Lecture 24: Lipids + Fatty Acids
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Biological Roles of Lipids and Fatty Acids
Energy Stores
Structural Supports
Signalling Molecules (Hormones, Cofactors, Binding Sites)
Light Absorbing Pigments
Electron Carriers
Unsaturated
possessing at least one carbon to carbon double bond
Fatty Acids
Carboxylic acids with a 4-36 unbranched carbon chain
Fatty acid Nomenclature
Determine the Root (the number of carbons
→1 = mono, 2 = di, …, 16 = hexadecaneConvert Alkane to fatty acid
→ replace -e with -oic acid
→ or if there is a double bond: replace -e with [# of double bonds]enoic acidPlace ratio of carbons to double bonds in front of name
→ [total carbons]:[double bonds] eg: 18:1State where double bonds are
→use Δ^ + position(s), counted from the carboxyl end
eg: Δ^(9,13)
Unsaturated Fatty Acid Nomenclature
Based on the number of double bonds:
1 = ___enoic acid
2= ___dienoic acid
3 = ___trienoic acid
And indicate the position of the double bond with: [total carbons] : [# of double bonds] (∆^[carbon number with double bond],…)
→ex: 20:5(∆^5,8,11,14,17) Eicosapentaenoic Acid
Palmitic Acid - Carbon skeleton, structure, systemic name
Carbon skeleton: 16:0
Structure: CH3(CH2)14COOH
Systemic Name: n-Hexadecanoic acid
Stearic Acid
Carbon skeleton: 18:0
Structure: CH3(CH2)16COOH
Systemic Name: n-Octadecanoic acid
Oleic Acid
Carbon skeleton: 18:1(∆9)
Structure: CH 3−(CH 2) 7−CH=CH−(CH 2) 7−COOH
Systemic Name: cis-9-Octadecenoic acid
Linoleic Acid
Carbon skeleton: 18:2(Δ9,12)
Structure: CH₃(CH₂)₄CH=CHCH₂CH=CH(CH₂)₇COOH
Systemic Name: cis-,cis-9,12-Octadecadienoic aicd
α-Linolenic acid
Carbon skeleton: 18:3(Δ9,12,15)
Structure: CH3CH2CH=CHCH2CH=CHCH2CH=CHCH2CH=CH=CH(CH2)COOH
Systemic Name: cis-,cis-,cis-9,12,15-Octadecatrienoic acid
Arachidonic acid
Carbon skeleton: 20:4(Δ5,8,11,14)
Structure: there's no way I gotta now this
Systemic Name: cis-,cis-,cis-,cis-5,8,11,14-Icosatetraenoic acid
Naming ω-fatty acid (omega)
When naming you count from ω-C
ω-3 fatty acid
Derrived from alpha-linolenate and is an essential fatty acid
ω-6 fatty acid
Derrived from linoleate and is an essential fatty acid
ω-9 fatty acid
derived from oleate, is not essential
Triacylglycerols
Used for fatty acid storage wherein Glycerol is esterified to 3 fatty acids
TAGs
more concentrated energy source than glycogen with more energy released on oxidation. Can store months of stores
Glycogen
is highly hydrated energy storage
more rapidly accessable than TAG
contains less than a day of stores
Classes of Membrane Lipid
Phospholipids
Glycolipids
Cholesterol
Amphipathic
one end of a membrane is hydrophobic while the other is hydrophilic
Phospholipids are composed of
Fatty acids →hydrophobic
A Glycerol and Sphingosine backbone
A Polar head group composed of Phospate and Alcohol, that faces the opposite direction than the fatty acids
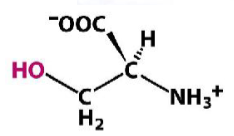
Serine
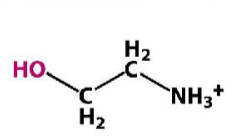
Ethanolamine
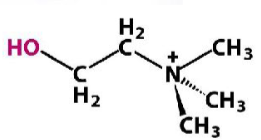
Choline
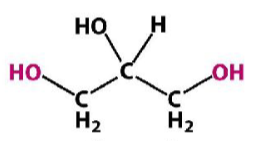
Glycerol
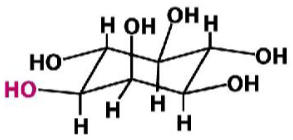
Inositol
Glycolipids
Composed of:
Sugar head group
Sphingosine backbone
Cerebroside (Glucose or Galactose)
Globoside (sugars)
Ganglioside→ more branched oligosaccharide that is negatively charged
Cholesterol (sterols)
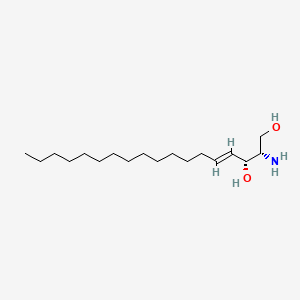
Sphingosine
How to determine type of omega fatty acid (ω-X, how to find X)
Total amount of carbons - # carbon of last double bond
→EX: 22:6 ∆4,7,10,13,16,19 →22-19 = 3 → omega-3 fatty acid