lecture 32 - skeletal, smooth (and cardiac) muscle 1 - PoNF
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
functions of muscle
generate force and movement
maintain posture
stand against gravity
what are muscles
bundles of muscle fibres held together by connective tissue sheaths
how are muscles attached to bone
tendons
how are muscle cells replaced after injury
satellite cells
- differentiate to form new muscle cells
- type of myoblasts
- limited supply
when a muscle is injured, how do other muscles compensate
hypertrophy
do muscles ever completely recovery
no
3 main types of muscle
skeletal, smooth, cardiac
structure of skeletal muscle
striated
multinucleate
contractile proteins
peripheral nuclei
striated muscle
skeletal
cardiac
Formation of Skeletal Muscle Fibers
formed in utero from mononucleate MYOBLASTS
what are striations
bundles of myofibrils
stripes and line markers of skeletal muscle
thicker lines - myosin
thinner lines - actin
Z lines - denser protein deposits which help link together all the actin filaments
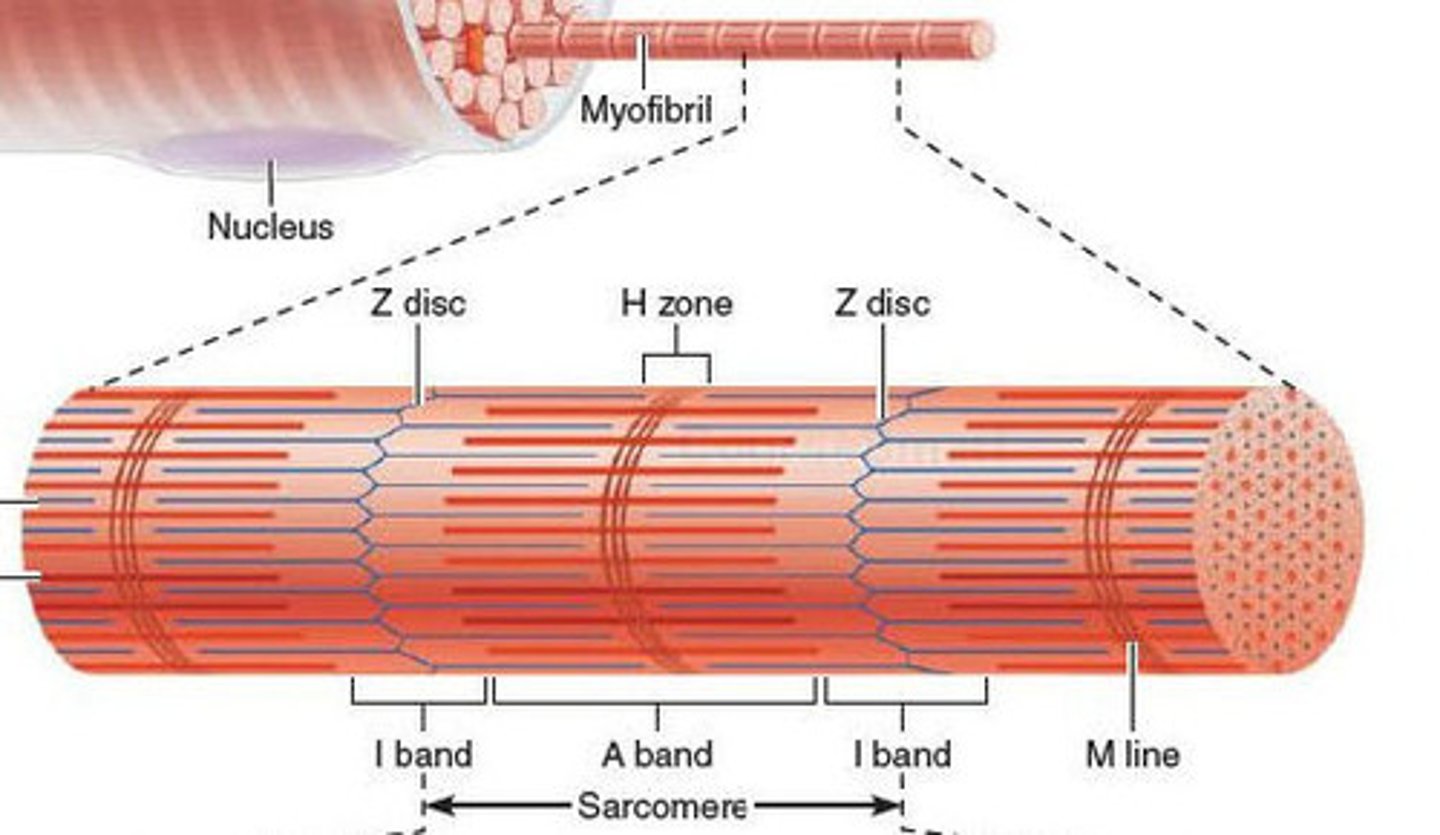
What is a sarcomere?
contractile unit of a muscle fiber
how are myosin filaments arranged? and why?
3D space in triangular patterns and the actin filaments filaments surround in a hexagonal pattern
- gives strength and durability
- helps sliding filament theory
- safety mechanism
what happens to a muscle when it contracts
shortens and thickens
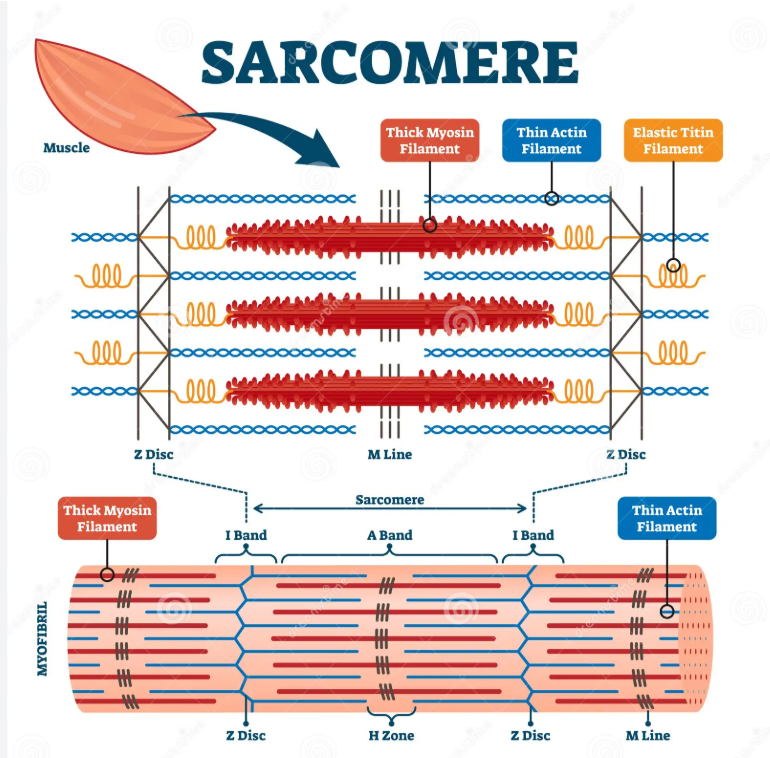
what causes shortening of the muscle in contraction (sliding filament theory) (5)
actin and myosin filaments slide past each other in an active process causing a contraction
myosin has lots of cross-bridges
Z discs of sarcomere move closer towards each other and towards M line
I band reduced (only actin)
H zone reduced (only mysosin and M line)
what remains constant despite shortening of sarcomere?
A band
Function of myosin heads
Stores ADP until contracting which then stores ATP
myosin cross bridges
attach to thin filament and force thin filament toward center of sarcomere
binding sites of myosin cross bridge
2 actin binding sites
2 ATP binding sites
when do muscles fail to relax
ATP levels fall way below normal - actin and myosin do not detach from each other
power stroke of skeletal muscle
movement of myosin head that releases ADP
cross bridge cycle (after Ca2+ removes troponin from tropomyosin) (4)
1 myosin head binds to bidning site on actin - cross bridge formed
2 myosin head bends and pulls actin filaments together (power stroke, ADP release)
3 ATP binds to myosin head so it can detach
4 myosin head hydolyses ATP to ADP and Pi and uses energy released to return to original position
increased calcium levels effect on contraction
more contraction
function of troponin, tropomyosin and Ca2+ during contraction
Ca2+ regulates contraction
tropomyosin partially covers myosin binding site on actin
held in position by troponin
Ca2+ binds to troponin
troponin alters shape - pulls tropomyosin away allowing myosin heads to bind to actin
removal of calcium - blocks site again
describe the process of excitation-contraction coupling (4)
action potential in transverse tubule depolarises DHP
DHP (special Ca2+ channel) opens RyR in tubule
Ca2+ released from sarcoplasmic reticulum lateral sac into cytoplasm
Ca2+ binds to troponin allowing actin-myosin binding
describe the process of excitation-contraction relaxation (4)
sarcoplasmic Ca2+ATPase pumps Ca2+ back into SR
decrease free cytosolic Ca2+
Ca2+ unbinds from troponin
tropomyosin recovers myosin binding site on actin
why does blood surround muscles
full access to ATP and O2 in muscles
removal of waste products such as CO2 and ADP + Pi
what is the motor unit
motor neurones + muscle fibres
small motor unit innervation
1 motor neurone innervates FEW muscle fibres (fine motor control)
large motor unit innervation
1 motor neurone innervates MANY muscle fibres (simple movements like squat jumps)
force exerted by muscle
tension
force exerted ON a muscle
load
contraction with constant length
isometric contraction
contraction with shortening of length
isotonic/concentric contraction
twitch contraction
quick, jerky response to a stimulus - single action potential
latent period of muscle twitch
period after stimulus before contraction begins
3 muscle twitch phases
latent phase
contraction phase
relaxation phase
as muscle load increases
contraction velocity and distance shortened decreases
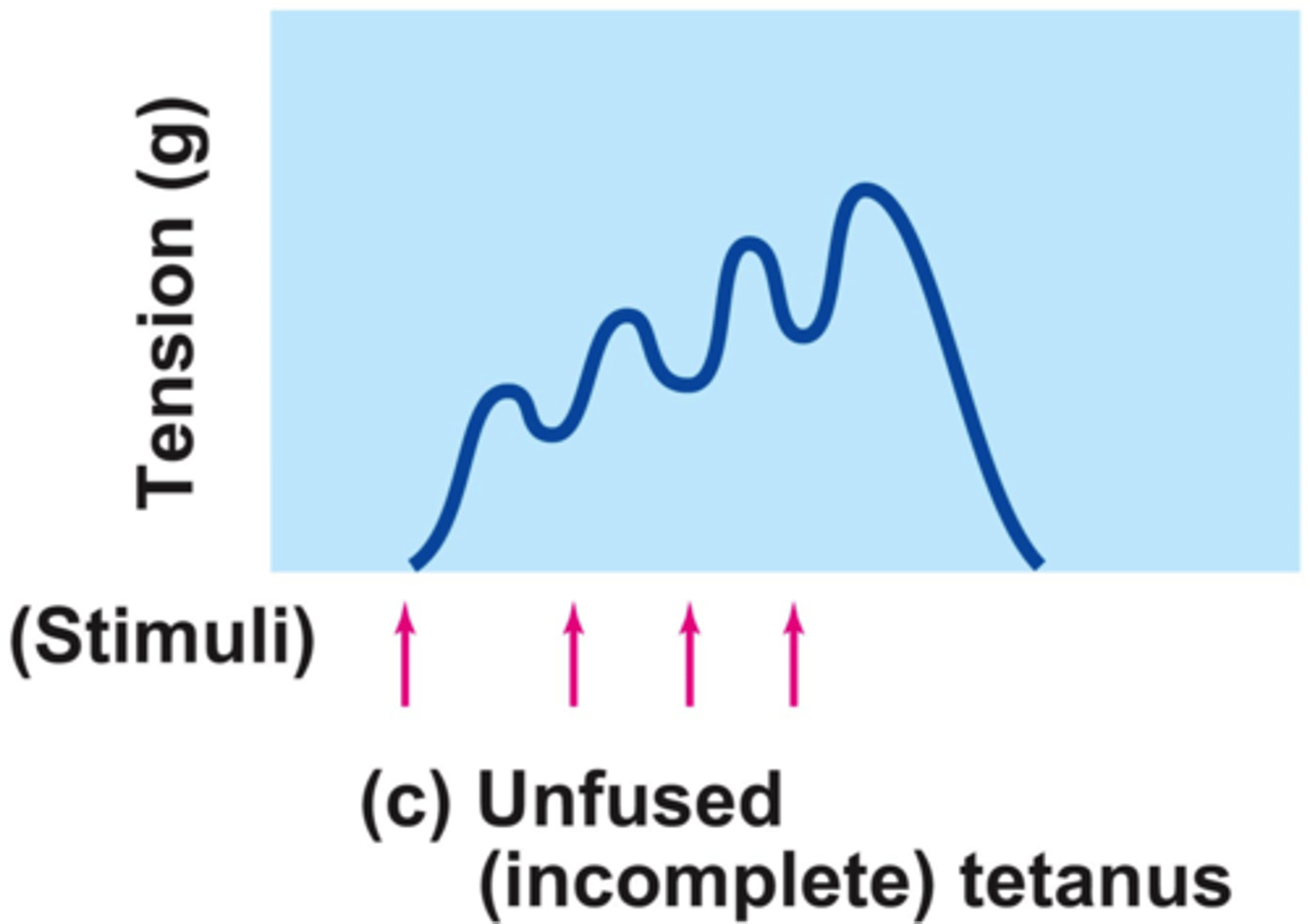
tetanus
small action potentials - summation
multiple frequent stimuli - max tension
Why is tetanic tension greater than twitch tension?
[Ca2+] never gets low enough to allow troponin/tropomyosin too re block myosin binding sites
unfused tetanus (most common)
some relaxation occurs between contractions
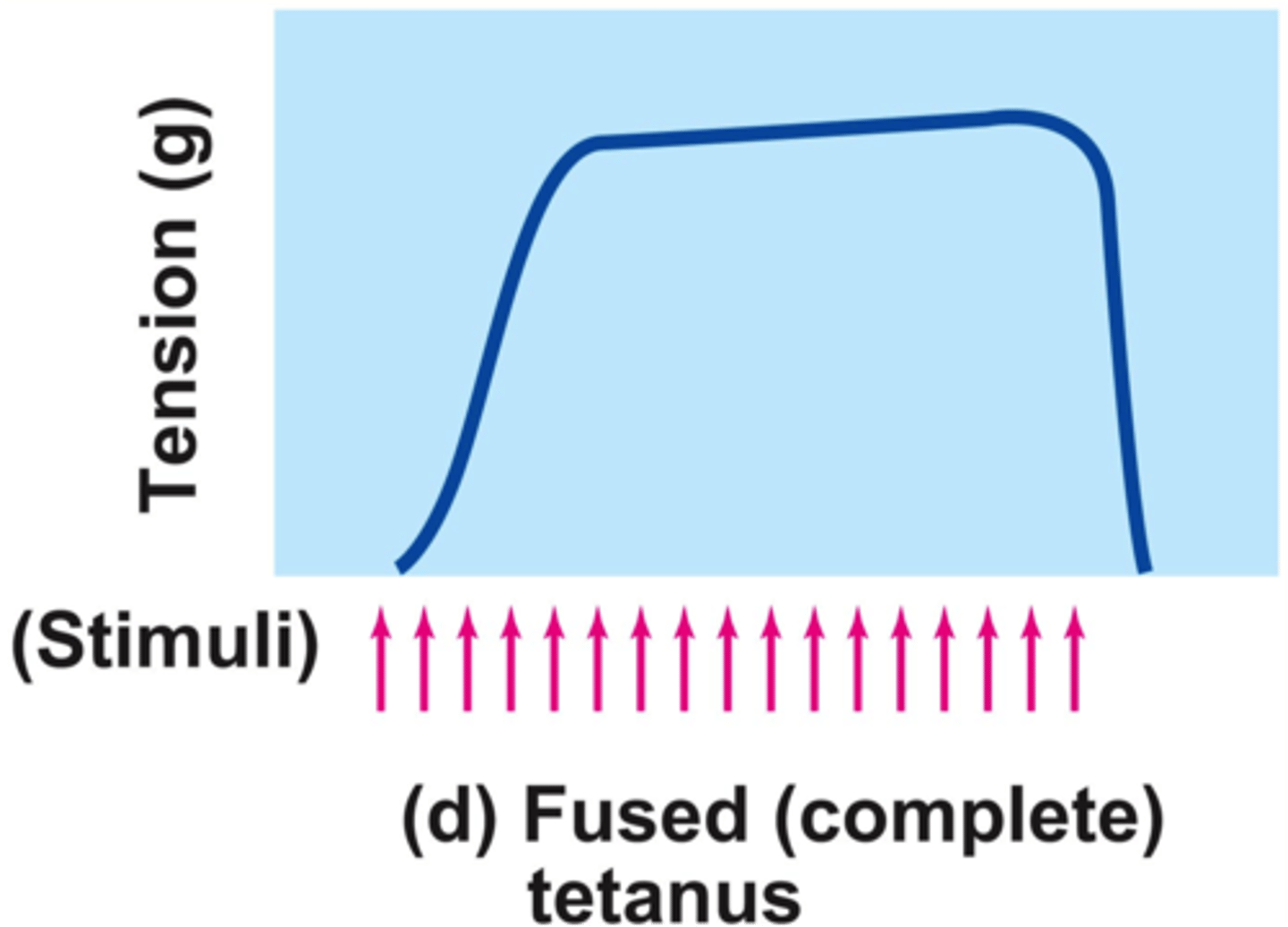
fused tetanus
No evidence of relaxation before the following contractions
The result is a sustained muscle contraction
less overlap of filaments
less tension
too much overlap of filaments
too much tension that filaments interfere with each other
Muscles work in
antagonistic pairs