IGCSE PHYSICS: ELECTROMAGNETIC EFFECTS
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
What is electromagnetic induction?
The production of a potential difference (EMF) caused by relative movement between a conductor and a magnetic field.
In what direction is the potential difference induced?
In the opposite direction to the movement which produced it.
When is a current produced?
When the ends of the coil are connected to a complete circuit.
How can you increase the induced EMF?
● Moving the wire more quickly
● Increasing the length of wire
● Using a stronger magnetic field
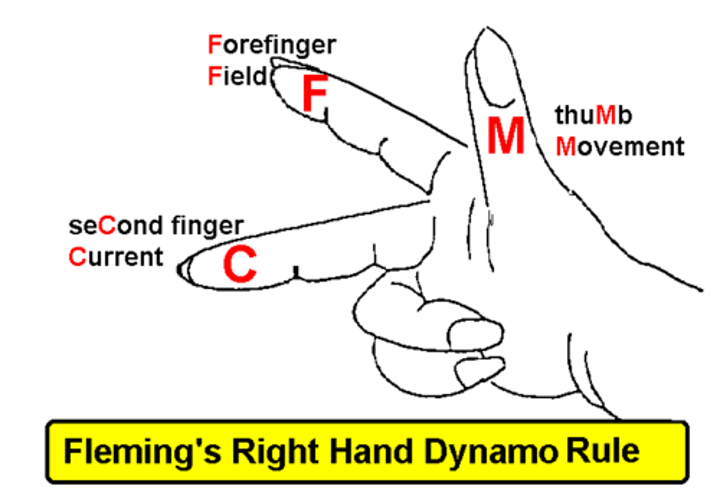
How can you work out the direction of the induced current?
Using Fleming's right hand rule.
How are electrical generators set up?
In the same way as a motor, with a rectangular loop of wire between permanent magnets. The main difference is the presence of a turbine to spin the coil.
Describe how an electrical generator works
● A turbine spins the coil of wire between the magnets.
● The wire cuts through the magnetic field, experiencing a changing magnetic field.
● A potential difference is induced.
● A current is produced.
What kind of current is produced by an ordinary generator?
An alternating current.
How does a split ring commutator work?
It disconnects and reconnects the wires every half rotation, switching the current so the motor spins continuously.
How do transformers work?
● An alternating current flows through the primary coil, producing an alternating magnetic field.
● This causes the secondary coil to experience a changing magnetic field, inducing a potential difference, which produces an alternating current in the secondary coil.
Why do step up transformers increase voltage?
There are more coils experiencing the change, so a larger p.d. is induced.
State one assumption used in transformer calculations
The transformer is 100% efficient (the power is assumed to be the same in both coils).
Give the transformer equations linking number of coils, p.d. and current
N₁/N₂=I₂/I₁=V₁/V₂
What is produced around a current carrying wire?
A magnetic field.
How can you determine the direction of a magnetic field around a wire?
Using the Right Hand Grip Rule. Produce a thumbs-up shape with your right hand and point your thumb in the direction of the flow of current. The field lines wrap around in the direction of your fingers.
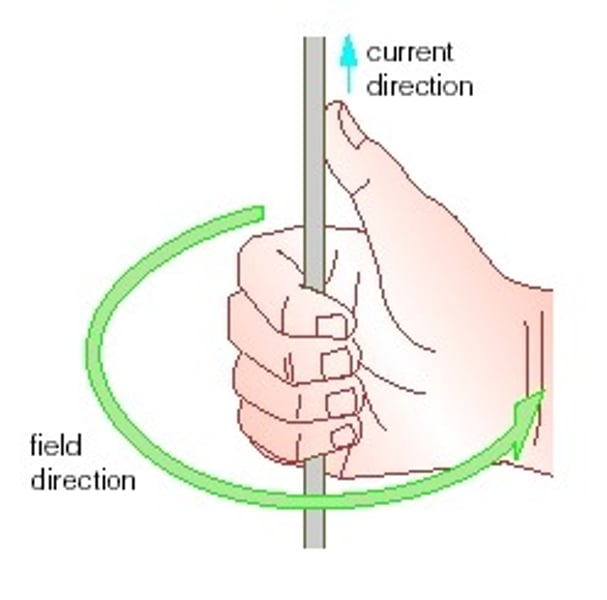
What is a solenoid?
A coil of wire with a magnetic field, which can be used as an electromagnet.
How does coiling a wire affect the magnetic field?
It increases the field strength, as the magnetic fields of each turn of wire are added together.
How can you increase the strength of a solenoid magnet?
● Using an iron core to carry field lines (as they
travel more easily through metal than air)
● Increase the number of turns in the coil
● Increase the current
What is the motor effect?
If a current-carrying wire is placed in a magnetic field it experiences a force, pushing the wire out of/away from the field.
Describe the mechanism of the motor effect
● When a current-carrying wire produces a magnetic field within the field of a permanent magnet, the two fields interact.
● The wire experiences a force pushing it away from the magnetic field, at right angles to the direction of the permanent field and the current
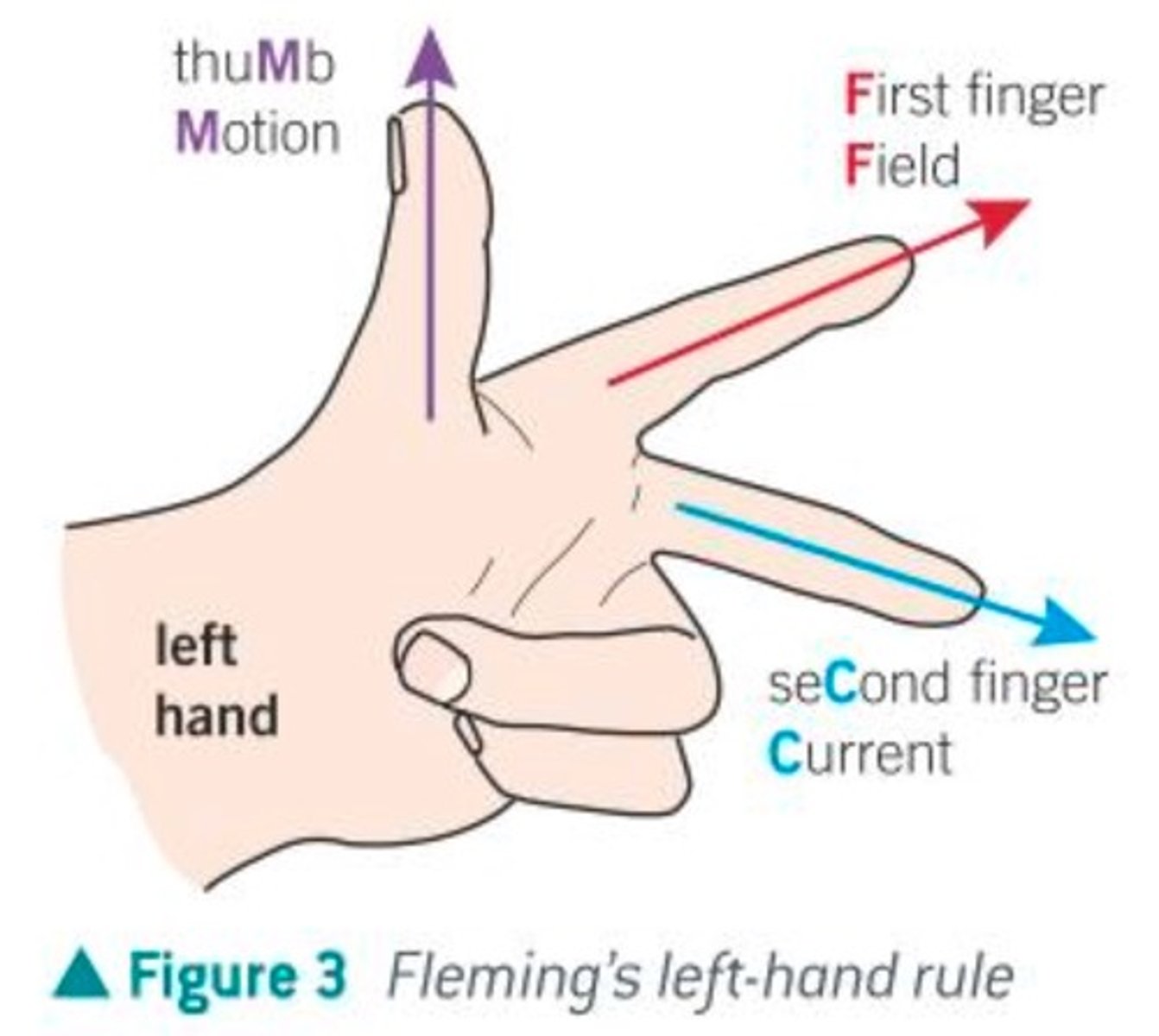
How can you predict the direction of the
motor effect?
Using Fleming's left hand rule.
Thumb = Movement
First finger = Field
Second finger = Current
What is conventional current?
A model for current which flows in the opposite direction to electrons.
Conventional current flows from positive to negative.
What kind of current is used in Fleming's rule?
Conventional current.
Which factors affect the strength of the motor force?
● The length of wire placed in the field
● The current in the wire
● The strength of the permanent field
dad is not happy
dad is happy