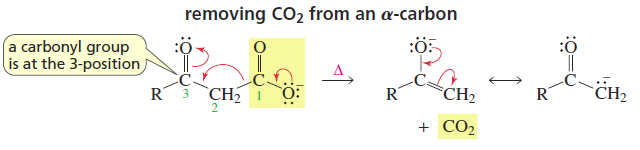CHEM 262 Unit 5 Reactions + Amide/Nitrile BS
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
white men sicken me
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
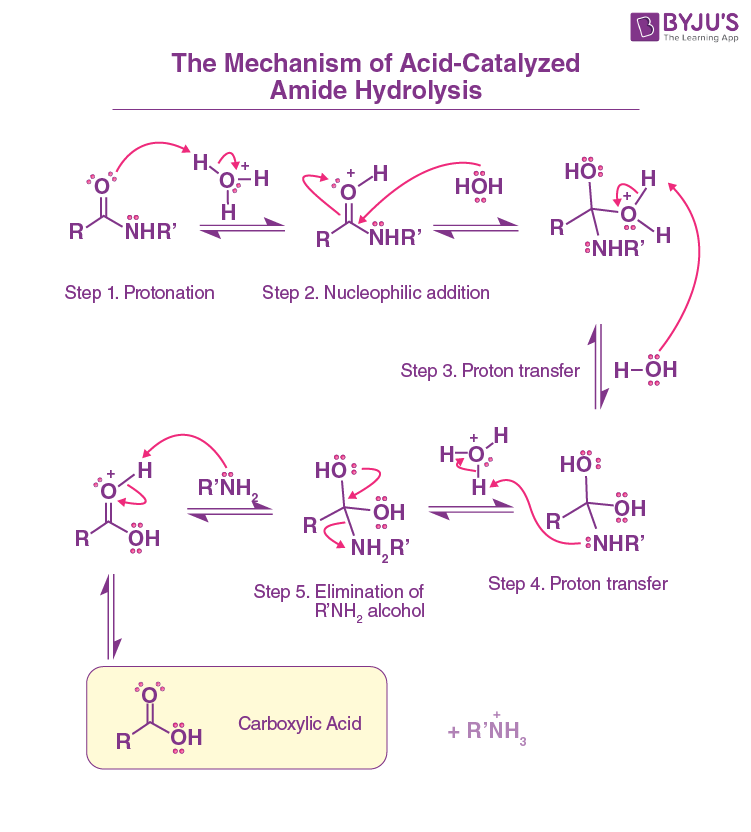
Amide Hydrolysis with Acid
Reactants/Reagents: Strong Acid (cat.), Heat, H2O
Product: Cboxa + Prot. Amine
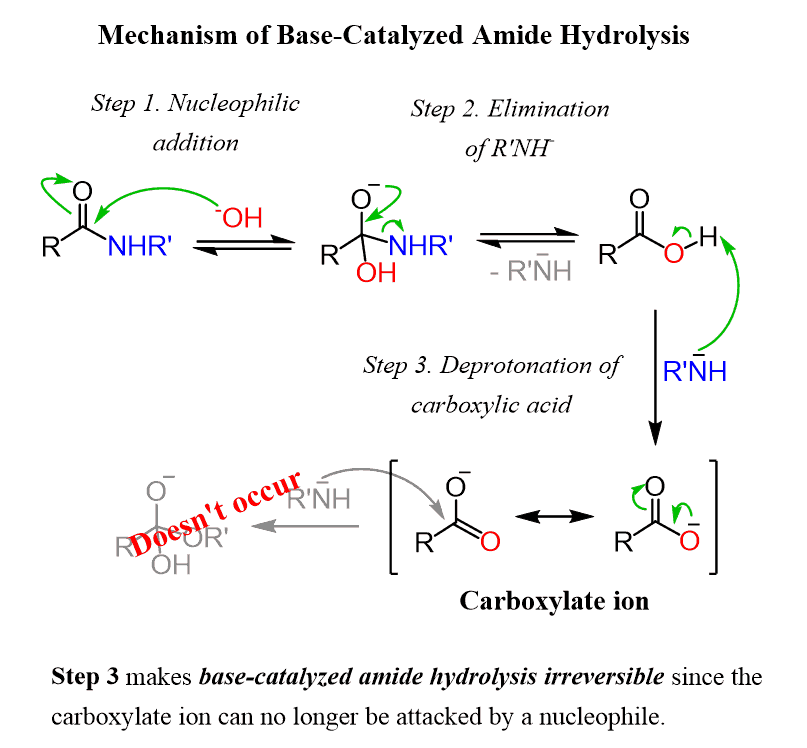
Amide Hydrolysis with Base
Reactants/Reagents: OH- (cat.), Heat, H2O
Products: Cbox + Amine
Amide Alcoholysis
Reactants/Reagents: ROH, strong acid (cat.), heat
Products: Ester + Prot. Amine
Same mech as hydrolysis
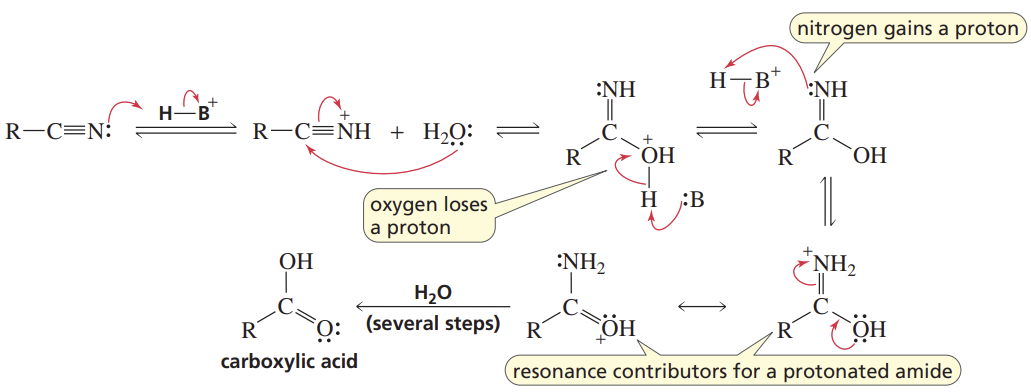
Nitrile Hydrolysis
Reactants/Reagents: Strong acid (cat.), H2O, heat
Products: Cboxa
Nitrile Hydrogenation
Reactants/Reagents: H2, Ramey Nickel
Products: Primary amine
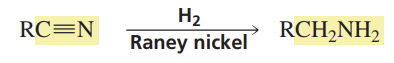
Acid-Cat Keto-Enol Tautomerization
Reactants/Reagents: Keto or Enol, Acid (cat., like H3O+)
Products: Enol or Keto, depending on stabilities
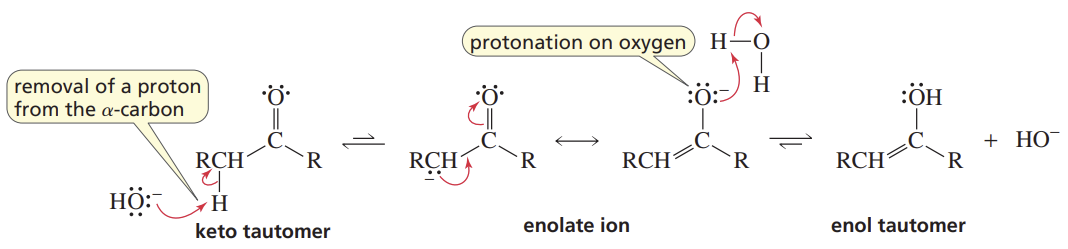
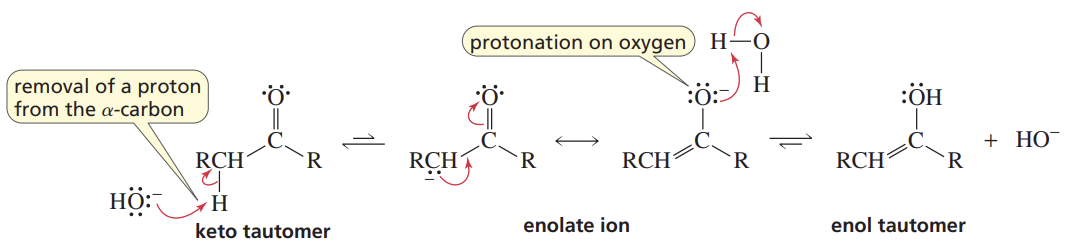
Base-Cat Keto-Enol Tautomerization
Reactants/Reagents: Keto or Enol, Base (cat., like -OH)
Products: Enol or Keto, depending on stabilities
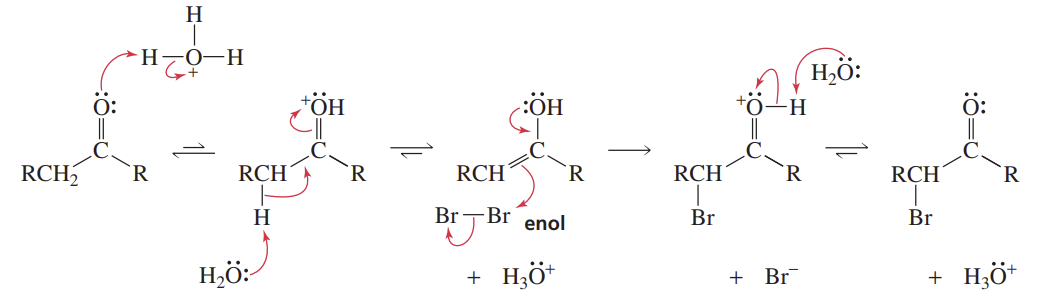
Acid-Cat α-Carbon Halogenation
Reactants/Reagents: Br2/Cl2/I2, acid (cat., like H3O+)
Products: Alde/Keto with ONE α-H replaced w/ halogen
Each successive halogenation occurs slower as EWG dec. cnyl O basicity required for initial prot.
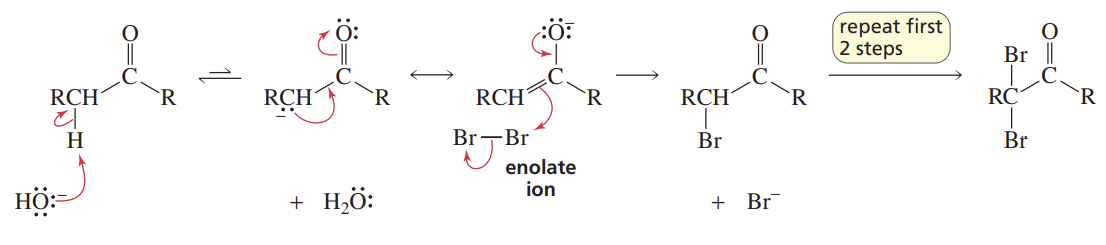
Base-Cat α-Carbon Halogenation
Reactants/Reagents: Br2/Cl2/I2, base (cat., like -OH)
Products: Alde/Keto with ALL α-Carbons replaced w/ halogen
Each successive halogenation occurs faster as EWG inc. α-H basicity
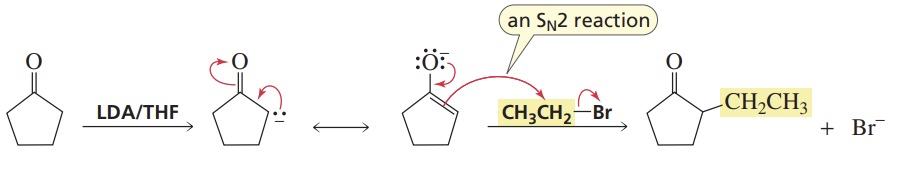
α-Carbon Alkylation
Reactants/Reagents: LDA/THF (for enolate), alkyl halide (RX)
Products: Alkylated alde/keto/ester/nitrile
Asymmetrical reactants will have multiple potential prod — Use 0C for thermo prod, -78C for kinetic prod
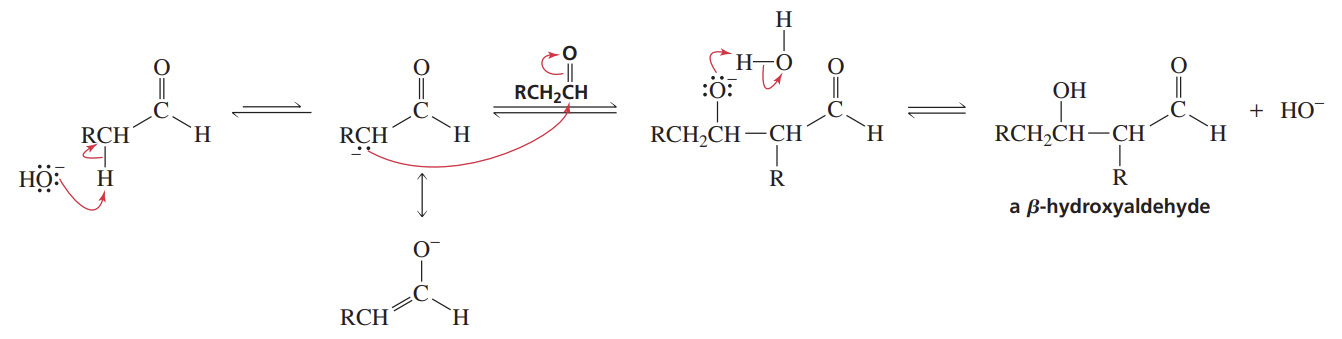
Aldol Additions
Reactants/Reagents: 2 molecules of alde/keto, -OH, H2O
Products: β-hydroxyaldehyde/ketone with nuc C (enolate) linked to og cnyl C
Rev., so prod must be removed while formed (-OH, H2O, heat → og alde/keto)
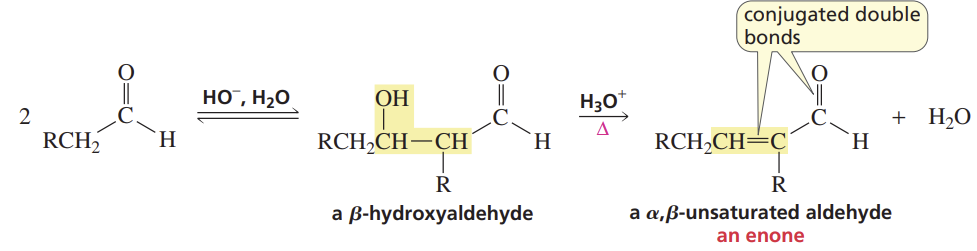
Aldol Dehydration in Acid
Reactants/Reagents: Aldol prod (β-hydroxyaldehyde/ketone), H3O+, heat
Products: α,β-unsaturated alde/keto (enome, OH removed) + H2O
May occur under conditions w/o heat if potential prod = more stable (ex: conj w/ DB, cnyl)!!!
Aldol Dehydration in Base
Reactants/Reagents: Aldol prod (β-hydroxyaldehyde/ketone), -OH
Products: α,β-unsaturated alde/keto (enome, OH removed) + -OH
E1cB rxn that only occurs if carbanion = stabilized by e- delocal
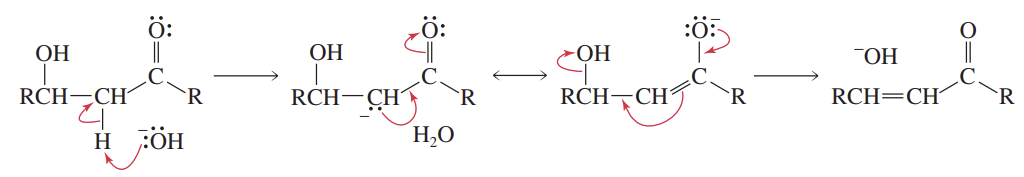
Techniques for Crossed Aldol Additions
Can favor 1 product if 1 reactants =/= have α-H (=/= form enolate)
Start with non-α-H reactant + add other alde/keto slowly w/ HCl — small chance for self-rxn
Can favor 1 product if both reactants have α-H
Rx intended enolate precursor w/ LDA/THF (+ intended temp) + add other alde/keto slowly w/ HCL
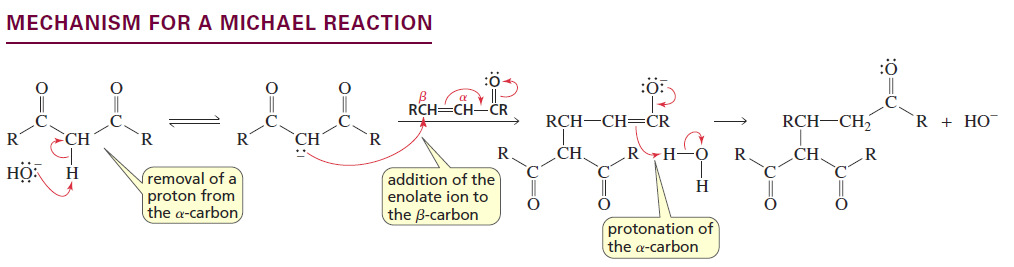
β-Carbon Alkylation (Michael Reaction)
Reactants/Reagents: α,β-unsaturated alde/keto/ester/nitrile + enolate (typically from dicnyl compounds), base (NaOH or NaOR if ester), water
Products: 1,5-dicarbonyl compounds
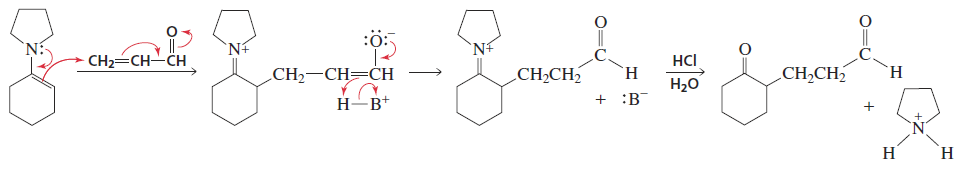
β-Carbon Alkylation (Via Enamine)
Reactants/Reagents: α,β-unsaturated alde/keto/ester/nitrile + enamine (form of enolate), acid (HB), HCl to remove nitrogen ring at end
Products: 1,5-dicarbonyl compounds
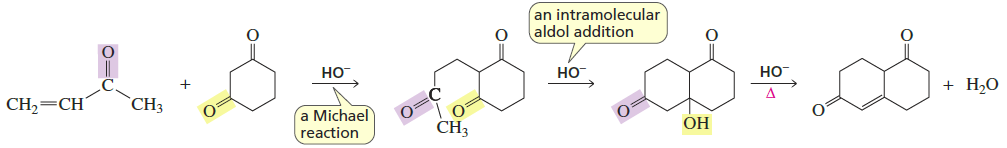
Robinson Annulation
Reactants/Reagents: α,β-unsaturated alde/keto/ester/nitrile + enolate (typically from dicnyl compounds), base (ex: NaOH), heat
Products: α,β-unsaturated cyclic compound + H2O
Michael Reaction → Aldol Condensation → Product
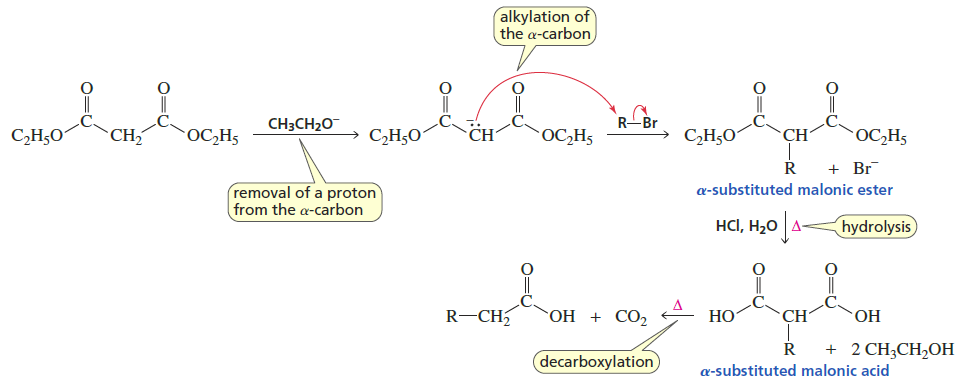
Malonic Ester Synthesis
Reactants/Reagents: Malonic acid diester, base (-OR matching ester), alkyl halide, acid, water, heat
Products: Carboxylic acid with # C of AH + 2 C’s from malonic acid diester, CO2
Enolate Formation → Alkylation → Hydrolysis → Decarboxylation
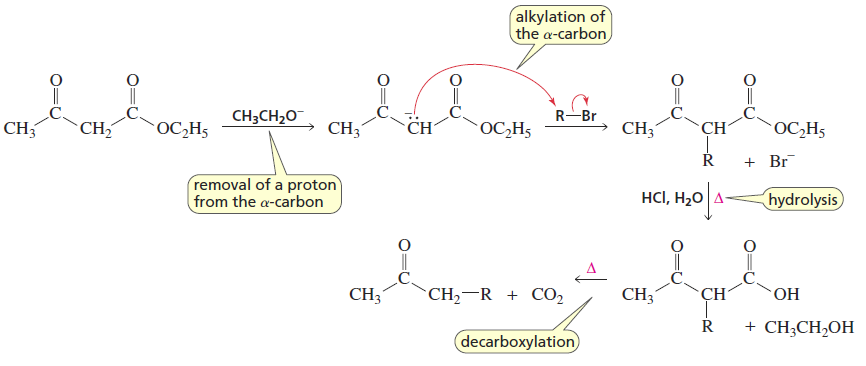
Acetoacetic Ester Synthesis
Reactants/Reagents: Acetoacetic ester, base (-OR matching ester), alkyl halide, acid, water, heat
Products: Methyl ketone with ketone from acetoacetic ester, R group from alkyl halide
Same mech as malonic ester synthesis
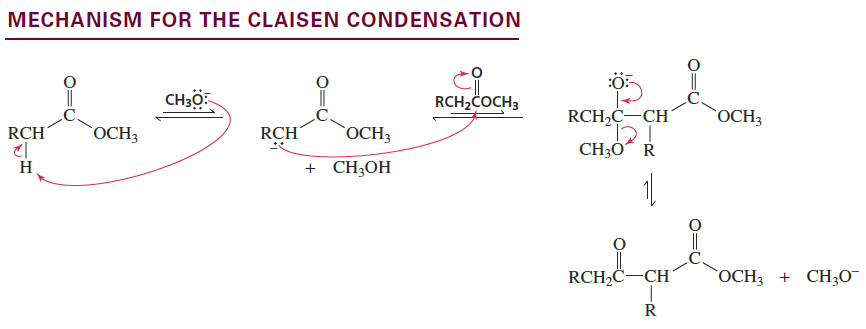
Claisen Condensation
Reactants/Reagents: 2 ester molecules, base (-OR matching ester), acid (ex: HCl)
Products: β-ketoester + alcohol (ROH lost from ester)
Ester that forms enolate requires 2 α-H’s as, after prod forms, deprot. required to prevent reverse reaction (anion more stable than product). Crossed Claisens occur w/ same techniques as Crossed Aldols
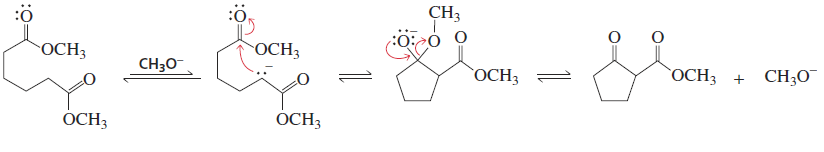
Dieckmann Condensation
Reactants/Reagents:1,6- and 1,7-diesters, base (-OR matching ester), acid (ex: HCl)
Products: 5- and 6-membered dicnyl rings
Intramolecular Claisen condensation
Decarboxylation
Reactants/Reagents: Any compound w/ carboxylate attached to conjugated C/system, heat, acid (if tautomerization favored for intra prot transfer)
Products: Enol/Keto, CO2
Esters can decarboxylate, but need more heat cuz delocal with OR