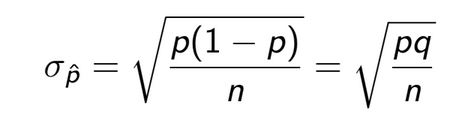4. Binomial distribution
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
binomial distribution
a statistical probability distribution that states the likelihood that a value will take one of two independent values under a given set of parameters or assumptions
difference btwn normal and binomial distribution
binomial distribution deals with discrete events (like "heads or tails" in a coin toss) while normal distribution deals with continuous data (like height or weight) where any value within a range is possible
the 4 criteria of a binomial experiment
there are a fixed number of trials/observations (n)
the trials are independent (one outcome does not effect another outcome
each outcome is either a success or a failure
the probability of success is fixed for each trial
Can be remembered as BINS
binary outcome
independent trials
N # of trials
same p per trial
two things probabilities rely on
number of trials (n)
probability of success
stat crunch for binomial
stat
calc
binomial
type in number of trials and chance of it being less than or equal to two numbers
variance of a binomial
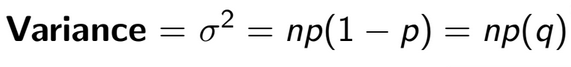
using normal distribution to help solve binomial distr.
two requirments must be met:
np≥10
n(1−p)=nq≥1
If these are met then this equation may be used (σ) = np(1−p)np(1−p)
standard deviation for a sample proportion is