[14-15] emphysema and lung cancer types.
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
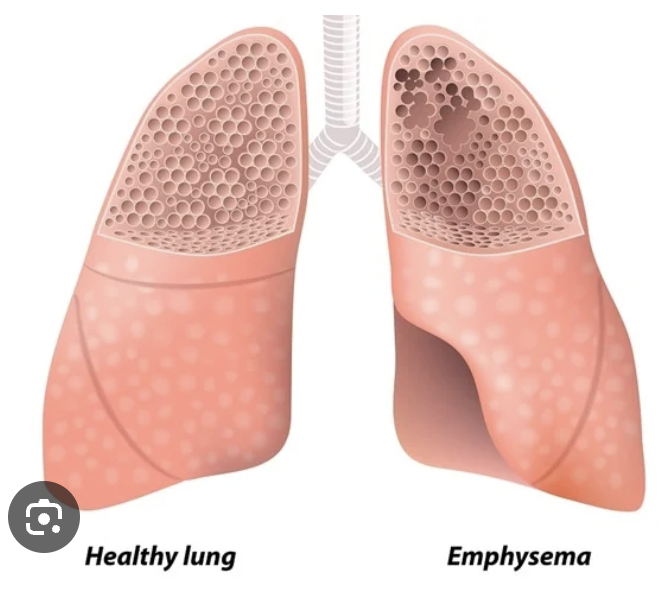
Irreversible enlargement of the airspaces distal to the terminal bronchiole, with destruction of their walls without obvious fibrosis.
What is emphysema?
What is a major cause of emphysema?
Association with cigarette smoking.
What are the types of emphysema based on anatomic distribution?
Centri-acinar (95% of cases)
pan-acinar
para-septal
irregular emphysema.
What is the difference between "Pink Puffers" and "Blue Bloaters"?
"Pink Puffer" refers to patients with emphysema, while "Blue Bloater" refers to patients with chronic bronchitis.
Increased antero-posterior chest diameter ("barrel" chest), increased total vital capacity, hypoxia, cyanosis, respiratory acidosis.
What are common clinical features of emphysema?
Retains CO2, shortness of breath, ineffective cough, barrel chest, thin limbs, significant weight loss, labored "pursed lip" breathing, anxious, speaks in short sentences.
Describe the appearance and symptoms of a "Pink Puffer".
What enzymes are involved in the destruction of the alveolar wall in emphysema?
Proteolytic enzymes like elastase.
What does elastase do in the pathogenesis of emphysema?
Induces destruction of elastin.
How does cigarette smoking contribute to emphysema?
Attracts neutrophils and macrophages (sources of elastase), inactivates alpha1-antitrypsin( which Neutralizes elastase, preventing the destruction of elastin.)
What genetic deficiency is associated with pan-acinar emphysema?
Hereditary alpha1-antitrypsin deficiency.
Codes for a structural alteration that interferes with hepatic secretion, leading to accumulation of hepatic cytoplasmic droplets and liver damage.
What is the effect of the piZ allele in alpha1-antitrypsin deficiency?
Decreased activity of alpha1-antitrypsin, pan-acinar emphysema, and hepatic cirrhosis.
What condition is associated with the homozygous state (piZZ)?
What part of the acini does centri-acinar emphysema affect?
Central or proximal parts of the acini formed by respiratory bronchioles, sparing distal alveoli.
Central or proximal parts of the acini formed by respiratory bronchioles, sparing distal alveoli.
What part of the acini does centri-acinar emphysema affect?
Where is centri-acinar emphysema more common and severe?
Upper lobes, particularly in the apical segments.
What part of the acini does pan-acinar emphysema affect?
Entire acinus from the respiratory bronchiole to the terminal blind alveoli is the area affected by…
Where is pan-acinar emphysema most severe?
Lower zones and anterior margins of the lung, especially at the bases.
What part of the acini does distal acinar (para-septal) emphysema affect?
Distal part of the acinus (alveoli and lesser alveolar ducts), with normal proximal portion.
“Adjacent to the pleura, along lobular connective tissue septa, and at the margins of the lobules” (is the common location for…)
Where is distal acinar emphysema typically located?
“Irregular involvement of the acinus, airspace enlargement with fibrosis, associated with inflammatory processes leading to scarring.”
What characterizes irregular emphysema?
“Localized accentuation of emphysema with the formation of large sub-pleural blebs or bullae (>1 cm in distended state), possible in any type of emphysema, sometimes related to old tuberculous scarring.”
What is bullous emphysema?
:Entrance of air into the connective tissue stroma of the lung, mediastinum, or subcutaneous tissue.” is..
What is interstitial emphysema?
Coughing with bronchiolar obstruction causing increased pressures within alveolar sacs, leading to alveolar tears and air entering the lung’s stroma. Other causes include chest wounds and fractured ribs puncturing lung parenchyma
What causes interstitial emphysema?
Chronic bronchitis, interstitial emphysema, pneumothorax due to rupture of surface blebs (apical bulla).
What are potential complications of emphysema?
type of emphysema most commonly associated with heavy cigarette smoking and chronic bronchitis.
centri-acinar (centri-lobular) emphysema
type of emphysema most commonly associated with a1-antitrypsin deficiency
Pan-acinar (Pan-lobular) Emphysema
What is the main symptom of metastatic lung cancer?
Dyspnea.
“Parenchyma, pleura and pleural space (malignant effusions), lymphatics” are common sites of
What are common sites of lung metastasis?
What primary cancers commonly metastasize to the lung?
Breast cancer
colon cancer
renal cell carcinoma.
What are common sites of lung cancer metastasis?
Hilar lymph nodes, adrenal gland (50% of cases), liver (30% of cases), brain (20% of cases).
Poorly differentiated tumors, no evidence of squamous or glandular differentiation, no criteria for small cell carcinoma.
What characterizes large cell carcinoma?
Localization: Peri-hilar region; High nucleus to cytoplasmic (N) ratio;
Neuroendocrine features; Immunopositivity for synaptophysin, chromogranin.
Describe the macro-/microscopic features of small cell lung carcinoma.
What is another name for small cell lung carcinoma?
Oat cell carcinoma.
In whom is squamous cell carcinoma almost exclusively found?
Smokers.
Where is squamous cell carcinoma typically located?
Centrally in the lung.
Squamous dysplasia precedes…
What precedes squamous cell carcinoma?
What is the most common primary lung cancer in women and never-smokers?
Adenocarcinoma.
Where is adenocarcinoma most often located(in the lungs)?
Peripheral regions of the lung.
What genetic mutation is associated with adenocarcinoma?
EGFR mutations.
Acinar
papillary
solid with mucous formation
bronchiolo-alveolar (lepidic growth).
What histologic variants of adenocarcinoma exist?
What histologic variants of adenocarcinoma exist?
Acinar
papillary
solid with mucous formation
bronchiolo-alveolar (lepidic growth).
Adenocarcinoma
squamous cell carcinoma
small cell lung carcinoma
large cell carcinoma
bronchial carcinoid.
List the types of lung carcinoma in decreasing incidence.
What is the classification for therapeutic purposes of lung cancer? (using small cell carcinoma and non small cell carcinoma)
Small cell carcinoma (not indicated for surgery), non-small cell carcinoma (surgery considered).
What para-neoplastic endocrine syndromes are associated with lung cancer?
ACTH-like activity (small cell carcinoma)
syndrome of inappropriate anti-diuretic hormone (SIADH) (small cell carcinoma)
parathyroid-like activity (squamous cell carcinoma).
ACTH-like activity (small cell carcinoma)
syndrome of inappropriate anti-diuretic hormone (SIADH) (small cell carcinoma)
parathyroid-like activity (squamous cell carcinoma).
What para-neoplastic endocrine syndromes are associated with lung cancer?
A tumor involving the apex of the lung, often associated with Horner syndrome (ptosis, miosis, anhidrosis).
What is Pancoast tumor?
A clinical manifestation of lung cancer which causes compression or invasion of the superior vena cava causing facial swelling, cyanosis, and dilatation of veins of the head, neck, and upper extremities.
What is superior vena cava syndrome?
Cough
haemoptysis
bronchial obstruction leading to atelectasis and pneumonitis
superior vena cava syndrome
Pancoast tumor with Horner syndrome
hoarseness
often bloody pleural effusion
para-neoplastic endocrine syndromes.
What are the common symptoms of lung cancer?
p53, RB1, p16.
What tumor suppressor genes are associated with lung cancer?
What tumor suppressor genes are associated with lung cancer?
p53, RB1, p16.
KRAS, MYC, HER-2/neu, BCL-2, EGFR.
What oncogenes are associated with lung cancer?
Radiation exposure
asbestos
certain metals (chromium, cadmium, beryllium, arsenic, nickel)
molecular genetic mutations.
What are other causes of lung cancer besides smoking?
What type of lung cancer is more common in never-smokers?
Adenocarcinoma, more common in women.
What types of lung cancer are most common in smokers?
Small cell and squamous cell carcinomas.
What is the primary cause of lung cancer?
Cigarette smoking (85-90% of cases).
What is the most common fatal cancer in both men and women?
Lung cancer.
Intermittent attacks of diarrhea, flushing, and cyanosis.
What are the symptoms of carcinoid syndrome?
Persistent cough, haemoptysis, impairment of drainage of respiratory passages with secondary infections, bronchiectasis, emphysema, atelectasis.
What are the clinical manifestations due to intraluminal growth of bronchial carcinoids?
Increased pleomorphism, cytologic atypia, prominent nucleoli, increased mitotic index (2-10 mitoses per 10 HPF), foci of necrosis, possible disorganized growth and vessel invasion.
(benign)
What characterizes atypical carcinoids?
Delicate fibro-vascular stroma, fairly uniform round nuclei, salt-and-pepper chromatin, moderate eosinophilic cytoplasm, immunopositivity for serotonin, neuron-specific enolase (NSE), calcitonin, etc.
What are the key microscopic features of bronchial carcinoids?
Solid, trabecular, gyriform, glandular.
What are the microscopic growth patterns of bronchial carcinoids?
Tumor growth in the form of a finger-like or spherical polypoid mass projecting into the bronchial lumen, peripheral tumors are solid and nodular, size: 3-4 cm, localized mainly in the main stem bronchi
Describe the macroscopic features of bronchial carcinoids.
What are the subtypes of bronchial carcinoids?
Typical carcinoids, atypical carcinoids.
What type of tumors are bronchial carcinoids?
Broncho-pulmonary neuroendocrine tumors (NETs).
Nodules of connective tissue (most commonly cartilage) intersected by epithelial clefts, lined by ciliated columnar epithelium or non-ciliated epithelium.
Describe the microscopic findings of a hamartoma.
Size: 3-4 cm;
Endo-bronchial lesions: Sessile or pedunculated;
Parenchymal lesions: Sub-pleural with cystic foci;
Cut surface: Grey or yellow (if fat is present).
Describe the macroscopic features of a hamartoma.
What is the most common benign lesion of the lung?
Hamartoma.
Adenochondroma.
What is another name for a hamartoma?
“Coin lesion.”
What is another name for a solitary pulmonary nodule?
What are common causes of a solitary pulmonary nodule?
Granulomas (e.g., Tbc, Histoplasmosis), malignancy (primary cancer), bronchial (chondroid) hamartoma.
What type of tumor is a papilloma?
Benign tumor.
Where are papillomas commonly located?
Large bronchi.
What is the difference between multiple and solitary papillomas in terms of age and HPV association?
Multiple: Found in children, associated with HPV.
Solitary: Found in middle to advanced age, no association with HPV.
a type of neoplasm with “Mucosal protrusions, pedunculated lesions, lobular pattern”
Describe the macroscopic findings of papillomas.
a type of neoplasm with “Fibro-vascular stalk, squamous epithelium without atypias or mitoses.”
Describe the microscopic findings of papillomas.