patho cell+cancer
1/119
Earn XP
Description and Tags
exam 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
120 Terms
pathophysiology
the study of structural and functional changes of cells, tissue, and organs caused by disease AND the effects they have on total boy function
disease
acute or chronic illness that one acquires or is born w/
– causes physiologic dysfunction in 1 or several systems
biologic agents
bacteria, viruses, yeasts/fungi, parasites (causes of disease)
physical forces
trauma, burns, radiation (causes of disease)
chemical agents
poisons, alcohol (causes of disease)
true
(T/F) cells have the adaptability to adapt to stressors:
– Reversible changes in cell size/#/type/function
– Chemically mediated
– Genetics remain the same but certain genes may be expressed differently in response
– cell goes to normal once stimulus removed
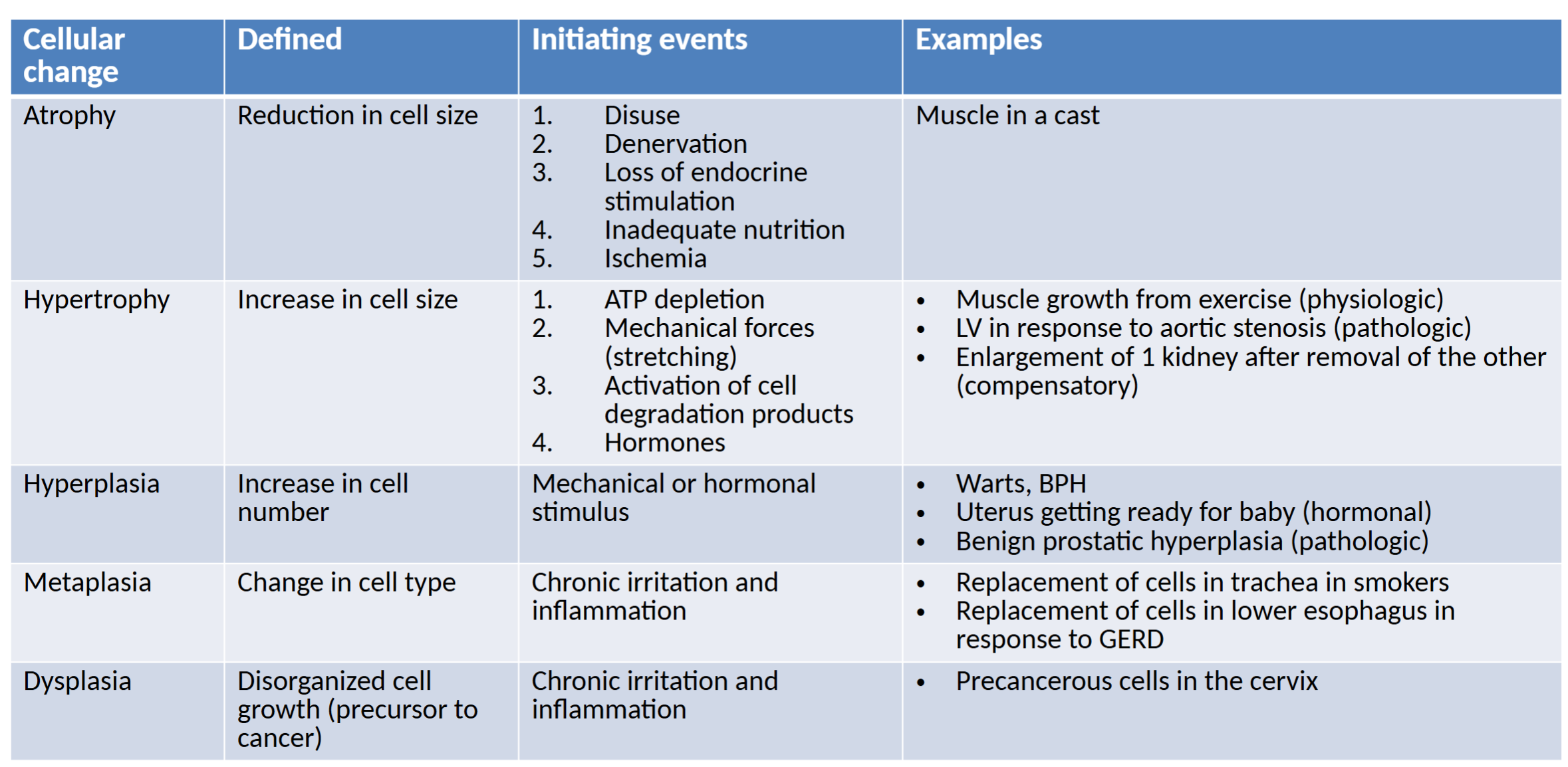
atrophy
decrease in cell size & function
– occurs in response to disease/dysfunction
– # of organelles reduced, cells become more efficient, entire tissue can be affected
pathos
=suffering
physiology
=functions of the human body
causes of atrophy
Disuse, Denervation (removal/damage of nerve restricting expected stimulus), Loss of Endocrine Stimulation, Inadequate Nutrition, Ischemia (decreased blood to tissue)
reduced protein synthesis
mechanism of atrophy
– ↓ workload → ↓ O2 consumption/↓ protein synthesis → muscle atrophy
– ↓ insulin and ↓ insulin-like growth factor→ less protein synthesis→ muscle atrophy
proteolysis
destruction of protein-mechanism of atrophy
– ubiquitin-proteasome system– proteins designated for destruction are bound to ubiquitin→ proteasomes degraded them into amino acids
hypertrophy
increase in cell size and function
– ↑ in functional components of cells due to increased workload
compensatory hypertrophy
1 organ takes on extra work and increases in size and function because another organ is failing
hypertrophy- initiating events
Mechanical Forces (stretching due 2 workload), Premature Depletion of ATP, Sympathetic Stimulation/Agonists (epinephrine, norepinephrine), Hormones
hyperplasia
increase in the number of cells
– occurs in response to a stimulus and should stop when the stimulus has been removed (hormones/growth factors)
metaplasia
a change in which 1 adult cell type is replaced by another cell type (reversible)
– whatever initiating event results in reprogramming of undifferentiated stem cells
– cells differentiate into more suitable cell but remain the primary cell type
dysplasia
deranged cell growth- resulting in cells of various sizes, shapes, and lvls of organization
– precursor to cancer
cellular change chart
intracellular acumulations
cells may accumulate substances in the cytoplasm that arent used asap
3 sources— Normal Body Substances, Abnormal Endogenous Products (produced in error/lysosomal storage disorders), Exogenous products
steatosis
intracellular accumulations of lipid in liver cells
– alcohol abuse is a common cause
Proteins (accumulation)
accumulation of structural __ is associated w some disease (alzheimers)
– may damage cells by 1.enzymes being produce to break down __ then cause collateral damage and 2. ↑ __ in cytoplasm pushes against organelles→ dysfunction
Iron
__is stored in tissue in 2 forms: Ferritin (normalcy) and Hemosiderin (when lvls of _ are high)
hemosiderosis
condition in which excess iron is stored as hemosiderin
– caused by: Prolonged IVs of iron, Frquent transfusions/hemolysis (RBCs lysis→ hemoglobin release→ turned into hemosiderin)
jaundice
condition characterized by yellowing of the skin due to increased bilirubin in blood
– causes: hemolysis, abnormal metabolism of bilirubin, obstruction of bile duct→ bilirubin retention
– yellow/green pigment in bile derived from hemoglobin
calcium
can accumulate in injured and dead tissue
1. Metastatic: calcification in functioning tissue (→disorders that promote hypercalcemia [hyperparathyroidism, Paget disease])
2. Dystrophic: calcification in Dead tissue
urate
Excessive metabolism of purines or decreased excretion of __ by kidneys
– lvls of __ in blood become excessive→ sodium urate crystals form→ promote inflammation (gout)
tay-sachs disease
most common lysosomal storage disorder, 80% of Ashkenazi Jews,
– no enzyme=accumulation of fatty acids in nerve cell lysosomes= CNS nerve cell toxicity
– onset by 6 months of age-death by 5
variables 4 cell injury
intention/duration determines extent of injury. reversible to a point. variables:
1. Severity of insult
2. Blood supply (low lowers survival rate)
3. Nutrition
4. Regenerative capacity (depends on organ/location)
cell injury mechanisms
1. Free radical formation/reactive oxygen species
2. Hypoxia leading to ATP depletion
3. Impaired calcium homeostasis
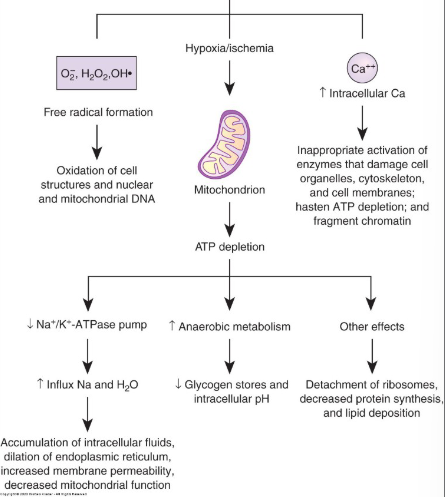
free radicals
__ __ and reactive oxygen species (ROS) are highly reactive and are products of many normal metabolic rxtions
– ROS usually neutralized by antioxidants but when it exceeds you have oxidative stress
oxidative stress
stems from excess of ROS, promotes ↑ Membrane permeability, Organelle destruction, Fragmentation and misfolding of proteins, Damage to DNA, RNA, proteins, etc.
– associated w disease
true
(T/F) hypoxia can lead to ATP depletion bc cells now have to revert to anaerobic respiration→ ↓ ATP, ↑ lactic acid, ↓ pH
Cascade effect—Na+ enters cell → water follows Na+ → cellular swelling → enzymes, proteins, and RNA lost through hyperpermeable membrane – Enzymes damage surrounding cells
36, 2
Aerobic respiration yields __ ATP, CO2 and H2O
Anaerobic respiration yields __ ATP, and lactic acid
respiration results
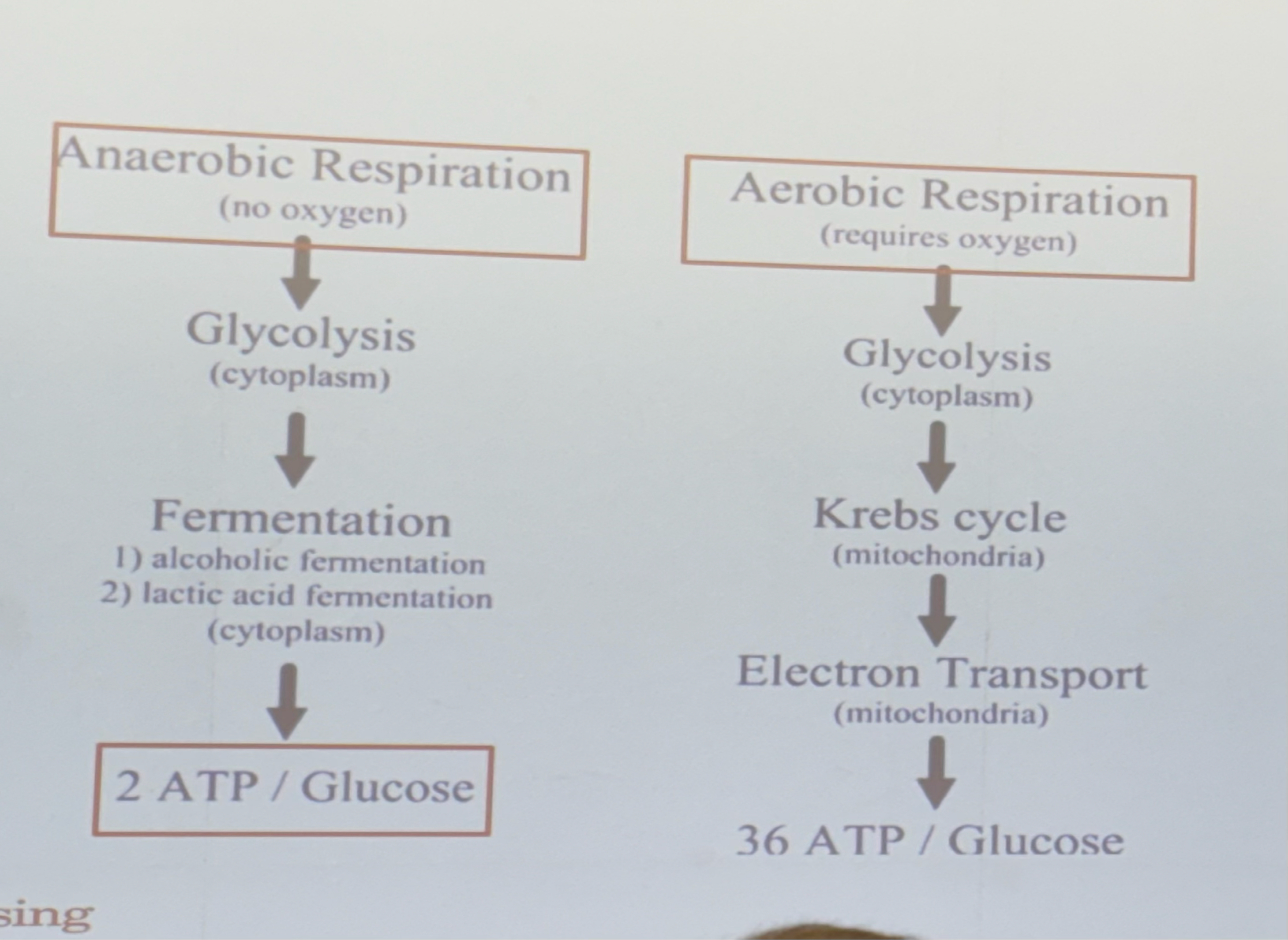
reperfusion injury
restoration of oxygen(/blood) to ischemic tissue causes a surge of free radicals and ROS
– leads to mitochondrial swelling, direct damage to nucleic acids & proteins
impaired calcium homeostasis
acts as a messenger and signal for intracellular responses—maintained by Ca2+/Mg2+ pump
When not managed intracellular calcium can activate enzymes:
– Phospholipases– damage cell membrane, Proteases – damage cytoskeleton+membrane proteins, ATPases– break down ATP
causes of cellular injury
physical agents, radiation, chemicals, biologics, nutritional imbalances
physical agents
causes of cell injury-
Mechanical Forces (bone fracture, disruption of blood),
HHypothermic injury (chilling or freezing cells),
Hyperthermia (uncontrolled ↑in body temp)
Electrical Injury (disruption of electrical currents; nerves/heart)
hypothermic injury
1. Frostnip: mild/completely reversible
2. Chilblains: more serious but no intracellular ice crystals
3. Frostbite: intracellular ice crystals, tissues freeze (Maybe reversible, Maybe gangrene)
4. Flash freeze: rapid cooling after touching cold metals/volatile liquids, intracellular ice crystals
Primary accidental hypothermia: Unintentional drop in core temperature <35°C in a previously healthy person
Secondary hypothermia: drop in body temperature as a
consequence of a systemic disorder (hypothyroidism, etc.)
true
(T/F) hypothermia slows NA+K+ATPase → cellular swelling —hypothermia promotes vasoconstriction and ↑blood viscosity
– thus leads to ischemia/infarction/necrosis
heat cramps
cramping of voluntary muscles due to vigorous exercise
– due to loss of salt & water
heat stroke
core body temp rises and cant be controlled—no sweating,
– Water loss and vasodilation → ↓BP and ↑HR
rectal temp >41 is lethal
radiation injury
causes of cellular injury- Ionizing Radiation, Non-ionizing Radiation, Ultraviolet Radiation
Ionizing Radiation
radiation promotes ionization of atoms&molecules in cells
– damages caused: genetic mutation, interference w cell replication, immediate cell death, prolonged exposure can cause cancer
non-ionizing radiation
damage caused by vibration & rotation of atoms+molecules
– IR light, ultrasound, microwaves
ultraviolet radiation
damaged caused by Reactive O2 Species or Direct damage to DNA
– risk depends on type of UV Rays, intensity of exposure, and melanin amount
chemical injury
causes of cellular injury- Lead Poisoning, Mercury Poisoning, Drugs/Meds
Lead Poisoning
found in older homes
Pb has many biochem properties-
– Anemia: Pb interferes w/ enzymes needed for RBC synthesis → hemolysis → anemia
– Cognitive dysfunction: Pb promotes demyelination of cerebral cortex
– Musculoskeletal: Pb competes with calcium for bone and can get deposited in bone
Biologic Agents
causes of cellular damage-
Bacteria
– unicellular organisms w no organized nucleus, can develop resistance to antibiotics, some contain endotoxins or release exotoxins to promote cell injury
Viruses
– organisms composed of protein coat & nucleic acid core, ex: HIV, HPV, herpes
Human Immunodeficiency VIrus
the retrovirus that can cause acquired immunodeficiency syndrome(AIDS)—leads to profound suppression of immune syst.
– transmitted by blood to blood, perinatally, or sexually
– categorized by CD4 Count—lower count=worse & measures Viral Load—higher load=worse
– opportunistic infections and body wasting occur
biologic agents
causes cellular injury-
Fungi (single/multicellular organisms that proliferate by budding)
Parasites (multicellular orgs that gain a benefit from the host)
Types of Fungi
– Tinea capitis- ring worm, on scalp
– Tinea corporis- ringworm, on trunk of body
– Tinea pedis- athletes foot
– Tinea cruris- jock itch
– Tinea versicolor- discolored patches
nutritional imbalances
causes of cellular injury- Body requires many vitamins, minerals, and nutrients to survive
– Vit C deficiency→ scurvy
– Vit D deficiency→ rickets (weakness in bones)
– Niacin deficiency→ pellagra (skin scaling)
true
(T/F) in reversible cell injury the cells lose function, but dont die
– Fatty Changes can occur— (associated w severe injury) intracellular accumulation of fat in vacuoles, due to increased fat load or impaired metabolism of fats
apoptosis
normal process by which body eliminates old and injured cells
– shrinking and fragmentation but integrity of plasma membrane maintains and NO inflammation
– changes induces phagocytosis by macrophages
necrosis
UNregulated cellular death while still part of a living organism
1. Unregulated enzymatic break down cellular components
2. Integrity of plasma membrane NOT maintained
3. Initiation of the inflammatory response
4. interferes with replacement by new cells and tissue regeneration
liquefaction
necrosis by which cell or tissue become liquefied
– some cells die but catalytic enzymes remain. Abscess.
coagulation
necrosis by conversion into a grey, firm mass
– acidosis denatures the enzymes + structural proteins
– seen w/ infarcted tissue-myocardial infarction
caseation
necrosis by conversion into a “cottage cheesy” substance by infiltration of fats
– tuberculosis
dry gangrene
massive tissue necrosis—tissue is dry and shrinks, color changes to brown/black
– slow, often due to arterial insufficiency, form of coagulation necrosis
wet gangrene
massive tissue necrosis—area is cold, swollen, and pulseless. skin is moist, black and under tension
– rapid, often due to problems w venous return, form of liquefactive necrosis
gas gangrene
massive tissue necrosis— common in trauma+compound fracture in which dirt has become embedded
– due to Clostridium perfringens bacteria
– Spreading edema and Hemolysis
chromosomes
in the nucleus of every cell-the genetic material responsible for the structure+function of the body
– divided into Germline cells (gametes: sperm+egg cells) and Somatic Cells (all other cells)
Somatic cells
Every other cell besides sex sperm/egg cells. Contains 23 pairs of chromosomes—22 pairs of autosomes (nearly identical and homologous) and 1 pair of sex chromos (2 homo X or 1 nonhomo X and Y)
DNA
Contains deoxyribonucleic acid and histone proteins. __ provides the genetic code for the synthesis of proteins
– each strand is made up of 4 nucleotides
Nucleotide
Made up of a nitrogenous base, deoxyribose, and phosphate.
The 4 nitrogenous bases= 2 purines: Adenine and Guanine and 2 pyrimidines: Cytosine and Thymine
true
(T/F) Germline cells contain 23 single copies of chromosomes
true
(T/F) Adenine forms a bond w/ Thymine. Guanine forms a bond w/ Cytosine— the resulting structure is a double helix
Protein
made up of sequences of amino acids (of which there are 20). Specific combination of amino acids creates a polypeptide, which form a __
transcription
step in protein synthesis:
— RNA polymerase binds to DNA at promoter
— DNA unwinds, RNA bases pair with DNA to form mRNA: A→U, C↔G. stops at termination sequence
— Introns are removed and mRNA moves to ribosome.
translation
step in protein synthesis:
- mRNA binds to ribosome, tRNA anticodons pair with mRNA codons
- each tRNA brings an amino acid and they link to form a polypeptide
DNA replication
process to preserve genetic info when cells divide:
1. DNA unwinds to expose the nucleotide bases
2. DNA polymerase moves along the template strand and creates a complementary strand of DNA nucleotides
– Cytosine + Guanine and Adenine + Thymine
3. DNA polymerase “proofreads” and excises+replaces not complementary bases
4. Now there are 2 identical pairs of chromosomes
Prophase
phase of mitosis
– the DNA coils+shortens, reveals two identical chromatids attached at a centromere, the nuclear membrane disappears
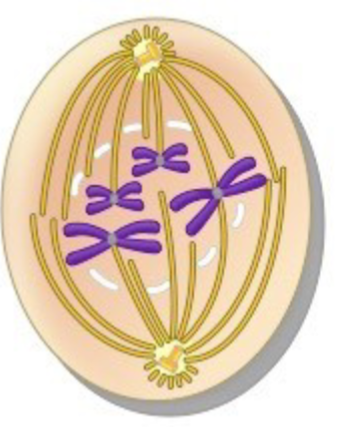
metaphase
phase of mitosis:
– the chromos line up at the cellular equator in the middle of cell, spindle fibers radiate from centrioles at each pole to the centromere
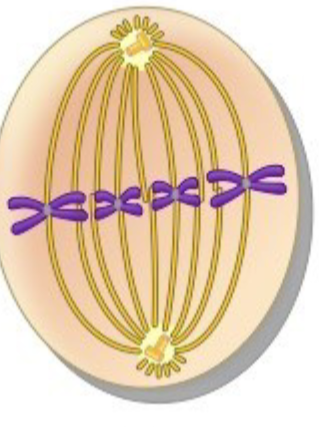
anaphase
phase of mitosis
– the centromeres split and the sister chromatids are pulled apart toward opposite poles
telophase
phase of mitosis
– the new nuclear envelope is formed, spindle fibers disappear and the cell divides
–result: 2 daughter cells w/ the same genetic info (diploid)
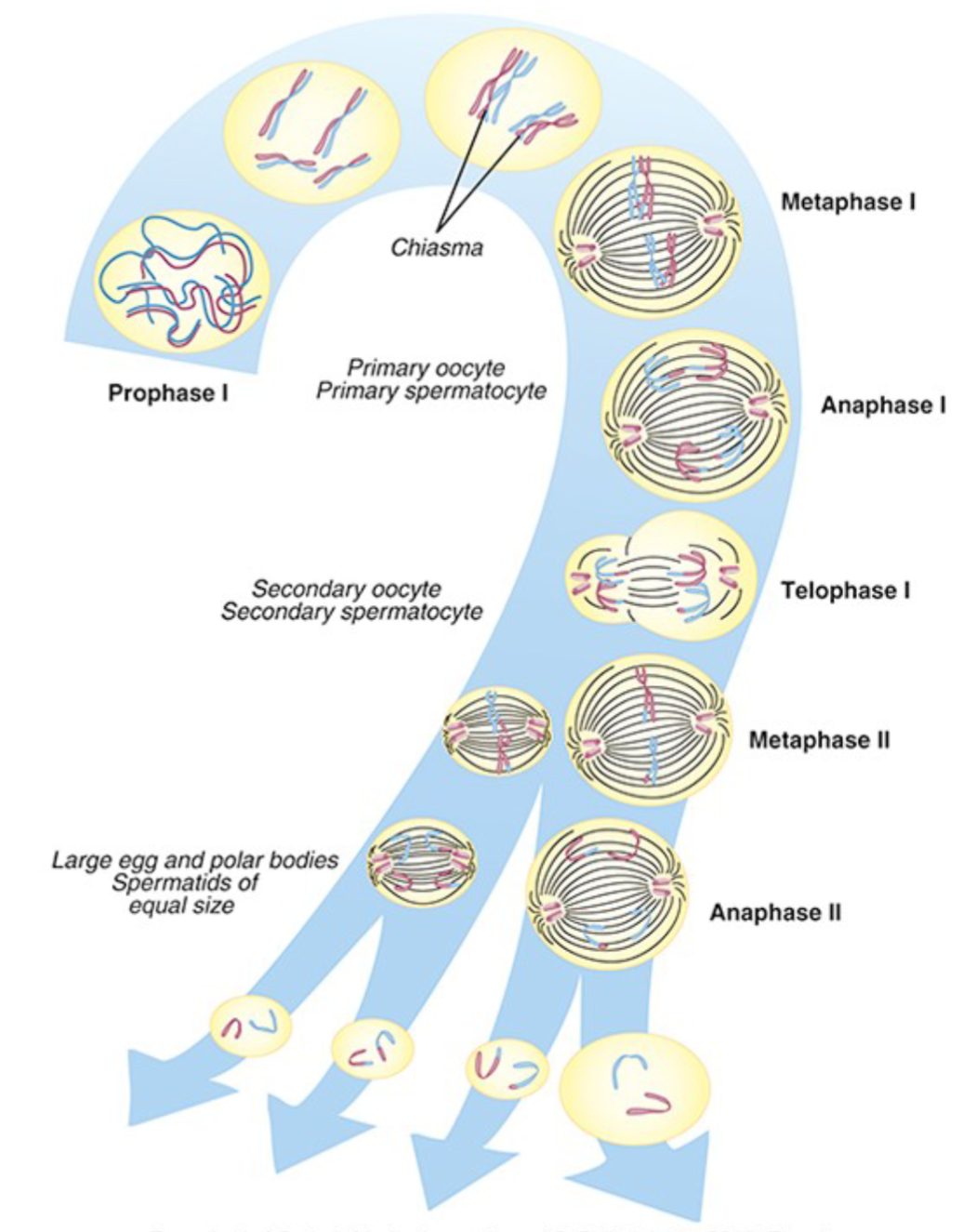
meiosis
the process by which gametes are formed—will end up with half of the genetic info
• Prophase I: replicated chromosomes coil up
• Metaphase I: homologous chromosomes line up on equator
of cell opposite one another– Spindle fibers radiate from the centrioles and attach to centromere
• Anaphase I: homologous chromosomes are pulled to opposite poles of the cell
• Telophase I: nuclear envelope forms and cell divides into two daughter cells
Metaphase II: chromosomes line up along the equator again– Spindle fibers radiate from the centrioles and attach to
centromere
• Anaphase II: Chromatids are pulled apart and move toward
opposite poles
• Telophase II: cell divides into two germ cells
Result: Each germ cell now has half the genetic information
(haploid)
polyploidy
cells that have a multiple of the normal # of chromosomes (23)
– triploidy- 2 copies of each chromos
– tetrapoidy- 4 copies of each chromosome
– nearly all triploidy+tetraploidy pregnancies are aborted
aneuploidy
cells that DONT have a multiple of 23 chromos (usually due to nondisjunction)
– Trisomy: 3 copies of 1 chromos (13,18, or 21 can survive)
– Monosomy- 1 copy of 1 chromos (lethal)
– fertilized eggs containing no X chromos (lethal)
nondisjunction
when the chromosomes fail to separate during meiosis I
– causes multiple mutations
trisomy 21
down syndrome - intellectually disabled
– 50% have congenital heart defects, 54-90% have obstructive sleep apnea, almost all develop symptoms of Alzheimers by 40
turner syndrome
syndrome characterized by presence of one x chromosome without a homologous X or Y chromosome
– pt usually AFAB and sterile
– short, webbing of neck, sparse body hair, normal intellect
klinefelter syndrome
syndrome characterized by 2 or more X chromos with a Y chromos (XXY)
– pts usually AMAB and sterile
– elevated stature, gynecomastia, small testes, sparse body hair, some intellectual disability
inversion
reversal of the order of the genetic code resulting from 2 breaks (insrevion)
translocation
interchanging of material from 2 non-homo chromos
– non-homologous chromosomes → non-homomosous chrologomes
fragile sites
microscopic breaks and gaps in DNA
cri du chat
syndrome w/ deletion of the short arm of chromosome 5
– high pitched cat-like cry, wide set eyes w prominent epicanthal fold, intellectual disability
fragile x syndrome
syndrome w multiple (>200) repeats of a 3 nucleotide sequence in long arm of X chromosome—silencing of the genes responsible for neuronal synaptic connections
– 2cd most common cause of intellectual disability & autism
– Face elongated,Repeats, ADHD, Giant genitals, Intellectual impairment, Large hands/feet, Ears protruding, X-tensible joints
true
(T/F) different forms of a gene are called alleles and a person receives one allele from each parent.
genetype
the genetic makeup of the alleles
carrier
a person is a __ for a disease if they have the allele for a disease but are phenotypically normal
– (often bc the disease causing allele is recessive-so to express the disease, both “bb” alleles have to be present)
cystic fibrosis
autosomal recessive — ↓ number and abnormal function of ion channel for Cl- and HCO3-
1. Thickening of mucus in lungs
– ↑ reabsorption of Na — airway obstruction→ recurrent infections
2. ↑ mucin production in GI→ tract disruption
3. ↓ absorption of Na+ and Cl- in sweat glands
huntington disease
autosomal dominant (regardless of hetero or homo), repeats of 3 nucleotide leading to extra long protein prone to fragment
– neuronal dysfunction and death
– onset age 45, involuntary+impaired movement, cognitive impairment, depression
true
(T/F) in cancer, repetition of certain gene sequences can increase expression of some genes (gene amplification)
true
(T/F) cancer is second leading cause of death in the us
neoplasm
new growth
differentiation
process by which cells become specialized
– regulated by genes and external stimuli (environment, cytokines, exposure)
– cells also lose ability to proliferate and tissues rely on progenitor/stem cells
-carcinoma
suffix meaning malignant neoplasm of epithelial tissue
– ex: adeno__= malignant neoplasm of glandular epithelial tissue