MAME Quiz 2
1/82
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapters 1-3, Finkel article, Redfield and Reynolds calculations, HW questions (ONLY ADDED CHAPTERS 1 AND 2 SO FAR)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
What is a microbe, by definition?
All organisms that can be observed only with a microscope and are smaller than about 100 um
What are the 7 main reasons to study microbes?
Microbes cause diseases of macroscopic organisms, including humans.
Microbes help to make our food and other useful products.
Microbes degrade and detoxify pollutants (like DDT).
Microbes are models for exploring principles in ecology and evolution.
Microbes living today are models for early life on Earth and perhaps even life on other planets.
Microbes mediate biogeochemical processes that affect global climate.
Microbes are everywhere, doing nearly everything.
True or false: Pathogenic microbes are the exception, not the rule.
True. Pathogenic microbes are much less abundant than beneficial ones.
True or false: An adult human has more bacterial cells in their body than they do human cells.
True. However, the biomass of the human cells far outweighs the bacteria.
This man was one of the founders of microbiology and also disproved the idea of spontaneous generation.
Louis Pasteur
Organisms that rely on microbes to digest the polysaccharides in the grasses they eat are called ______.
Ruminants
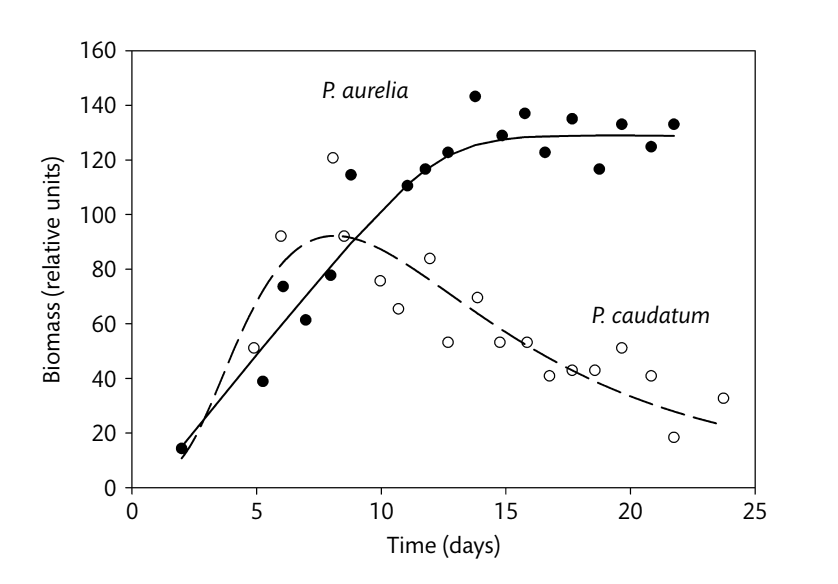
What principle does this graph demonstrate?
The competitive exclusion principle, which states that no two species can occupy the same niche at the same time.
As a general rule, the SMALLER/LARGER an organism is, the more abundant they are.
Smaller organisms are generally more abundant.
How many (heterotrophic) bacteria are there in a given L of seawater?
109
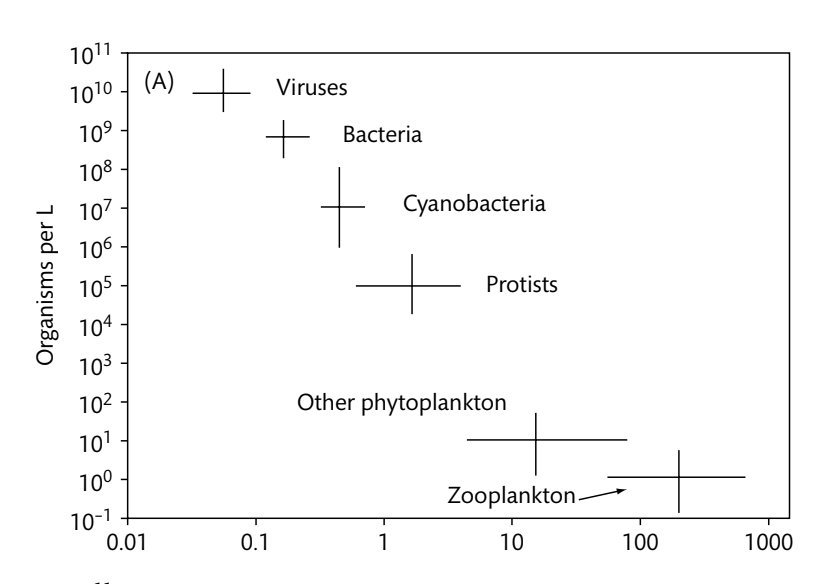
How many cyanobacteria are there in a given L of seawater?
107
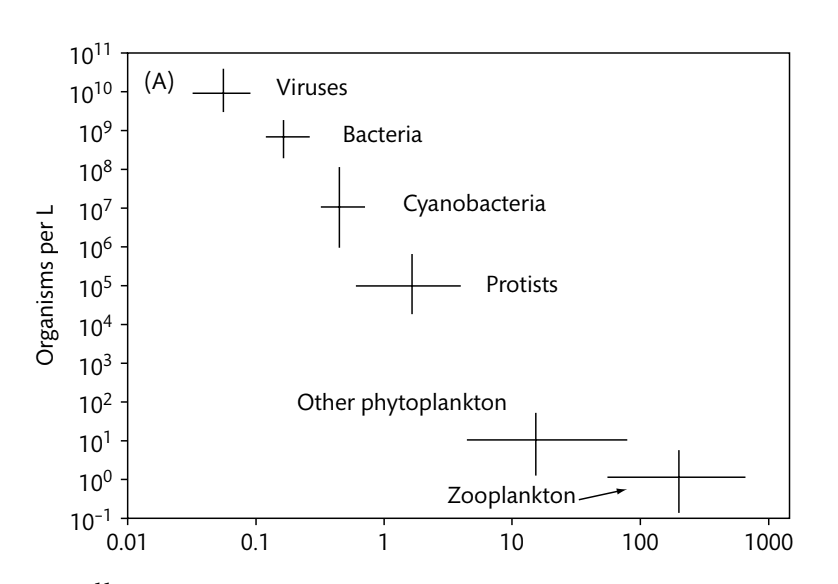
How many protists are there in a given L of seawater?
105
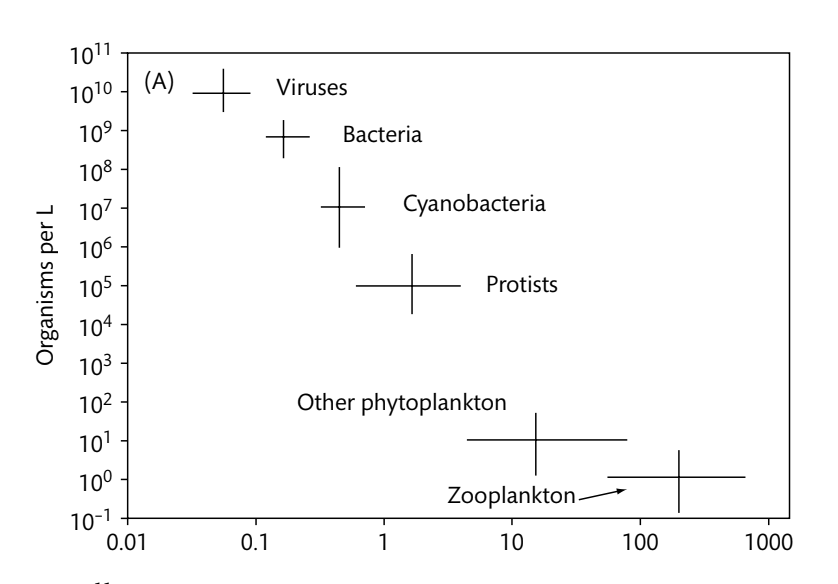
What factors contribute to “The Great Plate Anomaly”
An agar plate is a foreign habitat to most bacteria and microbes, and they are not adapted to thrive in a petri dish
There are also sometimes with the direct count method, as inert particles can be confused with microbes due to staining problems
Who was the first scientist to use rRNA sequencing (of the 16s genome) to identify archaea?
Carl Woese
What are the important distinguishing characteristics between prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
A prokaryotic cell looks empty when viewed by light microscopy since it doesn’t have membrane-bound organelles
Size (eukaryotes are bigger)
Prokaryotes are usually simple cocci, Eukaryotes may be rod or bacillus shape, or comma-like cocci
Eukaryotes are usually autotrophic or heterotrophic, but prokaryotes have more variations from methanogens to nitrogen fixation
True or false: the composition of microbes grown in the laboratory differs from that of microbes in natural environments.
True. These differences give clues about how microbes survive in nature.
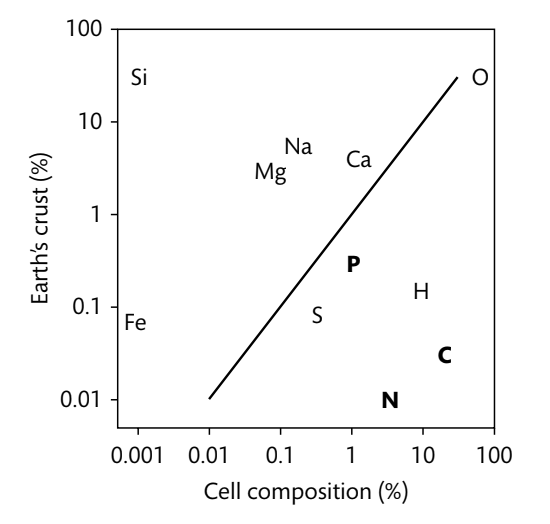
Which 3 elements seen in this figure most commonly limit microbial growth in nature?
Carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus. Some of these elements are very enriched in cells, while others are only present in low amounts.
What is the most important micronutrient for microbes?
Fe (iron)
What is the definition of homeostasis?
A microbe’s capacity to maintain elemental ratios the same even when those ratios change in their growth conditions
What is the Redfield ratio of planktonic nutrients?
106:16:1 (C:N:P)
Vascular plants on land have vastly more carbon per nitrogen or phosphorus than aquatic primary producers. Why?
Land plants have large amounts of cellulose, lignin, and other structural polysaccharides needed for structure on land.
Bacteria, especially heterotrophic bacteria, tend to be more _____ rich and have lower ____ ratios than other microbes.
They are more Nitrogen rich and have lower C:N ratios.
_______ account for not only a large fraction of total RNA (80%), but also of dry weight (20-40%). Given the high cost of synthesizing this, a cell will only have the amount it needs for protein synthesis.
Ribosomes. Because of the connection with P-rich ribosomes and growth, C:P ratios vary with growth rate.
To facilitate the transport of molecules across membranes, all cells have _____ that span the phospholipid bilayer.
Membrane proteins
Small hydrophobic molecules and gases may pass the lipid bilayers, but ____ or _____ compounds cannot.
hydrophilic, charged
For most compounds, if concentrations are ______ inside the cell than outside, diffusion will not work.
higher
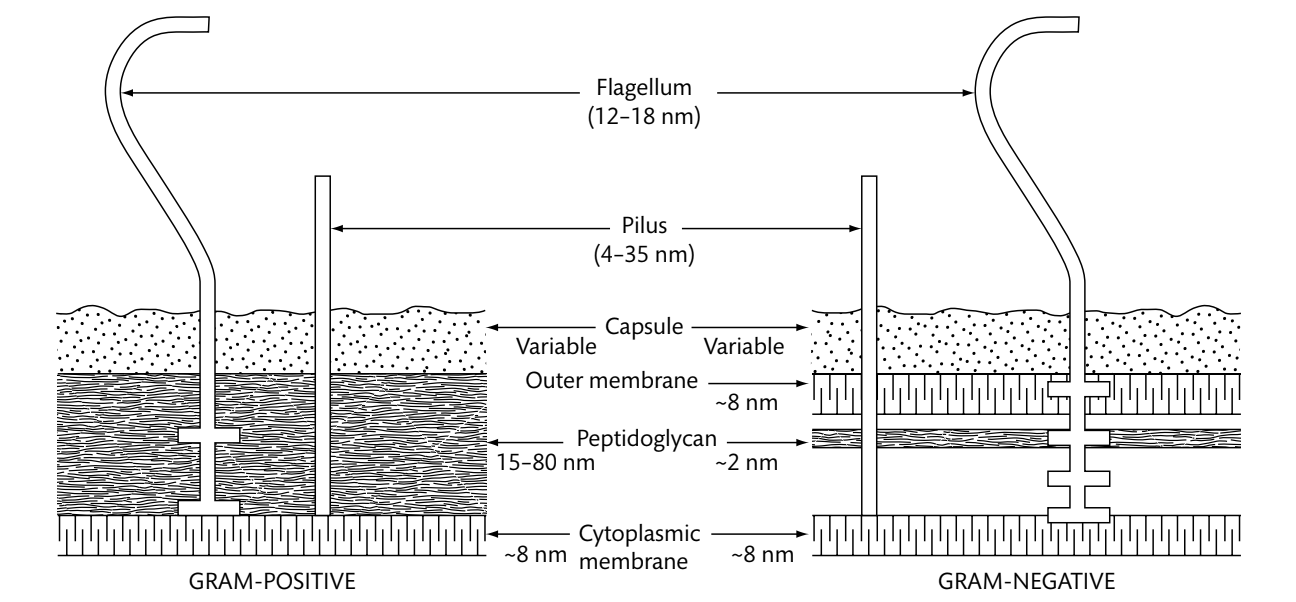
As this figure shows, peptidoglycan is the main component of the cell wall in _____.
bacteria (especially gram-positive bacteria)
Cyanobacteria have a gram NEGATIVE/POSITIVE type cell wall.
Negative, but the peptidoglycan layer is much thicker than typical of gram-negative bacteria.
What is the difference between polar and peritrichous flagella?
Polar is when a bacterium has a flagella on each side (pole) of its body, and peritrichous flagella are all over the body.
________ and _______ are like flagella, except they are shorter and not involved in motility.
Fimbriae and pili (used to attach the bacterium to surfaces or other cells)
The membranes of bacteria and eukaryotes are similar and consist of ester-linked lipids. What kind of lipids do archaea have?
Archaea have ether-linked lipids.
All cells are about ____% water by weight.
70%. This means that all organisms require water for growth, and liquid water is needed for any substantial microbial activity.
Of all the environmental parameters, _____ has one of the most profound effects on microbial activity.
temperature. The rate of all chemical reactions increases with temperature (generally increases x2 with each 10 C temperature increase)
Svante Arrhenius was one of the first scientists to understand ______
how greenhouse gases impact climate change.
With the exception of some extreme halophiles, water activity is HIGHER/LOWER and solute concentrations are HIGHER/LOWER in a cell than in the external environment.
Water activity is lower and solute concentrations are higher.
What adaptations do microbes have for UV light?
Some microbes have “sunscreen” made of pigments like carotenoids that absorb light
Other microbes adapted their behavior to live at a depth where UV rays can’t reach.
Microbes also have enzymes like RecA to repair damage done by UV
Piezophiles (deep-sea microbes living at high pressures) are thought to have evolved from what?
Piezophiles probably evolved from low-pressure psychrophiles found in high-latitude environments. Both have similar adaptations, like highly unsaturated lipids and similar protein and DNA alterations.
What is a GF/F filter?
It stands for Glass Filter Fine, and it is used to determine if something is particulate or dissolved. The filter retains molecules of about 0.6 um, and anything that slips through is considered dissolved.
How does chemotaxis help microbes find nutrients?
Cells can follow trace elements to lead them to the nutrients they need.
True or False: It is the genes encoded by the microbial genomes, and not the “taxonomy” (i.e., the “phylogeny”) of the microbes, that dictate the success, or failure, of the microbe in certain circumstances.
True. Genes determine success.
True or False: In most natural bacteria, there is usually only 1 chromosome.
True. However, some may have plasmids at certain points in their lives.
True or False: Phylogeny is based on the sequence of the SSU ribosomal RNA gene
18S for prokaryotes
16S for eukaryotes
(Partially) False. It is 16S for prokaryotes and 18s for eukaryotes, but is is based on the SSU ribosomal RNA gene.
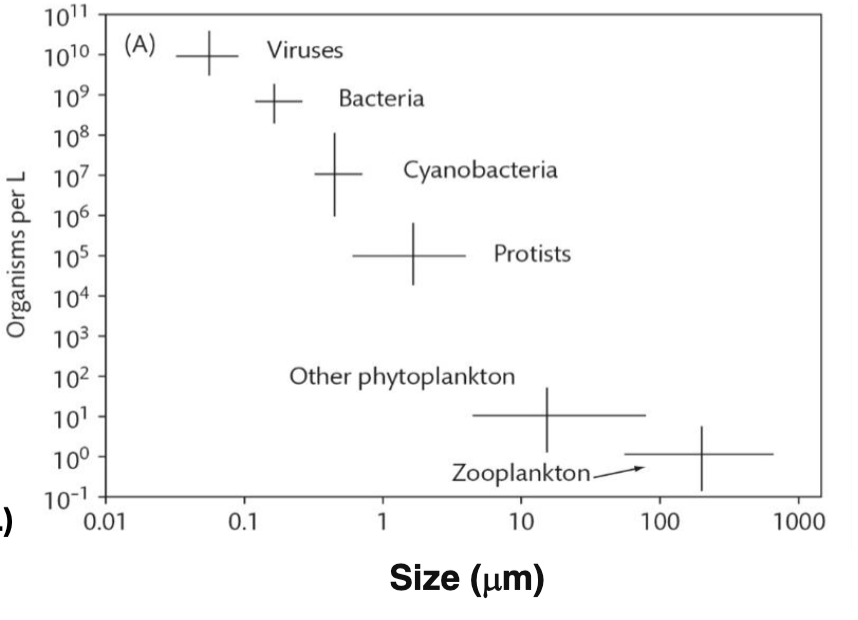
In a typical drop of seawater, total viruses are ____-fold more abundant than total bacteria.
A. 1000-fold
B. 100-fold
C. 10-fold
D. 2-fold
C. 10-fold
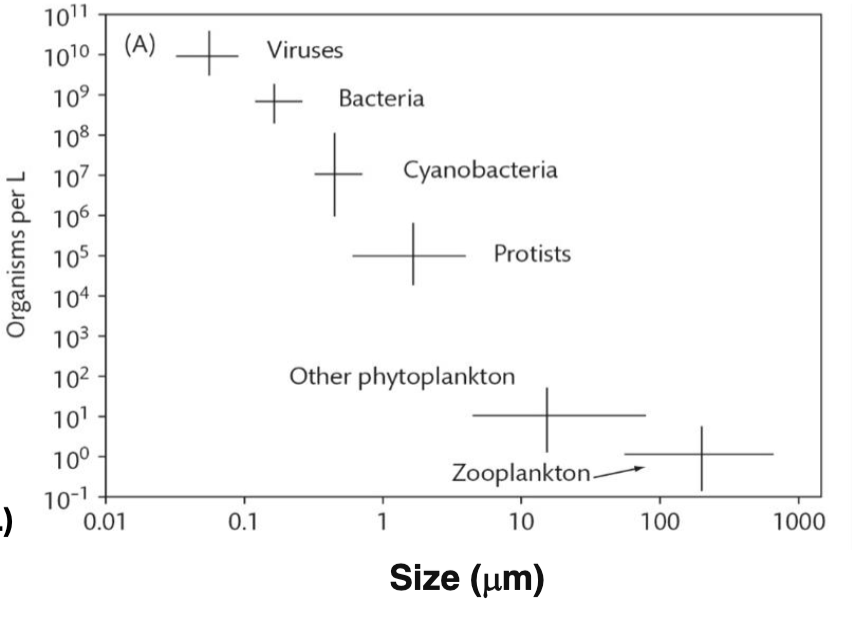
On average, marine viruses are ____-fold smaller than the average marine bacterium.
A. 1000-fold
B. 100-fold
C. 10-fold
D. 2-fold
SIZE is on the X-axis (size, in microns)
C. 10-fold
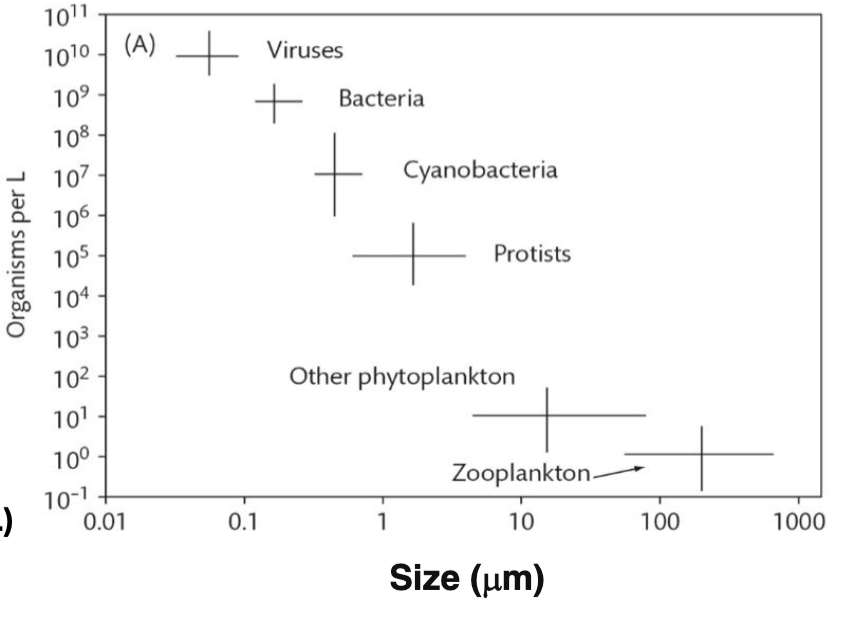
True or False: The graph shows that marine cyanobacteria are more phylogenetically diverse than marine bacteria.
False. It only gives information about size and abundance, not diversity.
What are the most common body shapes for aquatic microbes?
Coccus (sphere), Bacillus (rod), and Vibrio (comma).
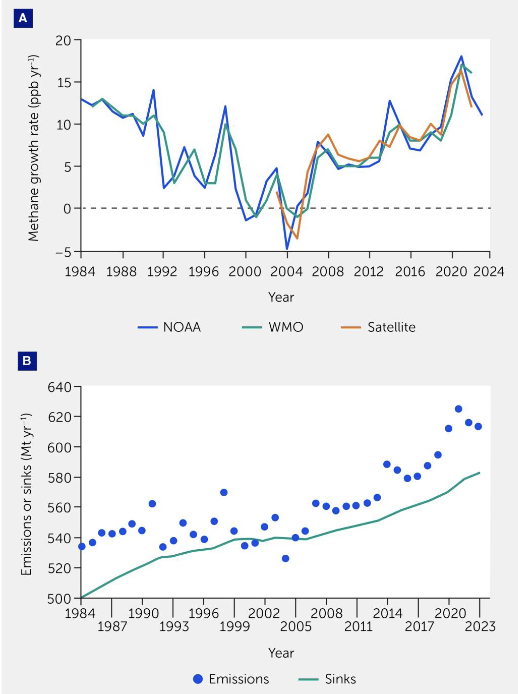
What do these figures represent?
Accelerating methane growth rates and emissions over recent decades. (A) Observed methane annual growth rates (ppb yr−1) through 2022 or 2023 (B) Estimated emissions and sinks through 2023
Anaerobic environments are still common on earth. They include environments like:
(a) a bog
(b) the rumen (the first compartment of a cow’s stomach)
What is a hyperpiezophile?
An organism that grows under high pressures (>80MPa)
What is a hyperthermophile?
An organism capable of growth in temperatures >80 C.
True or False: the term “protist” encapsulates both autotrophic and heterotropic organims.
True. Examples of autotrophic protists include diatoms and algae, whereas a heterotrophic protist would be zooplankton.
True or False: Fungi is a eukaryotic microbe.
True! They are non-photosynthetic microbes, like yeast.
What three things do all metabolisms need?
Carbon, energy, and electrons
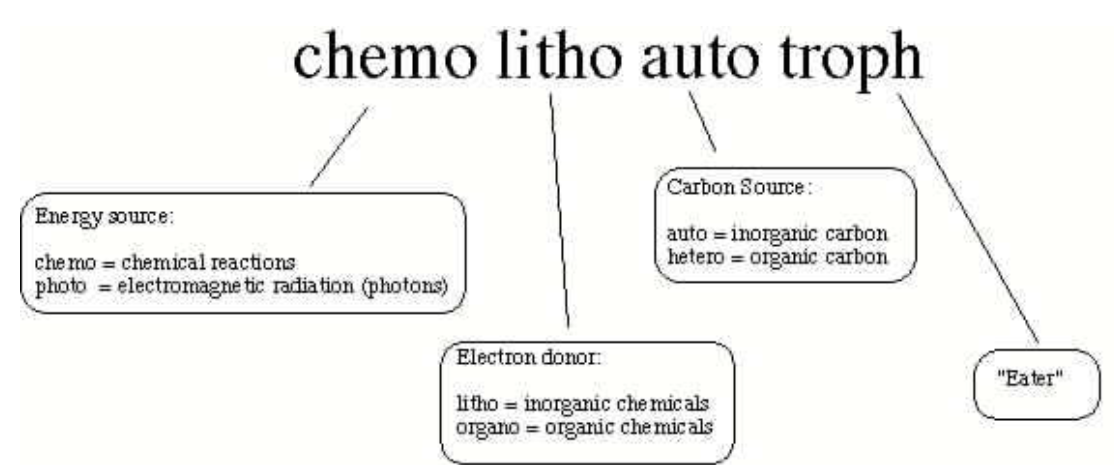
This type of metabolism is seen in extreme environments:
Chemolithoautotroph

Which one of the red molecules is Dissolved Inorganic Content (DIC) and which is Dissolved Organic content (DOC)?
The CO2 is DIC and the right side is DOC.
In an oligotrophic environment, being small is more advantageous. WHY?
Smaller cells have larger S/V ratios and thus can have a more efficient exchange of nutrients with it surroundings than can a large cell.
What does
Metabolism = Catabolism + Anabolism
mean?
Catabolism = conservation of energy, e.g. making ATP
Anabolism = Biosynthesis of macromolecules (primarily CHNOPS)
Together, this is metabolism.
What is the Redfield Ratio hypothesis?
The atomic ratios between the chemical components of marine plankton (C, N, P) are identical with their relative proportions in the open ocean.
What is the function of the Redfield Ratio hypothesis?
Measuring Redfield ratio in unfiltered an seawater can give you idea of the NET HETEROTROPHY or NET PHOTOTROPHY – And can tell you which elements are limiting at that place at that time.
With an increased growth rate, the proportion of _____ increased.
Ribosomes, and therefore N
What do pili do?
Adhesion
Communication
Transfer information (sex)
True or False: Most open-ocean bacteria have flagella.
False. Only about 5% have flagella in most cases.
A cell’s adhesion starts with pili, but it says because of ______
EPS (extracellular polysaccharides)
True or False: Biofilms are usually composed of one type of microbe.
False. They are not like baklava with layers composed of the same ingredients- biofilms are complex.
Which of the below 3 listed processes are important for forming bacterial colonization of a surface?
-Antibiotic resistance
-Quorum sensing
-Flagellum formation
Quorum sensing.
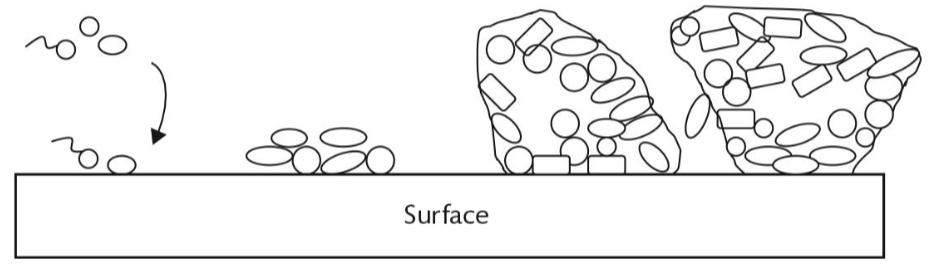
What are the 3 main steps to biofilm production shown in this figure?
Colonization
Growth
Polymer production
What turns on EPS production?
EPS production gets “turned on” after quorum sensing signaling happens, and everyone in the community expresses the needed genes for extruding this CHO-rich substance
Why is the C:N:P ratio in a biofilm different than the Redfield equation?
C:N:P from a biofilm is composed of biomass AND the EPS, so it will be RICH in C, compared to biomass collected on a filter of planktonic organisms from ocean (which will be more like 106:16:1).
What is the difference between EPS and EPM?
EPM = Extracellular Polymeric Matrix
EPS = Extracellular Polymeric Substance
There is no difference, they are different names for the same thing.
True or False: Biofilms are more likely to develop on aged plastics.
True. Understanding the makeup of the bacterial community colonizing the plastic particles helps predict how quickly the plastics will age
POM is composed of:
Particulate organic matter
Living cells and detritus
DOM is composed of:
dissolved organic material, such as sugars, amino acids, etc.
Text box for GF/F (she REALLY emphasized this shit)

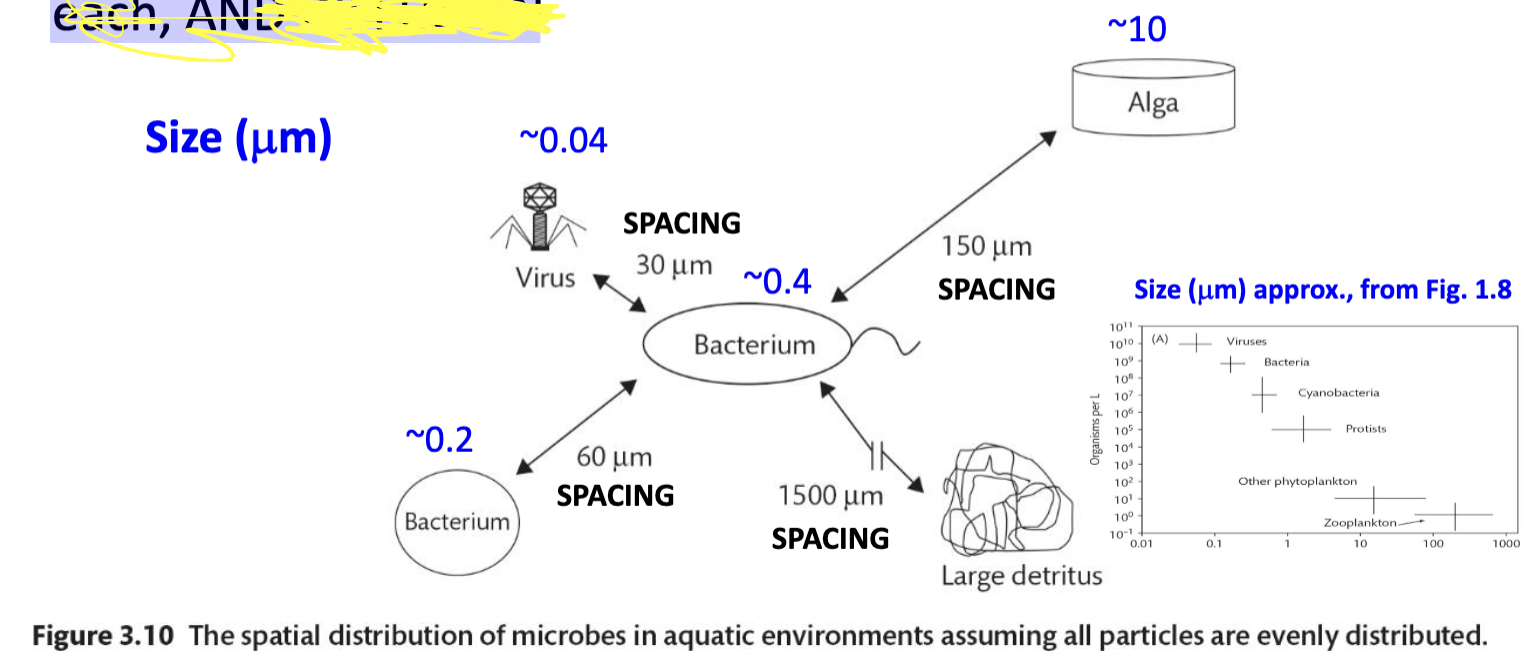
SPACING between detrital particles, viral particles & microbes such as bacterioplankton and phytoplankton:
Depends on the ______ of each, and ______.
Concentration, diffusion
AMMONIA/AMMONIUM is easily taken up across cell membrane without extra effort (or specialized gene to make the transport protein. AMMONIA/AMMONIUM is not easily taken up by cells (requires a special transport protein in the membrane)
Ammonia is easily taken, ammonium is not.
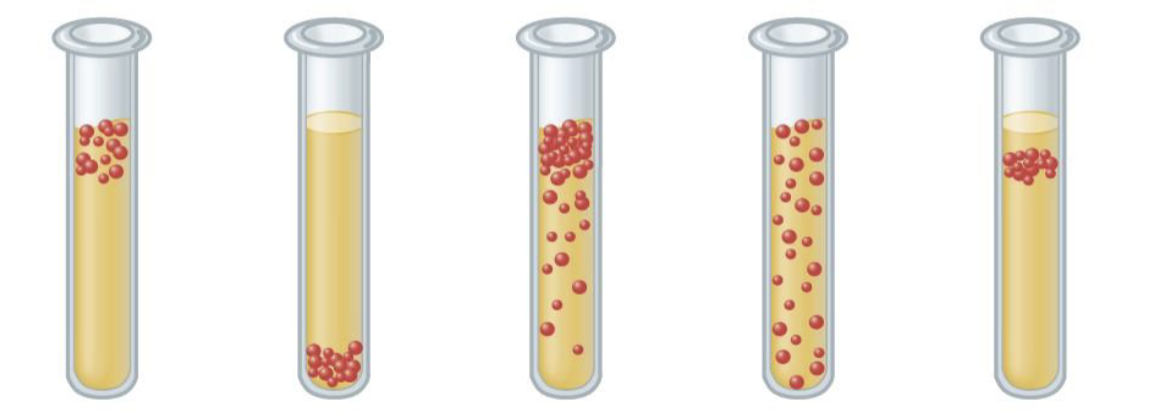
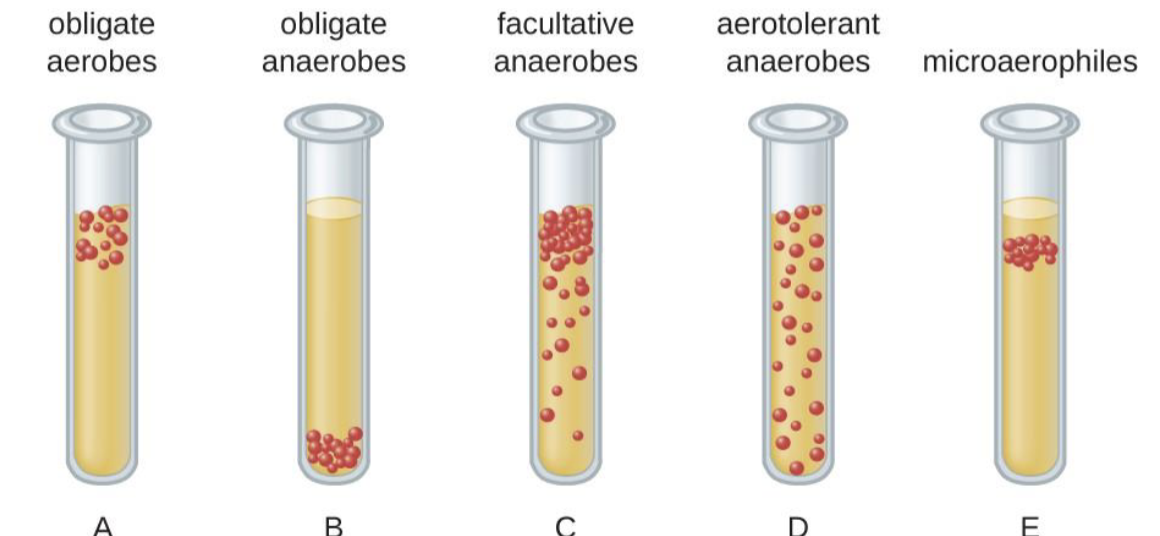
What are all the correct classifications for the bacteria within these tubes?
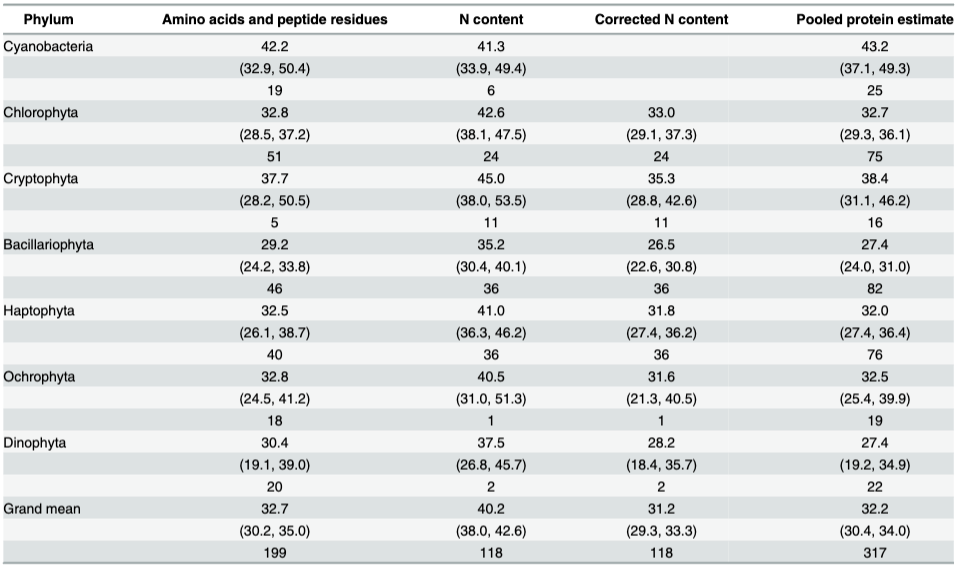
What does this figure represent?
Protein content and means across the groups.
According to the Finkel article, what is the median macromolecular composition of exponentially growing microalgae?
32.2% protein
17.3% lipid (fats)
15.0% carbohydrate (sugars)
17.3% ash (the inorganic residue that remains after the sample is combusted: P, S, Na, Cl, K, Ca, Mg. In the Bacillariophyta and calcified microalgae, Si and Ca are the ash)
5.7% RNA (genetic material)
1.1% chlorophyll-a (photosynthetic pigment)
1.0% DNA (genetic material)
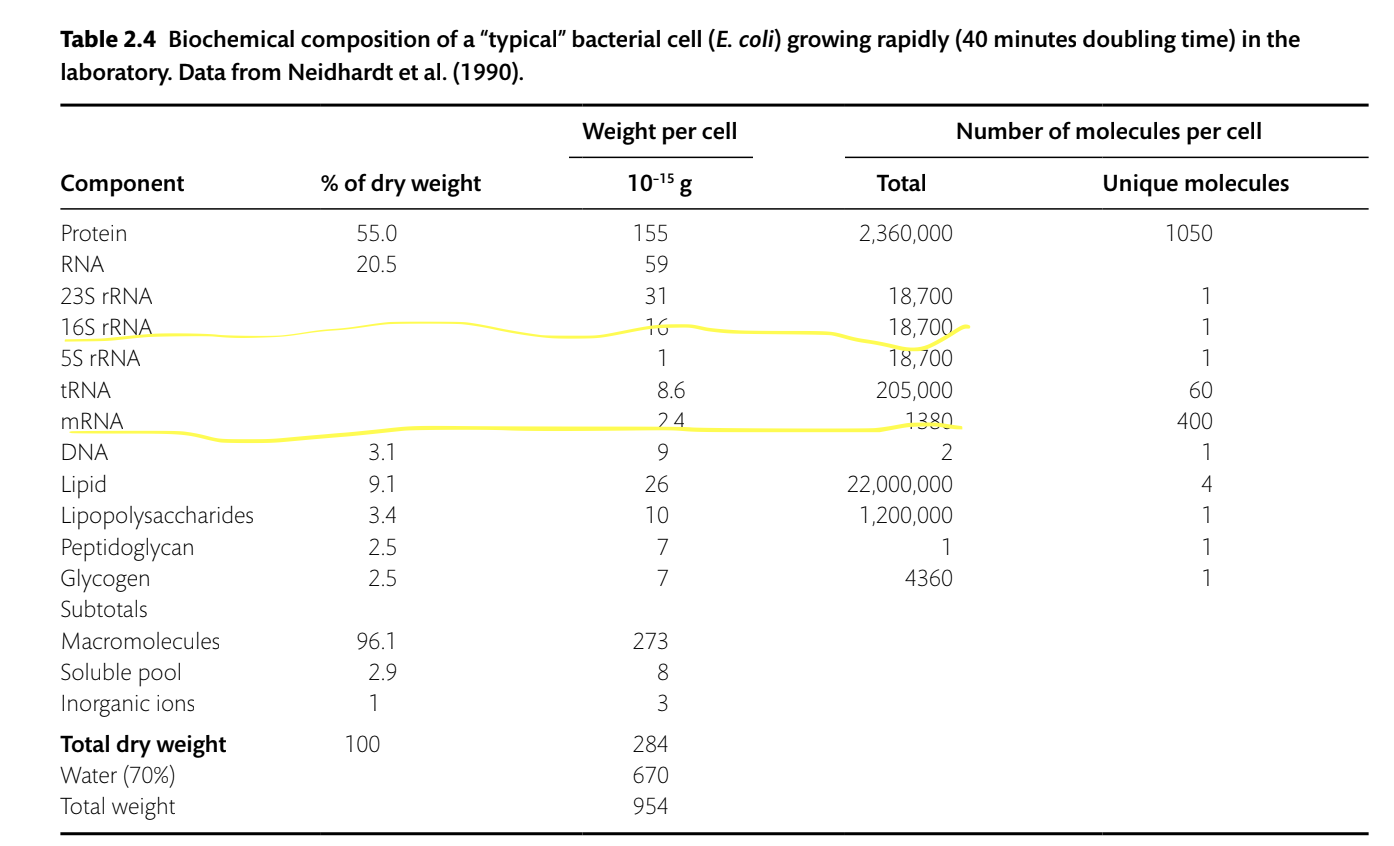
In a typical rapidly-growing, exponential phase culture of E. coli, the ratio of 16S SSU rRNA molecules to mRNA molecules is approximately______
13:1 (13 rRNA molecules to 1 transcript molecule)
Dissolved carbon dioxide results in ocean acidification. Which factor is NOT influenced by decreasing ocean pH?
a. Charge on certain compounds (ie. ammonia vs ammonium)
b. Absorption of key nutrients to solid surfaces
c. Solubility of iron (Fe)
d. Salinity of ocean water
d. Salinity of ocean water
Which type of macromolecule is enriched in N?
Protein.
Why do most common oceanic bacteria not have quorum-sensing genes?
Unlike biofilm environments, the spaces between a bacterium and another bacterium of the same species is quite large in the open ocean.
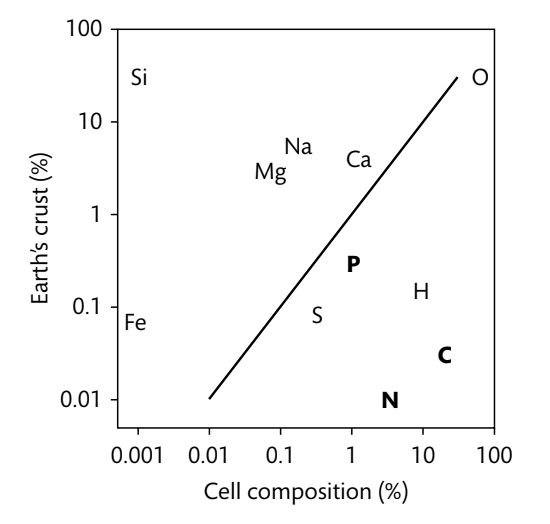
This image demonstrates that Fe, Si, Mg, Na, and Ca are enriched in the _________.
Lithosphere
What do you call a bacterium that consumes organic compounds for both carbon and energy?
Chemoorganotrophs, also called chemoorganoheterotrophs.