Bio - lab practical #2 (animals)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/165
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:29 AM on 4/10/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
166 Terms
1
New cards
phylum Porifera
pore bearing sponges, ex. grantia and other sponges, symmetry - asymmetrical, no germ layers, no protostomes or deuterostomes, heterotrophic, carnivorous eating zooplankton, all aquatic, no mouth, no anus, acoelomates, no true digestive system, invertebrates
2
New cards
grantia
phylum Porifera, class Calcerea, common name grantia, sessile
3
New cards
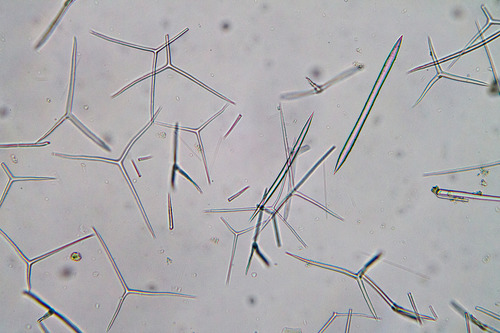
sponge spicules
thin tiny structures forming sponge skeletons
4
New cards
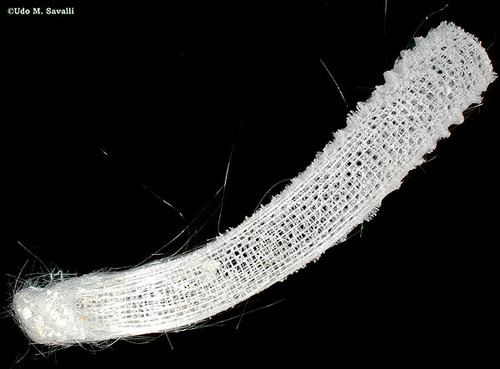
glass sponges
stinger animals, have stinging cells called cnidocytes that shoot sharp harpoons called nematocysts, symmetry - radial, diploblastic (ectoderm, endoderm), no protostomes or deuterostomes, all heterotrophic (carnivorous), all aquatic, 1 opening as mouth and anus, acoelomates, incomplete digestive system
5
New cards
3 classes of Cnidaria
hydrozoans, scyphozoans, anthozoans
6
New cards
class Hydrozoans
polyp stage dominates the life cycle obelia, hydra, Portuguese man-o-war (physalia), gonionemius
7
New cards
protostomes vs deuterostomes
protostomes the blastopore develops into the mouth, deuterostomes the blastopore develops into the anus
8
New cards
incomplete digestive system
digestive system that consists of a digestive cavity and a single opening that serves as both mouth and anus
9
New cards
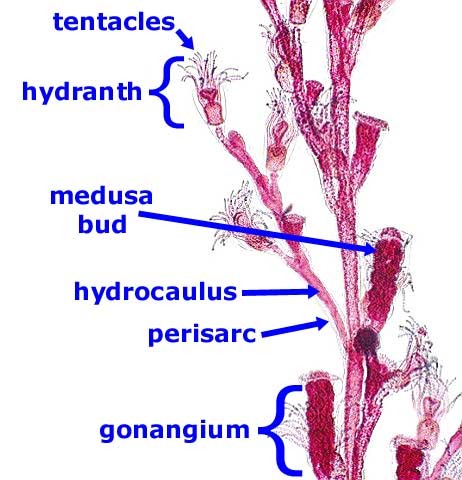
Obelia
phylum Cnidaria, class Hydrozoa, polyp and medusa stage
10
New cards
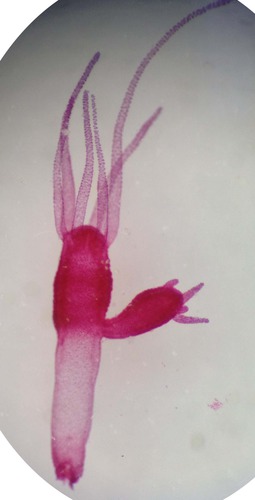
hydra
phylum Cnidaria, class Hydrozoa, polyp stage only
11
New cards
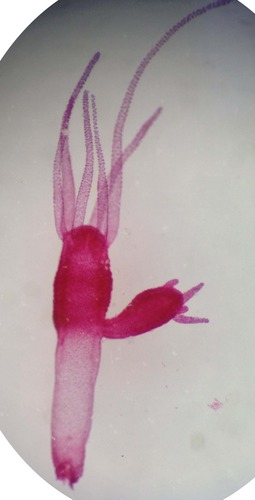
hydra budding
bud develops as an outgrowth due to repeated cell division at one specific site
12
New cards
animals are characterized as
eukaryotic, multicellular, ingestive-feeding heterotrophs
13
New cards
ingestive-feeding heterotrophs
derive energy from organic carbon molecules made by other organisms
14
New cards
asymmetrical
no symmetry
15
New cards
sponges are
filter-feeding heterotrophs and have no photosynthetic pigments
16
New cards
sessile
organism that does not move, it remains attached to one place
17
New cards
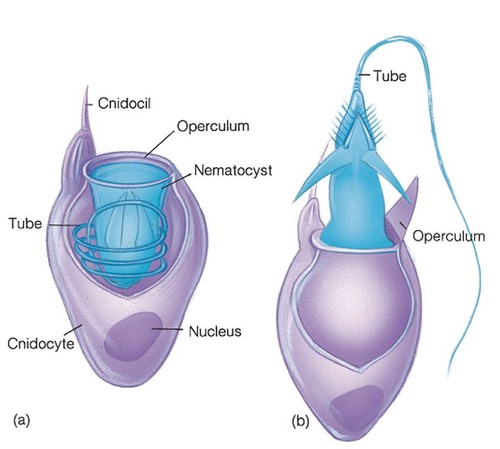
nematocysts vs cnidocysts
cnidocytes are stinging cells in Cnidarians, nematocysts are the sharp harpoons that are shot by the cnidocytes
18
New cards
types of symmetry
asymmetry, radial symmetry, bilateral symmetry
19
New cards
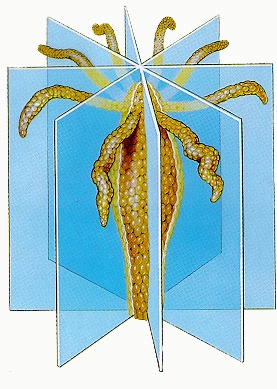
radial symmetry
quality of having many lines of symmetry that all pass through a central point
20
New cards
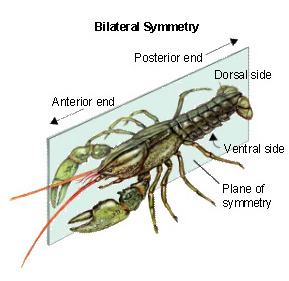
bilateral symmetry
property of being divisible into symmetrical halves on either side of a unique plane, distinct anterior and posterior ends
21
New cards
structure of sponges
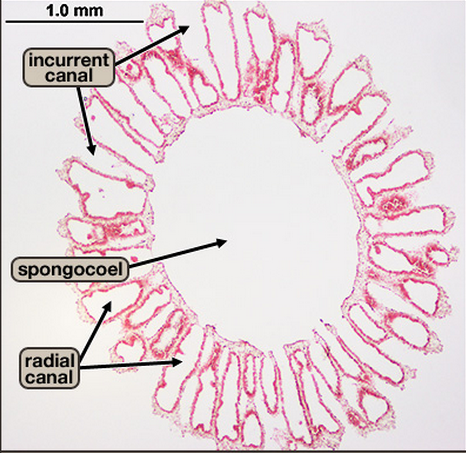
epithelial layer - flat cells that line the outside of a sponge, spongocoel - a central cavity (inside the sponge), choanocytes/collar cells - flagellated cells that line the spongocoel, ostium cells - pores where moving flagella draw water through pores and into spongocoel, osculum - a large hole at the ends of sponge where filtered water exits through
22
New cards
amoebocytes
creeping mobile cells with many functions, including digestion and the ability to differentiate into other cell types as needed, secrete the skeleton of calcareous spicules (containing calcium), siliceous spicules (containing silicon), or proteinaceous spongin fibers
23
New cards
calcareous spicules contain
calcium
24
New cards
siliceous spicules contain
silicon
25
New cards
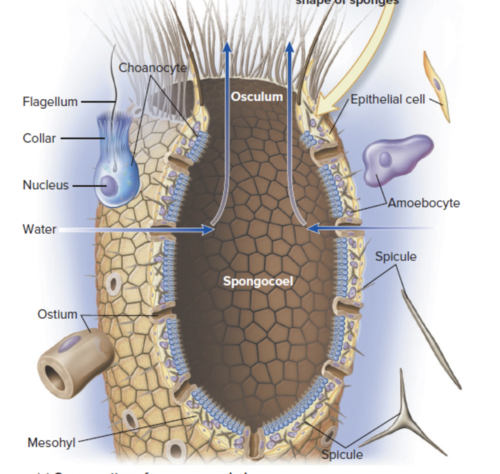
cross section of sponge morphology
know flagellum, choanocyte, osculum, spongocoel, spicule, amoebocyte
26
New cards
shrimps relation to sponges
glass sponge houses several different species of shrimp, when a male and female shrimp enter the spongocoel, they may grow too large to escape
27
New cards

euplectella
phylum Porifera, commonly known as glass sponges
28
New cards
other functions of spicules besides support
protection
29
New cards
sponge reproduction
asexual or sexual, asexual includes budding and the release gemmules, sexual is choanocytes and amoebocytes differentiate into gametes, sperm are released into the water and are captured by choanocytes or amoebocytes of other sponges, the captured sperm are transported to eggs and fertilization occurs
30
New cards
gemmules
stress-resistant aggregates of amoebocytes
31
New cards
cells of Cnidarians are organized into true
tissues (nervous, muscular, or reproductive)
32
New cards
2 basic body plans of Cnidarians
polyps and medussae
33
New cards
polyps
cylindrical animals with a mouth surrounded by tentacles atop the cylinder
34
New cards
medussae
free-floating aquatic animals with a structure similar to a jellyfish, mouth faces downwards and are surrounded by hanging tentacles
35
New cards
polymorphism
many forms, alternation of polyp and medusae stages
36
New cards
gastrovascular cavity
digestive chamber with a single opening, in which cnidarians, flatworms, and echinoderms digest food; one opening that is both mouth and anus
37
New cards
extracellular digestion
digestion outside the cell
38
New cards
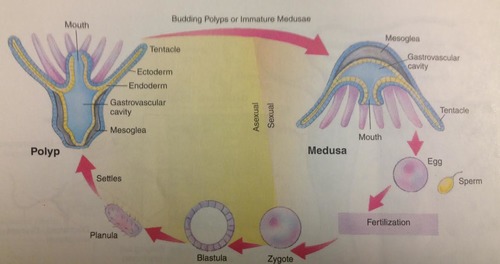
life cycle for Cnidaria
male and female medusae use meiosis to produce gametes that, in water are fertilized, these gametes are the only haploid state; all other stages are diploid
39
New cards
are cnidocytes significant to fundamental processes for Cnidarians
yes, they capture food which allows the organism to grow and reproduce
40
New cards
do sponges appear to have any other organs or organ systems
no
41
New cards
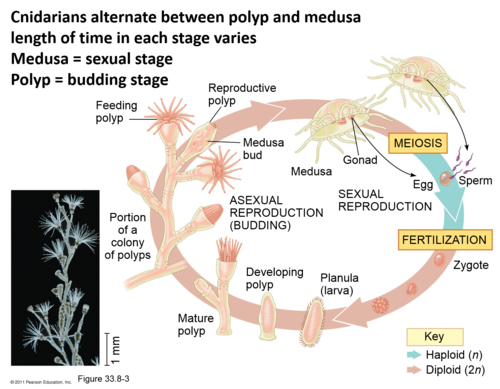
life cycle of a Obelia
polyps reproduce by asexual budding, forming colonies, reproductive polyps may also give rise to medusae, which reproduce sexually via gametes
42
New cards
what specialized cells of tentacles aid in capturing prey
cnidocytes
43
New cards
what structures determine whether a polyp of Obelia is a gastrozooid (feeding polyp) rather than a gonozoid
upward-pointing tentacles
44
New cards
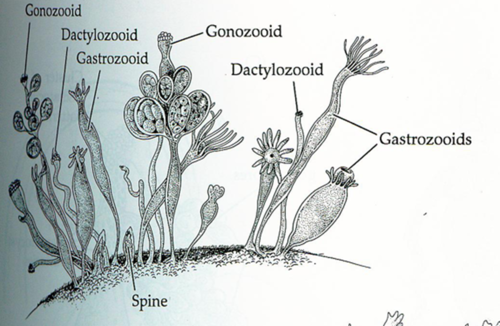
gastrozoid
feeding polyp
45
New cards
touching a Portuguese man-of-war
touching the nematocysts on the dangling tentacles is lethal for small fish and painful (but rarely lethal) for swimmers
46
New cards
gonionemus is a
Hydrozoan with an atypically large medusa
47
New cards
class Anthozoa
sea anemones (Metridium) and Coral, largest class of Cnidarians \\n no medusa, asexual reproduction is fragmentation
48
New cards
class Scyphozoans
Aurelia (jellyfish), medusae and polyp stages
49
New cards
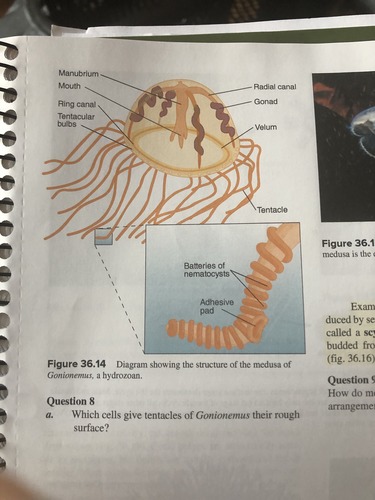
jellyfish labeled
recognize the ring canal, tentacles, and gonads, phylum Cnidaria, class Scyphozoa
50
New cards
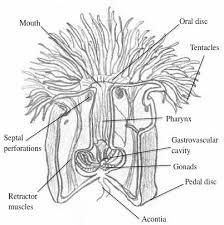
sea anemone labeled
recognize oral tentacles (on top), mouth, oral disk, pedal disk, phylum Cnidaria, class Anthozoa
51
New cards
corals secrete a hard skeleton of
calcium carbonate
52
New cards
advantage of a partitioned gastrovascular cavity
increased surface area for greater rate of absorption
53
New cards
group within the kingdom Protista probably gave rise to sponges
flagellates (choanoflagellates), sponges posses a flagellum and collar cells
54
New cards
types of flukes (Trematoda)
Fasciola - sheep liver fluke, Clonorchis (Opisthorchis) - Chinese liver fluke, Schistosoma - blood flukes
55
New cards

phylum Platyhelminthes
non-segmented flatworms, subphylum Turbellaria (nonparasitic) - Dugesia planarian (planaria), subgroup Trematoda (parasitic) - Flukes (Clonorchis/Opisthorchis and Fasciola) and Schistosoma, subgroup Cercomeromorpha (parasitic) - Taenia tapeworm, triploblastic (ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm), neither pro nor deu, all heterotrophic, most aquatic, freshwater, terrestrial, and parasitic environments, 1 opening as mouth and anus, incomplete digestive system, acoelomate, nerve cord, symmetry - bilateral
56
New cards
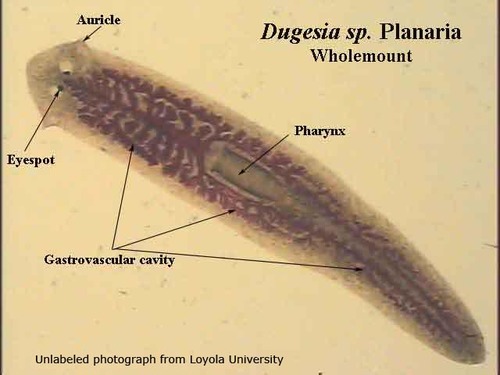
Dugesia planarian
nonparasitic, head has lateral loves and sensory organs called eyespots, most digestion in the gastrovascular cavity is extracellular but phagocytic cells line the cavity and complete digestion of small particles intracellularly, powers of regeneration, phylum Platyhelminthes, subphylum Turbellaria
57
New cards
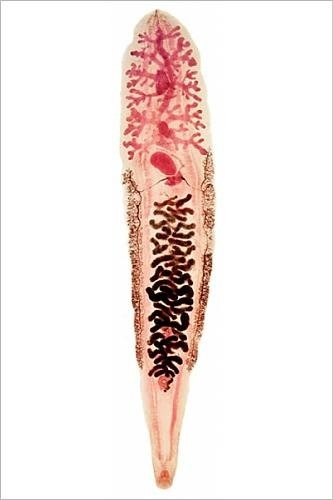
Clonorchis/Opisthorchisoriental liver fluke
oriental liver fluke, phylum Platyhelminthes, subgroup Trematoda
58
New cards
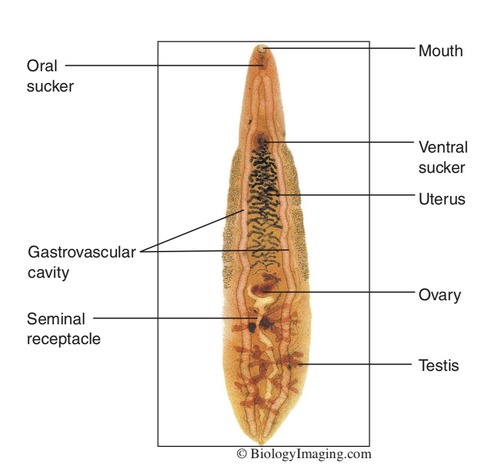
Opisthorchis labeled
know ventral sucker, mouth, gastrovascular cavity and testis, phylum Platyhelminthes, subgroup Trematoda
59
New cards
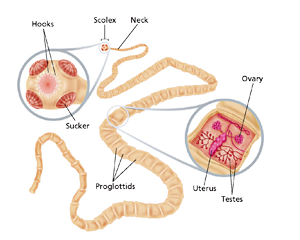
Taenia tapeworm labeled
know proglottid and scolez, phylum Platyhelminthes, subgroup Cercomeromorpha
60
New cards

phylum Nematoda
non-segmented roundworms, ex. ascaris (parasitic, intestinal), vinegar eel, roundworms, all parasitic, bilateral symmetry, triploblastic, protostome, heterotrophic, most aquatic, also freshwater, terrestrial and parasitic environments \\n complete digestive system with separate mouth and anus openings, pseudocoelomate, false body cavity, mesoderm does not line cavity, open circulatory systems, cause diseases in humans, other animals, and plants (Elephantiasis)
61
New cards
acoelomates
mesoderm is a solid mass of tissue with no internal cavity
62
New cards
pseudocoelomates
body cavity between mesoderm and endoderm (pseudocoelom)
63
New cards
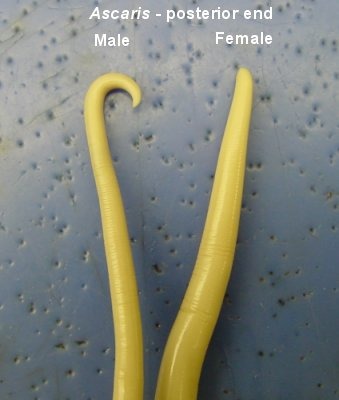
ascaris female vs male
male end curls or hook shape
64
New cards
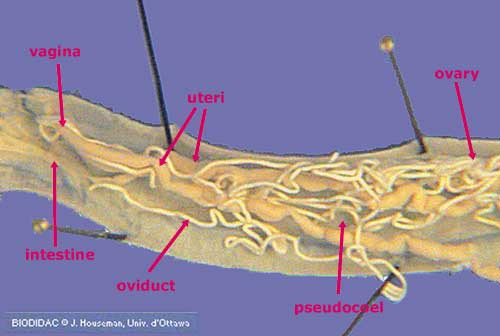
ascaris labeled
know ovary, uterus, and intestine, infects intestinal tract of humans and other invertebrates, phylum Nematoda
65
New cards
triploblastic
3 germ layers
66
New cards
protostome
animal whose mouth is formed from the blastopore
67
New cards
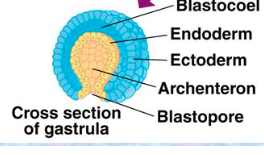
blastopore
opening of the archenteron in the gastrula that develops into the mouth in protostomes and the anus in deuterostomes
68
New cards
pseudocoelom
fluid-filled space between the body wall and digestive tract, internal organs are suspended in this cavity
69
New cards
open circulatory system
system in which blood is not always contained within a network of blood vessels
70
New cards
flatworms and roundworms have a cellular
mesoderm in addition to ectoderm and endoderm
71
New cards
mesoderm
solid mass of tissue with no internal cavity
72
New cards
coelomate
major organs are suspended in a coelomic cavity completely surrounded by the mesoderm
73
New cards
nervous system of the flatworm can be divided into 2 ___ that can be seen running along its sides, ladder like arrangement
nerve cords (Platyhelminthes)
74
New cards
hermaphroditic
both male and female sex organs (subphylum Turbellaria)
75
New cards
subphylum Trematoda and subgroup Cercomeromorpha are
parasitic
76
New cards
subgroup Turbellaria are
nonparasitic
77
New cards
epicuticle
resists digestive enzymes
78
New cards
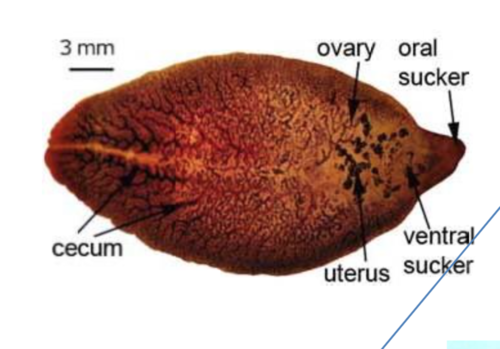
Fasciola labeled
know oral sucker and ventral sucker, phylum Platyhelminthes, subgroup Trematoda
79
New cards
life cycle of oriental liver fluke
know that it involves snails, fish, and humans, hermaphroditic, larvae of flukes develop in snails and fish, humans are infected when they eat raw or poorly cooked fish
80
New cards
how does the position of the mouth of Dugesia and flukes compare
in the fluke it is at the anterior end, in the planaria it is in the middle
81
New cards
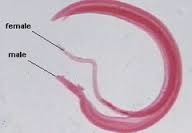
Schistosoma
blook fluke, inhabits the intestinal veins and other organs of many vertebrates, causes the disease schistosomiasis infects more than 200 million people in countries tropical and temperate climate, snails are intermediate hosts
82
New cards
intermediate host
tapeworms, endoparasites of the gut vertebrates and are covered by a cuticle similar to that of Trematodes, the cuticle efficiently absorbs nutrients from their host (humans)
83
New cards
definitive host
contains sexually mature, egg-laying stages of the life cycle
84
New cards
subgroup Cercomorpha
tapeworms, endoparasites of the gut vertebrates and are covered by a cuticle similar to that of Trematodes, the cuticle efficiently absorbs nutrients from their host (humans)
85
New cards
tapeworms are the most ___ Platyhelminthes
specialized
86
New cards
scolex
head of an adult tapeworm, can contain suckers or hooks
87
New cards
proglottids
segments of a tapeworm about 10-15 m long each, has a complete reproductive system
88
New cards
Taenia tapeworm
common name tapeworm, humans are infected by eating uncooked meat from pigs, secondary/intermediate host - pigs, primary host - humans, phylum Platyhelminthes, subgroup Cercomeromorpha
89
New cards
tapeworms have no digestive system or mouth, how do they obtain food
diffusion through the body wall
90
New cards
cuticles in Nematodes
resists digestive enzymes
91
New cards
advantages of a digestive tract having a separate entrance and exit
one way passage for food, allows for specialization of the digestive tract
92
New cards
Nematodes have only
longitudinal muscles and lack circular or diagonal muscles, produces a characteristic/whiplike motion
93
New cards
disadvantages of a flatworms digestive system only having one opening
it needs to empty the digestive tract before it can eat again, no continuous feeding
94
New cards
phylum Mollusca
soft bodied, class Polyplacophora - chitons, class Gastropods - snails and slugs, class Bivalvia - clams, class Cephalopoda - squids, octopus, nautilus, biradial/bilateral symmetry, triploblastic, heterotrophs, aquatic/terrestrial, complete digestive system, reduced hydrostatic acoelomate, non-segmented, all classes have open circulatory systems except Cephalopods have a closed circulatory system, well-developed nervous system
95
New cards
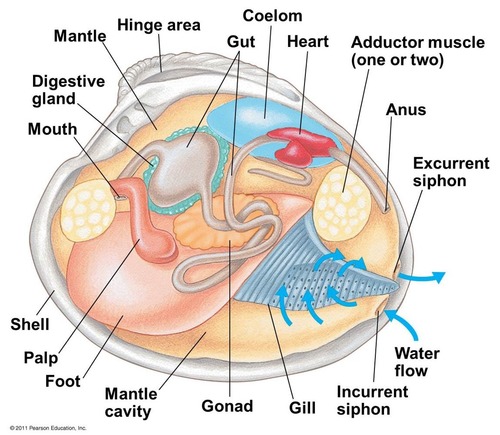
clam labeled
know foot, adductor muscles, siphons, gills, mantle, labial palp, stomach, heart, phylum Mollusca, class Bivalvia
96
New cards
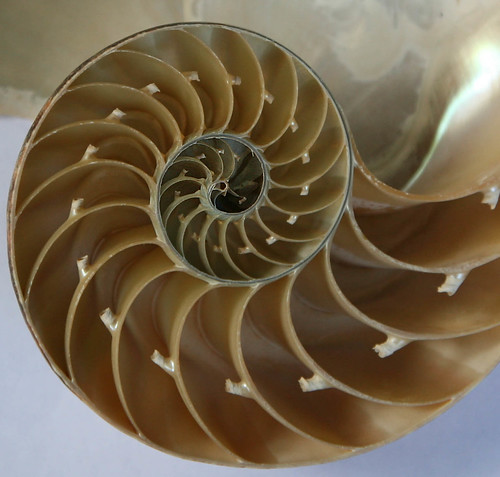
nautilus
only cephalopod with an external shell, phylum Mollusca, class Cephalopoda
97
New cards
chiton labeled
phylum Mollusca, class Polyplacophora
98
New cards
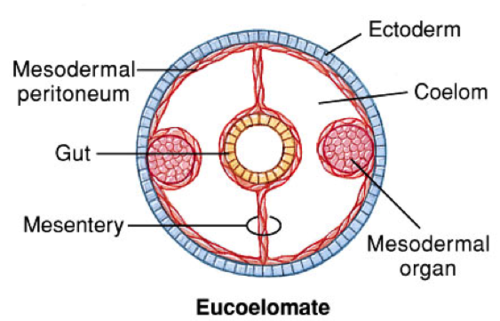
eucoelomate
true body cavity
99
New cards
phylum Annelida
segmented roundworms, class Polychaeta - nereis, parapodia, setae bristles, class Oligochaete - earthworms, class Hirudinea - leeches, bilateral, triploblastic, heterotrophic, aquatic/terrestrial, developed eucoelom, Schizoroelus, specialized segmentation and cephalization, metameric serial repetitions along a central axis, closed circulatory system, complete digestive system, well-developed nervous system
100
New cards
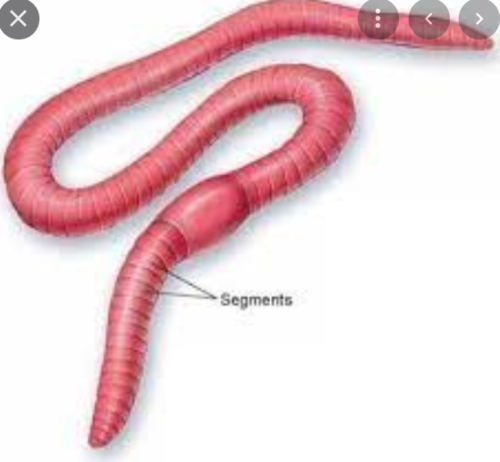
metameric segmentation
serial repetition of segments and organ systems