DSA22 - Infectious Diarrheas
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
> Bacteroides fragilis
> E. coli
What bacteria are part of the normal flora (aka infex by them is likely d/t breach of mucosal barrier or polymicrobial infex)?
> Yersinia
> Vibrio
> Salmonella
> Shigella
What bacteria are NOT part of the normal flora (aka are ALWAYS pathogens for GI tract)?
After Abx upset the balance of the normal flora (may favor infex by overgrowth of this or exogenous pathogens)
Given that C. diff is in the intestinal microflora in low populations normally, how does infection by it occur?
B/c large amounts of bacteria present in normal colon flora make interpretation difficult
Why is gram staining not usually done on stool?
Since it has a curved spiral or S-shaped rod that's different from other Gram(-) rods in GI flora
Why may gram staining be useful if Campylobacter is suspected as the pathogen?
> E. coli
> Salmonella
> Campylobacter
> Shigella
What are the 4 most common causes of bacterial diarrhea in the U.S.?
Obtain stool from rectal swab, and use selective enrichment media to inhibit non-pathogenic gram-positive organisms that are part of normal gut flora
What is the first step in Stool Culture?
Use Differential and Selective media to separate bacteria into groups based upon fermenting lactose
What is the second step in Stool Culture?
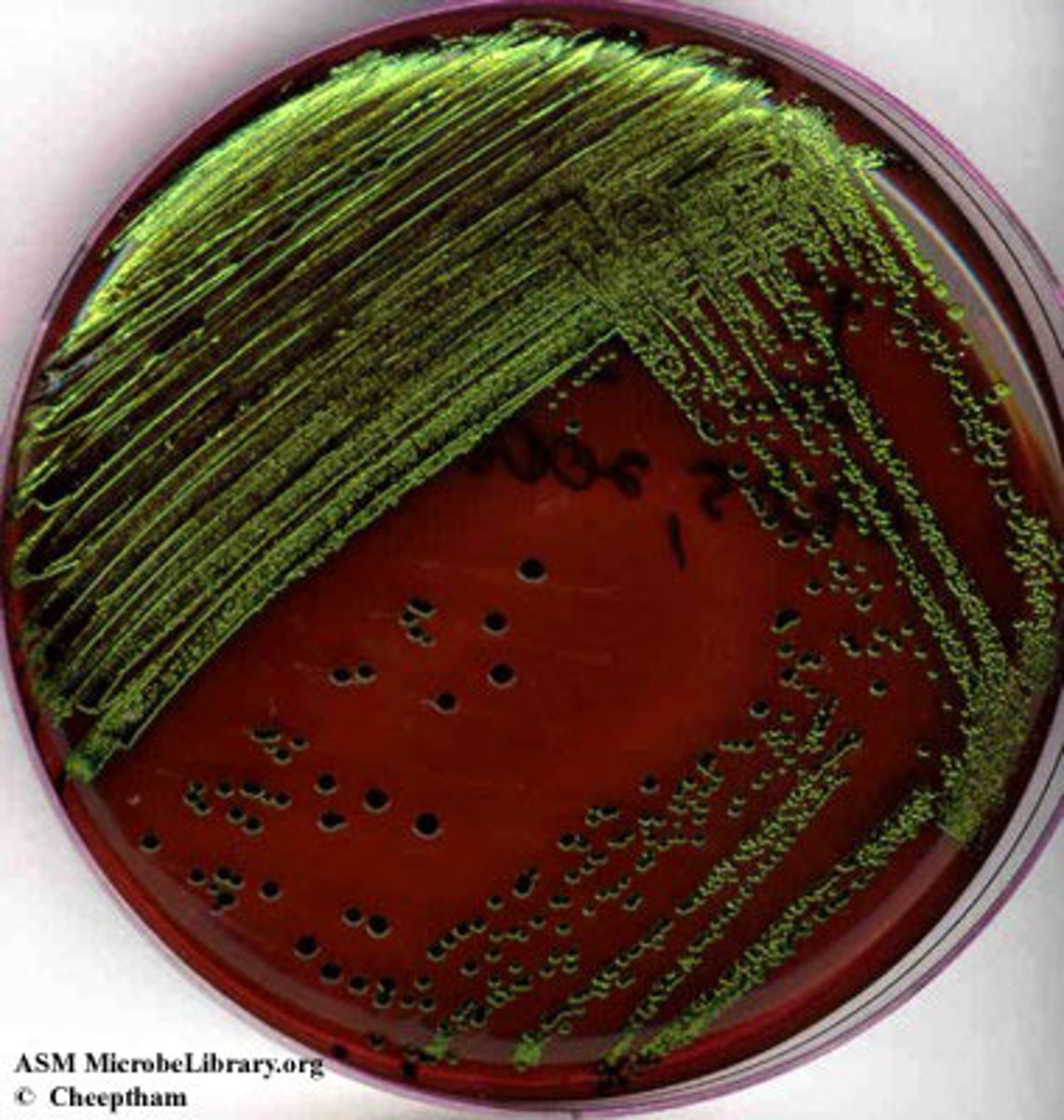
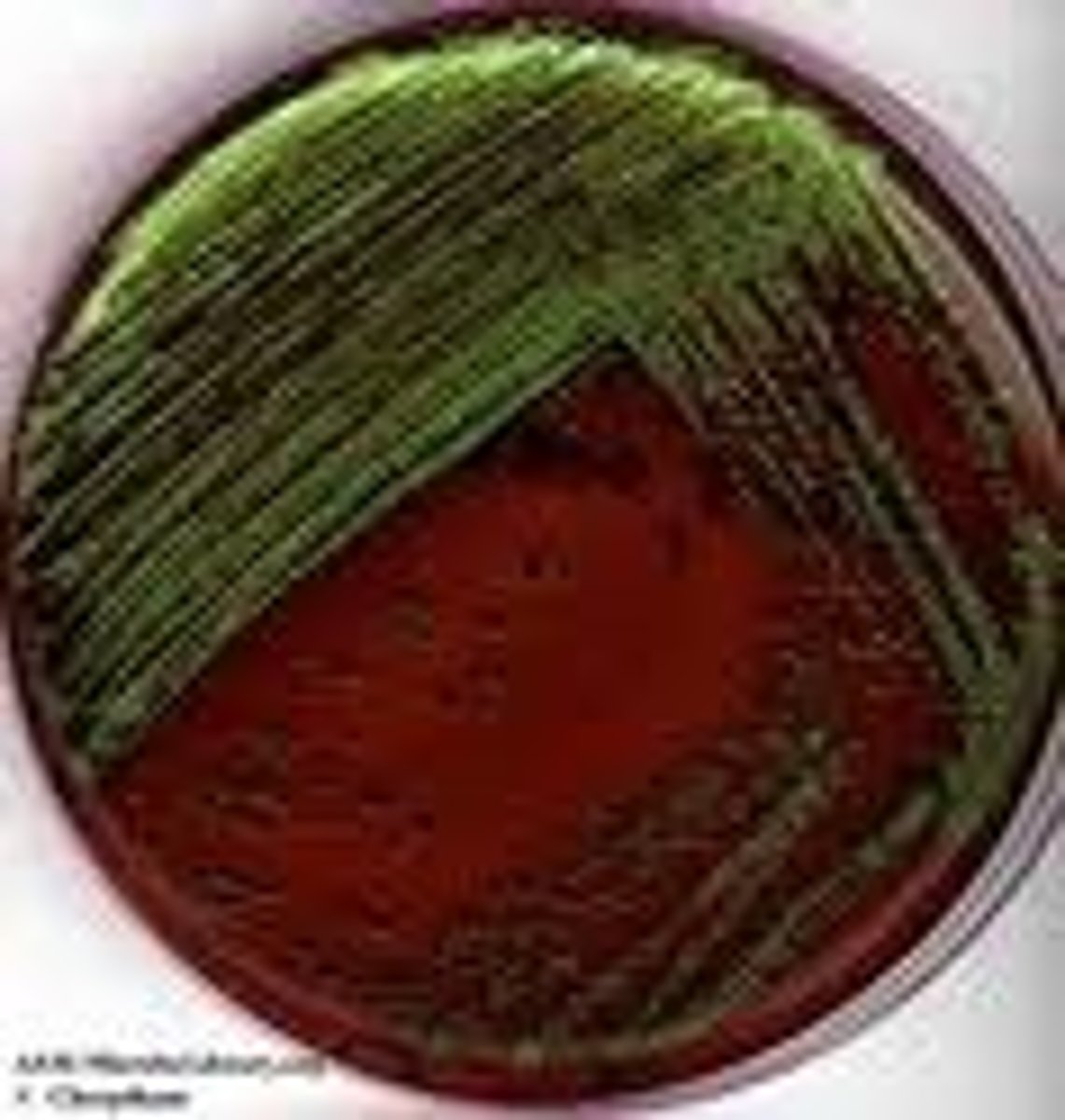
E. coli
What is a lactose-fermenting, gram negative bacteria that causes GI Infex?
Shows good growth of black colonies with metallic green sheen (d/t fermentation of lactose and acid production)
How do lactose-fermenting bacteria appear on Eosin Methylene Blue (EMB) agar?
Colonies ferment as PINK
How do lactose-fermenting bacteria appear on MacConkey agar?
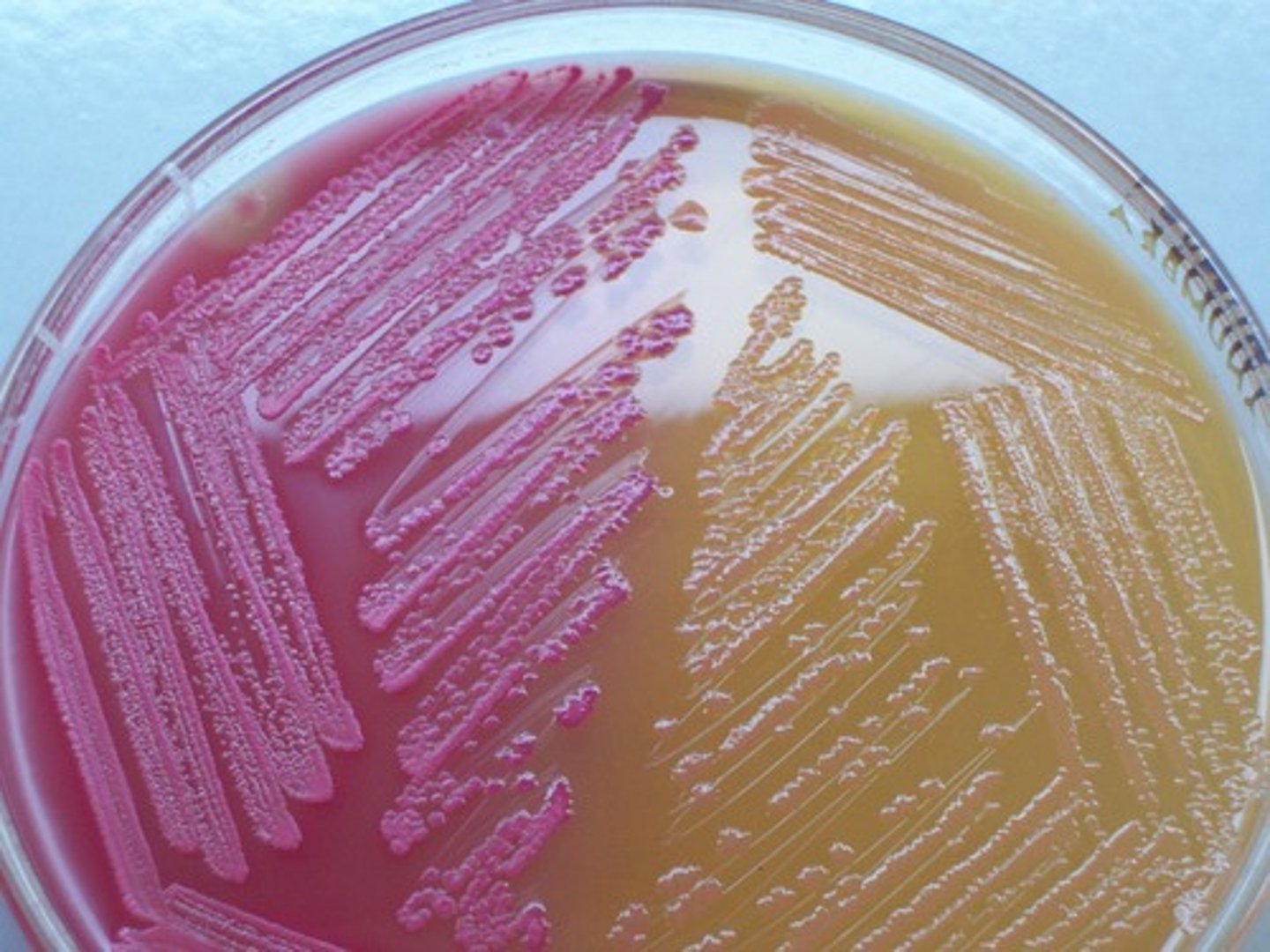
> Shigella (non-motile)
> Yersenia
> Salmonella (motile)
> Vibrio cholera
What are NON lactose-fermenting, gram negative bacteria that causes GI Infex?
Bacterial invasion of intestinal epithelial cells
What does a positive fecal smear for Leukocytes indicate?
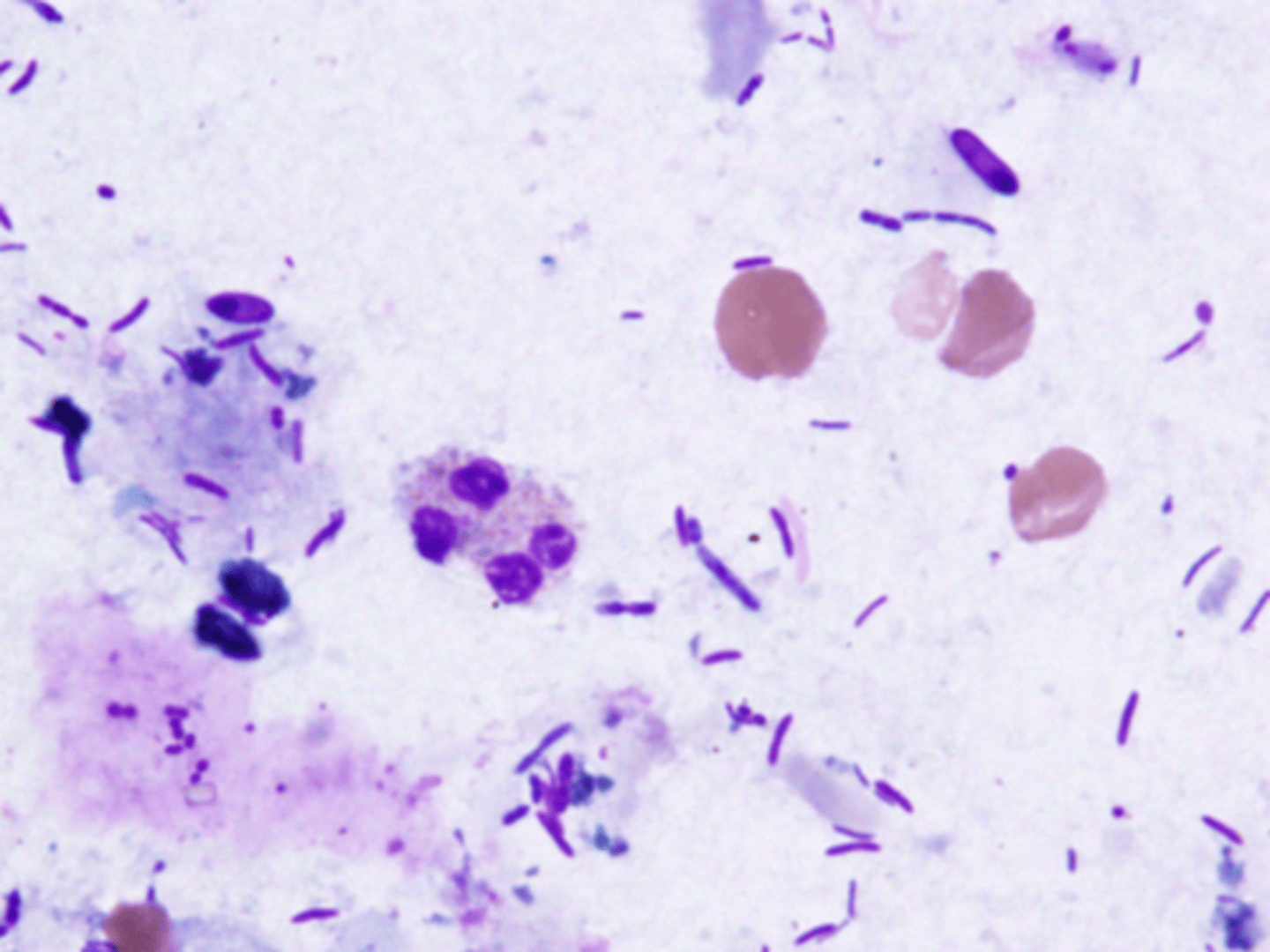
Shigella (MC = S. flexneri, Mortality = S. dysenteriae)
Identify Pathogen causing Diarrhea:
Gram-negative rod, Non-Motile (no flagella)
-Path: INVASIVE = Adheres to epithelial cells in preparation for invasion of mucosa via M Cells (Spreads from cell to cells) causing death and sloughing of contiguously invaded cells + inflammatory response
-Sx/PE: (1-7 days, Sx = 6 days)
Mainly infects LEFT COLON
> Inflammatory/Bloody Diarrhea
> FEVER & SEPSIS
> Abdominal Pain
**May be confused with IBD**
-Dx:
> (-) Lactose = Clear on EMB Agar
> (-) Oxidase
> (-) H2S
-Tx: SELF-LIMITING
-Prog:
> Reactive Arthritis (HLA-B27 +) if 20-40 y/o
> HUS
Salmonella
Identify Pathogen causing Diarrhea:
Gram-negative rod, MOTILE (flagella), acid labile, facultative intraclelular
-Hx:
> Reptiles (turtles)
> Amphibians
> Typhoid = Contaminated water or food
> Undercooked meat/eggs/poultry
-Path: INVASIVE = spreads through blood and invades GI tract via M cells; only infectious at high doses
-Sx/PE:
> Typhoid = (d/t typhi and paratyphi), starts 12-72 hrs after
>> FEVER
>> Abdominal Cramps
>> Rose colored spots on abdomen
>> Intestinal ulcers
>> Hepatosplenomegaly
>> Constipation --> Diarrhea
> Non-Typhoid = Foodborn Gastroenteritis (d/t enteritidis)
>> N/V
>> Watery --> Blood stools
-Dx:
> (+) Lactose = Green on EMB Agar
> (+) H2S = Black on Hektoen enteric agar
> Non-Typhoid/Foodborne Gastroenteritis = Intestinal ulceration & hemorrhage, sometimes in Peyer's patches -->
> Typhoid = Dissemination of the organism from the Peyer’s patches occurs via the lymphatic system and the bloodstream --> cellular replication within the reticuloendothelial system -> systemic symptoms + Stored in gallbladder for chronic carriers (risk of GB Carcinoma)
-Tx: SELF-LIMITING, but supportive care + Rehydration (oral)
-Prog:
> Reactive Arthritis (HLA-B27 +) if 20-40 y/o
> UnTx (HUS) = delirium, obtundation, intestinal hemorrhage, bowel perforation, and death within 1 month of onset
Campylobacter jejuni
Identify Pathogen causing Diarrhea:
Gram-negative (comma, spiral, S-shaped) curved rod w/ polar flagella; requires O2 at low levels
-Hx:
> Fecal-Oral transmission
>> Animal Intestines (poultry)
>> Undercooked poultry (MC = Chicken)
>> Unpasteurized milk
>> Contaminated drinking water
> A/w...
>> Reactive arthritis (HLA-B27 +)
>> Guillain-Barre Syndrome
-Path/Sx/PE:
> Cholera-like toxin = Watery Diarrhea
THEN
> Invade mucosa = Bloody Diarrhea
-Dx:
> Culture
>> Grows at 37C to 42C
>> (+) Oxidase
>> Microaerophilic
> Histology: Acute, self-limited colitis with cryptitis and crypt abscess
Helicobacter pylori
Identify Pathogen causing Diarrhea:
Gram-negative curved rod w/ polar flagella; requires O2 at low levels
-Sx/PE: Watery Diarrhea
-Dx:
> Grows at 37C
Yersinia enterocolitica
Identify Pathogen causing Diarrhea:
Nonmotile, Gram-negative, Facultative Intracellular Bacillus
-Hx:
> Transmitted via pet feces, contaminated milk, or pork
> A/w Reactive Arthritis (if HLA-B27 +)
-Path: Can invade Peyer's patches -> organisms multiply in mesenteric lymph nodes -> lead to granulomatous microabscesses in the lymph tissue -> inflammation of mesenteric lymph nodes (mesenteric adenitis)
-Sx/PE:
> Low-grade fefver
> Diarrhea (bloody if severe)
> Children = Pseudoappendicitis (Inflammation of terminal ileum and mesenteric LNs, but appendix normal) --> RLQ Pain d/t mesenteric adenitis and/or terminal ilietis
-Dx:
> Non-lactose fermenting
> (-) Oxidase
> Requires Iron
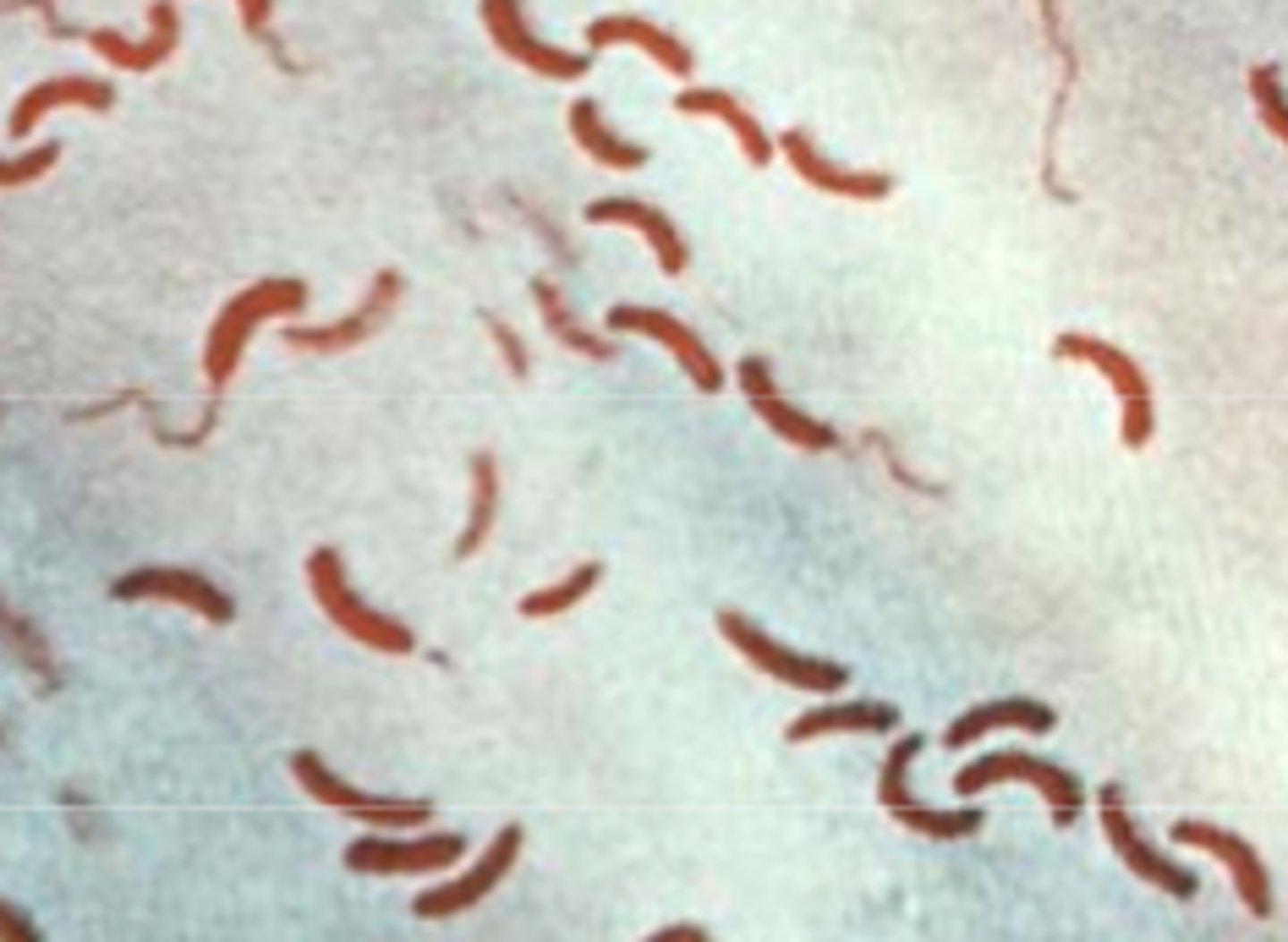
Vibrio cholerae
Identify Pathogen causing Diarrhea:
Comma Shaped, Gram-negative, Facultative anaerobe w/ one polar flagellum
-Hx:
> Developing countries (India, Bangladesh)
> Ingestion of contaminated water or uncooked food (raw shellfish/seafood)
-Path: TOXIGENIC = Adheres to mucosa and secretes enterotoxin and stimulates epithelial cell secretion
> Permanently activates Gs Protein --> Stimulates Adenylate Cyclase --> More cAMP ==> Cl- secretion
> Infex requires large dose of bacteria (stomach acid kills some bacteria)
-Sx/PE:
> "RICE WATER" Diarrhea
-Dx:
> (+) OXIDASE
> (+) Glucose
> (-) Lactose
> Grows in alkaline media
> Requires thiosulfate citrate bile salts sucrose agar (TCBS) agar
> (-) Fecal Smear
-Tx: Fluid Replacement (if severe enough)
-Prog: 50-70% Mortality if untreated
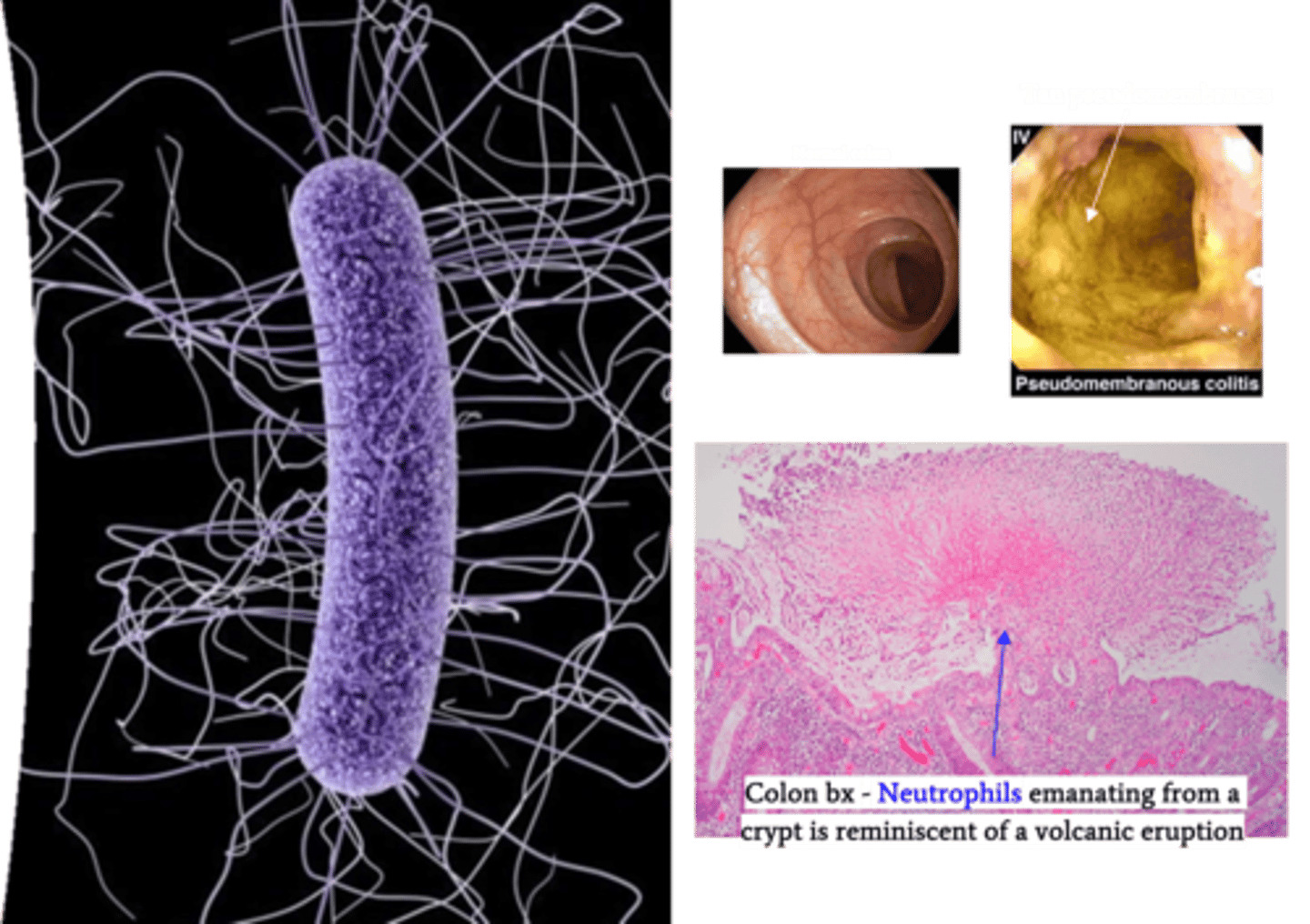
Clostridium difficile
Identify Pathogen causing Diarrhea:
Anaerobic, Gram-positive, spore forming bacillus
> MCC of Hospital Accquired Diarrhea
-Hx:
> Ubiquitous (found in water, air and soil)
> Abx Therapy
>> Clindamycin
>> Ampicillin
>> Cephalosporins
>> Fluoroquinolones
> PPIs
> Advanced Age
-Path: TOXIGENIC (Toxins A & B)
> Part of normal gut flora --> Abx ==> DISRUPTS normal colonic flora --> colonization and overgrowth
> Toxin A = enterotoxin damaging brush border of gut (disrupts tight junctions btwn enterocytes) ==> Malabsorption & Diarrhea
> Toxin B = cytotoxin that induces actin depolymerization -> damage of the cytoskeletal structure and cell death -> significant inflammation within the bowel wall
-Sx/PE:
> Asx
> Gastroenteritis:
>> Watery Diarrhea
>> Abd cramping
>> Fever
> Severe Infex: Pseudomembranous colitits
> Fulminant Infex: Toxic Megacolon
-Dx:
> (+) Enzyme Immunoassay (EIA) for Toxins A & B
> Gross: Pseudomembranous colitis
>> Tan yellow pseudomembranes made up of an adherent layer of inflammatory cells and debris at sites of mucosa injury
> Histology: Pseudomembranous colitis
>> Neutrophils "erupting" from crypt like "volcanic eruption"
-Tx:
> Supportive Care
> Abx (Vancomycin & Fidaxomicin)
> Recurrent = Fecal Microbiota transplant (stool microbiome from a donor is transferred to the patient via capsules, colonoscopy or enema)
E. coli - ETEC (Enterotoxigenic)
Identify Pathogen causing Diarrhea:
Gram-negative rod
-Hx:
> MCC of Traveler's Diarrhea
> Fecal-Oral Route (Contaminated food/water)
-Path:
> Heat-labile Toxin = activates cAMP --> Cl secretion --> Water in Gut
> Heat stable Toxin = activates cGMP --> Cl secretion --> Water in Gut
-Sx/PE:
> Watery (Non-Inflammatory) Diarrhea
> Cramps
> No Fever OR Low-Grade Fever
-Dx:
(+) Lactose on EMB
E. coli - EPEC (Enteropathogenic)
Identify Pathogen causing Diarrhea:
Gram-negative rod
-Hx:
> Children
-Path: Adheres to apical surface --> flattens/blunts villi --> less absorption
-Sx/PE:
> Watery (Non-Inflammatory) Diarrhea
-Dx:
(+) Lactose
Enteroinvasive E coli (EIEC)
Identify Pathogen causing Diarrhea:
Gram-negative rod
-Path: INVASIVE = Adheres to epithelial cells in preparation for invasion of mucosa
-Sx/PE:
> Inflammatory/Bloody Diarrhea (Necrosis)
> FEVER & SEPSIS
> Abdominal Pain
-Dx:
> (+) Lactose
> (+) Fecal Smear
Enterohemorrhagic E coli (EHEC)
Identify Pathogen causing Diarrhea:
Gram-negative rod (Shiga toxin-producing, aka STEC)
-Hx:
> Undercooked beef or raw leafy veggies
>> Meat may become contaminated when organisms are accidentally mixed in, especially when it is ground
> Drinking or Swimming water
> Not washing hands (person to person)
-Path: Toxin causes Disease --> Shiga-like toxin --> Endothelium swells/vessel lumen narrows + Fibrin/platelets in microvasculature --> Hemolysis + Inflammation
-Sx/PE: (1-8 days, usually 3-5 days)
> Inflammatory/Bloody Diarrhea (Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome)
>> Microangiopathic Hemolytic Anemia (MHA)
>> Thrombocytopenia
>> AKI
> FEVER & SEPSIS
> Abdominal Pain
-Dx:
> Serotype: E. coli O157:H7
> (+) Lactose
> (+) Fecal Smear
Listeria monocytogenes
Identify Pathogen causing Diarrhea:
Gram-positive, facultative intracellular rod - "tumbling motility"
-Hx:
> Unpasteurized dairy products
> Cold Deli meat/Hot Dogs
> Vaginal transmission (delivery to neonate)
> Multiplies in those with poor cell-mediated immunity
-Sx/PE:
> Watery Diarrhea
> Pregnant women =
>> Flu Sx
>> GI Sx
>> Spontaneous abortion (2nd or 3rd trimester)
>> Neonatal meningitis
> Septiciemia
-Dx:
> Grows well at refrigerated temps
Vibrio parahaemolyticus
Identify Pathogen causing Diarrhea:
Gram-negative curved rod
-Hx:
> Warm coastal waters of U.S. and Canada (higher during summer)
> Transmitted via ingestion of raw or undercooked shellfish (OYSTERS)
-Path: Mainly affects colon
-Sx/PE: 1-7 days
> Watery Diarrhea (may cause bloody diarrhea)
> Abd Cramps
> N/V
> Fever
> Headache
-Tx: Self-Limiting
Vibrio vulnificus
Identify Pathogen causing Diarrhea:
Flagellated, halophilic, motile, gram-negative curved rod
-Hx:
> Marine environments
> Via ingestion of contaminated seafood
> Via direct wound contact w/ contaminated water or seafood
> Primary Sepsis = Immunocompromised (Chronic Hepatitis, Diabetes, Cancer, Renal Disease, HIV)
-Sx/PE:
> Primary (limited) Gastroenteritis = Watery Diarrhea
> Primary Wound Infex
> Primary Septicemia
Food with preformed toxin
If pts have rapid onset of Sx (6-12 hrs) and mostly have watery diarrhea & vomiting, what was most likely the cause?
> Staphylococcus aurues
> Bacillus cerus
> Clostridium perfringes
> Clostridium botulinum
What organs often create preformed toxins in food (if improperly cooked or stored with foods with toxins or spores)?
Staphylococcus aureus
Identify Pathogen causing Diarrhea:
Gram-positive cocci clusters --> Ingested enterotoxin
-Hx: Short incubation period (1-6 hrs) & Anywhere when food sits out at room temp
> Mayonnaise (potato or egg salads)
> Custards
> Cream Pastries
> Meat
-Path: D/t ingestion of heat stable enterotoxin (not destroyed by cooking)
-Sx/PE:
> N/V
> Secretory (Watery) Diarrhea
-Dx:
> Stool and/or Food Culture
> Toxin Assay
Bacillus cereus
Identify Pathogen causing Diarrhea:
Gram positive rod --> Ingested enterotoxin
-Hx: Undercooked/Reheated Rice ("Reheated rice syndrome")
> Heat-resistant spores survive cooking
> Cooked rice at room temperature
-Path/Sx/PE:
> Nausea/Vomiting (Emetic):
>> D/t direct ingestion of Cereulide toxin (heat stable)
>> Abdominal Cramps + N/V
>> Often from Rice disrhes
> Diarrheal Type:
>> Abdominal Cramps + WATERY Diarrhea
>> 8-16 hrs after ingestion
>> D/t several enterotoxins (heat labile)
>> Cooking food reduces risk
>> From meats, veggies, sauces
-Dx:
> Stool and/or Food Culture
> Toxin Assay
Clostridium botulinum
Identify Pathogen causing Diarrhea:
Gram-positive, spore-forming, obligate anaerobic rod --> Ingested enterotoxin
-Hx:
> Infant = Spores ingestion from honey
> Wound = Bacterial growth
> Foodborne
>> Adults
>> Improperly canned foods (anaerobic environments promotes growth)
>> Undercooked foods
-Path: Neurotoxic
> Proteases that cleave SNARE proteins --> prevents ACh release at NM junction
> Grows and produces toxin in unrefrigerated high moisture foods that are low in acid and exposed to little or no oxygen (canned foods of asparagus, green beans, beets, and corn)
-Sx/PE: w/n 12-36 hrs of ingestion
>> Diplopia
>> Dry mouth
>> Difficulty swallowing/speaking
>> Diarrhea
>> Vomiting
>> Constipation
>> Abdominal Swellling
>> Descending Flaccid Paralysis ==> Resp Failure/Dyspnea
-Dx:
> Stool and/or Food Culture
> Toxin Assay
Clostridium perfringens
Identify Pathogen causing Diarrhea:
Gram-positive, spore-forming, obligate anaerobic rod --> Ingested enterotoxin
-Hx:
> Meats/Poultry
> Legumes
-Path: Incubation period (8-16 hrs); Heat resistant spores --> Spores germinate, release enterotoxins
-Sx/PE: LATE ONSET
> Secretory (Watery) Diarrhea
> Abdominal Pain
> Headache
-Dx:
> Stool and/or Food Culture
> Toxin Assay
> Norovirus
> Rotavirus
> Enteric Adenovirus
What are the most common causes of VIRAL Diarrhea in the U.S.?
Norovirus (aka Norwalk Virus)
Identify Pathogen causing Diarrhea:
ssRNA virus in Caliciviridae family
> MCC of Gastroenteritis in developed countries
> MCC of Water Diarrhea in adults & Rotavirus-vaccinated children
-Hx:
> Local outbreaks from contaminated seafood
> Cruise ships
> Business Conferences
-Path: Illness develops 12 to 48 hrs after contaminated food or water is ingested
-Sx/PE:
> May be Asx
> Watery Diarrhea (x2-3 days)
> N/V
-Dx:
> (-) Fecal Smear
-Tx: Self-Limiting
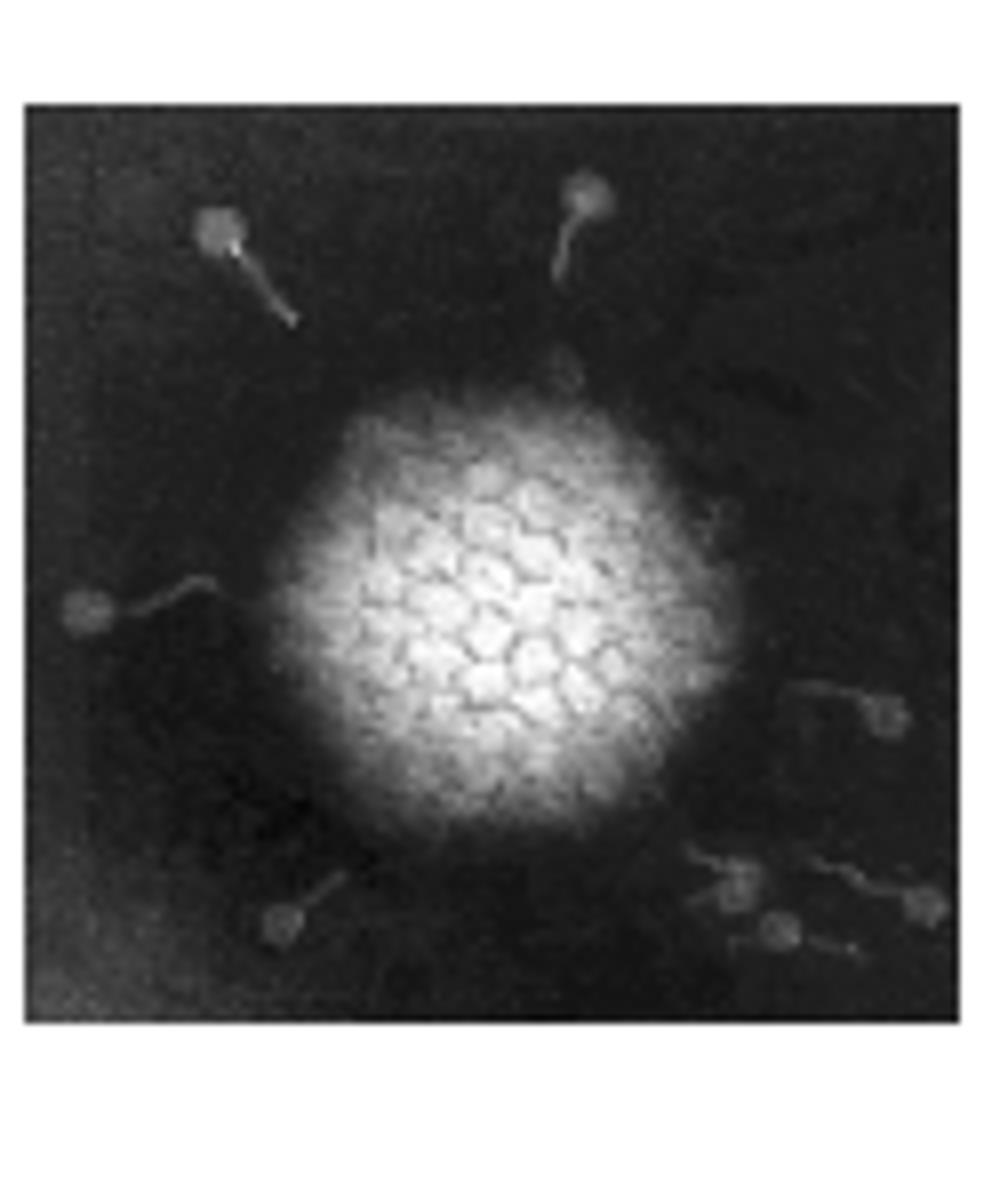
Rotavirus
Identify Pathogen causing Diarrhea:
Non-enveloped dsRNA virus
> MCC of Watery Diarrhea in Unvaccinated children < 5 y/o
-Hx:
> Fecal-Oral Transmission (Daycare Centers)
-Path: Virus destroys the absorptive capacity of villi -> incompletely absorbed nutrients osmotically active -> water secreted into GI tract ->
-Sx/PE:
> Watery Diarrhea
-Dx:
> Virus found in Stool
> (-) Fecal Smear
-Tx:
> Vaccine to prevent in children < 6 mo
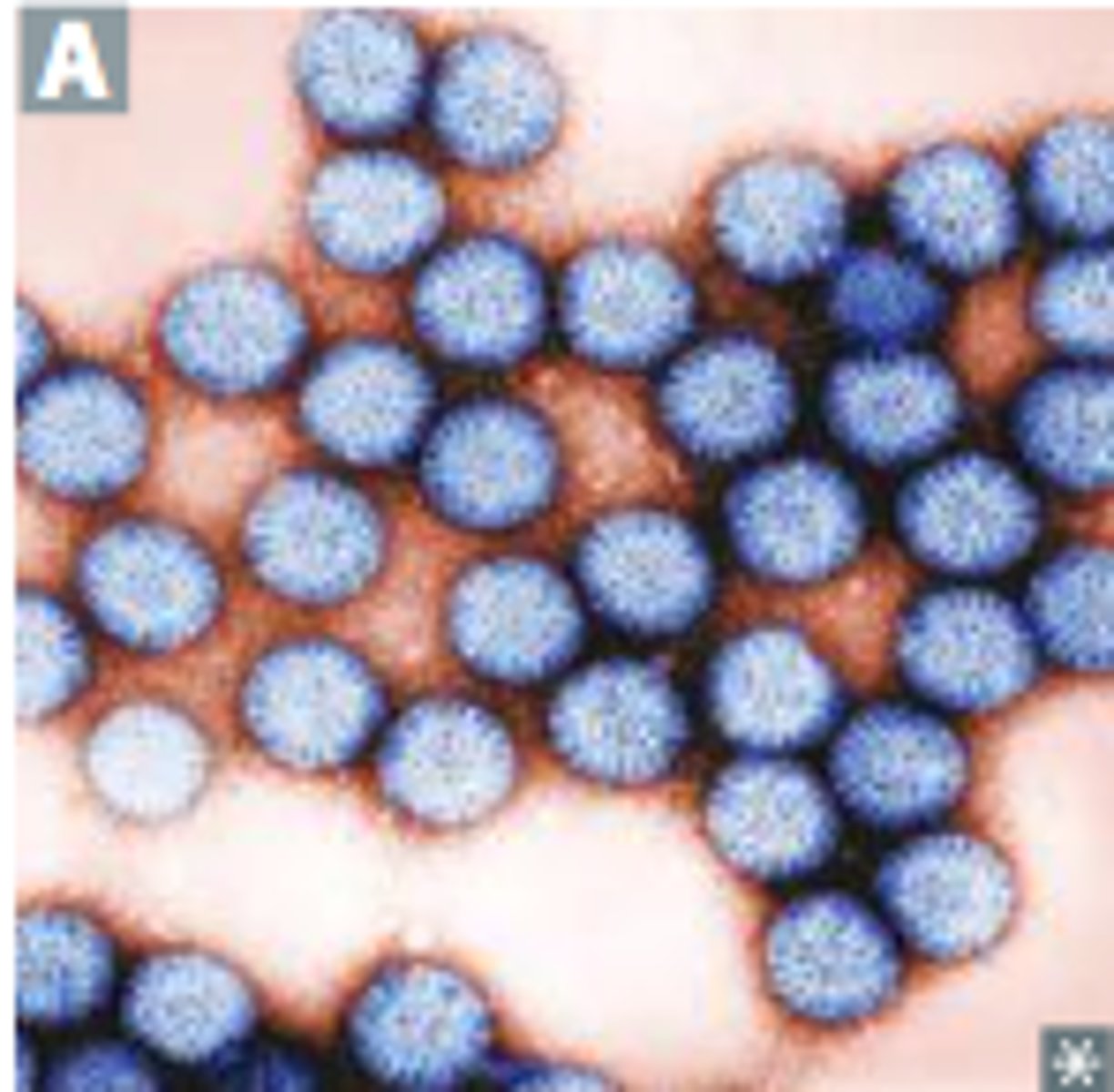
Enteric Adenovirus
Identify Pathogen causing Diarrhea:
dsDNA Virus
-Hx:
> Children
-Sx/PE:
> Watery Diarrhea
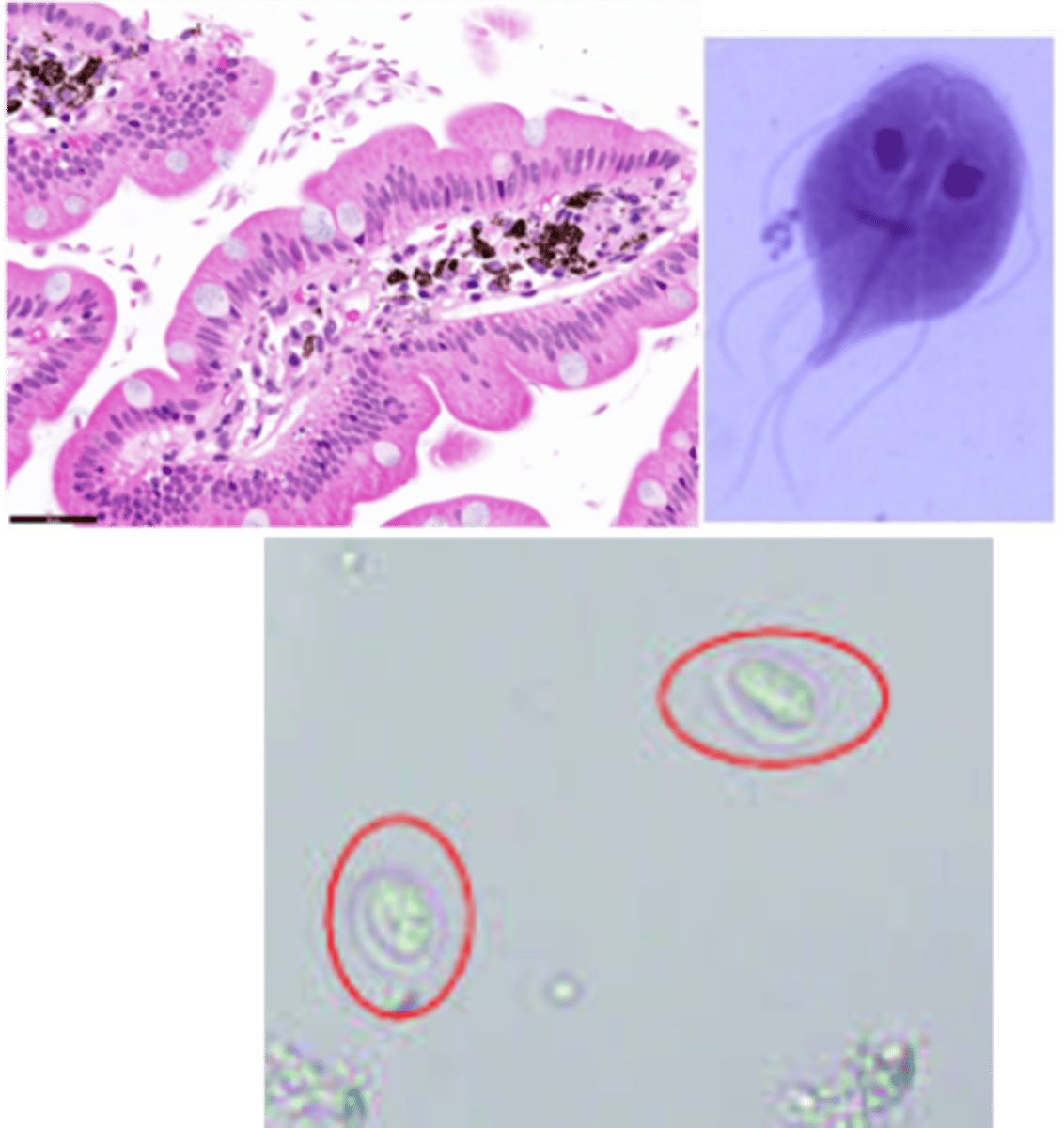
Giardia lamblia
Identify Pathogen causing Diarrhea:
Pear-shaped parasite, with hair-like flagella for motility
-Hx:
> Fecal-Oral Transmission (cysts in stool --> contaminate water)
> Found in moist environments, esp in mountain streams
> A/w campers/hikers
-Path: Ingested cysts from contaminated water -> trophozoite in intestine ==> ATTACHES (not invade) by sucking discs to microvilli in SI (Mainly Duodenum) ==> Fat malabsorption
-Sx/PE:
> Watery & Fatty Diarrhea
> Steatorrhea
-Dx:
> Smear: Protozoan cysts & Trophozoites in stool
> ELISA: Antigens in Stool
> Histology:
>> Pear to crescent-shaped trophozoites that usually float freely between the intestinal villi
>> Can sometimes cause blunting of villi, mimicking celiac disease
Cryptosporidium parvum
Identify Pathogen causing Diarrhea:
-Hx:
> Fecal-Oral Transmission (cysts in stool --> contaminate water)
> Oocysts in water --> Infex (MC in Swimming pools - chloride doesn't destroy)
-Path: Protozoae forms eggs (oocysts)
-Sx/PE:
> Immunocompetent = Mild, Watery Diarrhea
> HIV/ADS = SEVERE DIARRHEA
-Dx:
> Stool: Spheres atop brush border via acid-fast staining, or direct fluorescent Ab (DFA1)
> ELISA = Antigens
> PCR
-Prog:
> Immunocompetent = SELF LIMITED
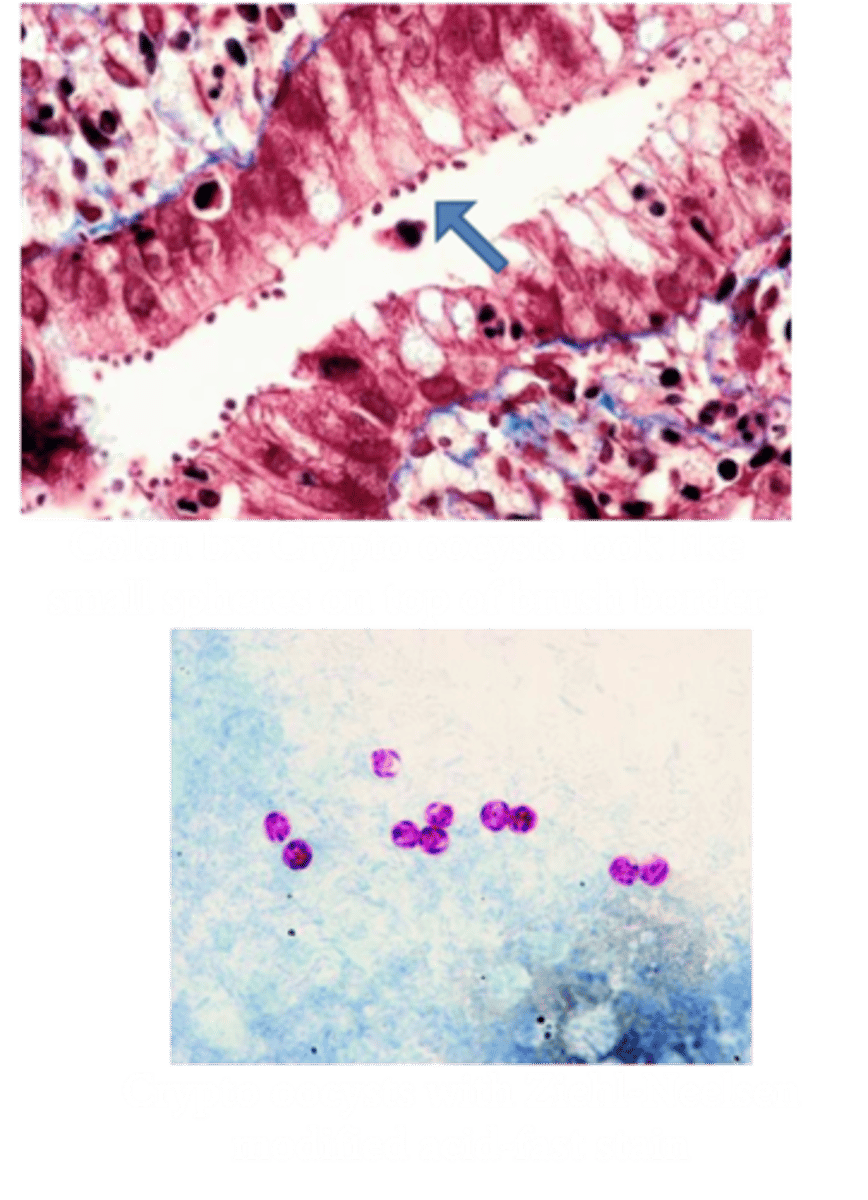
Cyclospora
Identify Pathogen causing Diarrhea:
-Hx:
> Fecal-Oral Transmission (cysts in stool --> contaminate water)
> Contaminated fresh food products
>> Soft Fruits (raspberries, blackberries, and strawberries)
>> Leafy veggies (lettuce & mixed salad)
>> Herbs (basil & cilantro)
-Path: Freshly passed in stools, unsporulated oocyst is not infective --> Oocysts excyst in the GI tract, freeing the sporozoites which invade the epithelial cells of the SI --> Inside cells, they undergo asexual multiplication and sexual development to mature into oocysts, which will be shed in stools
-Sx/PE:
> Watery Diarrhea
-Dx:
> Stool: Modified acid-fast stain of oocysts or modified ("hot") safranin techniques
> UV Microscopy = Blue/Green Oocysts
> PCR of Stool
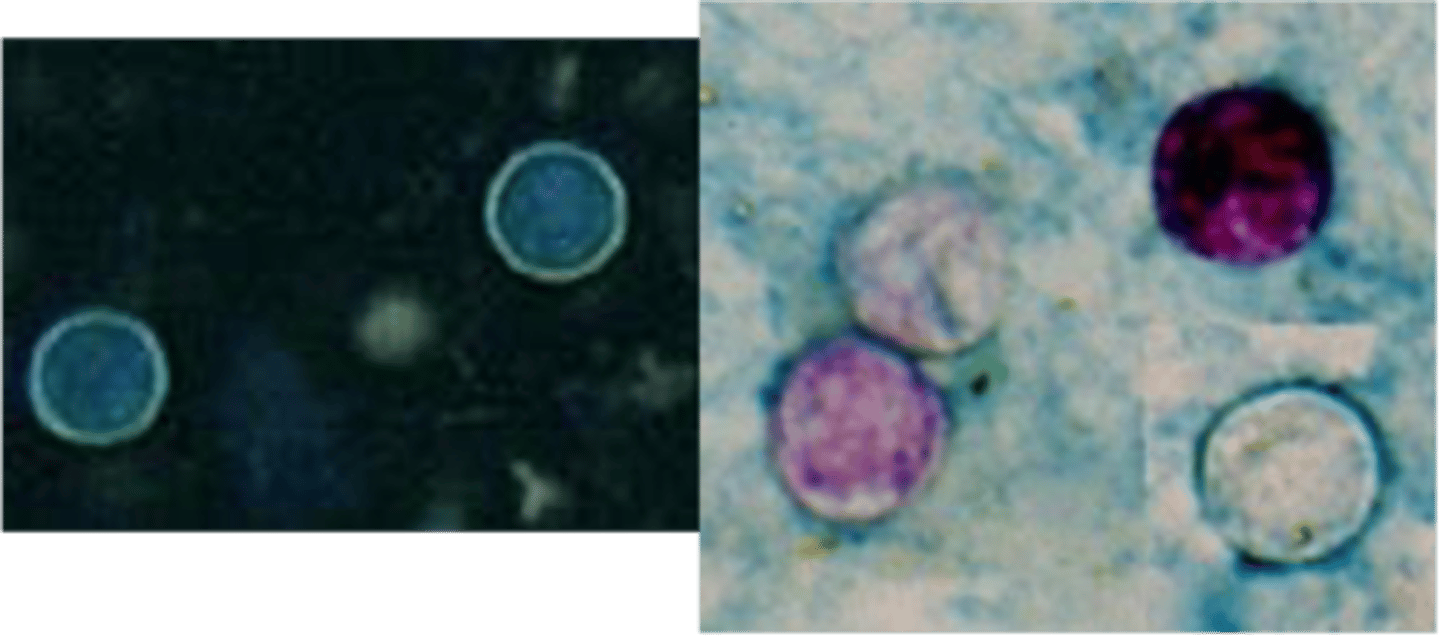
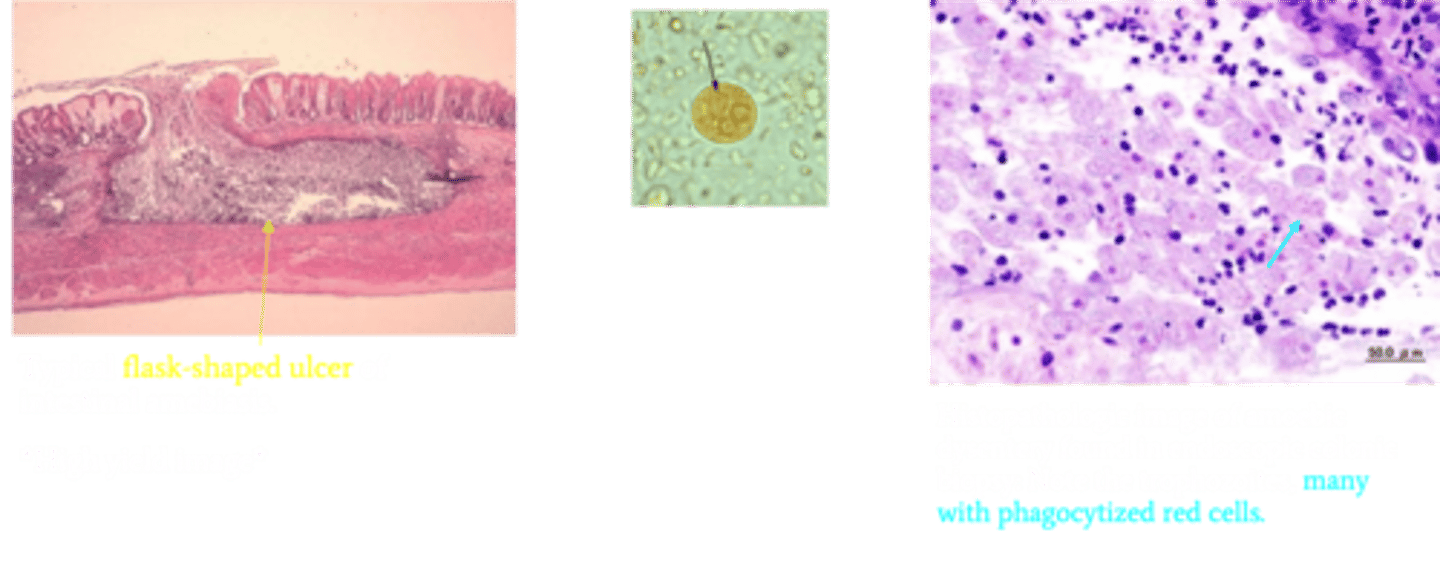
Entamoeba histolytica
Identify Pathogen causing Diarrhea:
Amebiasis/Amebic dysentery
-Hx:
> Mainly in developing countries
-Path: Cysts are ingested, resist acid in the stomach, excyst to the trophozoite form in the colon, and then invade the epithelium, leading to ulceration --> Form trophozoites in small intestine and invade tissue
-Sx/PE:
> BLOODY Diarrhea (dysentery)
> Ascends portal system ==> Liver Abscess
>> RUQ Pain
>> "Anchovy paste" exudate in abscess
-Dx:
> Smear = Trophozoites
> ELISA = Fecal Antigen
> Histology:
>> Typical flask-shaped ulcer of intestinal amebiasis
>> Many trophozoites w/ phagocytized red cells