Module 3: Control and Coordination
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
111 Terms
Dendrites
shorter, more numerous, receive information, converts chemical signals into electrical signals
Cell body
integrates electrical signals; contains the nucleus and other cell organelles
Axon
Single long fibers, conducts electrical signals away from the cell
Chromatophilic substance
Rough ER; transport system
Myelin
insulation surrounding axons
Nodes of Ranvier
gaps in the insulation
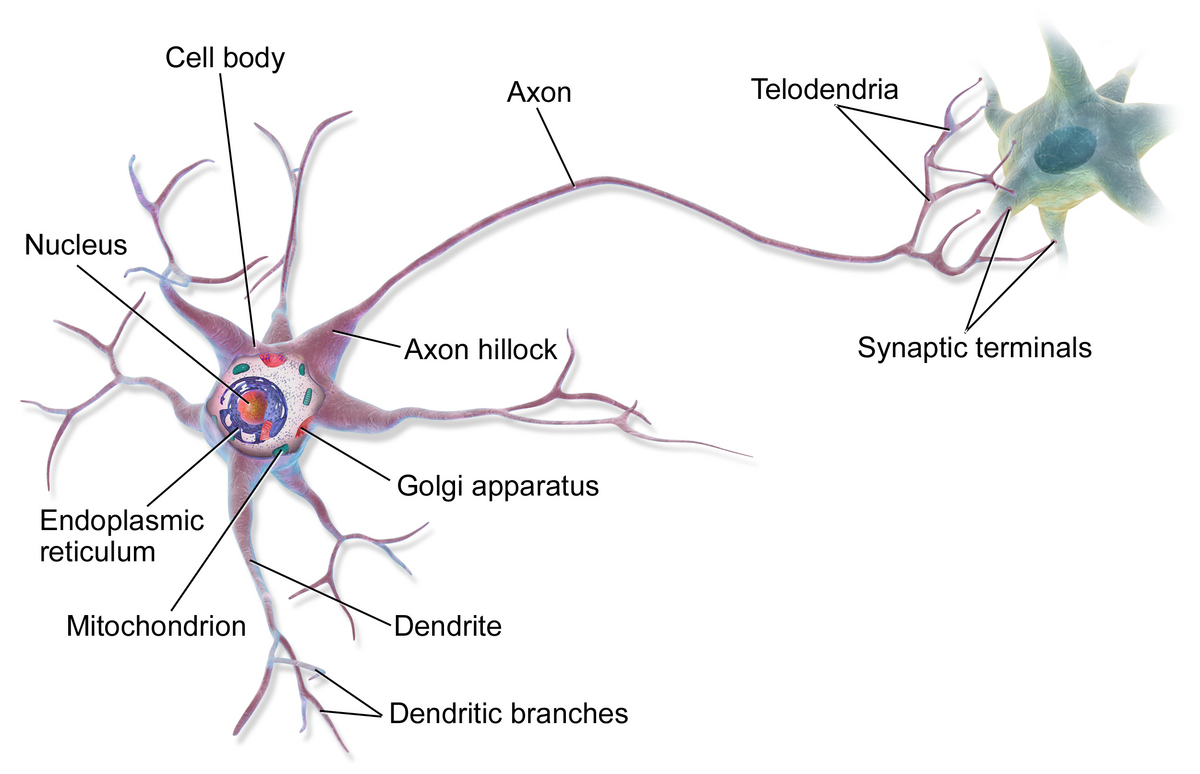
Multipolar neurons
contains the axon and two or more dendrites in the CNS (brain & spinal cord) (motor neurons, most CNS neurons)
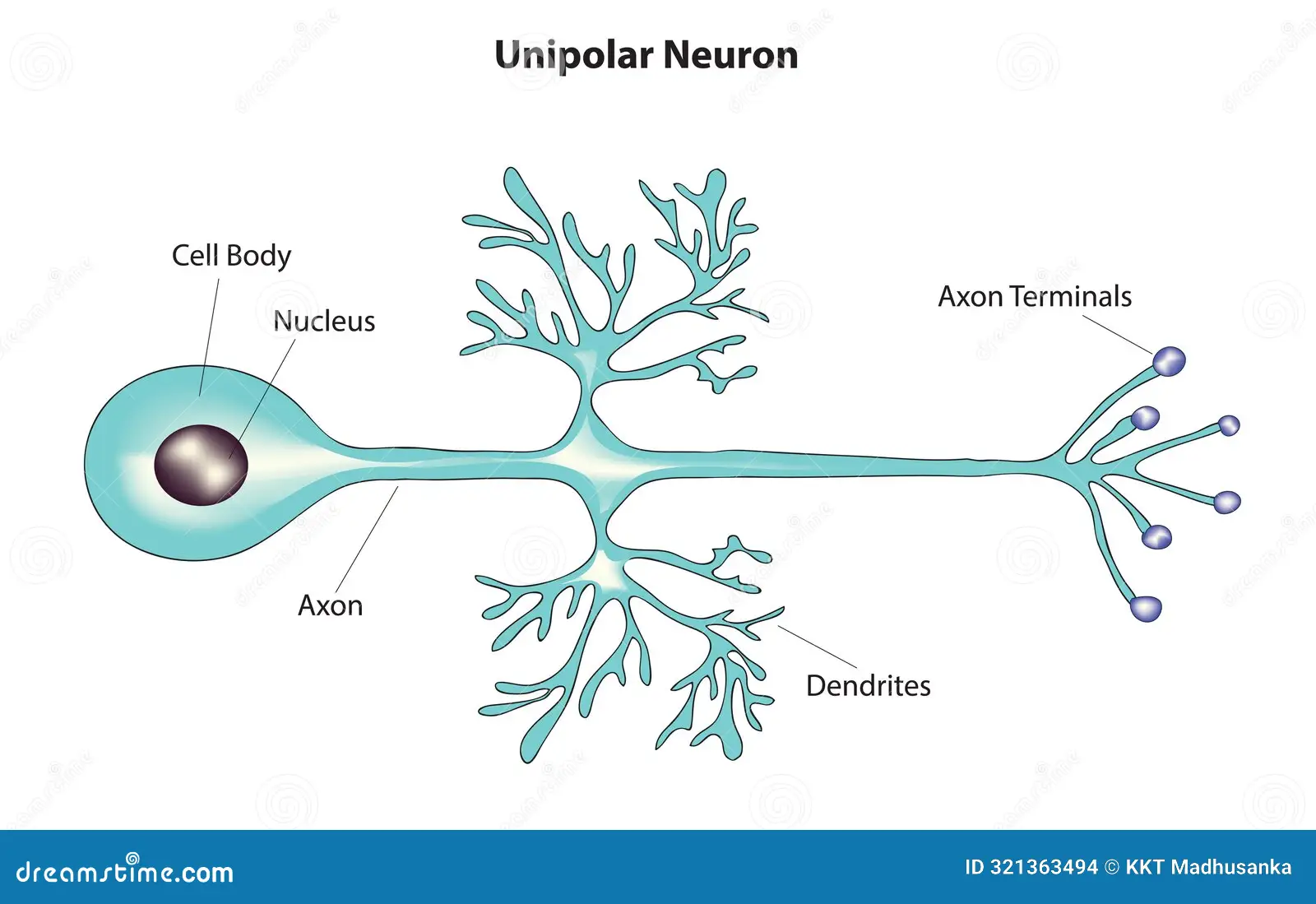
Unipolar neurons
have only one process; have an axon that emerges from the cell body (sensory neurons in PNS)
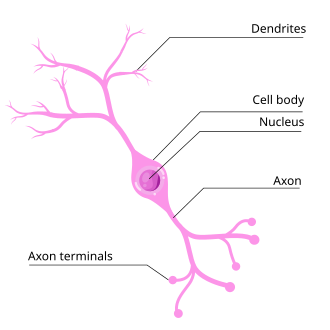
Bipolar neurons
have two processes; one is the axon and one the dendrite (retina, olfactory epithelium)
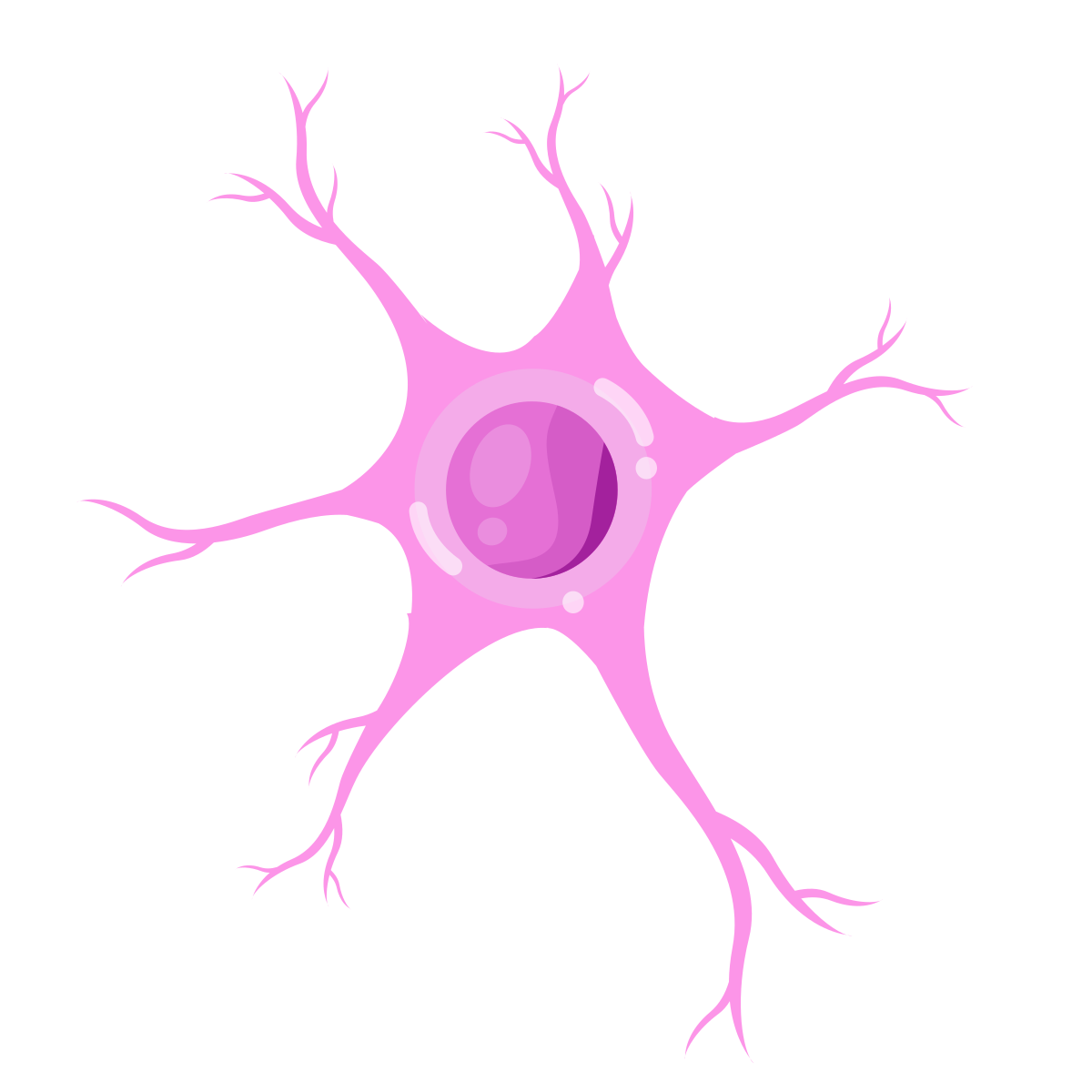
Anaxonic neurons
lack an axon (interneurons in brain)
Sensory (afferent) neurons
receive sensory input from the environment and transmit it to the CNS
Interneurons
facilitates communication between other neurons/determines where information is sent
Motor (efferent) neurons
transmits signals from the CNS to muscles, enabling movement
Graded potentials
wave of electrical excitation proportional to the magnitude of the stimulus that triggers it
Action potentials
all-or-nothing response
Synapses
gaps between junctions of neurons where neurotransmitters are released
Convergence (summation)
Multiple signals merge into a single pathway
Divergence (distribution)
a single neuron branching out to communicate with many other neurons
Inhibition
The process of reducing or preventing a neuron from firing an impulse
Evolutionary pressures related to brain expansion and bipedal locomotion influenced changes in human skull and pelvic anatomy & trade-offs between the skeletal and nervous systems
Larger brains were an advantage for social interactions in unpredictable environment
Narrowing of the pelvis favored delayed fusion of the metopic suture, allowing for massive increase in brain size during early life
Human brains grow rapidly before birth through the first year and into childhood
Neuroglial cells
support, nourish and insulate neurons; they guide neuron development and regulate chemical communication
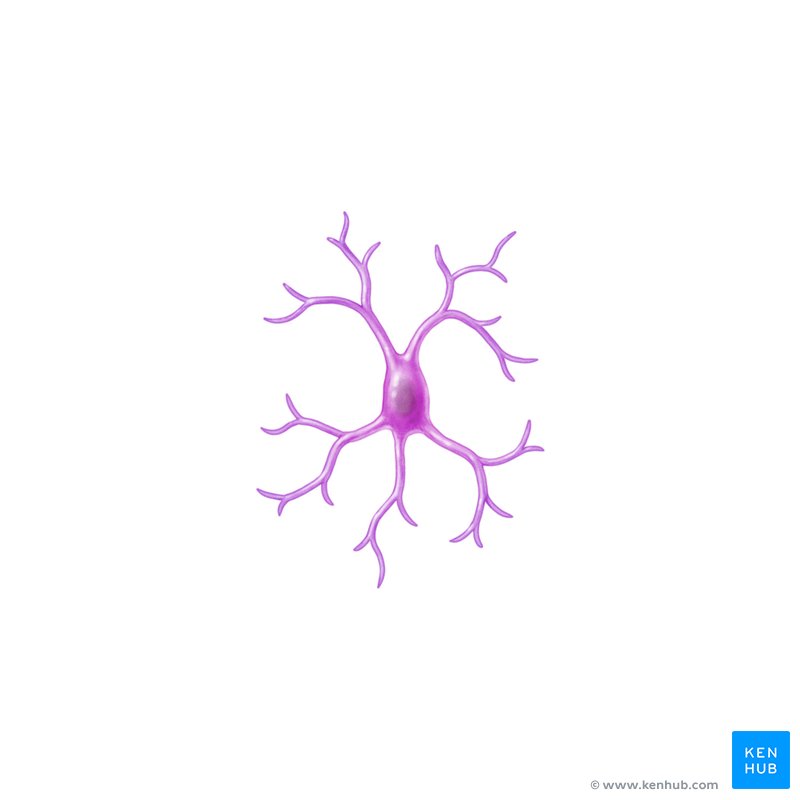
Microglia
ovoid-shaped cells with high branched, narrow cell processes
immune function; digest debris, kills bacteria
Provide protection for the brain and spinal cord
Oligodendrocytes
Make myelin sheath that provides insulation around the axons
Found in the CNS

Astrocyte
Star-shaped glia
Connect blood vessels to neurons; Maintain blood-brain barrier
Nutrient supply
Ependymal cells
Forms membranes around tissues
Line the ventricles of the brain and spinal cord
Assist in producing, monitoring, and circulating CSF
form blood-CSF barrier
Schwaan cells
Form the insulating myelin sheath around the neurons in the PNS
Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
An autoimmune disease where myelin sheath is damaged or demyelination (gaps or loss of myelin sheath)
Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Causes
Conduction can be slowed or blocked causing impaired communication between neurons
Nerves are unable to send or receive signals
Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Symptoms
Weakness or numbness in the limbs
Difficulty walking or coordinating movement
Burning sensations
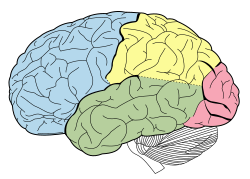
Cerebrum
wrinkly large part of the brain
high mental function, solving problems
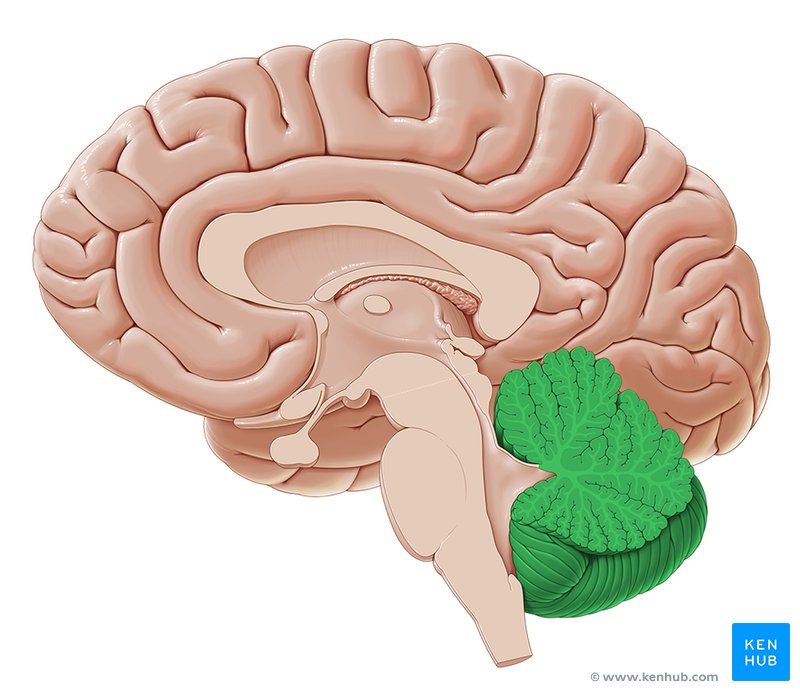
Cerebellum
balance and coordination
white matter within gives it a tree-like appearance (arbor vitae)
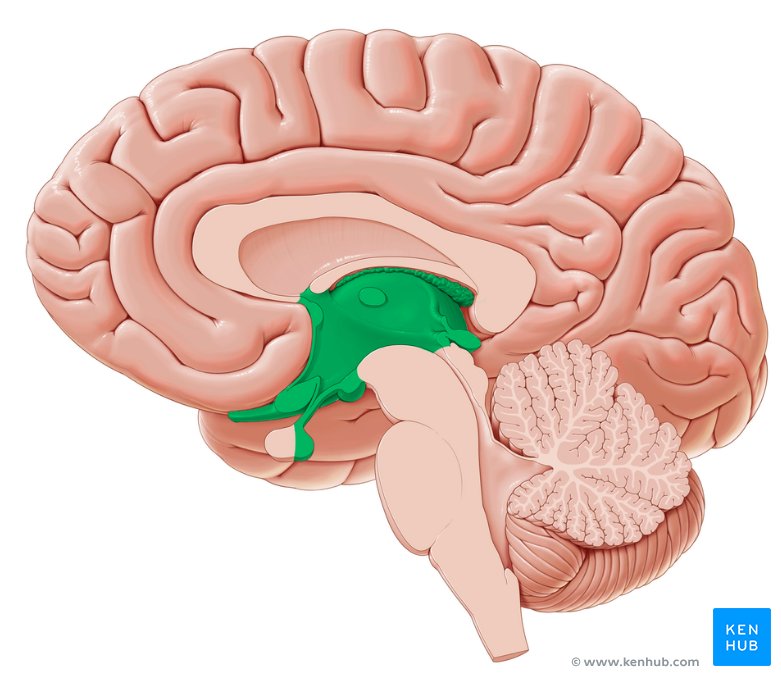
Diencephalon
Primary relay and processing center for sensory information and autonomic control
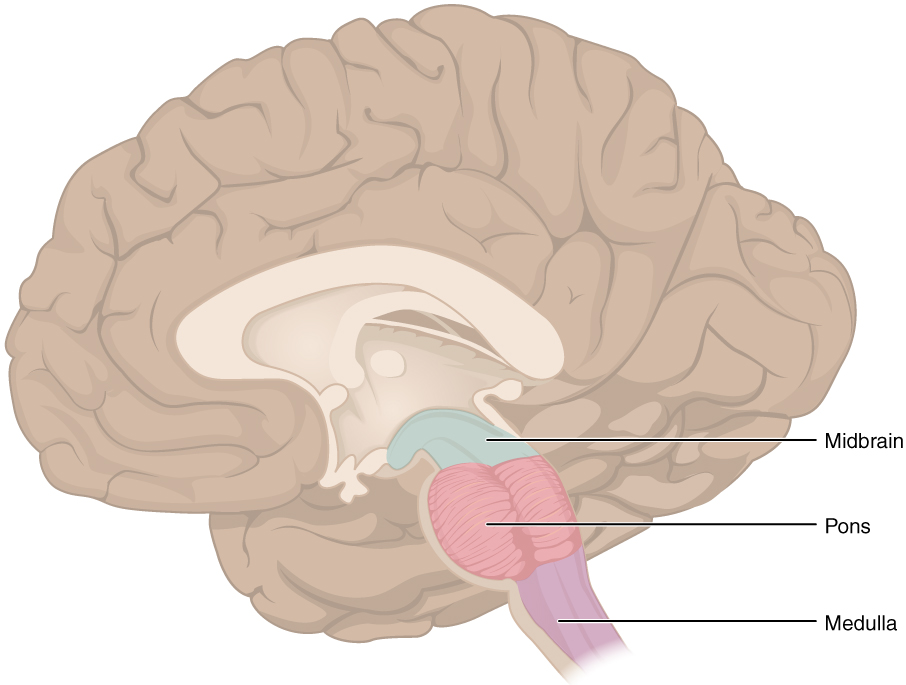
Brainstem
regulates visceral functions
Fissures
deep groove
Sulcus
shallow groove
Gyrus
bumps
Frontal lobe
executive functions; Associated with decision-making, problem-solving, and planning
Parietal lobe
perception, sense-making, math; Processes sensory information like touch, temperature, and pain.
Occipital lobe
Primary region for visual processing
Temporal lobe
Important for auditory processing and memory.
Corpus callosum
connects the two hemispheres
The left side of the brain controls the right side of the body!
Thalamus
relays sensory and motor information from various locations to the cerebral cortex; regulates consciousness, sleep, and alertness
Hypothalamus
maintain homeostasis by controlling blood pressure, thermoregulation, and our sleep-wake cycle
Midbrain
visual reflexes, eye movements
Pons
relay sensory information
Medulla
heart, respiration, blood pressure
Limbic system
behavior and emotional response
amygdala and hippocampus
Amygdala
storage of memories associated with emotion
Also associated with fear response and aggression
Hippocampus
(“sea horse”)
storage and retrieval of memories
Cervical enlargement
(C5 - T1)
Increased number of nerves needed to supply the upper limbs
Lumbar enlargement
(T11 - L2)
Widened area of the spinal cord that gives attachment to the nerves which supply the lower limbs
Conus medullaris
Cone shaped terminal portion of the spinal cord
Provide all motor and sensory innervation to lower limbs
Cauda equina
Send and receive messages between the lower limbs and the pelvic organs
Grey matter
made up of the cell bodies of neurons
White matter
consists of axons
Dorsal horn (spinal cord)
contains neurons that receive somatosensory information from the body
Ventral horn (Cross-sectional of spinal cord)
contains motor neurons that exit the spinal cord to innervate skeletal muscle
Lateral horn (spinal cord)
contains neurons that innervate visceral and pelvic organs
Alzheimer’s disease
a neurodegenerative disease and is the most common form of dementia
Alzheimer’s disease causes
Amyloid proteins build up in brain cells and form plaques.
Another protein, tau, twists into tangles.
These plaques and tangles eventually lead to the death of cells because they prevent the cells from sending signals and carrying out their normal function.
The hippocampus is one of the first areas affected
Alzheimer’s disease symptoms
forgetting words or names, misplacing objects, trouble planning/organizing, trouble with simple tasks
Cranial nerve I
Olfactory
Sensory
Sense of smell
Cranial nerve II
Optic
Sensory
Transmits information from the eye’s retina. Vision.
Cranial nerve III
Oculomotor
Motor
Controls most of the muscles of the eye (extrinsic and intrinsic) Moves the eyeball and constricts pupils
Cranial nerve IV
Trochlear
Motor
Innervates an extrinsic eye muscle, eyelid. Moves eye downward and outward.
Cranial nerve V
Trigeminal
Sensory and motor
The main sensory nerve of the face. It controls chewing muscles.
Cranial nerve VI
Abducens
Motor
Controls one of the eye muscles (lateral rectus). Moves eye outward.
Cranial nerve VII
Facial
Sensory and motor
Innervates the muscles of facial expression
Controls taste (front 2/3 of tongue)
Cranial nerve VIII
Vestibulocochlear
Sensory
Hearing and balance (also called auditory nerve)
Cranial nerve IX
Glossopharyngeal
Sensory and motor
Taste, swallowing, speech, and salivation
Cranial nerve X
Vagus
Sensory and motor
Innervates all of the organs in the thoracic and abdominal cavities
Cranial nerve XI
Accessory
Motor
It just supplies the shoulder muscles
Cranial nerve XII
Hypoglossal
Motor
Speech, swallowing, and chewing
Rami
branches of a spinal nerve
Ventral rami (Spinal Nerve)
(larger) innervate the ventral and lateral portions of the trunk, and limbs
Dorsal Rami (Spinal Nerve)
(smaller) innervate deep muscle and skin of the back
Dorsal ganglion (spinal nerve)
contain only sensory cell bodies only
Dorsal root (Spinal Nerve)
contain sensory axons only
Ventral root (spinal nerve)
contain motor axons only
Plexuses
main portions of the spinal nerves combine to form complex networks
Cervical plexus
most branches are cutaneous nerves that supply sensory impulses from the skin of the neck, ear, back of the head and shoulders
Phrenic nerve
Phrenic nerve
sole motor nerve supply to the diaphragm for breathing
Brachial Plexuses
Suprascapular nerve
Axillary nerve
Radial nerve
Median nerve
Ulnar nerve
Lumbar plexus
Femoral nerve
Obturator nerve
Sacral plexus
Sciatic nerve
Pudendal nerve
Sciatic nerve
supplies the entire lower limb (leg) except anteromedial thigh
Shingles
a viral infection that causes a painful rash
Shingles Causes
It is caused by the varicella-zoster virus (VZV), the same virus that causes chicken pox.
Shingles Symptoms
Pain, burning, tingling, or numbness in a localized area, usually on one side of the body or face. Red bumps that appear in a cluster or line.
Shingles relationship to cranial and spinal nerves
After primary infection (chickenpox), the virus lies dormant in neurons, including the cranial nerve ganglia and dorsal root ganglia. Once reactivated, the virus follows a dermatome, an area of the skin where the sensation is supplied by one spinal nerve.
The trigeminal nerve (V), facial nerve (VII), and vestibulocochlear nerve (VIII) are frequently involved in shingles cases.
Meninges
membranes located between bone and soft tissue
Dura mater
Arachnoid
Pia mater
Cerebral spinal fluid (CSF)
clear liquid surrounding brain and spinal cord; cushions the brain; can be used in diagnostics with a lumbar puncture It protects the brain by acting as a shock absorber.
Pituitary gland
Location: Brain
Function: Releases hormones that control other glands
Thyroid gland
Location: Throat
Function: Releases hormones that help control metabolism
Parathyroid Gland
Location: Throat
Function: Releases hormones that control level of calcium in blood
Adrenal Gland
Location: Above kidneys
Function: Releases hormones that control stress response
Pineal Gland
Location: Brain
Function: Releases hormones that control sleep-wake cycles
Pancreas
Location: Under stomach
Function: Releases hormones to maintain blood sugar
Testes
Location: Lower abdomen/groin
Function: Release and make sex hormones
Ovaries
Location: Lower abdomen/groin
Function: Release and make sex hormones that control menstrual cycle and pregnancy