MCAT Chemistry
1/149
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
150 Terms
Mass Unit:
Kilogram (kg)
Distance Unit:
Meter (m)
Temperature Unit:
Kelvin (K)
Amount of a Substance Unit:
Mole (mol)
Electric Current Unit:
Ampere (A)
Time Unit:
Second (s)
Luminous Intensity Unit:
Candela (cd)
Conversion Units:

Speed of Light (c):
3.000 × 108 m/s
Gas Constant (R):
8.314 J/K·mol
Avogadro’s # (NA or L):
6.022 × 1023/mol
Planck’s Constant (h):
6.626 x10-34 J·s
Gravitational (G):
6.673 x10-11 N·m2/kg2
Mass and Charge of a Neutron
Mass: ~1 amu
Charge: 0
Mass and Charge of a Proton
Mass: ~1 amu
Charge: +1
Mass and Charge of an Electron
Mass: ~0 amu
Charge: -1
Changing the subatomic particles causes:
Neutrons… Protons… Electrons…
Neutrons: New mass → isotope
Protons: New element → protons define element
Electrons: New charge → ions: anions (gain electrons (-)) and cations (lose electrons (+))
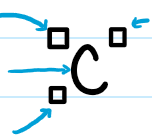
Elements of a Nuclide Symbol
Left Top: mass # (neutrons + protons)
Letter(s): element symbol
Left Bottom: atomic number
Right Top: charge

A. Cobalt-60 has more neutrons than Nickel-60
Atomic Models:
Bohr Model: n + p in nuclei & e orbit around
Quantum Mechanical Model: e are in orbitals
Quantum Mechanical Orbitals (shape, # of orbitals, # of electrons total)
s: sphere ; 1 ; 2e
p: dumbbell ; 3 ; 6e
d: no shape ; 5 ; 10e
f: no shape ; 7 ; 14e
Each orbital holds 2e and there are different levels of each
Photons Equation:
E = hf
Distance between shells
The larger the distance the more energy the higher the frequency
Ground state = lowest energy
Electron movement between shells
1st → 2nd…
5th → 4th…
1st → 2nd → 3rd… = absorb / excite a photon
5th → 4th → 3rd… = release a photon (returning to ground state)

D. Electrons transitioning from the 4th to the 1st shell
Offset of Electron Configuration Sublevels
d sublevel is offset by 1: when s and p are 4, d is 3
f sublevel is offset by 2: when s and p, f is 4
Sublevels on the Period Table
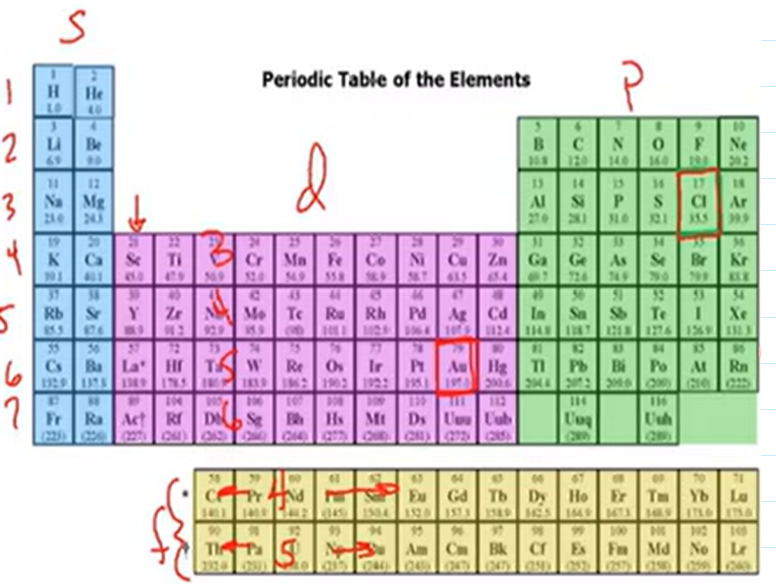
Noble Gas Shortcut
Take the noble gas BEFORE and only write the electrons that come AFTER
Ex. N: 1s22s22p2 = [He]2p2

C. 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104p65s2
Alkaline Earth Metal will end in #s2 due to location on periodic table
Electron Configuration of Ions
Add or subtract electrons
Ex. N3- = add 3e ; Mg2+ = subtract 2e
Orbital Notation Rules:
Pauli Exclusion Principle
Aufbau Rule
Hund’s Rule
Pauli Exclusion Principle: one arrow up and the other down, no 2e- w/ same exact configuration
Aufbau Rule: start at the lowest energy level
Hund’s Rule: awkward bus rule, put one up arrow in every line (within the same shell) before putting a down arrow next to an up arrow

Electron Configuration Exemptions:
Chromium & Copper
Excited Atoms


D. 1s22s22p63s23p6
Alkaline earth ions have a +2 charge, so 2 less e- (removing the s2 orbital)

C. 1s22s22p6
Periodic Table Trands
Metals: left side
Non-Metals: right side, except H
Metalloids: in between
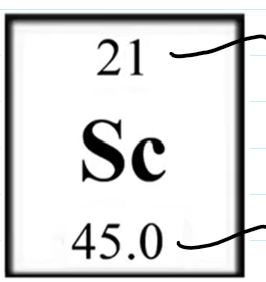
Top: Atomic Weight
Bottom: Atomic Weight
Atomic weight is closest to the most abundant isotope

C. There is a greater abundance of 35Cl
Atomic weight of Cl (35.5) is closer to 35 than 37E
Exceptions to Octet Rule
Hydrogen (H): 2e
Boron (B): 6e
Phosphorus: 8e+
Sulfur: 8e+
Formal Charge Equation:
FC = evalence - ½·ebond - efree
Calculate the Formal Charge of HCN
FCH = 1 v.e. - ½ (2e in bond) - 0 free e- = 1 - 1 = 0
FCC = 4 - ½ (8) - 0 = 0
FCN = 5 - ½ (6) - 2 = 5 - 3 - 2 = 0
Formal Charge of HCN is 0
Calculate the Formal Charge of NH+4
FCH = 0
FCN = 5 - ½ (8) - 0 = 1
Formal Charge is 1 (reflected through + charge)
Calculate the Formal Charge of PO3-4
FCo = 6 - ½ (2) - 6 = -1 (the 3 oxygens with single bonds to the P → -1 × 3 = -3)
FCo - 6 - ½ (4) - 4 = 0 (the 1 oxygen with a double bond to P)
FCP = 5 - ½ (10) - 0 = 0
Formal Charge is -3
Ionic Bonds:
Occurs in elements that have an electronegativity difference GREATER THAN (>) 1.7 OR metal and non-metal bond despite EN difference
Electrons are transferred from one atom to another
Very high melting point
Very high boiling point
Liquid state conducts electricity
Covalent Bonds:
Elements that have an electronegativity different of LESS THAN (<) 1.7
Triumphed by metal and non-metal bonds
Electrons are shared between atoms
Polar, Nonpolar, Coordinate
Lower mp than ionic
Lower bp than ionic
Bond Order: Type, Length, Strength, Contains
1: single, longest, weakest, sigma
2: double, medium, medium, sigma + pi
3: triple, shortest, strongest, sigma + 2 pi
Polar Covalent Bonds
Elements that have an electronegativity difference from 0.4 to 1.7
Electrons are unequally shared between atoms
Dipoles: p = q · r ; p = dipole moment, q= charge, r = charge separation
Lower mp than ionic, higher than nonpolar
Lower bp than ionic, higher than nonpolar
Nonpolar Covalent Bonds:
Elements that have an electronegativity difference < 0.4
Electrons are shared equally between atoms
Diatomics and Alkanes
Lower mp than polar
Lower bp than polar
Coordinate Covalent Bonds
Electrons are shared between atoms
Both electrons are denoted by one of the atoms
Hybridized characteristics of both ionic and covalent bonds
Intermolecular Forces
London Dispersion Forces: induced dipoles, size dependent (the more e-, the stronger it is, easier to polarize)
Dipole-Dipole: polar molecules, strongest in solid and liquid
Hydrogen Bonding: results from H bonded to N, O, or F
Intermolecular Forces Strength
Hydrogen > Dipole-Dipole > London Dispersion
Which has the highest boiling point?
a. CH4
b. C2H6
c. C3H8
d. n-C4H10
d. n-C4H10
They are all London Dispersion Forces, but d is the largest molecule
Which has the highest boiling point?
a. H2O
b. H2S
c. NH3
d. PH3
a. H2O
H bond and stronger than NH3 H bond
Which has the highest boiling point?
a. CH3Cl
b. H2O
c. n-C5H12
d. NaCl
d. NaCl
Ionic compound, so highest bp of all bonds
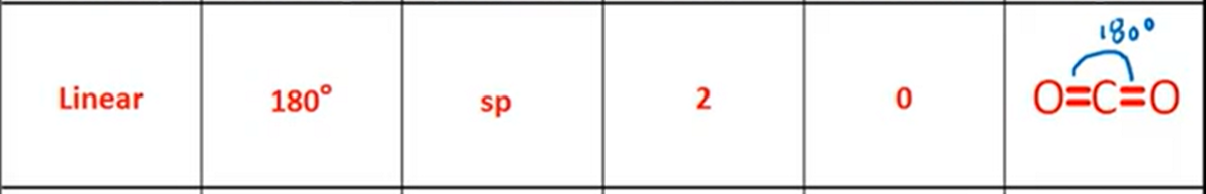
VSPER: Linear
Bond Angle, Hybridization, Bonds, Lone Pairs, Diagram
VSPER: Trigonal Planar
Bond Angle, Hybridization, Bonds, Lone Pairs, Diagram
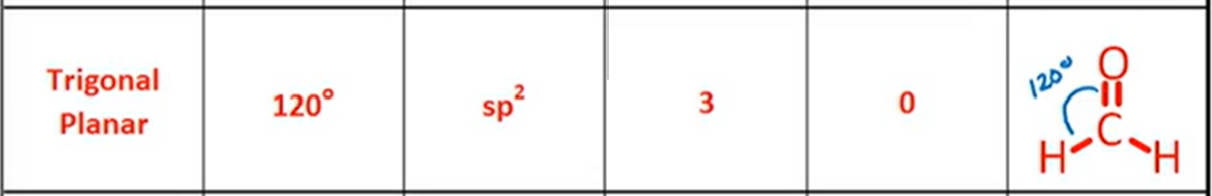
VSPER: Bent
Bond Angle, Hybridization, Bonds, Lone Pairs, Diagram
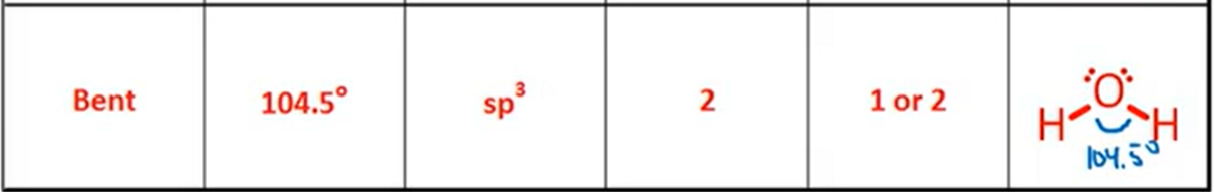
VSPER: Trigonal Pyramidal
Bond Angle, Hybridization, Bonds, Lone Pairs, Diagram
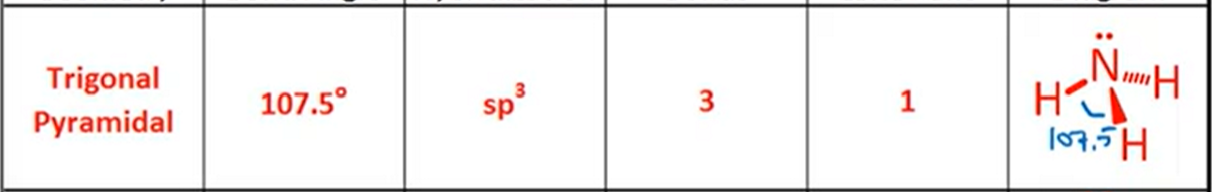
VSPER: Tetrahedral
Bond Angle, Hybridization, Bonds, Lone Pairs, Diagram
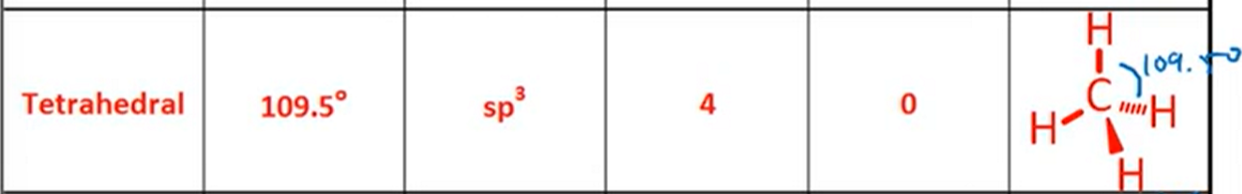
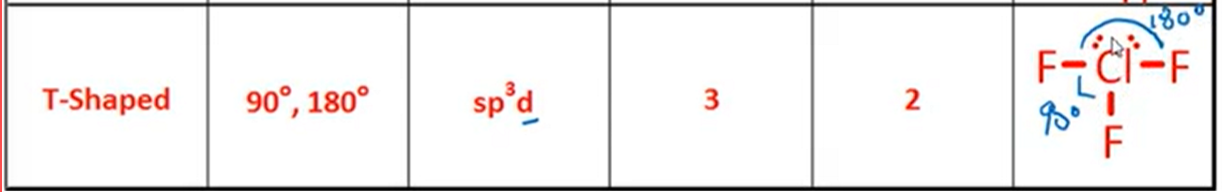
VSPER: T-Shaped
Bond Angle, Hybridization, Bonds, Lone Pairs, Diagram
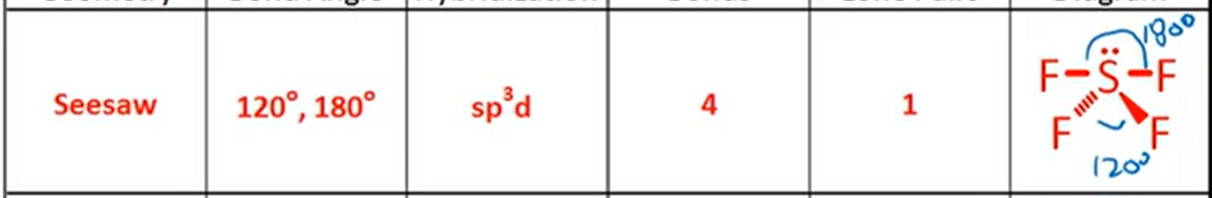
VSPER: Seesaw
Bond Angle, Hybridization, Bonds, Lone Pairs, Diagram
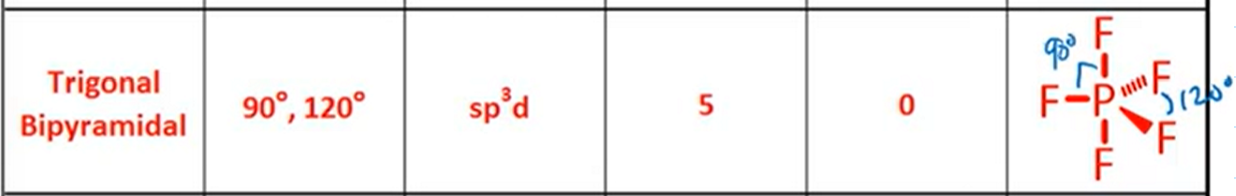
VSPER: Trigonal Bipyramidal
Bond Angle, Hybridization, Bonds, Lone Pairs, Diagram
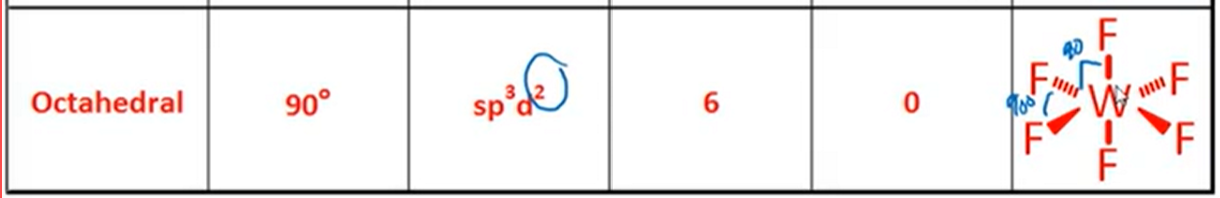
VSPER: Octahedral
Bond Angle, Hybridization, Bonds, Lone Pairs, Diagram
Empirical Formula
Simplest whole number ratio of elements in a compound
Ex. H2O2 → HO
Ex. C6H12 → CH2
Molecular Formula
Actual number of atoms of each element in a compound
Equivalents
The number of moles of a particular atom in a mole of a compound
Percent Composition by Mass Equation:
%C = grams of x / grams total
Percent Composition by Mole Equation:
% C = moles of x / moles total
Percent Yield Equation:
% Y = actual yield / theoretical yield
Limiting Reagent
The reactant that is consumed first, halting further reaction
Excess Reagent
The reactant that remains after the reaction has terminated

Find the moles of each element
Divide by the smallest number
Get formula from moles and find formula weight
Divide molecular weight by empirical formula weight
Multiply the molecular units by the empirical formula
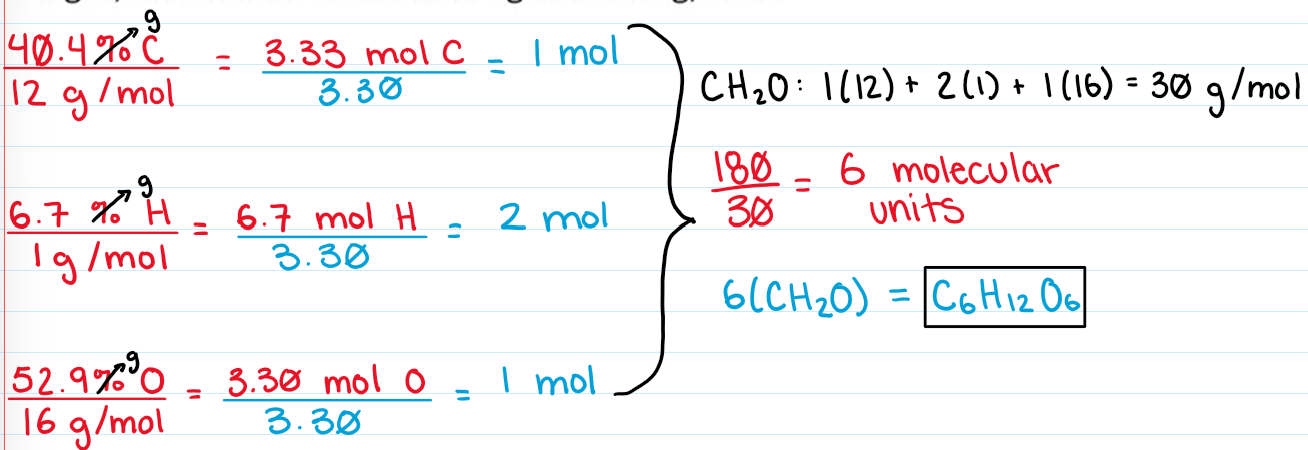


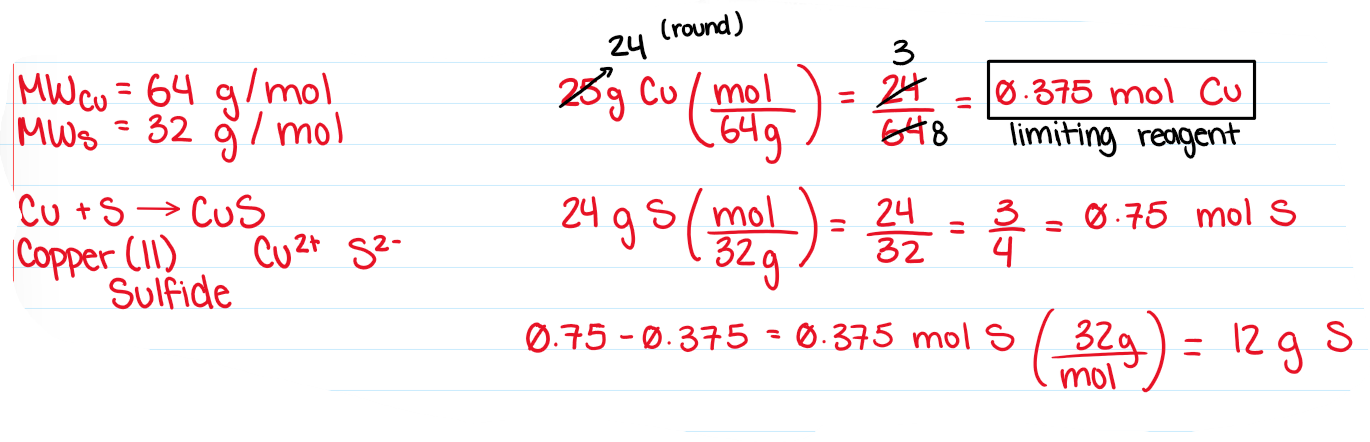
Reaction Classifications
Combination: S + O2 → SO2
Decomposition: 2 HgO → 2 Hg + O2
Single Displacement: Zn + CuSO4 → Cu + ZnSO4
Double Displacement: CaCl2 + 2 AgNO3 → Ca(NO3)2 + 2 AgCl
Rate
How fast a reaction goes
Measured in M/s
Relative Rates

Factors Affecting Rate
Temperature (increases)
Activation Energy (the higher it is, the slower the rate)
Catalyst: k = Ae-Ea/RT ; k = rate constant, A = frequency, Ea = negative = bigger activation (smaller k), R = constant, T = temp
Rate Law
Rate = k[Reactants]0,1,2,3,etc
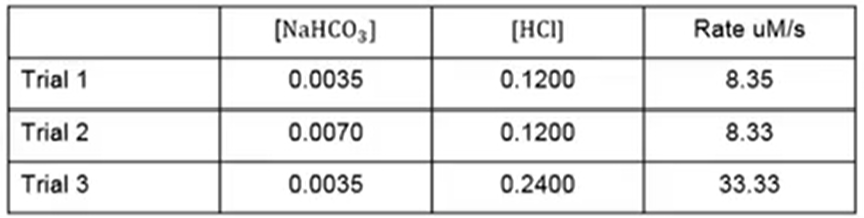
NaHCO3 + HCl → H2O + CO2 + NaCl
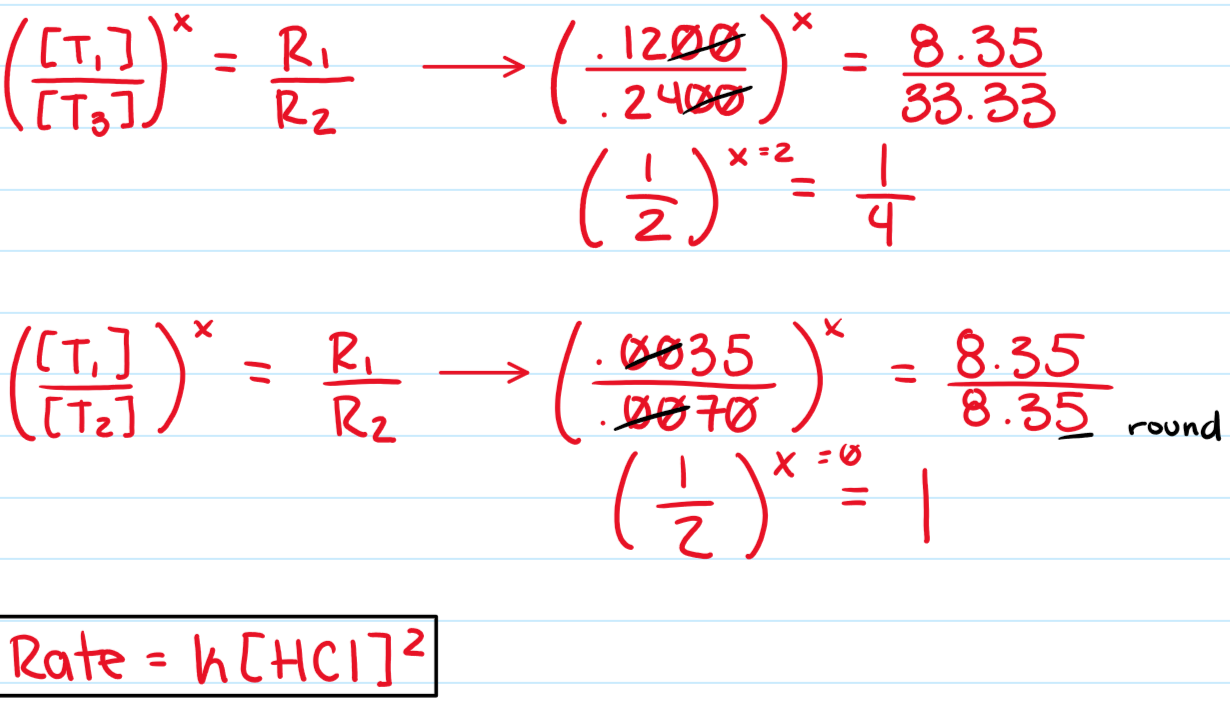

B. Warming the reaction mixture
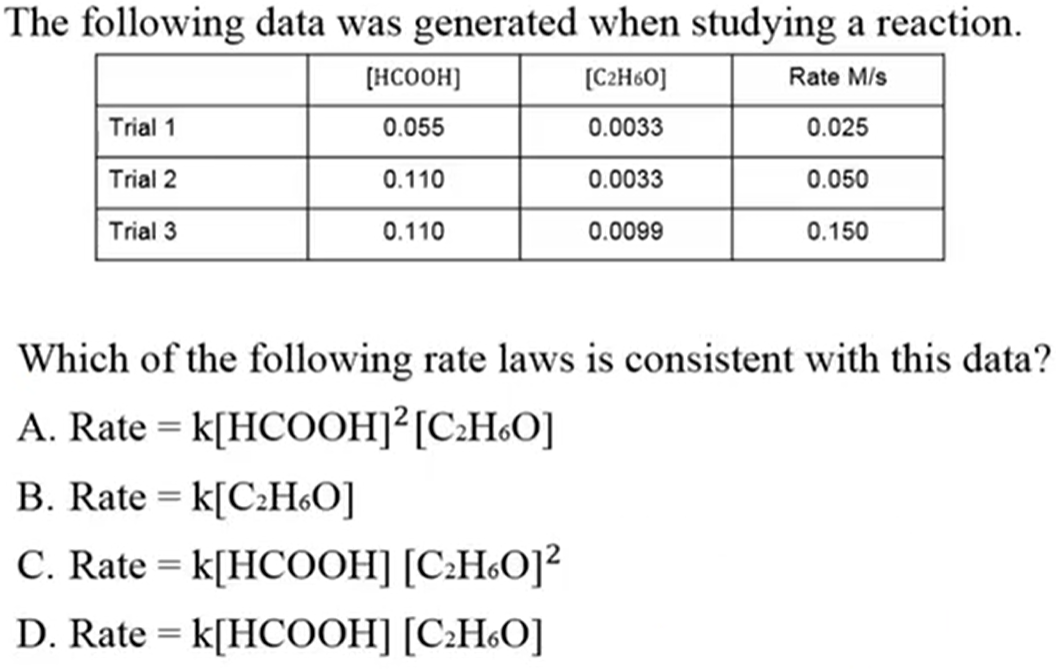
D. Rate = k[HCOOH][C2H6O]
1:1 ratio, so both to the power of 1
Gibbs Free Energy when positive and negative
Positive: reaction is nonspontaneous
Negative: reaction is spontaneous
Keq
Keq < 1 = Reactant Favored
Keq > 1 = Product Favored
Keq = 1 = Equilibrium
Collision Theory of Chemical Kinetics
Reaction rate increases as rate of intermolecular collisions increases
Collisions increase or decrease due to:
Reaction concentration (Le Chatelier’s, Keq)
Temperature (physiological limits)
Medium (correct solute)
Presence of catalysts
MEMORIZE:
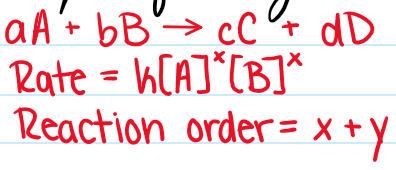
Reaction Orders Shortcut:
Zeroth = Zero Dependence
First = On Dependent
Second = Squared or Two
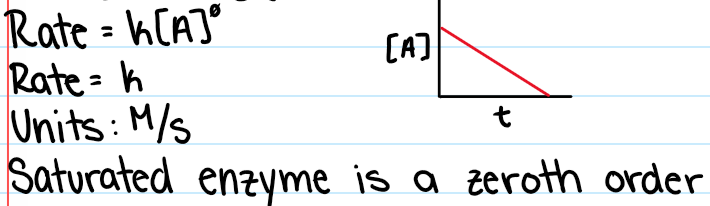
Zeroth Order Reactions
Reactants concentration will have no effect on rate
First Order Reactions:
Rate will increase / decrease linearly to reactant concentration
Double reactant = double rate
Second Order Reactions:
Rate will increase / decrease exponentially to reactant concentration
Double reactant = quadruple rate
Each reactant will have its own rate, and the rate of the overall reaction will be the…
Sum individual reactant rates
Zero Order
First Order
Step with ONE reactant

Second Order
Step with TWO reactants
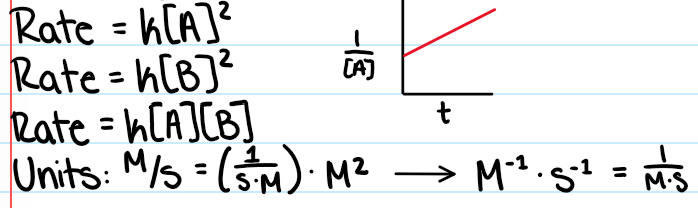
Mixed Order
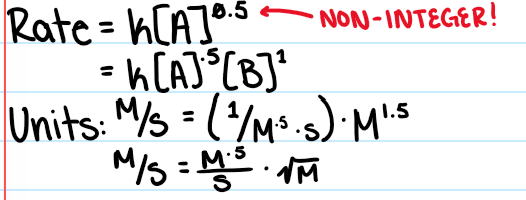
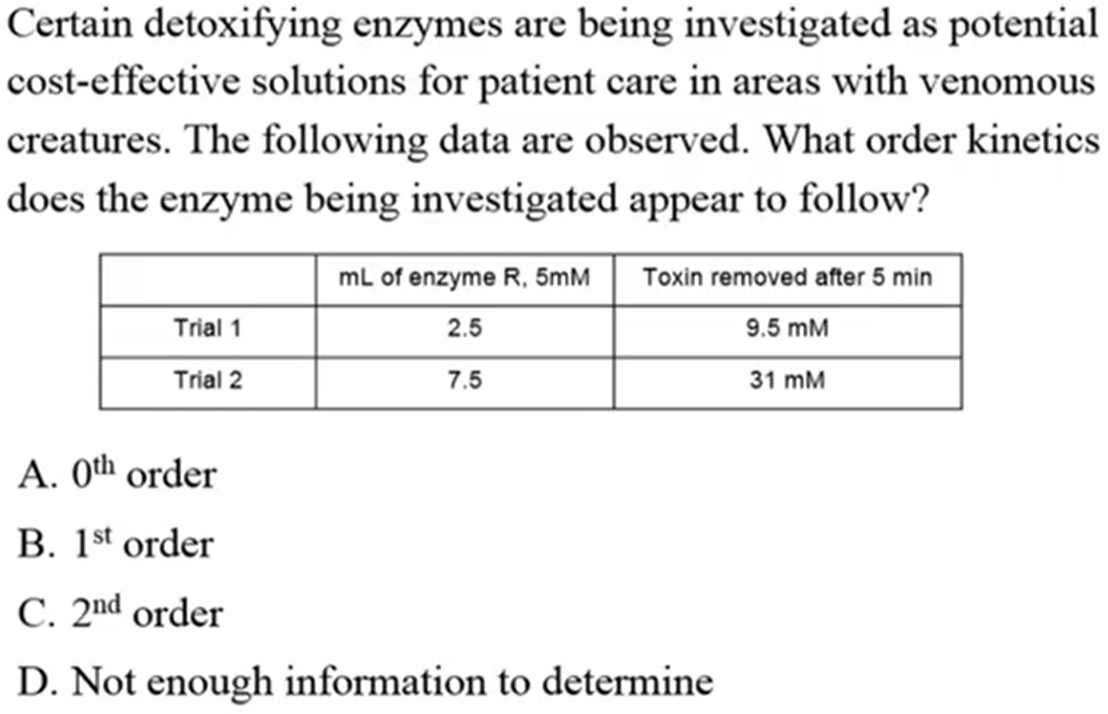
B. 1st Order
1:1 ratio
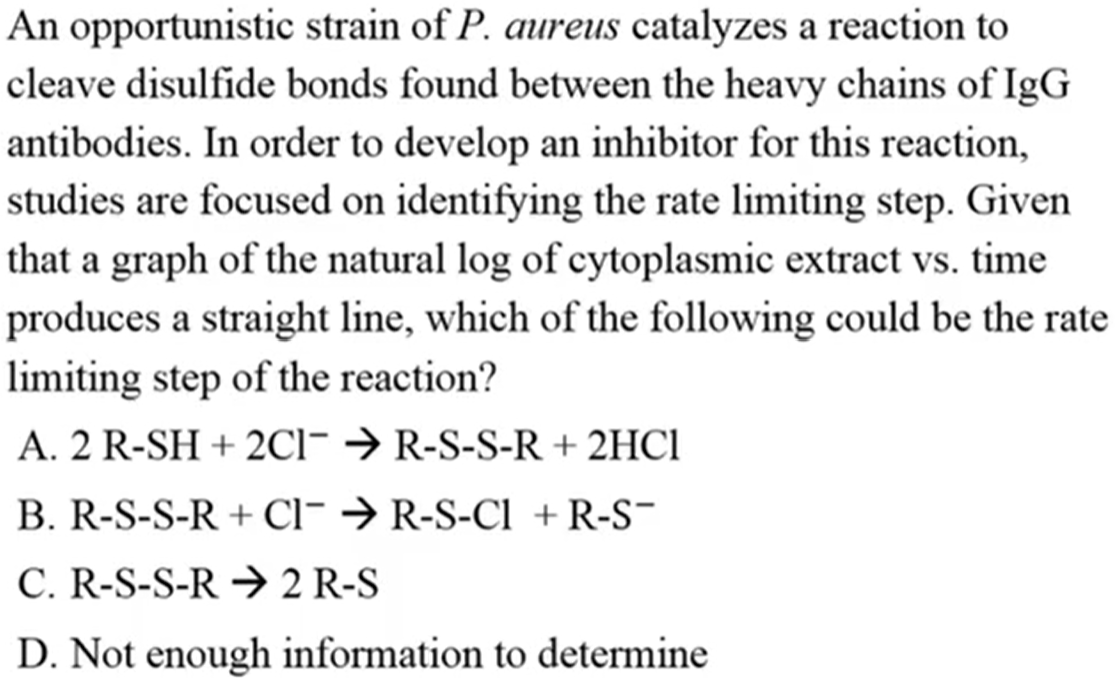
C. R-S-S-R → 2 R-S
Equilibrium Constant
K = Products / Reactants
K > 1 = Product Favored
K = ~1 = Equilibrium
K < 1 = Reactant Favored
Law of Mass Action
K = [products]coefficients / [reactants]coefficients
ONLY include Gases and Aqueous

C. [NADH][FAD]{H+] / [NAD+] [FADH2]
products/reactants