Bio Dino Final Study
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
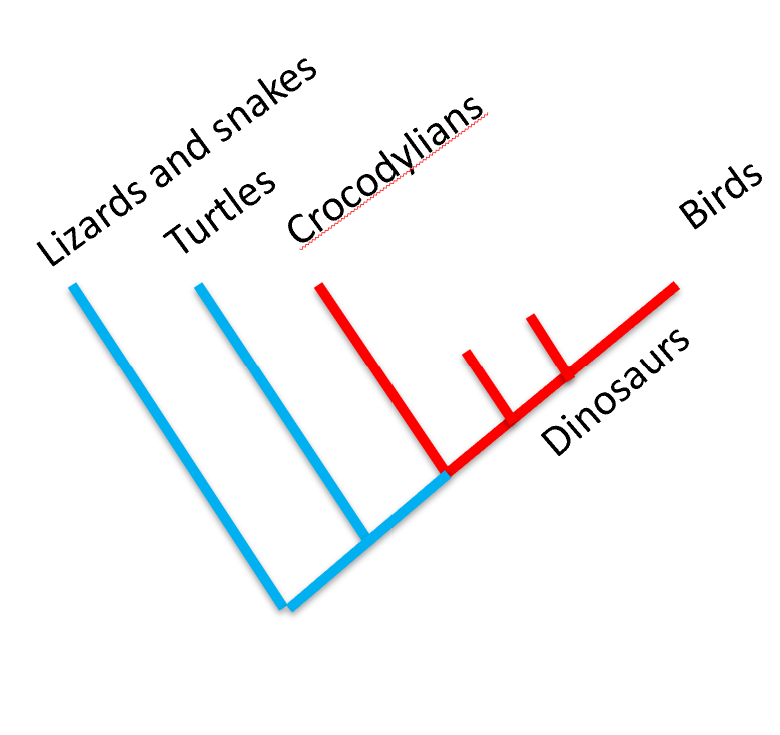
*Faunas of the Late Triassic through Cretaceous
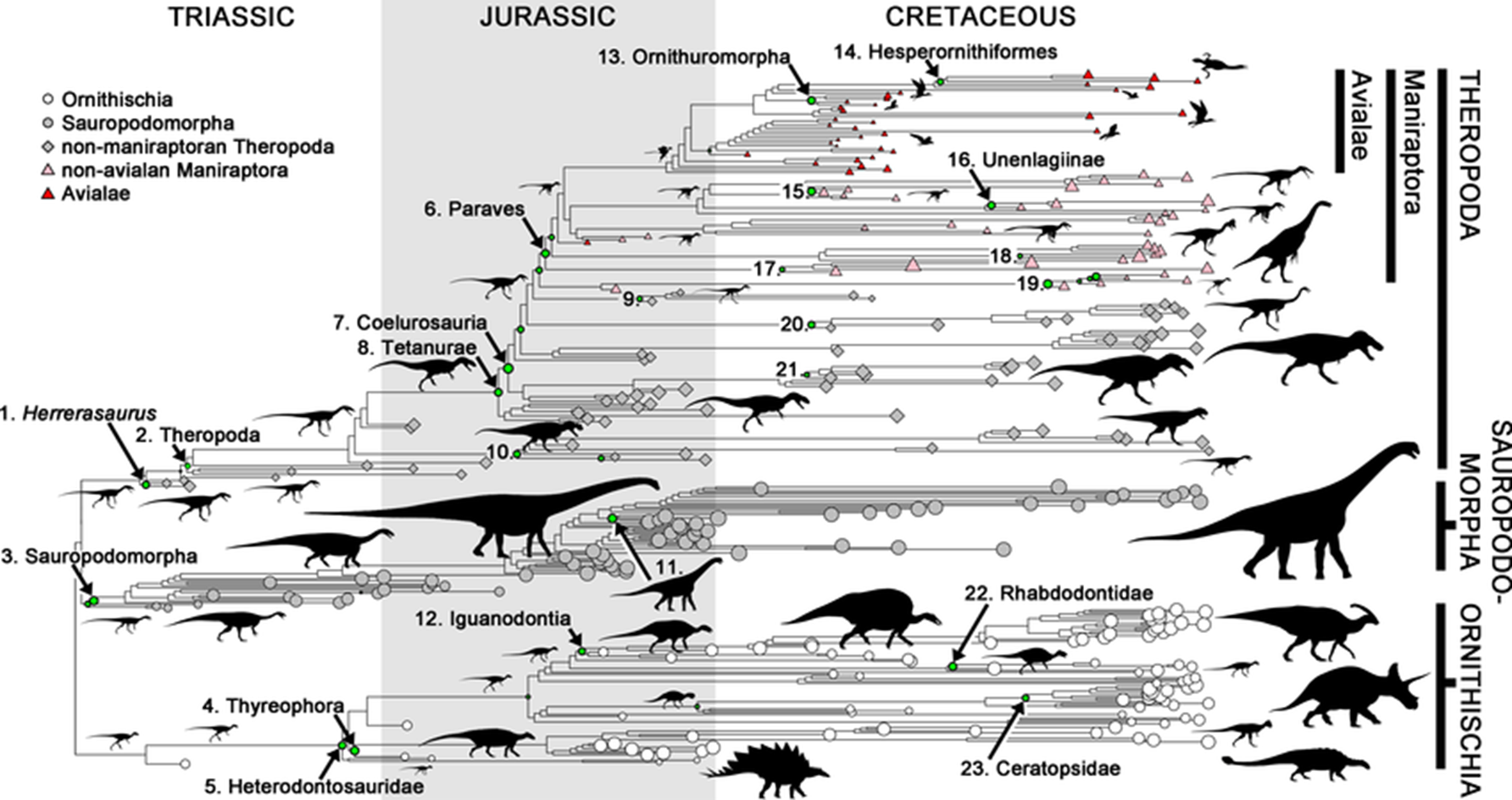
Triassic faunas were dominated by non-dinosaurian terrestrial vertebrates that went extinct at the end of the period
Dinosaurs became larger and dominated ecosystems during the Jurassic
Early faunas were similar around the world because of Pangaea, but after
the Jurassic they diverged into Gondwanan and Laurasian faunas
Faunas of the Late Triassic through Cretaceous
Triassic: Non-dinosaurian terrestrial vertebrates dominate (e.g., rhynchosaurs, labyrinthodont amphibians).
Dinosaurs first appear in Late Triassic, slow diversification.
Jurassic: Dinosaurs dominate ecosystems (sauropods, theropods, ornithischians).
Cretaceous: Faunal divergence between Laurasia and Gondwana; hadrosaurs and ceratopsians in Laurasia, titanosaurs in Gondwana.












*Pattern of extinction at the end of the Triassic


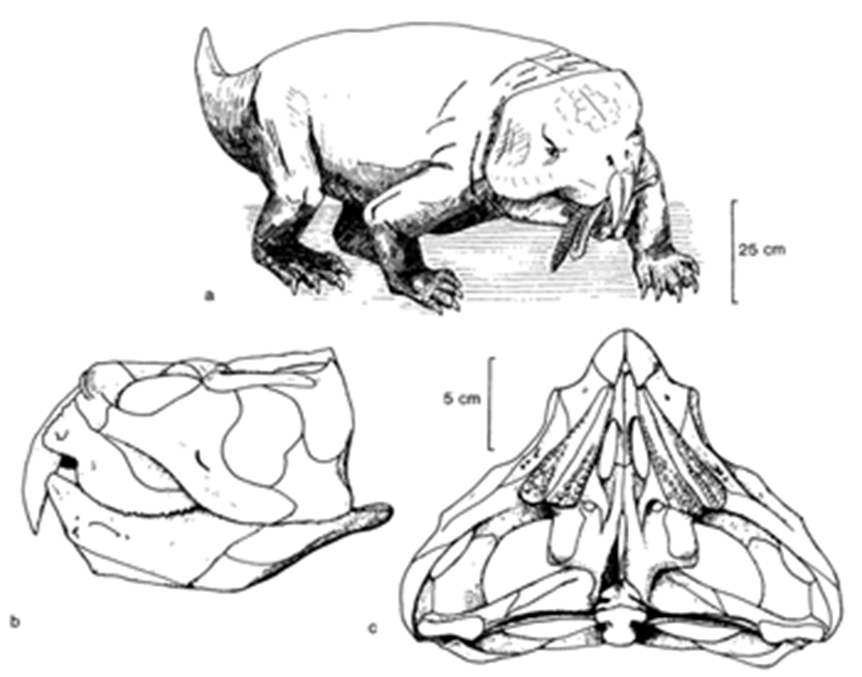



Pattern of Extinction at End of Triassic
Large volcanic eruptions (Central Atlantic Magmatic Province) released massive CO2.
Resulted in greenhouse warming, ocean acidification.
Extinction of rhynchosaurs, labyrinthodonts, large crocodilian relatives.
Allowed dinosaurs to dominate early Jurassic ecosystems.
*Faunal differences between Laurasia and Gondwana in the Cretaceous







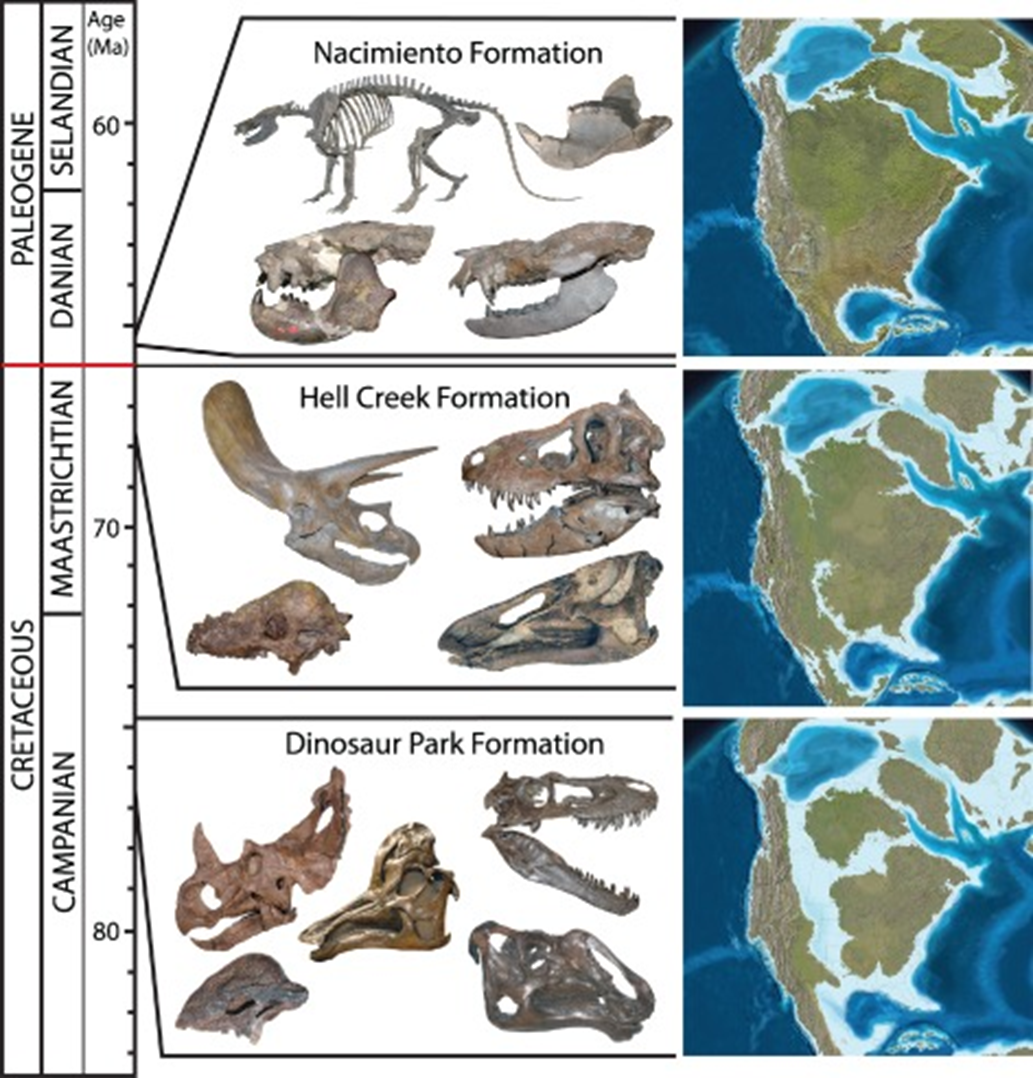







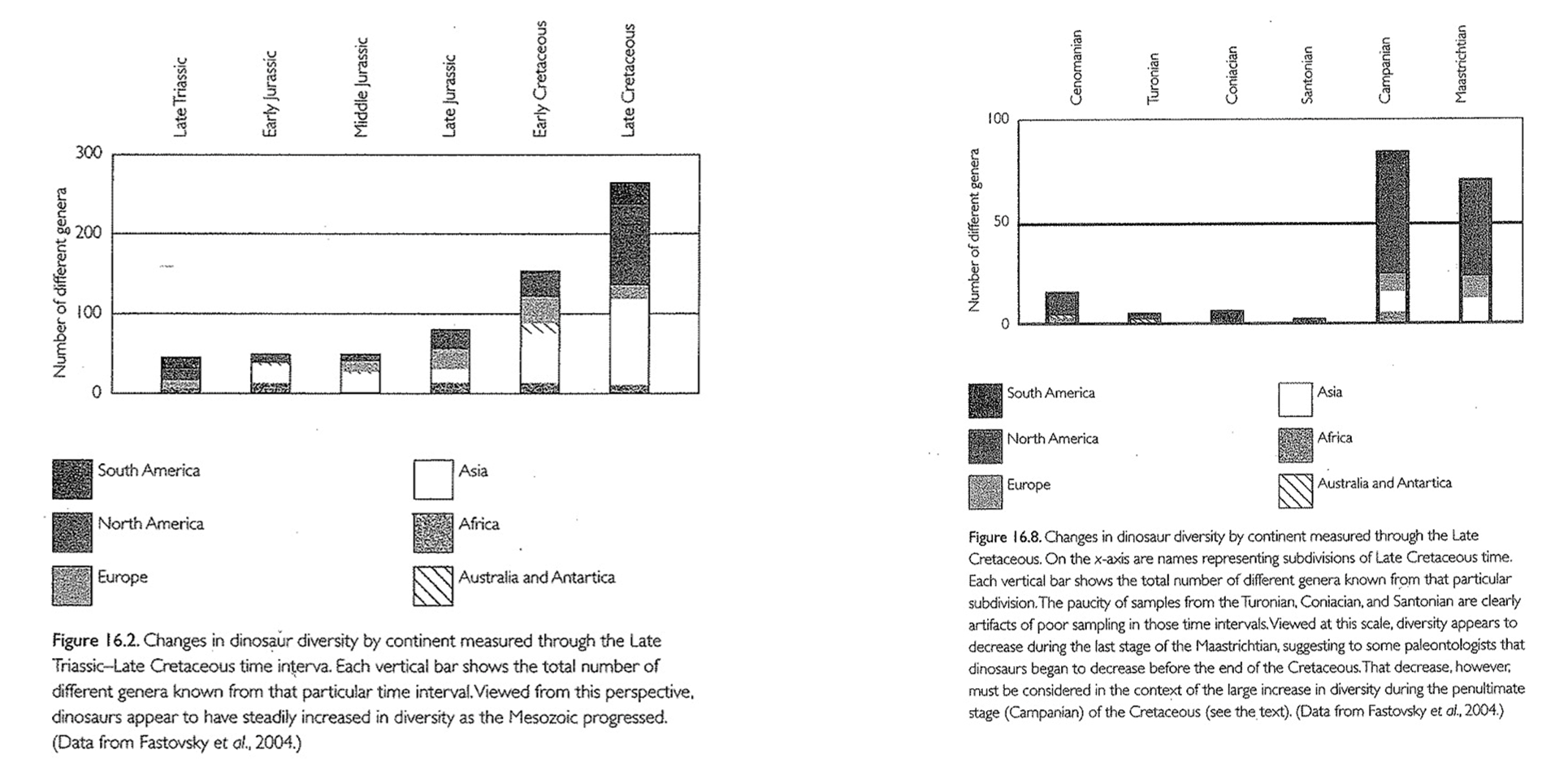





Faunal Differences Between Laurasia and Gondwana
Laurasia: Diverse ceratopsians, hadrosaurs, tyrannosaurs.
Gondwana: Dominance of sauropods (titanosaurs), abelisaurid theropods.
Different evolutionary paths due to continental drift after breakup of Pangaea.
*Ancestral features of archosaurs





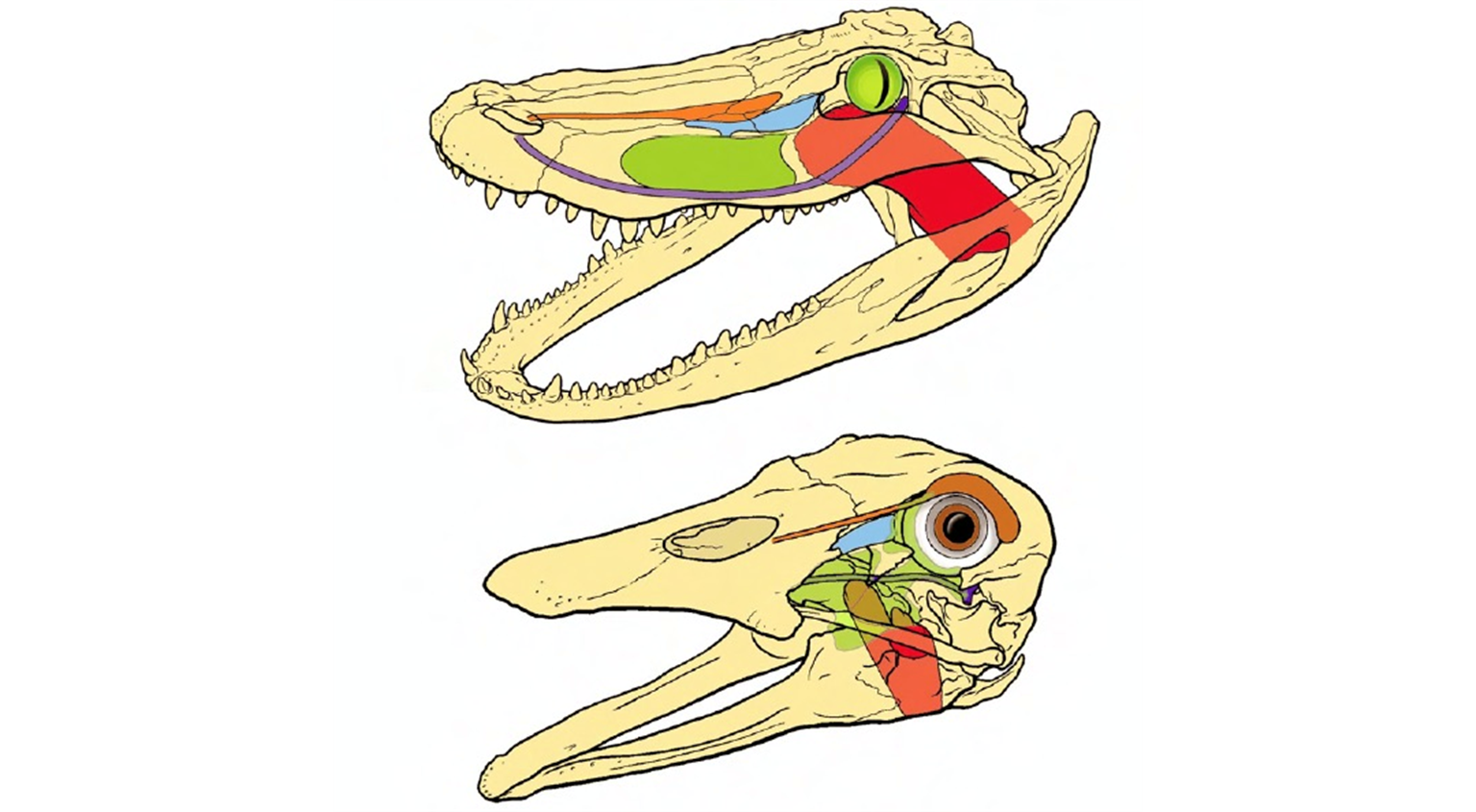




Ancestral Features of Archosaurs
Four-chambered heart, efficient breathing (unidirectional airflow).
Parental care (nesting behavior).
Hard-shelled eggs and uric acid excretion.
Color vision suggested by phylogenetic bracketing.
*Features of birds that may have evolved within non-avian dinosaurs—
Combined, your slides support that these features of birds may have evolved within non-avian dinosaurs:
Feathers (Lecture 23)
Unidirectional airflow (Lecture 19)
Air sacs in skull (Lecture 19)
Parental care / Brooding (Lecture 19, and supported visually in Lecture 23)
Vocalization (Lecture 19)
Four-chambered heart (Lecture 19)
Hard-shelled eggs (Lecture 19 and Lecture 22)
Pigmented/colorful feathers (Lecture 23, based on melanosomes)
Why?
These features are found in both birds and crocodilians, or directly evidenced in non-avian dinosaurs (e.g., fossils of brooding Oviraptor, feathered Anchiornis). That makes them inferred ancestral traits of dinosaurs — which means they may have evolved within non-avian dinosaurs.



*Which biomolecules are known in non-avian dinosaurs














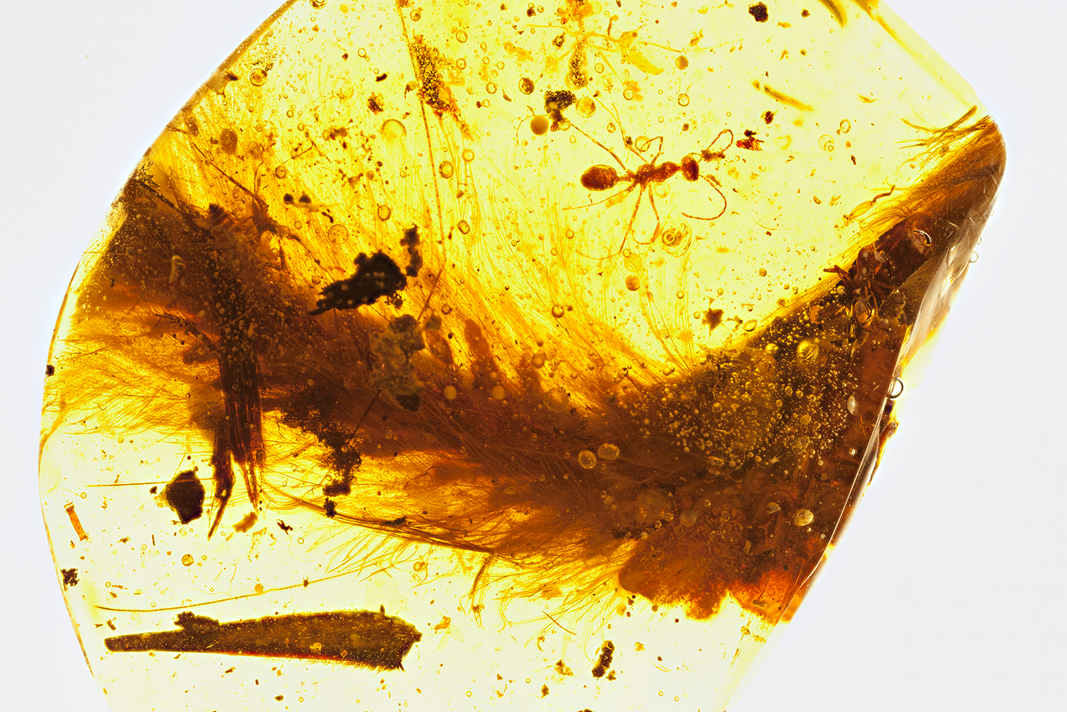








Biomolecules in Non-Avian Dinosaurs
Collagen preserved in bones and eggshells.
Keratin found in claw fossils.
Blood vessel and osteocyte structures (controversial).
Fossil melanosomes indicating pigment preservation.
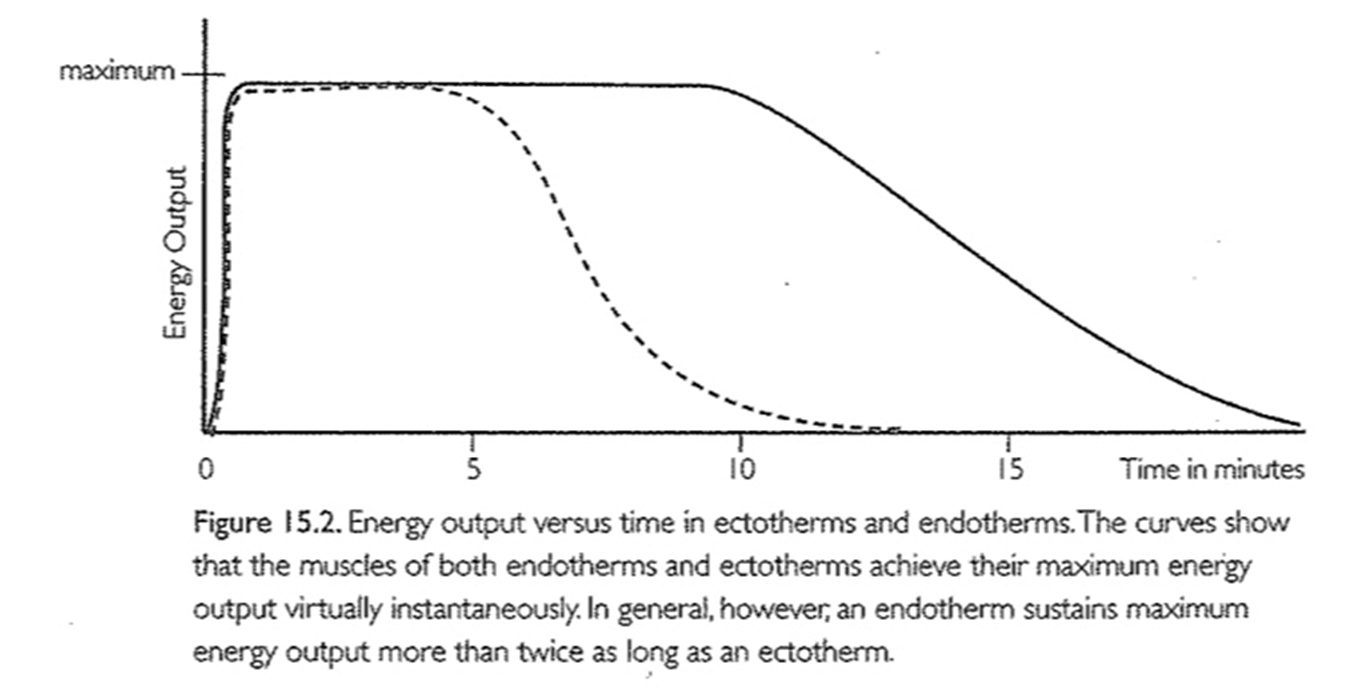
*The evidence for and against endothermy in non-avian dinosaurs












Evidence for Endothermy in Non-Avian Dinosaurs
Bone histology: extensive vascular canals, rapid growth rates.
Polar dinosaur fossils suggest tolerance to cold climates.
Feathers in theropods suggest heat insulation.
Stable isotope ratios consistent with constant body temperatures.
8. Evidence Against Endothermy
Lack of nasal turbinates in fossils (but preservation bias possible).
Presence of LAGs (Lines of Arrested Growth) indicating seasonal growth variation.
*The evidence for color in feathers and eggshell




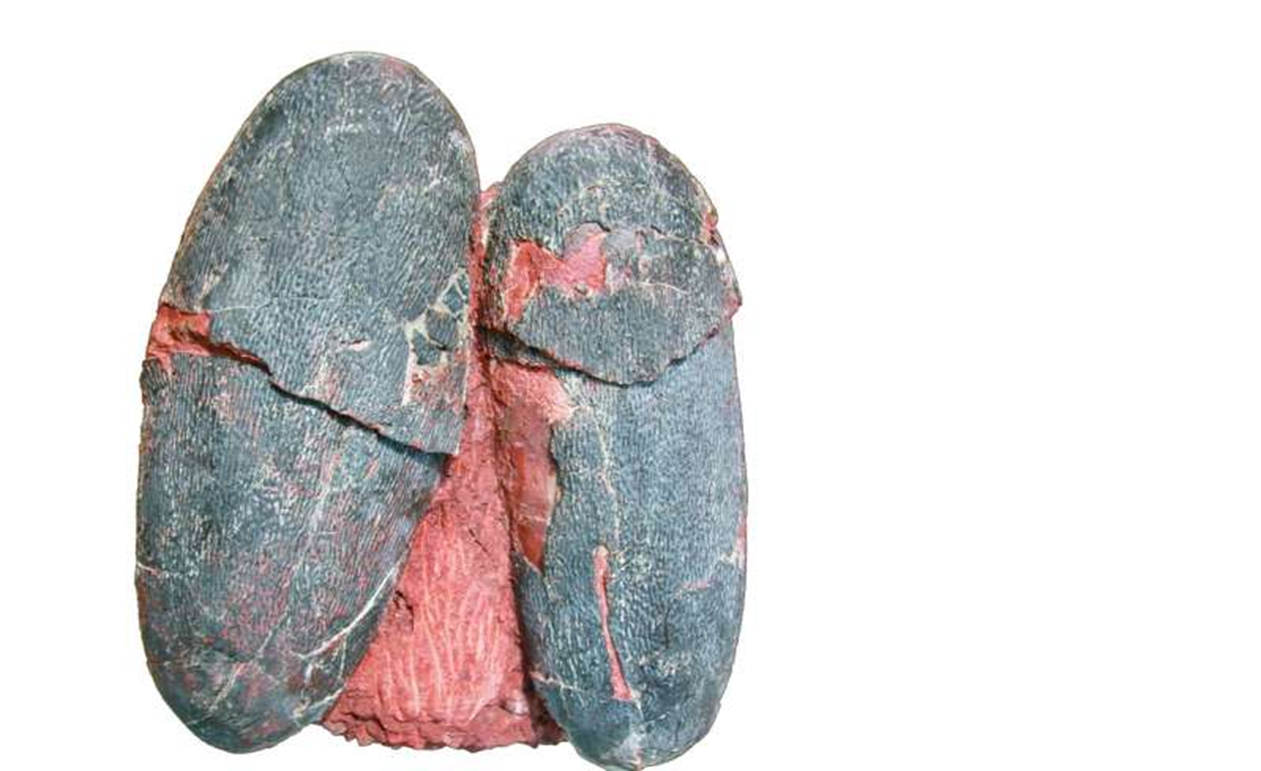
























Evidence for Color in Feathers
Microscopic melanosome structures indicate black, brown, and reddish hues.
Anchiornis color pattern reconstructed from melanosome shape.
10. Evidence for Color in Eggshells
Pigments such as biliverdin and protoporphyrin detected in fossilized eggshells.
Indications of blue-green colored eggs.
*What features are characteristic of large living terrestrial animals






















Features of Large Living Terrestrial Animals
Low surface area relative to volume -> slow heat loss.
Gigantothermy: maintain stable internal temperatures due to sheer size.
Sparse body coverings to avoid overheating (similar to elephants).
*What kind of evidence indicates diets in dinosaurs















EXAMPLES:




Evidence Indicating Dinosaur Diets
Tooth morphology: serrated teeth in carnivores, broad teeth in herbivores.
Gastroliths (stomach stones) in herbivores.
Coprolites (fossilized feces) providing dietary information.
Isotope analysis reflecting trophic level.
*The pattern of extinctions at the end of the Cretaceous









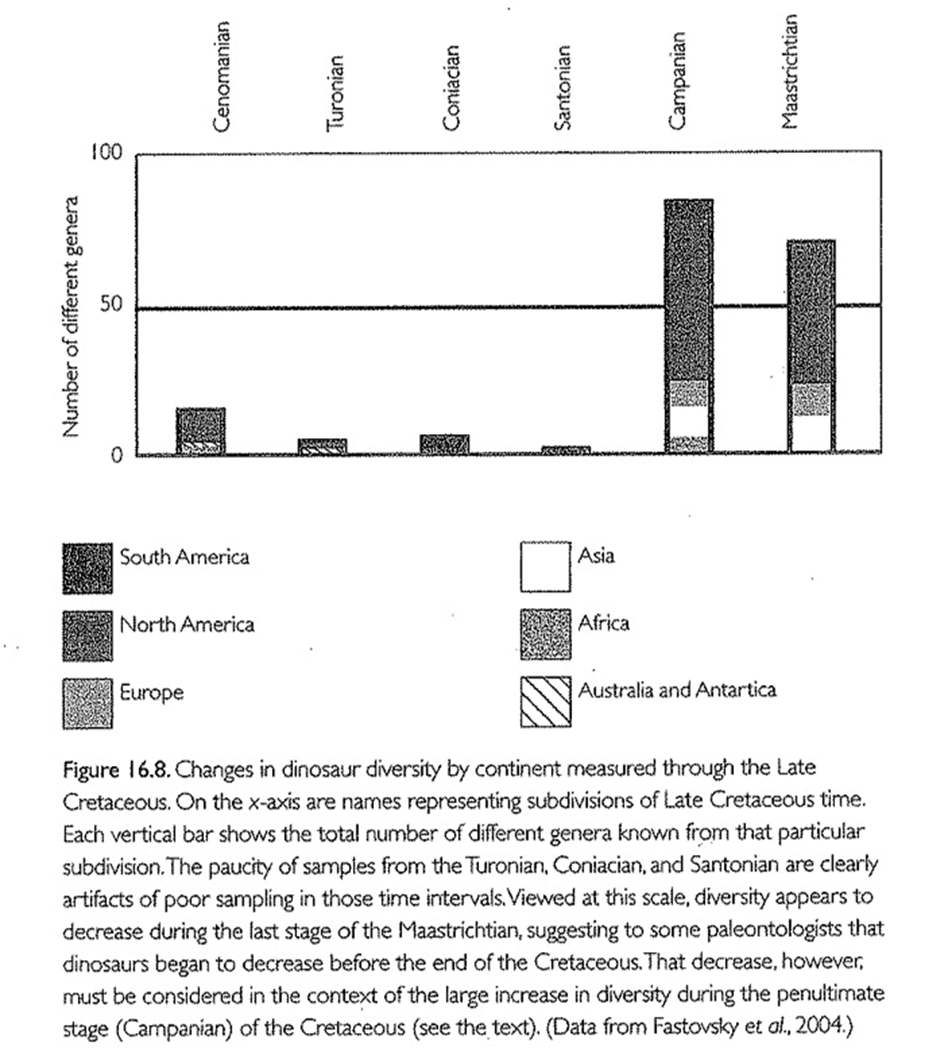
Pattern of Extinctions at End-Cretaceous
Abrupt disappearance of non-avian dinosaurs, marine reptiles, ammonites.
Major losses in terrestrial and marine ecosystems.
*Current hypotheses for the cause of the extinction of non-avian dinosaurs











Current Hypothesis for Cause of Extinction
Asteroid impact at Chicxulub, Mexico.
Evidence: Global iridium layer, shocked quartz, tsunami deposits.
Immediate global climate disruptions ("impact winter").
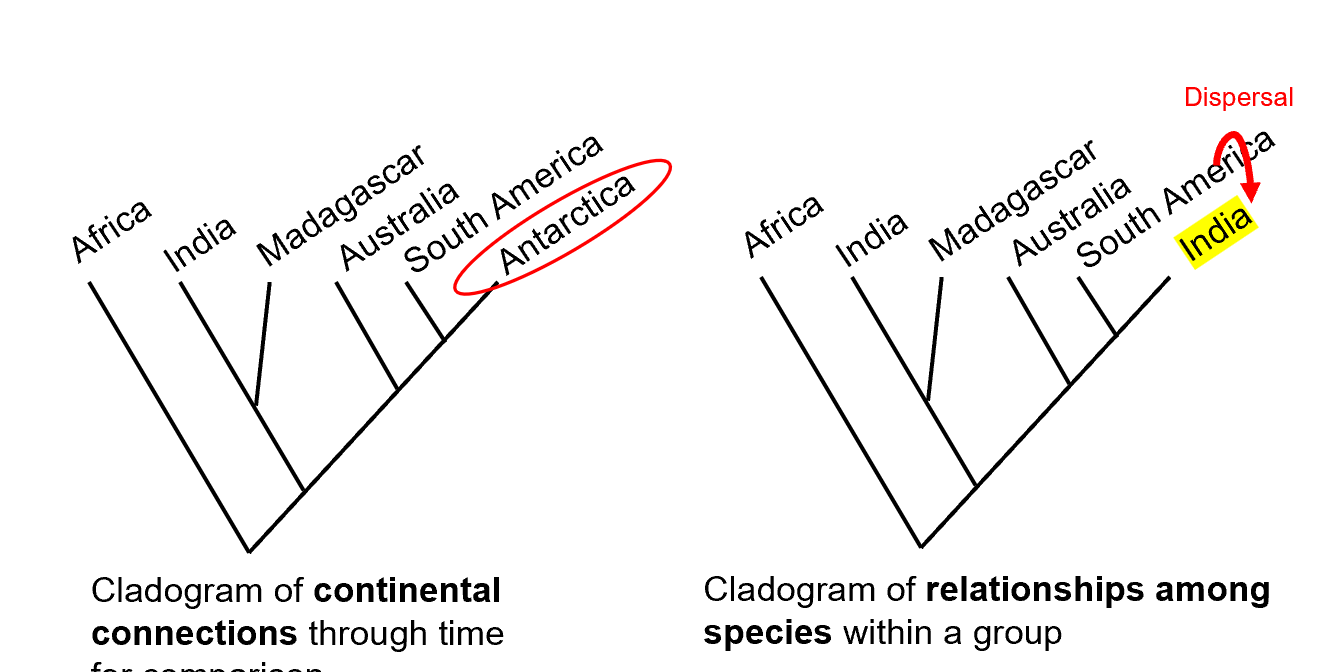
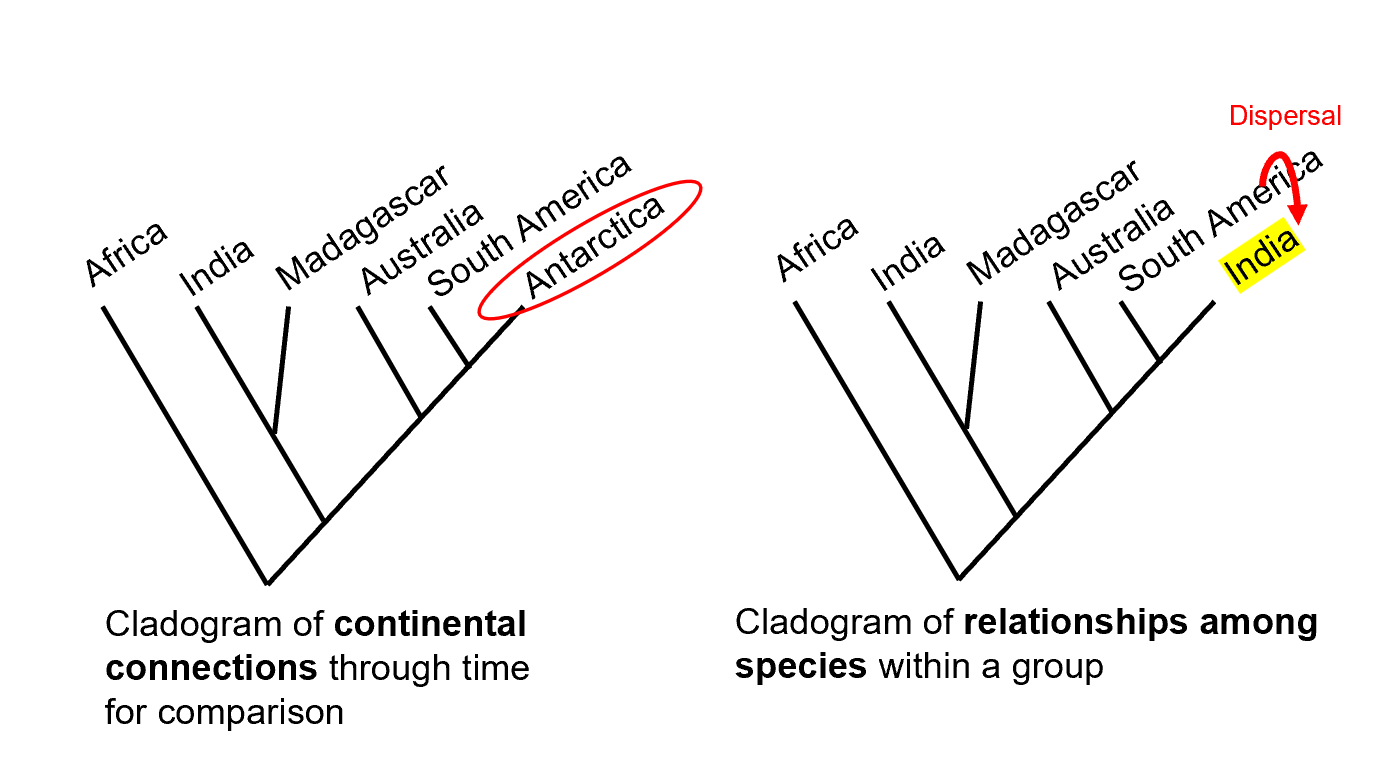
*Vicariance versus dispersal
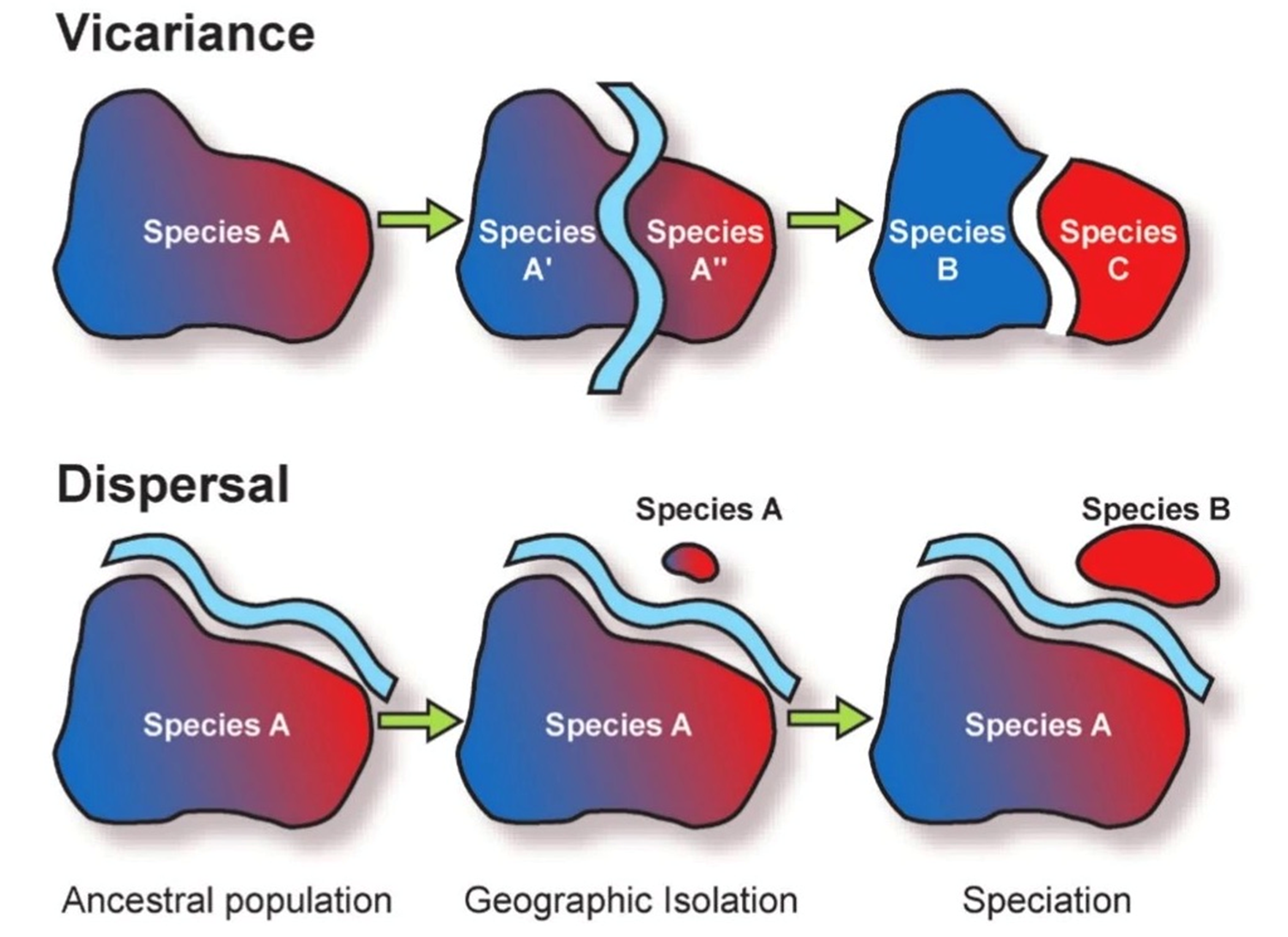
Vicariance vs Dispersal
Vicariance: Evolutionary divergence due to geographic separation (continental drift).
Dispersal: Species physically move to new areas (e.g., across shallow seas).
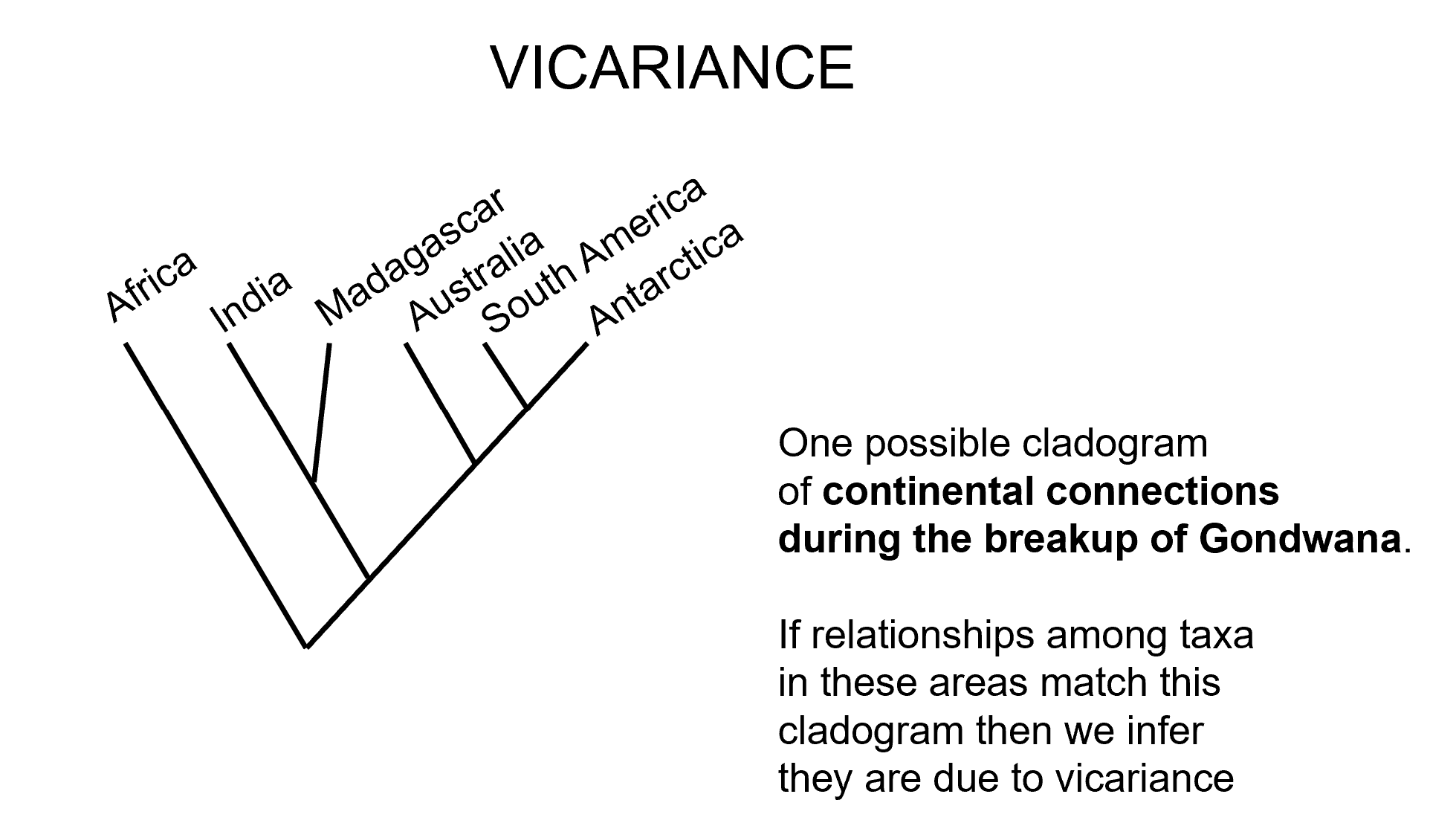
*Character optimization







Character Optimization
Mapping features (e.g., feathers) onto phylogenetic trees.
Helps infer when and how traits evolved.
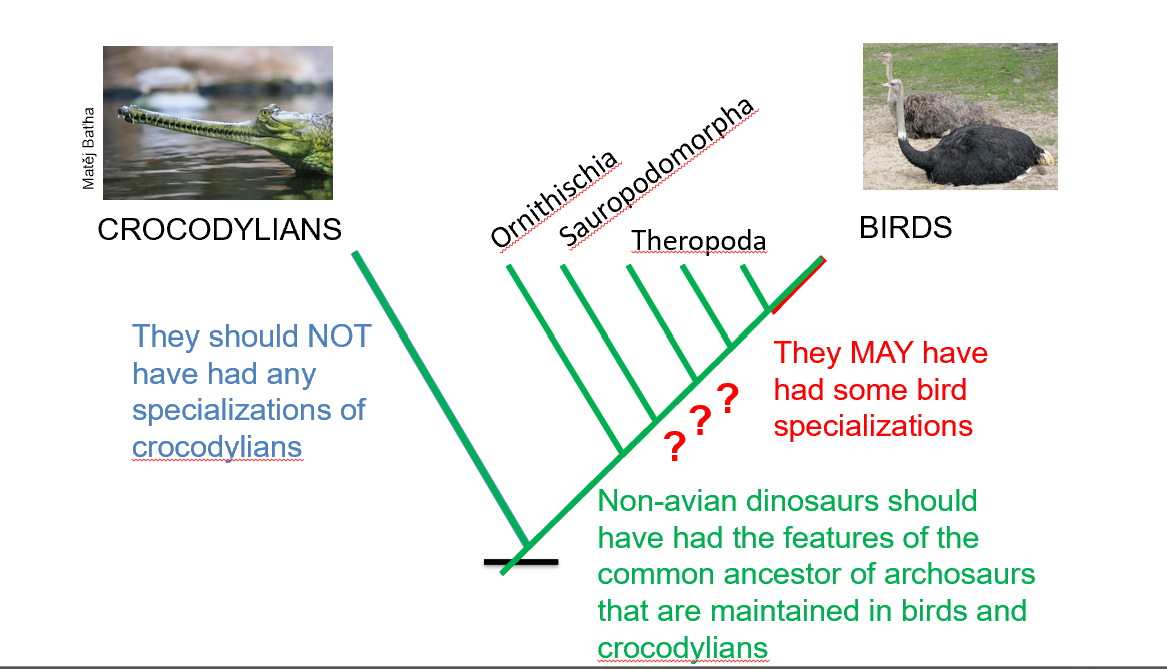
*How features that are not preserved are inferred using phylogeny and optimization







Inferring Features Not Preserved
Use close relatives in cladograms.
Example: If all close relatives have feathers, extinct forms likely had them too
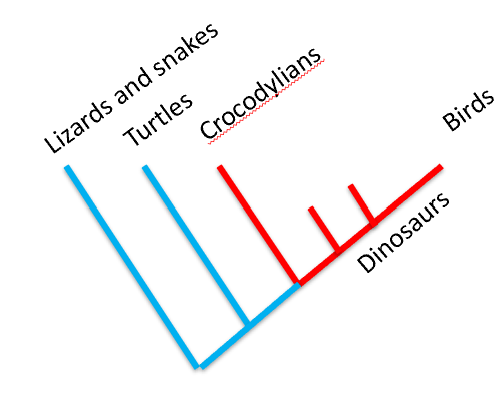
*How DNA and amino acid sequences are used to infer phylogeny




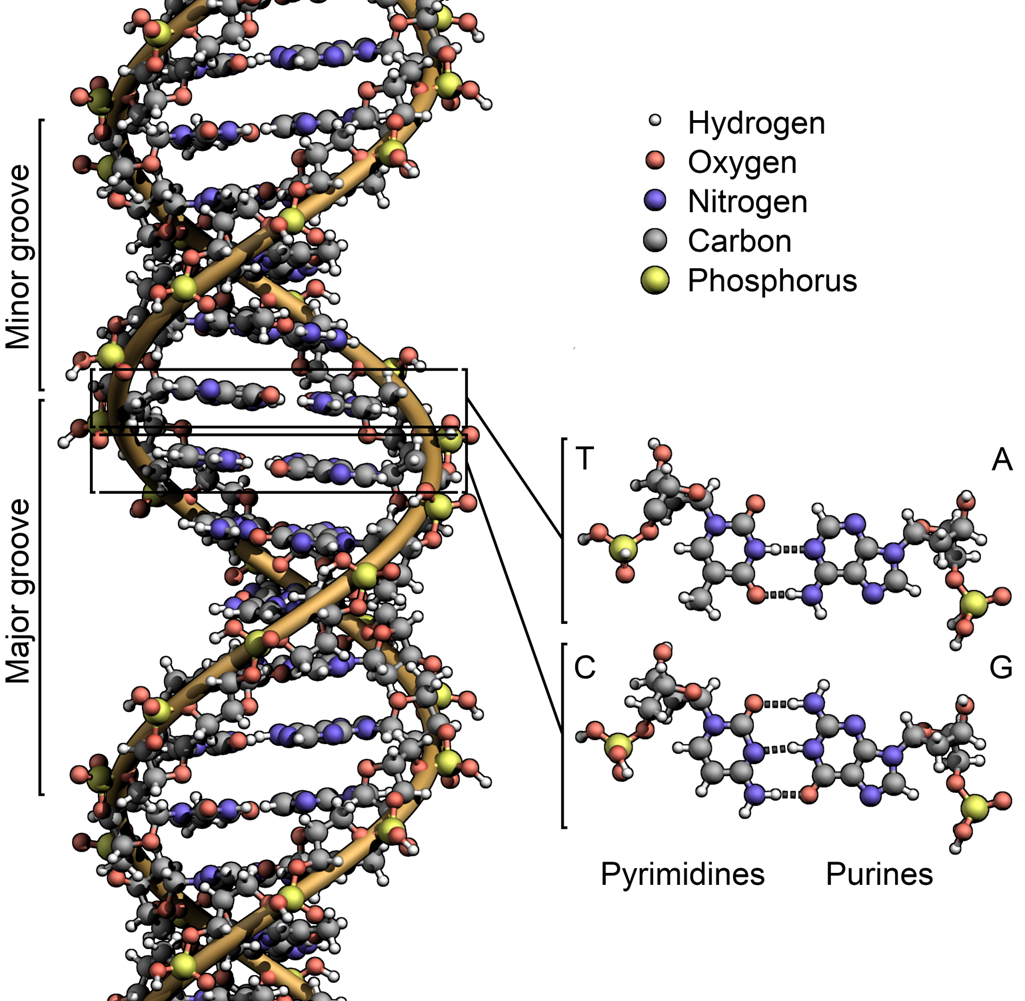









Using DNA and Amino Acid Sequences for Phylogeny
Sequence similarities reveal evolutionary closeness.
Molecular clocks estimate divergence times.
Birds and crocodylians as closest living relatives within Archosaurs.
*How trackways are used to estimate speed


















How Trackways Estimate Speed
Measure stride length (SL) and hip height (h).
Use Alexander's formula: v = 0.25 * g^0.5 * SL^1.67 * h^-1.17 where g = gravitational acceleration (9.8 m/s^2).
*How hearing sensitivity and nocturnality can be inferred from ears and eyes












Inferring Hearing Sensitivity from Ears
Fossil cochlear duct size indicates hearing range.
Larger cochlea = better sensitivity to low frequencies.
22. Inferring Nocturnality from Eyes
Large scleral rings relative to skull size suggest nocturnal habits.
Found in some small theropods.
*How LAGs are used to study dinosaur growth rates


















Using LAGs to Study Growth Rates
LAGs: annual markers like tree rings.
Show growth rates, seasonal slowdowns, possible endothermic patterns.
*How the sex of a dinosaur can be determined using bone histology


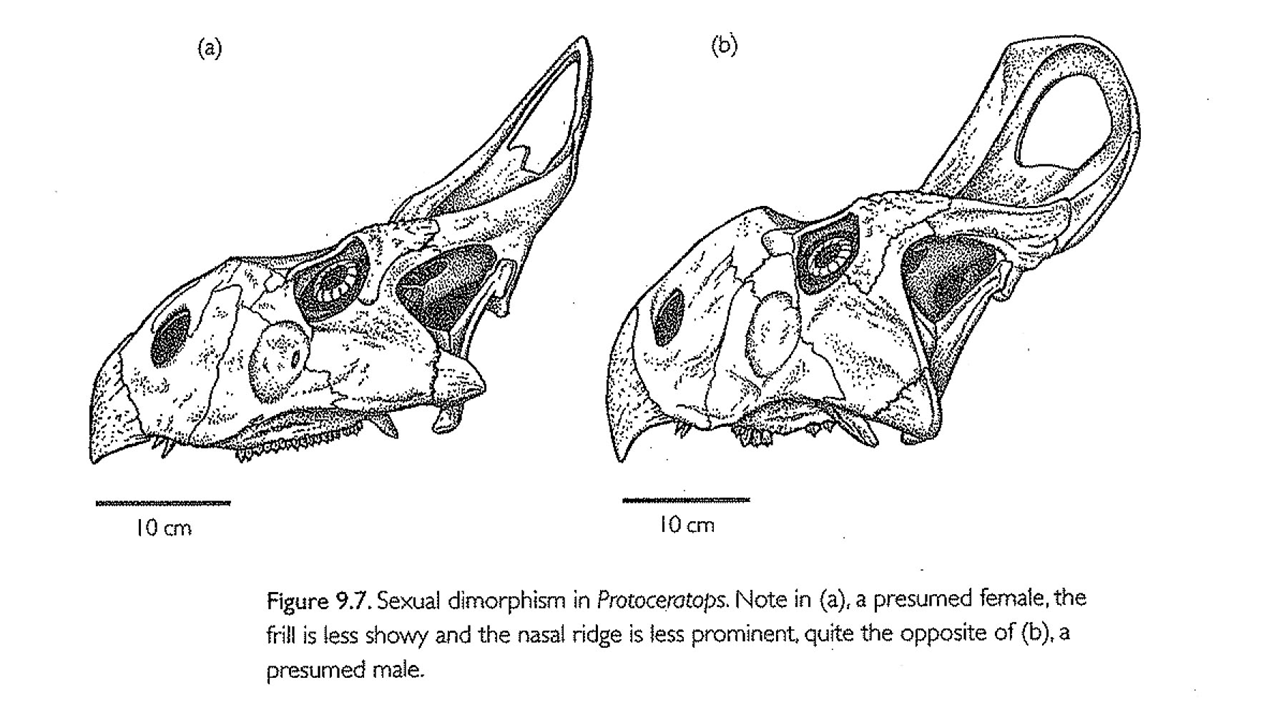













Determining Dinosaur Sex via Bone Histology
Medullary bone detected inside femurs of some fossils.
Indicates female, linked to egg-laying cycles.
*How surface/volume ratio affected dinosaur thermoregulation, egg size
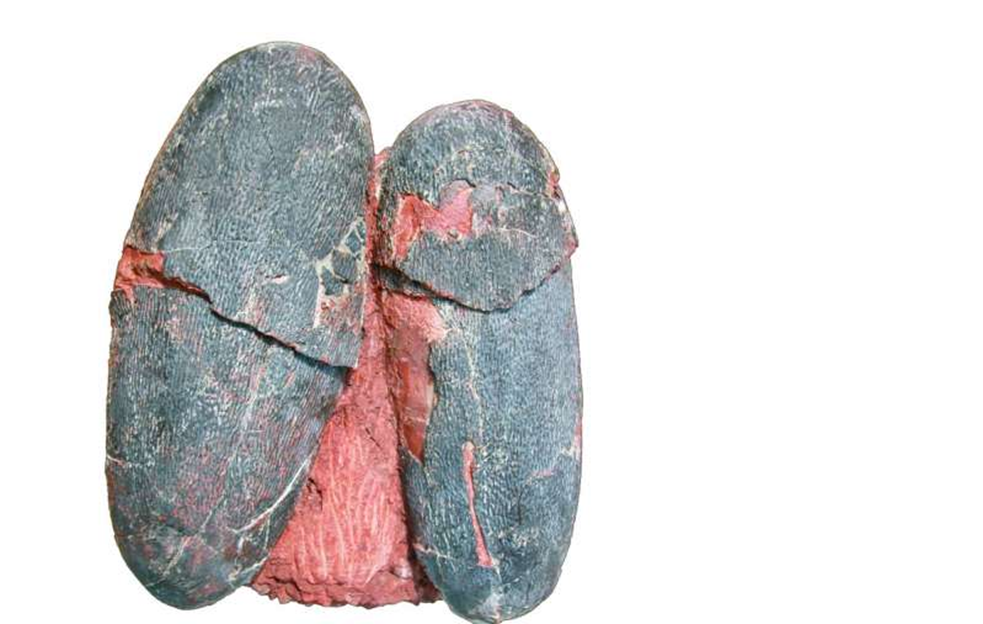
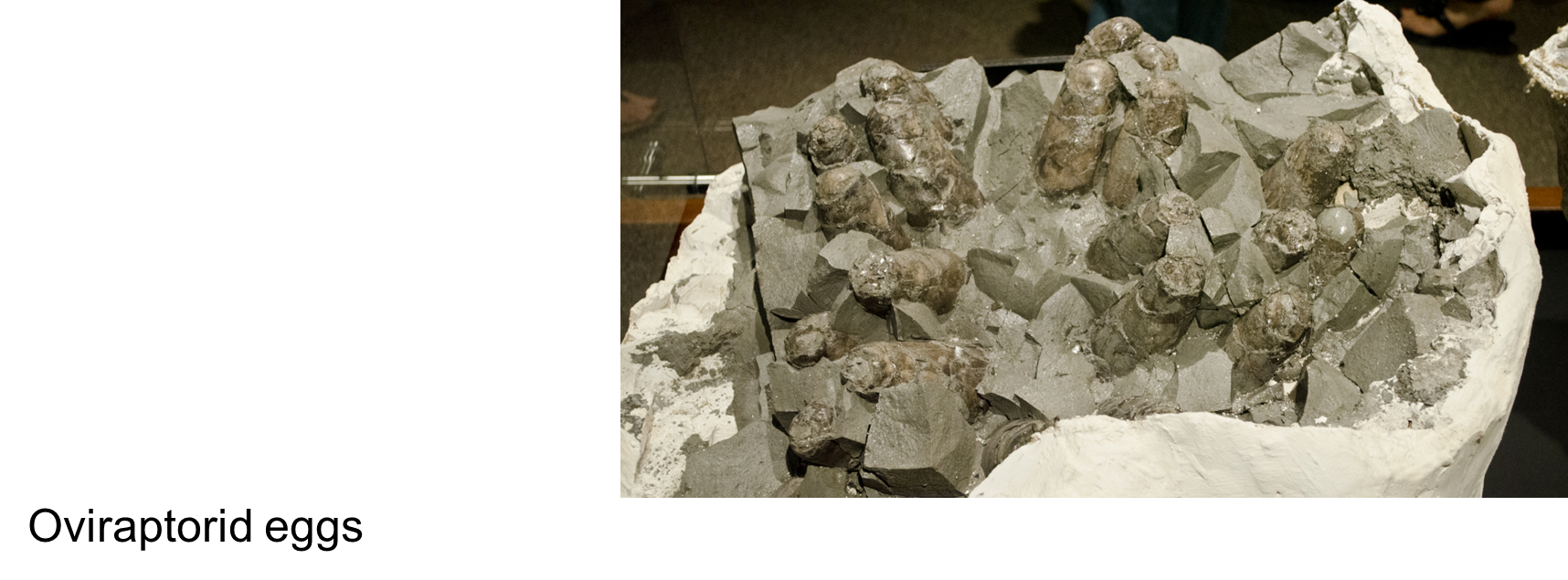



























Surface/Volume Ratio and Thermoregulation
Large dinosaurs retained body heat easily.
Small dinosaurs lost heat rapidly.
26. Surface/Volume Ratio and Egg Size
Larger eggs have smaller surface-to-volume ratio.
Heat retention becomes problematic; careful nest placement required.
*Ectothermy, homeothermy and poikilothermy









Homeothermy Definition
Maintaining relatively constant internal body temperature regardless of environment.
30. Poikilothermy Definition
Body temperature fluctuates with ambient conditions.
Ectothermy Definition
Body temperature primarily determined by external sources (e.g., sun).
*How extinctions are studied in the fossil record








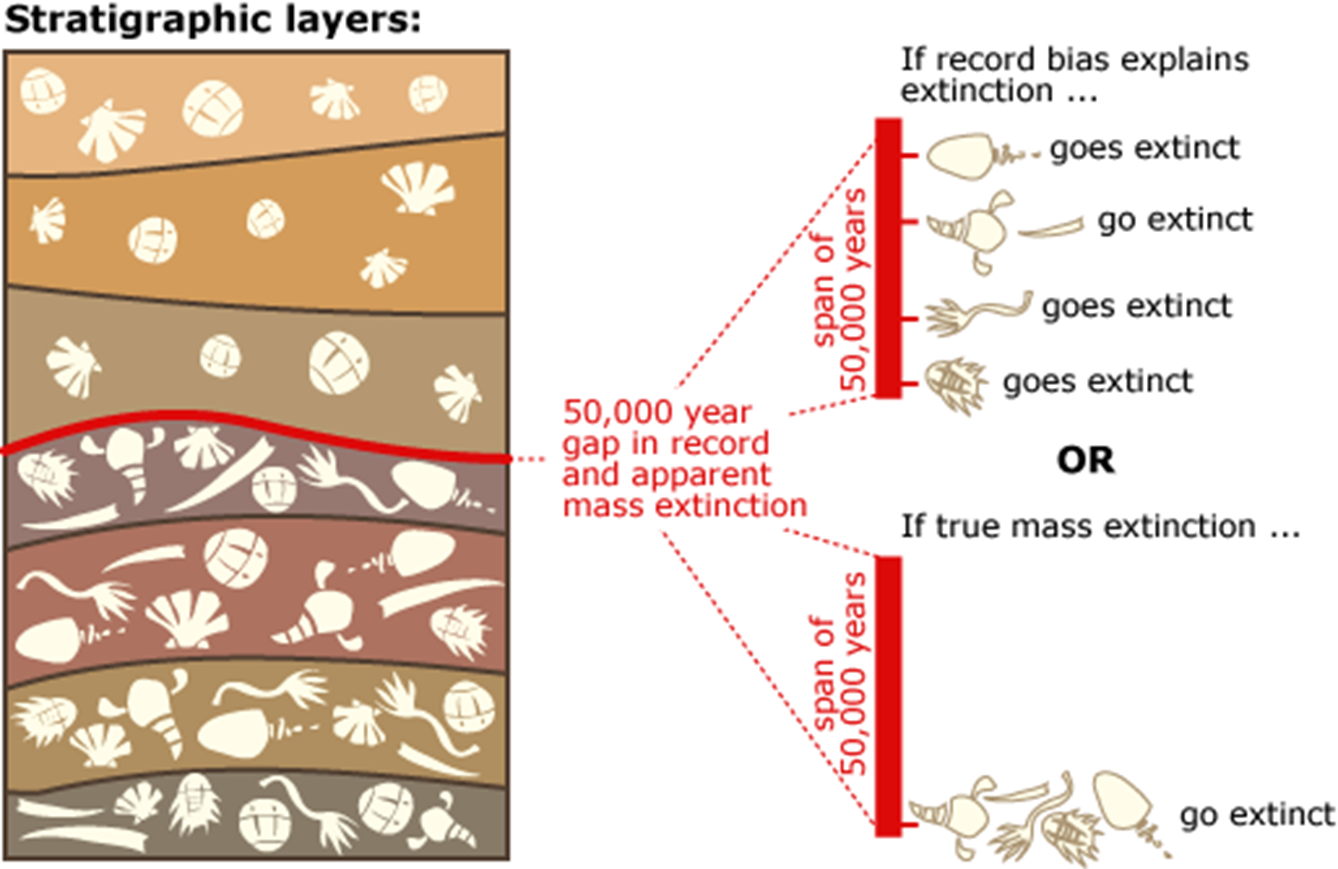

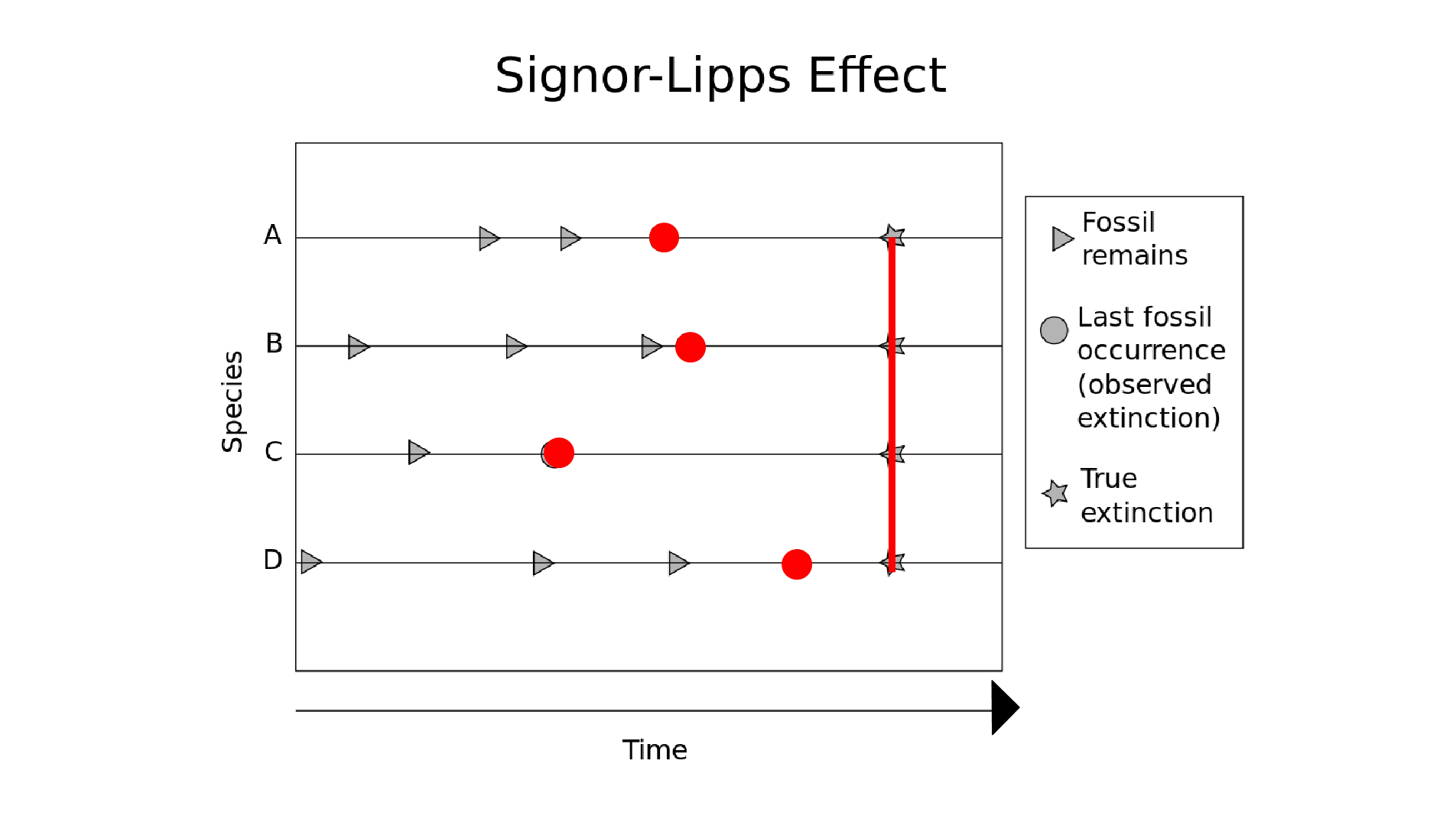







How Extinctions Are Studied in Fossil Record
Fossil appearance/disappearance across strata.
Importance of continuous sedimentation.
Recognizing pseudoextinction when one group evolves into another.
*Explain how trackways are used to determine the speed of the trackmaker. If given the equation and graph from McNeil Alexander and relevant data be prepared to calculate the speed.
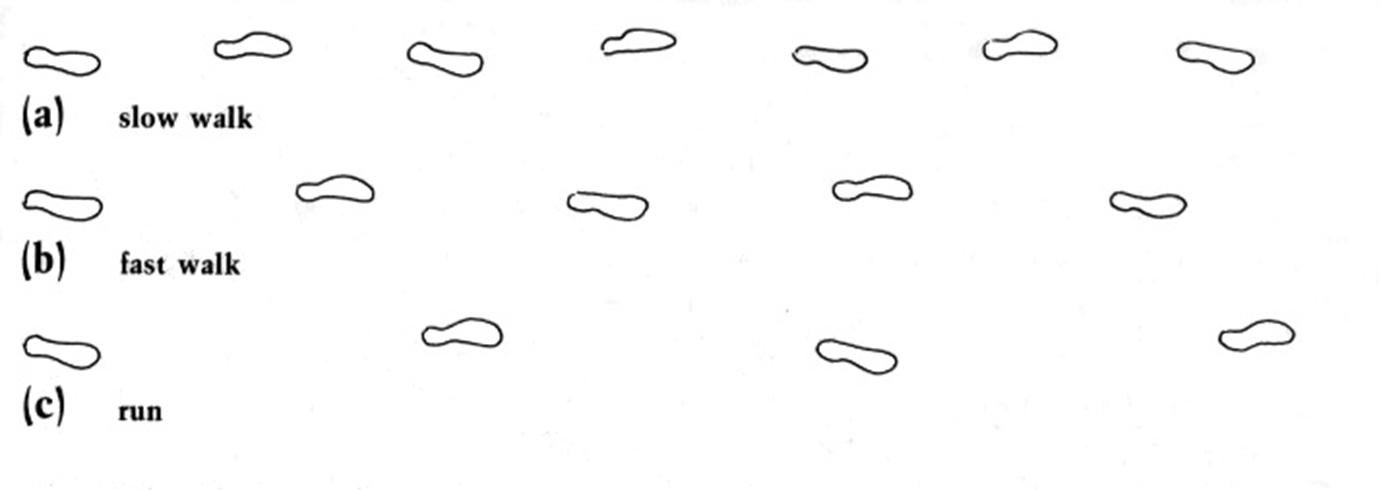

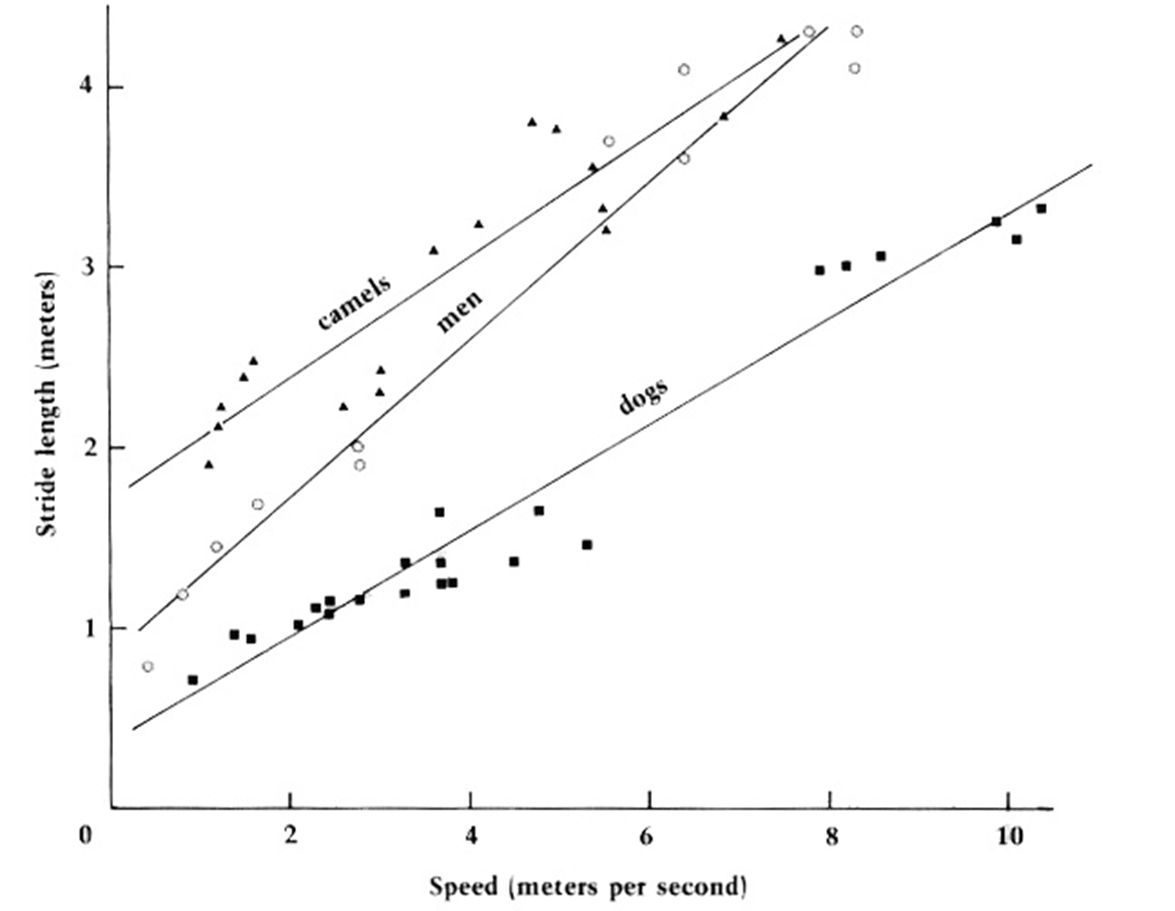



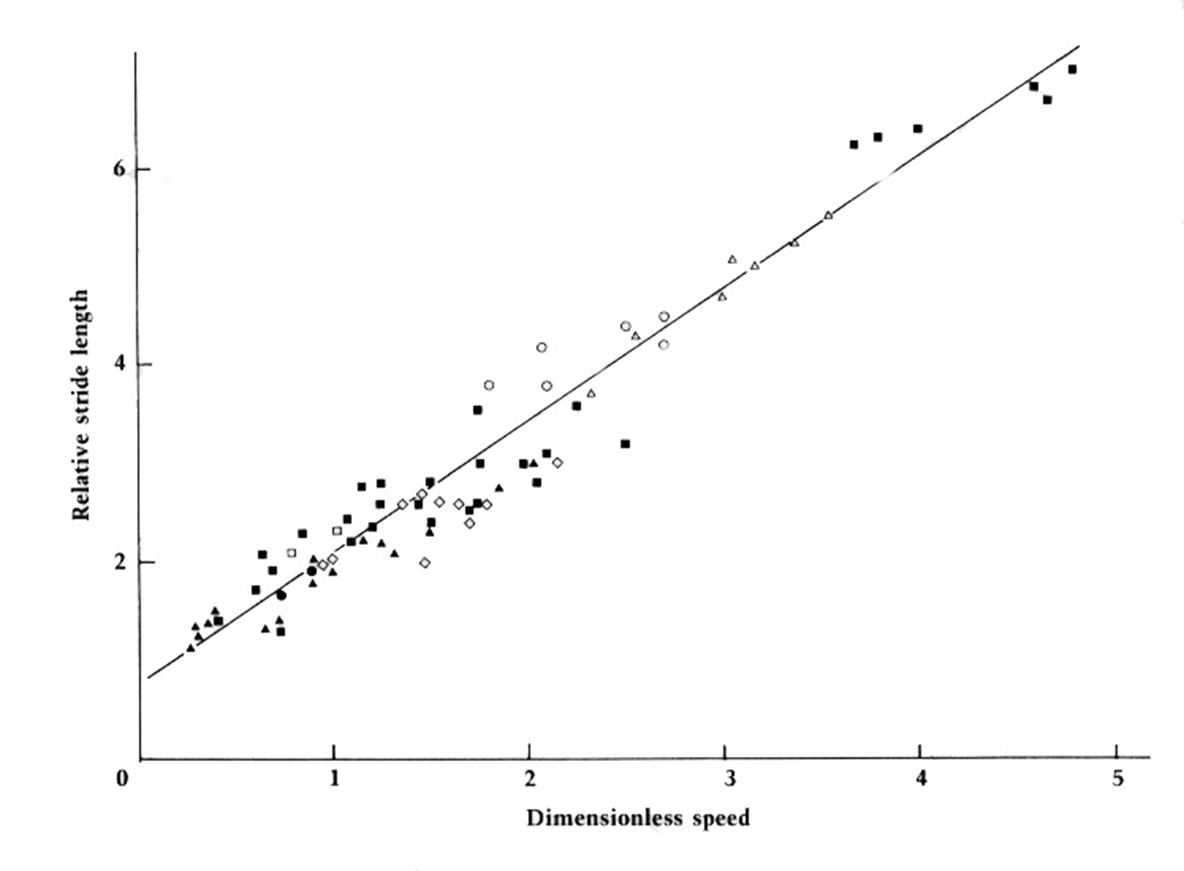



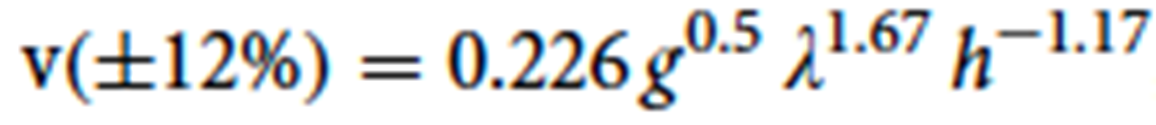





Practice Q1: How Trackways Determine Speed
Stride length divided by hip height estimates gait.
Alexander’s equation applies observed measurements to speed calculations.
*What is the evidence for endothermy in non-avian dinosaurs?













Practice Q2: Evidence for Endothermy
Fast juvenile growth.
Polar dinosaur fossils.
Oxygen isotope uniformity across individuals.
Feather insulation.
*How is color inferred in non-avian dinosaur feathers? In eggs?










Practice Q3: Inference of Color in Feathers and Eggs
Melanosomes for feather colors.
Eggshell pigments (biliverdin, protoporphyrin) detect color.
*How does surface/volume ratio affect thermoregulation?





Practice Q4: Surface/Volume Ratio and Thermoregulation
Large dinosaurs had thermal inertia.
Likely didn't need insulation if large enough.
*What is the current hypothesis for what caused the extinction of non-avian dinosaurs,and what is the most popular alternative hypothesis?
























Practice Q5a: Current Extinction Hypothesis
Asteroid impact.
Immediate catastrophic climate effects.
37. Practice Q5b: Alternative Extinction Hypothesis
Deccan volcanism.
Gradual climate stress leading to ecosystem collapse.
*List 5 non-skeletal features of living birds that may have evolved in dinosaurs
List 5 non-skeletal features of living birds that may have evolved in dinosaurs
Feathers
Shown in many non-avian theropods (Lecture 23: Anchiornis, Sinosauropteryx, Caudipteryx).
Unidirectional airflow in lungs
Shared by birds and inferred in some theropods (Lecture 19).
Parental care / Brooding behavior
Fossils of dinosaurs like Oviraptor found on nests (Lecture 22 and Lecture 19).
Vocalization
Present in both crocs and birds, inferred in dinosaurs via phylogenetic bracketing (Lecture 19).
Hard-shelled eggs
Mineralized eggs found in many dinosaur clutches (Lecture 22 and 23).
🧬 Bonus (also valid based on your slides if you need more):
Colorful feathers (inferred from preserved melanosomes — Lecture 23).
Four-chambered heart with separated circulation (Lecture 19).
Air sacs in skulls (Lecture 19).
These are all non-skeletal traits because they relate to soft tissue, physiology, behavior, or reproduction — and are backed directly by the slides you uploaded.






Practice Q6: Five Non-Skeletal Bird Features from Dinosaurs
Feathers.
Brooding and parental care.
Hollow bones.
Unidirectional airflow lungs.
Complex vocalization potential.
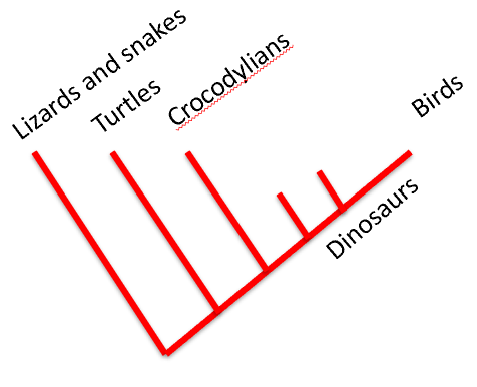
*Be prepared to optimize characters on a cladogram
Practice Q7: Character Optimization on a Cladogram
Placing features on trees to find ancestral versus derived traits.
Example: Feathers mapped deep into Theropoda.

*

Areas of Endemism



*















*








*Vicariance versus dispersal Pt.2
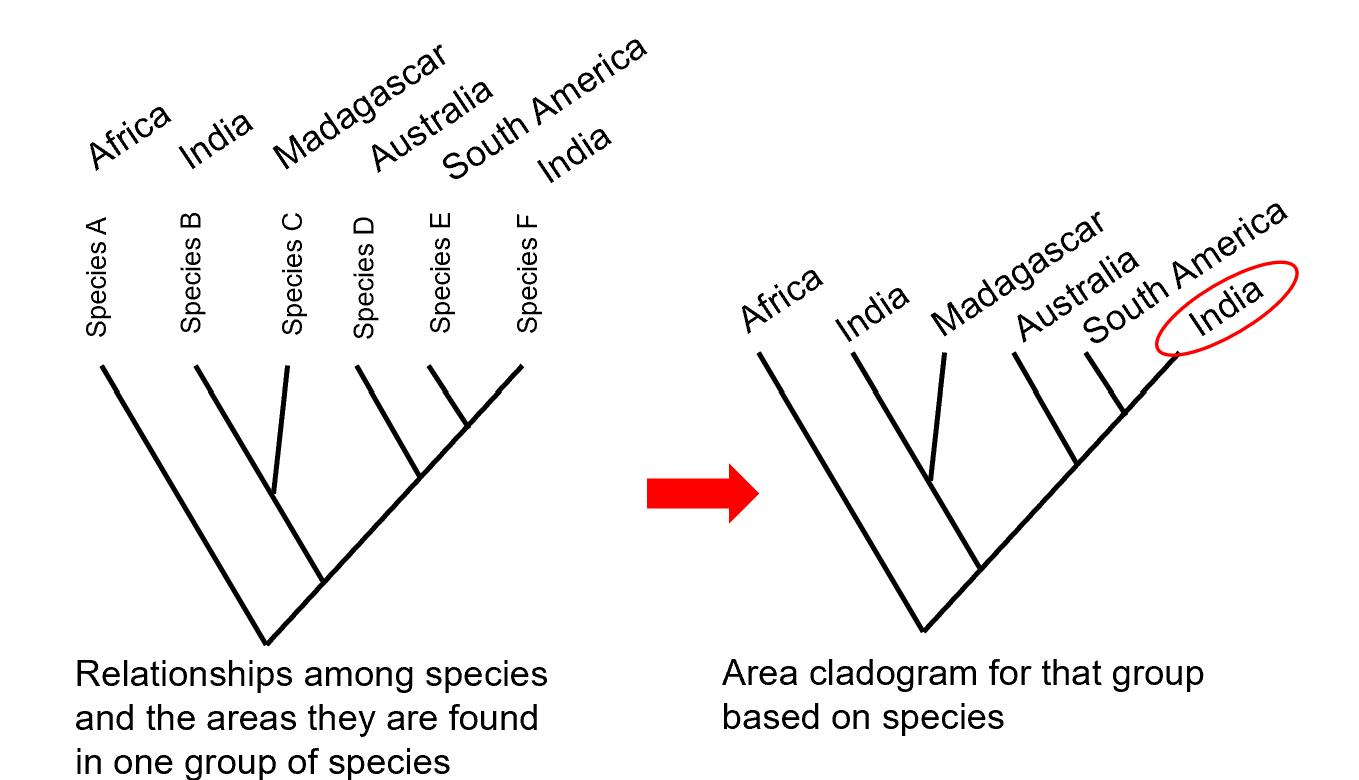
*Vicariance versus dispersal Pt.3
physiology/Metabolism

*endothermy










Dinosaur Size