apsych c18--treatment of psychological disorders
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
psychodynamic therapy
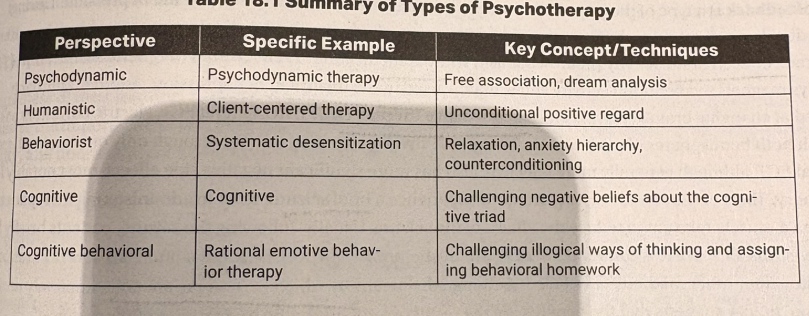
viewing the cause of disorders as unconscious conflicts. thus, they think that you must dig REALLY deep to address a problem
hypnosis—altered state of consciousness to see trauma (not much research to back it up)
free associate—say whatever comes to mind without thinking, see and interpret what a patient says
dream interpretation
humanistic therapy
helping people understand and accept themselves, and thus self-actualize
person-centered, meaning that the therapist provides the client with unconditional positive regard (blanket acceptance) to help them develop healthily
nondirective—encouraging clients to direct the conversation, with the therapist actively listening and saying things like “i see what your feeling about this is ___”
achieving sense of purpose
behavioral therapies
trying to change learned behavior
applied behavior analysis
counterconditioning
exposure therapy
applied behavior analysis
helps with developmental disorders
counterconditioning
unpleasant response is replaced with pleasant one. ex: emily is afraid of eating arugula and cries when she eats it. so, she starts putting arugula in her sandwiches and realizes it tastes good.
systematic desensitization
replacing anxiety with relaxation by constructing a fear hierarchy (pg. 175, in this example the fear is of spiders)
start with fear-related thing that would cause the least anxiety. once that can be accomplished without anxiety (by using relaxation techniques) you move up to the next level

flooding
starting at the scariest scenario, and showing clients they shouldn’t back down from a problem
modeling
watching someone ELSE interact with something you are afraid of and talking about what you saw
cognitive therapies
aka cognitive restructuring, challenging people’s patterns of maladaptive thinking to help them be successful
cognitive behavioral therapies (combo of cognitive and behavioral)
rational emotive behavior therapy (REBT)
questioning both the likelihood that an anxiety would actually happen and if the impact would be so great to show clients that it would not be that bad
ex: emily forgets to wash her hands and started OCDing because she is afraid that she will die from germs. her therapist tells her to try not washing her hands and also explains to her that not washing her hands will probably not be that bad
somatic therapy and different medications
used by biological-oriented psychologists, produce bodily changes
psychoactive medications treat psychological problems
schizophrenia: antipsychotic medications like Thorazine
downside is often tardive dyskinesia (muscle tremors)
depression: antidepressants, monamine oxidase inhibitors, tricyclic antidepressants, serotonin inducers
anxiety: anti-anxiety drugs like Xanax and Valium
bipolar disorder: lithium
biofeedback
a patient is taught to recognize and then control various responses such as breathing and brain activity
transcranial magnetic stimulation—employs magnets to change brain activity
electroconvulsive therapy—shocks brain, causing brief seizure and temporary loss of memory. benefits may be caused by change in the blood flow of your brain
psychosurgery—taking out a part of a person’s brain completely (lobotomy)!! only a last resort
clincal vs. counseling
clinical psychologists (more severe problems)
counseling therapists (less severe problems like family therapy)
summary of types of psychotherapy