6.2 - Movement across membranes
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Concentration gradient
difference in concentration of a substance between two regions
Simple diffusion
net movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration (only occurs if the membrane is fully permeable to that substance)
Passive movement
net movement of molecules down a concentration gradient from higher to lower concentration without the need for energy (eg. simple or facilitated diffusion, osmosis)
Osmosis
net movement of water across a semi-permeable plasma membrane from an area of lower water potential to an area of higher water potential
What cannot move by active transport or simple/facilitated diffusion?
large chemical molecules, thus moved in vesicles
General endocytosis
uptake of molecules into a cell via vesicles, requiring ATP and fluidity as part of the plasma membrane is pulled inwards surrounding the molecules and pinching off making a vesicle
Two types of endocytosis
phagocytosis (substances taken in are particles - eg. bacteria) and pinocytosis (substances are in solution - eg. end products of digestion)
Exocytosis
export of molecules from a cell via vesicles, requiring ATP and fluidity as materials for export (like digestive enzymes) made in RER are transported to the Golgi apparatus where they’re enclosed in vesicles and moved to the plasma membrane along microtubules, fusing with it and releasing contents outside
Facilitated diffusion
diffusion across a membrane allowing large and/or charged molecules to pass via channel proteins forming pores (hydrophilic interior, specific only allowing one substance through, some permanently open while others gated) or carrier proteins (combine with diffusing molecules and release them on the other side of the membrane)
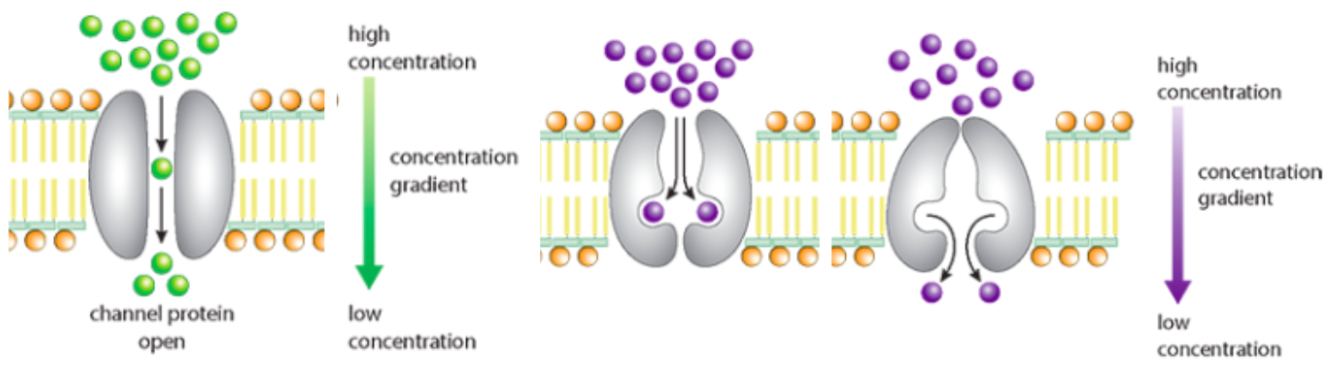
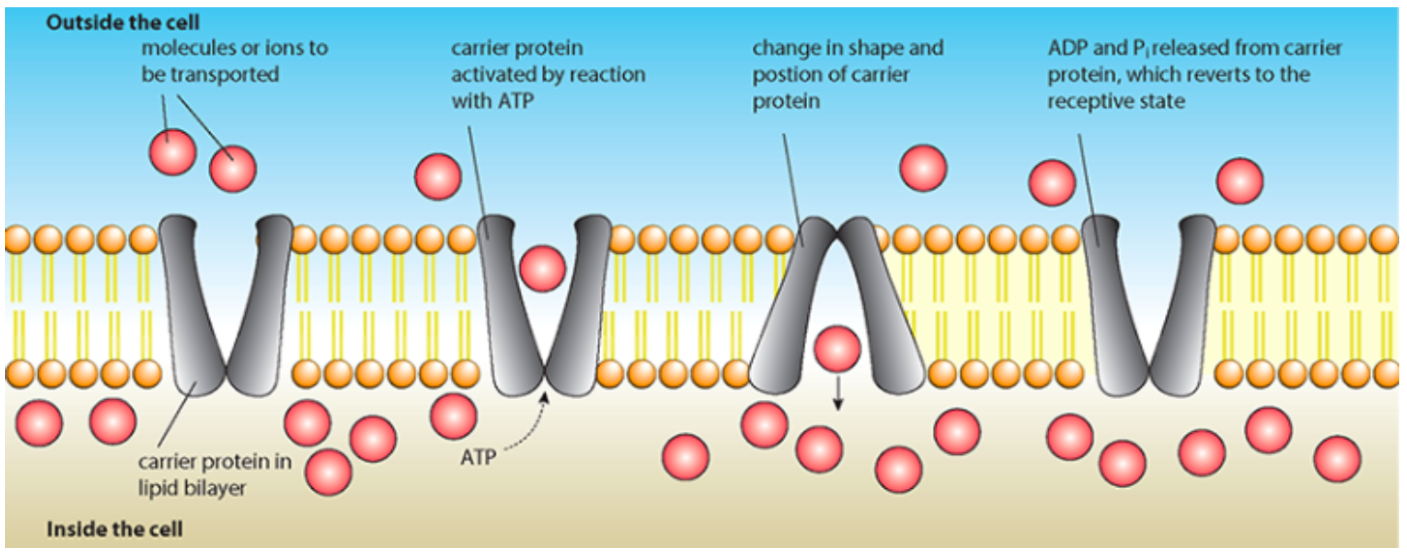
Active transport
movement of molecules from an area of lower to higher concentration against a concentration gradient, using metabolic energy (from breakdown of ATP) and pump proteins, it is specific
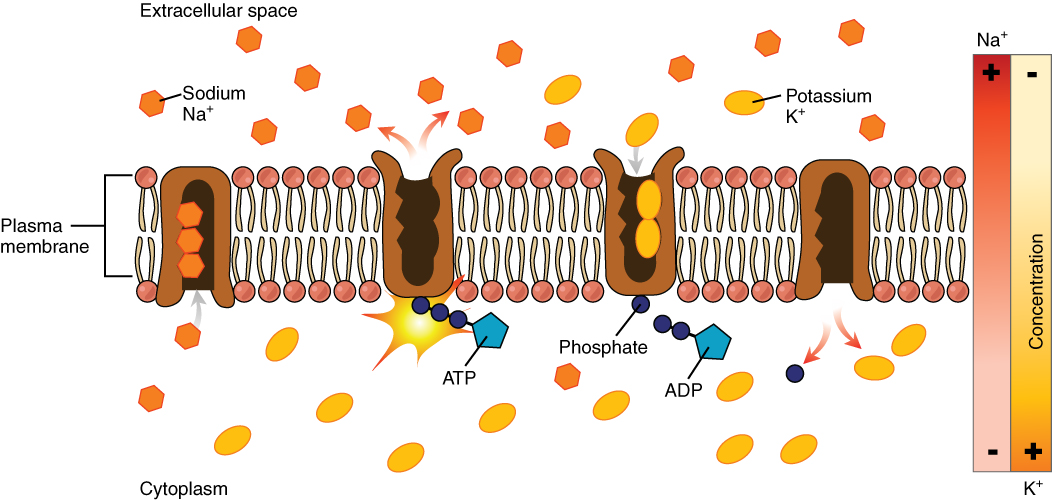
Sodium-potassium pump
protein pump doing active transport binding 3 Na+ and ATP, hydrolysing ATP to change shape and releasing the Na+ ions in the extracellular space binding 2 K+, release of the phosphate allows the channel to revert to the original position and release the K+ ions intracellularly