Adv.Biology Midterm Review
1/262
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
263 Terms
fact
an objective, verifiable observation (example: water boils at 100C)
principle
a statement based on repeated experimental observation that describes an aspect of the world (example: greenhouse effect)
law
a broad concept or principle that describes patterns in nature and are often accepted as facts (example: Newton’s laws of motion)
theory
an explanation of an observed phenomenon and organizes facts and research from scientists to explain why but never becomes a fact or law (example: evolutionary theory)
What is science based on?
experimentation
What is the best glassware for measuring?
graduated cylinders
What is the curved line on a graduated cylinder called?
meniscus
What is the best glassware for performing small chemical reactions?
test tubes
What are used for growing bacteria cultures?
Petri dishes
What is an observation?
a description of something you can see, smell, tough, taste, or hear and is not an opinion (must be objective)
What is an inference?
a guess about an object or outcome based on your observations; you can make many inferences from a single observation
What can observations be?
either qualitative or quantitative
What is a qualitative observation?
describes qualities
What is a quantitative observation?
uses numbers to measure something
What is precise data?
how close your measurements are to each other (is this data consistent? Is the data specific?)
What is accurate data?
how close your measurement is to the correct/accepted value (is the data correct? Give the most accurate data)
What does conducting background research lead to?
defining the purpose/objective for the experiment
What is the format for a hypothesis?
“If (IV) then (DV) iv= independent variable= cause dv=dependent variable=effect
What is an independent variable?
what the experimenter will deliberately change or manipulate in the investigation; is usually on the x-axis of a graph; should be the only thing different between experimental groups
What is a dependent variable?
what changes in response to the independent variable; on the y-axis of a graph; usually represented by the data you collect in an investigation/what is measured
What is science?
leads to the advancement of knowledge, answers questions based on our observations
What is technology?
leads to the advancement of society, solves problems based on our needs, the application of scientific discoveries to meet human needs and goals through the development of products and processes
What is engineering?
applies scientific and mathematic principles to solve problems (science plus technology field)
What is implementation?
build and test, continually making improvements
What is evaluation?
determine if you solved the problem and met all of the constraints of the project
What is matter?
anything that has mass and occupies space and is composed of atoms
What is an atom?
the smallest part of an element that still has the properties of that element
What are the 6 elements necessary for life?
C,H,O,N,P,S
What is a cell?
the most basic unit of life
What are atoms made of?
subatomic particles
Where are the subatomic particles located?
protons and neutrons in the nucleus and electrons in the electron cloud
What can we gather from the periodic table?
elements’ symbols, atomic number, average atomic mass, etc
What is an element’s atomic number?
the number of protons that can identify the element and equals the number of electrons in a neutral atom
What is average atomic mass?
the sum of protons and neutrons in the most common isotope of the element
What is an isotope?
2 or more forms of the same element, with different numbers of neutrons (written as the element’s name, mass number- protons + neutrons, or as the symbol)
What is a compound?
2 or more atoms of different elements bonded together
What is a molecule?
2 or more atoms covalently bonded together
How do covalent bonds occur?
when nonmetallic atoms share electrons
How do ionic bonds occur?
when electrons are transferred from a metal to a nonmetal
What is water?
a molecule made of 2 atoms of hydrogen covalently bonded to 1 atom of oxygen, is critical for all of life’s processes and has special properties because its polar
What is a polar molecule?
unequal distribution of charges, one side is more positive, one is more negative and dissolves in water
What is a non polar molecule?
no separation of charge, no positive or negative poles are formed, doesn’t dissolve in water
Why can a water molecule be attracted to each other?
it has hydrogen bonding
What holds water molecules together internally?
stronger covalent bonds
What holds different water molecules together externally?
weaker hydrogen bonds
What are the 5 properties of water?
cohesion
adhesion
high specific heat
less dense as a solid
water is a terrific solvent
What is cohesion?
the attraction between molecules of the same substance; tendency of molecules of the same kind to stick together, causes high surface tension
What is surface tension?
measure of how difficult it is to stretch or break the surface of a liquid/resist an external force
What is adhesion?
the type of attraction that happens between 2 different molecules, forms stronger bonds than cohesion
What is high specific heat?
the temperature of water does not change easily; it has to absorb more heat energy to increase overall temperature compared to other compounds
What are some of the benefits of water having a high specific heat?
it helps regulate cell temperatures in organisms, allows life to live in water, buffers large fluctuations in temperature which keeps Earth’s climate moderate
What does it mean if water is less dense as a solid?
ice is less dense than liquid water so it floats in liquid water (this means life can exist under frozen surfaces of lakes/polar seas)
What is a solvent?
what does the dissolving
Why is water good at dissolving things?
it is polar
Why is water considered the universal solvent?
it dissolves more substances than any other liquid
What are macromolecules?
large organic molecules that make up all living things
What are the 4 macromolecules?
carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids
What are macromolecules made of structurally?
polymers made of monomers
What are monomers?
small basic sub units
What are polymers?
larger more complex structures made of monomers
What is a dehydration reaction?
builds a polymer by linking monomers (does this by removing a water molecule: both monomers have a hydroxy group, pull out OH from one and H from another to form water, oxygen to bond 2 monomers to form polymer)
What is hydrolysis?
breaks big polymers into smaller monomers by adding water, which breaks bonds
What is the main function of a carbohydrate?
short term energy storage
What are other uses of a carbohydrate?
structure, transport, signaling
What are carbohydrates found in?
sugars and starches
What are carbohydrates composed of?
C,H,O
What is the monomer of a carbohydrate?
monosaccharides (single sugar molecules)
What is the polymer of a carbohydrate?
polysaccharides (larger sugar molecules)
What is the energy storage of a carbohydrate?
4 calories/gram (the body can access and break it down easily, it is typically the first thing your body will break down)
What is the main function of a lipid?
long term energy storage
What are other uses of a lipid?
insulation, protection, and structure of cells
What are lipids found in?
fats, oils, phospholipids (in the cell membrane), steroids
What are lipids composed of?
C,H,O
What is the monomer of a lipid?
fatty acids
What is the polymer of a lipid?
triglycerides
What is the energy storage of a lipid?
9 calories/gram (when our body runs out of carbs, it will break down lipids next for energy)
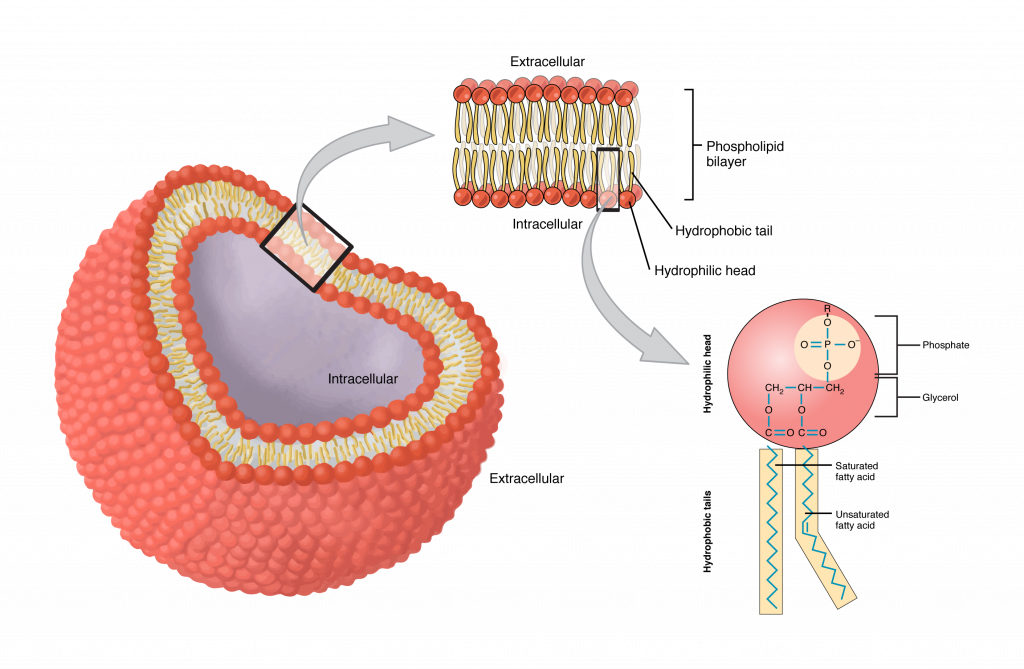
What is the structure of a phospholipid?
2 fatty acids+one phosphate (hydrophobic tail=fatty acids, hydrophilic head=phosphate group)
What is the phospholipid bilayer?
2 layers that make up then plasma membrane of our cells (makes membrane selectively permeable)
What are the main functions of proteins?
enzymes (control the rate of biochemical reactions), hormones (regulate cell processes), structurally make up bones and muscles, transport substances in and out of cells, antibodies that help immune system fight diseases, movement, receptors (aid in cell signaling), energy source in the food we eat
What are proteins found in?
meats, nuts, and dairy products (many are made by your body too)
What is the monomer of proteins?
amino acids
What is the polymer of a protein?
polypeptide (amino acids linked together by a peptide bond)
What is the energy storage of a protein?
4 calories/gram (usually the last resort if energy is needed)
What are the 4 levels to protein structure that dictate their function?
primary structure (amino acid sequence)
secondary structure (alpha helix or beta sheet)
tertiary structure (polypeptide chain in bent and folded into 3D structure)
quaternary structure (2 or more polypeptide chains bound together)
What is the main function of a nucleic acid?
informational molecules that store, transmit, and express our genetic information; contain the instructions for making protein
What are nucleic acids found in?
DNA and RNA
Where do we get nucleic acids from?
our parents
What are proteins made of?
C,H,O,N,P,S
What are nucleic acids made of?
C,H,O,N,P
What is the monomer of a nucleic acid?
nucleotides (5-carbon sugar, phosphate group, nitrogen-containing base)
What are the 5 nucleotides?
adenine, guanine, thymine, cytosine, uracil
What is the polymer of a nucleic acid?
nucleic acid (DNA or RNA)
What is the energy storage of a nucleic acid?
0 calories/gram (never broken down as a source of energy)
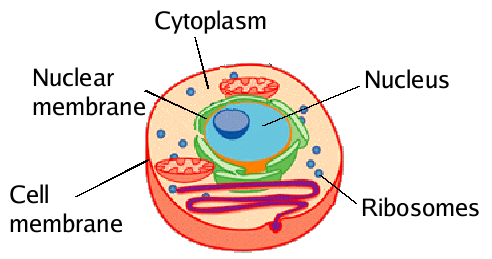
Cell Membrane
(both) Surrounds the outside of cell (made of two layers — phospholipid bilayer)
Controls what goes in and out of the cell
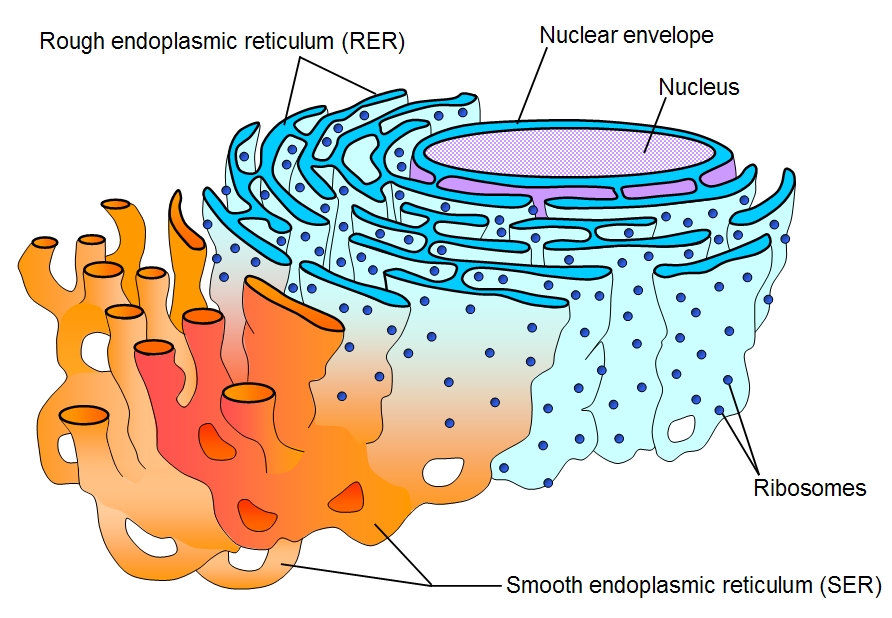
Ribosomes
(both) Made of Proteins and rRNA
Located on Rough ER and floating in cystoplasm
Makes Proteins
Smooth ER
(both) No ribosomes on surface; attached to Rough ER
Makes lipids (membrane)
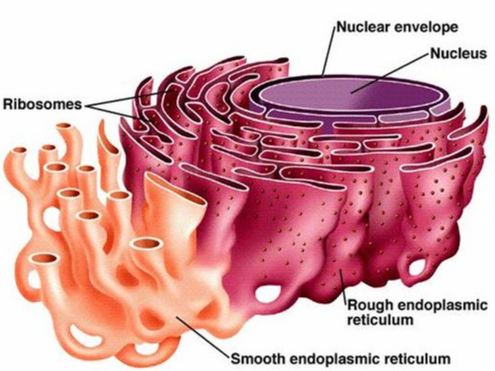
Rough ER
(both) Has ribosomes on surface; hugs nucleus
Makes proteins; packages proteins for secretion (discharge)
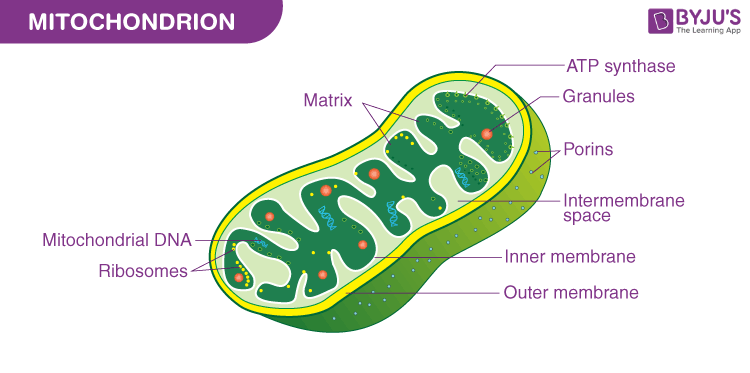
Mitocondria
(both) Two parts: inner membrane and matrix (fluid part)
Where cellular respiration (breaking down food to release energy as ATP (source of energy for cells)) happens
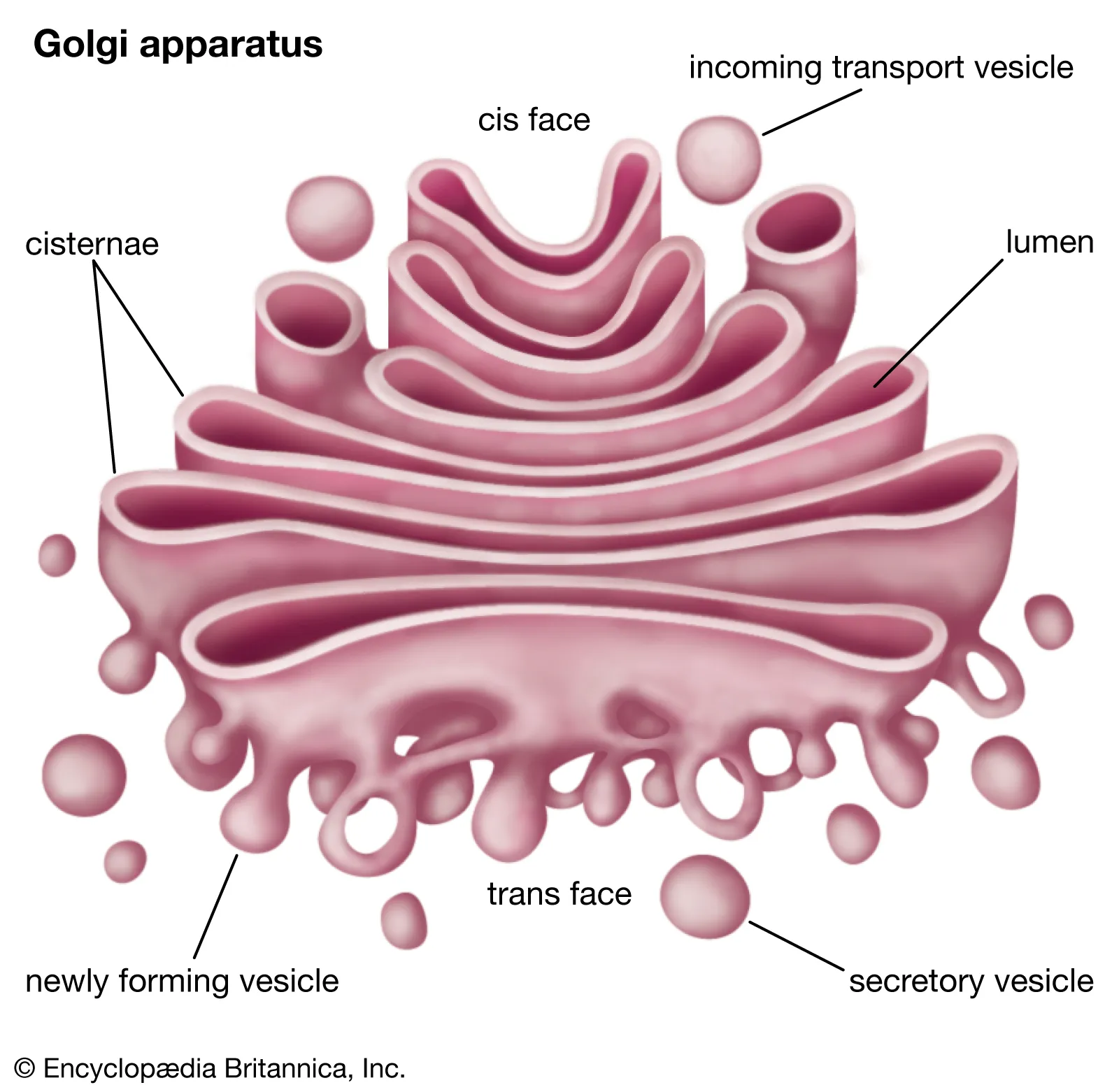
Golgi Apparatus
(both) folded membrane
Gets vesicles (carts for transporting pro. around cell) of protein from the ER; processes, sorts, and ships proteins where needed
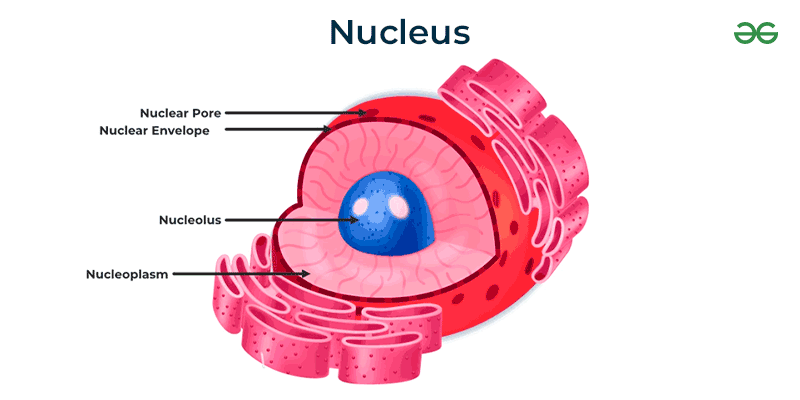
Nucleus
(both) Contains Genetic material (DNA); surrounded by a nuclear envelope/membrane with pores that control what goes in and out
Protects the DNA that controls the activities of the cell