Topic 6 - Male genitalia
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
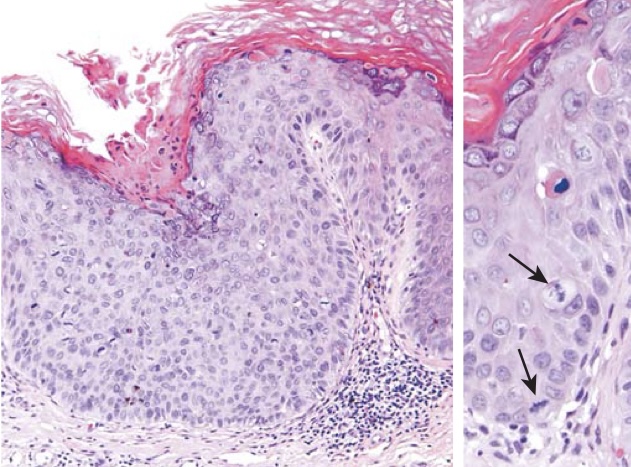
High grade penile intraepithelial neoplasm (PeIN). The epithelium above the intact basement membrane shows delayed maturation and disorganization (left). Higher magnification (right) shows several mitotic figures (arrows), one above the basal layer.
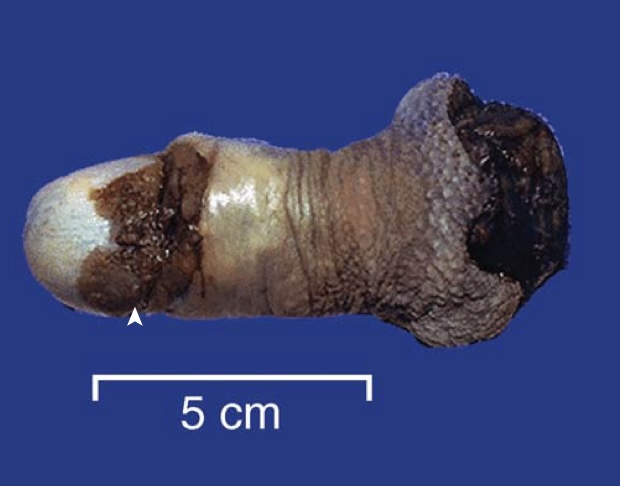
Carcinoma of the penis. The glans penis is deformed by an ulcerated, infiltrative mass.
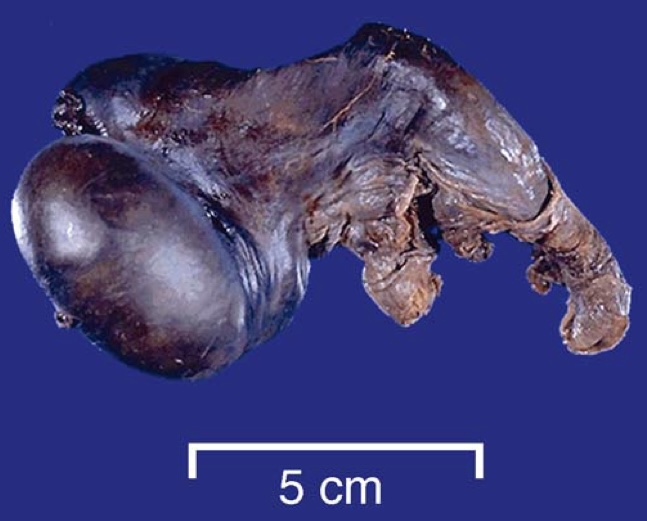
Testicular torsion. The dark discoloration is the result of hemorrhage and infarction that occurs when twisting of the spermatic cord cuts off venous drainage.
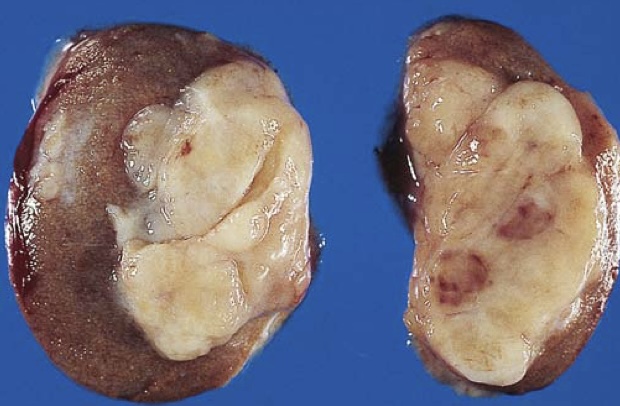
Seminoma of the testis appearing as a well-circumscribed, pale, fleshy, homogeneous mass.
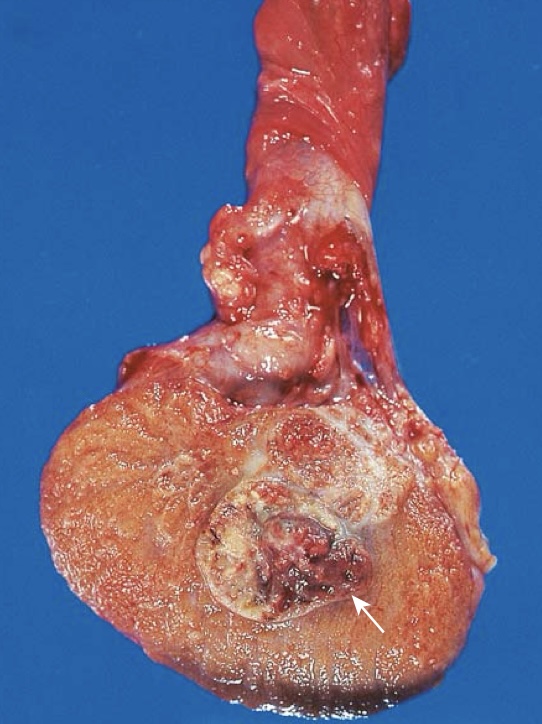
Embryonal carcinoma. In contrast with the other seminoma picture, this tumor is hemorrhagic (arrow).
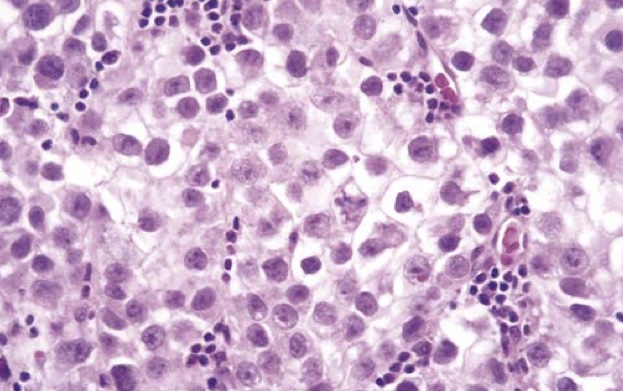
Seminoma of the testis. Microscopic examination reveals large cells with distinct cell borders, pale nuclei, prominent nucleoli, and a sparse lymphocytic infiltrate.
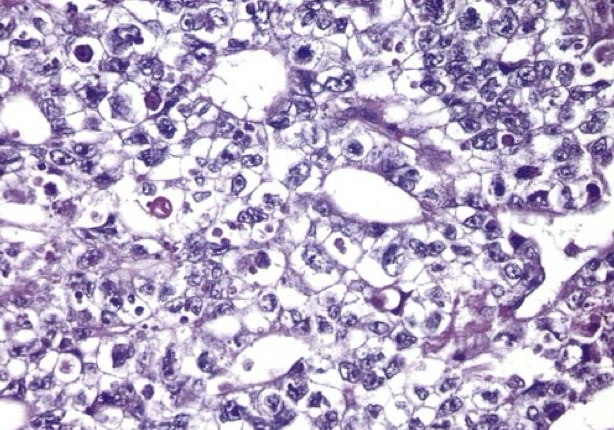
Embryonal carcinoma. Note the sheets of undifferentiated cells and primitive glandlike structures. The nuclei are large and hyperchromatic.
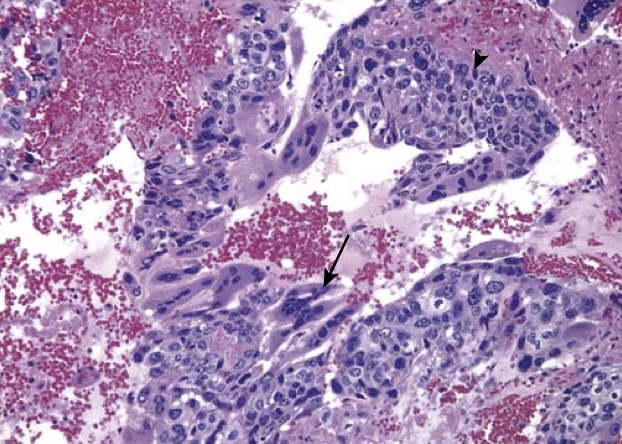
Choriocarcinoma. Both cytotrophoblastic cells with single central nuclei (arrowhead, upper-right) and syncytiotrophoblastic cells with multiple dark nuclei embedded in eosinophilic cytoplasm (arrow, middle) are present. Hemorrhage and necrosis are prominent.
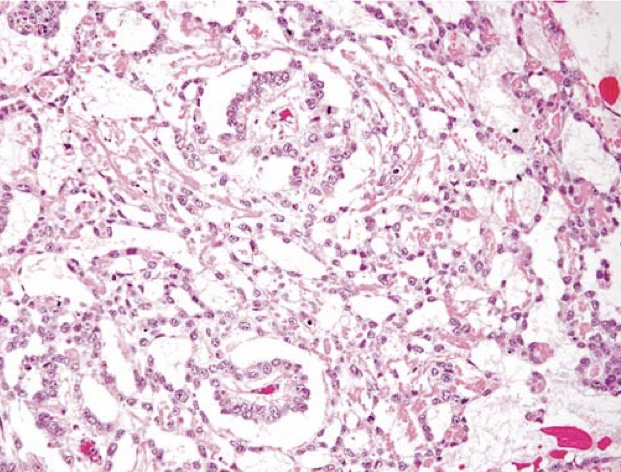
Yolk sac tumor demonstrating areas of loosely textured, microcystic tissue and papillary structures resembling a developing glomerulus (Schiller-Duval bodies).
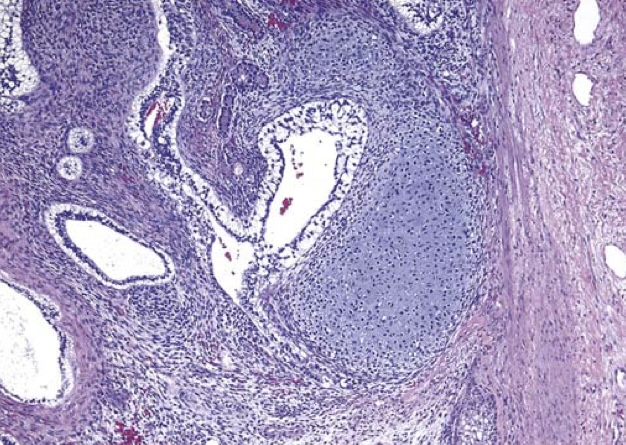
Teratoma of the testis, consisting of a disorganized collection of glands, cartilage, smooth muscle, and immature stroma.
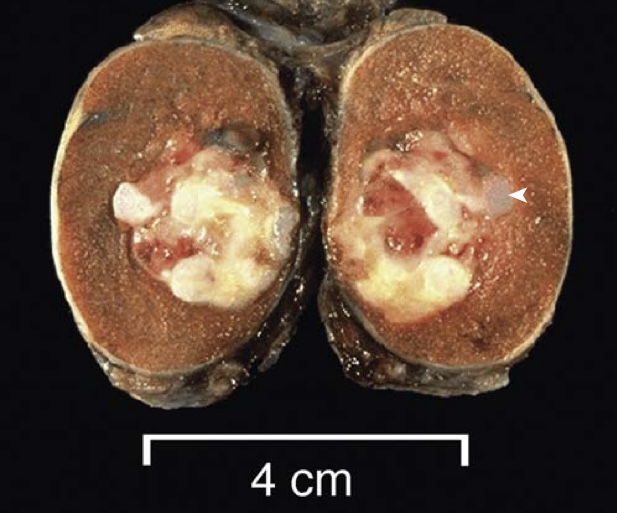
This small testicular neoplasm within the body of a normal-sized testis sectioned coronally has a mixture of bluish cartilage (arrowhead) admixed with red and white tumor tissue. Microscopically it contained mainly teratoma but also areas of embryonal carcinoma.
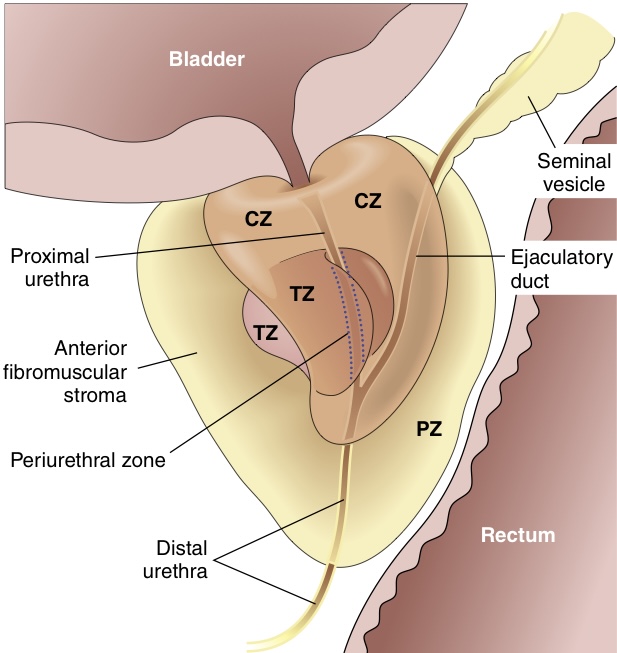
Adult prostate. The normal prostate contains several distinct regions, including a central zone (CZ), a peripheral zone (PZ), a transitional zone (TZ), and a periurethral zone. Most carcinomas arise from the peripheral glands of the organ, whereas nodular hyperplasia arises from more centrally situated glands.
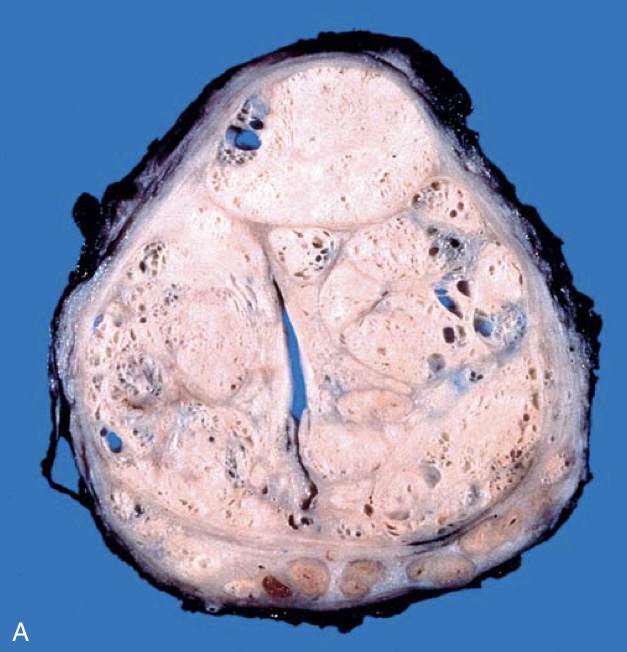
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). (A) Well-defined nodules of BPH compress the urethra into a slitlike lumen.
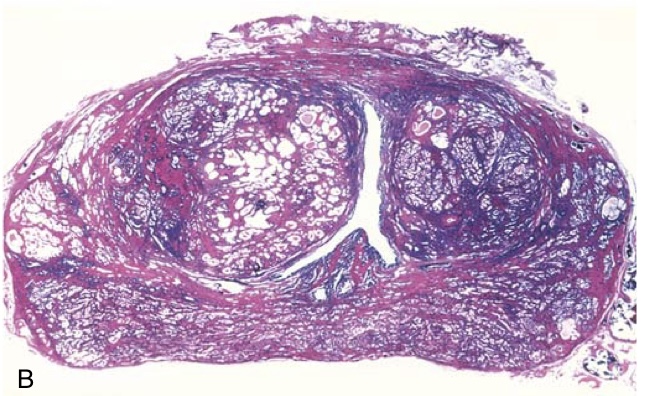
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). (B) Low-power photomicrograph demonstrates nodules of hyperplastic glands on both sides of the urethra. In other cases of nodular hyperplasia, the nodularity is caused predominantly by stromal, rather than glandular, proliferation.
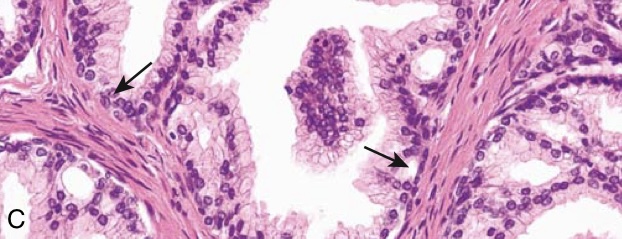
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). (C) Higher-power photomicrograph demonstrates the morphology of the hyperplastic glands, which are large and have papillary infoldings. Unlike prostatic adenocarcinoma, basal cells are present (arrows).
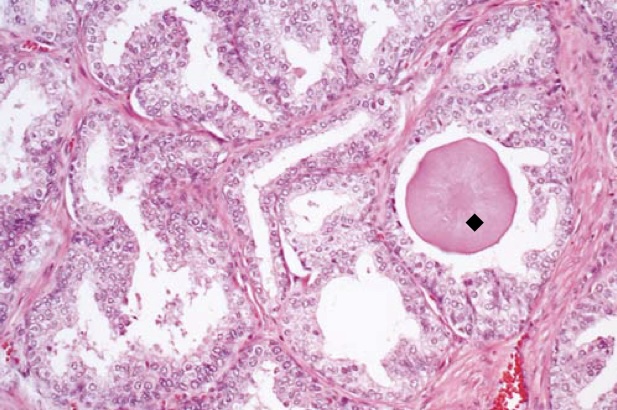
Benign prostatic hyperplasia with a rounded pink concretion (black diamond) typical of corpora amylacea.
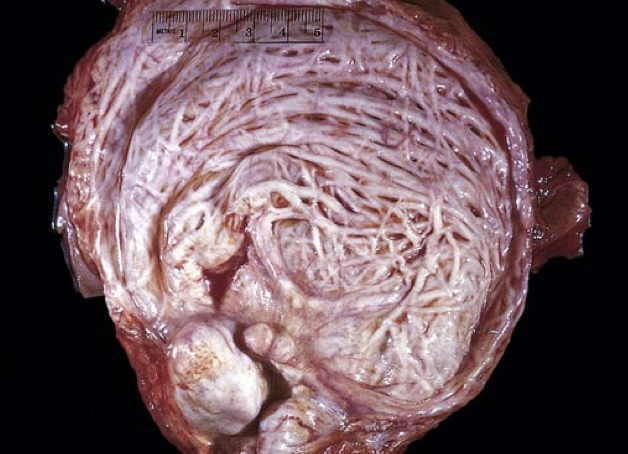
Hypertrophy and trabeculation of bladder wall secondary to benign prostatic hyperplasia.
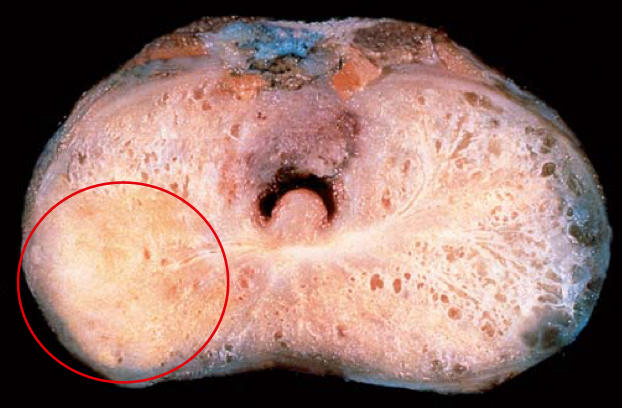
Adenocarcinoma of the prostate. Carcinomatous tissue is seen on the posterior aspect (circled, lower left). Note the solid appearance of the cancer, in contrast with the spongy appearance of the benign peripheral zone on the contralateral side.
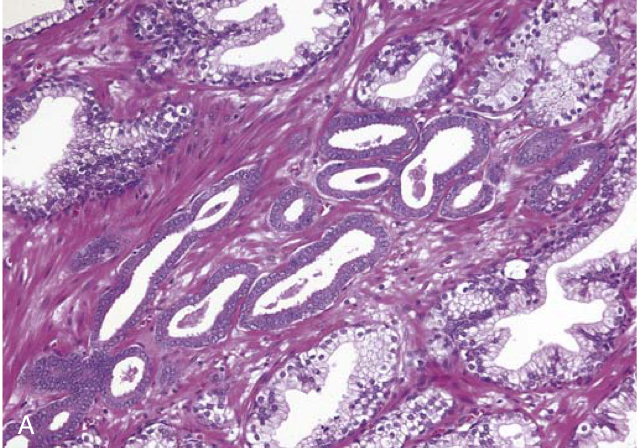
(A) Adenocarcinoma of the prostate demonstrating small glands crowded in between larger benign glands.
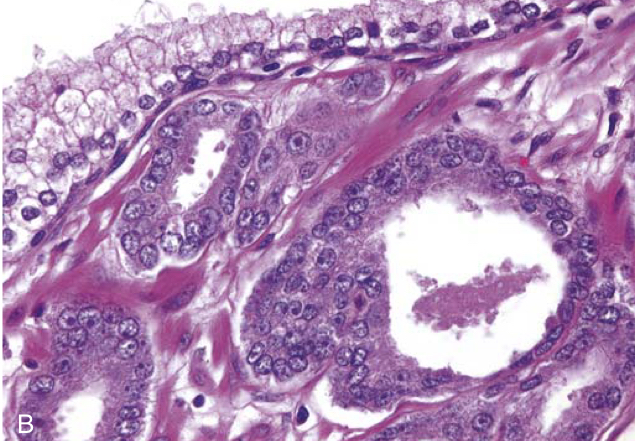
Adenocarcinoma of the prostate. (B) Higher magnification shows several small malignant glands with enlarged nuclei, prominent nucleoli, and dark cytoplasm, as compared with the larger, benign gland (top).
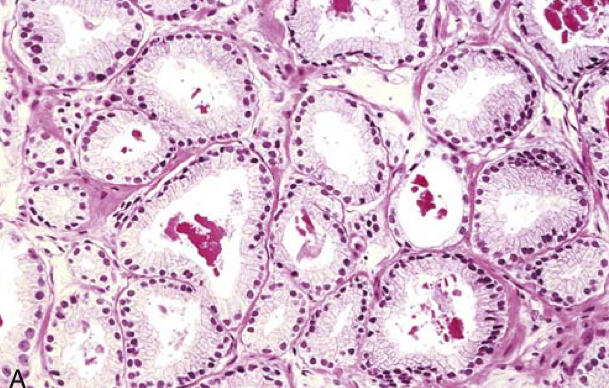
Gleason grading of prostate cancer. (A) Low-grade prostate adenocarcinoma (Gleason score 1 þ 1¼ 2) consisting of back-to-back uniform-sized malignant glands lined by a single layer of epithelial cells.
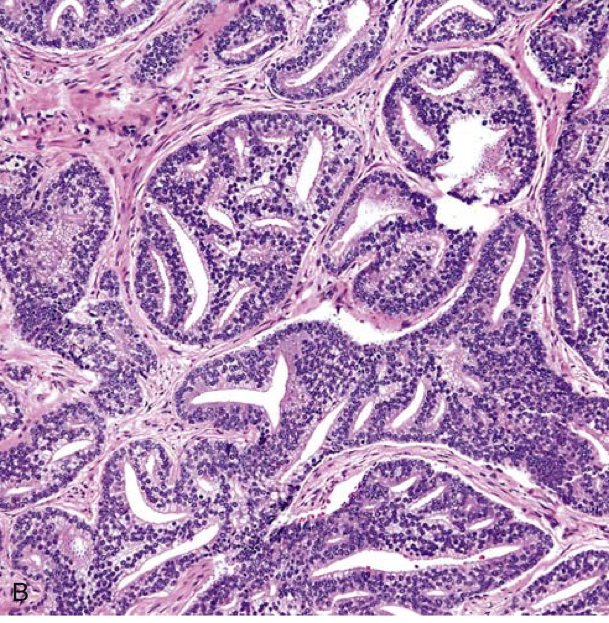
Gleason grading of prostate cancer. (B) A focus of Gleason grade 4 prostatic adenocarcinoma displays large cribriform glands with multiple cellular bridges crossing the central lumina.
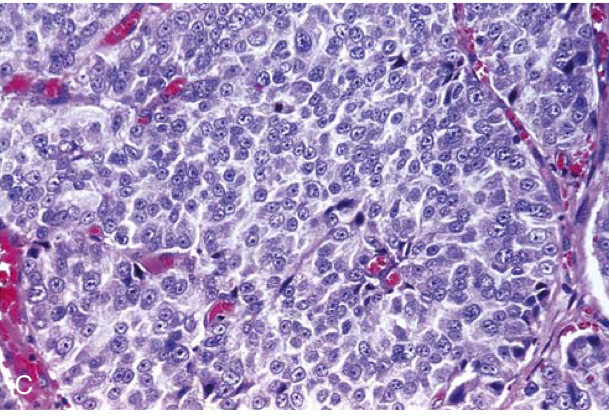
Gleason grading of prostate cancer. (C) Grade group 5 adenocarcinoma (Gleason score 5 þ 5¼ 10) composed of sheets of malignant cells with no identifiable gland formation.
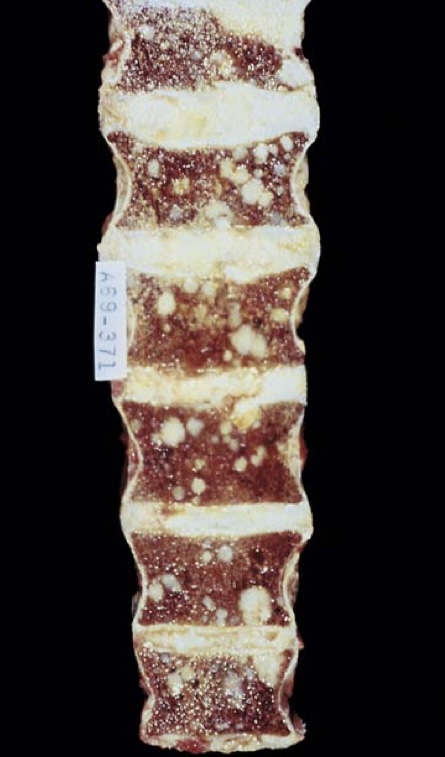
Metastatic osteoblastic prostatic carcinoma within vertebral bodies.
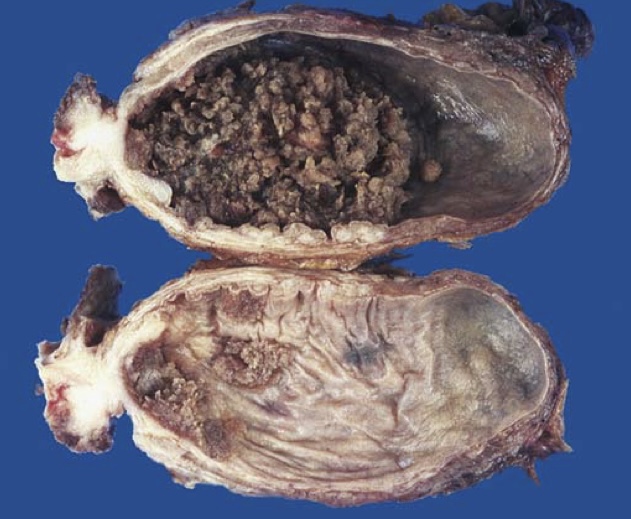
Papillary tumor of the bladder. Cross-section of bladder with the upper section showing a large papillary tumor. The lower section demonstrates multifocal smaller papillary neoplasms.
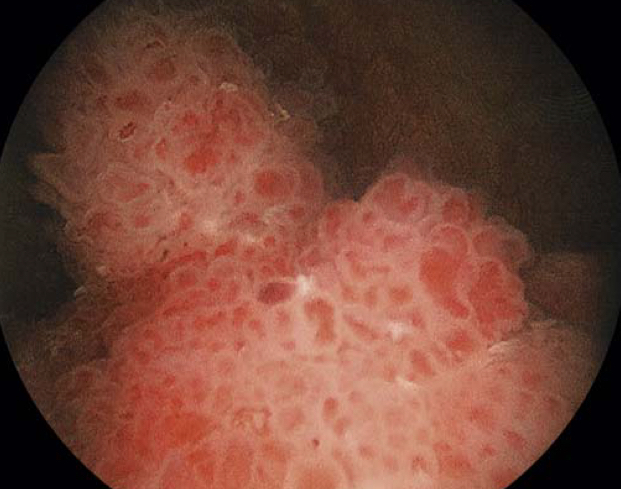
Cystoscopic appearance of a papillary urothelial tumor, resembling coral, within the bladder.
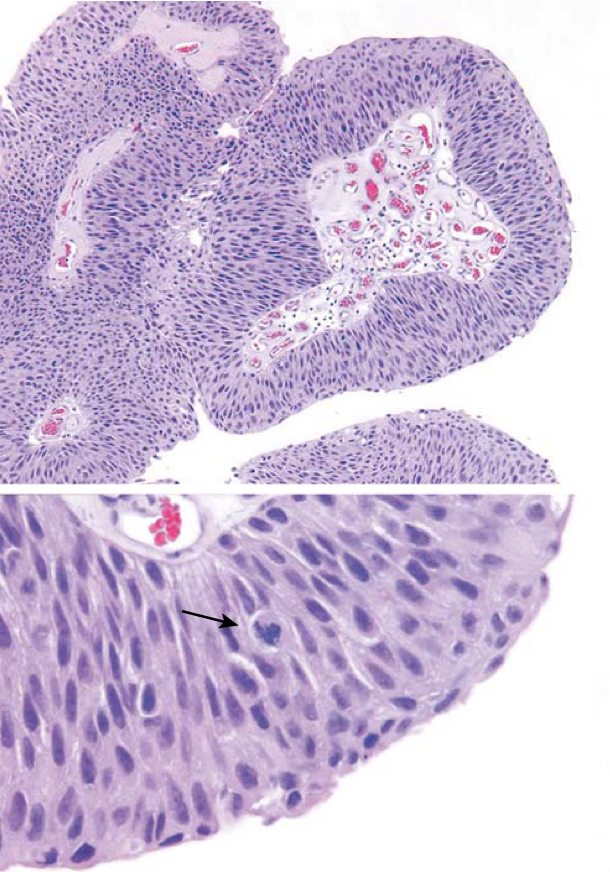
Noninvasive low-grade papillary urothelial carcinoma. Higher magnification (bottom) shows slightly irregular nuclei with scattered mitotic figures (arrow).
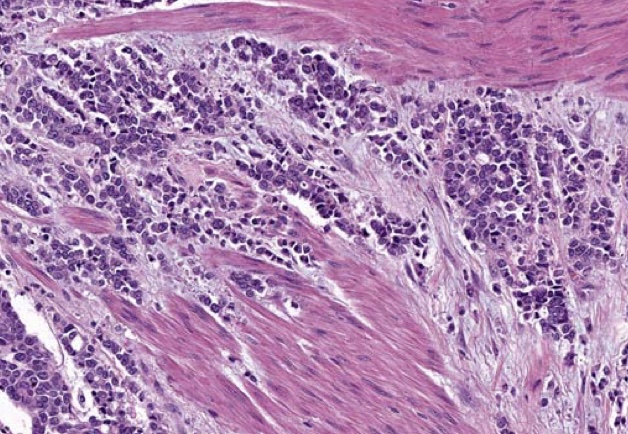
High-grade urothelial carcinoma invading into the muscularis propria.
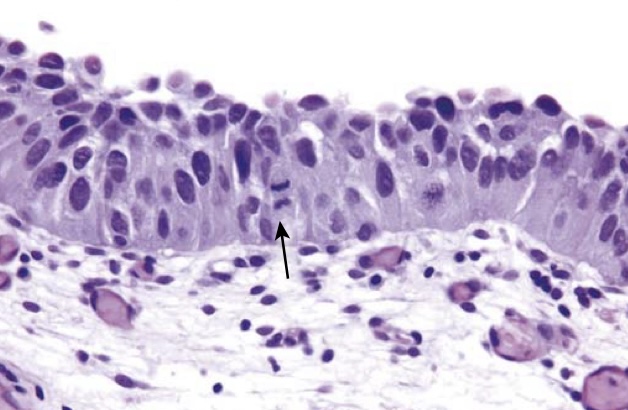
Carcinoma in situ (CIS) with enlarged hyperchromatic nuclei and a mitotic figure (arrow).
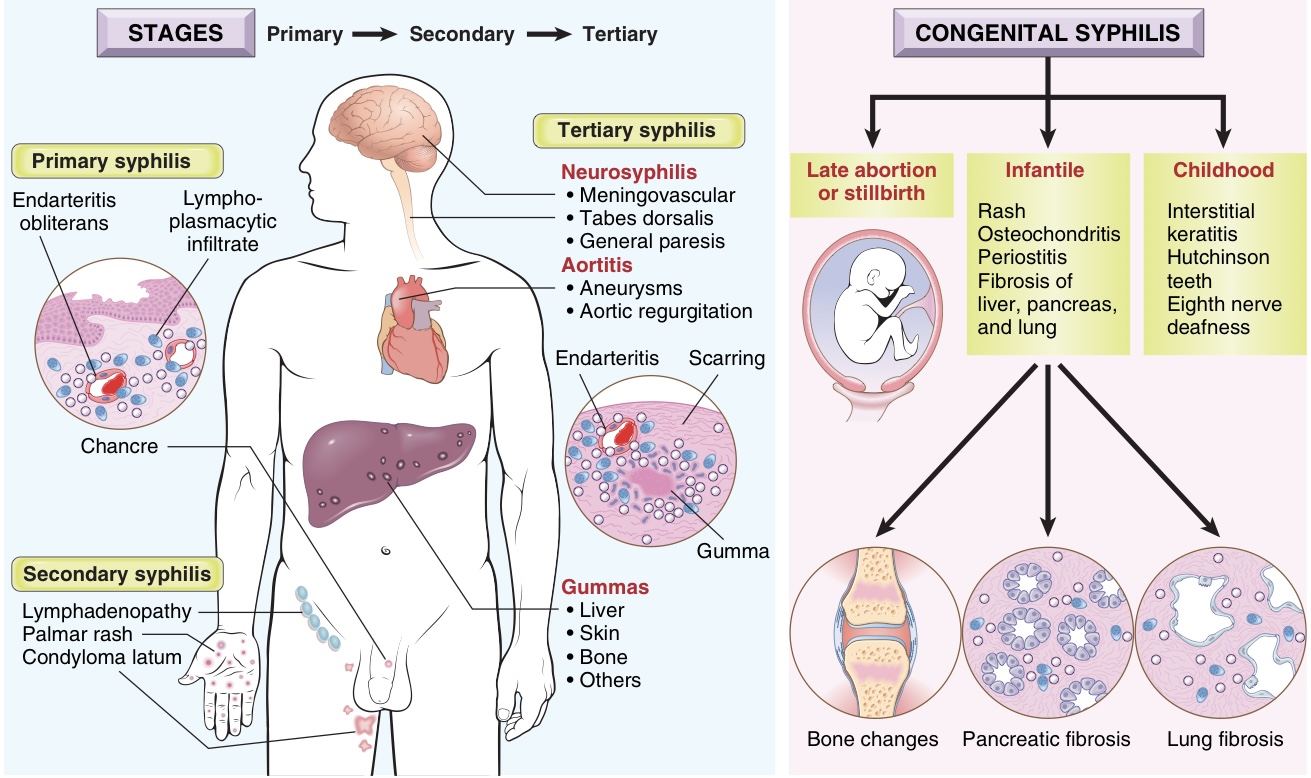
Protean manifestations of syphilis.
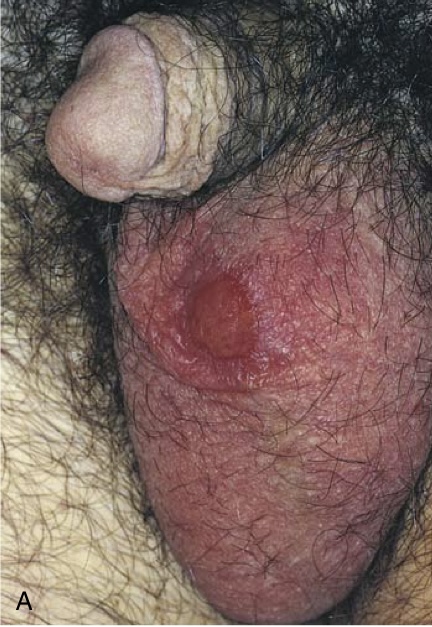
(A) Syphilitic chancre of the scrotum. Such lesions are typically painless despite the presence of ulceration, and they heal spontaneously.
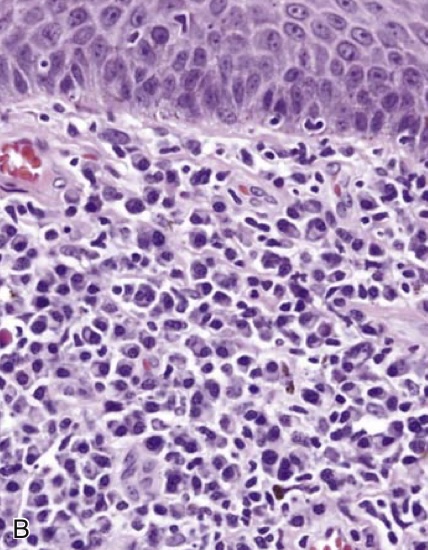
(B) Histologic features of the chancre include a diffuse plasma cell infiltrate beneath squamous epithelium of skin.
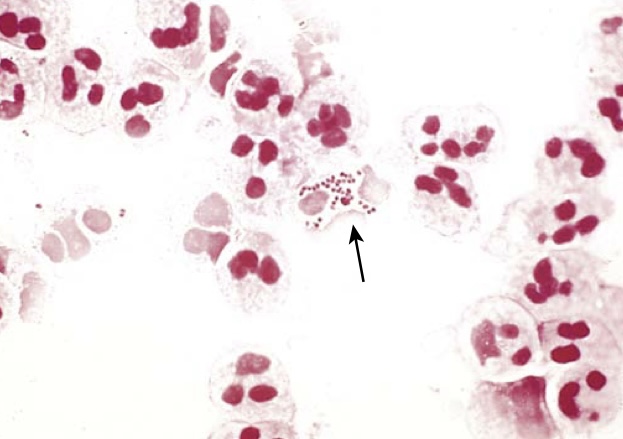
Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Gram stain of urethral discharge demonstrates characteristic gram-negative, intracellular diplococci (arrow).
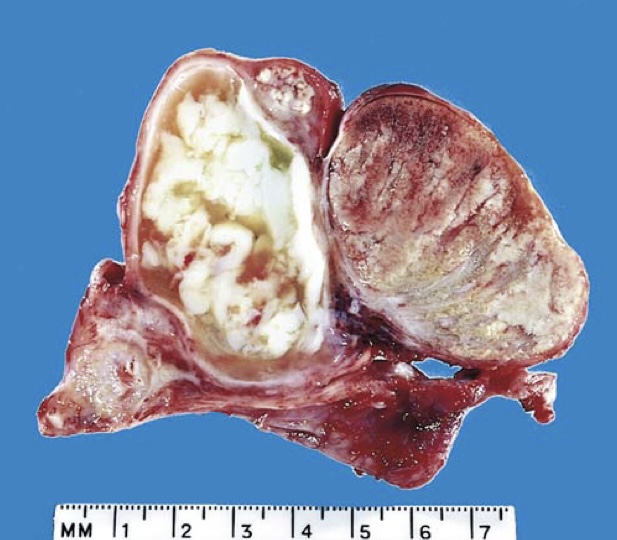
Acute epididymitis caused by gonococcal infection. The epididymis is involved by an abscess. Normal testis is seen on the right.
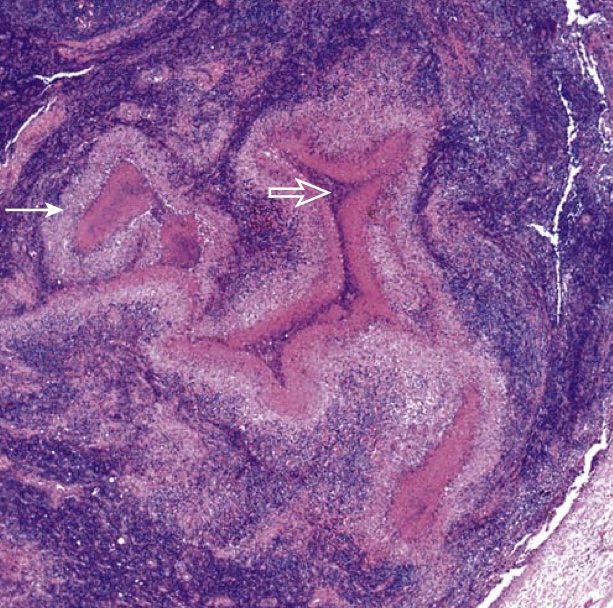
Lymph node involved by lymphogranuloma venereum shows stellate granulomas with central necrosis (thick arrow) surrounded by palisading histiocytes (thin arrow).
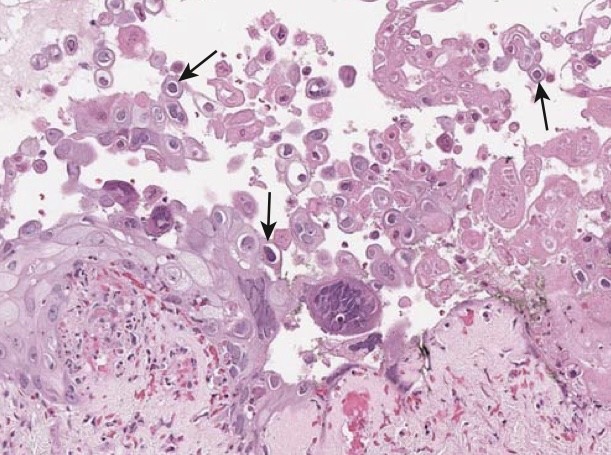
Herpes simplex. This biopsy shows an intraepithelial vesicle with necrotic cellular debris, abundant Cowdry-type A bodies (purple intranuclear inclusions surrounded by a halo, arrows) and multinucleate cells with nuclear molding, all of which are characteristic findings of herpes simplex virus infection.
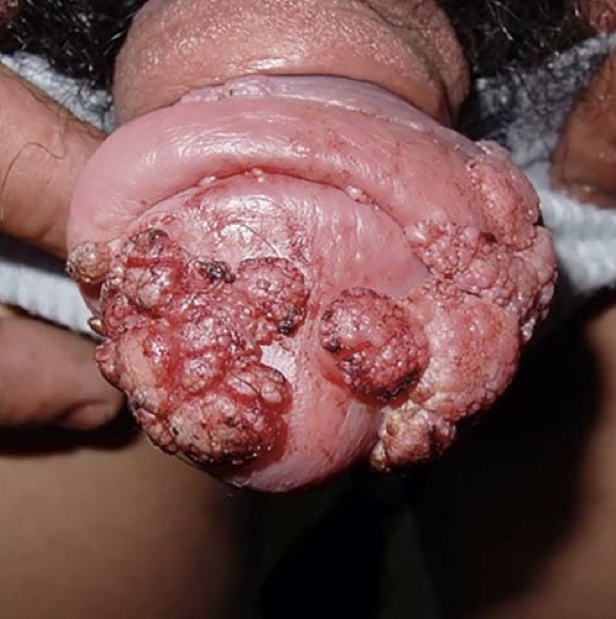
Condyloma acuminatum. Multiple condylomatous lesions involve the glans, coronal sulcus, and foreskin.