characterstics of the 9 phyla of animals
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
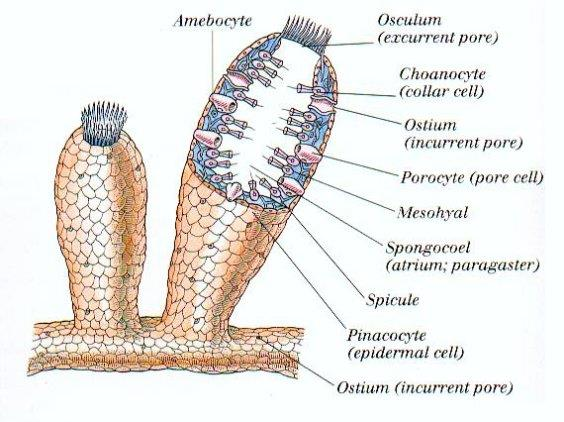
Porifera
like sponges
Loose group of cells
Diploblastic with mesoglea
Asymmetrical
No head
Acoelomates
No mount-anus development
Sessile
Internal skeleton of sponging or spicules of calcium carbonate or silicon dioxide
They don’t regulate body temperature
They’re waste is ammonia by diffusion
They reproduce sexually by hermaphrodites and asexually by fragmentation
They filter nutrients from water drawn into a central cavity
They can regenerate
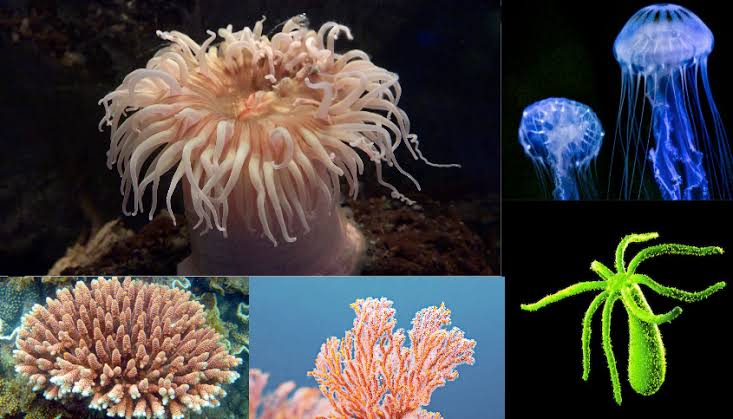

Cnidarians
examples are hydra and jelly fish
Primitive tissue
Diploblastic with mesoglea
Radial symmetry
No head
Acoelomates
No mouth-anus development
Sessile like hydra and motile (movement) like jelly fish
Muscular skeleton or water filled coelenteron that acts as hydrostatic skeleton
They don’t regulate body temperature
Waste is ammonia by diffusion
Life cycle: some go through a planula larva (free swimming) stage then go through two reproductive stages which is asexually budding producing polyp and sexually reproducing by Medusa
They have a Gastro vascular cavity or extra cellular digestion occurs and intracellular digestion is carried out inside body cells in lysosomes
Others (read through them on page 22)
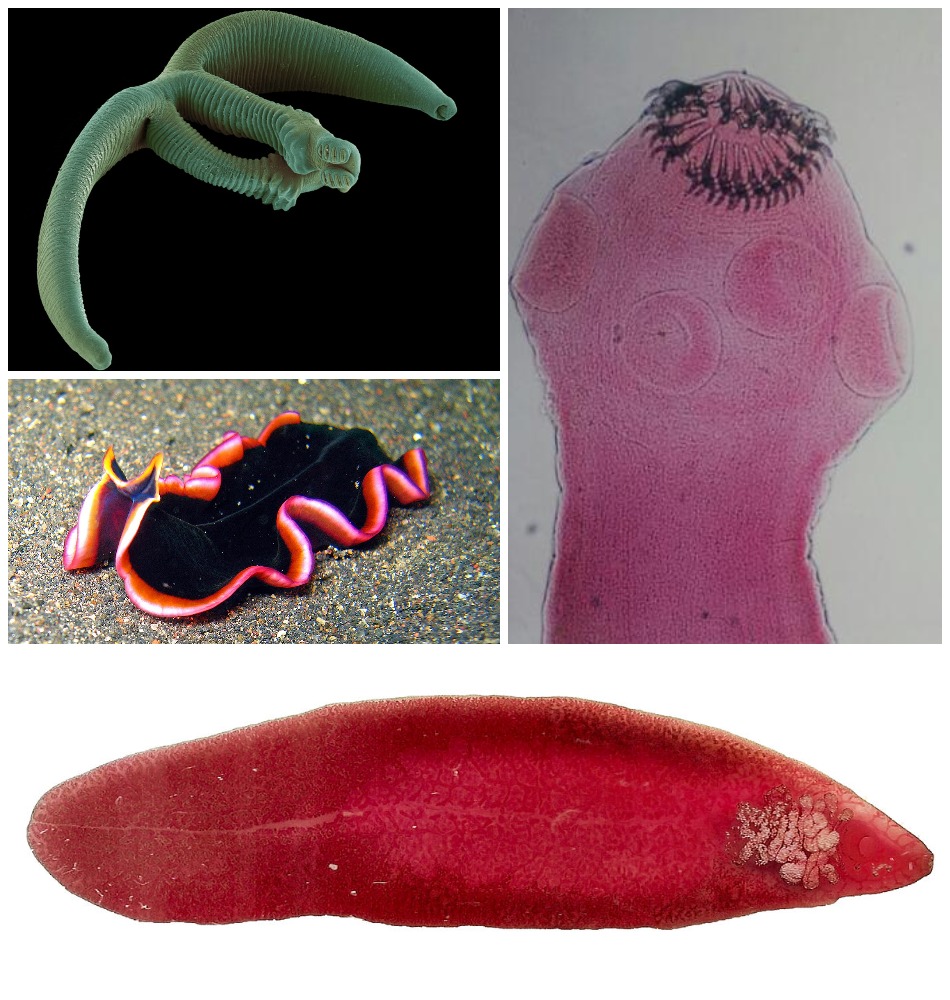
Platyhelminthes
examples are flatworms if they’re terrestrial and planaria if aquatic
Organs, but no organs system
Triploblastic (ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm)
Bilateral symmetry
Cephalisation (presence of head)
Acoelomates
Protostomes (mouth→anus)
Motile by locomotion
Hydrostatic skeleton which is closed body compartment that is filled with water together with muscles enables the animal to move from one place to another
They don’t regulate body temperature
Their waste is ammonia by flame cells if they’re aquatic and by nephridia if they’re terrestrial
They are sexually hermaphrodites and asexually fragmentation and budding
Digestive cavity has only one opening for both ingestion and egestion so food cannot be processed continuously
Others (page 22)

Nematodes
examples are roundworms
Organs with primitive organ system
Triploblastic (ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm)
Bilateral symmetry
Cephalisation (presence of head)
Pseudo-coelomates
Protostomes
Motile
Hydrostatic skeleton which is a closed body compartment that is filled with water and together with muscles enables the animal to move from one place to another
They don’t regulate body temperature
Their waste is ammonia nephridia
They reproduce sexually and asexually by fragmentation and budding
They have true digestive system. This means that at one end is a mouth and on the other end is an anus.
Others (read on page 22)
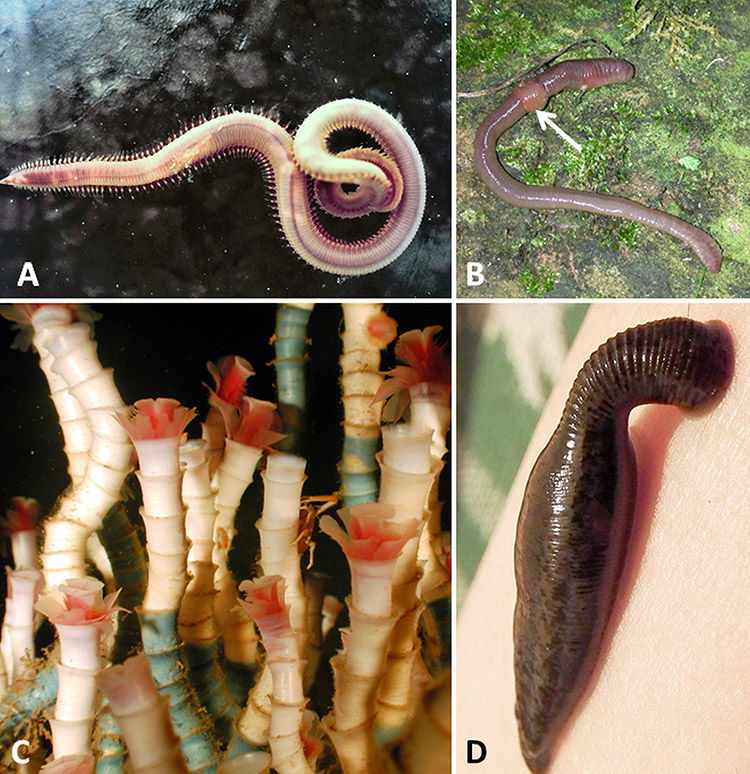

Annelids
examples are earthworms
Organs with primitive organ system system
Triploblastic (ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm)
Bilateral symmetry
Cephalization
Coelomates
Protostomes
Motile
hydrostatic skeleton which is a close body compartment that is filled with water and together with muscles enables the animals to move from one place to another
their waste is ammonia if they are aquatic and their waste as if terrestrial by nephridia
They were produced sexually by hermaphrodites and their asexual
Digestive system is a tube with in a tube consisting of crop gizzard and intestine
Others (read page 22)
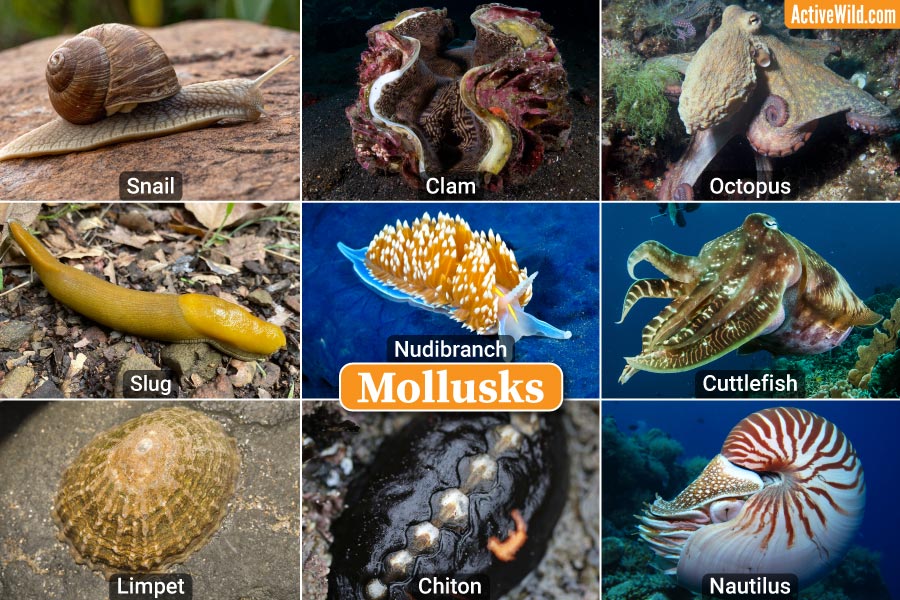

Mollusks
examples are snails slugs octopus squids
Organs with an organ system
Triploblastic
Bilateral symmetry
Cephalisation
Coelomates
Protostomes
Motile
Mantle that secrets a shell that offers protection (slugs have it but it’s very thin)
They don’t regulate body temperature
Waste is ammonia if aquatic and uric acid if terrestrial by nephridia
They reproduce sexually some are hermaphrodites and some need female and male mating
Food is transported to the digestive tract that starts at the head with the mouse continues down the oesophagus the crop then to the stomach to the intestines and ends of the anus
Others (read page 22)
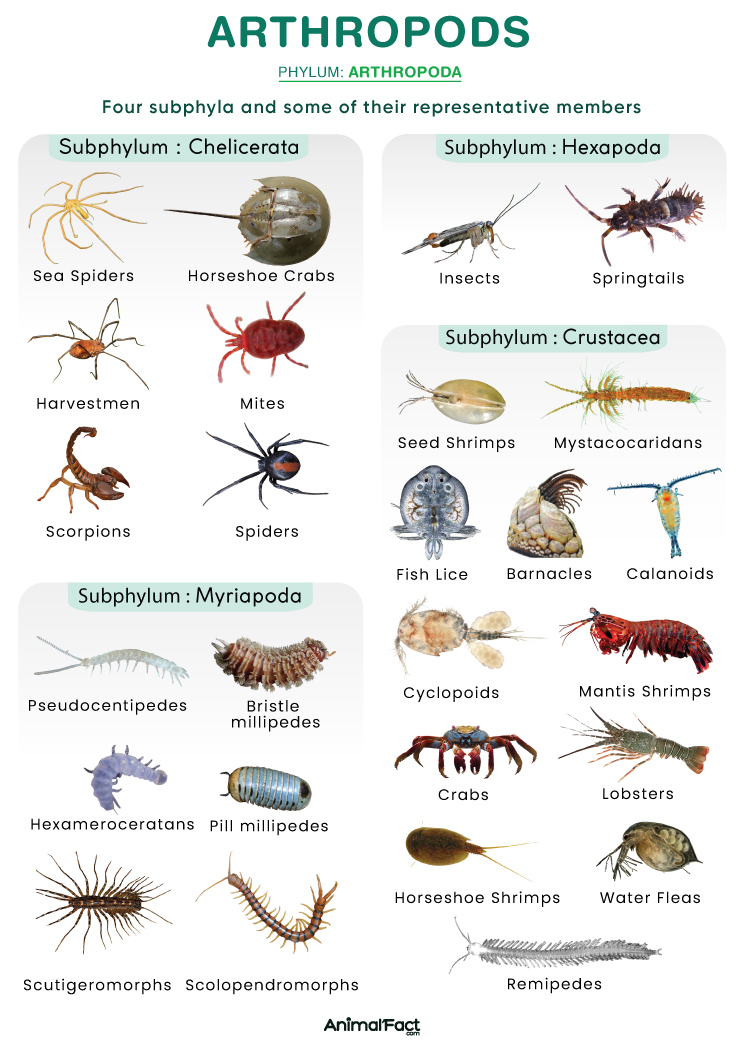
Arthropods
examples are class insects (grasshopper) and class crustaceans (crab or beetles) and class arachnids (spider) and class Chilopoda (centipedes)
Organs with organ system
Triploblastic
Bilateral symmetry
Cephalisation
Coelomates
Protostomes
Motile
Exoskeleton consisting of polysaccharides and chitin it does not grow within the animal it must be shed periodically
They don’t regulate their body temperature
waste is Uric acid by Malpighian tubes
If they are terrestrial internal sexual fertilisation if they are aquatic external sexual fertilisation, the female lays her eggs and the male releases sperms into the water and the eggs are fertilised in the water
They have a full digestive system made of mouth, oesophagus stomach, and anus
Others (page 22)


Echinoderms
Examples are sea stars (starfish) and sea urchins
Organs with organs system
Bilateral symmetry as (larva) and radial symmetry (adult)
Cephalisation
Coelomates
Deuterostomes
Motile
Internal skeleton covered with spines and skin
They don’t make you lead their body temperature
Their waste is ammonia by malpighian tubes
They reproduce sexually by external fertilisation and asexually by fragmentation and regeneration
Digestive system with mouth, stomach intestine and anus and the mouth is on the underside and the anus on the top surface sea stars can push their stomach outside of their body and inserted onto its prey, allowing them to digest the food externally
Others (page 22)
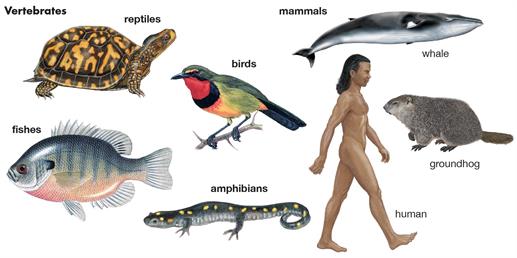
Chordates
examples are class amphibians and class birds and class fish and class mammals which includes order primates and class reptiles
Complex organ system
Triploblastic
Bilateral symmetry
Cephalisation
Coelomates
Deuterostomes
Motile
Endoskeleton that is made of bone and cartilage that grows within the body and grows as the body grows so no need for renewal
Mammals and birds are endothermic while amphibians and fish are ectothermic
Fish and amphibians waste is ammonia reptiles and birds waste is uric acid mammals and humans urea all by malpighian tubules
Sexual
They have a full sophisticated digestive system made mouth oesophagus stomach intestines and anus plus auxiliary organs like liver gallbladder and pancreas