Histo 11 | Lymphoid & Immune System
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
What is lymphoid tissue, and how is it structured?
Lymphoid tissue is a morphologically homogeneous but functionally heterogeneous collection of white blood cells and their precursors suspended in a reticular matrix.
Where is lymphoid tissue located?
Tonsils
Lymph nodes
Spleen
Thymus
Diffuse aggregates throughout the respiratory and gastrointestinal systems (e.g., Peyer’s patches).
What is the function of lymphoid tissue?
It serves as a storehouse of immune system cells, which can respond to antigenic activation and rapidly disperse via lymphatic or blood vessels.
What immune cells are found in lymphoid tissue?
Macrophages – Mostly originate from bone marrow.
Lymphocytes – Includes B and T cells.
Plasma cells – Produce antibodies.
Neutrophils and eosinophils – Migrate into lymphoid tissue during infection.
What are the two main types of lymphoid tissue?
Diffuse lymphoid tissue: Found in connective tissue beneath the epithelium of the GI and respiratory tracts and in the stroma of internal organs during infections.
Nodular lymphoid tissue: Dense spherical aggregates of lymphocytes found within diffuse lymphoid tissue.
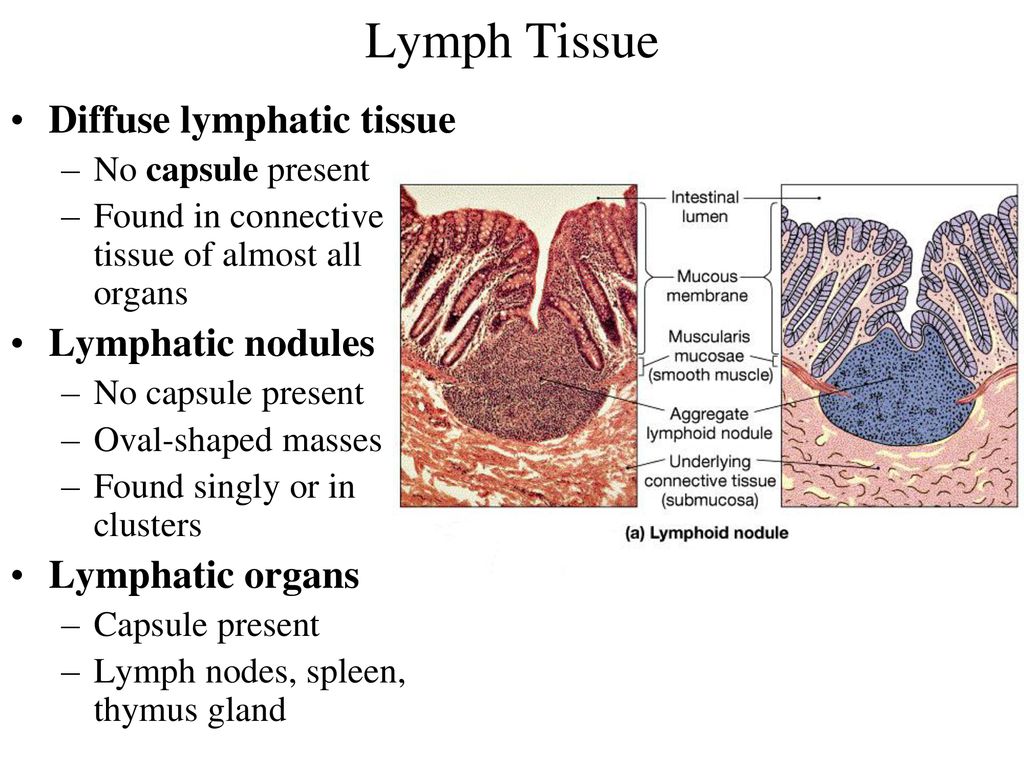
Are lymphoid nodules permanent structures?
No, they come and go based on the body’s immunological needs.
What are germinal centers, and what do they indicate?
Lightly stained centers within lymphoid nodules that represent active B-cell proliferation.
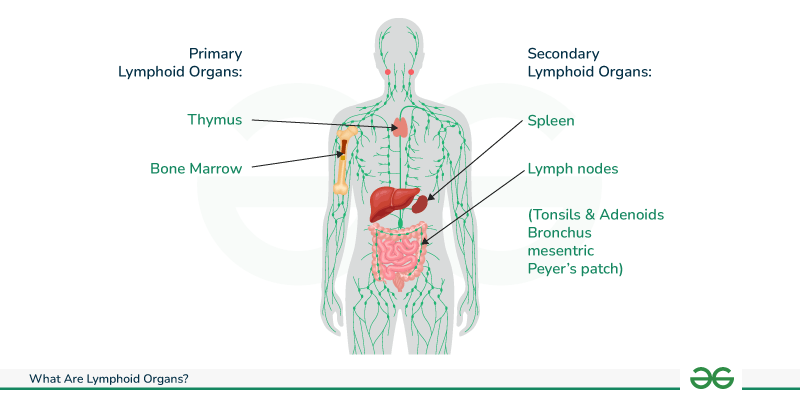
What are the functions of primary lymphoid organs?
They are responsible for the initial differentiation of B and T lymphocytes from precursors.
What is the function of the thymus?
It is the site of T lymphocyte development.
Where is the thymus located?
In the superior thoracic cavity.
What happens to the thymus after birth?
It seeds T cells throughout the body and then undergoes involution, where it is gradually replaced by fat in the late teenage years.
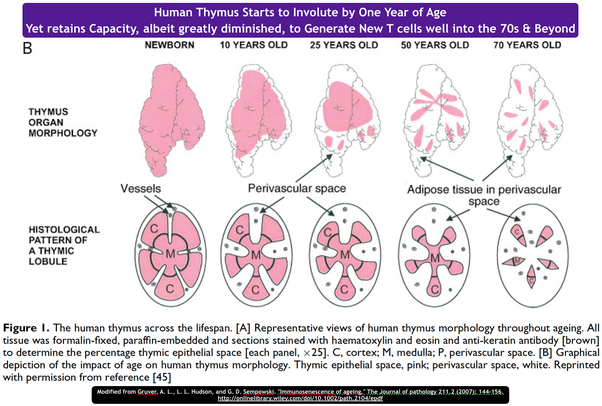
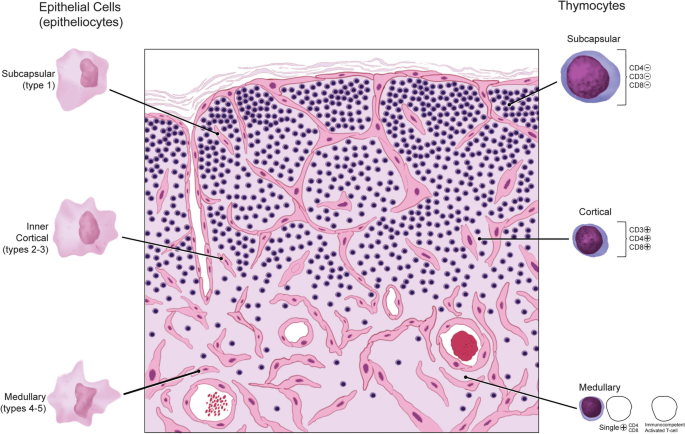
What are the histological features of the thymus?
Encapsulated with trabeculae dividing it into lobules.
Cortex (outer dark region) – Contains proliferating T cells and macrophages.
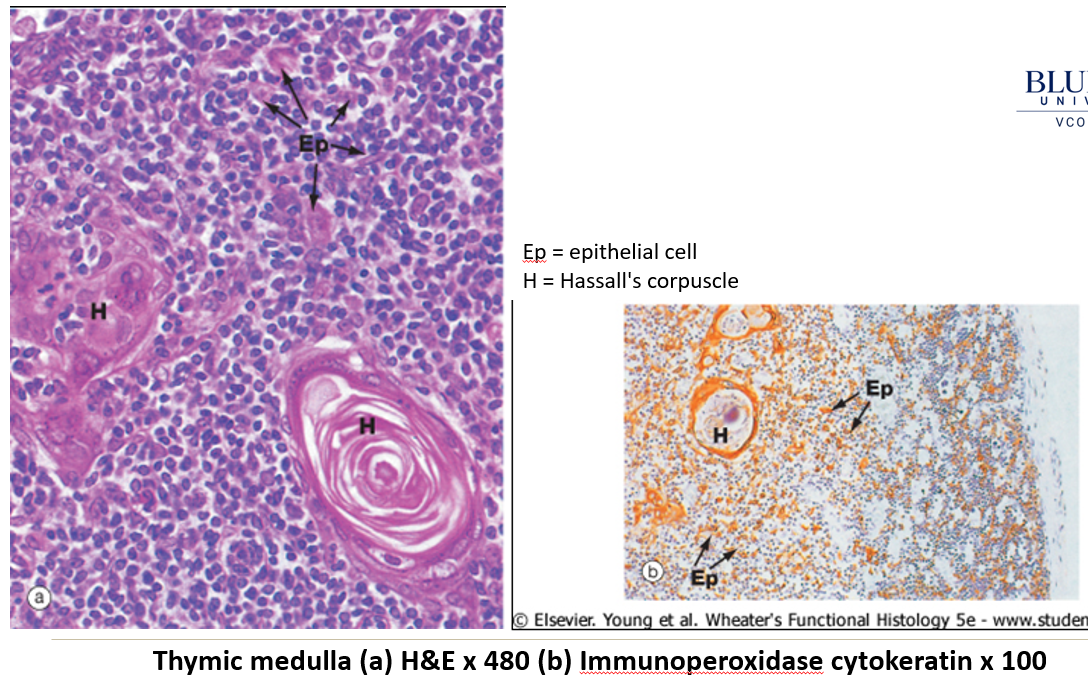
Medulla (inner light region) – Contains reticular cells, epitheliocytes, and Hassall’s corpuscles.
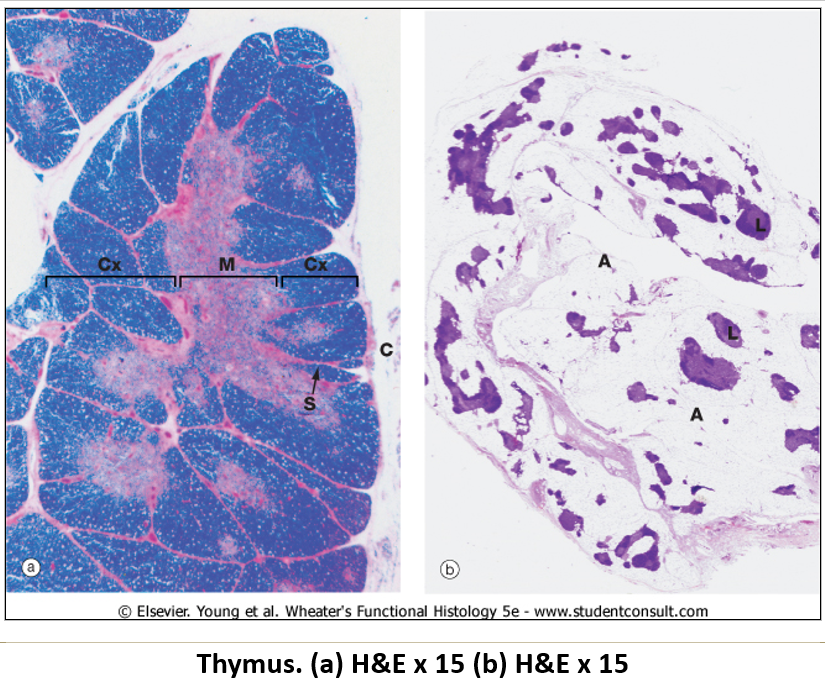
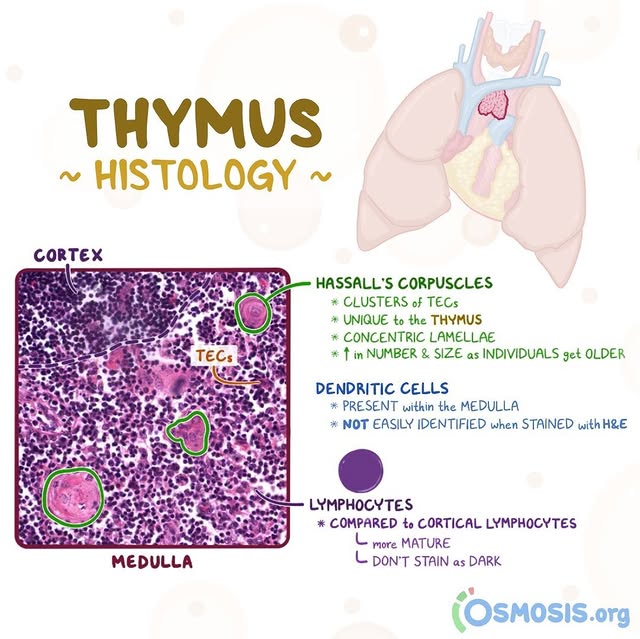
What is the function of Hassall’s corpuscles?
Layered structures in the thymus made of degenerating epithelial cells. They help in T cell maturation and clonal selection, ensuring only functional immune cells survive.
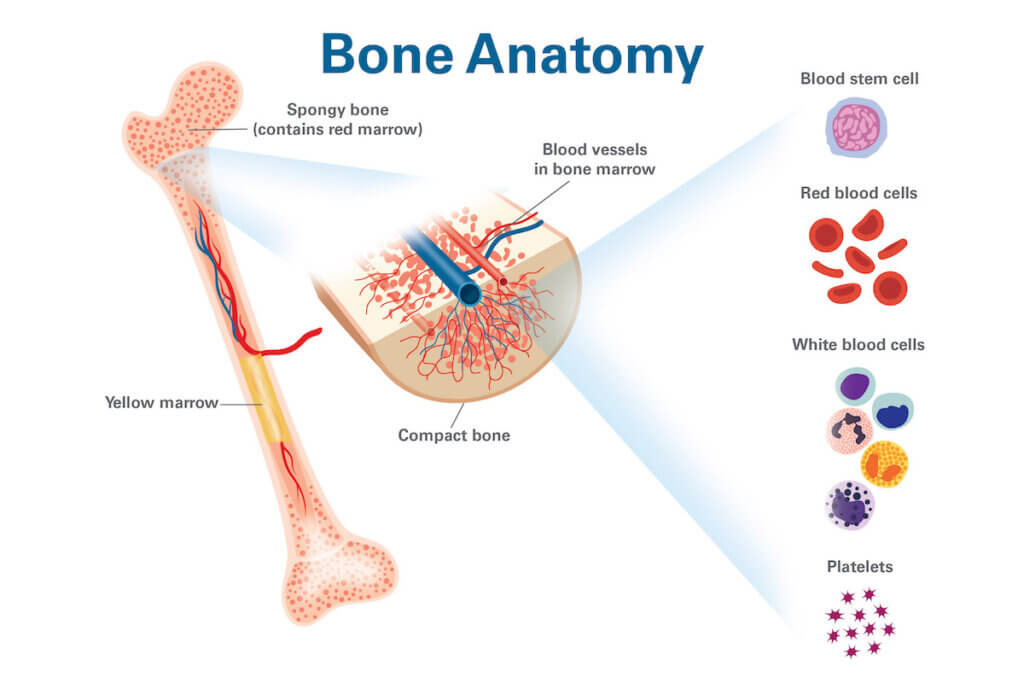
What is the function of the bone marrow in the lymphoid system?
It is the source of B lymphocytes and is sometimes called the bursa equivalent.
What are secondary lymphoid organs?
Organs seeded with immune cells from primary lymphoid organs, where ongoing immune function and cell production occur in adults.
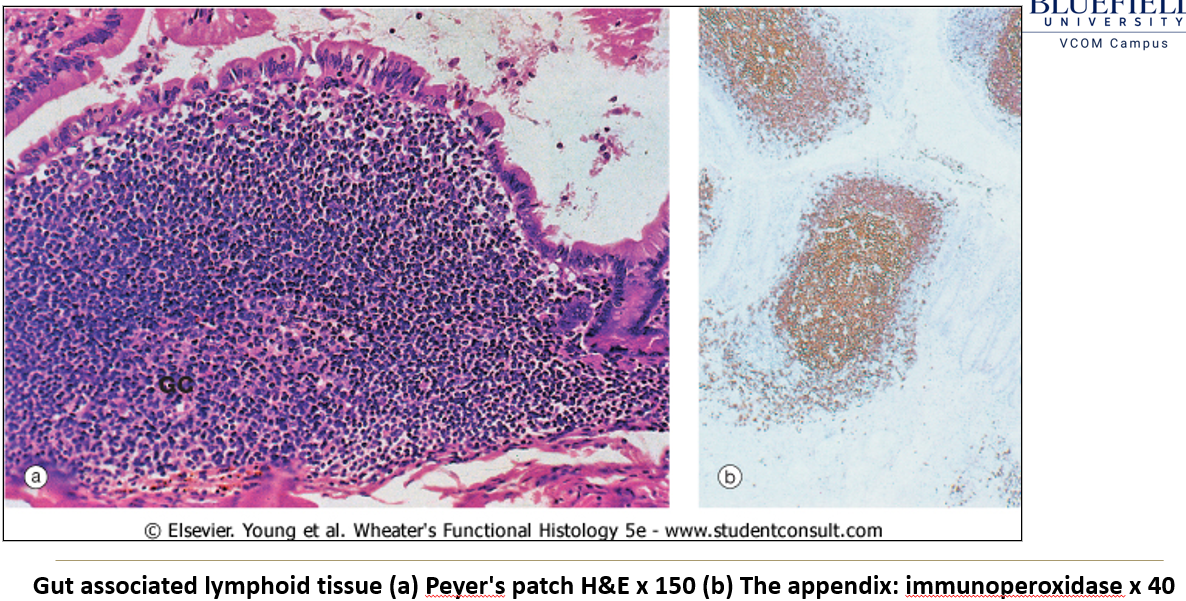
Where is GALT located?
In the connective tissue of the GI tract, where lymphocytes form diffuse and nodular aggregates.
Where are the main GALT structures found?
Ileum: Peyer’s patches.
Appendix: Lymphoid aggregates.
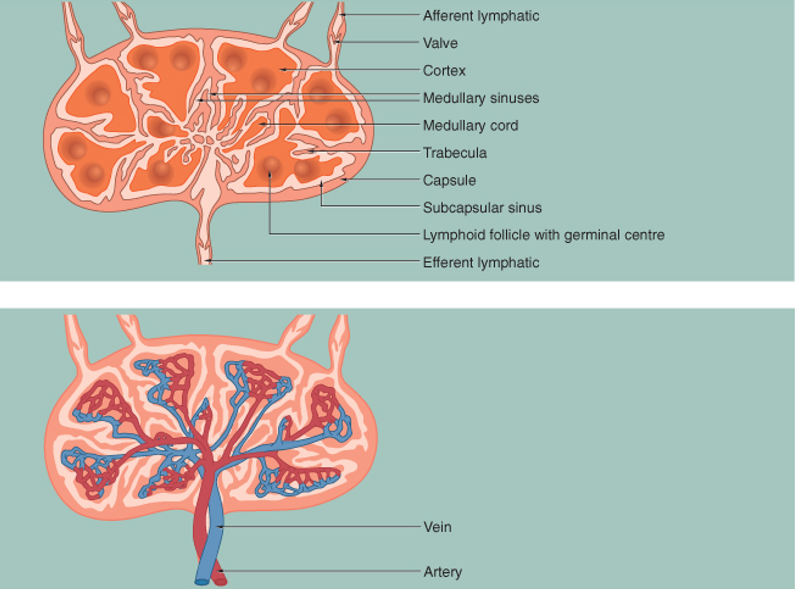
What is the structure of a lymph node?
Reticular connective tissue scaffolding.
Dense irregular connective tissue capsule.
Subcapsular sinus (receives lymph from afferent vessels).
Cortex: Contains diffuse and nodular lymphoid tissue.
Medulla: Contains medullary cords and sinuses.
Multiple afferent lymphatic vessels enter, but only one efferent vessel exits at the hilum.
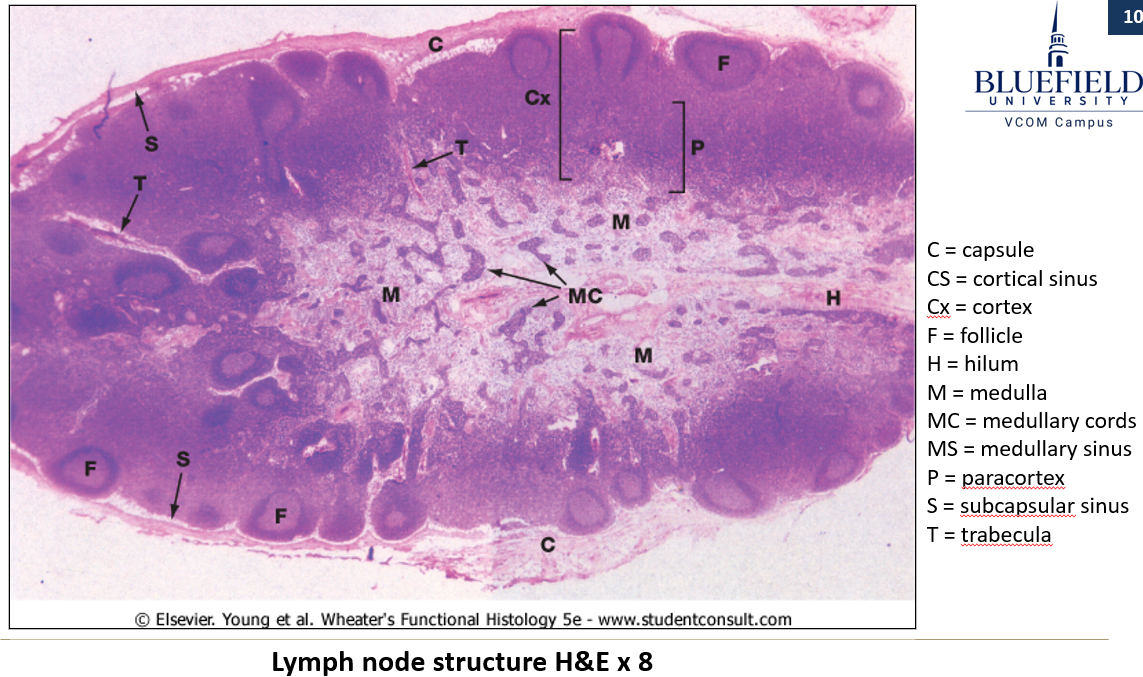
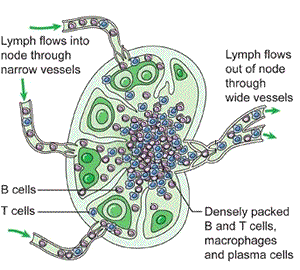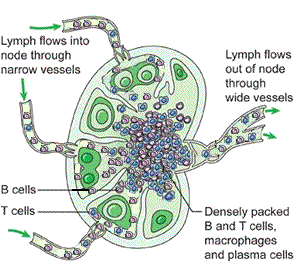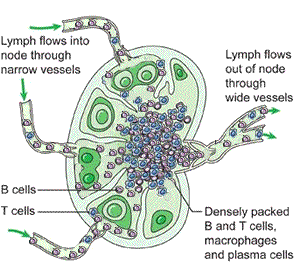
How do lymph nodes function?
Afferent lymph enters the subcapsular sinus and then moves through sinusoids between medullary cords for immune screening.
High endothelial venules allow lymphoid cells to exit circulation.
Antigen recognition stimulates mitosis of B cells, forming germinal centers.
T cells are primarily found between nodules.
What are the functions of the spleen?
Immunologically screens blood.
Macrophages remove old (senescent) RBCs.
Blood reservoir.
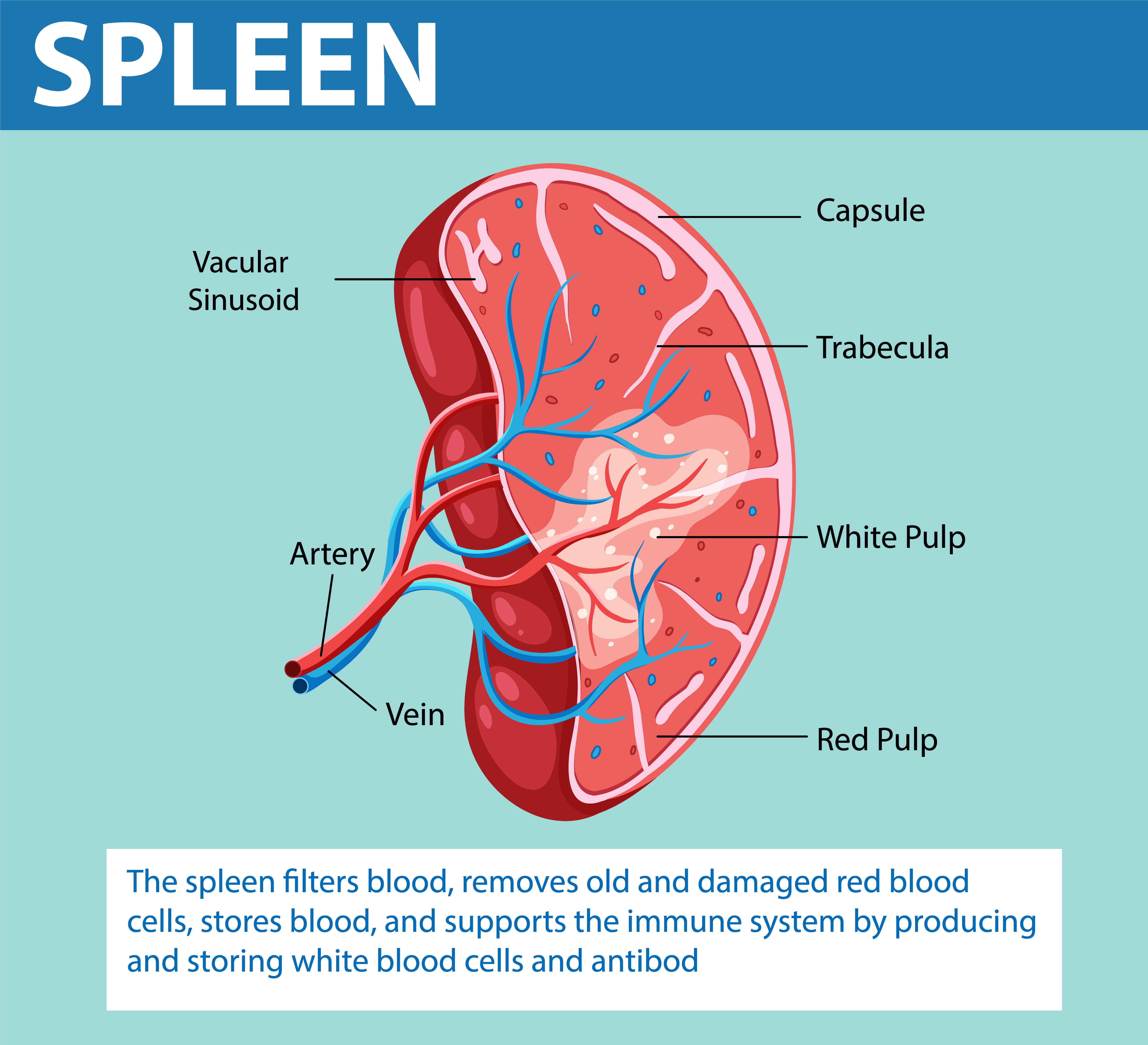
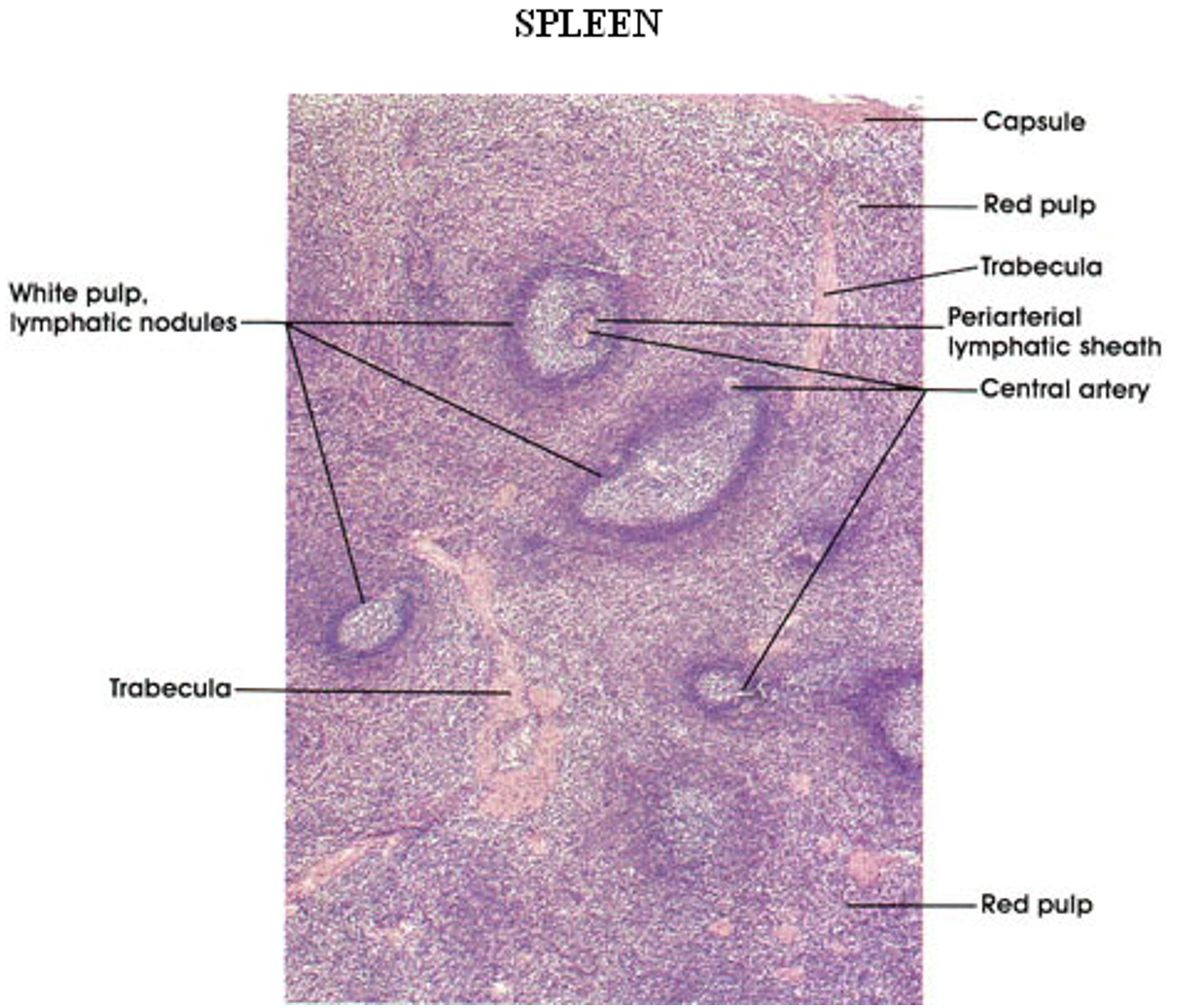
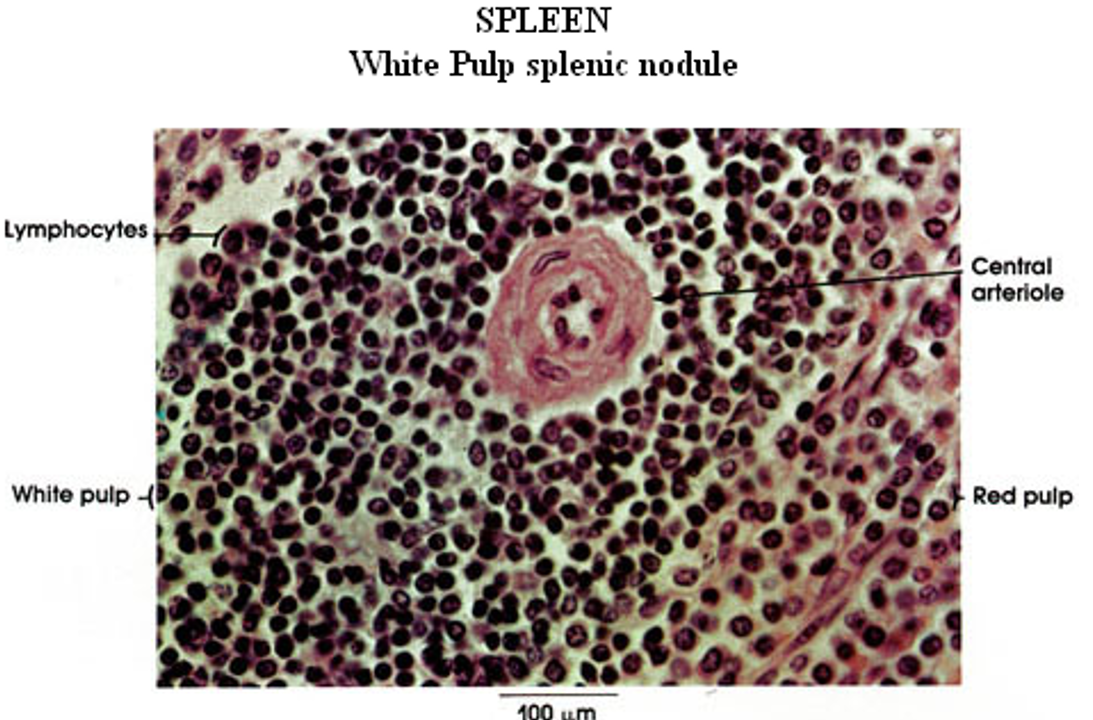
What is the histological structure of the spleen?
Connective tissue capsule with trabeculae.
Reticular fiber scaffolding.
Pulp composition:
Red pulp: Contains sinusoids filled with blood and lymphocytes.
White pulp: Consists mainly of lymphoid tissue.
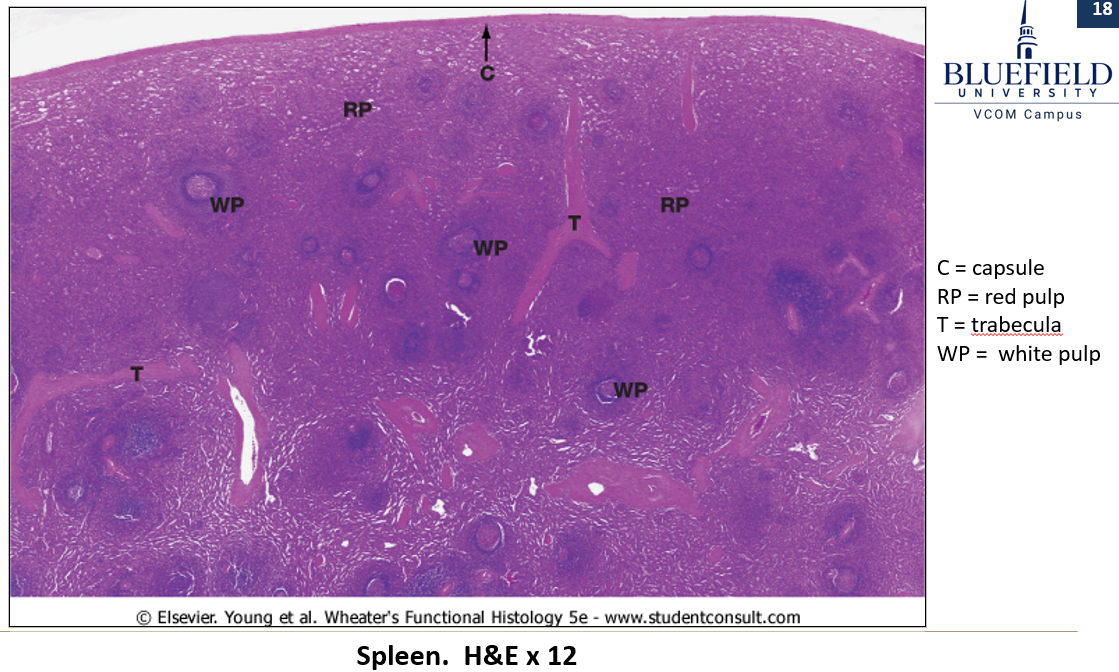
How does red pulp stain?
Stained light
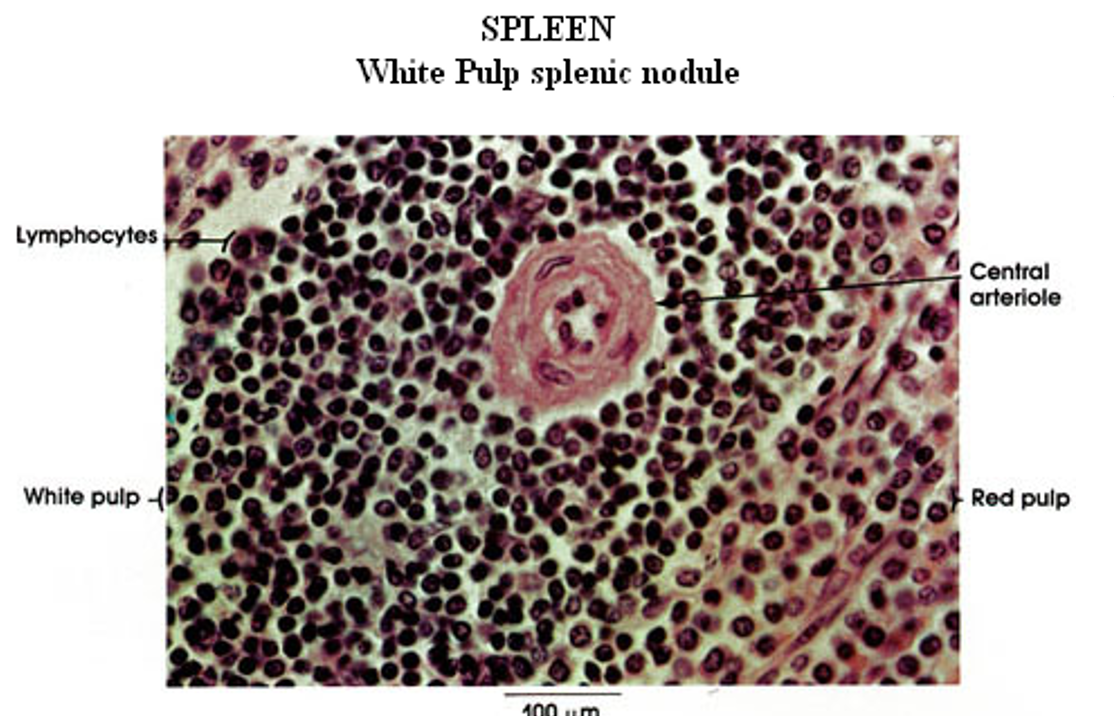
How does white pulp stain?
Stained dark
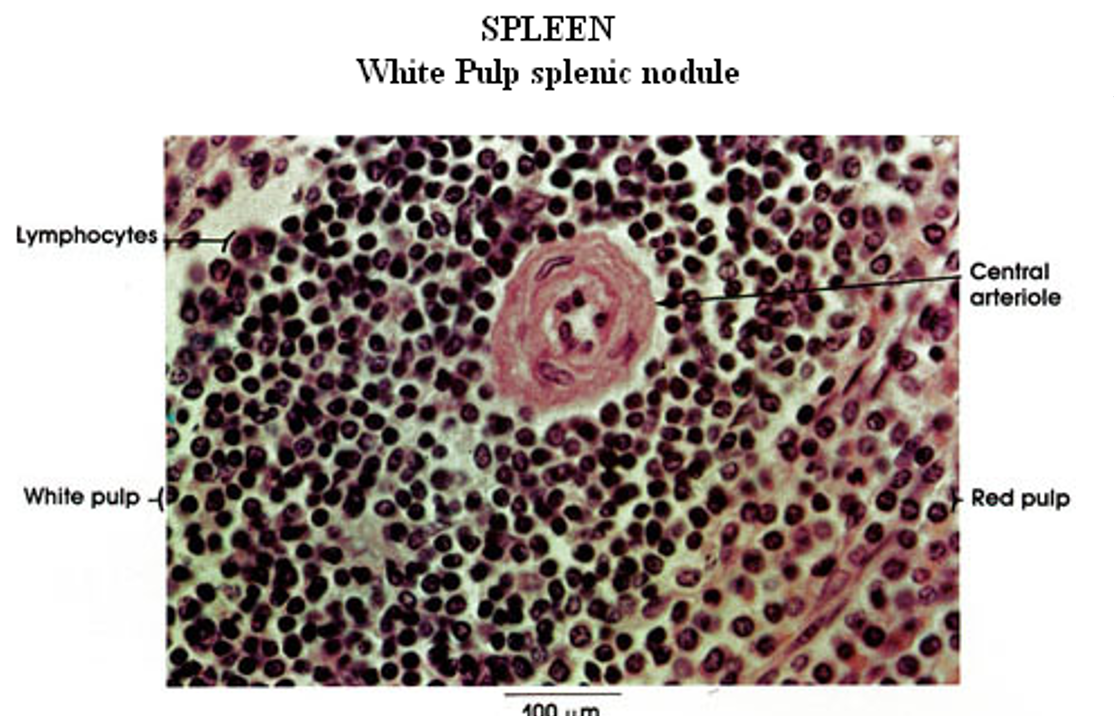
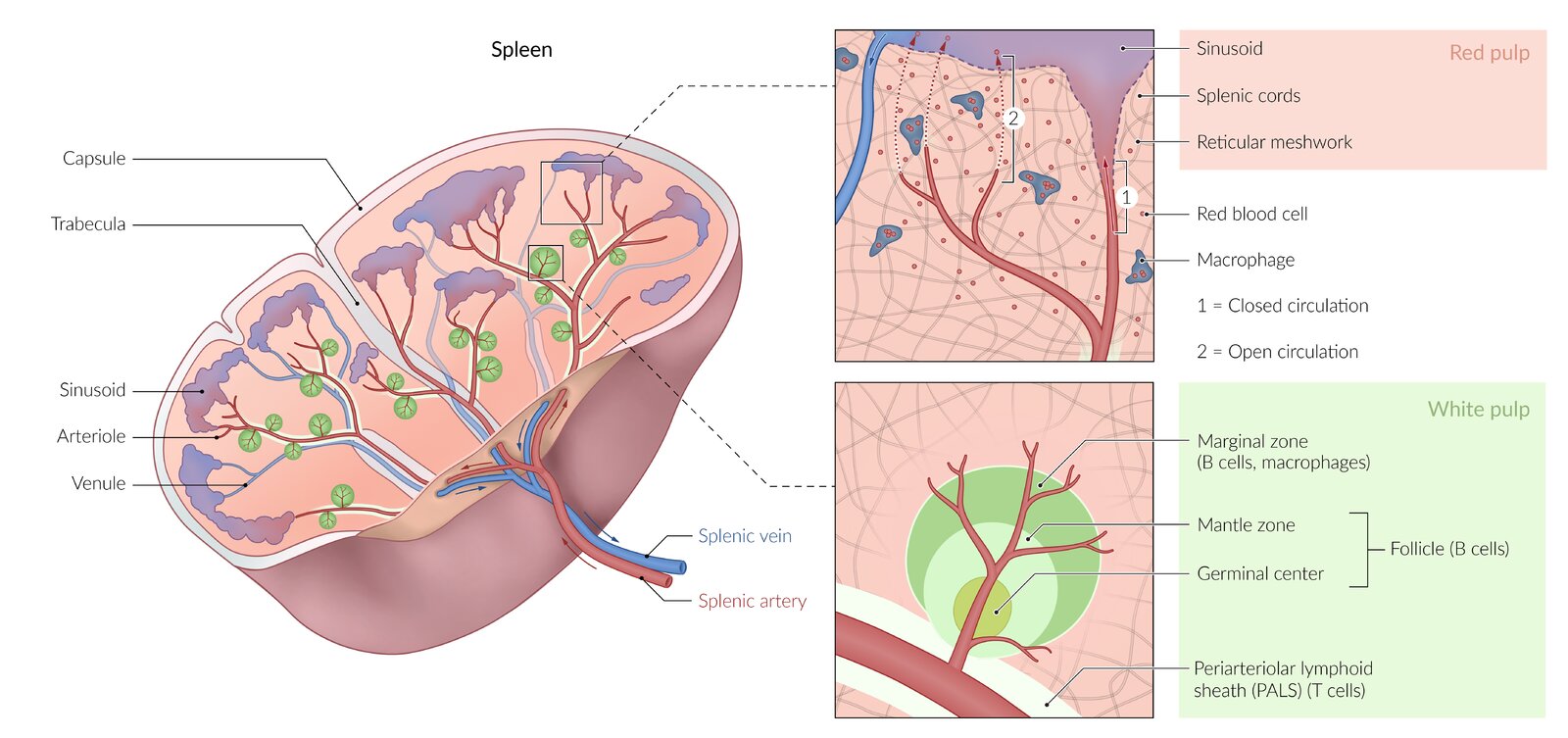
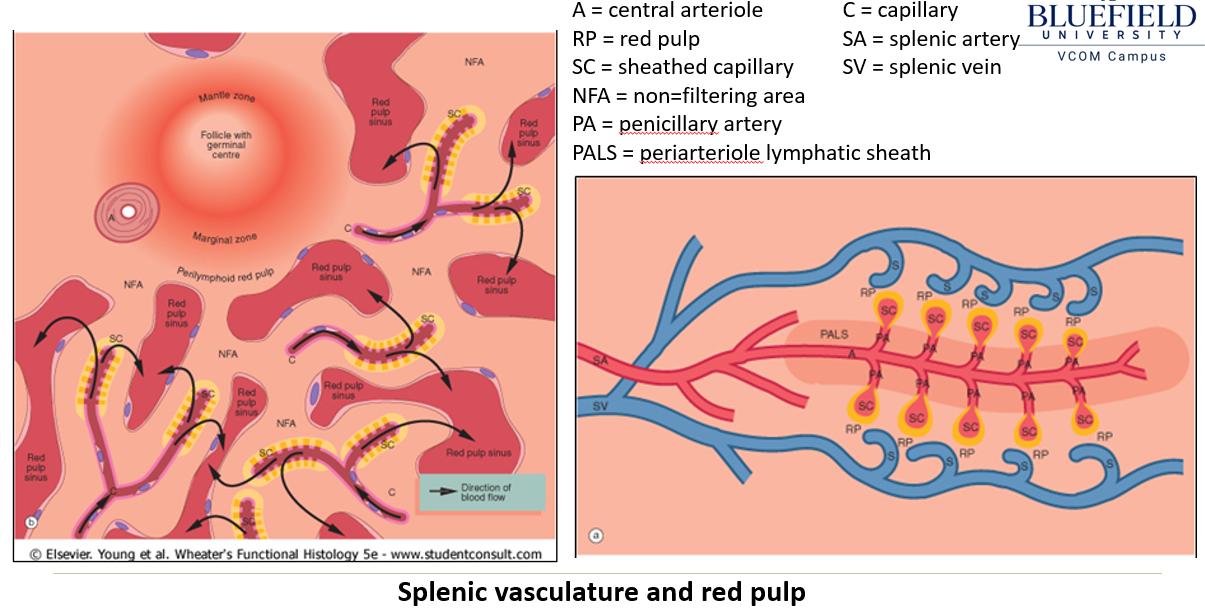
How does blood flow through the spleen?
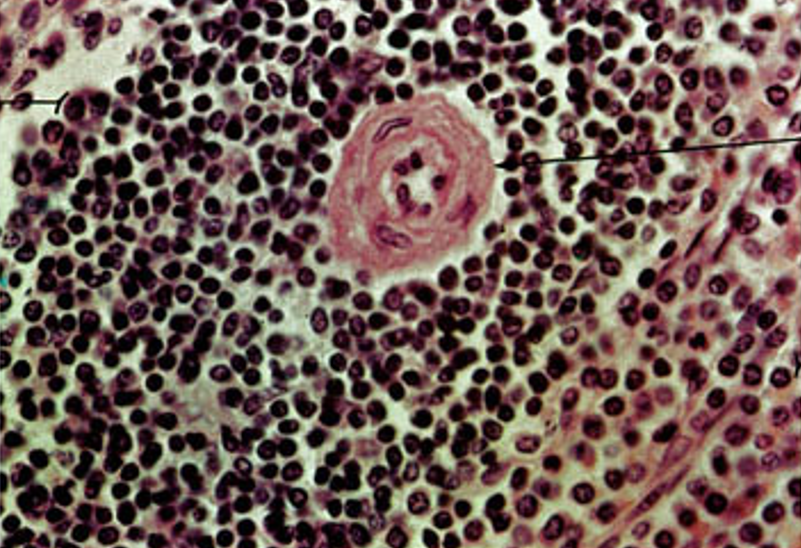
The splenic artery branches into trabecular and central arteries, where lymphocytes form the Periarteriole Lymphatic Sheath (PALs).
Central arteries lead to penicillary arterioles and sheathed capillaries lined with macrophages.
Blood enters the open circulation of the red pulp, interacts with lymphoid cells, then moves into red pulp sinusoids before draining into splenic veins.
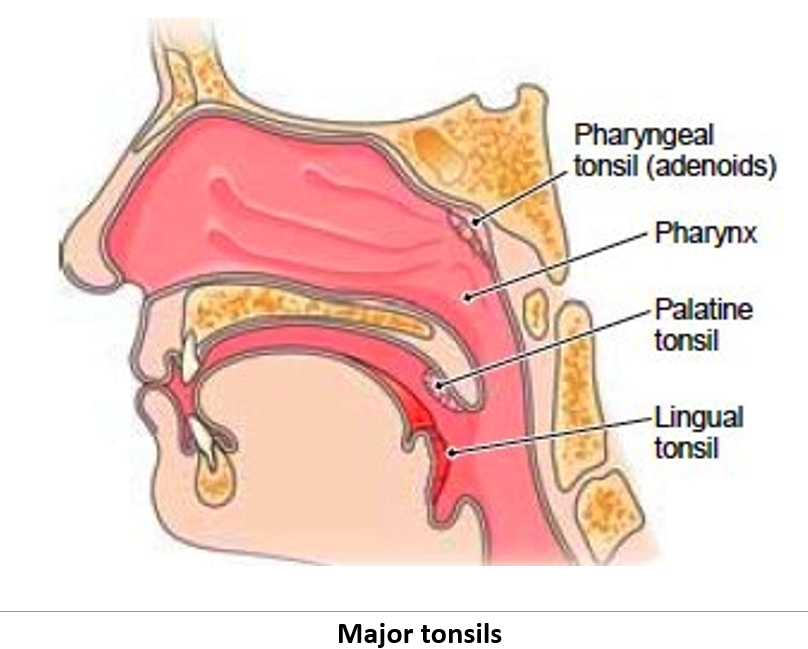
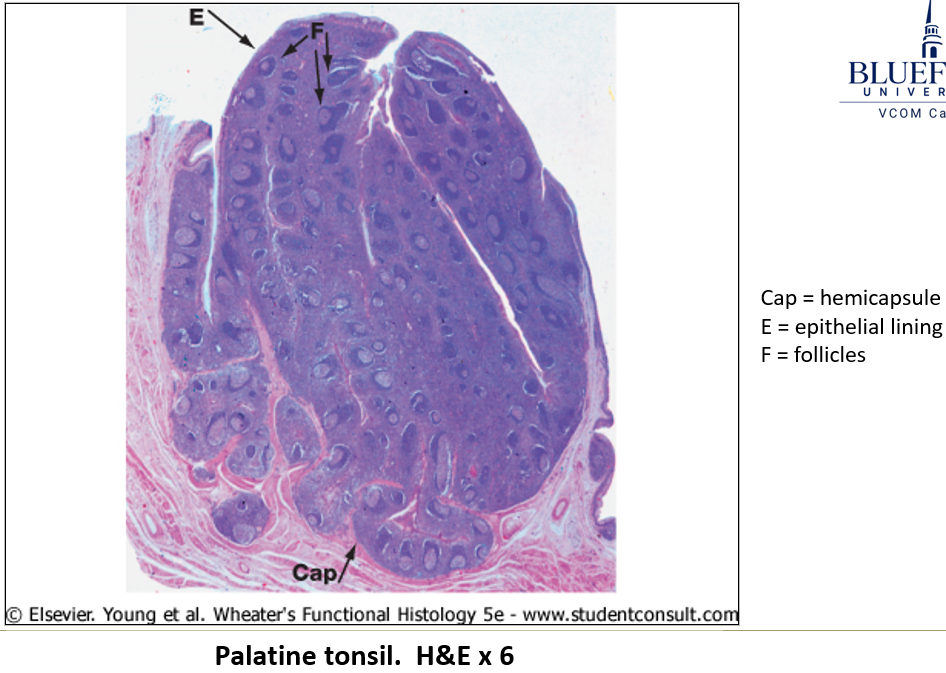
What is the function of the tonsils?
They form a ring around the pharynx, providing immune defense against inhaled and ingested pathogens. They trap and filter pathogens from inhaled air and ingested food
What are the three clinically important tonsils?
Palatine tonsils.
Lingual tonsils.
Median pharyngeal tonsil (when enlarged, called adenoids).
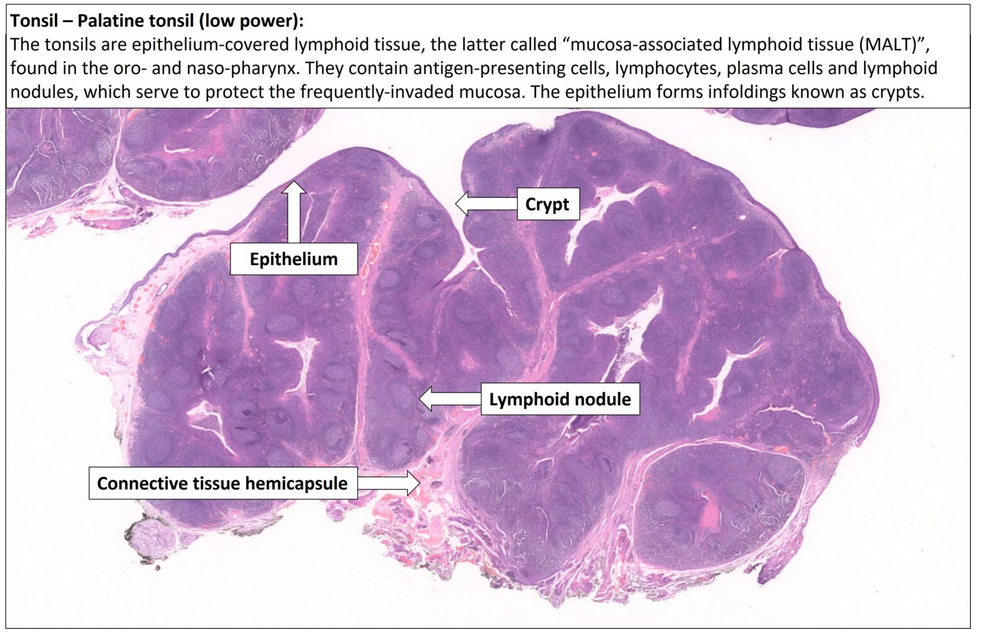
What are the histological features of tonsils?
Highly infolded epithelium with crypts to capture antigens.
Diffuse and nodular lymphoid tissue inside crypts.
Hemicapsule (dense irregular connective tissue).
Germinal centers enlarge during infection, leading to a swollen or sore throat.
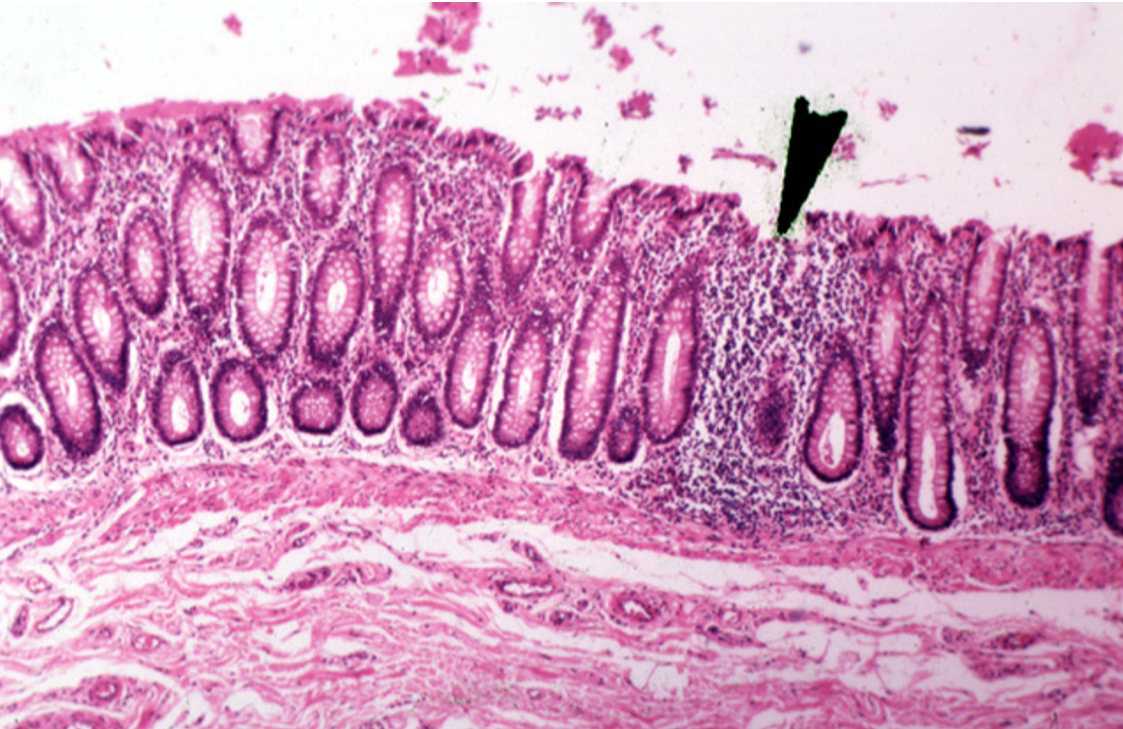
Identify this structure
Diffuse lymphatics
A concentration of purple dots observed
Identify this structure
Diffuse lymphatics
A concentration of purple dots observed
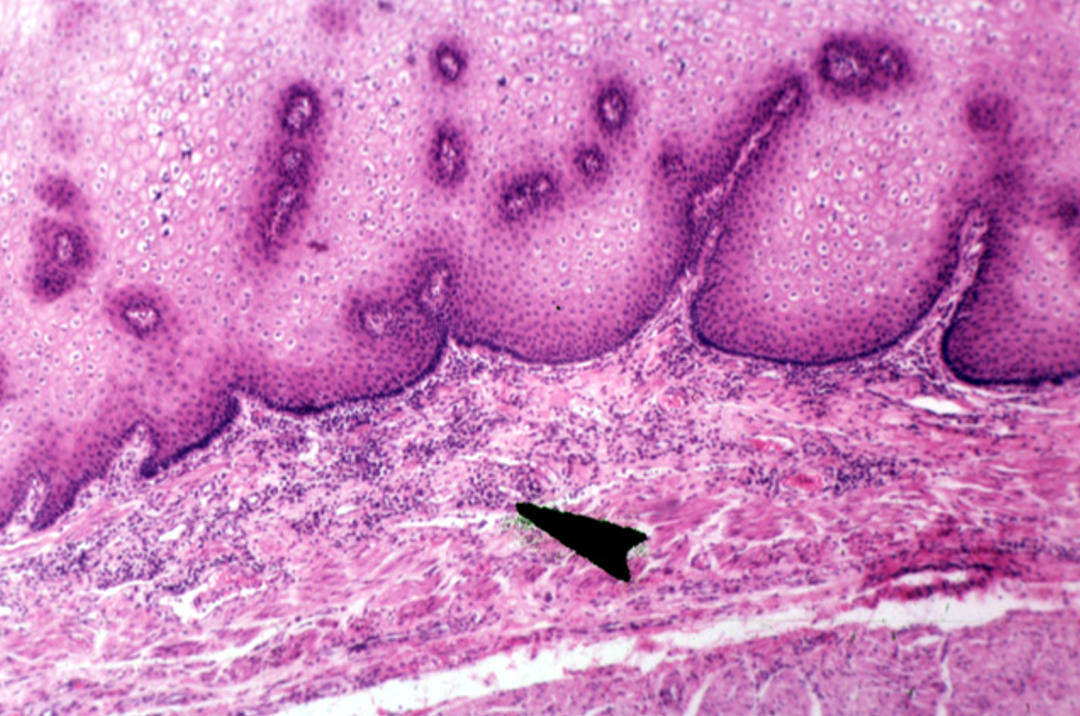
Identify this structure
Diffuse lymphatics
A concentration of purple dots observed
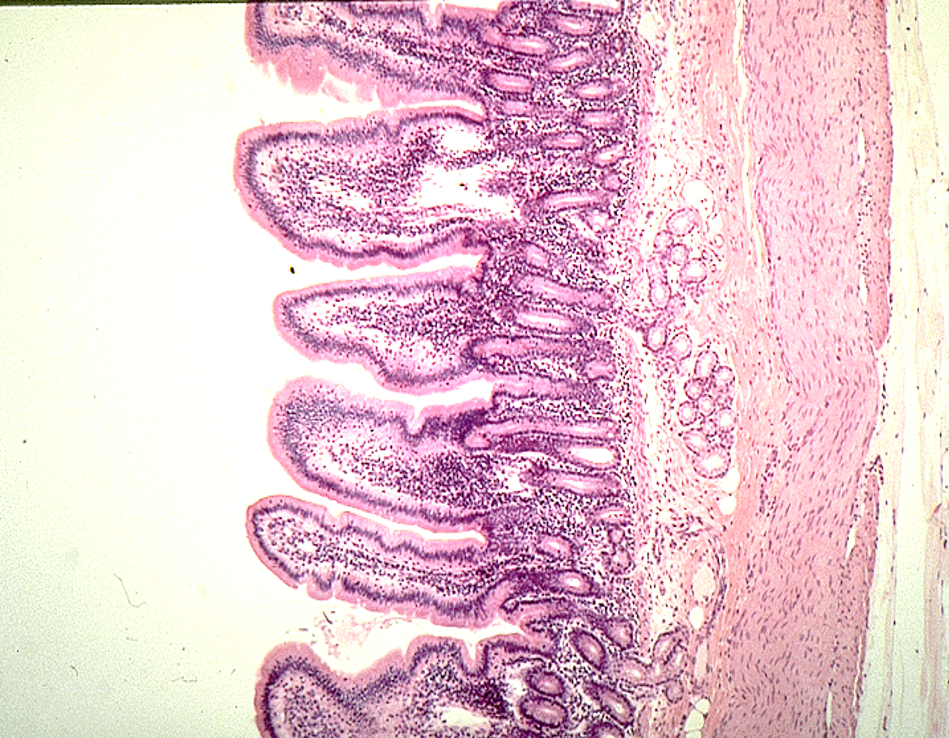
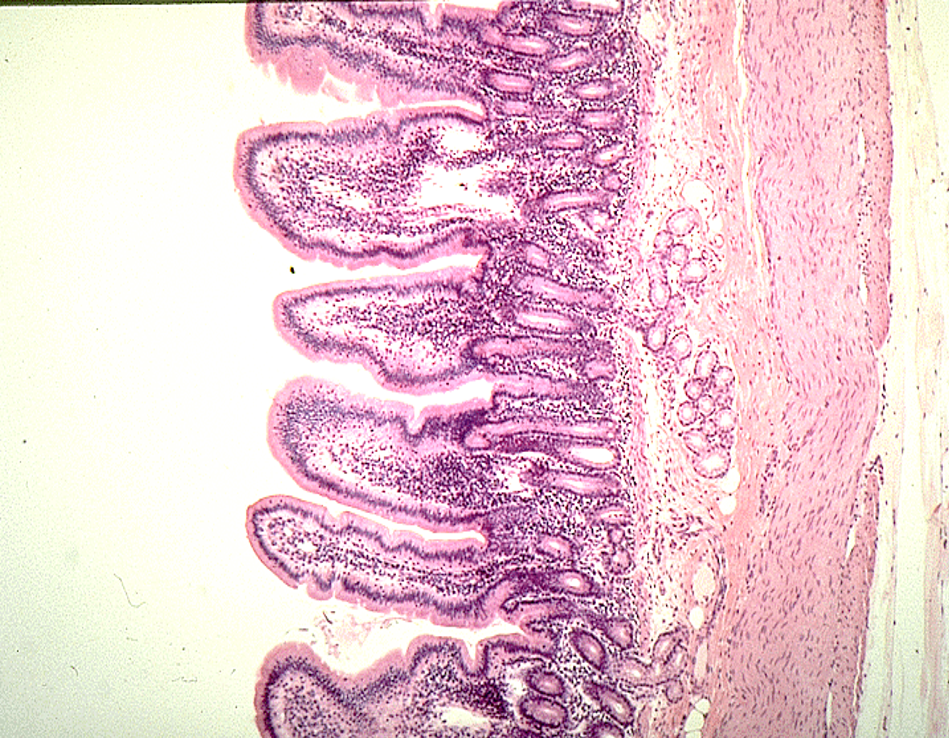
Identify this structure
Diffuse lymphatics
A concentration of purple dots observed
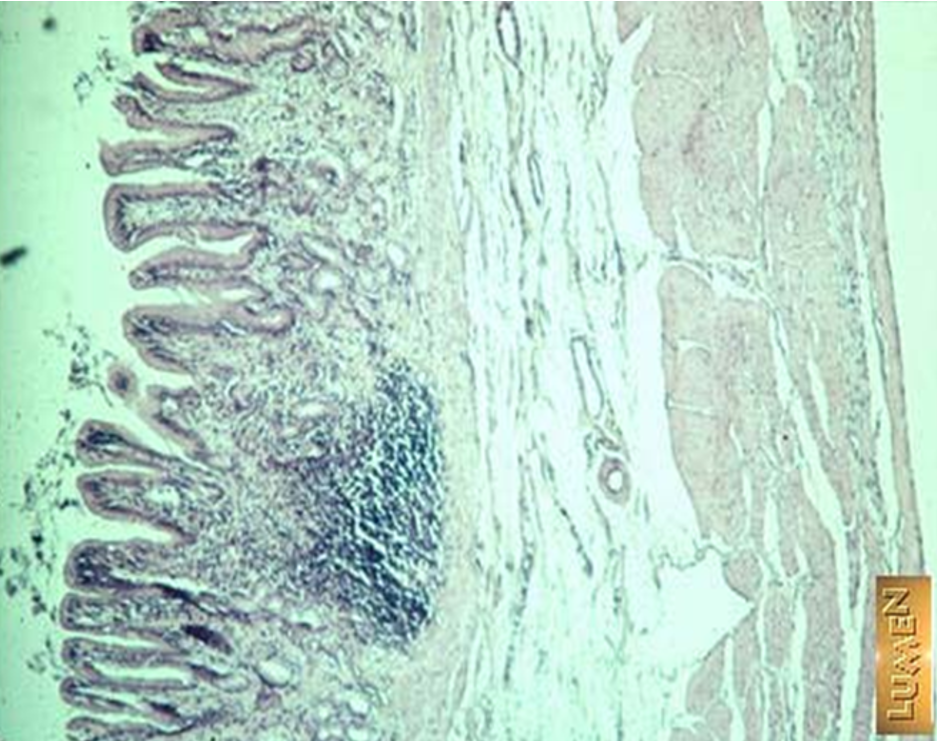
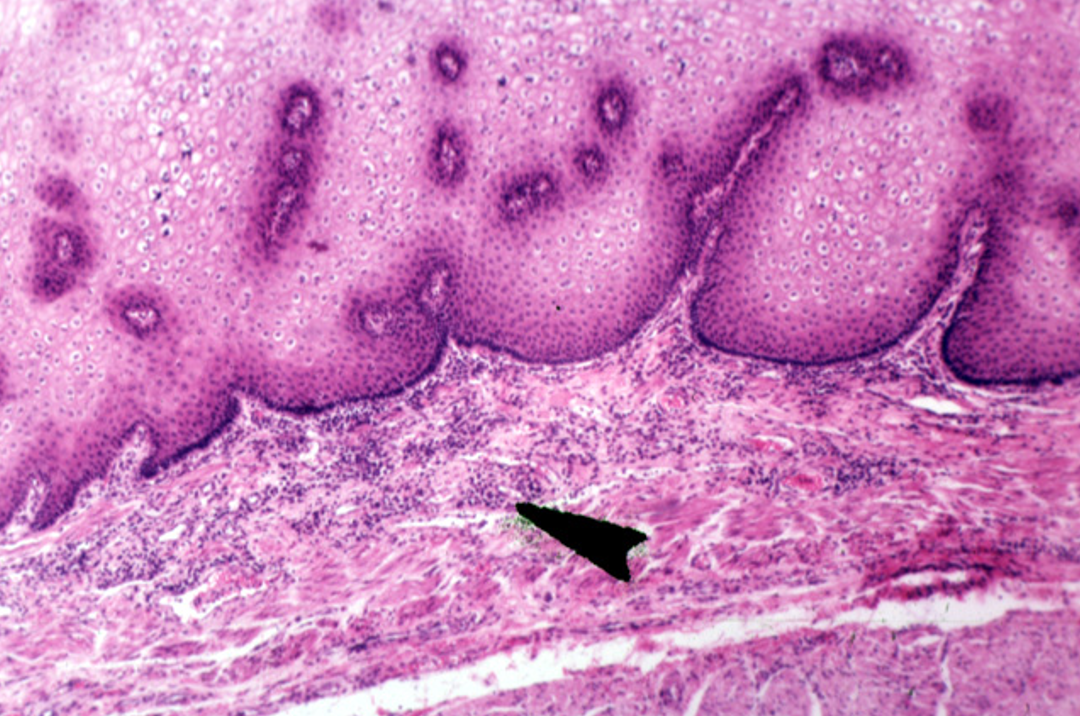
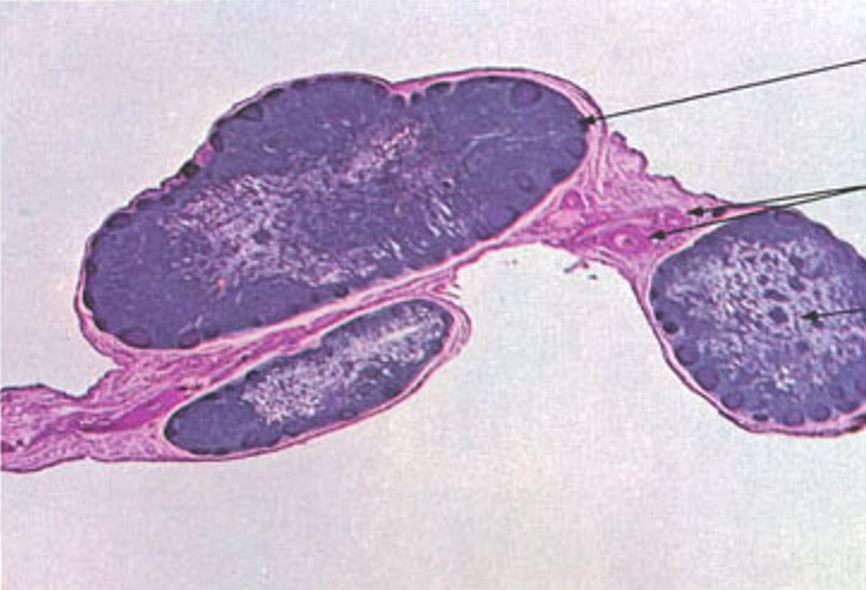
Identify this structure
Lymphatic nodules
Nodule w/ germinal center
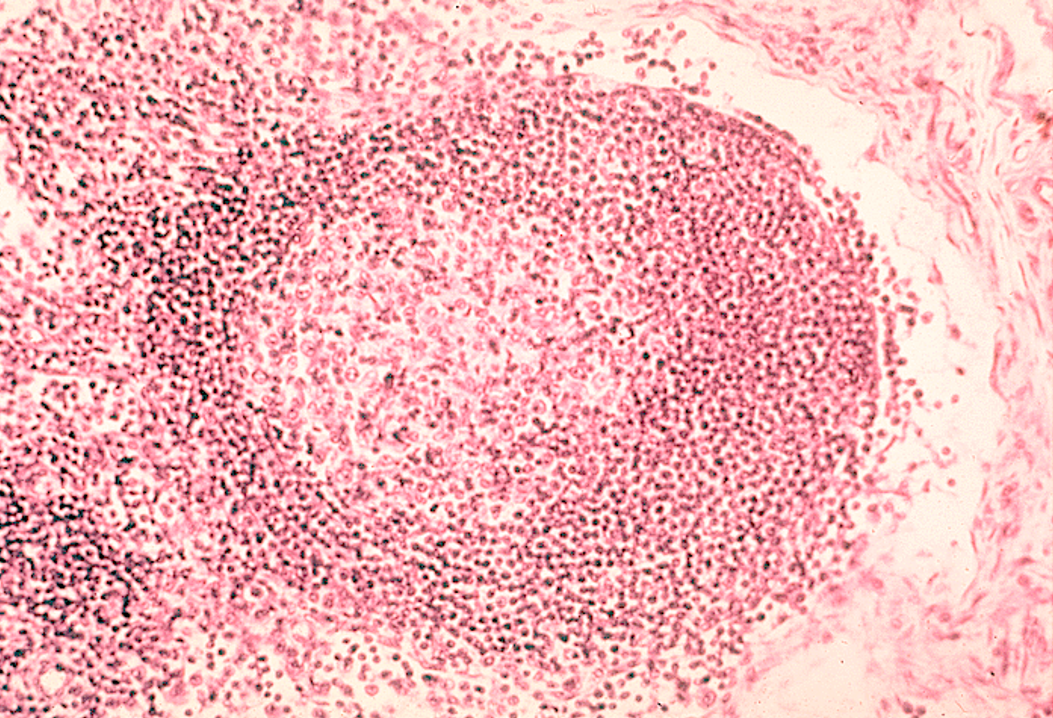
Identify this structure
Lymphatic nodules within Lymph Node
Nodule w/ lighter staining germinal center
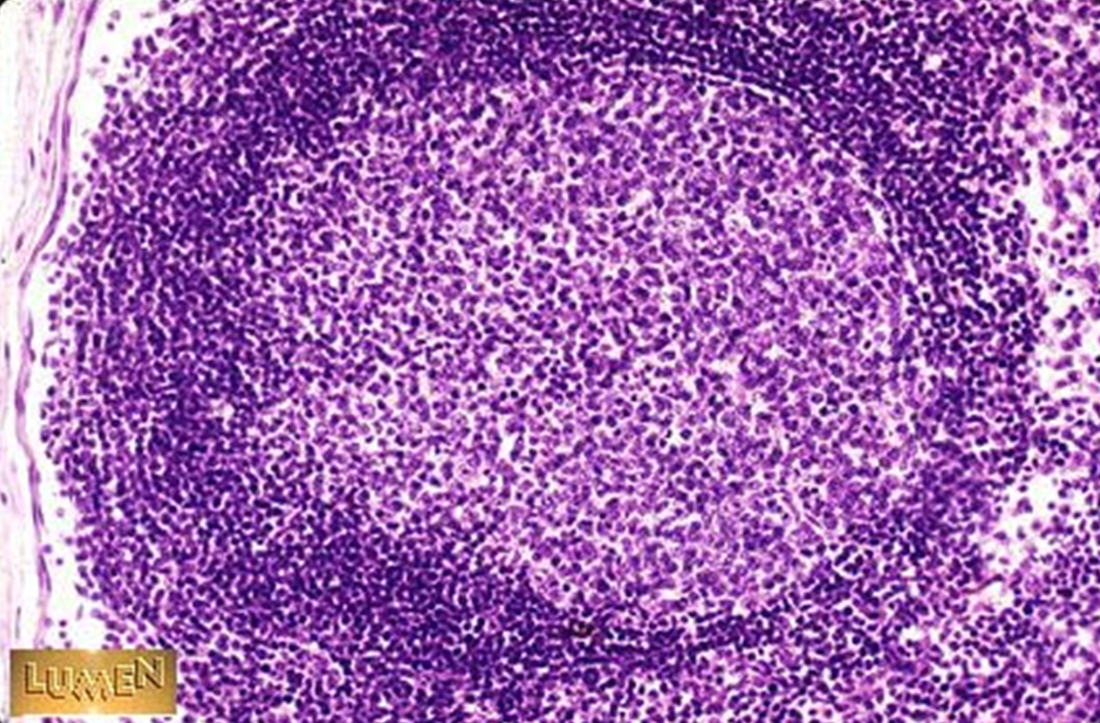
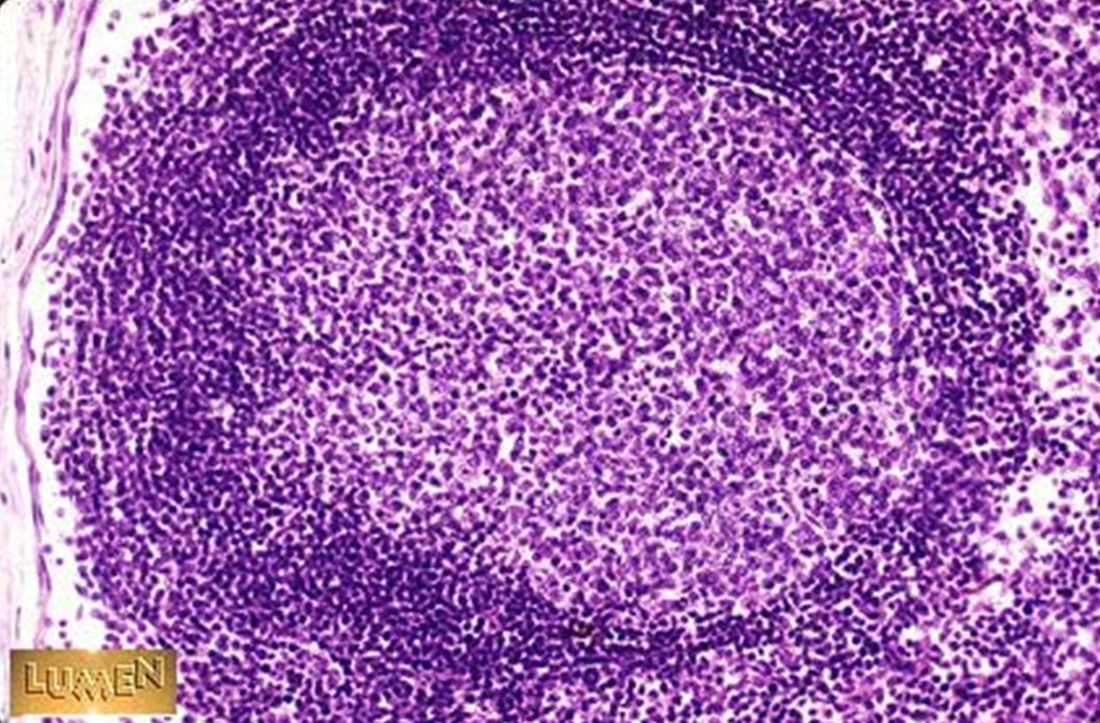
Identify this structure
Lymphatic nodules
Nodule w/ lighter staining germinal center
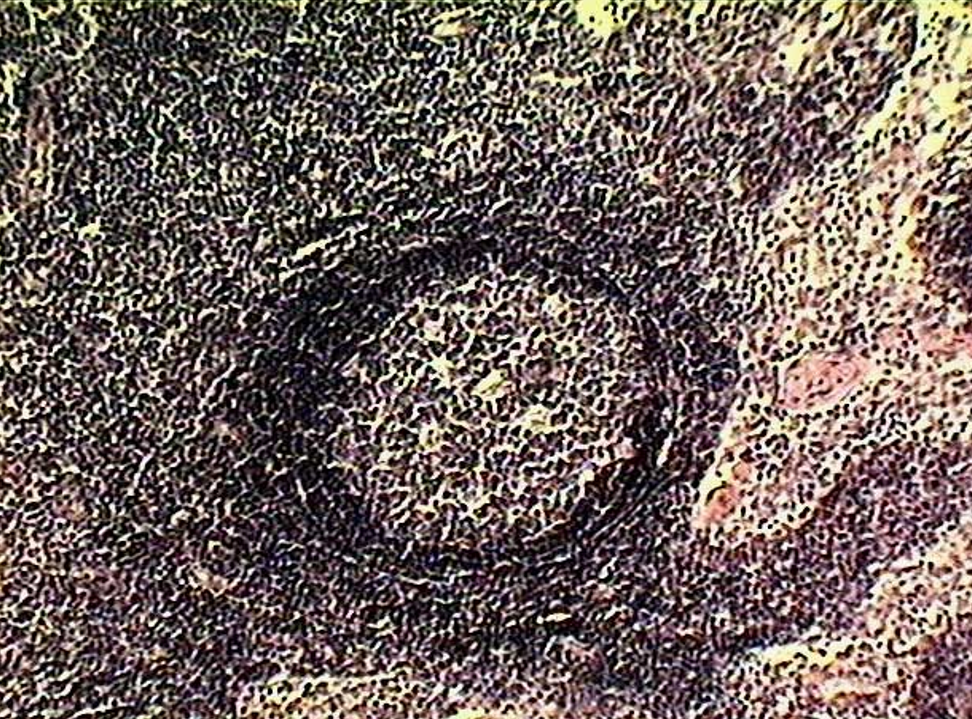
Identify this structure
Lymphatic nodules
Nodule w/ lighter staining germinal center
T cells on the outside
B cells in the center
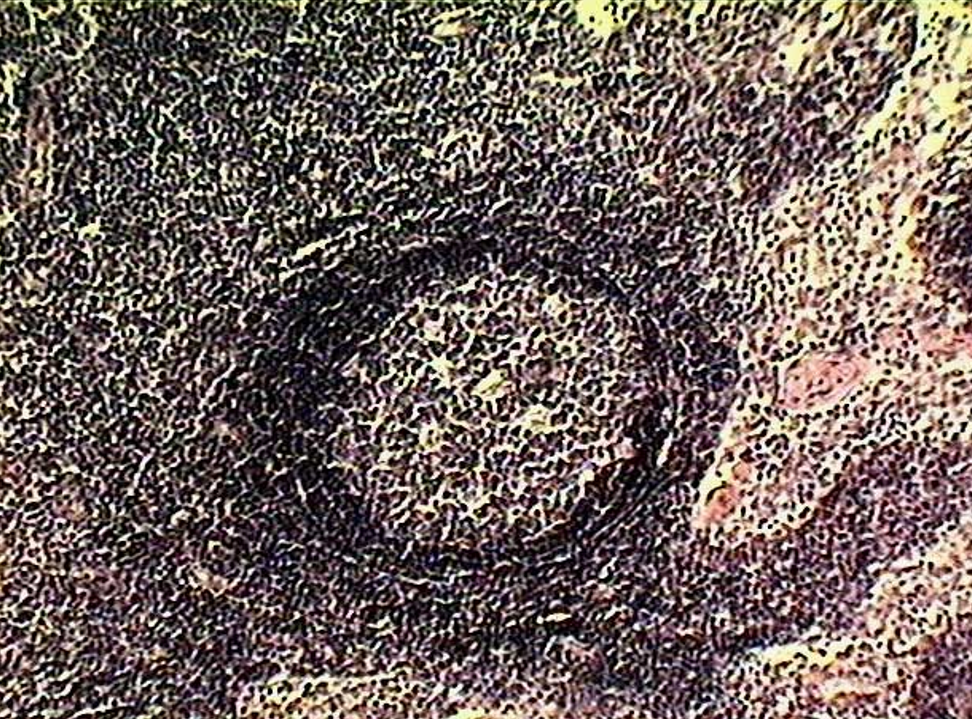
Identify this structure
Lymphatic nodules
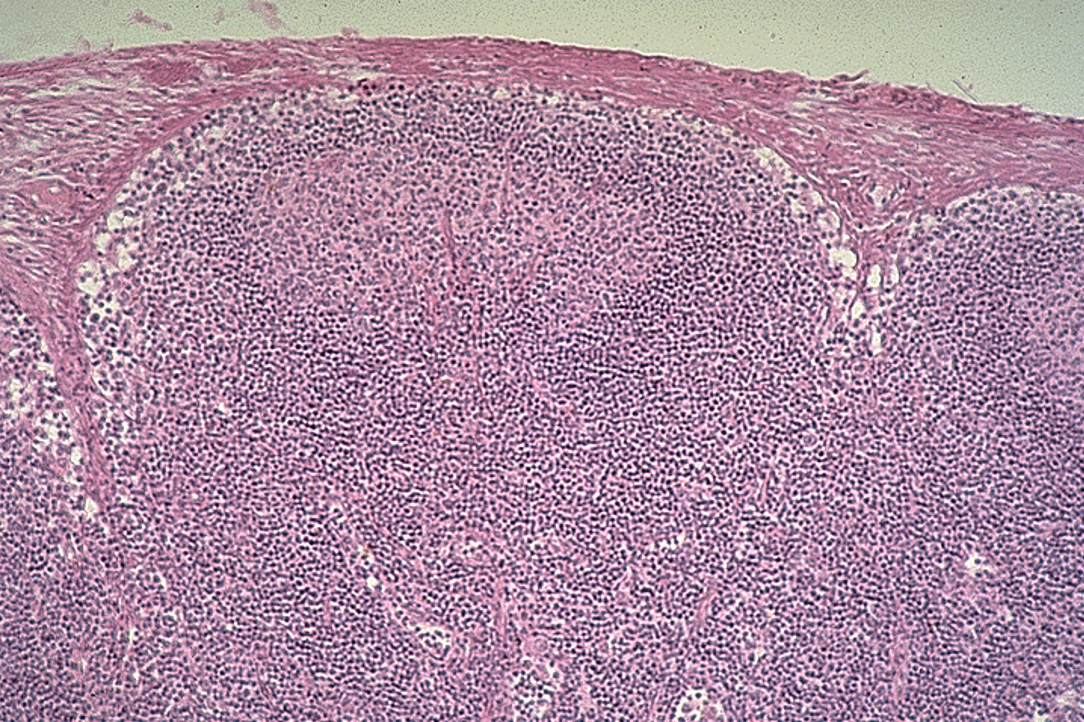
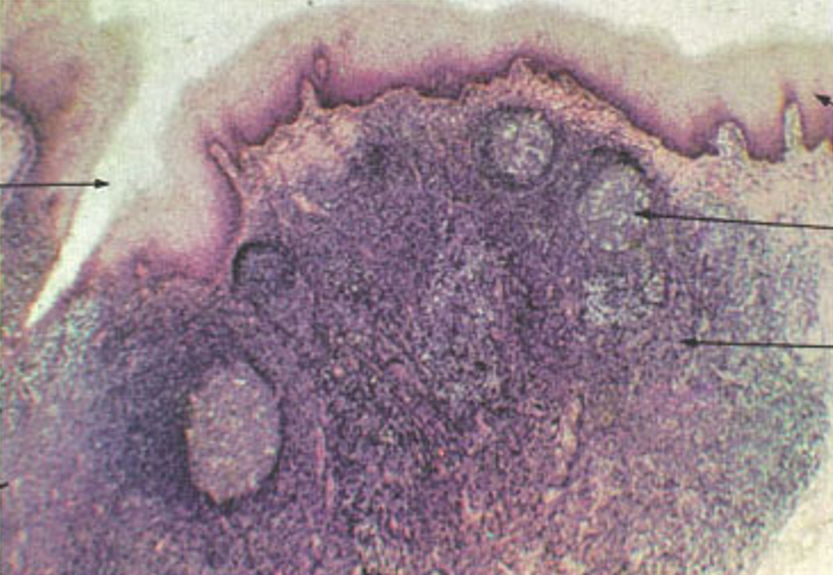
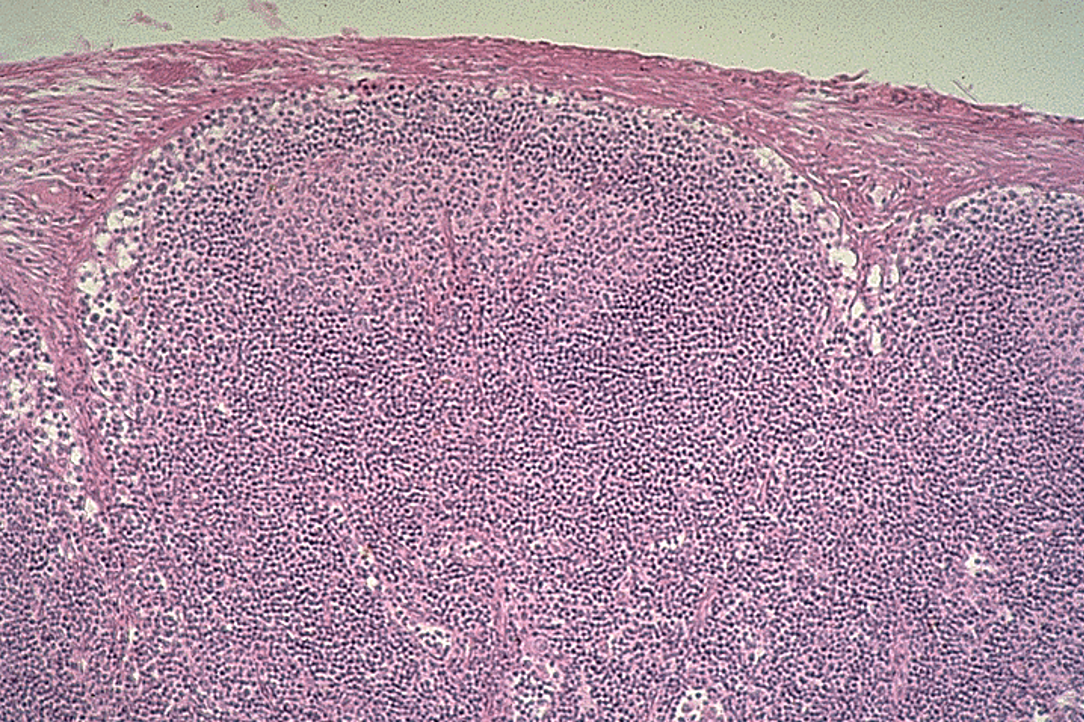
Identify this structure
Tonsils
Crypt and nodules w/ germinal centers observed
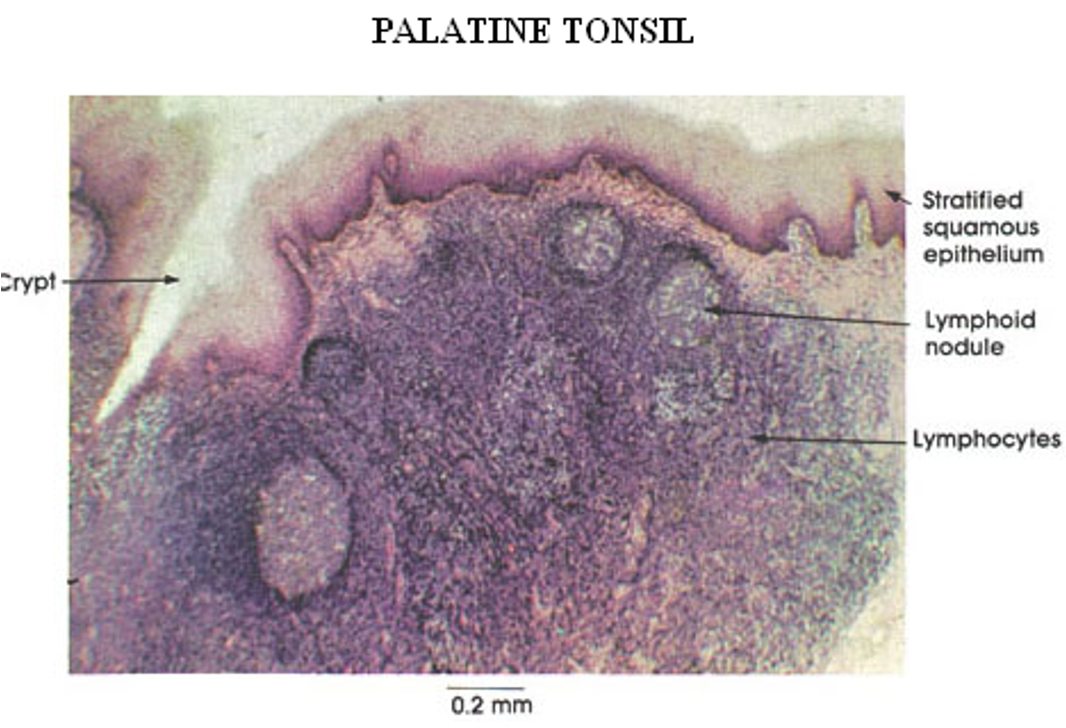
Identify this structure
Tonsils
Crypt and nodules w/ germinal centers observed
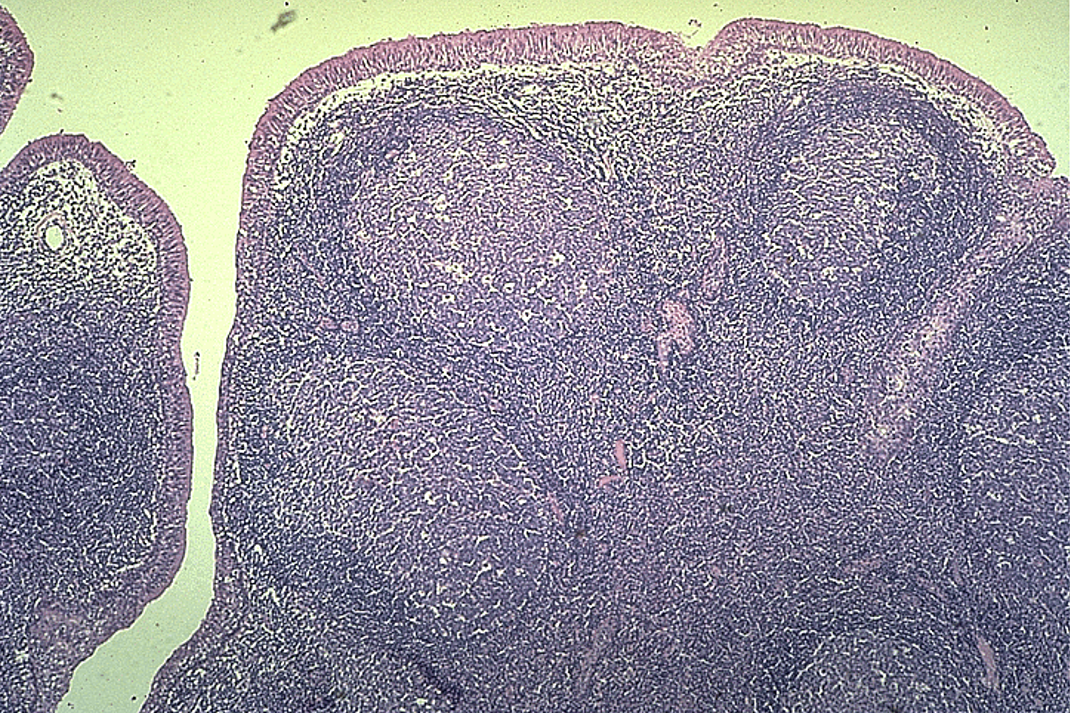
Identify this structure
Tonsils
Crypt and nodules w/ germinal centers observed
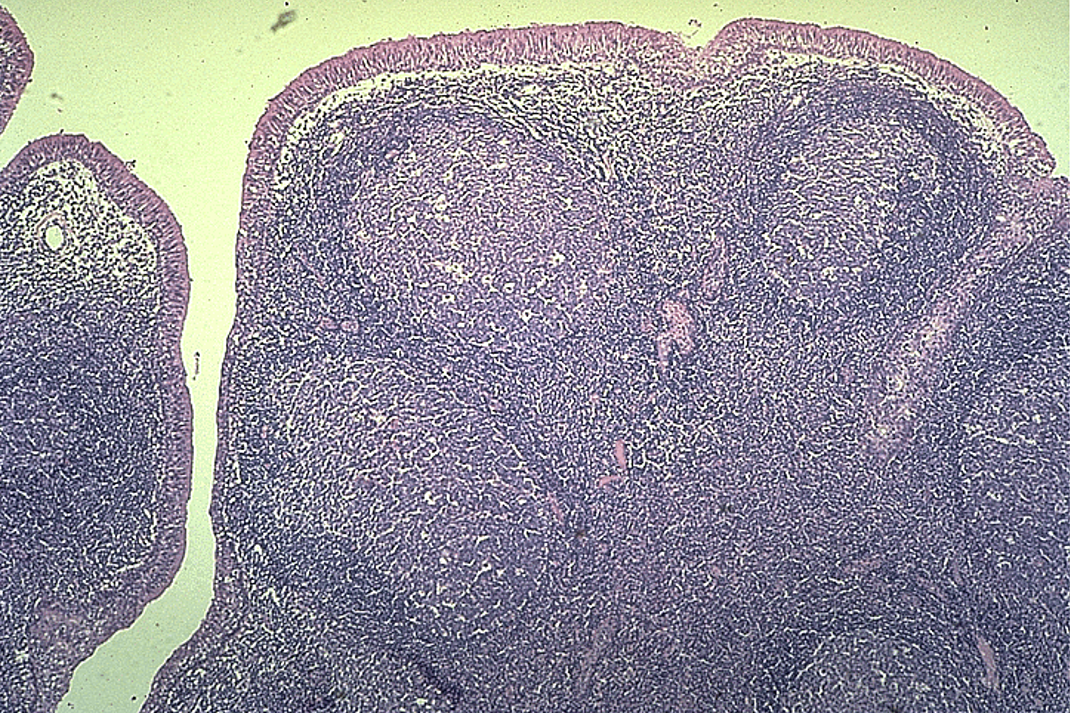
Identify this structure
Tonsils
Crypt and nodules w/ germinal centers observed
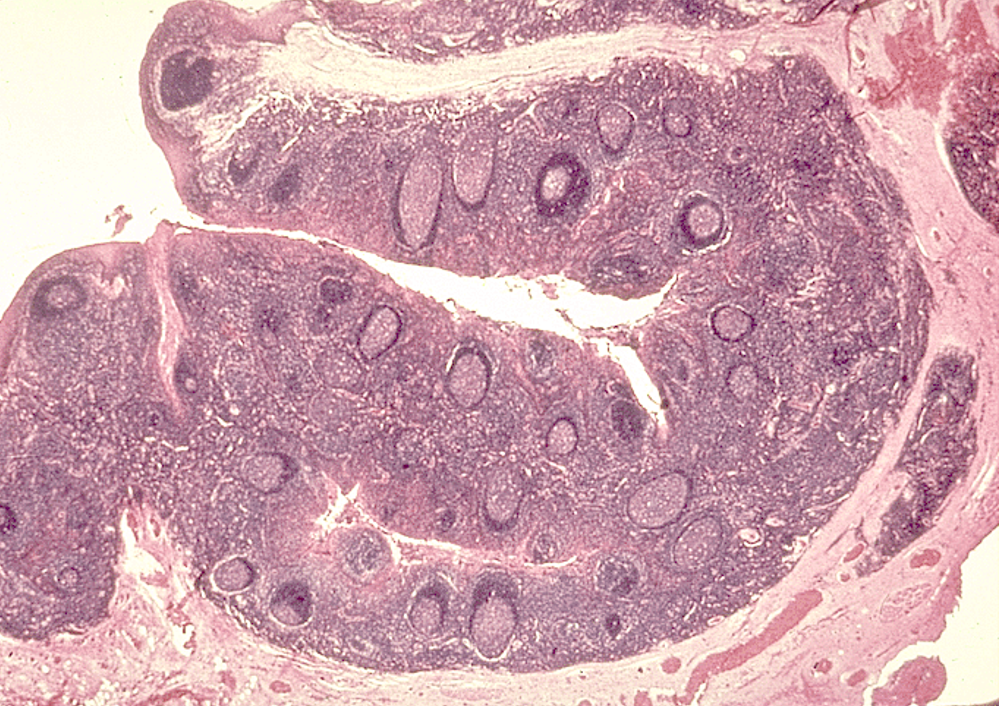
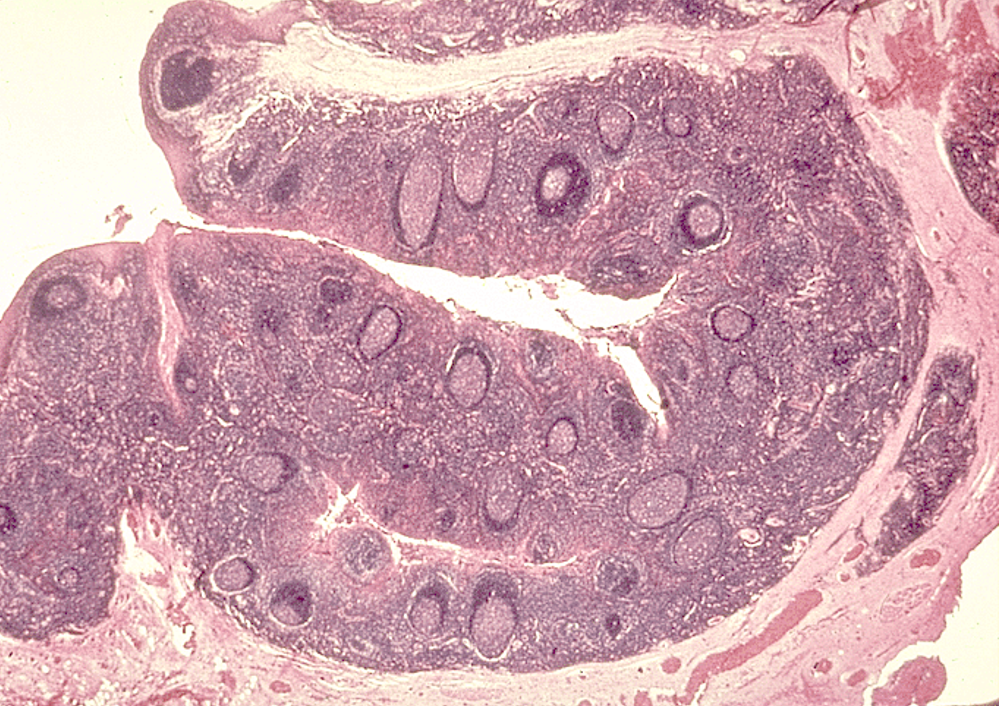
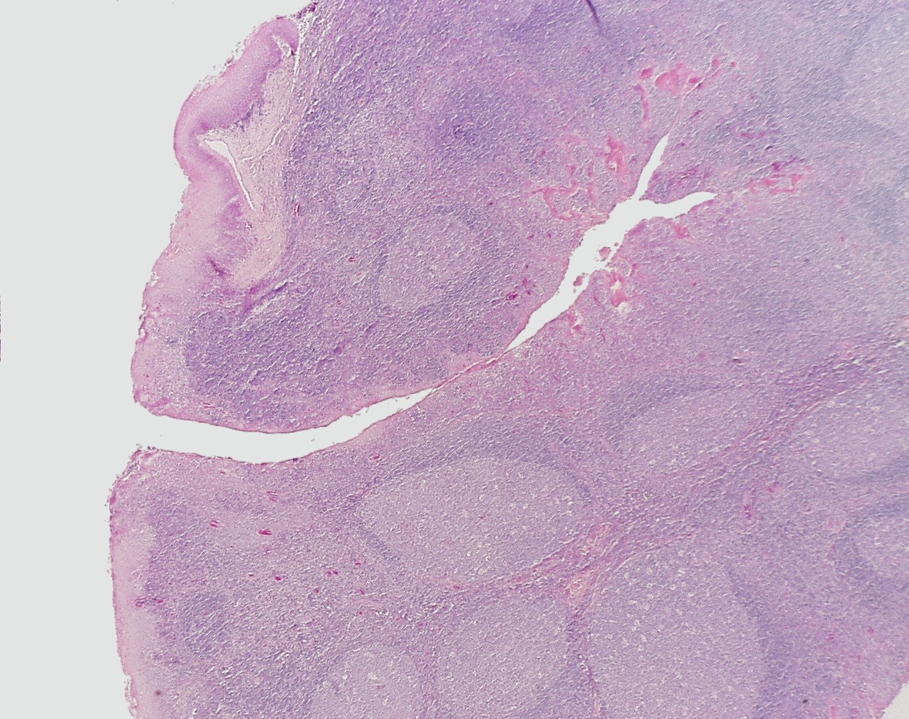
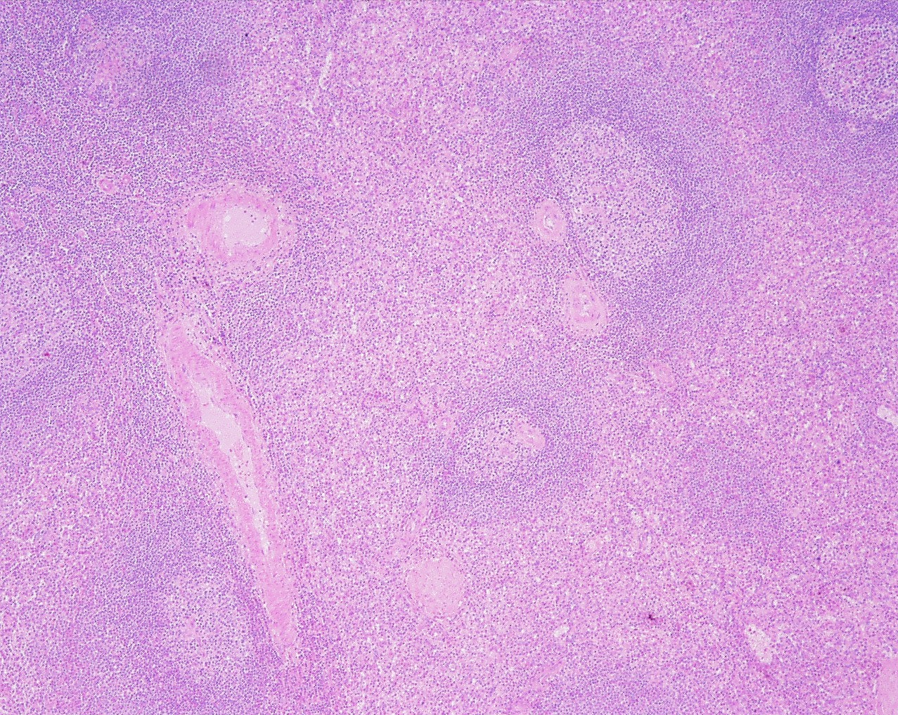
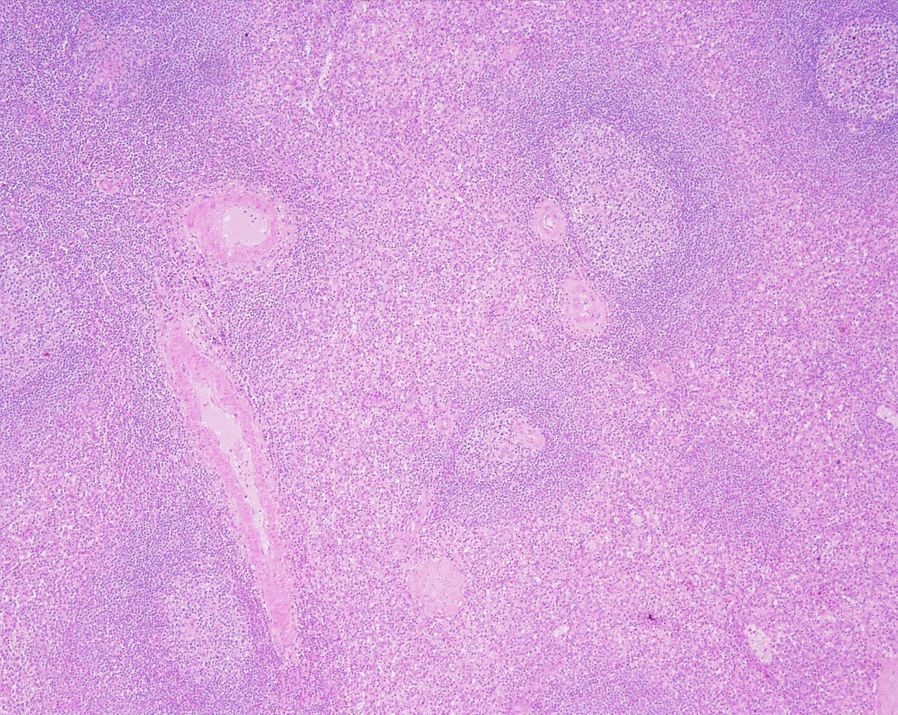
Identify this structure
Lymph Nodes
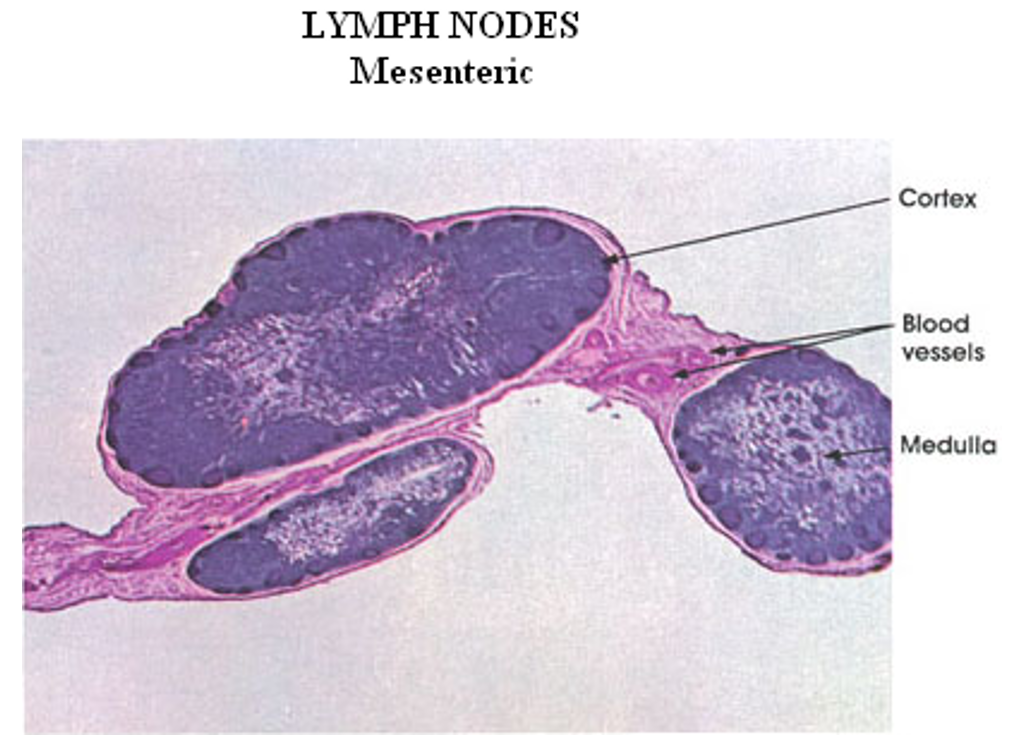
Identify this structure
Lymph Nodes
Capsule and subcapsular sinus observed
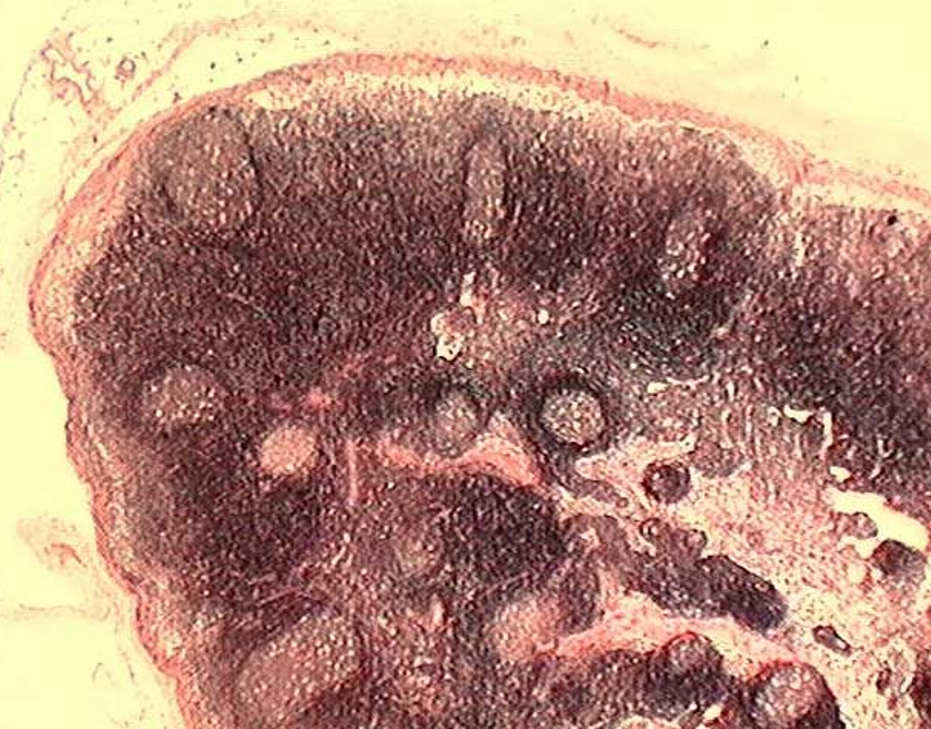
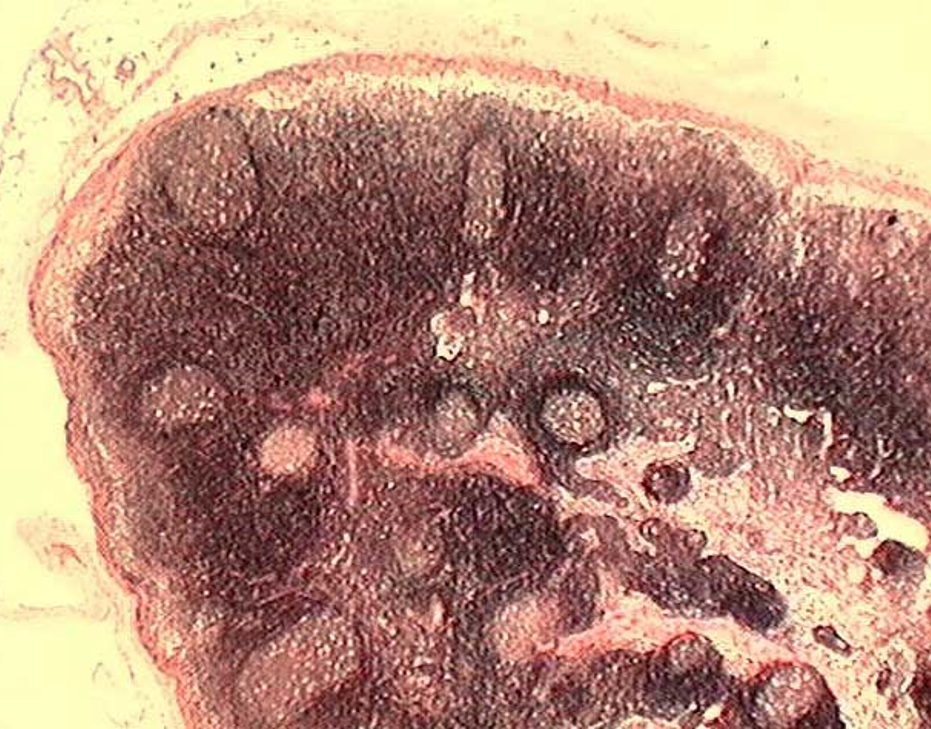
Identify this structure
Lymph Nodes
Capsule and subcapsular sinus observed
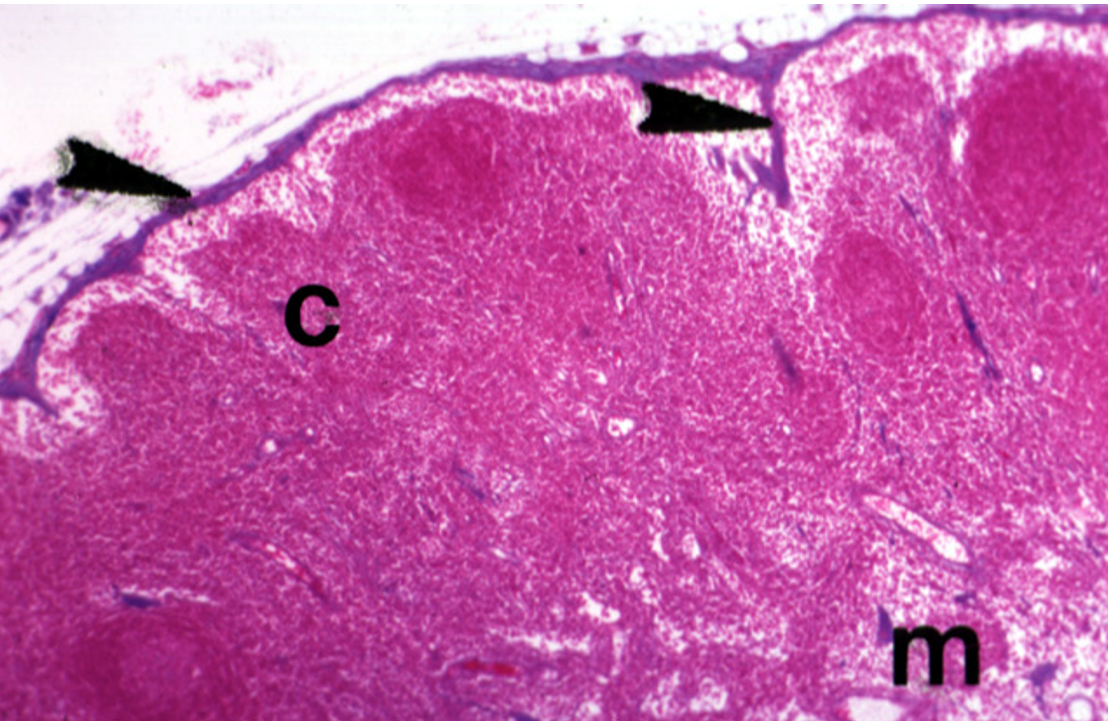
Identify this structure
Lymph Nodes
Capsule, germinal center and subcapsular sinus observed
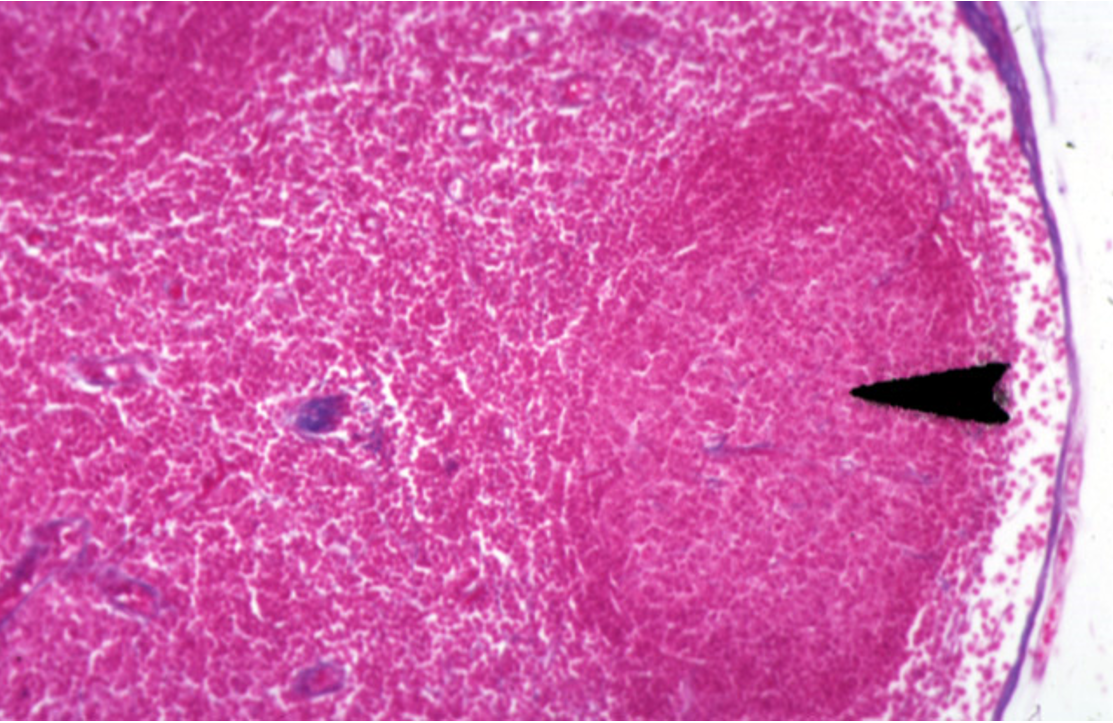
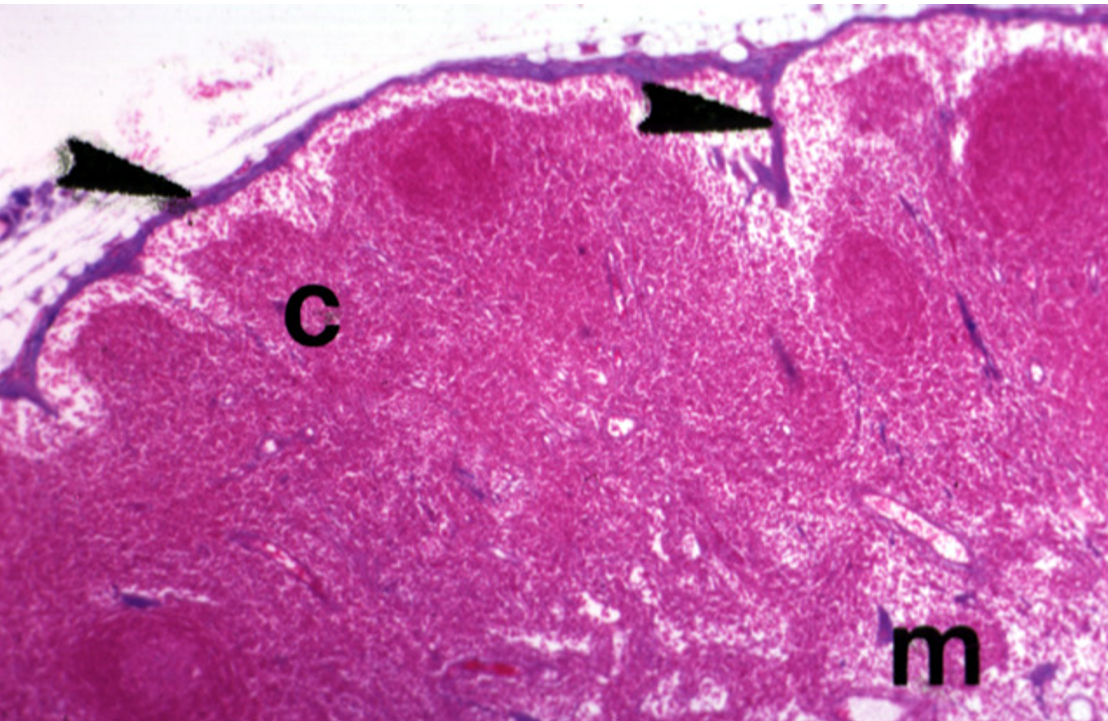
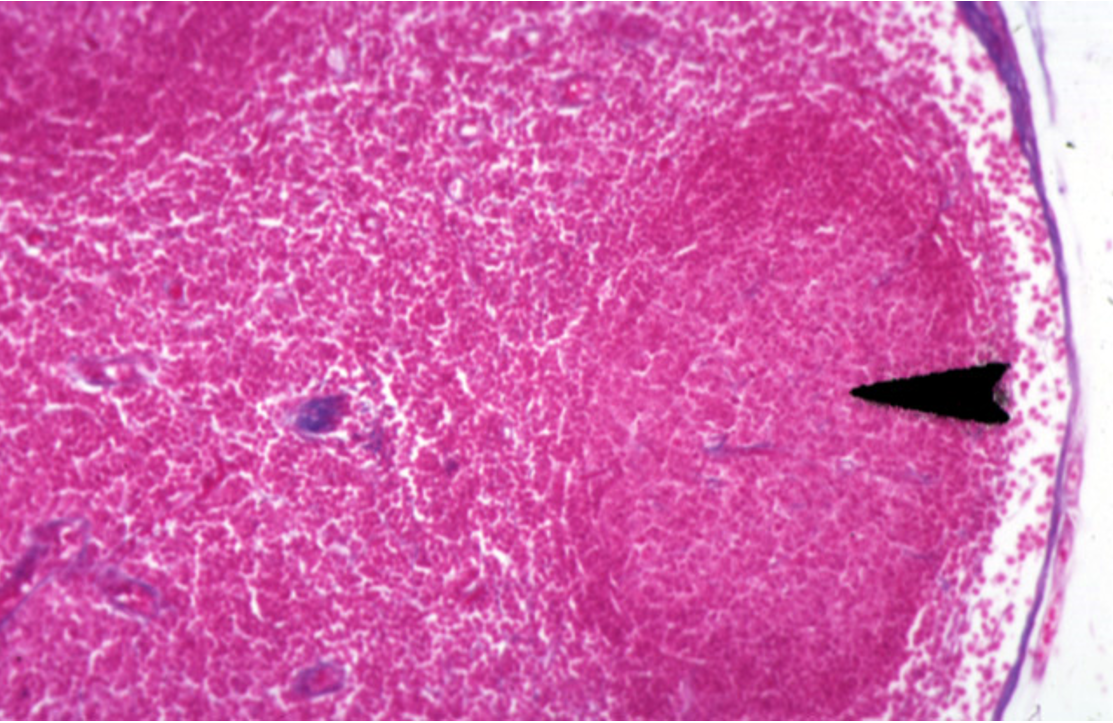
Identify this structure
Lymph Nodes
Dark-staining outer cortex, lymphatic nodules and sub-capssular sinus below the capsule observed
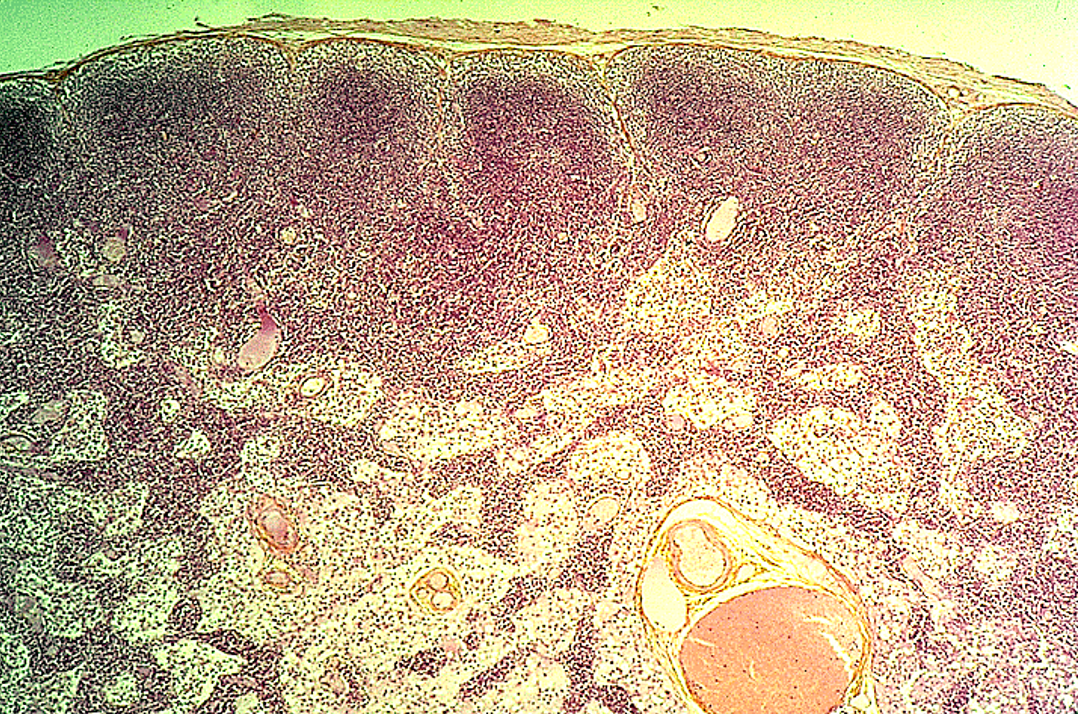
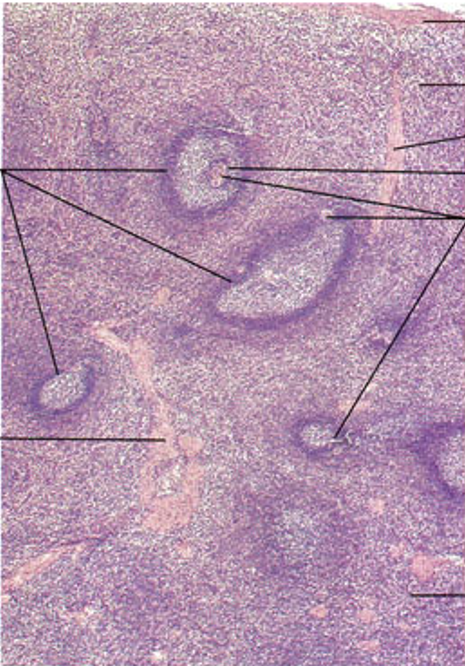
Identify this structure
Spleen
White & Red Pulp observed; Central arteriole observed
Identify this structure
Spleen
White & Red Pulp observed; Central arteriole observed
Identify this structure
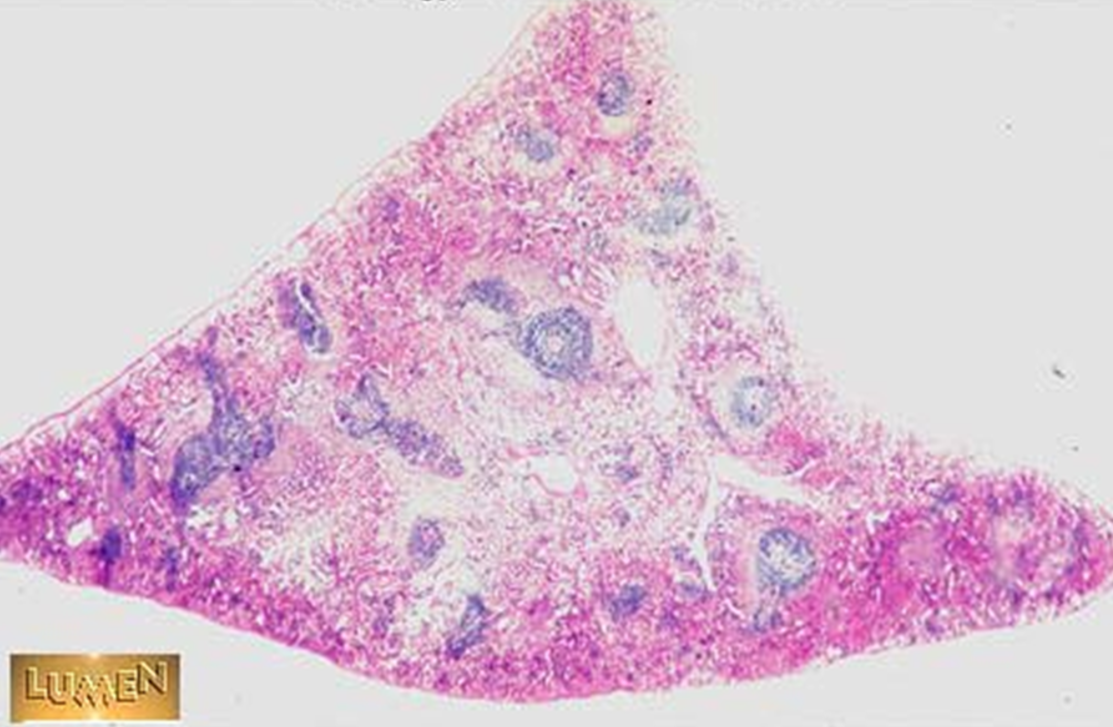
Spleen
Red & white pulp observed
Identify this structure
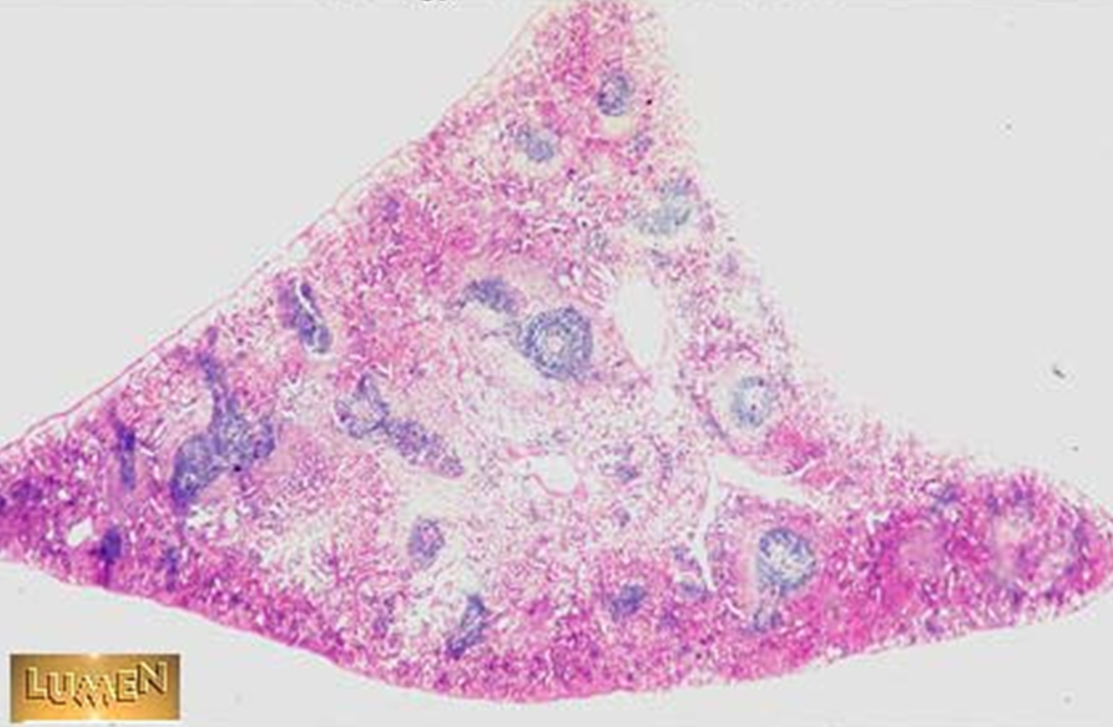
Spleen
White & Red Pulp observed
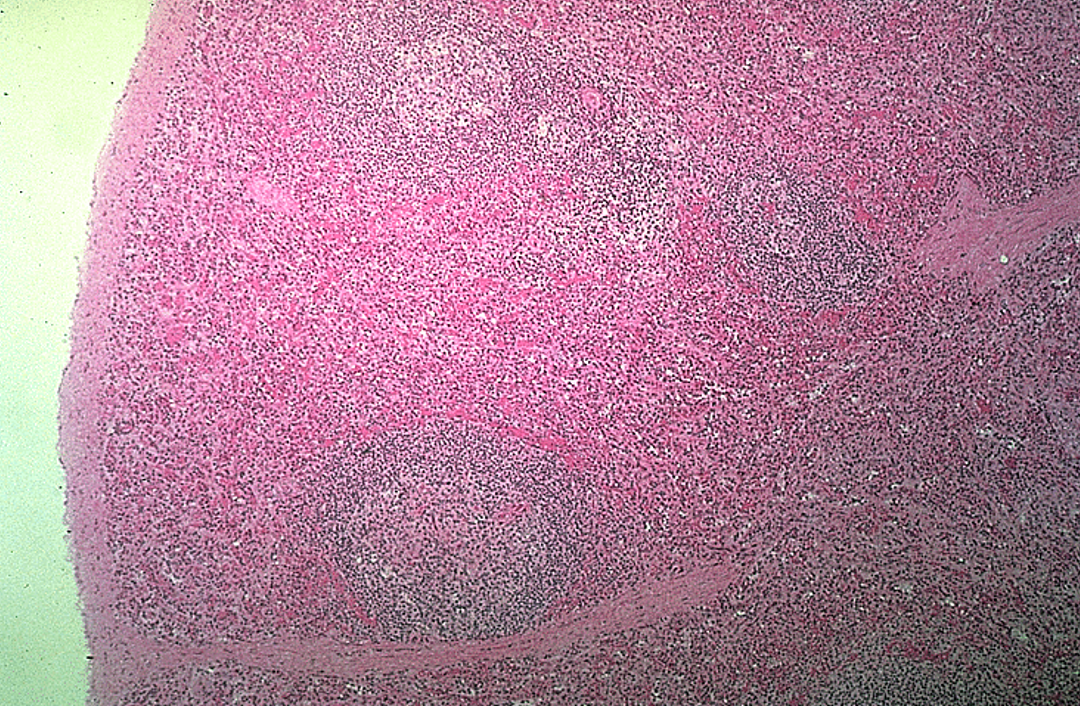
Identify this structure
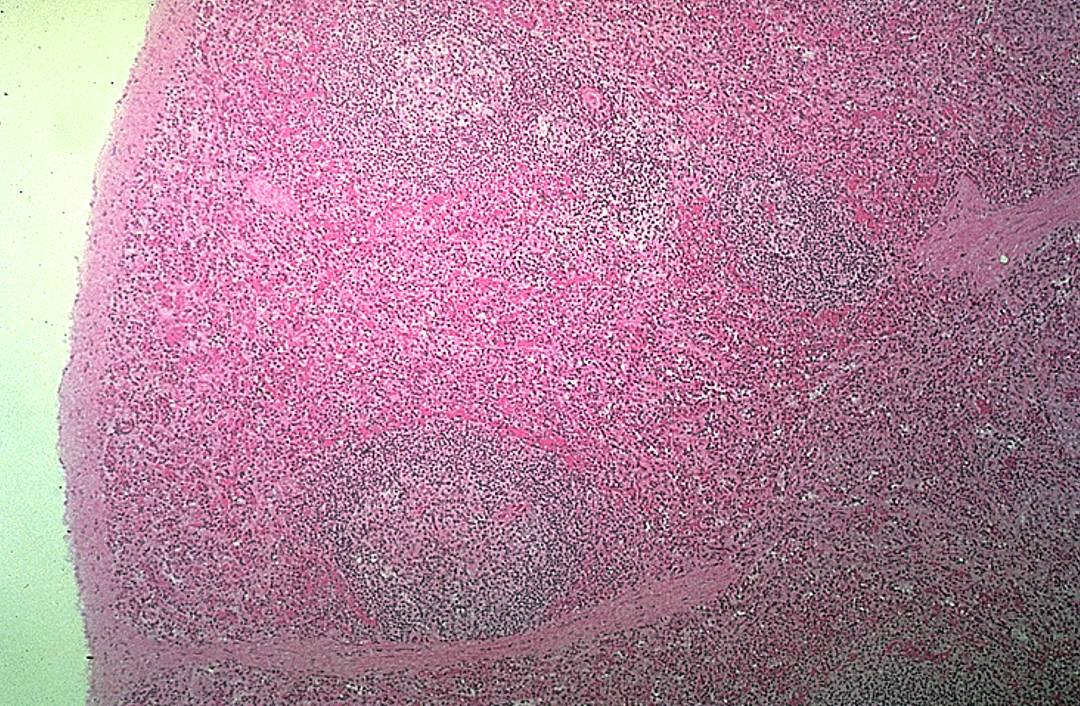
Spleen
Lymphatic nodule & germinal center observed
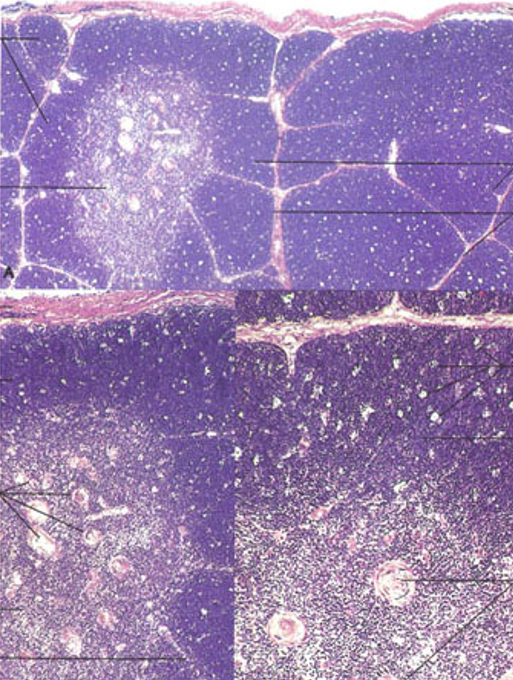
Identify this structure
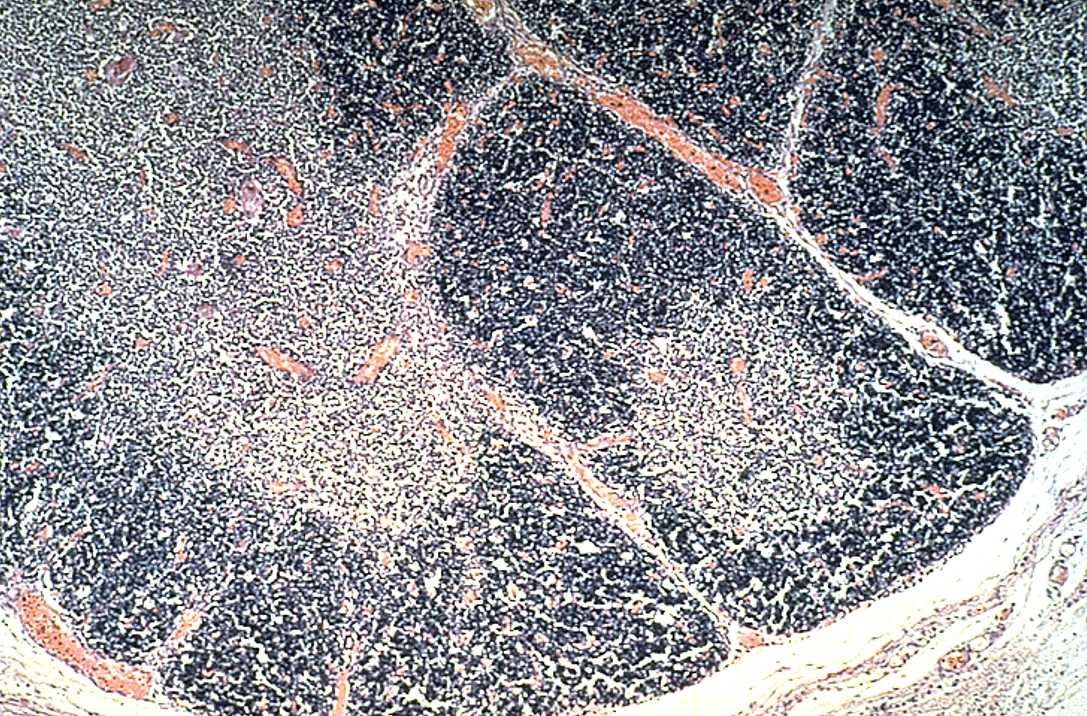
Thymus
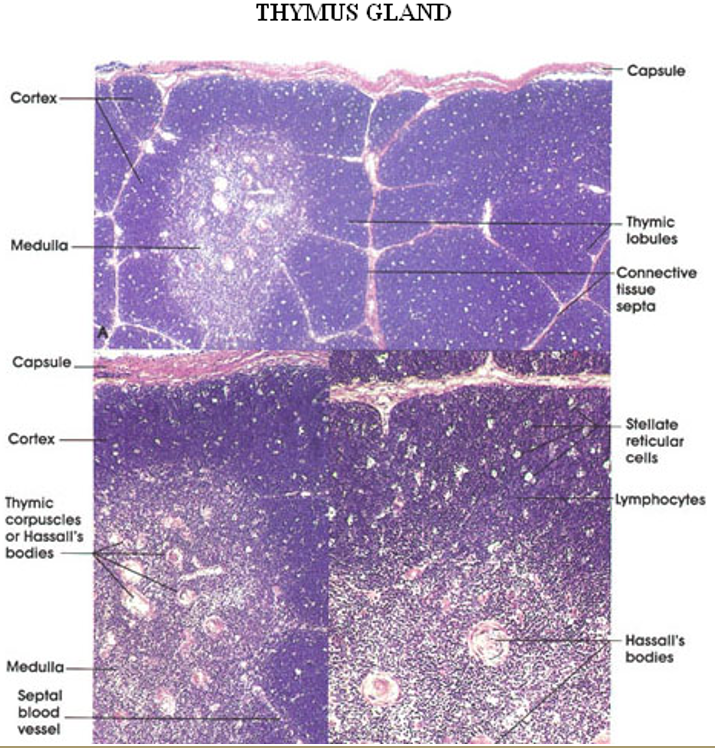
Identify this structure
Thymus
Identify this structure
Thymus
Dark outer cortex, lighter inner medulla with partitioning. The majority of cells in the thymus are T cells
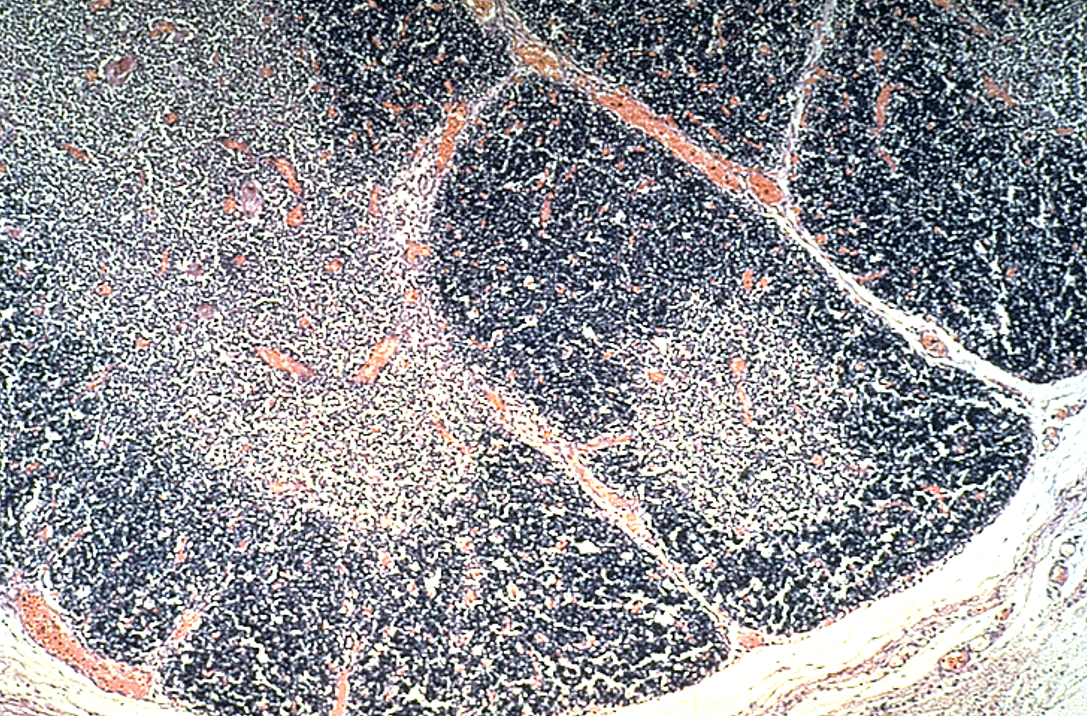
Identify this structure
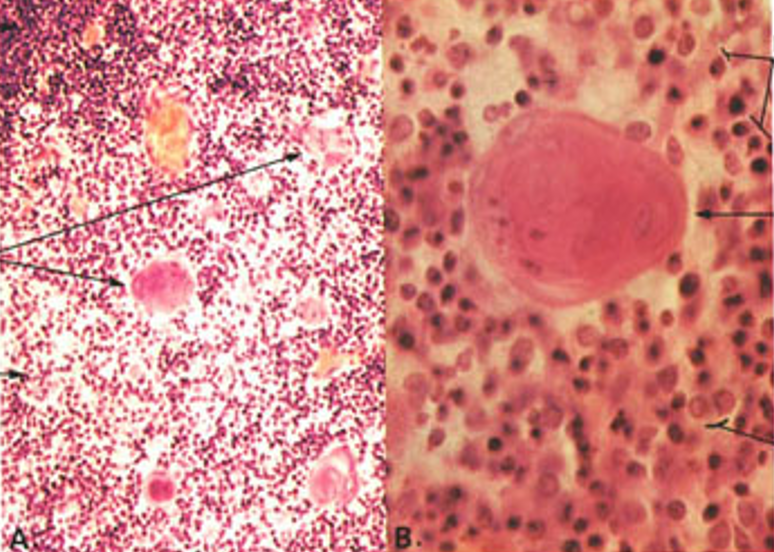
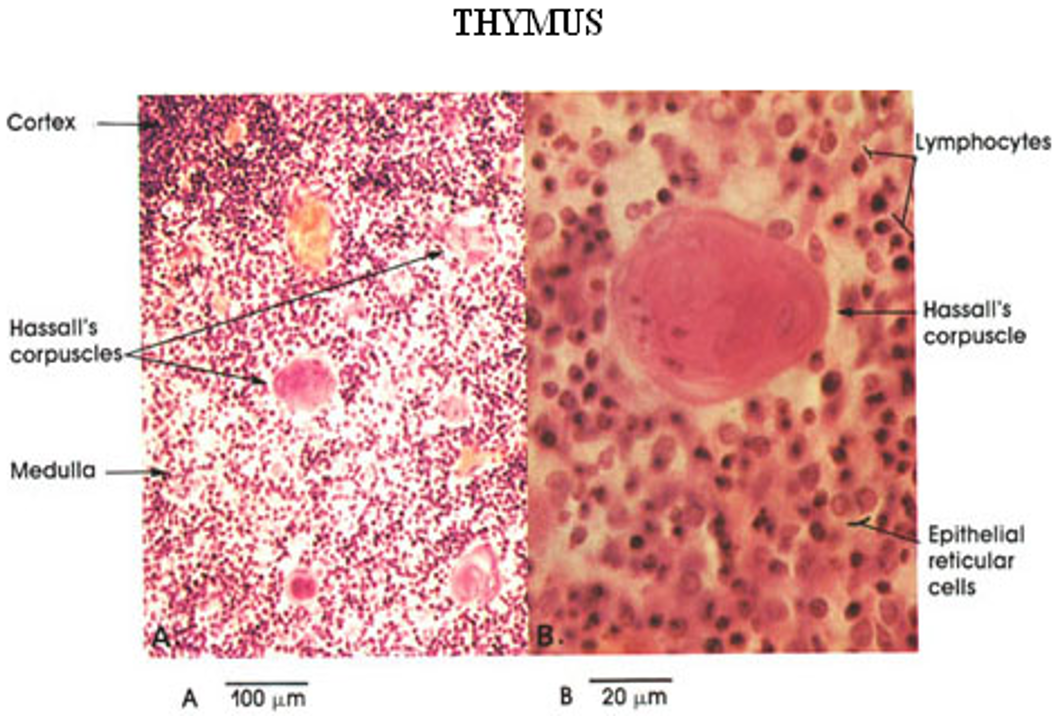
Thymus
Hassall’s corpuscles present
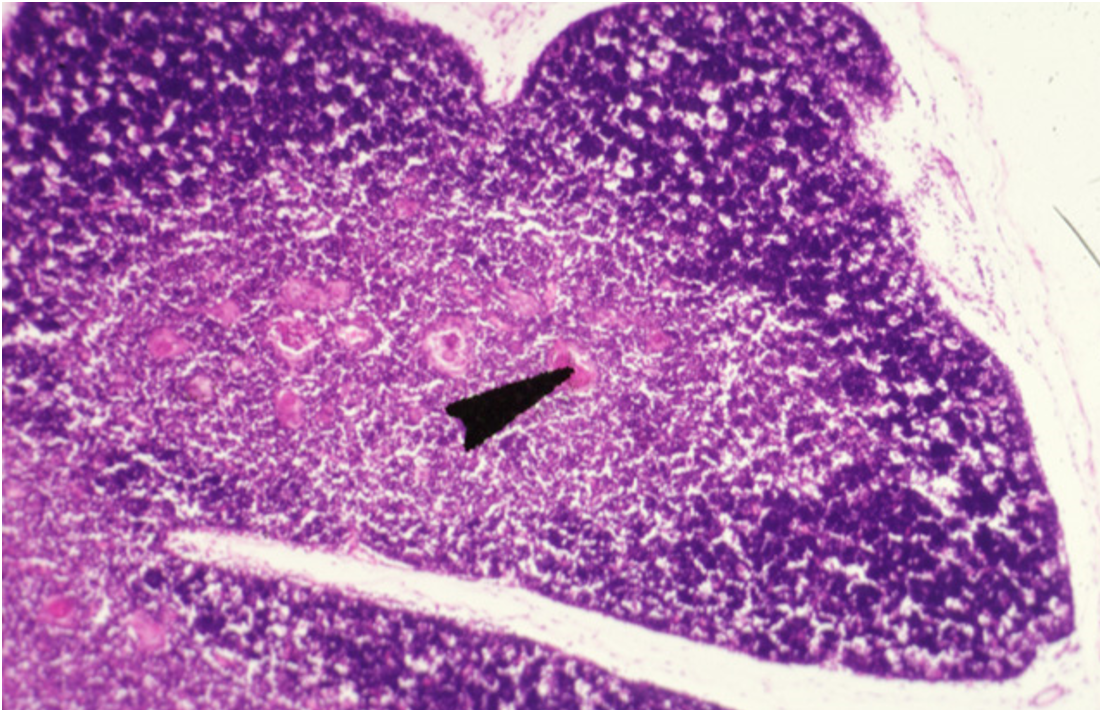
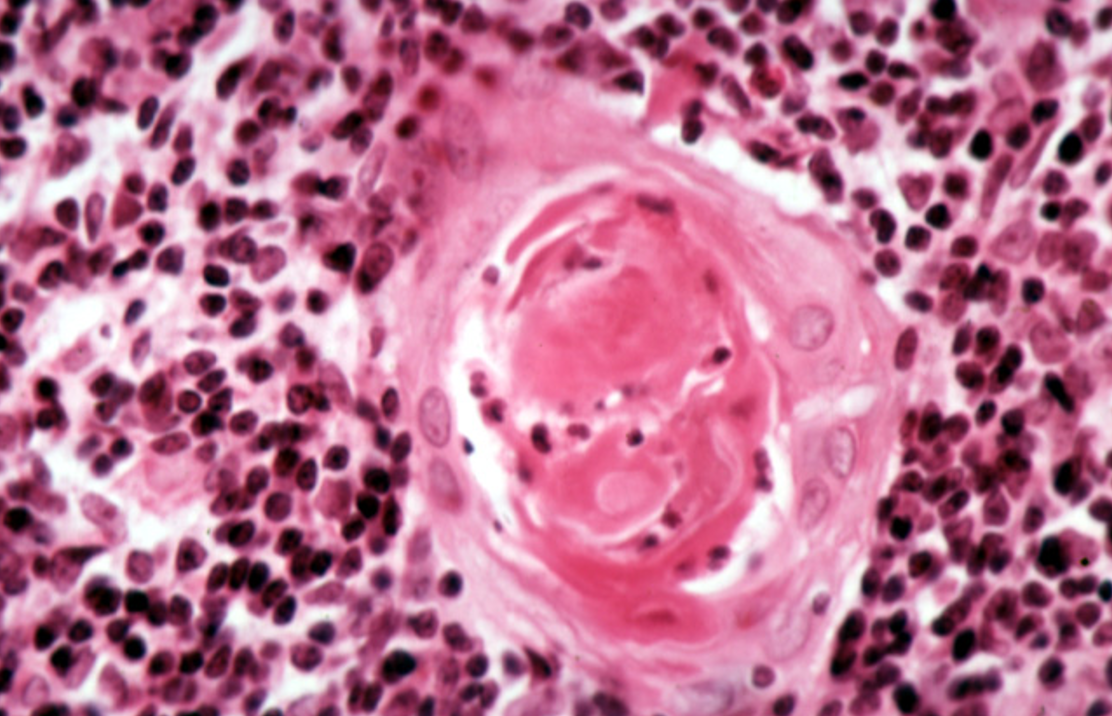
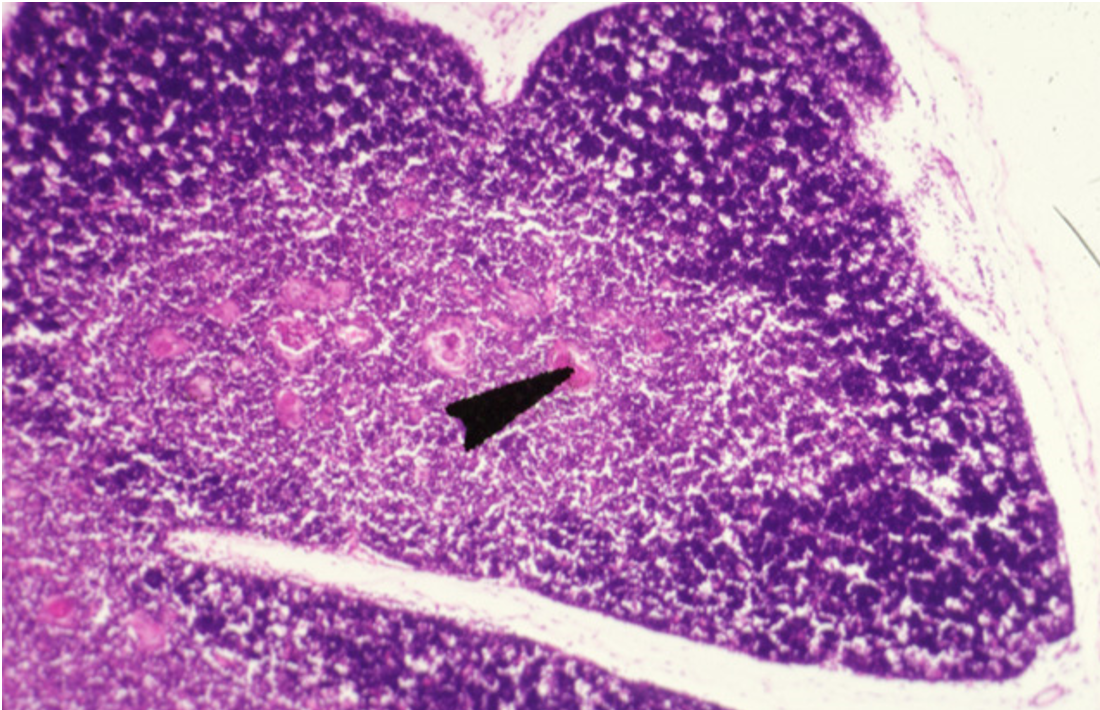
Identify this structure
Thymus
Hassall’s corpuscles
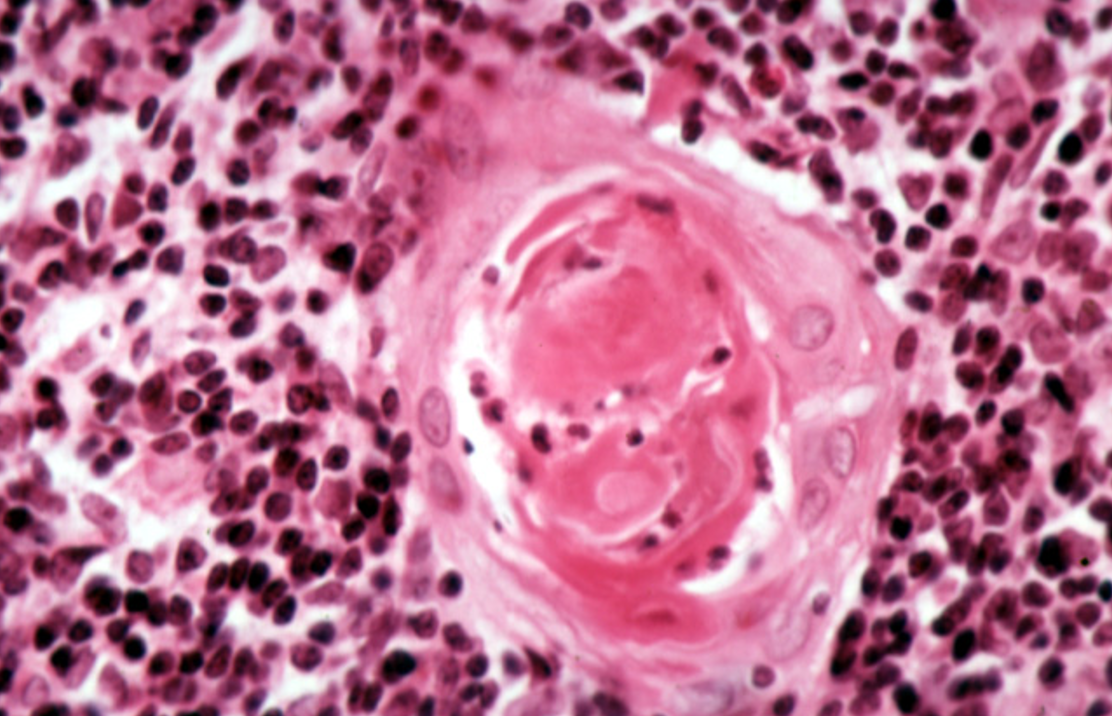
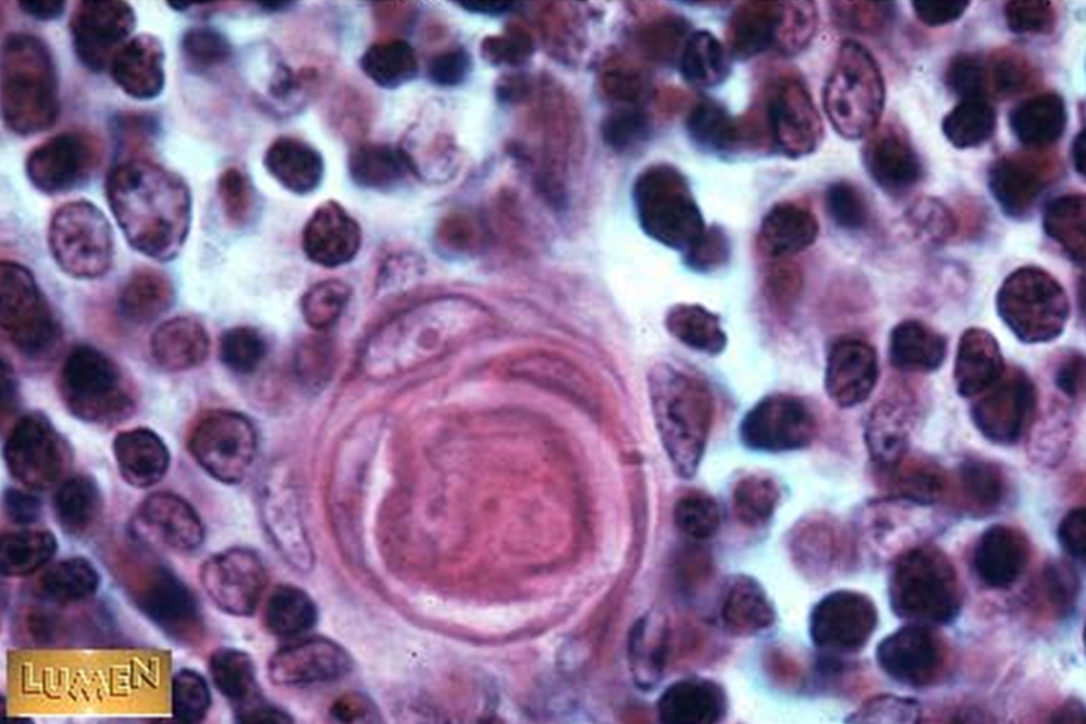
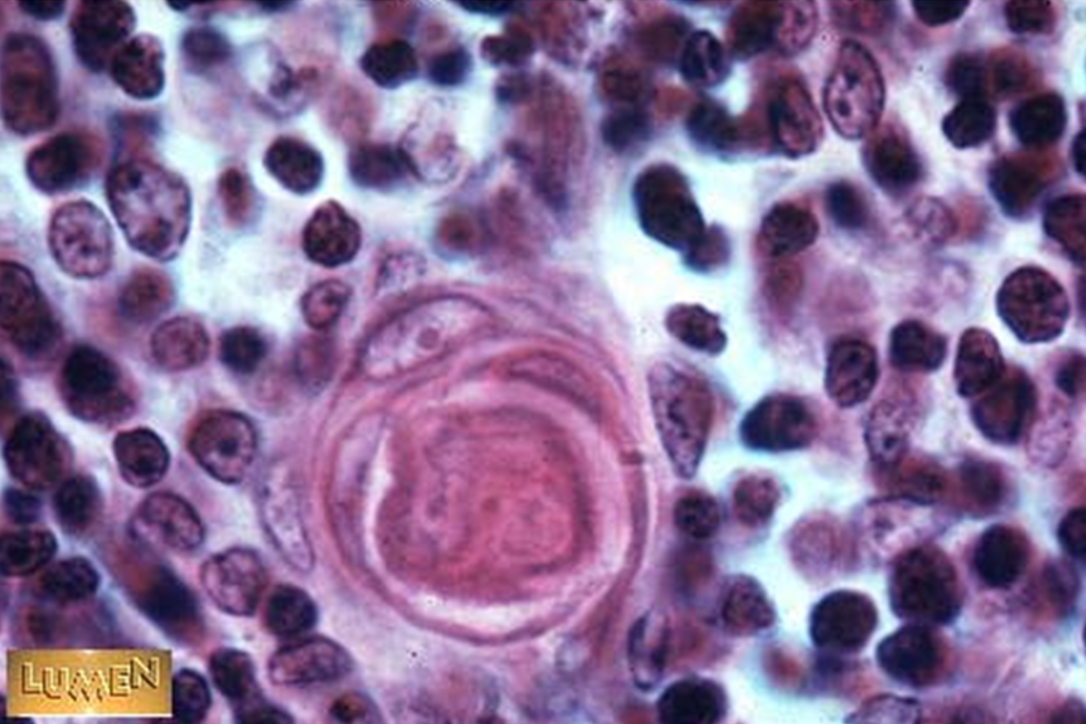
Identify this structure
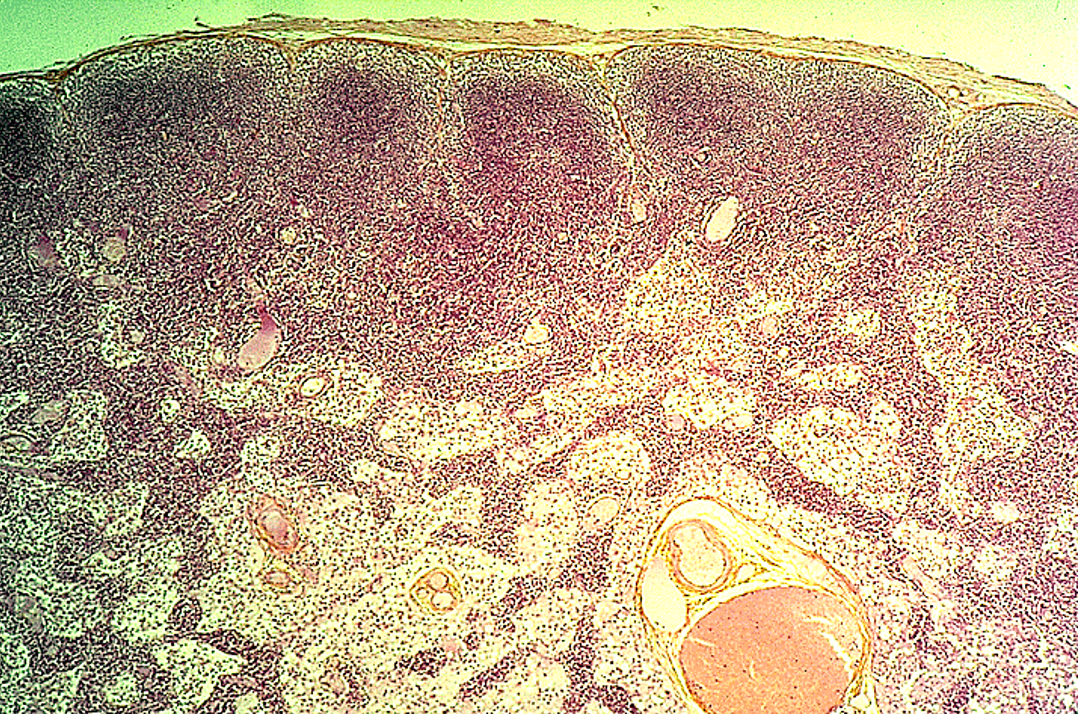
Thymus
Hassall’s corpuscles present in medulla of thymus
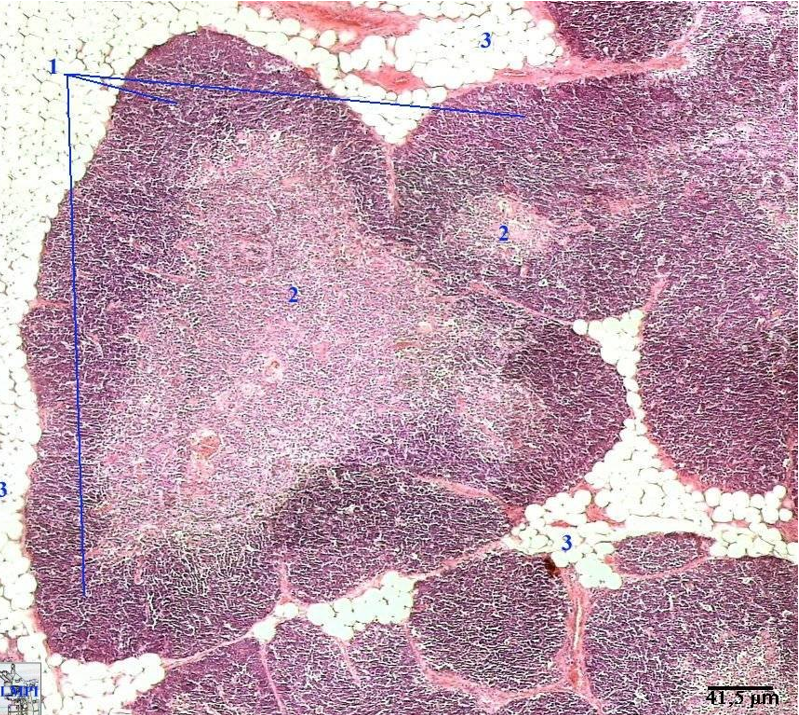
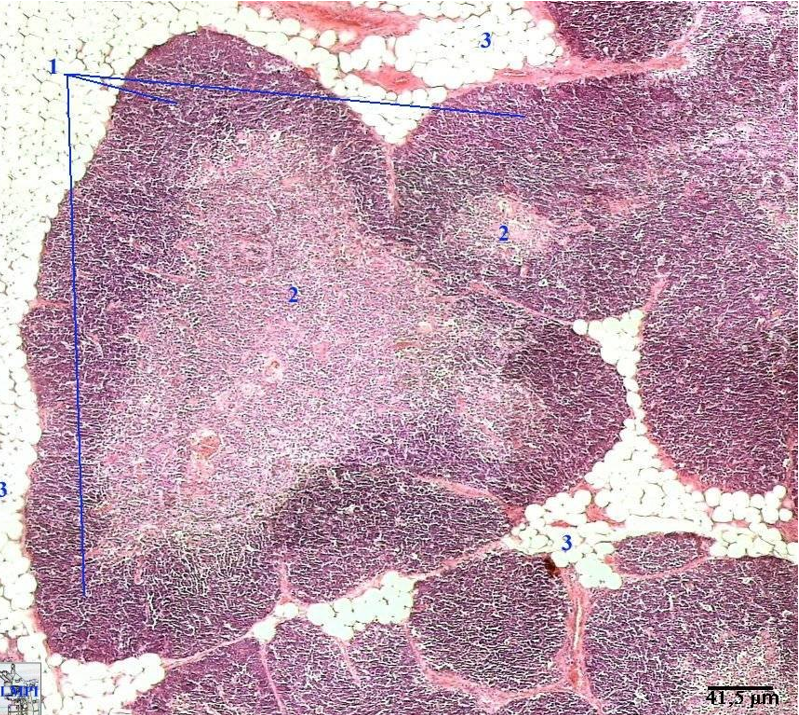
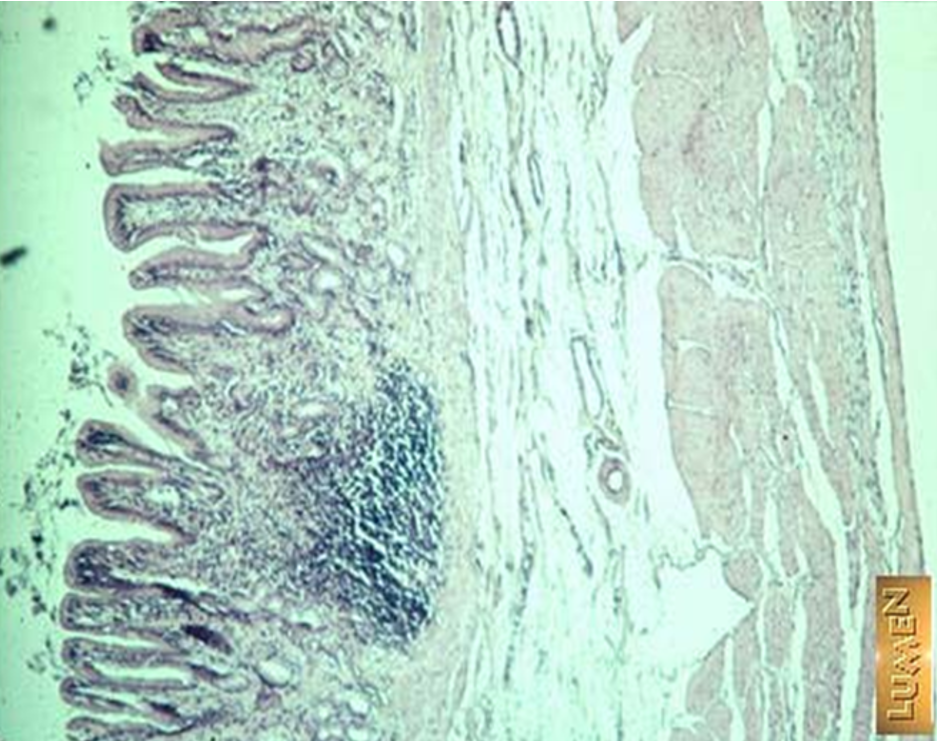
Identify this structure & process occuring
Thymus
Dark outer cortex, lighter inner medulla with partitioning. Involution is occuring. Thymus being replaced by adipose tissue.