Chapter 8 (not done technically)
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
96 Terms
Skeletal System Funtions
Protection, support, muscle attachment, movement
left and right maxillae (maxillary bones)
upper jaw
fused in along midline
lateral nasal cavity
part of orbit floor
roof of oral cavity
maxillary bones
Mandible
lower jaw
mental protuberance
chin (apart of Mandible - lower jaw)
alveoli (small pocket)
sockets for teeth
Calvaria
roof of cranium], superior cranium
Part of frontal bone, parietal bone (2), part of occipital bone
Base of the cranium
Part of ethmoid, sphenoid, temporal bones (2), part of occipital
All skull bones, except —- are fused together at immoveable
joints called sutures
mandible
Coronal suture, Sagittal suture, Superior part of lambdoid suture
Sutures of superior cranium
Coronal suture
frontal and parietal bones
Sagittal suture
left and right parietal bones
Superior part of lambdoid suture
occipital with parietal bones
Paranasal sinuses (cavities) found within
frontal, sphenoid, ethmoid, and maxillary bones
small bony openings connect ——
allow air to flow in and out of —-
cavities, sinuses
Paranasal Sinuses
connected to nasal cavity via ostia
cilia move mucous into nose [swallowed]
move mucous into nose [swallowed]
cilia
____ reduce weight of skull and
enhance voice resonance
sinuses
____ line sinses
Mucous membranes
Mucous membranes
filter [dust, bacteria, allergens],
warm, and humidify inspired air
___ bone is part of axial skeleton, but it does not articulate with
other bones
Hyoid
C-shaped bone in superior neck
Hyoid
the hyoid is attached by ___ to styloid and ___
processes of temporal bone and ligaments
to larynx(voice box)
muscle, mastoid
larynx
voice box
attachment points for muscles involved in swallowing and speech
hyoid

Hyoid Bone
Vertebral column
Spine
Vertebrae
Individual bones
separate vertebrae
Discs (fibrocartilage)
In vertebrae ___ indicates region
letter
In vertebrae ___ indicates position
number
Classified by structure and location
Vertebrae
Spinal column develops an ___-shape as infant grows
s
Primary curvatures
thoracic and sacral curves present during fetal period
Secondary curvatures
Cervical curvature - allows us to hold our heads up
Lumbar curvature - shifts weight of body onto sacrum
Secondary curvatures
Scoliosis
lateral curvatures in vertebral column
exaggerated cervical and lumbar curvatures
Lordosis (swayback)
Kyphosis (hunchback)
exaggeration of thoracic curvature
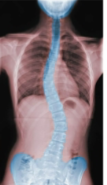
Scoliosis
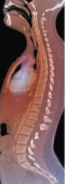
Lordosis
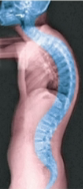
Kyphosis
Wrist consists of
8 short bones (carpals)
C1 in vertebrae
atlas, superior and inferior articular facets
lacks both vertebral body and spinous process
articulates with condyle of occipital bone and C2 respectively
Atlas (C1)
(axis) articulates with atlas
C2
Dens (in Axis C2)
superior tooth-shaped projection protrudes from body
allows joint to perform rotational movement (shaking head to indicate “no”)
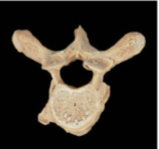
Thoracic Vertebrae, Larger and heart shaped; contain costal facets; circular
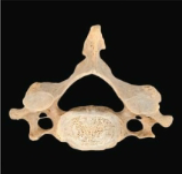
Cervical vertebrae, Small and oval, triangular
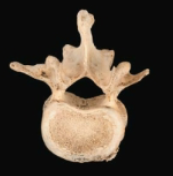
Lumbar vertebrae, largest and kidney shaped; flattened triangular
Intervertebral foramina
foramen through which spinal nerves pass
superior and inferior articular processes
Articular processes form joints between neighboring vertebrae
Spinous process of vertebrae
projects from most posterior aspect of vertebral arch
Transverse processes of vertebrae
project from lateral sides of vertebral arch
True ribs
vertebrosternal
Bone of Ankle and foot
tarsals, metatarsals, and phalanges
bones of foot don’t normally lay flat on ground
arched
__ help support and distribute body weight
muscles
Tarsals ___ short bones
7
Fibula
smaller lateral bone of leg, bears ~1/6 weight of tibia
articulates with lateral tibia
Head of fibula
Lateral malleolus
palpable distal end
articulates with lateral talus
helps stabilize ankle joint
Tibia
larger medial bone of leg
responsible for bearing weight of body
Medial and lateral condyles
proximal end of tibia and articulate with femoral condyles in knee joint
Tibial tuberosity
distal to condyles
on anterior surface
patellar ligament attaches here
Medial malleolus
palpable lump found at ankle
Intercondylar fossa
smooth anterior is patellar surface
Patella is a ___ bone, in tendon of anterior thigh muscle
sesamoid
Neck in femur
just distal to head
Head in femur
articulates with acetabulum at hip joint
large protuberance found lateral to neck
Greater trochanter in femur
Lesser trochanter in femur
medial and distal to greater trochanter
Pubis
smallest coxal bone
Angle formed by two pubic bodies (arch) in males
50-80 degrees
Angle formed by two pubic bodies (arch) in females
70-90 degrees
Ischium
posterior inferior portion of coxal bone
ischial body and ramus
Ischial tuberosity
posteroinferior aspect of ischium, bears all upper body’s weight when seated
Ulna
widest at proximal end and progressively narrows toward distal end
Radial head
articulates with humerus and ulna at elbow joint
Radial styloid process
lateral tip of radius
lateral boundary of wrist and provides joint stabilization
attachment sites for muscle
Medial and lateral epicondyle
Olecranon fossa
deep indentation on
posterior distal epiphysis
articulation with ulna
Protuberance
outgrowth of bone (bulge)
Line (in bone)
long, narrow ridge of bone
linea aspera on femur
Trochanter
large, rough, rounded projection on side of a bone only seen on femur
Process
outward projection of bone
Crest in bone
raised or prominent ridge on edge of a bone
Head
rounded, prominent extension of bone (forms part of the joint) a neck of bone connects it to bone shaft
Condyle
large, elevation or projection (smooth) on end of bone
articulates with another bone to form the joint, covered by hyaline cartilage
Fissure
narrow slit, in an individual bone or between adjacent bones
Foramen
hole in a bone
skull has 21 for passage of blood vessel
foramen magnum for spinal cord
Canal [meatus]
passageway [canal] through bone
Fovea
shallow pit
shallow depression
prevents muscles compressing a nerve or blood vessel
Groove [sulcus]
Fossa
shallow depression in bone
size and shape varies
Facet
flat, shallow surface where two bones articulate