Membrane Fluidity
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
What does it mean when we say cell membranes are fluid
It means the membrane’s lipids and proteins are not fixed in place, they can move and change shape, giving the membrane flexibility.
What mainly affects membrane fluidity
The types of fatty acids in the phospholipid bilayer (saturated vs. unsaturated)
What is special about unsaturated fatty acids
They have double bonds that create kinks in their hydrocarbon tails
How do unsaturated fatty acids affect membrane fluidity
The kinks prevent tight packing of lipids, making the membrane less viscous and more fluid
How do unsaturated fatty acids affect melting point
They have lower melting points, keeping membranes flexible at lower temperatures
What is special about saturated fatty acids
They have no double bonds, so their tails are straight
How do saturated fatty acids affect membrane fluidity
They pack tightly together, making the membrane more viscous and less fluid
How do saturated fatty acids affect melting point
They have higher melting points, so membranes stay strong and stable at high temperatures
What is homeoviscous adaptation
The process by which organisms adjust their membrane lipid composition to maintain proper fluidity under different temperatures
How do cells adjust fatty acid composition with temperature
At low temperatures → more unsaturated fatty acids (to stay flexible).
At high temperatures → more saturated fatty acids (to stay stable).
Why is regulating membrane fluidity important for poikilothermic organism
Because their body temperature changes with the environment, so they must adjust their membranes to keep them functional (e.g., Antarctic fish)
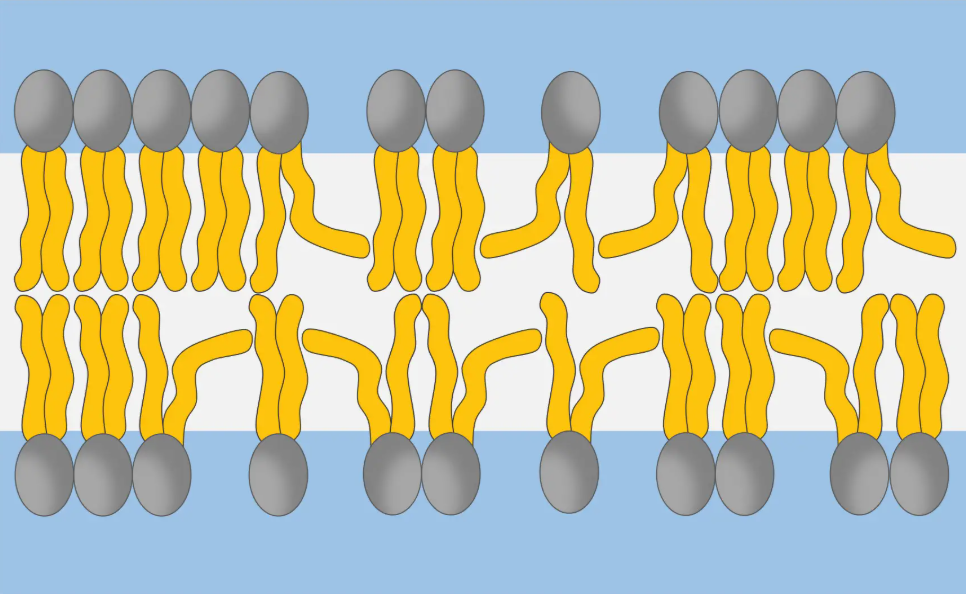
What is this digrame showing
Unsaturated Fatty Acids
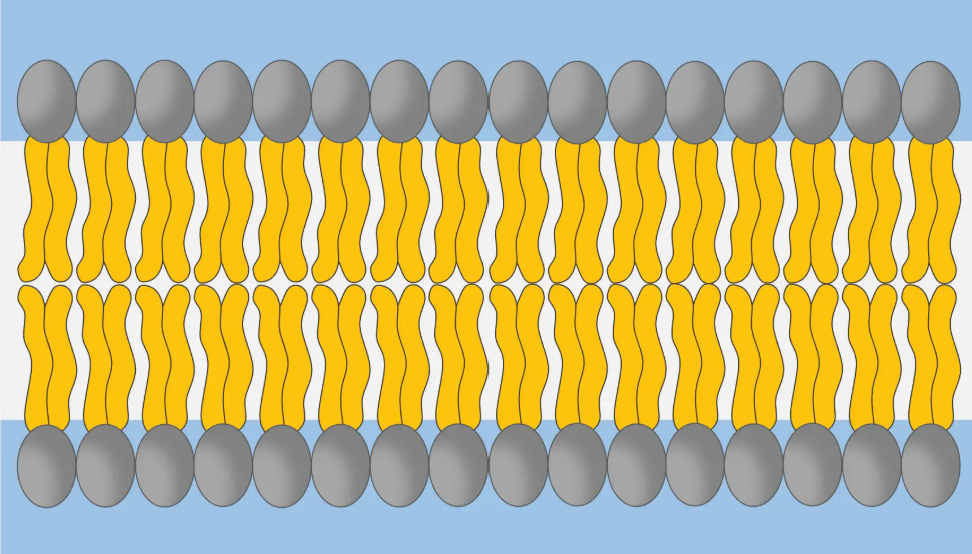
What is this digrame showing
Saturated Fatty Acids