isc bio exam 1 (copy)
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
mitochondrial eve
last common maternal ancestor of all humans through an unbroken line
y-chromosome adam
most recent common male ancestor of all living humans
LUCA
last universal common ancestor
bacteria’s characteristics
single cell, no nucleus, no membrane-bound organelles, no cytoplasmic structure
archaea’s characteristics
single cell, no nucleus, no membrane-bound organelles, live in extreme habitats but also soils + aquatic environments
eukarya
includes protists/protozoans, plants, fungi, and animals - has nucleated cells w/ cytoplasmic structure & membrane-bound organelles
phylogeny
the study of evolutionary relationships among biological entities, often based on genetic and morphological data
phylogenic trees
evolutionary trees/diagrams that represent a hypothesis about patterns of relationships among species
systematics
the study of evolutionary relationships
ancestral similarity
similarities from most recent common ancestor
derived similarity
similarity that arose more recently, does not come from the most recent common ancestor, and is only shared by a subset of the species
are ancestral similarities or derived similarities considered informational in cladistics?
derived similarities
character states
variations of a character/feauture/trait
ex. character “tail” has 2 states
i. presence of tail
ii. absence of tail
taxon
species or other higher-level groups
polarizing of characters
determining whether a character is ancestral or derived
outgroup method
method that assigns one species or multiple as the outgroup (closely related to the species under study, but not an actual part of it) and compares character states between the two groups
→ when the outgroup exhibits the same character state as the group under study, the state is considered ancestral
→ if not shown by outgroup, it’s considered derived
however: since outgroups also evolve, this method is considered most accurate when the character state is shown in multiple outgroups
what is a clade?
species that share a common ancestor
what does a clade include?
common ancestor + all descendants
synapomorphy
a derived character present in descendants but NOT in common ancestor
plesiomorphy
ancestral states/traits
symplesiomorphies
shared ancestral states/traits (shared among descendants and came from ancestor)
homplasy
character that is similar in different species, but those species don’t have a common ancestor
principle of parsimony
favoring the hypothesis that requires the fewest assumptions
molecular clock
uses the accumulation of DNA or protein mutations over time to estimate when different species diverged from a common ancestor
→ Scientists compare DNA sequences from different organisms, and the number of genetic differences observed is assumed to correspond to the amount of time that has passed since they shared a common ancestor
monophyletic group
includes most recent ancestor + all descendants
paraphyletic group
includes most recent ancestor, but not all descendants
polyphyletic group
characterized by convergent traits, parts of this group have no common ancestor
phylogenetic species concept
defines a species as the smallest group of organisms that share a unique, common ancestor and can be distinguished from other such groups
homologous structures/body parts
structures/body parts that were derived from common ancestor
homoplastic structures/body parts
body parts similar to common ancestor but did not directly come from them
at first, the Earth had a very ____________ environment, likely unable to support ____
inconsistent
life
in Earth’s early atmosphere, ___ levels shifted, changing the temperature
CO2
________ ______ caused the continents to move over time
tectonic plates
life emerged in the _______ time period
Archean
describe the process of weathering
water + CO2 in the atmosphere form carbonic acid (H2CO3)
carbonic acid interacts with rock to release HCO3^1- and Ca²+
those ions wash into the ocean to form calcium carbonate (CaCO3)
where may early organic molecules have originated from? (2 possibilities)
comets and asteroids that slammed onto the Earth
Earth’s early environment, which was a reducing environment, meaning it wouldn’t have taken that much energy to make the compounds
what does fixation of an element mean?
making the element biologically accessible
life started off as ______ cells and evolved over time
single
what does increased weathering mean for CO2 concentrations
they decrease
what does low CO2 concentrations lead to?
glaciation, which causes low sea levels
what are the four eukaryotic supergroups
excavata, SAR
archaeplastida
amoebozoa
opisthokonta
what is endosymbiosis
two cells living together with one inside the other
what are the 4 key environmental factors?
temperature, water, sunlight, soil
what are the two ways that organisms cope with environmental changes?
homeostasis
conforming to the environment
norm of reaction
ability to produce multiple phenotypes from one genotype
what are the 3 important characteristics of population ecology?
population range: the area throughout a population occurs
the pattern of spacing of individuals within that range
how the population changes in size throughout time
metapopulation
made up of distinct populations that may exchange members
source-sink metapopulations
populations in the better areas (the sources) send out dispersers that support the populations in the poor habitats (the sinks)
demography
the quantitative study of populations
populations grow if there are ____ births than deaths
populations shrink if there are ____ births than deaths
populations stay constant if there is a(n) _____ amount of births and deaths
more
less
equal
generation time
average interval between the birth of an individual and the birth of its offspring
cohort
group of individuals of the same age
fecundity rate
number of offspring produced in a standard time
mortality rate
number of deaths in a standard time
age structure
determined by the number of individuals in different age groups
life table
shows the date of a cohort from birth until death through a table
→ shows # of offspring and # of deaths in each time period
survivorship
the percent of an original population that survives to a given age
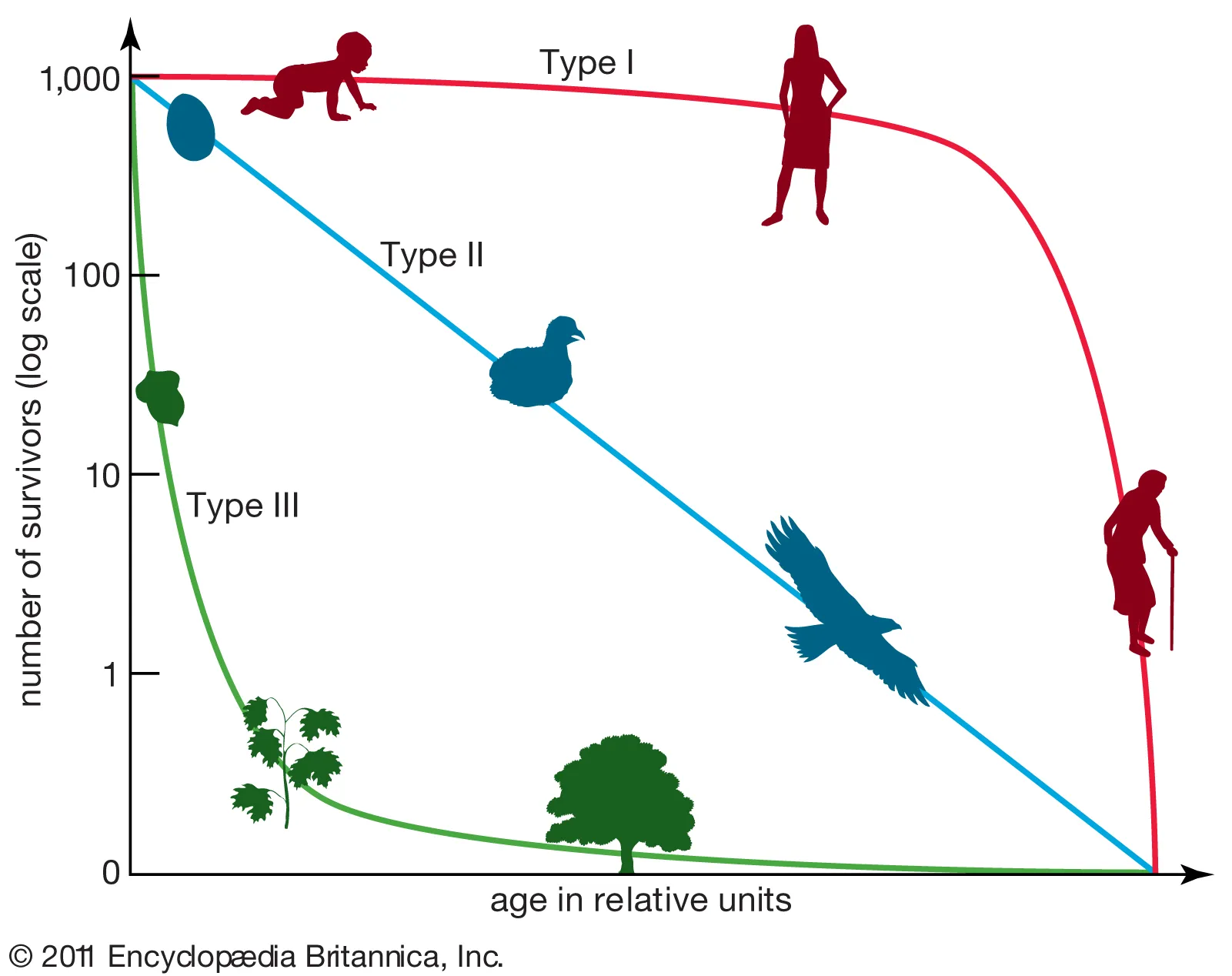
type 1: ______ mortality rate as they age
type 2: _______ likely to die at any age
type 3: _____ mortality rate as they age
higher
equally
lower
cost of reproduction
reduction in future reproductive potential due to current reproductive efforts
semelparity
an organism reproduces only once and then dies
iteroparity
an organism reproduces multiple times over many seasons
biotic potential
rate at which a population increases when there are no limits placed on its growth rate
carrying capacity
max population size that can be sustained by a specific environment due to lack of space, water, nutrients, etc.
density-dependent factors
factors that affect population size through time and depend on the size of the population
limitations to population growth regulated by biotic factors such as competition, predation, and disease, which are increased by high population densities
density-independent factors
factors that affect population size through time regardless of the size
limitations to growth of a population regulated by abiotic factors such as severe weather, fires, etc.
is bacteria monophyletic, polyphyletic, or paraphyletic?
monophyletic
is archaea monophyletic, polyphyletic, or paraphyletic?
paraphyletic
is eukarya monophyletic, polyphyletic, or paraphyletic?
monophyletic
Allee effect
population growth rate increases at high densities and decreases at low densities
k-selected organisms/populations
organisms/populations that are adapted to thrive when the population is near its carrying capacity
other characteristics: large body size, few offspring, high parental investment, long lifespans, and late sexual maturity
r-selected organisms/populations
organisms/populations with a short lifespan and high reproduction rates
other characteristics: little to no parental care
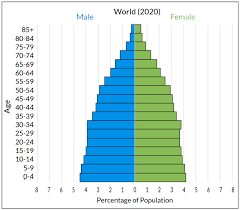
population pyramid
a bar graph that displays the number of people in each age category
→ usually males are to the left, and women are to the right
metabolism = biomass to the what power?
¾ (metabolism = biomass³/⁴)