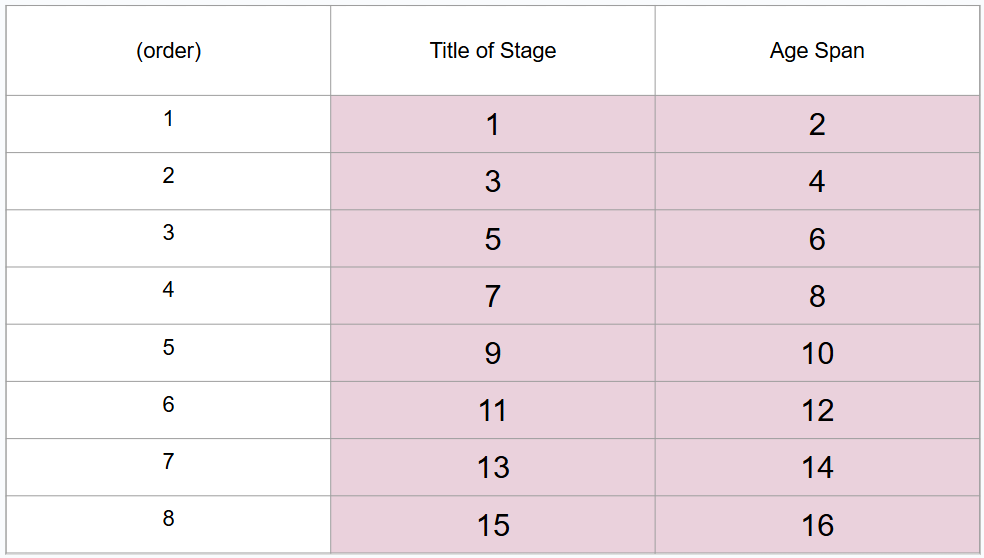
What is #5?
Early childhood
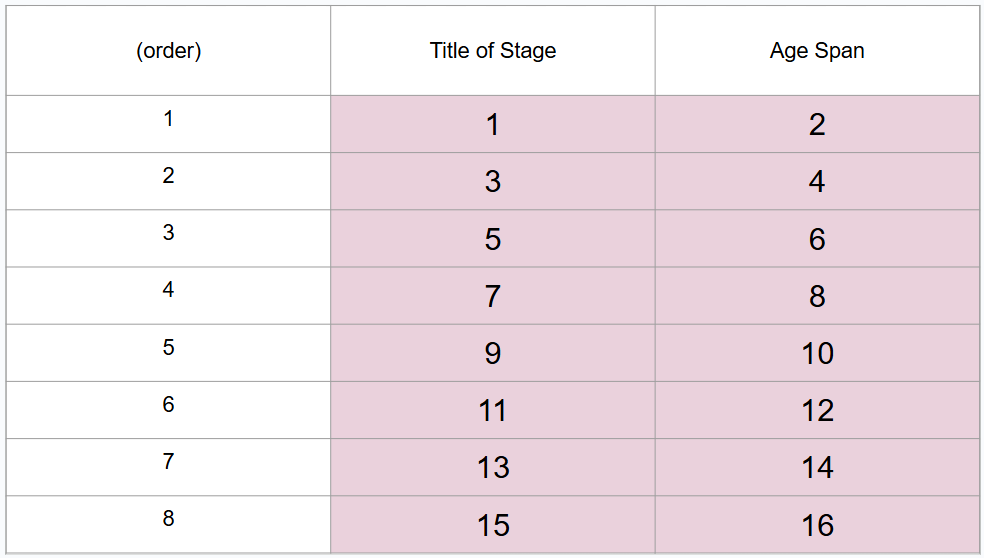
What is #6?
3 to 6 years
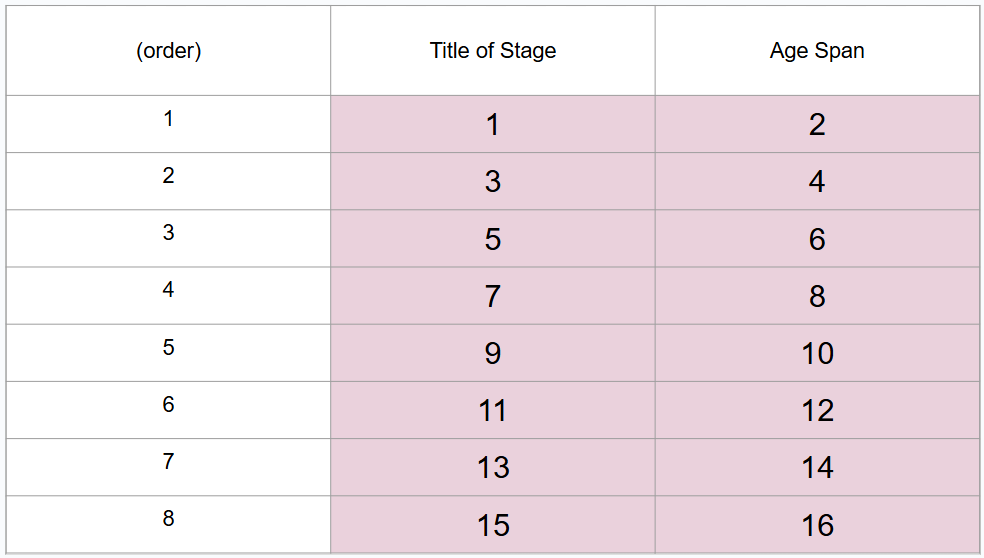
What is #7?
Middle childhood
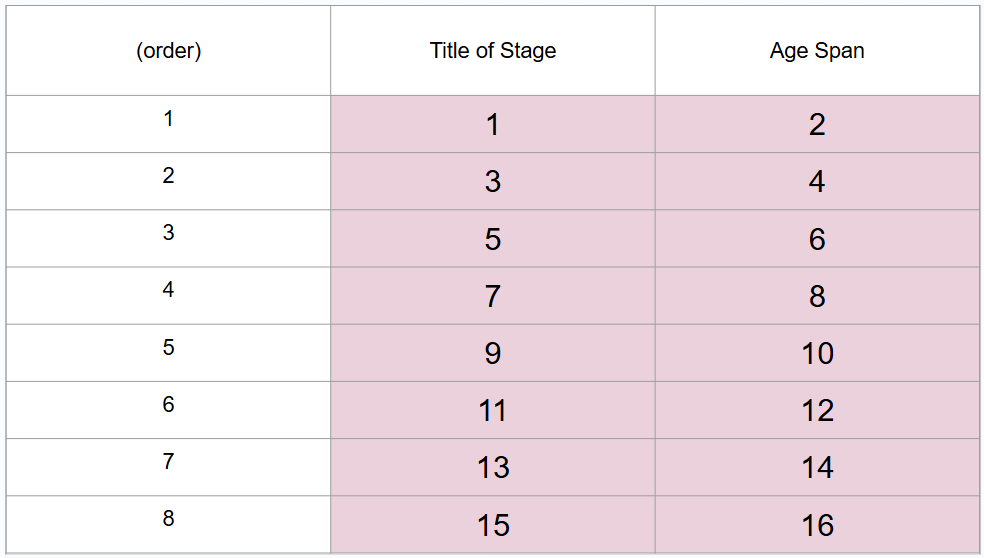
What is #8?
6 to 11 years
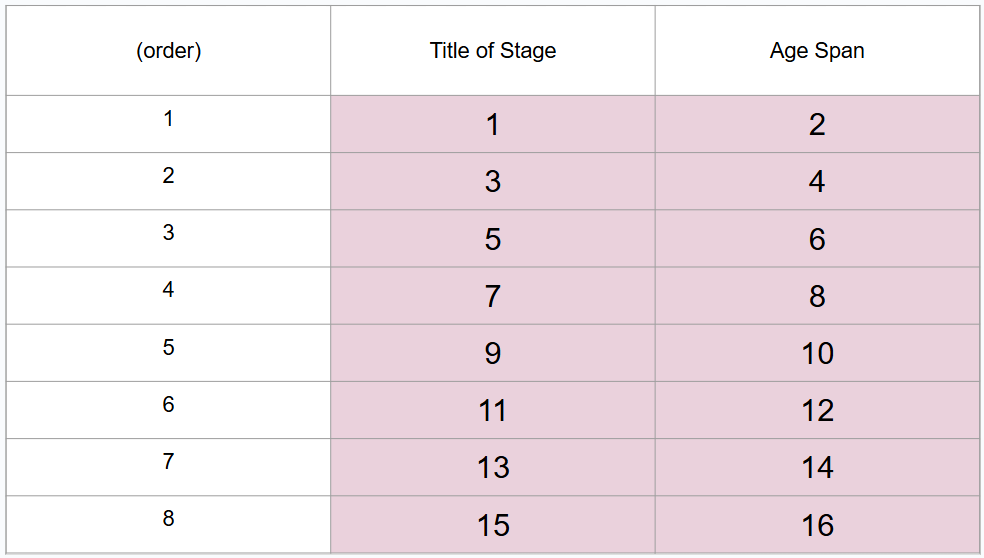
What is #9?
Adolescence
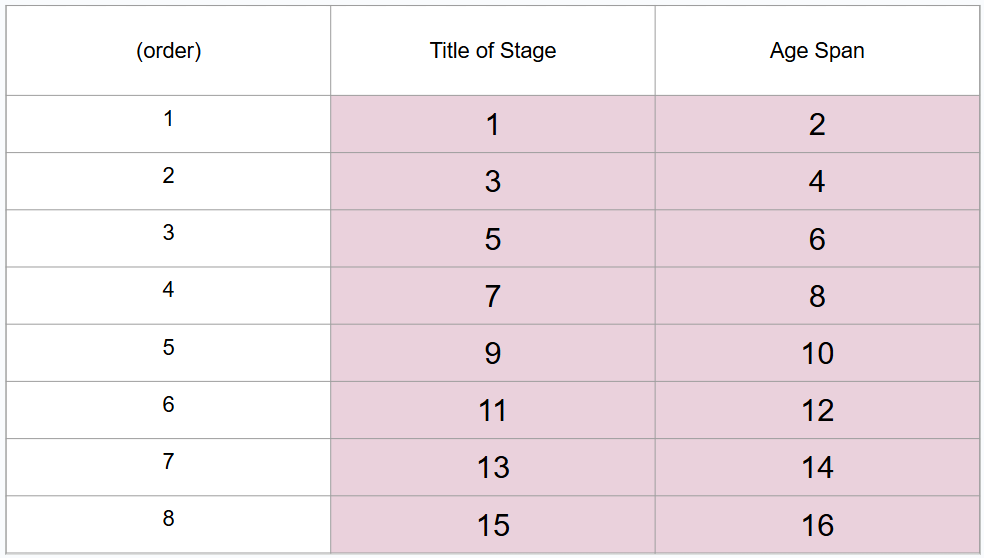
What is #10?
11 to 20 years
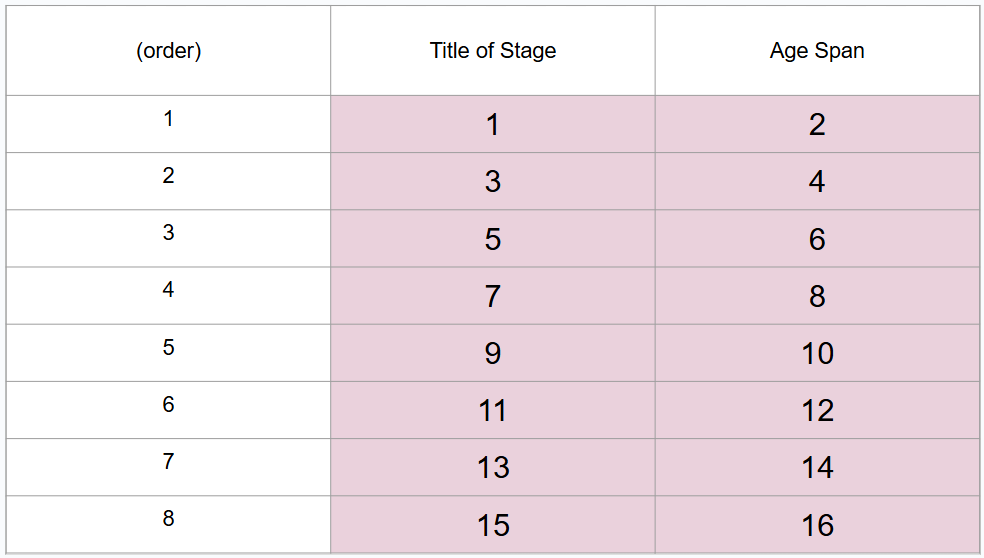
What is #11?
Young adulthood
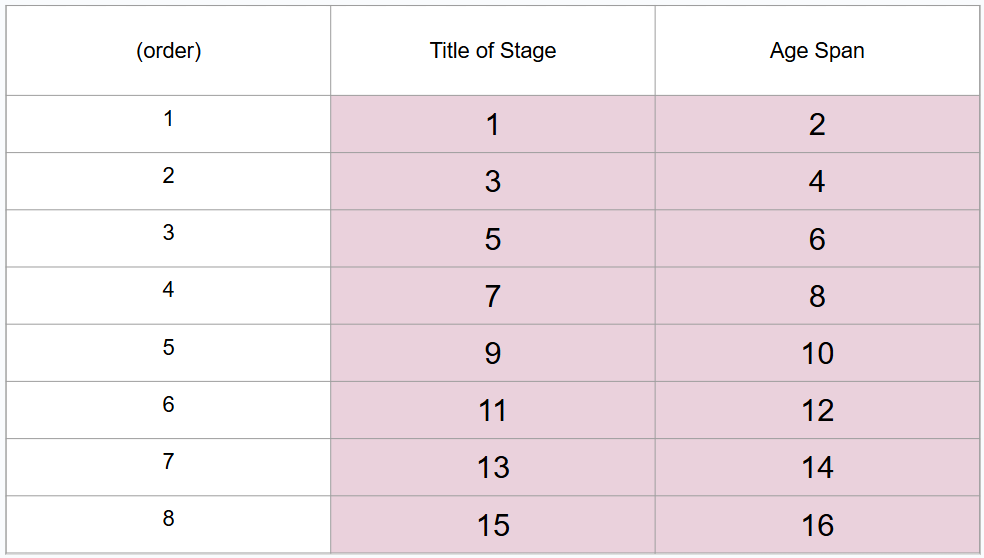
What is #12?
20 to 40 years
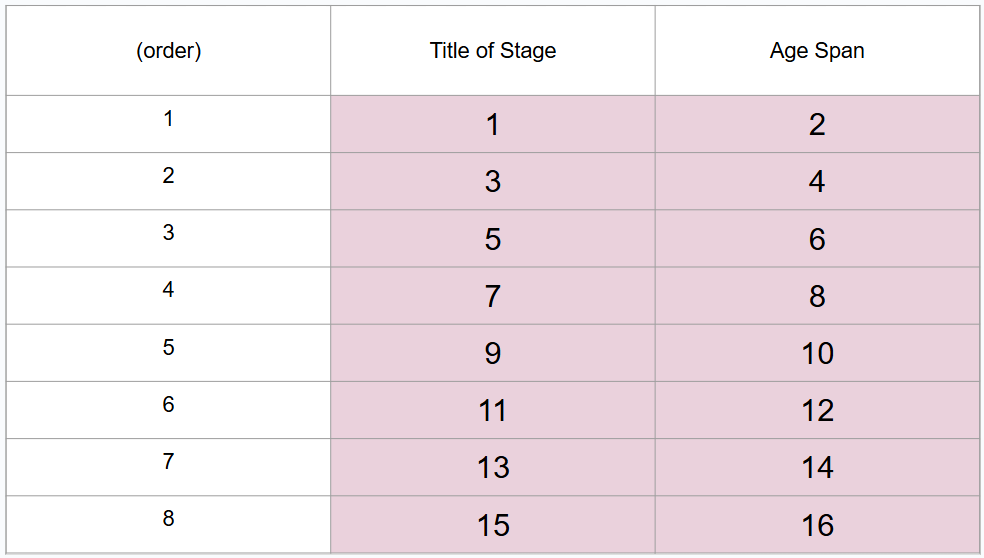
What is #13?
Middle adulthood
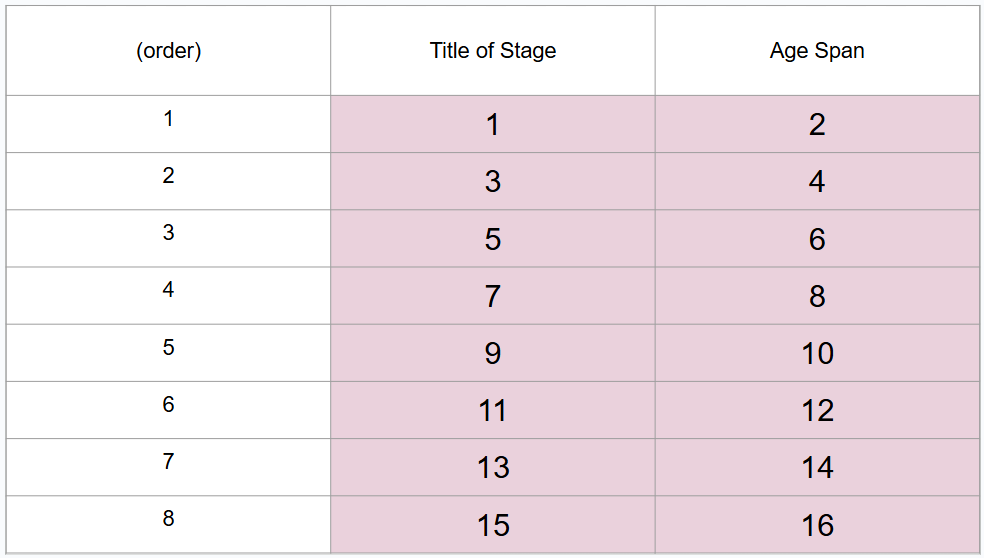
What is #14?
40 to 65 years
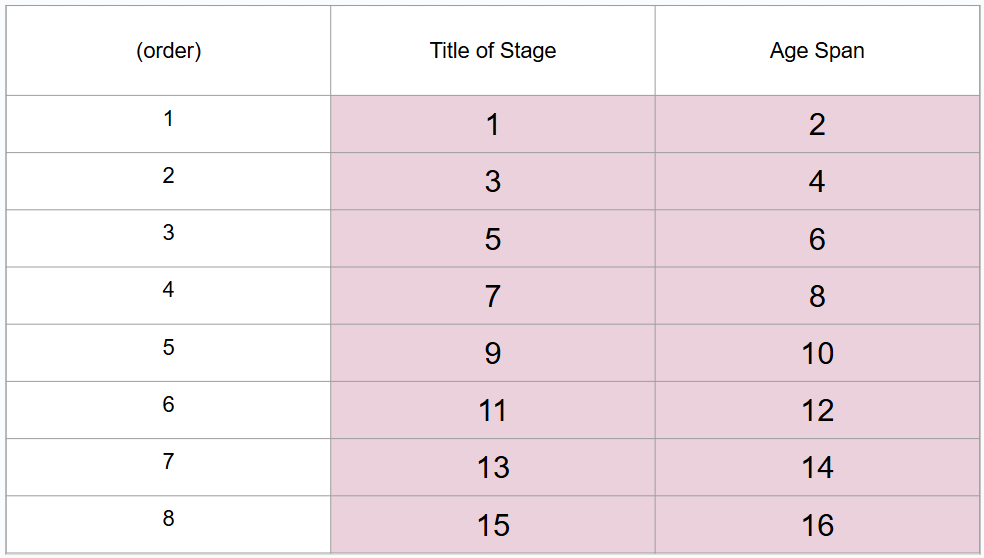
What is #15?
Late adulthood
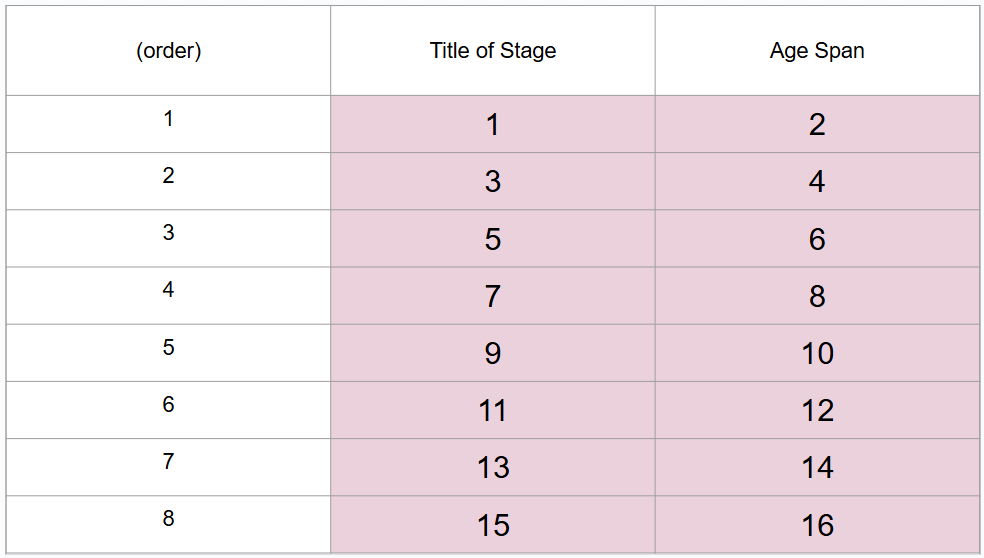
What is #16?
65 years and older
What have an important influence on development?
Heredity, environment, maturation, family context, socioeconomic status (SES), culture
True/False: Heredity, environment, maturation, family context, socioeconomic status (SES), culture all have an important influence on development
True
What is heredity?
Inborn traits and characteristics inherited from biological parents
What is environment?
Consists of world outside the self and learning through experience
What is maturation?
Unfolding of a natural sequence of physical changes and behavioral patterns such as walking and talking
What are 2 types of the family?
Nuclear family, extended family
What is nuclear family?
A household consisting of one or two parents and their children, including biological, adopted, and stepchildren
What is extended family?
A multigenerational network of grandparents, aunts, uncles, cousins, and more distant relatives
What are changes to nuclear family reflected in current/very recent generations?
Due to increasing numbers of single and childless adults, unmarried parents, and gay and lesbian households
What is socioeconomic status (SES)?
Combination of economic and social factors describing an individual or family, including income, education, and occupation
True/False: Children’s development is not impacted by the SES of their parents and the environment they are growing up within
False; children’s development IS impacted by the SES of their parents and the environment they are growing up within
What is culture?
A society or group’s total way of life which includes customs and traditions, laws, knowledge, beliefs, values, language, and physical products
What factors make up a person’s culture?
Customs and traditions, laws, knowledge, beliefs, values, language, and physical products
What are ethnic groups?
Consist of people united by a distinctive culture, ancestry, religion, language, or national origin
What are ethnic minorities?
Ethnic groups with national or cultural traditions different from the majority population
What are ethnic minorities often affected by?
Prejudice and discrimination
What is race?
Identifiable biological category and is considered a socially constructed term
What are normative influences on human development?
Biological and environmental events that affect many or most people in a society in similar ways
What are 2 categories of normative influences on human development?
Age-graded influences, historical-graded influences
What are nonnormative influences on human development?
Unusual events that have a major impact on individual lives by disturbing the expected sequence of life cycle
True/False: Normative influences on human development are unusual events that have a major impact on individual lives by disturbing the expected sequence of life cycle, whereas nonnormative influences on human development are biological and environmental events that affect many or most people in a society in similar ways
False; normative influences on human development are biological and environmental events that affect many or most people in a society in similar ways, whereas nonnormative influences on human development are unusual events that have a major impact on individual lives by disturbing the expected sequence of life cycle
What is meant by an “age cohort”?
A group of people born at the same time
What is a critical period?
A specific time when a given event, or its absence, has a specific impact on development
What is plasticity?
Modifiability of performance within a developmental domain
What are sensitive periods?
Those in which a person is particularly open to certain kinds of experiences
Who developed life-span developmental approach?
Baltes and his colleagues identified 7 key principles of life-span developmental approach
What are 7 principles of life-span developmental approach?
Development is lifelong
Development is multidimensional
Development is multidirectional
Relative influences of biology and culture shift over lifespan
Development involves changing resource allocations
Development shows plasticity
Development is influenced by historical and cultural context
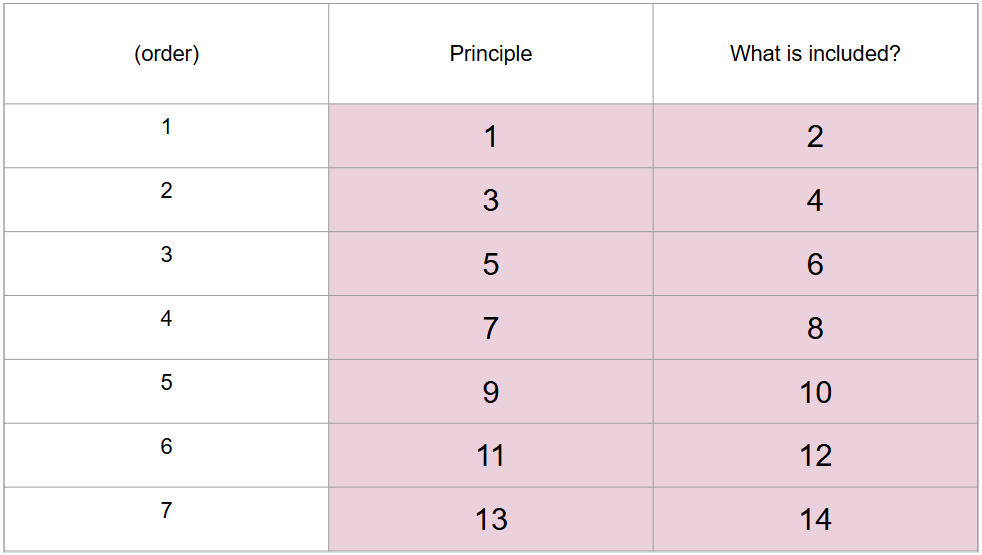
What is this?
Baltes life-span developmental approach
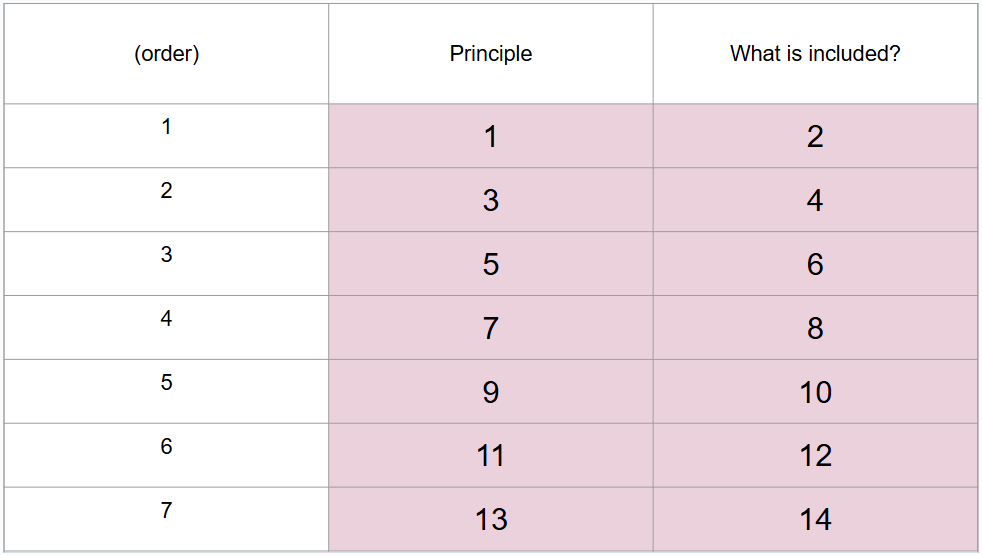
What is #1?
Development is lifelong
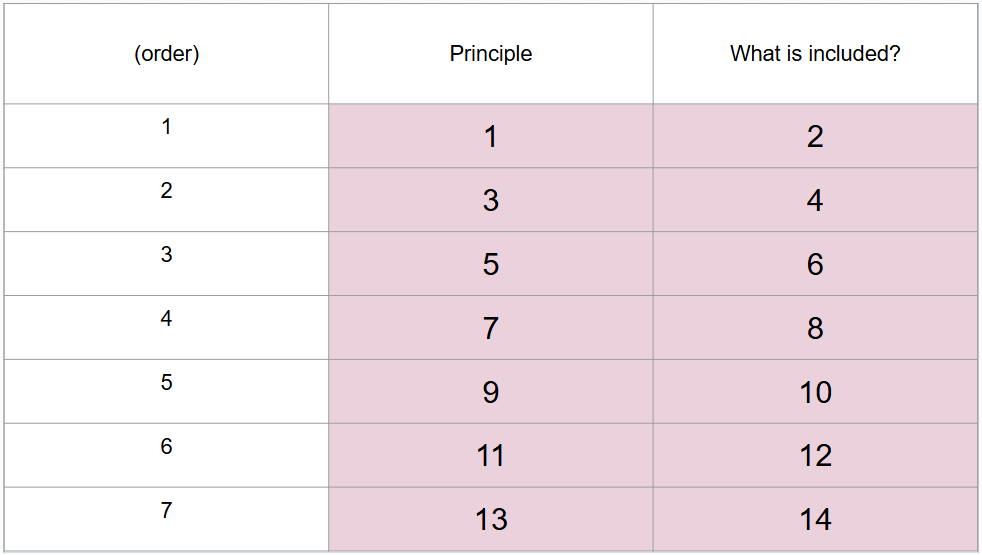
What is #2?
No period is more or less important than any other
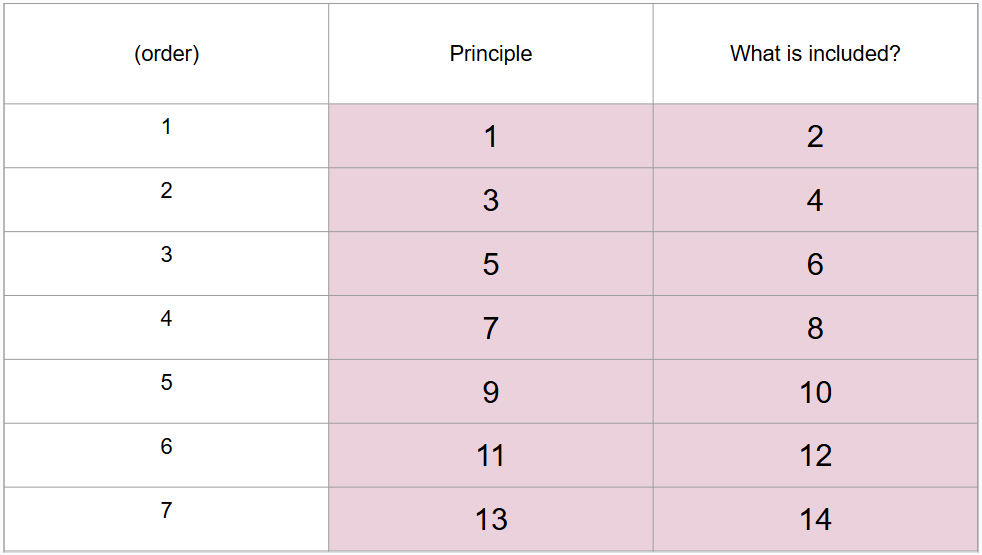
What is #3?
Development is multidimensional
What is #4?
Including biological, psychological, and social dimensions that develop at varying rates
What is #5?
Development is multidirectional
What is #6?
Showing gains and losses at any point
What is #7?
Relative influences of biology and culture shift over lifespan
What is #8?
Balance between these influences change over time and biological abilities weaken with age, but cultural supports may help compensate
What is #9?
Development involves changing resource allocations
What is #10?
In childhood and young adulthood, resources go towards growth whereas in old age, resources go toward regulation of loss
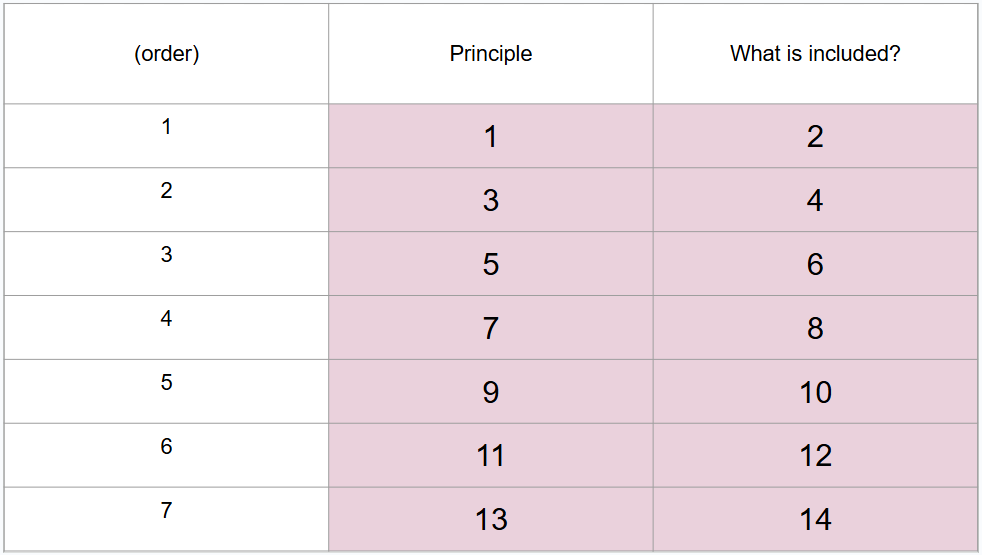
What is #11?
Developmental shows plasticity
What is #12?
Many abilities can be improved even late in life
What is #13?
Development is influenced by historical and cultural context
What is #14?
Each person develops within multiple contexts defined by maturation, time, and place