Infant Reflexes : Position /stimulus/ Reaction
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
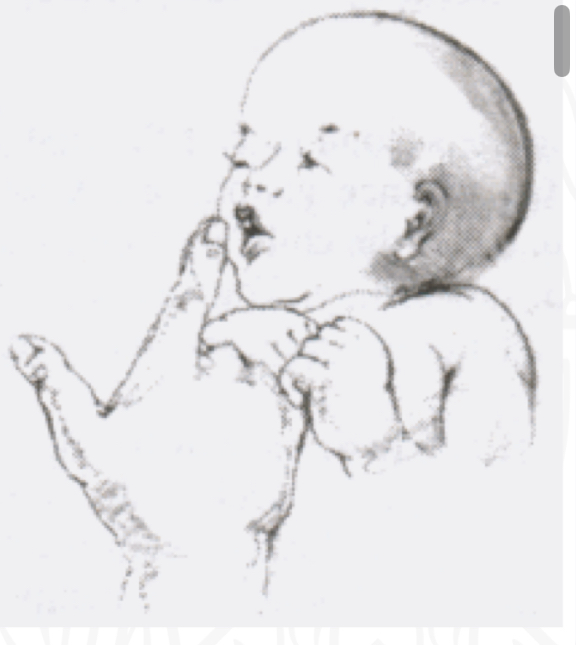
What is the stimulus for Rooting?
Stoke cheek/lip
What is the starting position for Rooting?
Supine, head mid-position
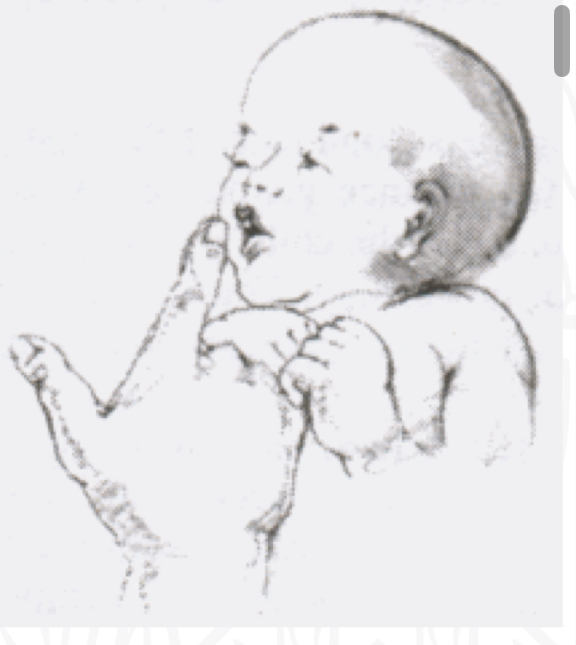
ID reflex:
Rooting
What is the reaction for Rooting?
Head turns towards stimulated side
Seeking with mouth
Why is Rooting reflex important?
Locating food source for survival
what is the position of Suck-swallow reflex?
Supine, head mid-position
What is the stimulus for Suck-Swallow reflex?
Nipple/finger inserted into infant’s mouth
Lips are tougher
What is the reaction for Suck-swallow reflex
Sucks vigorously and rhythmically
Why is Suck-swallow reflex important?
Feeding and nutrient intake
What is the Starting position for Palmar Grasp reflex?
Supine, head in mid-postion
What is the stimulus for Palmar Grasp Relfex?
Pressure to palm
What is reaction for Palmer Grasp reflex?
Finger flexion, reflexive grasp
What is palmer grasp reflex important
Tactile stimulation to palm
Preparation for voluntary grasp
Starting position of Plantar Grasp reflex?
Supine, leg extended
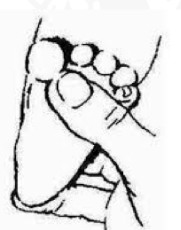
ID reflex
Plantar grasp
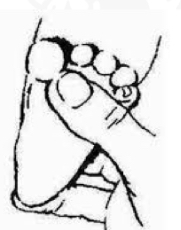
ID stimulus
Press finger/object along the metatarsal phalangeal groove of sole of foot
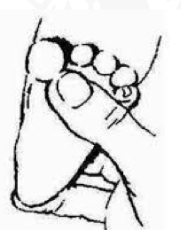
ID reaction
Toes curl into flexion
Why is plantar grasp important?
Tactile discrimination in feet
Preparation for standing and walking
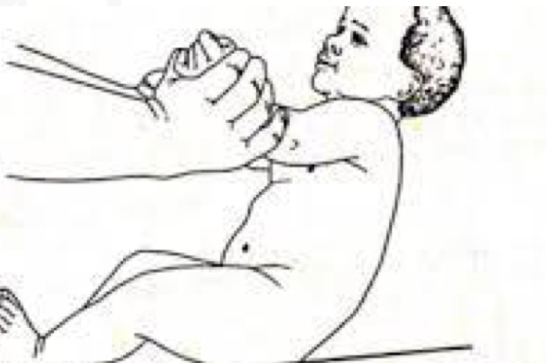
ID reflex:
Traction reflex
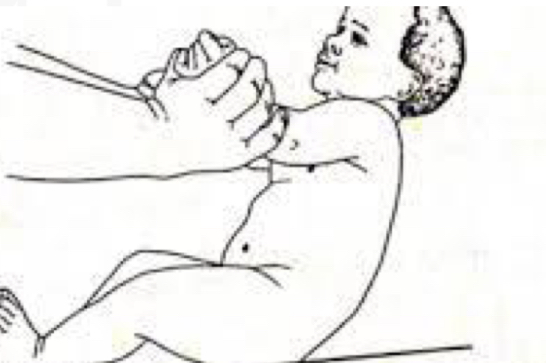
Starting Position:
Supine
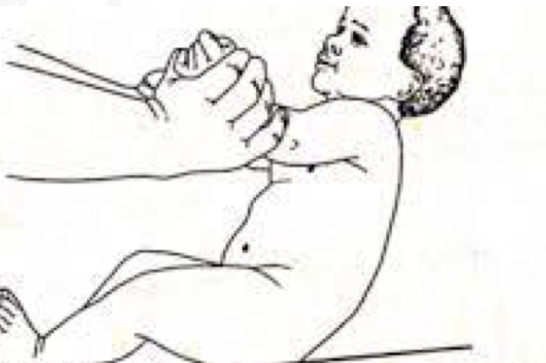
Stimulus:
Grasp infant’s forearms and pull to siT
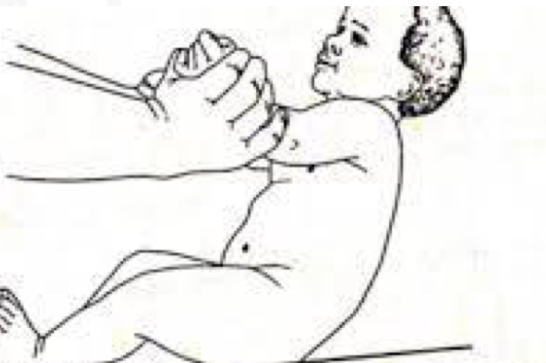
Reaction
Initial head lag followed by complete
Flexion of Upper extremities
Why is Traction reflex important?
Preparation for voluntary control of grasping
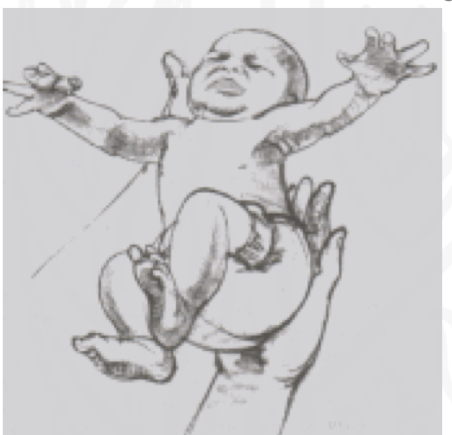
ID reflex:
Moro (Startle)
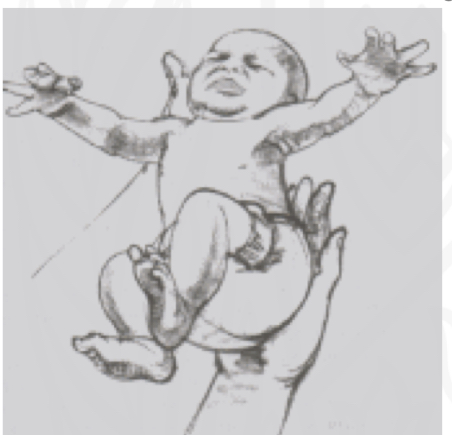
Starting position:
place infant a semi-reclined position
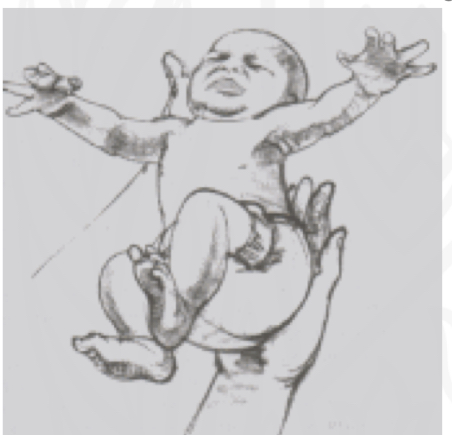
Stimulus:
Rapid postural change: sensation of falling
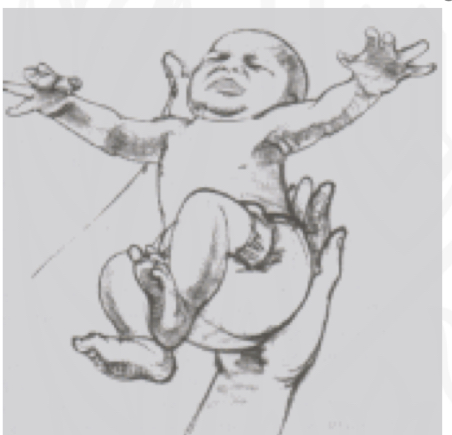
Reaction
Immediate extension and abduction of arms, axgtension and abduction of fingers, and arching of back; followed by flexion and Adduction
Why is Moro(Startle) reflex impotant/
“Alarm” system triggered by sudden loss of support
Starting position of Galant reflex
Prone suspension
Stimulus of Galant relfex
Hold infant in prone; stroke along one side of spine
Reaction of Galant reflex
Lateral trunk flexion on stimulated side
Why is Galant reflex important
Facilitates trunk control and stabilzation
Preparation for future crawling and creeping
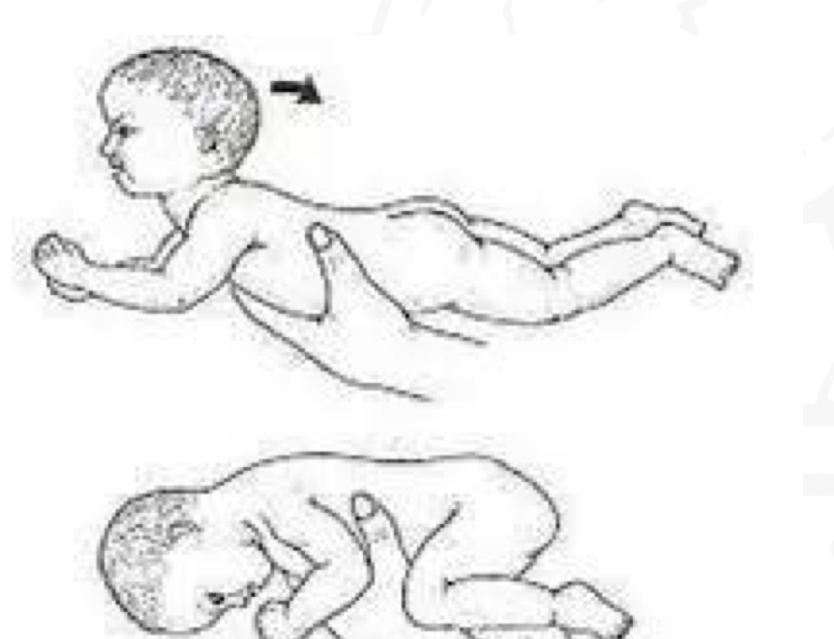
ID reflex:
TLR (prone)
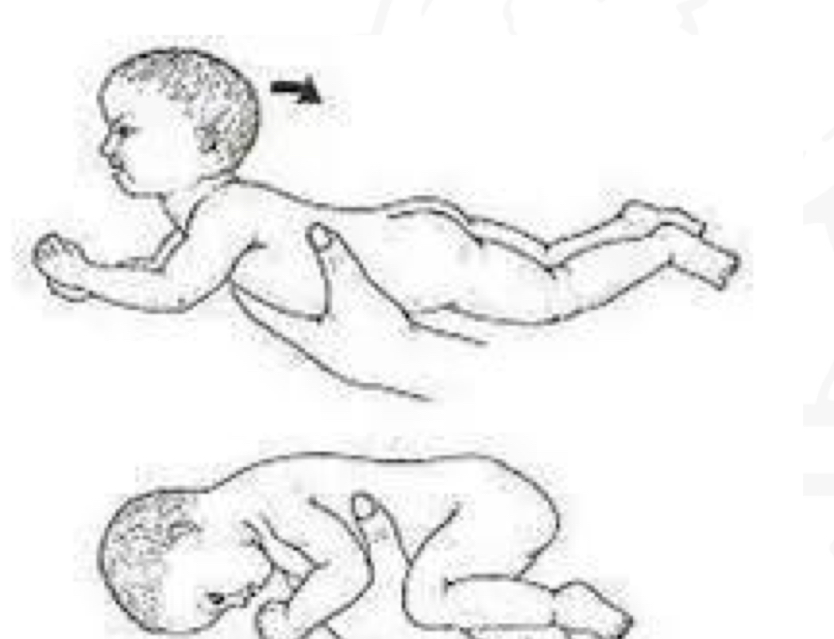
Starting position
Prone
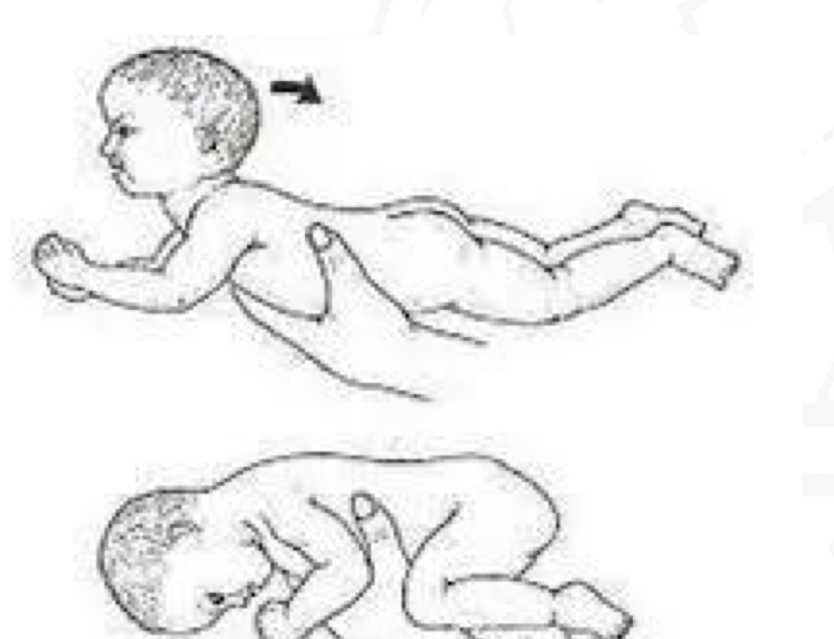
Stimulus
Placing infant in prone
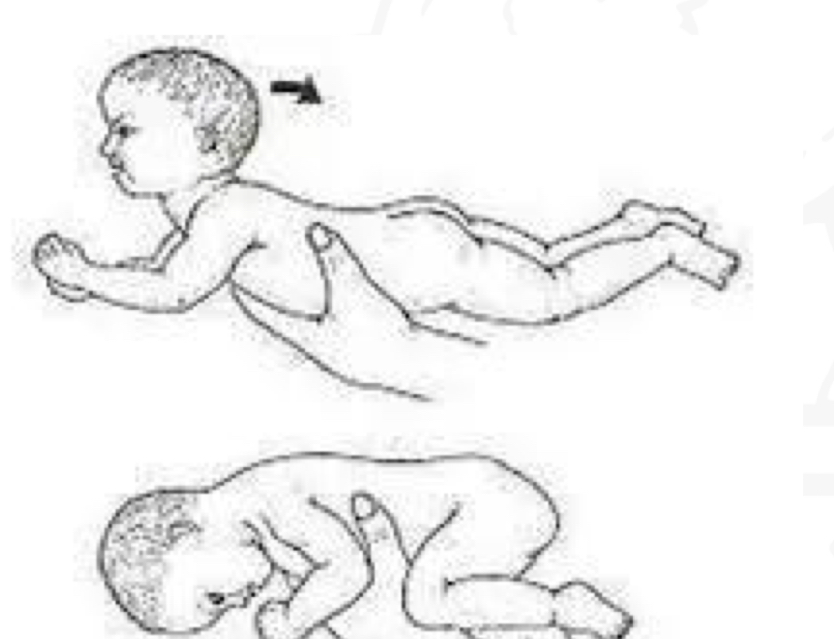
Reaction
Into flexor tone
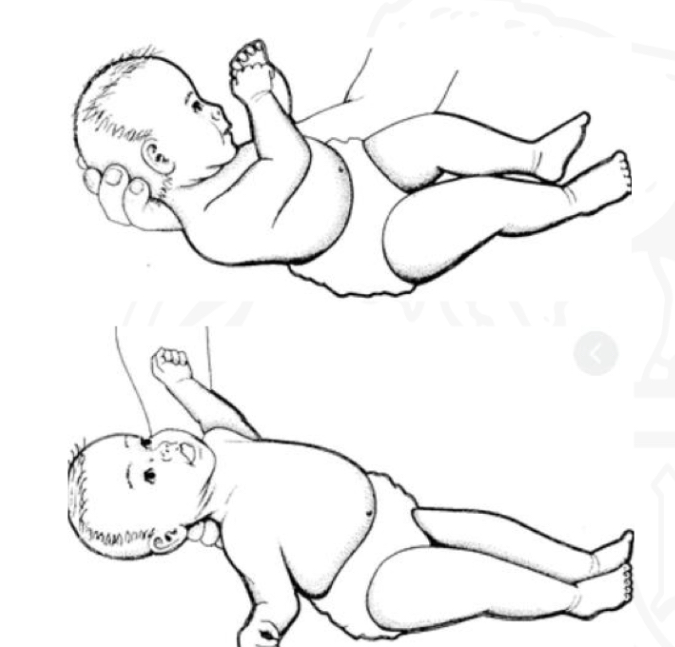
ID reflex
TLR (supine)
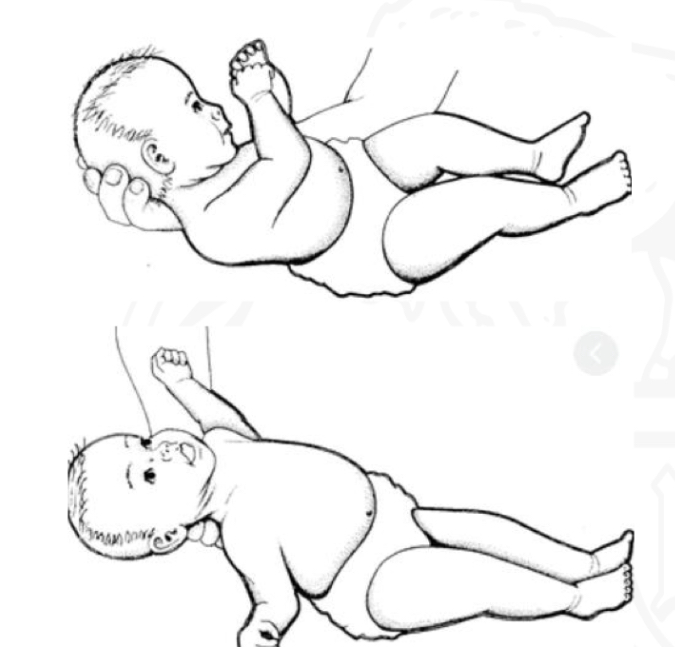
Starting position
Supine
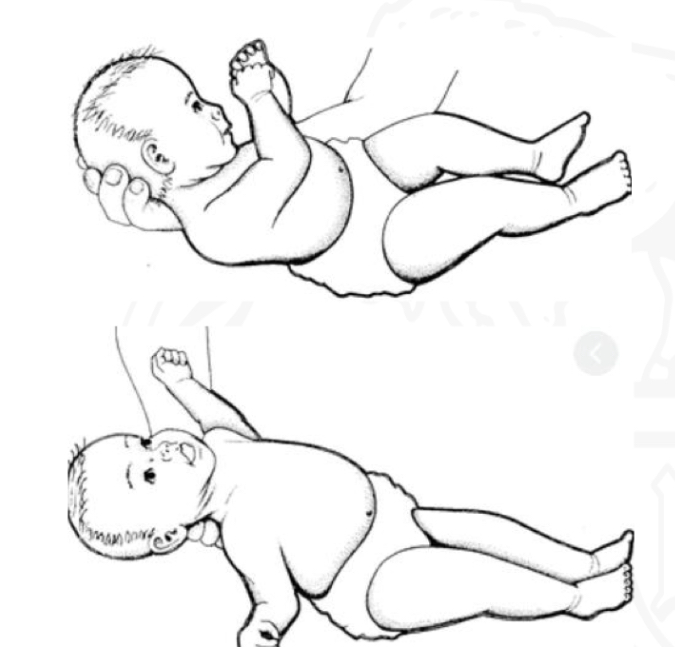
Stimulus
Placing infant in supine
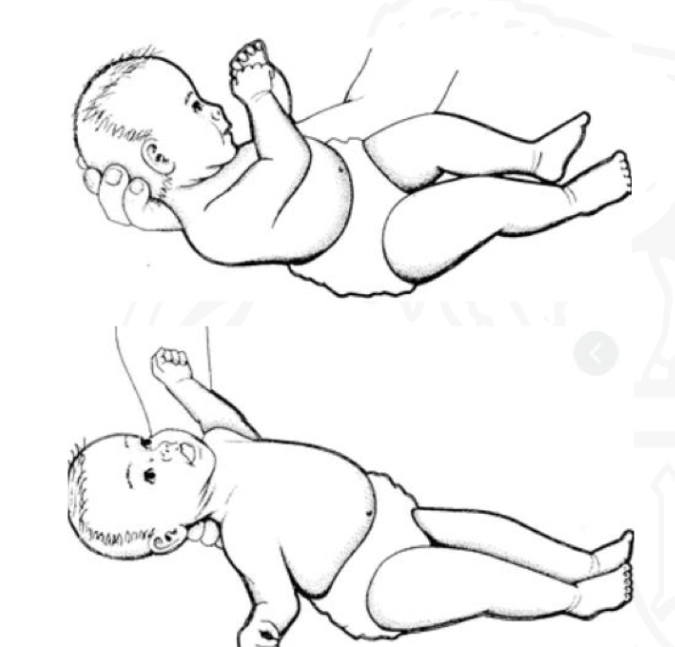
Reaction
Extensor tone
Why is TLR (prone and supine) important?
Preparation for voluntary muscle control needed for functional mobility
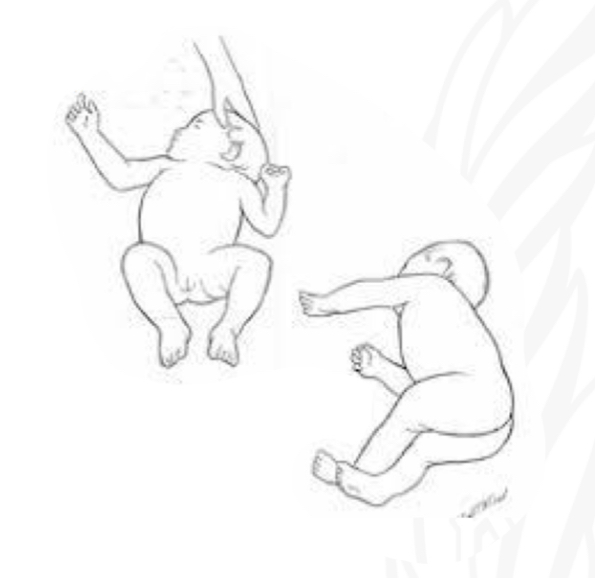

ID reflex
Neonatal neck righting
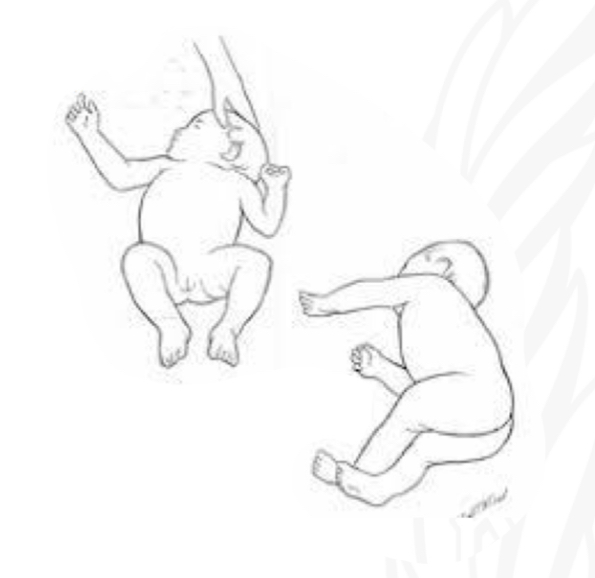

Starting position
Supine
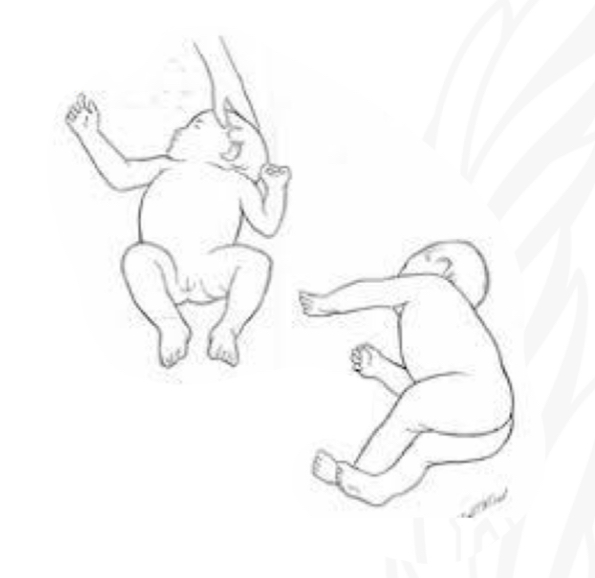

Stimulus
Fully turn/rotate head to one side
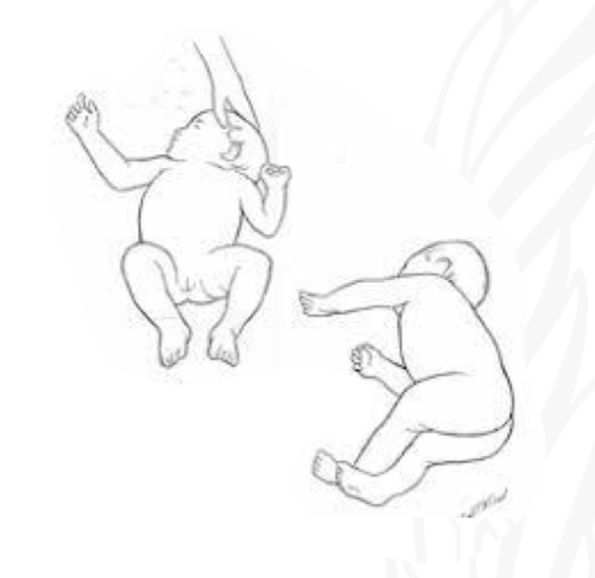

Reaction:
Log rolling: roll entire body with the side of head
No set,meta; roll; lees mature, no trunk rotation
Why is Neonatal neck righting important/
Develop head control
Preparation for crawling initiative rolling
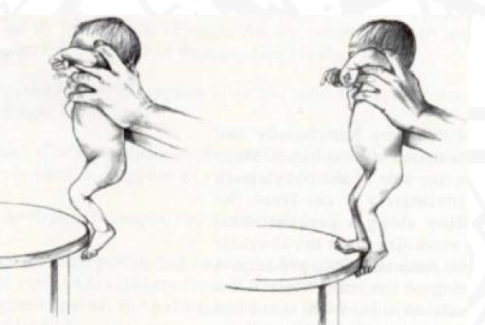
ID reflex
Placing
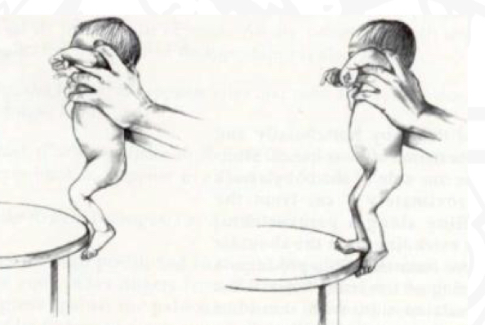
Starting position
Held verification position
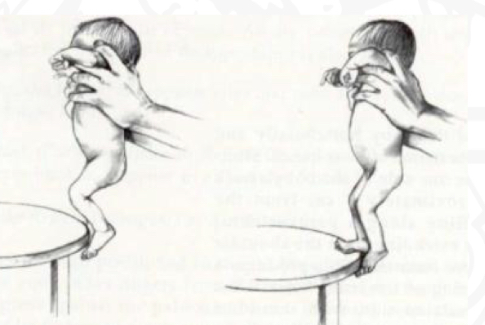
Stimulus
Touch dorsum (upper surface) of foot
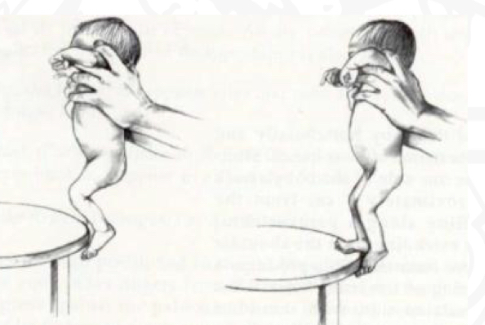
Reaction
Foot rise over the object
Importance of Placing reflex
Preparation for crawling, facilitated by quadruped
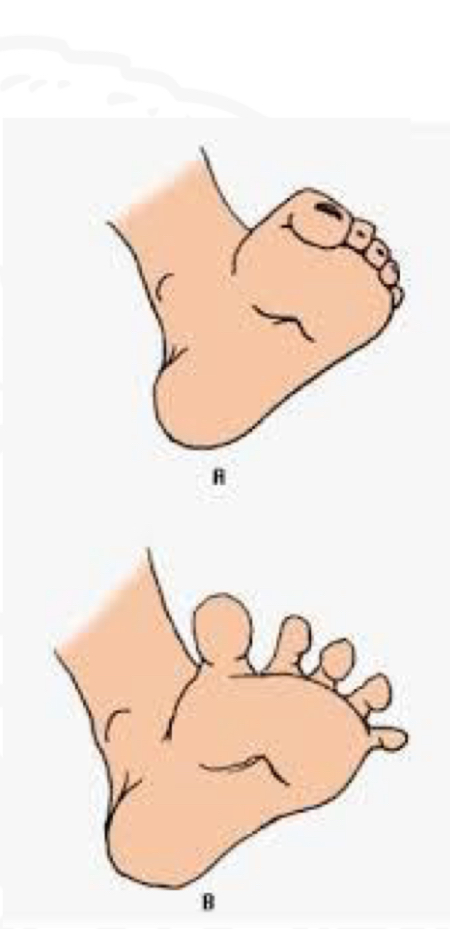
ID reflex
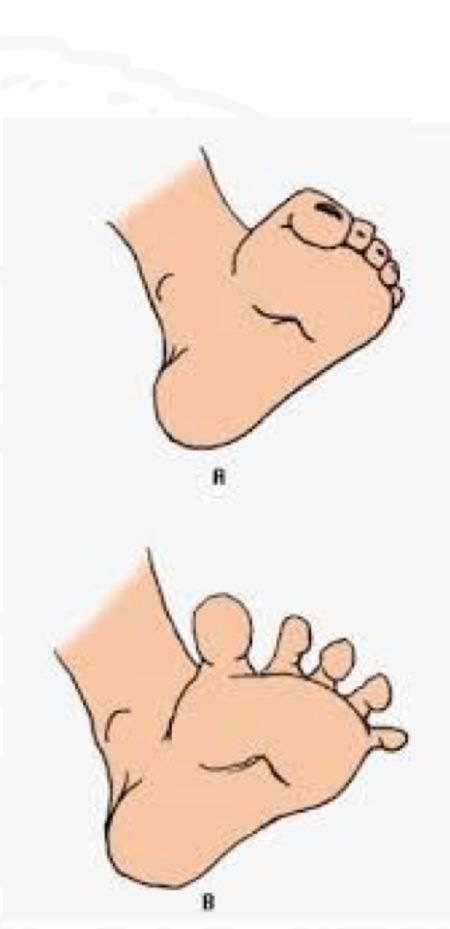
Babinski
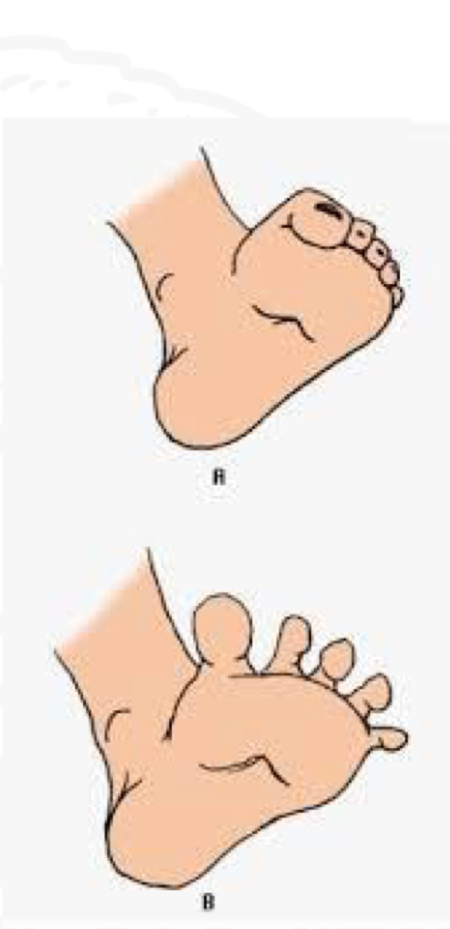
Starting position
Supine, feet extended
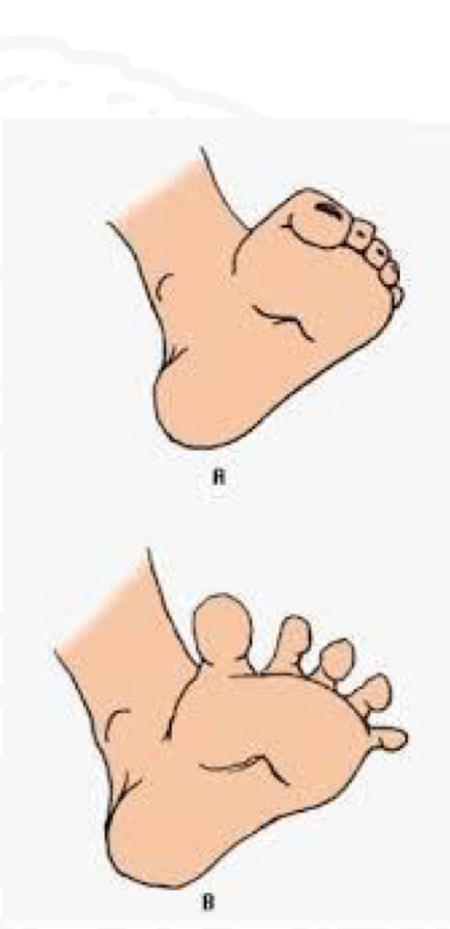
Stimulus
Stoke plantar heel to toes
Reaction
Big toe extends upward
Why is Babinski reflex important
Tactile discrimination in feet
Preparation for standing and walking

ID reflex
ATNR

Starting position
Supine, head in mid-position, arms and legs extended

Stimulus
Rotate head to one side

Reaction
Extension of arm and leg on face side, flexion of arm and leg on opposite side
Importance of ATNR
Attention of head in preparation for eye-hand coordination