Anterior and medial thigh
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Fascia
is a strong connective tissue that
strengthens and divides the muscles into functional groups
The functional groups of the thigh
Anterior compartment: flex the thigh at the knee, extend the leg at the knee and has femoral nerve innervation
Medial compartment: adductors of the thigh at the hip joint, obturator nerve innervation
Posterior compartment: extend the thigh at the hip joint, flex the leg at the knee and sciatic nerve innervation
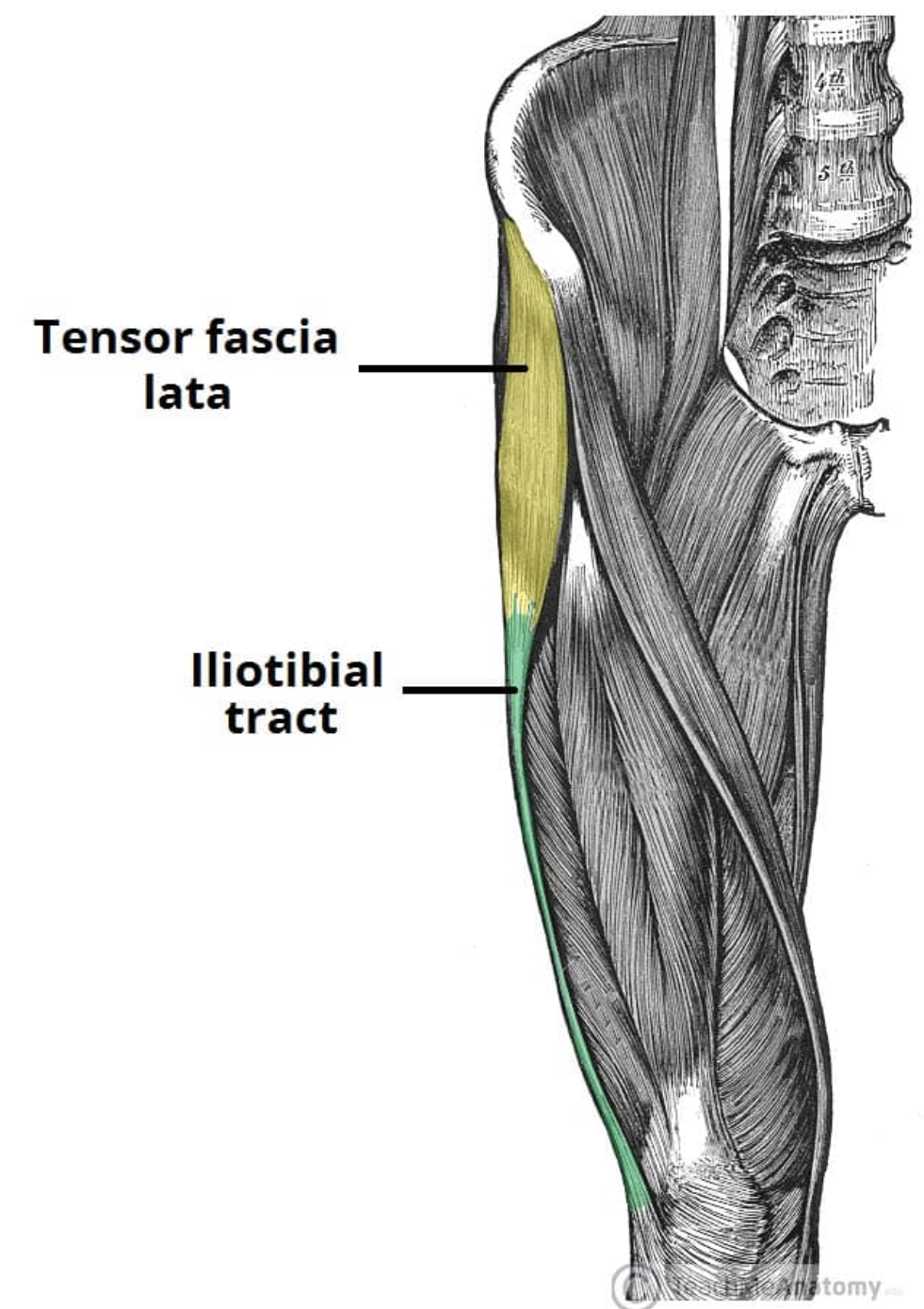
Iliotibial band
Band of Maissiat - fibrous structure connecting ilium and tibia
Unique to man
Origin - iliac crest / iliac tubercle
Vertical component of the fascia lata of the thigh
Femur
largest and strongest bone of the body
makes a quarter of one’s height
articulates proximally with the acetabulum and distally with the tibia and fibula
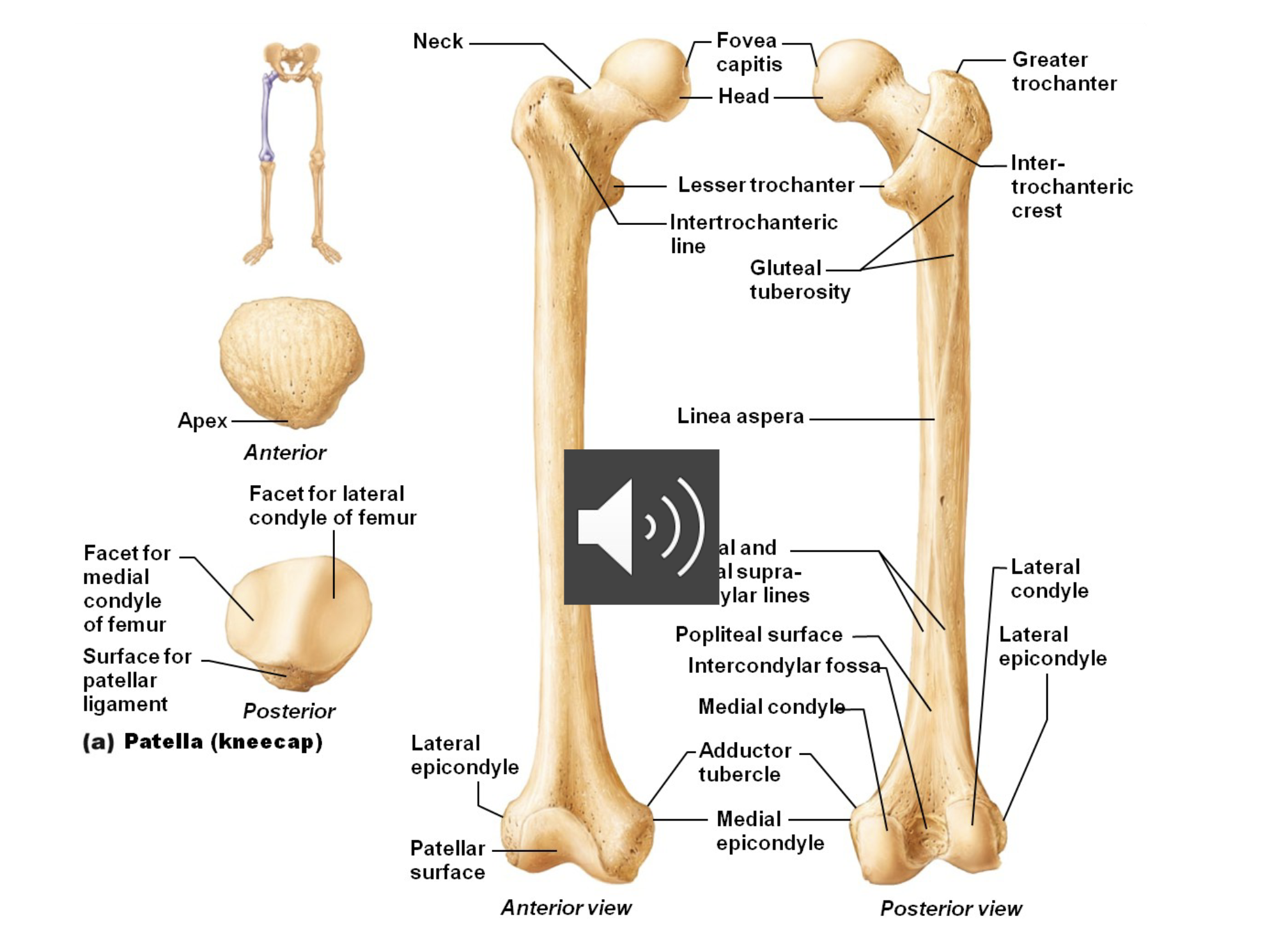
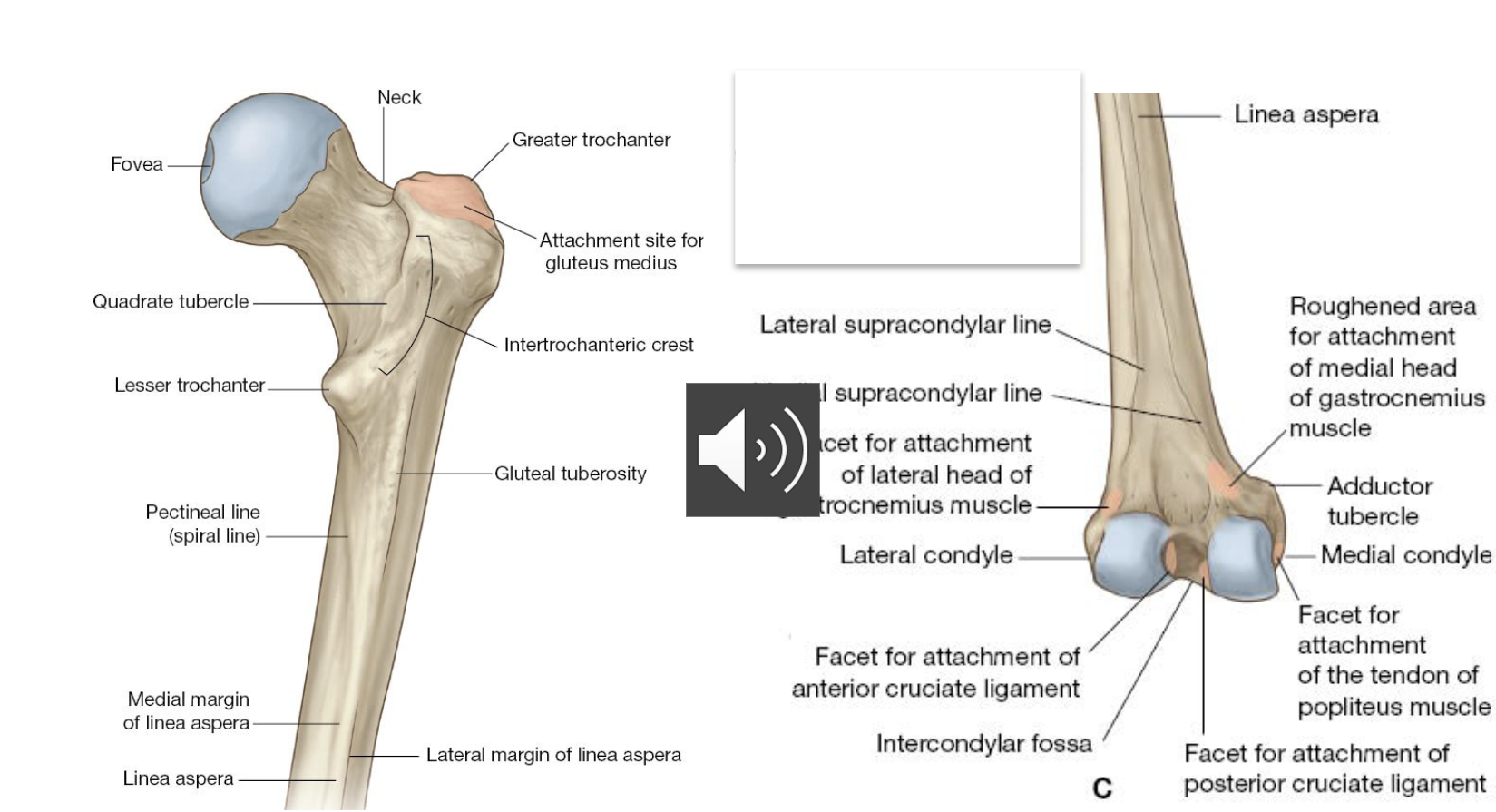
Labels of the femur
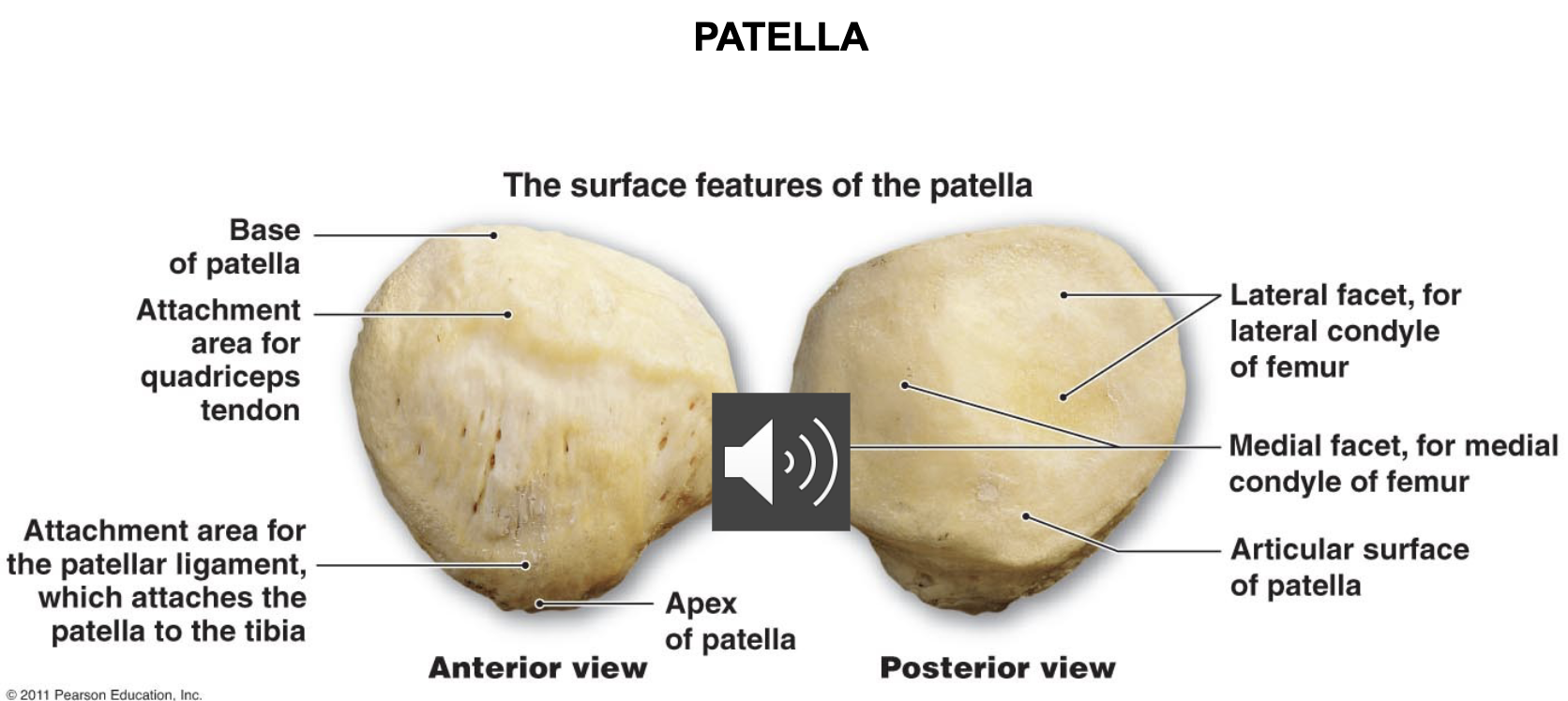
Patella
Sesamoid bone in quadriceps tendon
Acts as pulley for the forces of anterior thigh muscles acting on the tibia
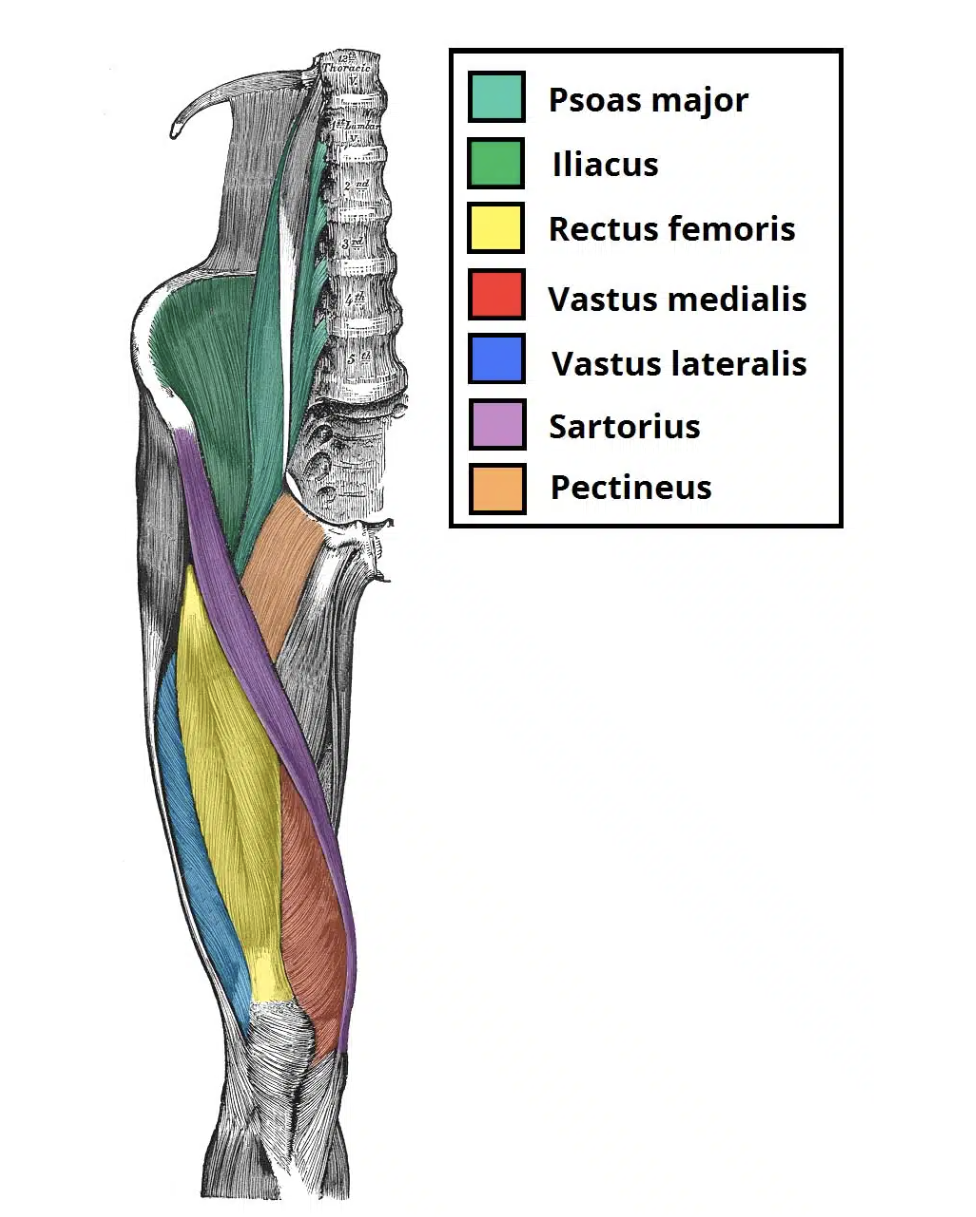
Uniarthrodial and Biarthrodial muscles
are one joint and two joint muscles
Muscles in anterior compartment of thigh
Uniarthrodial: Iliacus and psoas (iliopsoas), quadriceps femoris (vastus lateralis, vastus medialis oblique, vastus intermedius)
Biarthrodial: sartorius, quadriceps femoris (rectus femoris), tensor
fascia lata
Muscles in medial compartment of thigh
Uniarthrodial: adductor magnus, adductor longus, adductor brevis,
pectineus
Biarthrodial: gracilis
Muscles in the posterior compartment of thigh
Uniarthrodial: biceps femoris (short head
Biarthrodial: biceps femoris (long head), semitendinosus
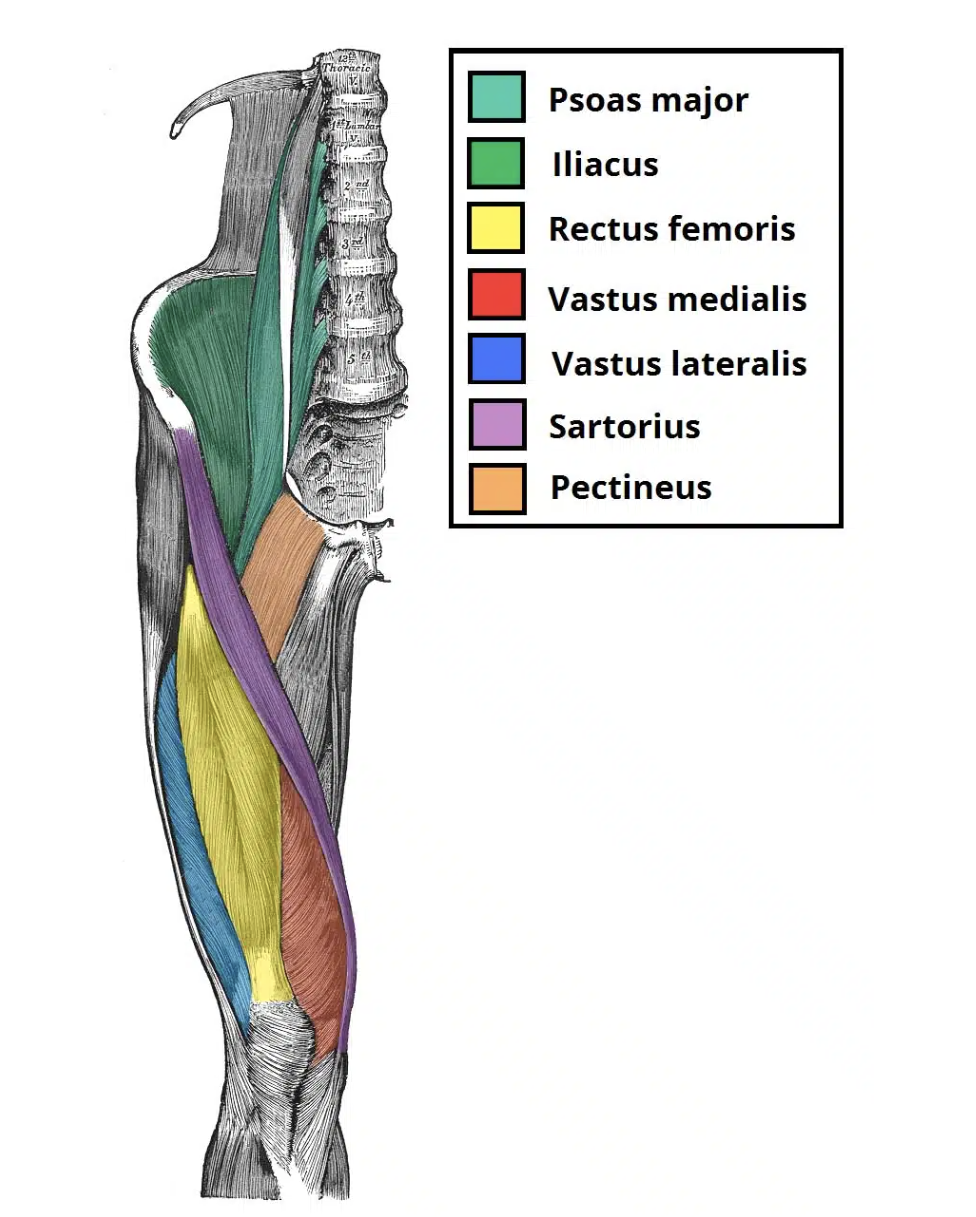
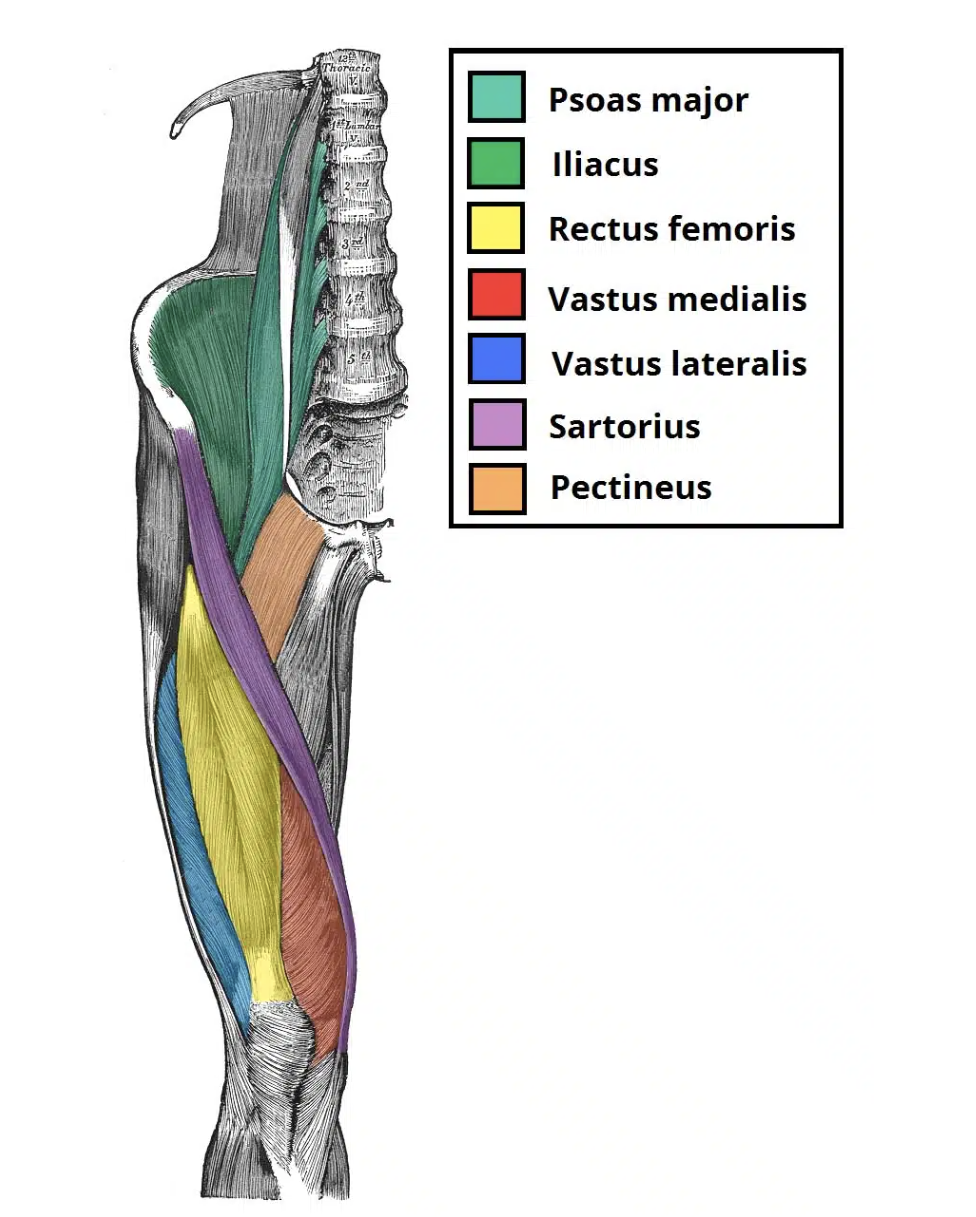
Anterior muscles of the thigh
Iliopsoas
Sartorius
Quadriceps Femoris
Muscles that move the thigh
Iliopsoas (iliacus and psoas major):
Flexes thigh at hip
Arises lumbar vertebrae & ilium
Inserts on femur
Iliopsoas
Action: Flexion of the hip, anterior hip tilt
Origin: Psoas: Bodies and transverse processes T12 – L5 and intervertebral discs.
Iliacus: Iliac fossa
Insertion: Lesser trochanter
Innervation:
Psoas: L1,L2,L3
Iliacus: Femoral nerve (L2,3,4)
Sartorius
Action: Flexion. Adduction &
external rotation of thigh.
Knee flexion
Origin: Anterior superior iliac spine
(ASIS)
Insertion: Medial tibia inferior and
medial to tibial tuberosity
Innervation: Femoral nerve
(Longest muscle in the body)
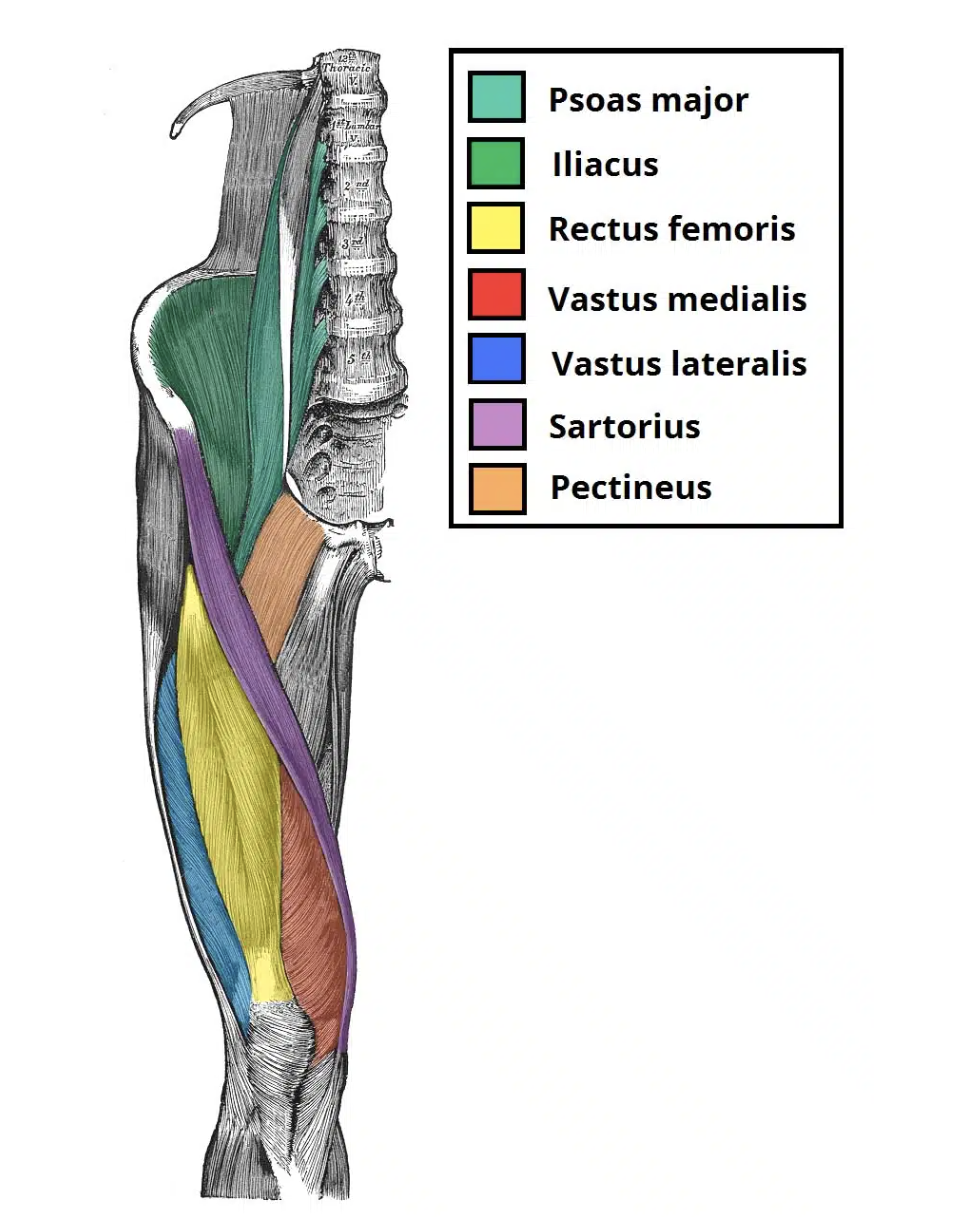
Quadriceps Femoris
Consists of four heads that form the flesh of the front and sides of the thigh:
Rectus femoris
Vastus lateralis
Vastus medialis
Vastus intermedius
all three vastus heads originate from the femur and the rectus head from the iliac spine
all four heads have a common insertion tendon which inserts into the patella then to the tibia via the patellar tendon
Rectus Femoris
Action: Flexion of hip, extension of knee(kicking)
Origin: Straight head: Inferior iliac spine
Reflected head: superior to acetabulum
Insertion: patella
Innervation: Femoral nerve
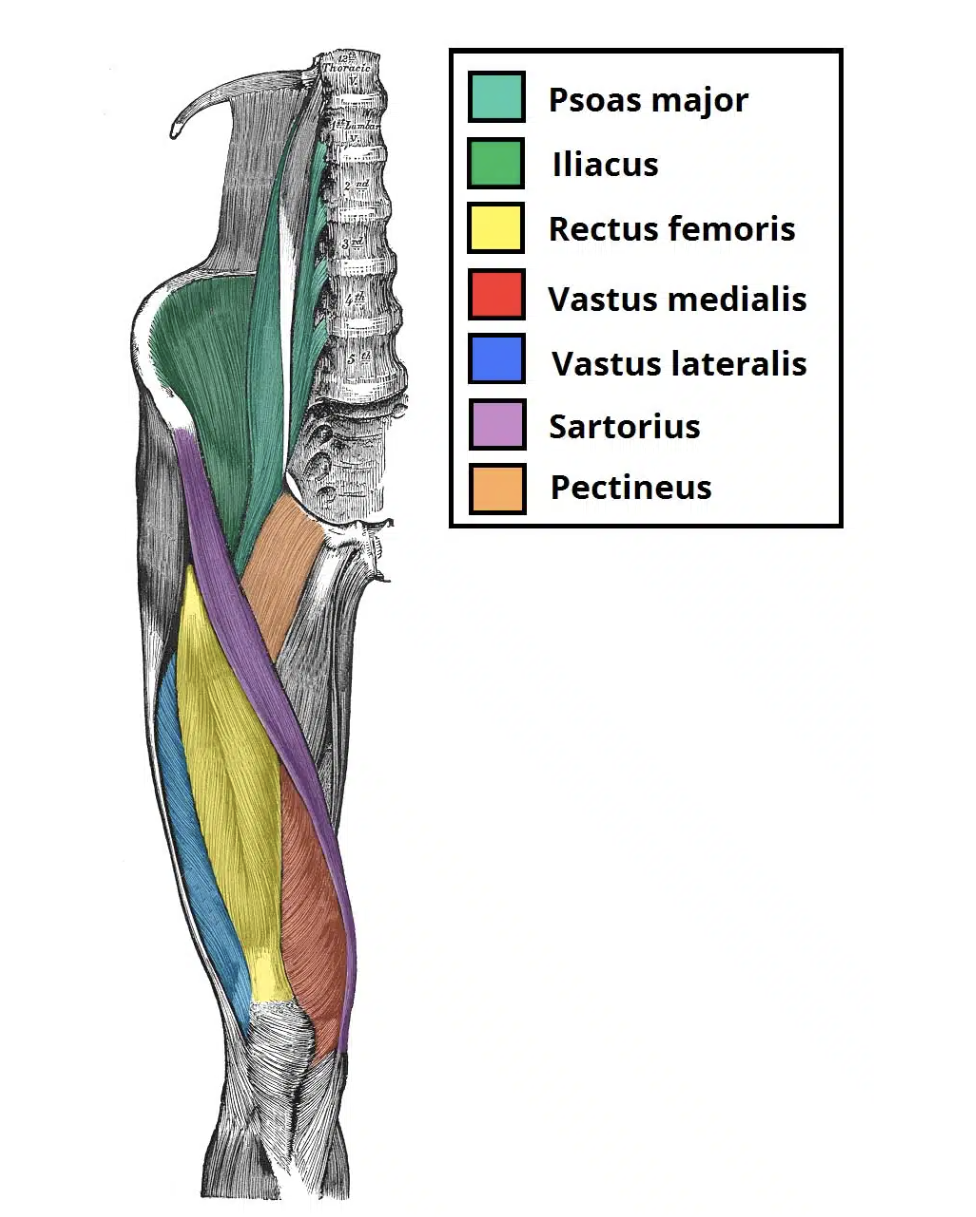
Vastus lateralis (VL)
Action: Knee extension
Origin: Lateral intertrochanteric
line, greater trochanter, gluteal
tuberosity, linea aspera
Insertion: patella
Innervation: Femoral nerve
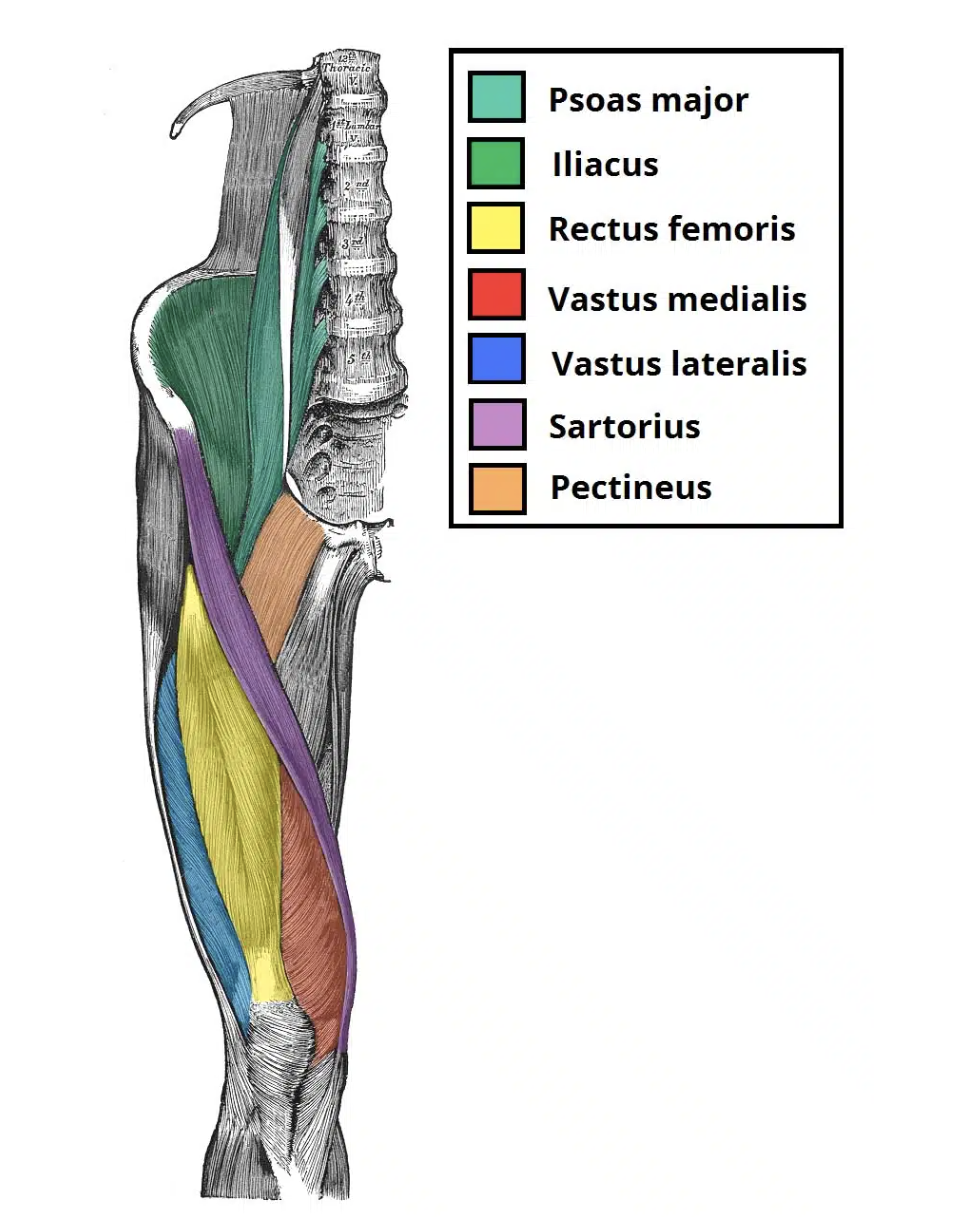
Vastus lateralis (VL)
Origin: Intertrochanteric line, greater
trochanter, gluteal tuberosity, linea aspera
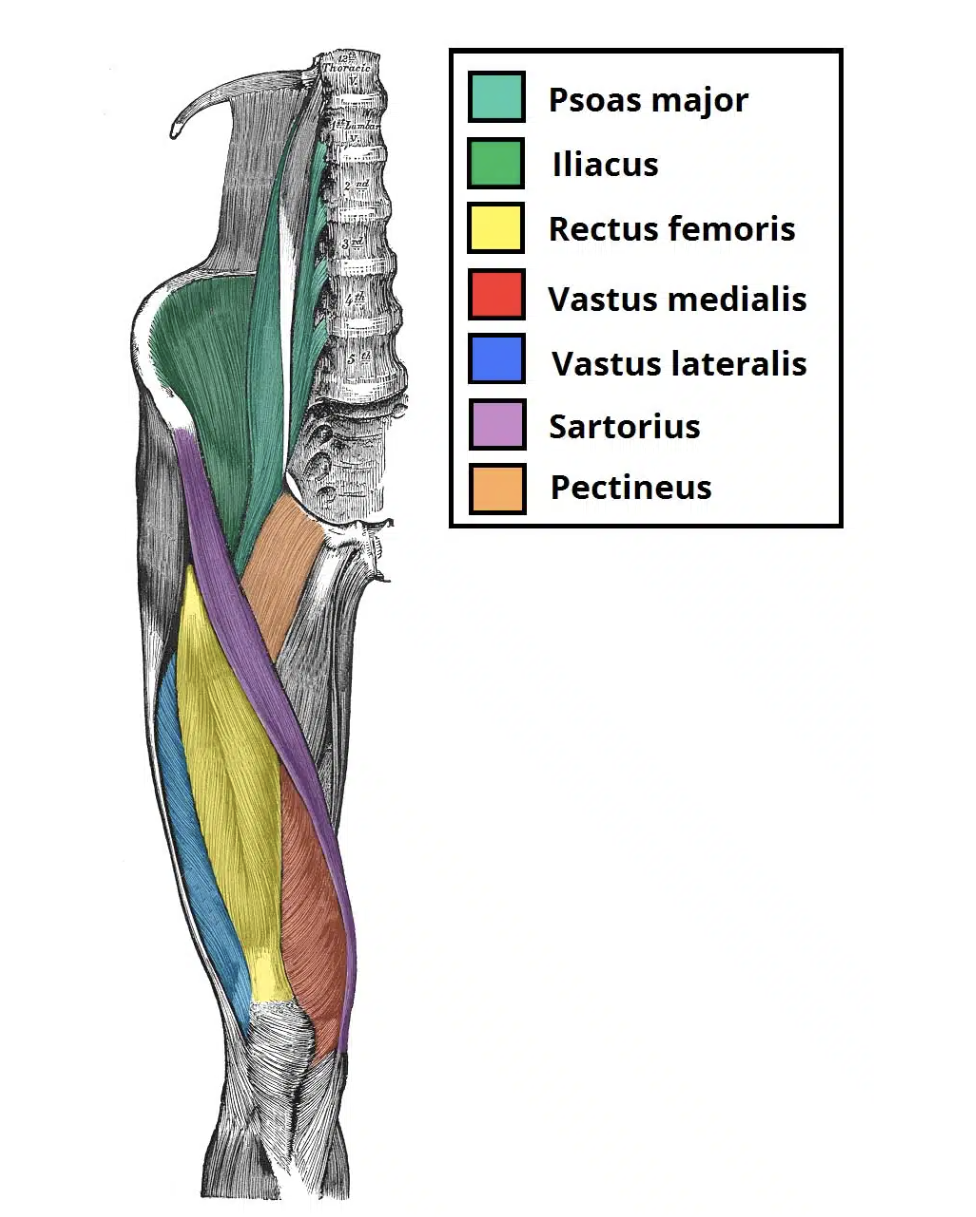
Vastus medialis obliqe (VMO)
Action: Knee extension
Origin: Medial intertrochanteric
line, linea aspera, medial
supracondylar line
Insertion: patella
Innervation: Femoral nerve
Vastus intermedius
Action: Knee extension
Origin: Upper anterior and lateral femur
Insertion: patella
Innervation: Femoral nerve
Tensor Fascia Lata
Action: Hip abduction
Origin: Anterior iliac crest, ASIS, deep surface of fascia lata
Insertion: ITB junction of upper and middle thirds
Innervation: Gluteal nerve (L5/S1)
Medial muscles of the thigh
Gracilis
Pectineus
Adductor longus
Adductor brevis
Adductor magnus
Gracilis
Action: Adducts, medially (internally) rotates thigh, and flexes the knee
Origin: Body of pubis, ischiopubic (inferior) ramus
Insertion: Medial proximal shaft of tibia
Innervation: Obturator nerve (L2,3,4
Pectineus (is proximal to the surface)
Action: Adducts, medially rotates, and flexes the thigh.
Origin: Superior ramus of pubis
Insertion: Femur (pectineal line).
Innervation: Obturator / Femoral nerve
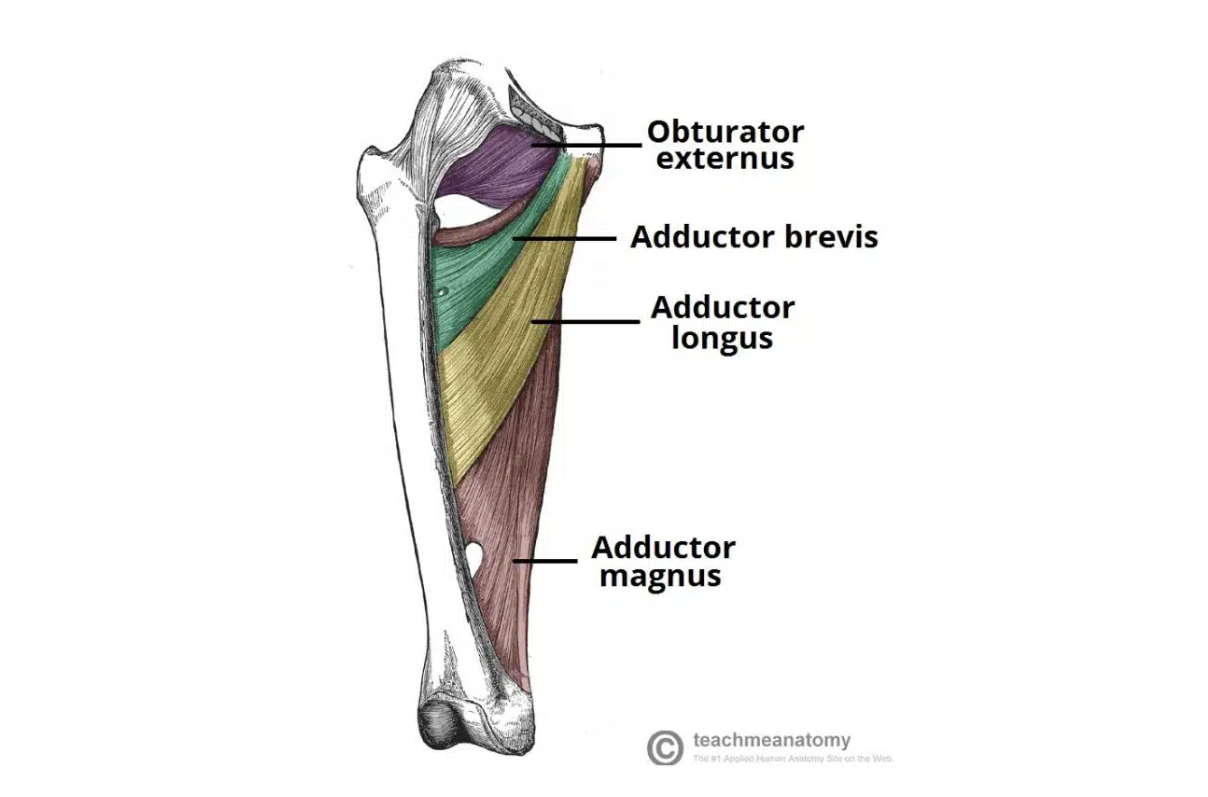
Adductor longus
Action: Adducts the thigh.
Origin: Body of pubis
Insertion: Linea aspera (middle third)
Innervation: Obturator nerve
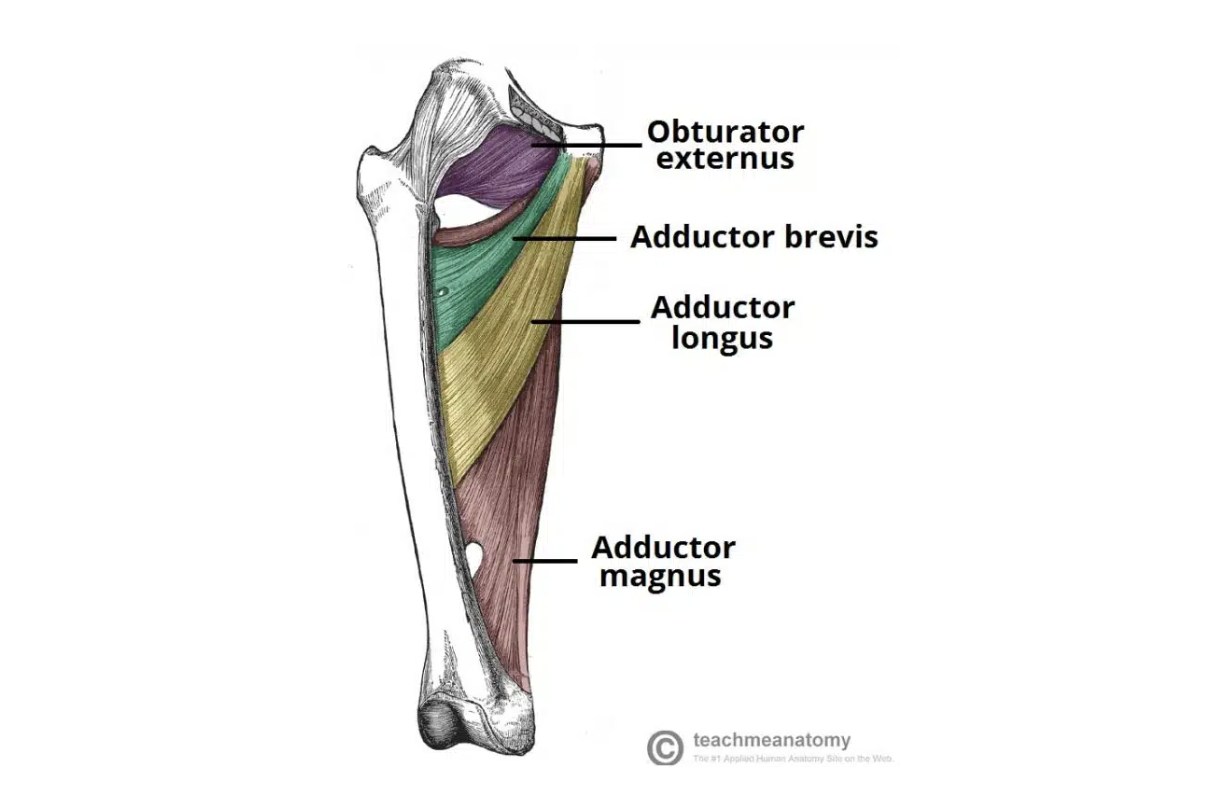
Adductor brevis
Action: Adducts the thigh and weak hip flexor
Origin: Body of pubis , inferior pubic ramus
Insertion: Posterior surface of proximal femur and linea aspera (upper third)
Innervation: Obturator nerve
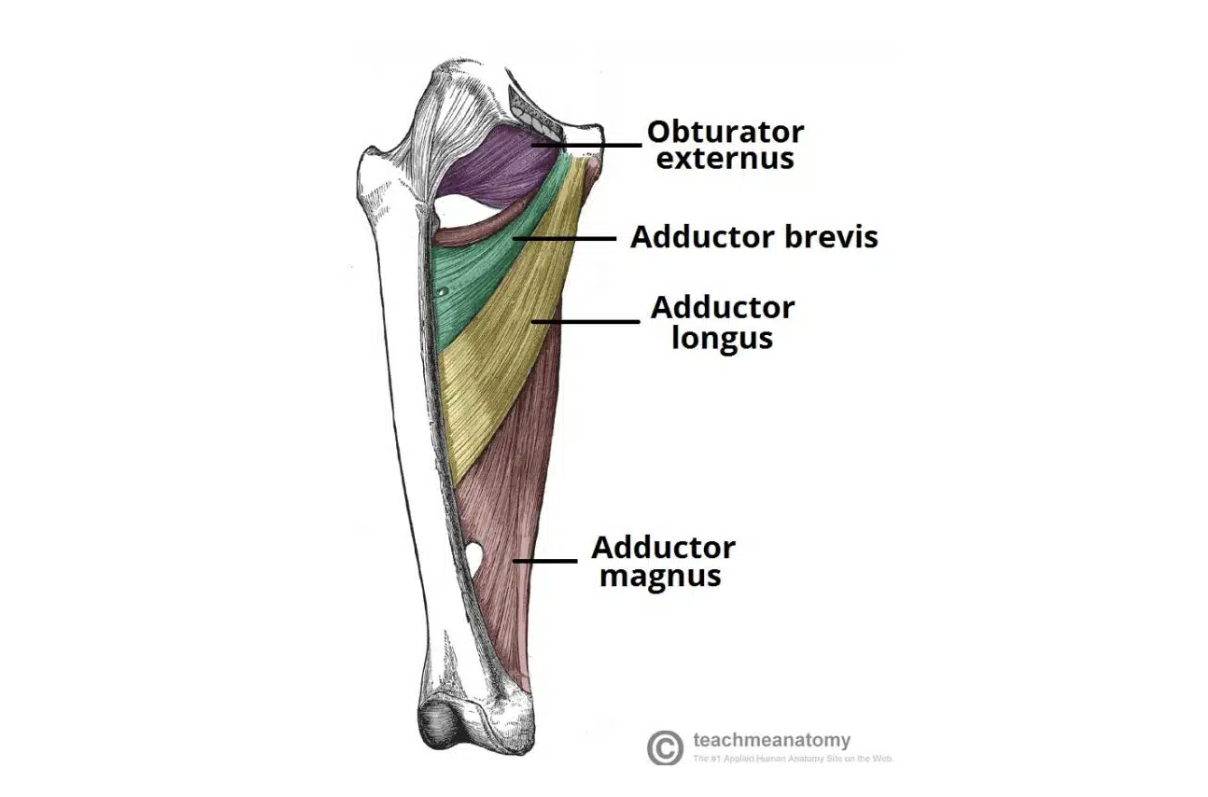
Adductor magnus
Action: Adducts thigh (adductor part)
Extends thigh (hamstring part)
Origin: Adductor part: ischial ramus (inferior ramus)
Hamstring part: ischial tuberosity
Insertion: Adductor part: post. surface of proximal femur and linea aspera, medial supracondylar line
Hamstring part: adductor tubercle
Innervation: Adductor part: obturator nerve
Hamstring part: sciatic (tibial division)
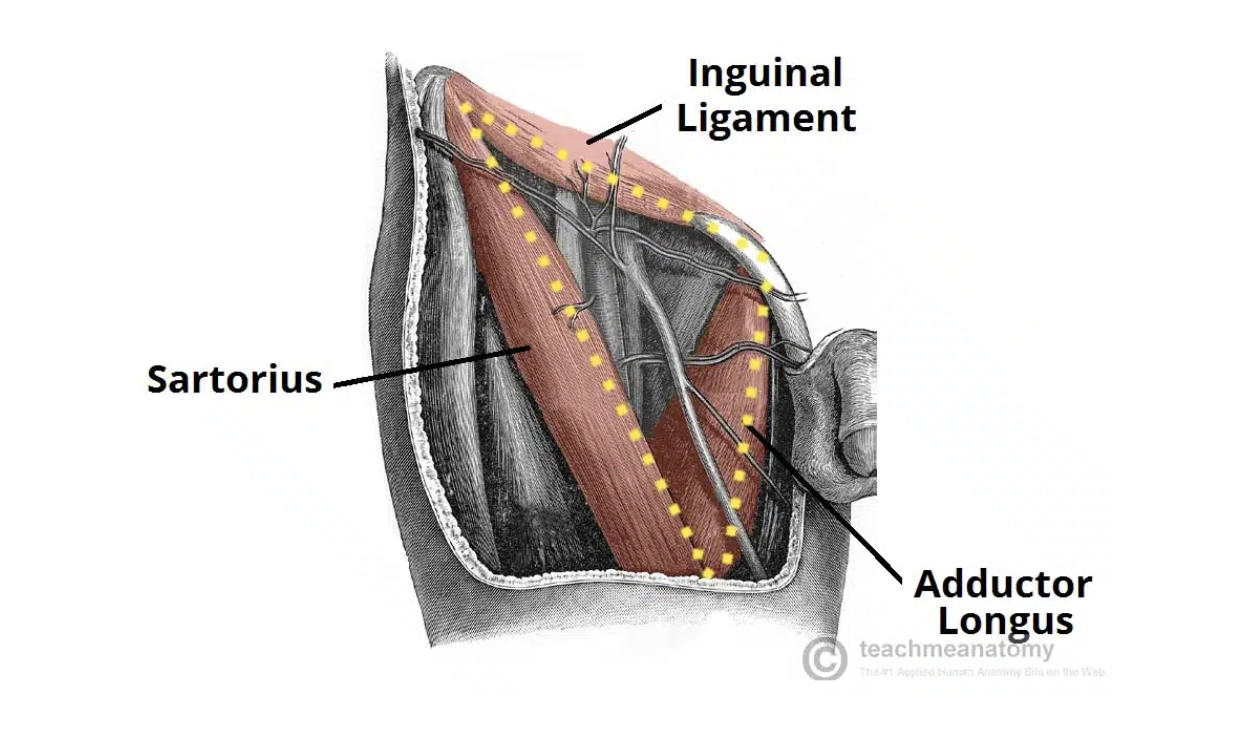
Femoral triangle
Base: inguinal ligament
Medial border: adductor longus
Lateral border: sartorius
Floor: iliopsoas, pectineus, adductor longus
Apex: continual with adductor canal that descends medially and through the adductor hiatus
Major structures of femoral triangle
From lateral to medial:
Femoral nerve, femoral artery, Femoral vein, lymphatic vessels
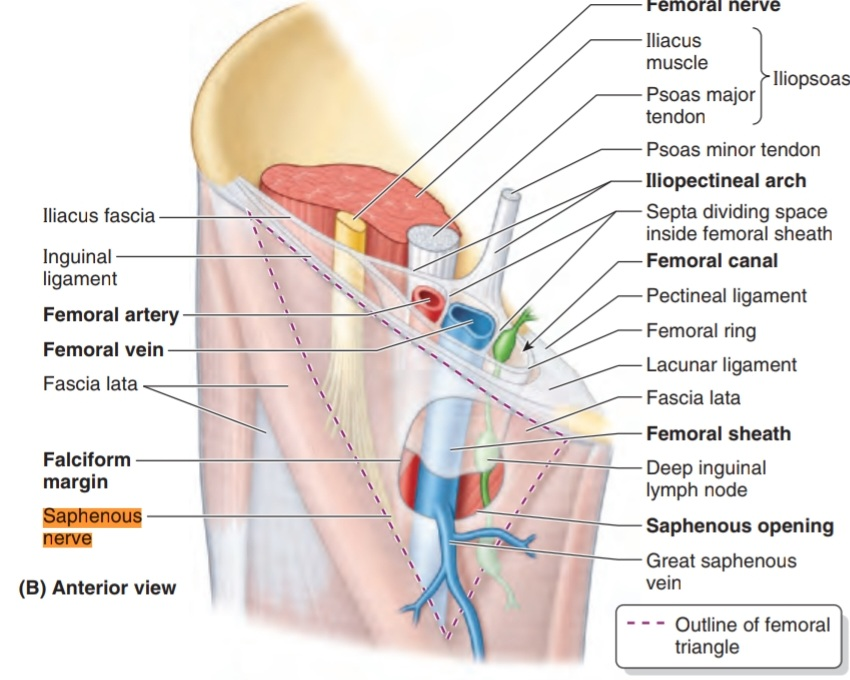
Femoral sheath
subdivided in three
compartments containing (from
lateral to medial): femoral artery,
femoral vein and lymphatics (femoral
canal)
Femoral sheath
contains fat, lymph vessels and a deep inguinal lymph
node
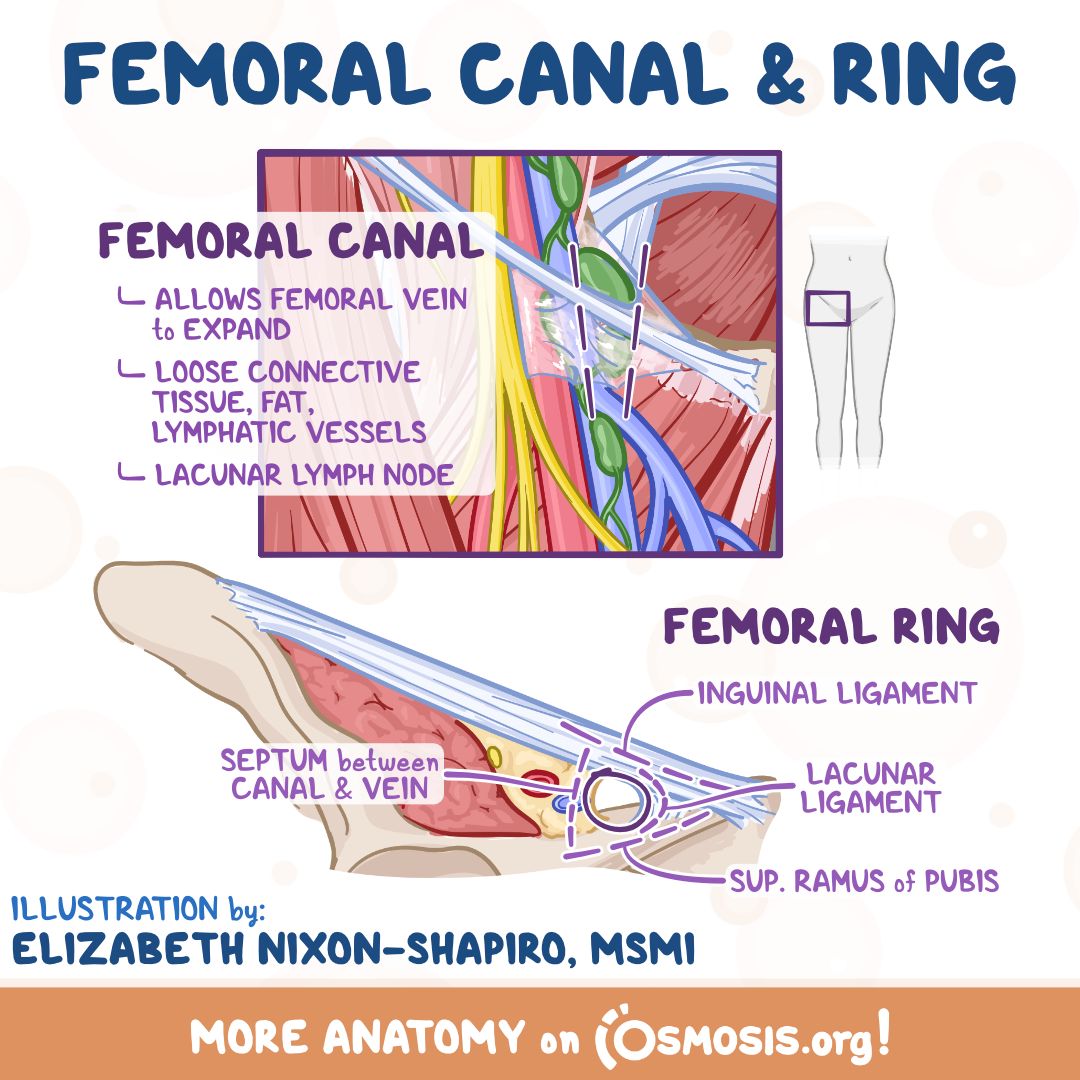
Femoral ring
upper end of femoral canal. It is potentially a weak point in the lower abdomen and is the site of
femoral hernias
Saphenous opening/ring
An opening in the fascia lata, in upper medial thigh, for passage of the great saphenous vein, lymph vessels and small arteries
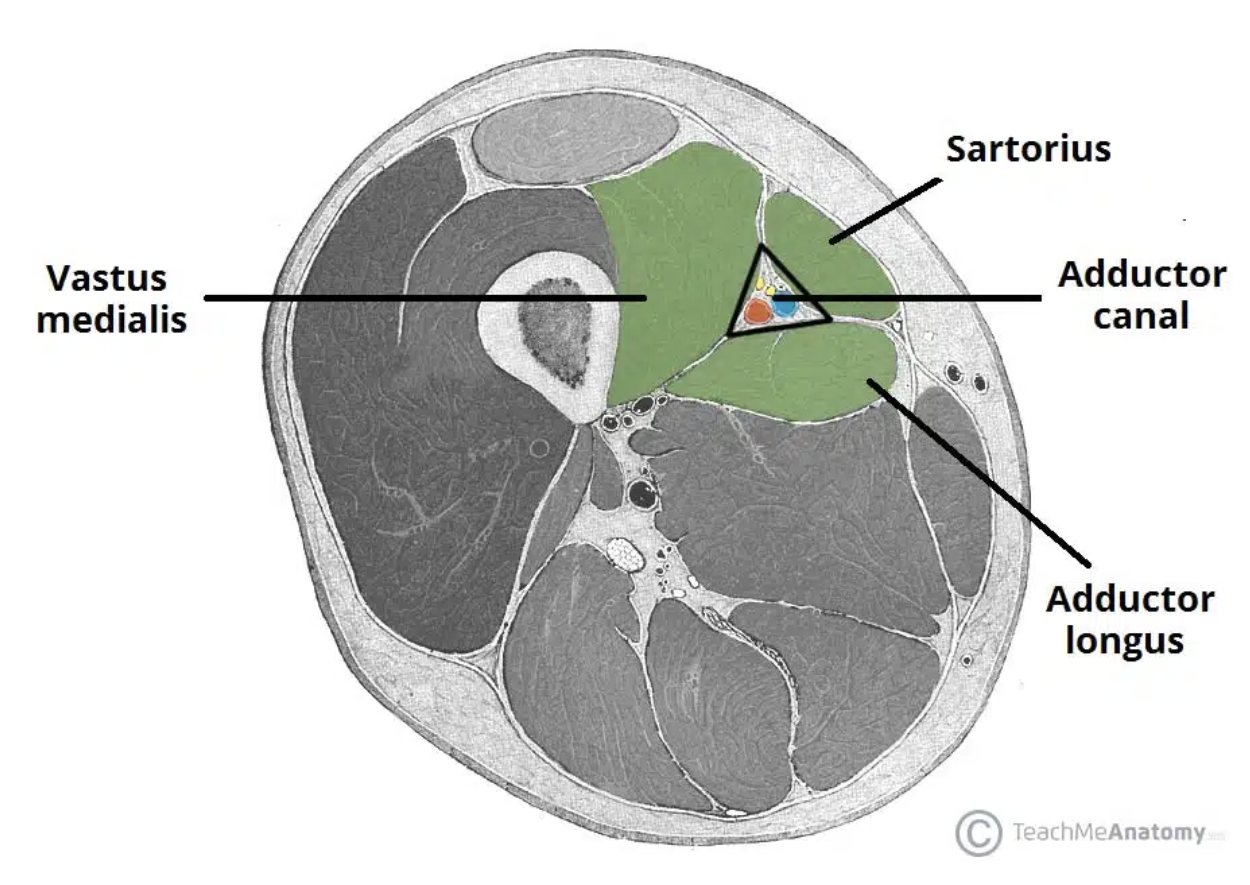
Adductor canal (subsartorial canal)
Canal between the muscles of lower medial thigh
Boundaries: Anteriorly - vastus medialis posteriorly - adductor longus and magnus,
medially (and the roof) - sartorius
Contents: femoral vessels, saphenous n. and n. to vastus medialis
Innervation of the lower limb
The lower limb’s nervous
control is through both the
lumbar and sacral plex
Femoral Nerve
The femoral nerve supplies motor innervation to the anterior thigh muscles:
• Quadriceps femoris (knee extensor)
• Sartorius (hip flexor)
• Iliacus (hip flexor)
Sensory information is perceived from :
Anterior and medial thigh
Medial leg (continuation as saphenous nerve – pierces fascia 10cm above the knee
Obturator Nerve
The obturator nerve supplies motor innervation to the medial thigh muscles:
• Adductors
• Gracilis
• Pectineus
• Obturator externus
Sensory information is perceived from :
• Superiomedial thigh
External iliac artery
The external iliac artery is renamed the femoral artery when it passes through the inguinal ligament
This area can be landmarked by creating a line from the iliac crest to the pubic symphysis
Femoral artery
The deep femoral artery (profunda
femoris) supplies blood to the hip
joint and many thigh muscles.
The femoral artery itself passes
through the adductor magnus muscle
(adductor hiatus) and travels down
the back of the leg to become the
popliteal artery
Veins
The popliteal vein curves around
the front of the top of the knee on
the anterior side of the thigh,
becoming the femoral vein.
The femoral vein meets up with the
great saphenous vein (superficial &
medial), forming the external iliac
vein.