A-Z NAVLE review part 2
1/683
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
684 Terms
What does the S1 heart sound signal?
Closure of AV valves and end of systole
What does the S2 hear sound signal?
Closure of semilunar valves and end of systole
When might an S3 heart sound be heard?
Increased venous return or pregnanct
What is the S4 heart sound associated with?
Atrial contraction
In what animal can the S4 heart sound be head?
Horses
What age of dogs is heart clock commonly seen at?
Middle to older dogs
What can cause increased vagal tone leading to heart block?
Drugs, endocarditis, DCM, HCM, hyperkalemia
What CS are seen with high-grade heart block?
Syncope, exerintol, and weakness
How does heart block appear on an ECG?
Decreased HR w/no QRS, large T
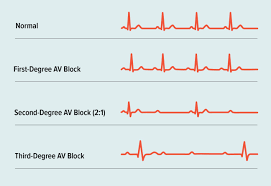
What are the different degrees of heart block?
1st-3rd degree
What is the long-term management for heart block?
Pacemaker
Should antiarrhythmic drugs be given for heart block, and why or why not?
Don’t give antiarrythmic drugs, may suppress rhythm
Which breeds are commonly affected by Sick Sinus Syndrome?
Female mini Schnauzers, Dachshunds, Pugs

What arrhythmias are seen with Sick Sinus Syndrome?
Supraventricular tachyarrhythmias
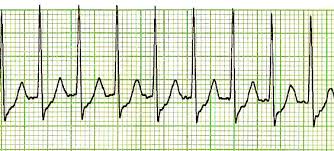
How does Sick Sinus Sinus appear on ECG?
Sinus bradycardia, sinus arrest, SA block
What is required for long-term treatment of sinus syndrome?
Permanent pacemakers
Do asymptomatic dogs w/abnormal ECGs indicative of Sick Sinus require treatment?
No
What are the different types of supraventicular tachycardia?
Atrial premature contractions, paroxysmal atria tachycardia, atrial flutter, and atrial fibrillation
What is the typical heart rate during supraventricular tachycardia?
>180 bpm
Is Supraventricular Tachycardia always hemodynamically sig?
Not always
How is the rhythm described in supraventricular tachycardia?
Regularly irregular rhythm
What does QRS complex look like on an ECG in supraventricular tachycardia?
Normal QRS
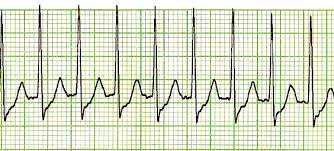
What is the treatment for supraventricular tachycardia to restore sinus rhythm?
Vagal maneuver to restore sinus rhythm
What types of drugs are used for chronic long term treatment of Supraventricular tachycardia?
Digoxin
Is Atrial fibrillation more common in dogs or cats?
Dogs
What conditions are associated with Atrial fibrillation?
MR, DCM, GDV, anesthesia, heatstroke, and trauma
Describe the pulse in atrial fibrillation?
Rapid irregular pulse w/chaotic rhythm
How is the rhythm described in atrial fibrillation?
Irregularly irregular
What does the ECG show in Atrial Fibrillation?
Chaotic pattern w/ no P waves
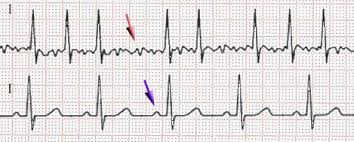
Can atrial fibrillation be cured?
No
What is the goal of treatment for atrial fibrillation?
Slow ventricular response rate so heart can fill better
What drugs are used for chronic, long-term treatment of Atrial fibrillation?
Digitoxin
What can cause ventricular premature contractions (VPCs)?
Myocarditis, DCM, lyte disorders, and trauma
Are VPCs typically hemodynamically sig.?
Rarely unless VPCs are frequent
When might VPCs cause hypotension or acid/base disturbances?
If VPCs are more frequent
How does VPC appear on an ECG?
Bizarre QRS >3 consecutive beats not preceded by P wave
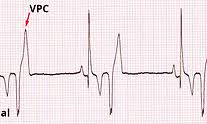
How is the heart rate described when there are multiple consecutive VPCs?
>160-180 bpm
What is the goal of treatment for VPCs?
Eliminate CS and prevent sudden death
What is the emergency treatment for ventricular arrhythmias?
IV lidocaine or procainamide or O2 administration
Which animal species and demographic is commonly affected by hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM)?
Middle aged male cats
What type of heart dysfunction is HCM?
Diastolic heart dysfunction
CS of HCM
Pale mm
Jug venous distension
Lack of femoral pulse
Murmur
Rear limb paralysis
Pain
Is arrythmia usually seen with HCM?
No not usually
What is the definitive diagnostic method for HCM?
Echocardiogram
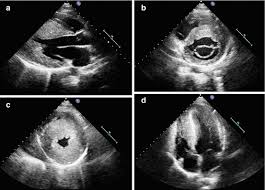
What is seen on an echo in HCM?
Enlarged heart at expense of lumen
What is the goal of treatment for HCM, and type of drugs are drugs are used?
B-blockers (Atenlol)
Ca2+ channel blocker (Dilitiazem)
Oxygen ± aspirin
Furosemide
Goal: To relax and slow the heart
Is digitalis used to treat HCM and why or why not?
No digitalis is not used because the heart pump is normal
Which animal species and demographic are commonly affected by Dilated Cardiomyopathy?
Large breed dogs
Which breeds are mentioned as commonly affected by DCM?
Doberman Pinscher, GSD, Saint Bernard, Irish Wolfhounds, Cockers
Is DCM common in cats?
Rare
What type of heart dysfunction in DCM?
Systolic dysfunction
What are CS of DCM?
Coughing, wt loss, weakness, ascites, syncope
What are the PE findings in DCM?
ADR, weak femoral pulses, arrhythmias (Afib and Vtach), gallops, jugular venous distension
What is seen on rads in DCM?
Pulmonary vein and vena cava enlarged, pulmonary edema
What is seen on an echo in DCM?
Dilation of atria and ventricles
What are the goals of treatment for DCM regarding afterload and contractility?
Decreased afterload and augment contractility
What class of drug is Enalapril, and for what condition is it used?
ACE inhibitor used to treat DCM
What type of drug is Digoxin and what conditions is it used for?
Cardiac glycosides used to treat DCM
What other types of drugs are used to treat DCM?
Diuretic if congested, procainamide if Vtach
How do ACE inhibitors work?
Inhibit angiotensin I → angiotensin II and production of aldosterone
What effects do ACE inhibitors have on peripheral vasoconstriction, Na and H2O retention?
Decreased peripheral vasoconstriction and NA and H2O retention
What are ACE inhibitors classified as regarding preload and afterload?
Afterload and preload reducers
What positive effects do ACE inhibitors have?
Vasodilation and reverse remodeling
What is the common suffix for ACE inhibitor drugs?
The “-pril” drugs
How is Enalapril activated and cleared?
Prodrug activated in liver, renal clearance
How is Benazapril clear?
Hepatic clearance
What are the potential side effects of ACE inhibitors?
Renal failure (decreased GFR), hypotension
Why should ACE inhibitors not be used w/NSAIDs
Together can affect kidney function and cause acute kidney injury
What type of vasodilator is Hydralazine?
Pure arteriolar vasodilator
What effect does Hydralazine have on afterload and BP?
Potent afterload reducer and decreased BP
What conditions is Hydralazine indicated?
Chronic valve disease and DCM
Does the dose of hydralazine need to be titrated?
Yes
What are potential side effects of Hydralazine?
Hypotension and increased HR
What type of drug is Amlodipine?
Ca2+ channel blocker
What type of vasodilator is Amlodipine?
Arteriolar vasodilator
For what is Amlodipine used in cats?
Treat hypertension in cats (with or without heart disease)
When is Amlodipine in conjuction w/ an ACE inhibitor in dogs?
To further decrease afterload
What is Nitroglycerin primarily used for?
Preload reducer, venous capacitance
What effect does Nitroglycerin have on preload?
Preload reducer, venous capacitance
Is Nitroglycerin used for emergency or chronic treatment?
Emergency use for CHF, blood in shunted to capacitance vv
What type of antiarrhythmic drug is procainamide?
Membrane stabilizer
How does Procainamide affect conduction and automaticity?
Slowed conduction, less automaticity
For what type of arrythmias is IV Procainamide used for emergency treatment?
Ventricular arrythmias
What type of antiarrythmic drug is Lidocaine?
Membrane stabilizer
What type of arrythmias is lidocaine used as emergency treatment?
Ventricular arrythmias
What is the half-life of IV lidocaine and how is it administed?
Short ½ life so required slow IV drip
What class of drug is Propanolol?
Class II Beta-blocker
What effect does Propanolol have on heart rate and contractility?
Negative chronotrope and inotrope
For what conditions is Propanolol used?
Tachycardia and HCM to decrease heart and increased filling time
How does Propanolol help in conditions like Atrial tachycardia and HCM?
Decreased heart and increasing filling time
What are some potential side effects of Propanolol?
Bronchoconstriction, bradyarrythmias, hypotension, heart failure, hypoglycemia
What calls of drug is Atenolol?
Class II B blocker, specific to B1
What makes Atenolol different from Propanolol in terms of side effects?
Don’t see bronchiolar effects
What type of drug is Ditiazem?
Ca2+ channel blocker
For what coditions is Diltiazem used?
Atrial tachycardia and HCM
What type of drug is Digoxin?
Cardiac glycoside
What effect does Digoxin have on contractility and heart rate?
Positive inotrope, negative chronotrope
For what condition is Digoxin used?
Supraventricular tachycardia, CHF, DHF
What is the sig side effect of Digoxin?
Arrhythmogenicity, N, V, D via stimulation of CRTZ
How is Digoxin dosed?
On lean body weight