3.4.6 Monopsony
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
Define a monopsony
When there is only one buyer in the market
What are the characteristics of a monopsony?
Single buyer of a good in a market
Aim to profit maximise
High barriers to entry
What is one example of monopsony power, as a pure monopsony rarely exists?
Moreover, food retailers have power when purchasing supplies from farmers; farmers can either sell them all their goods at a low price or risk not selling them at all.
How do monopsonists maximise profit?
They will pay their suppliers the lowest price possible to minimise their costs and make the most of their position as the only buyer.
This will enable them to maximise their profit.
The value of the goods they buy will depend on how much money they can make with these goods, and this is determined by the demand curve of the goods they make and sell.
What is the diagram of a monopsony?
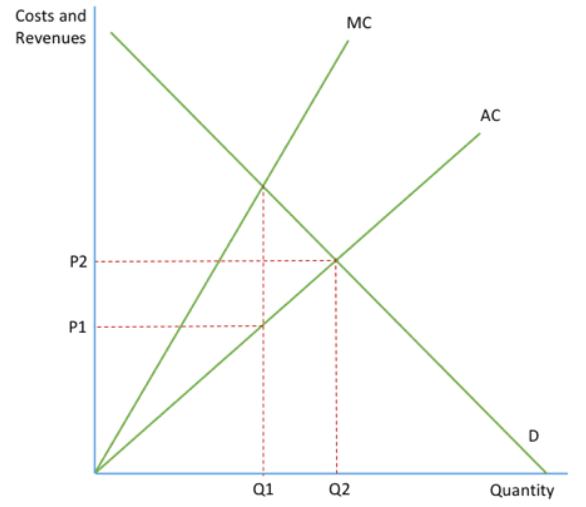
What are the costs and benefits to firms of the monopsony market structure?
The monopsony gains higher profits by being able to buy at lower prices. This increases the funding for research and development and leads to more return for shareholders.
They achieve purchasing economies of scale, which will lower costs and increase profits. Firms can exploit bargaining power over suppliers.
What are the costs and benefits of consumers of monopsony power?
Customers may gain from lower prices as reduced costs are passed on.
There may be a fall in quality as prices are driven down
What are the costs/benefits to employees of a monopsony?
The supplier will sell less goods and so employ less people, whilst the monopsonist may employ fewer, more or the same amount of people since they have less inputs to use for production but their costs are also lower.
Monopsonists may pay higher wages as they are making higher profits.
What is the cost to suppliers of a monopsony?
Suppliers will lose out as they will receive lower prices ; less will be supplied leading to some firms leaving the market. They will face a reduction in producer surplus
Evaluate the likely costs of a monopsony operating in the product market.
One cost is reduced producer surplus for suppliers. Suppliers are subject to monopsony abuse as they have no alternative buyers to sell their product to. draw short run shut down/ loss of producer surplus diagram. However, suppliers have a guaranteed income and do not have to spend on advertising/promotion as there is only one supplier.
Another cost is lower consumer welfare due to suppliers being dynamically inefficient due to lower snp. however lower prices leads to consumer surplus which is a form of consumer welfare
another cost is to employees, suppliers and monopsonists may have to let go of workers. however monopsonist have higher profits and can pay workers higher wages
judgement, depends on business objectives of monopsonist