AP Bio - Ch. 4-5 Test Study
1/82
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
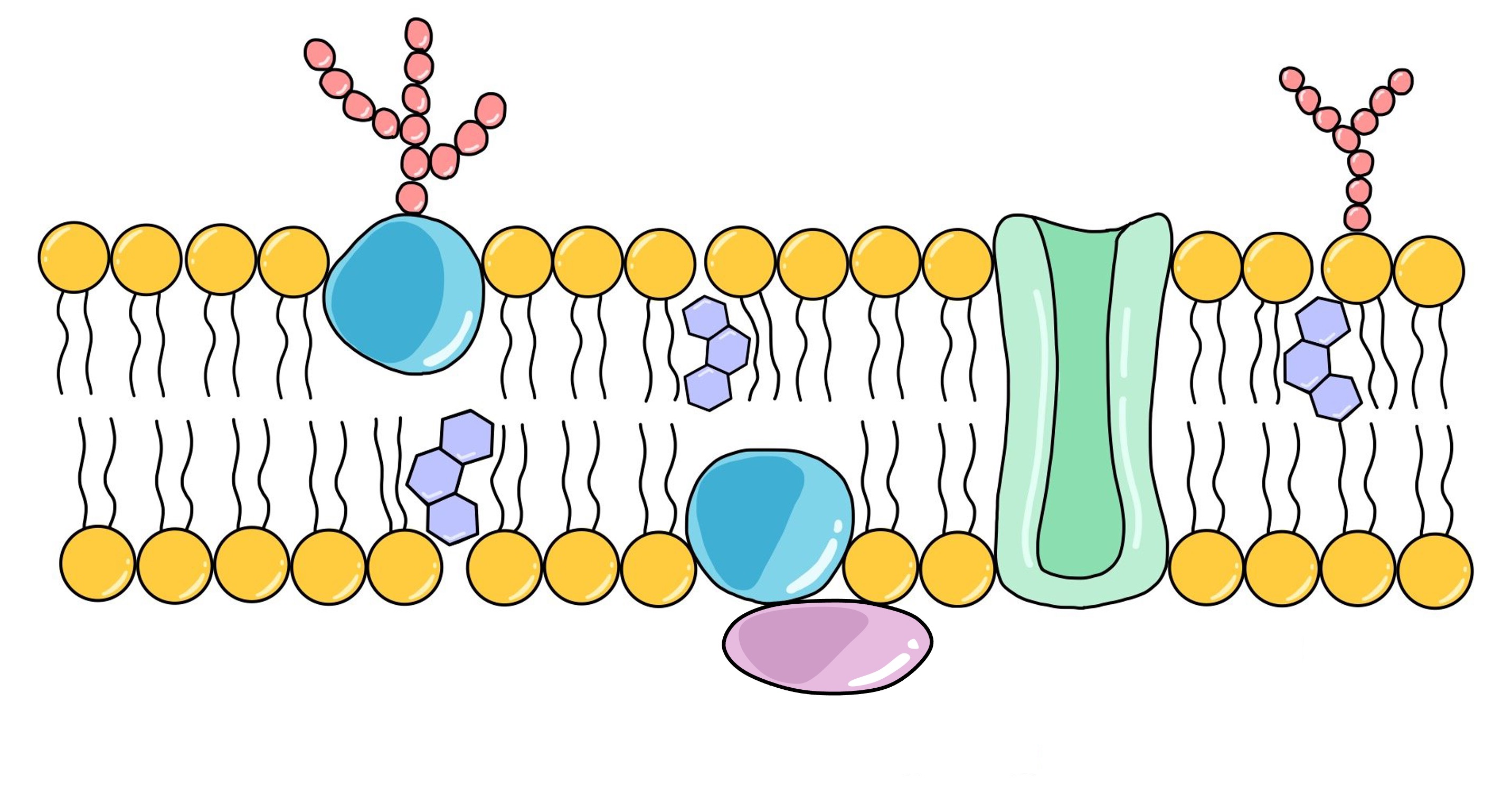
What is the pink blob on the diagram?
Peripheral Protein
What is the purple thing?
Cholesterol
What is the red thing?
Glycolipid
What component in the fluid membrane mosaic model helps membranes resist fluidity at high and low temperatures?
Cholesterol
Which component in the fluid mosaic model that plays an important role in cell-cell recognition?
Peripheral Protein
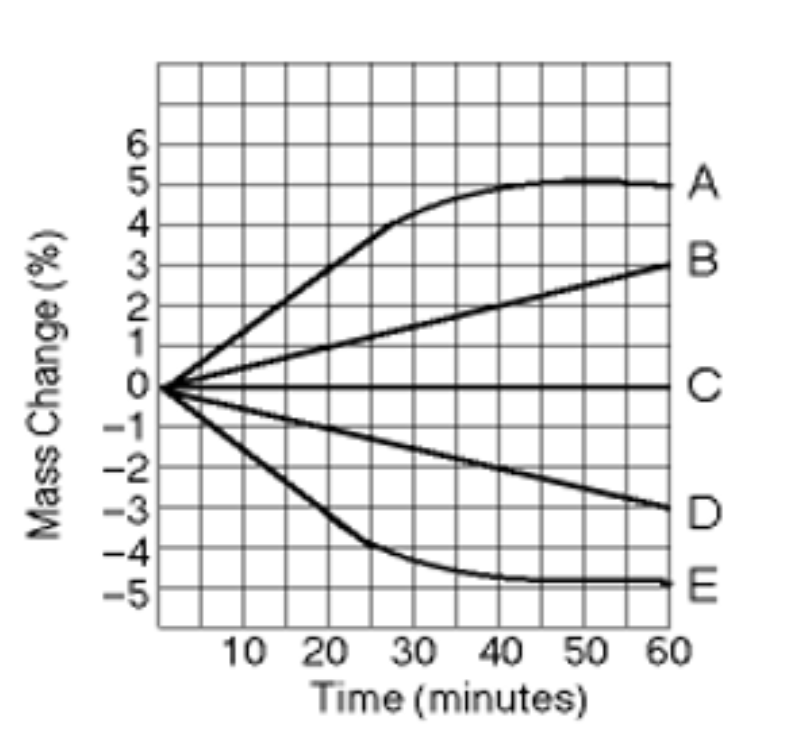
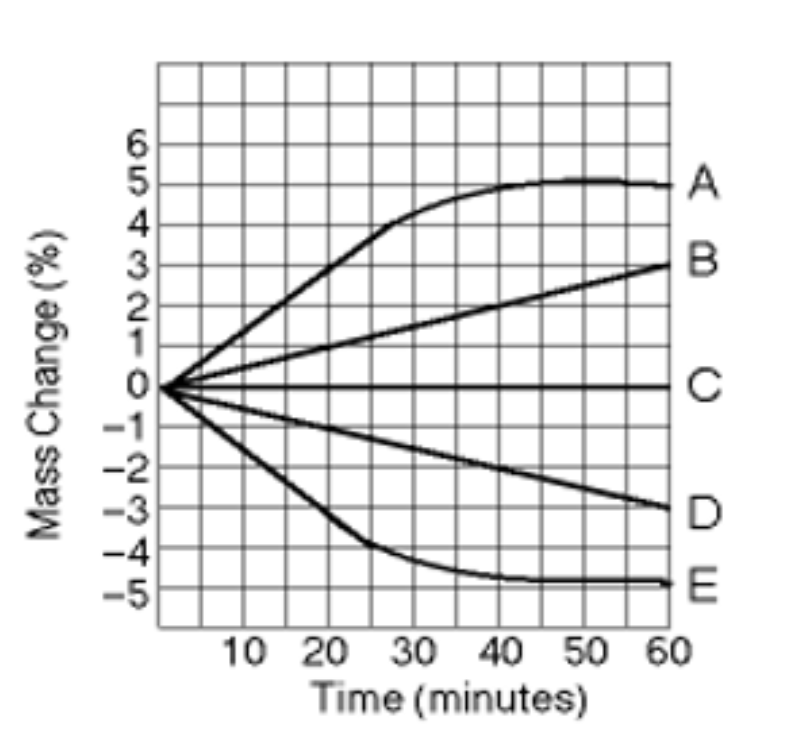
What tonicity is line A?
Isotonic
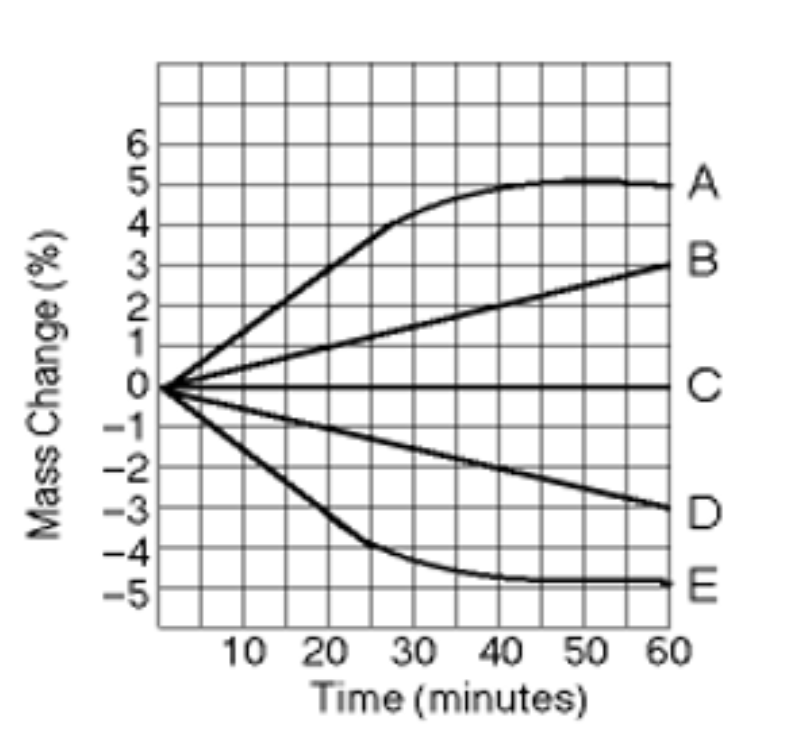
What tonicity is line C?
Isotonic
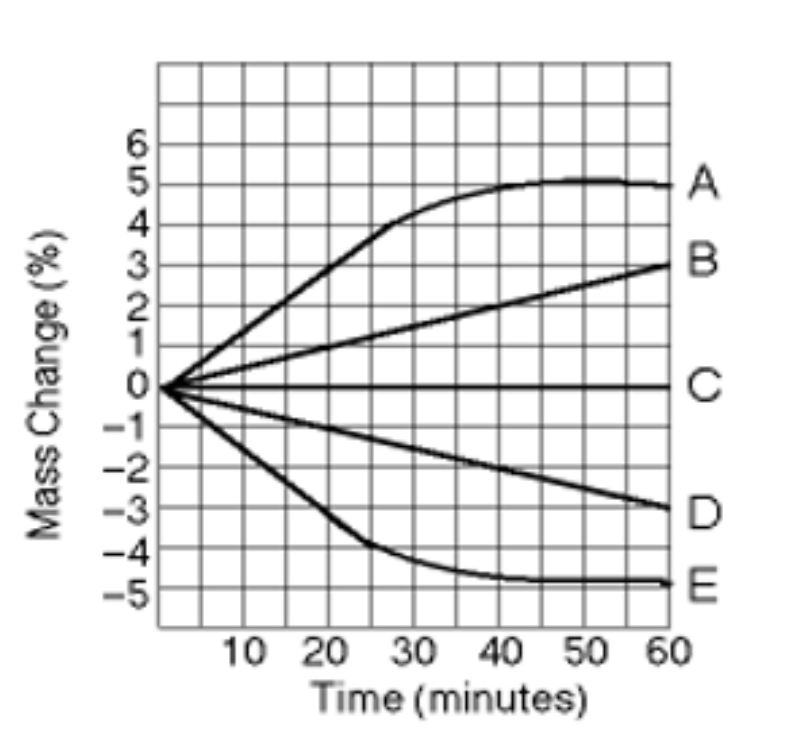
What tonicity is line E?
Isotonic
What tonicity is line B?
Hypertonic
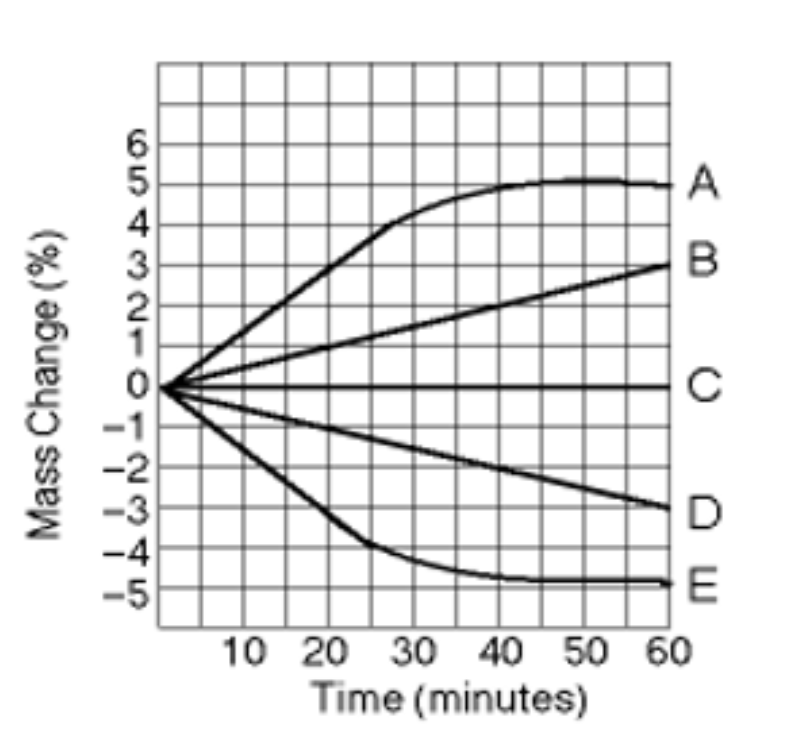
What tonicity is line D?
Hypotonic
Primary Structural Components of the cell membrane
Phospholipids and Proteins
At human body temperature (37C), cholesterol in membranes function to;
Make the membrane less fluid by restricting the movement of phospholipids
How do membrane phospholipids move?
Laterally along the plane of the membrane
Kind of molecule that can pass through a cell membrane most easily
Small Hydrophobic
Characteristic Feature of a Carrier Protein in a plasma membrane
Exhibits a specificity for a particular type of molecule
Molecule that diffuses through the lipid bilayer of a plasma membrane most rapidly
O2
Is this statement about diffusion correct?: It is a passive process in which molecules move from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration.
True
Is this statement about diffusion correct?: It is a passive process in which molecules move from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration.
False
Water can move quickly through the plasma membrane of some cells because
Aquaporin Channel Proteins
Mammalian blood contains the equivalent of 2% NaCl. Seawater contains an equivalent of 5% NaCl. What will happen if red blood cells are transferred to seawater?
Water will leave the cells, causing them to shrivel and collapse (Hypertonic)
Hypertonic Solution with Animal Cells
Water leaves, cell shrivels (crenation)
Hypotonic Solution with Animal Cells
Water enters, cell expands (lyse)
Isotonic Solution with Animal Cells
Equilibrium, Perfect for cell
Hypertonic Solution with Plant Cells
Water leaves, cell plasmolyzes
Hypotonic Solution with Plant Cells
Water enters, keeps cell shape, perfect for cell (turgid)
Isotonic Solution with Plant Cells
Equilibrium, Flaccid Cell
Submerging a plant cell in distilled water will result in;
The cell becoming turgid
Submerging a red blood cell in distilled water will result in;
Lysis of the cell
Does this membrane activity require energy from ATP hydrolysis? movement of sodium ions from a lower concentration in a mammalian cell to a higher concentration of extracellular fluid
Yes
What kind of transport is the phosphate transport system?
Cotransport
What is required for the sodium-potassium pump to transport potassium ions into an animal cell?
Energy from ATP
Proteins that allow the diffusion of ions across membranes in the direction of their concentration gradients are most likely;
channel proteins
The difference between pinocytosis and receptor-mediated endocytosis is;
Pinocytosis is nonselective in the molecules it brings into the cell, whereas receptor-mediated endocytosis does not.
When biologists wish to study the internal infrastructure of cells, they can achieve the finest resolution by using a;
TEM (transmission electron microscope)
What technique would be most appropriate to use to observe the movements of condensed chromosomes during cell division?
Standard Light Microscopy
Large numbers of ribosomes are present in cells that specialize in producing which molecule?
Protein
If a treatment were available that would disrupt the nuclear lamina in living cells, what would you expect to be the most likely immediate consequence for the cell?
A change in the shape of the nucleus
Which structure is the site of the synthesis of proteins destined for export from the cell?
rough ER
The liver is involved in detoxification of many poison and drugs which structure is primarily involved in this process and therefore abundant in liver cells?
smooth ER
What is the function of the golgi apparatus?
Protein modification and sorting
Hydrolytic Enzymes must be segregated and packaged to prevent general destruction of cellular components. In animal cells, which organelle contains these hydrolytic enzymes?
Peroxisomes
Which organelle occupies much of the volume of a plant cell?
Central Vacuole
Which of the following correctly describes the pathway taken by a protein destined for secretion?
Rough ER → Transport Vesicle → Golgi Apparatus → Transport Vesicle → Plasma Membrane
A cell has the following molecules and structures: Enzymes, DNA, ribosomes, Plasma Membrane, chloroplasts, and mitochondria.
An archaeal cell or a plant cell
Archaeal Cell
unicellular prokaryotic microorganisms
Which animal cell organelle contains enzymes that transfer hydrogen from various substrates to oxygen?
Peroxisomes
Thylakoids, DNA, and ribosomes are all found in:
Chloroplasts
The evolution of eukaryotic cells most likely involved:
Endosymbiosis of an oxygen using photosynthetic bacterium in a larger host cell--the endosymbiont evolved into mitochondria
Movement of vesicles in the cell depends on what cellular structures?
Microtubules and Motor Proteins
The extracellular matrix may influence animal cell behavior by communicating information from the outside to the cytoskeleton of the cell via which molecule or structure?
Integrin
Plasmodesmata in plant cells are most similar in function to which structures in animal cells?
Gap Junctions
Which structure plays a key role in maintaining the structural integrity of animal tissues?
Desmosomes and intermediate filaments
Which structure plays a major role in making skin water tight?
tight junctions
Which structure is not a part of the endomembrane system?
Chloroplast
Which structure is common to animal and plant cells?
Mitochondrion
Is this structure;function pair matched correctly?: microtubule;muscle contraction
Mismatched
Cyanide binds to at least one molecule involved in producing ATP. If a cell is exposed to cyanide, most of the cyanide will be found within the;
Mitochondria