Exam 2 Ec202
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Unemployment
Results in loss of income and production
structural unemployment
Changes in industry are present such as technology, geography and skill of workers
frictional unemployment
temporaty unemployment from normal job transitions
cyc;ical unemployment
due to recessions
unemployment rate
unemployed workers / # of workers in labor force
participation rate
labor force / working age population
consumer price index
used to measure price changes over time
( Cost of basket (current) / cost of basket (base year) ) times 100
calculation to measure CPI
food and drink, transportation, healthcare, clothing, recreation, education, housing
goods and services included in the CPI basket
Inflation
Rise in prices and decrease in value of currency
Phillips curve
The belief that there is an inverse relationship between unemployment and inflation
disruption of credit markets, decrease in asset value, poorest get poorer
Results of inflation
Nominal Interest Rates
Price of money now vs price in the future
Real interest rates
price of goods and services now vs in the future
deflation
falling prices that delay consumer spending
growth in supply
increase in population, employment and labor hours
real GDP
GDP adjusted for inflation
nominal GDP
GDP not adjusted for inflation
nominal GDP / real GDP x 100
GDP deflator
nominal GDP / GDP deflator x 100
real GDP
y = AK ^ a N ^ 1-a
Cobb-douglas production function
The key to long run growth
Total Factor Productivity
Constant Returns to scale
if K and N change, the output changes at the same rate
diminishing returns to scale
If one input changes, the output gains get smaller and smaller as the scale increases
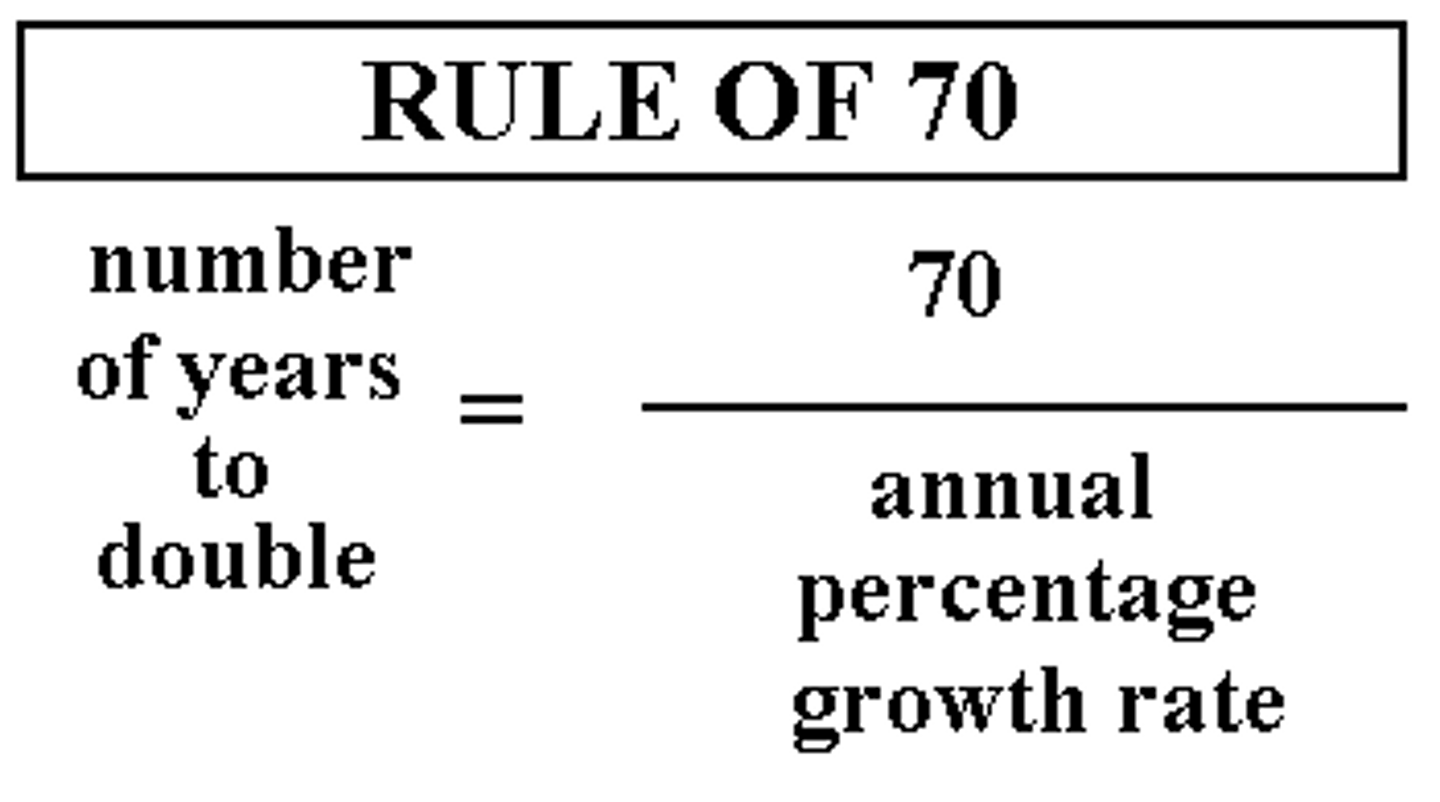
# of years it takes for a variable to double
the rule of 70
(y(t+1) -y(t))/ y(t)
Function to find Real GDP (yt+1 = future period) yt = earlier period
Marginal Propensity to Consume (MPC)
Change in consumption / disposable income
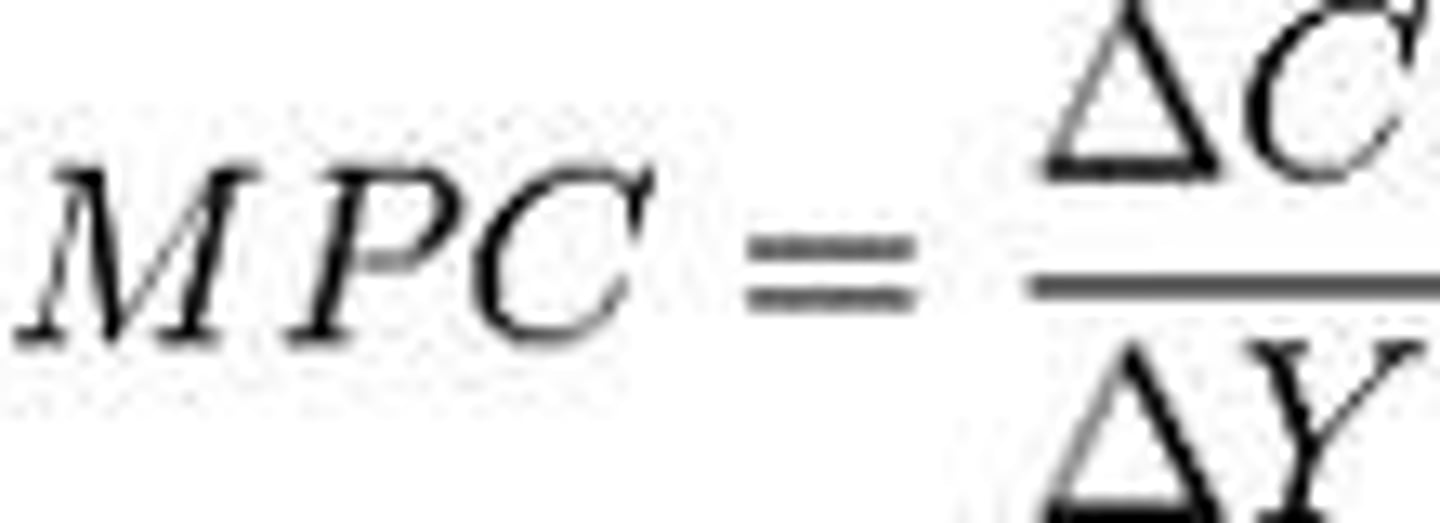
disposable income
GDP per capital - net taxes
marginal propensity to save
change in money saved / disposable income
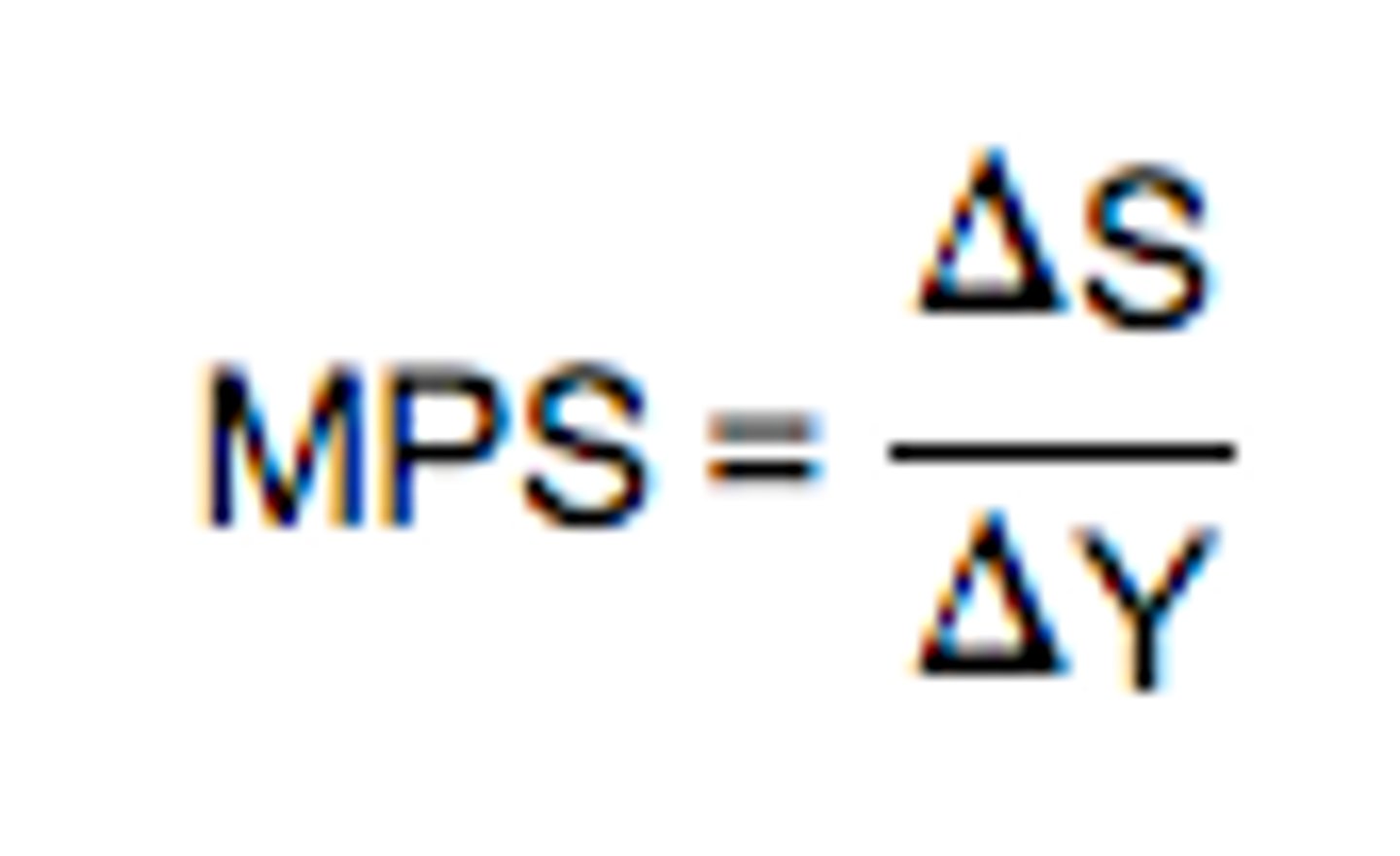
Y
real GDP
C
consumption
I
investment
G
Government spending
X
exports
m
imports
Y = C + I + G + (X - M)
Aggregate Expenditure Sum
John Maynard Keynes
Economist who shared ideas about aggregate supply and demand
aggregate supply
total output of goods at different price levels (relationship between supply and price)
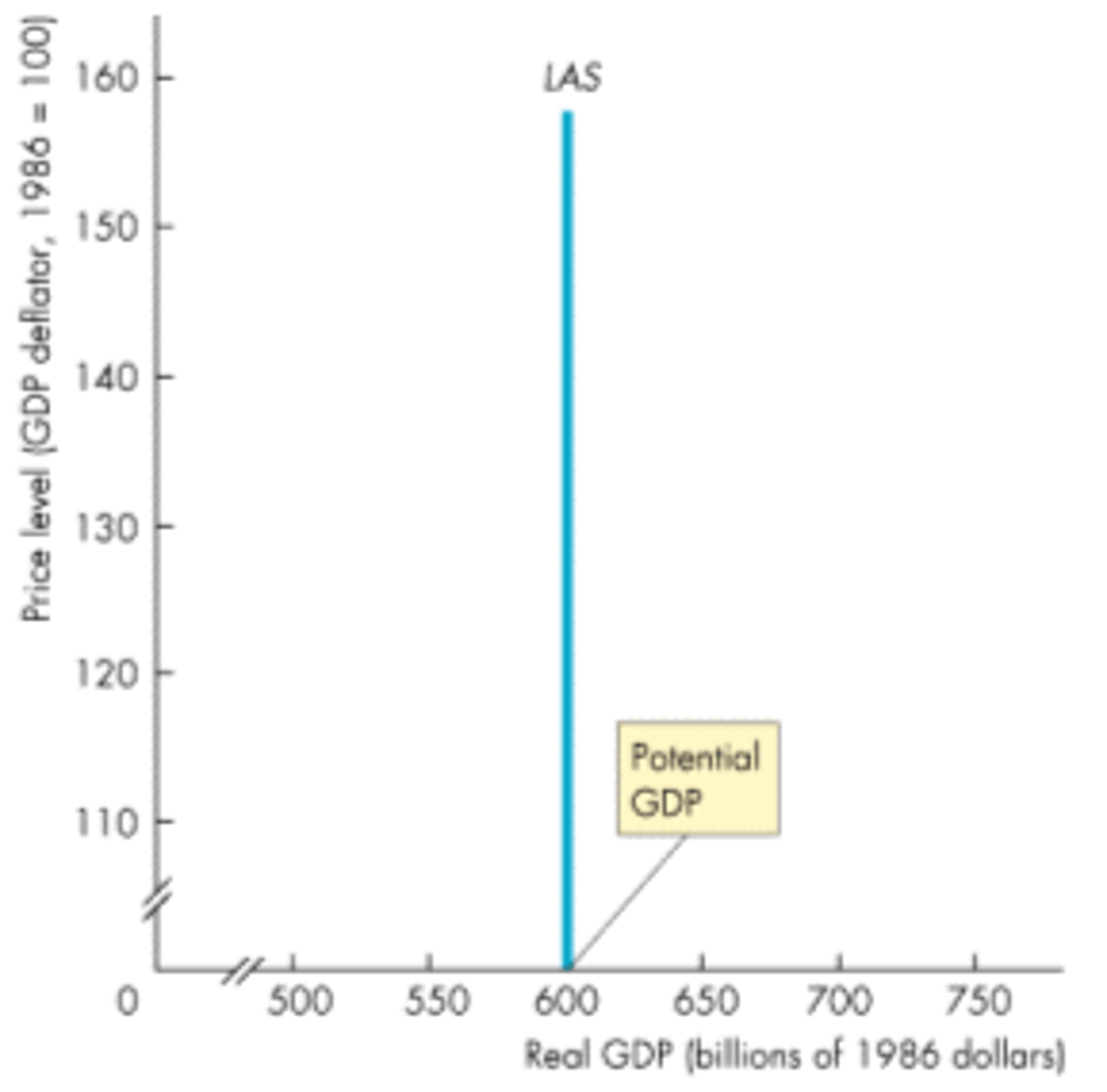
Long Run aggregate supply
the relationship between the quantity of real GDP supplied and the price level when the money wage rate changes in step with the price level to maintain full employment
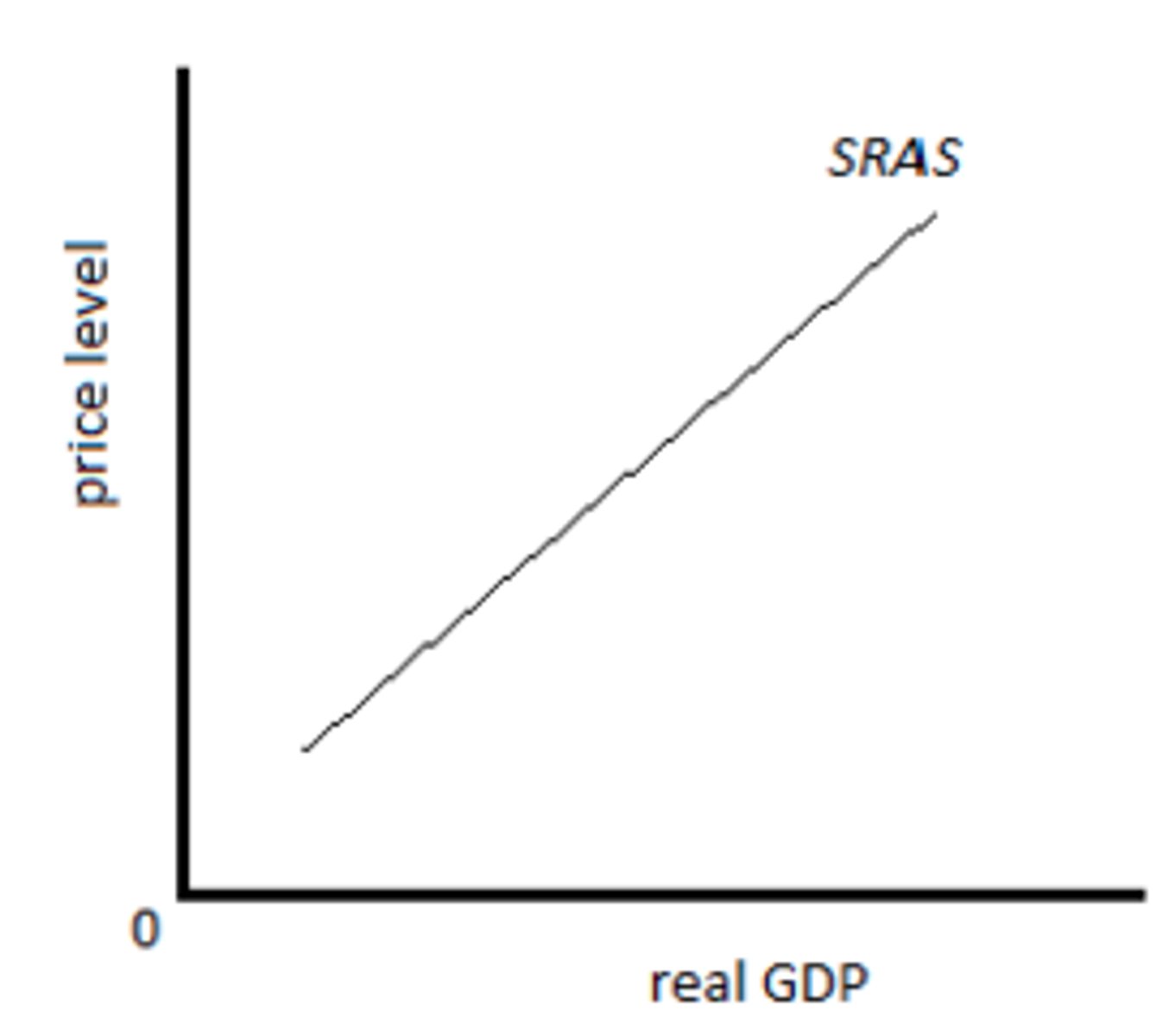
short run aggregate supply
The relationship between the quantity of real GDP supplied and the price level when the money wage rate, the prices of other resources, and potential GDP remain constant.
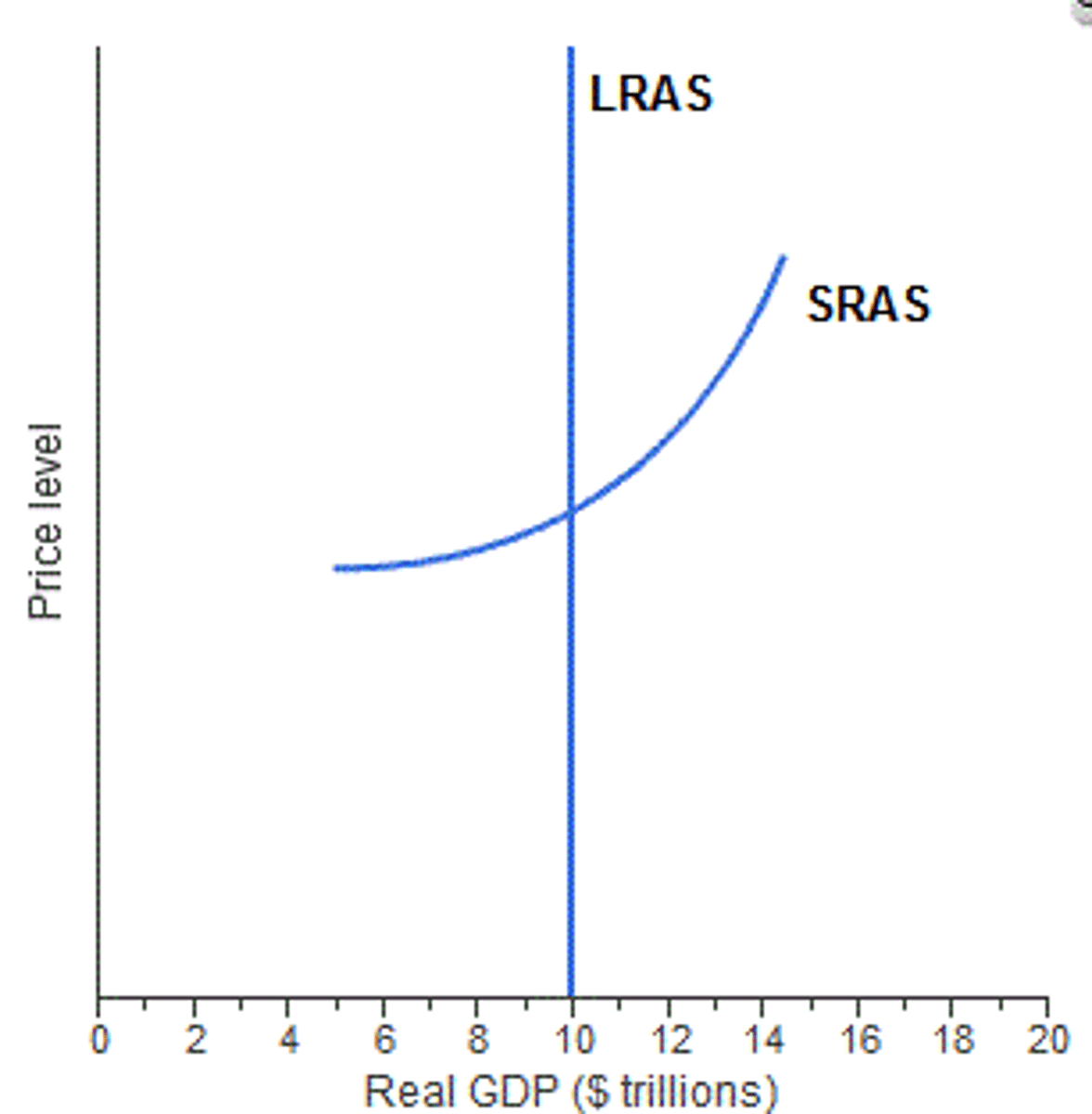
Long Run equilibrium
occurs when real GDP = Nominal GDP
Increased of aggregate demand
Caused by increases in spending by the government and consumers
short run equilibrium
When aggregate demand equals short run aggregate supply
potential GDP
GDP of a country when the employment rate is 100%
recession
GDP is less than its potential
when GDP is above potential GDP
Recession could be incoming