Antibiotics
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
what is prophylaxis?
Treatment in place to prevent the development or spread of a diseases
what is empiric?
Treatment given to a patient with an unidentified or suspected infection when a treatment is required.
what is specific?
Targeted treatment given to stop a specific infection
what is superinfection?
A secondary infection caused by microorganisms resistant to the antibiotics used earlier
what is a narrow spectrum?
Active against a selected group of bacterial types
e.g Penicillin G - Cell wall synthesis
Streptomycin - Enterobacteria and M. tuberculosis
Erythromycin - Most gram-positive bacteria, some gram-negative
what is a broad spectrum?
Broad spectrum - Can treat all/many organisms
e.g Tetracycline and chloramphenicol kill pathogens and commensals
(normal flora)
what is an extended spectrum?
Narrow spectrum drugs adapted for multiple targets
what is a minimum inhibitory concentration?
minimum concentration of antibiotic required to inhibit the growth
what is minimum bactericidal concentration?
minimum concentration of antibiotic required to kill the bacteria
what is time dependent killing?
killing pattern is dependent on the duration of pathogen exposure to an antibiotic
what is concentration dependent killing?
As the antimicrobial concentration increases the amount of microorganisms killed increases
what are examples of antibiotics that inhibit cell wall synthesis?
Beta-lactams - Penicillins, Cephalosporins
Glycopeptides - Vancomycin
Bacitracin
Cycloserine
what are examples of reversible antibiotics that inhibit protein synthesis?
Tetracycline (30S)
Chloramphenicol (50S) Macrolide
Erythromycin (50S) Macrolide
Clindamycin (50S) Macrolide
what are examples of irreversible antibiotic that inhibit protein synthesis?
Kanamycin (30S) Aminoglycoside
Gentamicin (30S) Aminoglycoside
what is gentamicin?
Inhibits 30S ribosomal subunit
- Bactericidal
- Synthesised from Micromonospora purpurea
- Mixture of at least 4 compounds
- IV/IM route, narrow therapeutic index
what is the gentamicin used to treat for?
Severe sepsis, intra-abdominal sepsis
Complicated urinary tract infections
Endocarditis
Works well with penicillins (weaken cell wall) → Enhance aminoglycoside uptake
Ineffective in anaerobic bacteria
what are the common side effects of gentamicin?
Concentrated in ear and kidney
Ototoxicity (1/4): Damage of inner ear auditory hair cells
Loss of high frequency sound leading to permanent deafness
Vestibular hair cells (balance), may recover post treatment
Nephrotoxicity (1/4): Podocyte effacement
Water soluble renal excretion
Elevated blood K+/Mg2+ levels
Also.. impairment of neuromuscular transmission
what are examples of antibiotics that target injure plasma membrane?
Lipopeptides e.g. Daptomycin
- Gram-positive bacteria
- calcium-dependent depolarisation of PM
- Inhibit ATP synthase
• Polymyxins
- Gram-negative bacteria
- Cyclic polypeptides
- Disrupt membrane structure
- bactericidal
what are the two subtypes of antibiotics targets that inhibit nucleic acid synthesis?
Inhibitors of DNA replication e.g. Ciprofloxacin, (Fluoroquinolone type of Quinolone)
- Synthetic
- Bind DNA
- Inhibit DNA gyrase and Topoisomerases
- broad-spectrum bactericidal
Inhibitors of RNA polymerase e.g. Rifampicin
- Binds DNA-dependent RNA polymerase
what is ciprofloxacin?
Inhibit DNA gyrase and Topoisomerases
- broad-spectrum bactericidal
Treatment
what is ciprofloxacin used to treat?
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Superficial bacterial eye infection
- Acute otitis externa
- Urinary tract infection
what are the common side effects of ciprofloxacin?
- Nausea/diarrhoea; hypersensitivity
- Lower seizure threshold
- Increase arrhythmias (prolong QT interval)
- Induce rupture of muscle tendons
- Promote C. Difficile colitis
what are the interactions of ciprofloxacin?
- Cytochrome P450 Inhibition
- NSAID → Increase seizures
- Drugs/conditions that prolong the QT interval
what are the examples of antibiotics targets that inhibit synthesis of essential metabolites?
Inhibition of nucleotide synthesis
Sulphonamides
- Bacteriostatic
- Bind Dihydropteroate synthetase
Trimethoprim
- Dihydrofolate reductase inhibition
what is trimethoprim?
Dihydrofolate reductase inhibition
what is trimethoprim used to treat?
- Respiratory-tract infections
- Prophylaxis of recurrent urinary-tract infection
- Invasive salmonella infection
what are the common side effects of trimethoprim?
- Diarrhoea,
- Electrolyte imbalance: Hyperkalaemia
- Fungal overgrowth
- Headache, nausea, vomiting
- Skin reactions
- Teratogenic risk in first trimester (folate antagonist)
what are the types of antimicrobial resistance?
Reduce uptake
Efflux
Inactivation by enzymes
Antibiotic Sequestration
Modification of target (or overproduction)
Antibiotic target bypass - new pathway
Reverse chemotaxis - away from antibiotic
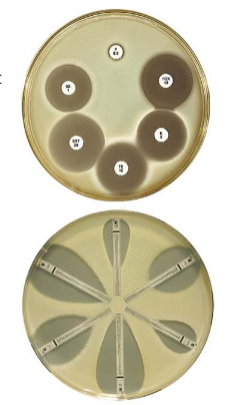
what is antimicrobial susceptibility testing?
Bacterial Identification
Growth (broth and agar) - Disk-diffusion/E-test strips (MIC)
Mechanism-specific tests e.g. - Beta lactamase detection
- Chloramphenicol acetyltransferase test (CAT)
- Automated methods - plate dilutions (MICs and MBCs)
- Genotypic methods - PCR
what is M. tuberculosis treatment?
Combination therapy used:
Isoniazid - Cell wall inhibition Prescribed with Vitamin B6; pyridoxine hydrochloride
Rifampicin – Inhibits DNA-dependent RNA polymerase
Resistance mechanisms of M. tuberculosis
what are the resistance mechanisms of M.tuberculosis?
Drug-resistant TB strains emerging in both hospital and community settings exhibit different levels of sensitivity:
Rifampicin resistance (RR)
MDR - Resistance to at least two most powerful anti-TB drugs (isoniazid and rifampicin)
Extensive drug resistance (XDR) - Resistant to rifampicin, isoniazid, fluoroquinolones and a second line injectable agent)
what is the isoniazid resistance mechanism?
- Requires activation by KatG (Catalase-peroxidase)
- Active isoniazid inhibits cell wall precursors
Resistance - katG (Catalase peroxidases) Mutations
- Loss compensated by Alkyl hydroperoxidase
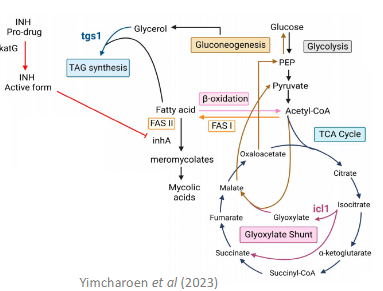
what is the rifampicin resistance mechanism?
Inhibits DNA-dependent RNA polymerase
Resistance
- ropB mutation
- Reduce permeability
- Efflux pump
why are combination therapies used all the time to overcome resistance?
Antagonism
- Cost
- Increased side effect risk
- Enhance resistance development – inducible resistance
- Interactions between drugs of different classes
- Often unnecessary
what causes urinary-tract infections?
Predominantly caused by bacteria from the gastrointestinal tract entering the urinary tract
Escherichia coli is the most common cause
what are lower UTIs?
Associated inflammation of bladder (cystitis) and urethra (urethritis)
Infection can ascend the urinary tract and lead to an upper UTI
what are the symptoms of lower UTIs?
Dysuria, increased urinary frequency and urgency, urine that is strong smelling, cloudy or contains blood, and persistent lower abdominal pain
what are upper UTIs?
Affect the proximal part of the ureters (pyelitis) or the proximal part of the ureters and the kidneys (pyelonephritis)
Can cause renal scarring, abscess or failure, and sepsis
what are the symptoms of upper UTIs?
Loin/side/lower back pain and fever
what are first-line antibacterial therapy treatments for acute uncomplicated lower UTIs?
Nitrofurantoin or Trimethoprim (Dihydrofolate reductase inhibition)
what are the second line treatment methods for acute uncomplicated UTIs?
(If no improvement after 48 hours)
Nitrofurantoin (if not used first line)
Fosfomycin
Pivmecillinam hydrochloride
Amoxicillin (if culture susceptible)
what is acute uncomplicated pyelonephritis?
Proximal part of the ureters and the kidneys
Immediate antibacterial prescription
Midstream urine sample obtained before
what are the treatment methods for acute uncomplicated pyelonephritis?
First line, oral
Cefalexin (beta-lactam, cell wall) or Ciprofloxacin (DNA gyrase and Topoisomerases)
First line, IV (Severely unwell)
Amikacin (aminoglycoside), ceftriaxone, cefuroxime, ciprofloxacin or gentamicin
what is catheter- associated urinary-tract infection?
Considered a “Complicated” UTI
Remove/changing catheter as soon as possible if it has been in place for longer than 7 days
Immediate antibacterial prescription
Urine sample obtained befor
what are the treatment methods for catheter-associated UTIs with no upper UTI symptoms?
First line, oral - Nitrofurantoin or trimethoprim
Second line, oral - Pivmecillinam hydrochloride
what are the treatment methods for catheter-associated UTIs with upper UTI symptoms?
First line, oral - Cefalexin, trimethoprim, co-amoxiclav or ciprofloxacin
First line, IV (Severely unwell) - Amikacin, ceftriaxone, cefuroxime, ciprofloxacin or gentamicin
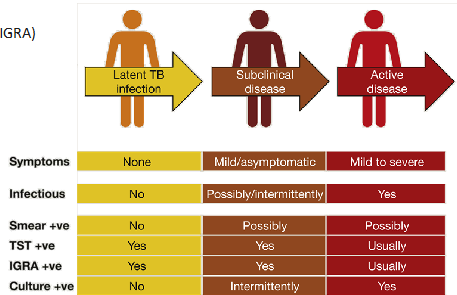
what is Latent TB infection?
Positive TB skin test (TST)
- Positive Interferon-γ release assay (IGRA)
- No symptoms of TB
- Normal chest X-ray
- Not contagious
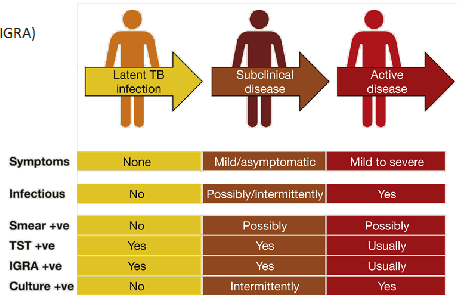
what is active TB disease?
- Positive TB skin test
- Symptoms
- Abnormal chest X-ray
- Contagious
what is latent TB infection treatment for patients below 65 and HIV?
3 months of isoniazid (cell wall) (with pyridoxine hydrochloride) and rifampicin (RNApol) or 6 months of isoniazid (with pyridoxine hydrochloride)
what is Latent TB infection treatment for patients between 35-65?
Only offered treatment if hepatotoxicity is not a concern
what is latent TB infection treatment for patients below 35 and if hepatoxicity is a concern?
3 months of isoniazid (with pyridoxine hydrochloride) and rifampicin
what is active TB disease treatment in its initial phase?
Using four drugs
Rifampicin, ethambutol hydrochloride (cell wall), pyrazinamide (pH) and isoniazid (with pyridoxine hydrochloride)
- Started without waiting for culture results if clinical signs of TB shown
- Modified according to susceptibility testing
- Continued for 2 months (Often regardless of results)
what is the continuation phase of active TB disease treatment?
Rifampicin and isoniazid (with pyridoxine hydrochloride)
- Continued for 4 months
- 10 months if CNS involved
- Modified according to susceptibility testing
what is rifampicin resistance?
6-month treatment with antituberculosis drugs that the mycobacterium is likely to be sensitive
what is MDR?
Resistance to at least two most powerful anti-TB drugs (isoniazid and rifampicin)
- 6-month treatment with antituberculosis drugs that the mycobacterium is likely to be sensitive
what is extensive drug resistance?
(XDR) - Resistant to rifampicin, isoniazid, fluoroquinolones and a second line injectable agent
In consultation:
Bedaquiline (diarylquinoline, inhibition of mycobacterial ATP synthase)
Delamanid (nitroimidazole, mycolic acid biosynthesis, essential for cell wall formation)
what is directly observed therapy?
Patients supervised taking dose → Better patient uptake → Reduce drug resistant TB
Documented
Side effects monitored
when is directly observed therapy offered?
Have a current risk or history of non-adherence
Have previously been treated for tuberculosis
Have a history of homelessness, drug or alcohol misuse
Are in prison or a young offender institution, or have been in the past 5 years
Have a major psychiatric, memory or cognitive disorder
Are in denial of the tuberculosis diagnosis
Have multi-drug resistant tuberculosis
Request directly observed therapy after discussion with the clinical team
Are too ill to self-administer treatment
what are the side effects of isoniazid?
Hepatic disorders (jaundice, nausea, vomiting)
Via: 1) Oxidate stress
2) Mitochondrial disfunction
what is rifampicin?
Many, decreases exposure to other drugs
Induces CYPs and inhibits some CYP activity
what are the side effects of rifampicin?
Nausea, thrombocytopenia, vomiting