Alcohols
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
Why does solubility of alcohols decrease as the carbon chain length increases
The chains are non-polar so exhibit london dispersion forces only and disrupt the hydrogen bonding network which forms between nthe alcohol functional group and water molecules.
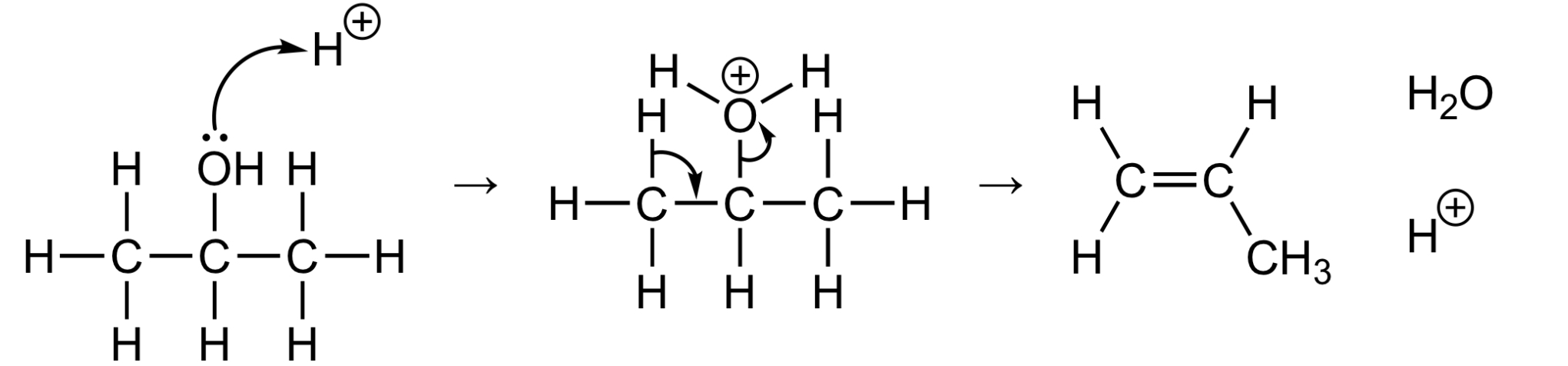
What are the conditions needed for the dehydration of alcohols
Heated in the presence of concentrated sulphuric acid or phosphoric acid (H3PO4)
What kind of mechanism does dehydration take place by
Via elimination reaction
Outline the mechanism by which the dehydration of alcohols occurs
What is needed for the halogenation of alcohols
A halogenating agent
What is the halogenating agent for the chlorination of alcohols
Phosphorous pentachloride (PCl5)
What is formed in the chlorination of alcohols
chloroalkanes
Misty HCl fumes
Phosphoryl chloride (POCl3)
What is the halogenating agent for the chlorination of a tertiary alcohol
Concentrated HCl
What are the conditions necessary for the bromination of alcohols
Heated under reflux
With sodium bromide or potassium bromide
50% concentrated sulphuric acid
What are the steps involved in the bromination of alcohols and what is formed
an acid base reaction occurs between the sulphuric acid and the K/NaBr
HBr is formed
HBr reacts with alcohol in a substitution reaction
Water and bromoalkane is formed
What are the steps required in the iodination of alcohols and what is formed
red phosphorous is reacted with iodine
Forms phosphorous (III) iodide (PI3)
Phosphorous (III) iodide reacts with alcohol to form iodoalkane and phosphoric (III) acid
Give the equation for the reaction between red phosphorous and iodine
2P + 3I2 → 2PI3
Give the equation for the reaction between phosphorous (III) iodide and an alcohol
PI3 + 3CH3(OH) → 3CH3I + H3PO4
What is observed when acidified potassium dichromate (VI) solution is used to oxidise a chemical
Colour change from orange to green
Give the ionic half equation for potassium dichromate (VI) when it is used as an oxidising agent
Cr2O72- + 14H+ + 6e- → 2Cr3+ + 7H2O
What are the conditions necessary for the oxidation of alcohols
Heating with a mixture of dilute sulphuric acid with sodium/potassium dichromate (VI) solution
What is formed when primary alcohols are heated with acidified potassium dichromate (VI) in distillation
An aldehyde
What is the general structural formula for aldehydes
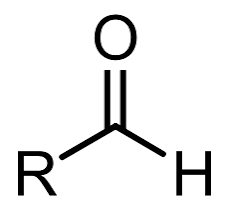
What is the iupac suffix for aldehydes
-al
What is formed when primary alcohols are heated under reflux with acidified potassium dichromate (VI)
Carboxylic acid
Why are anti-bumping granules used
They provide a large surface area which provides nucleation sites for smaller bubbles to form on and prevent larger and potentially hazardous bubbles from forming
Why is the ethanal obtained in the distillate in the partial oxidation of ethanol pure and not contain any unreacted ethanol
Ethanol exhibits hydrogen bonding, ethanal does not
Why is it necessary for alcohols to be heated under reflux for it to be fully oxidised
Allows reaction to be heated in order to significantly increase the rate of reaction while avoiding organic products or reactants with low boiling points from boiling and escaping from reaction vessels
What do secondary oxidise to form
Ketones
What is the general structural formula of ketones
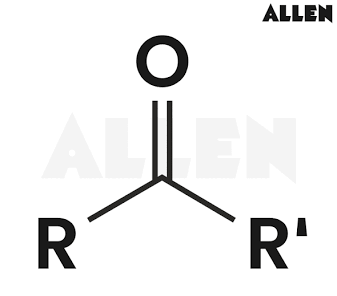
What is the IUPAC suffix for ketones
-one
Why can’t tertiary alcohols be oxidised to form
There are no hydrogen atoms bonded to the central carbon atom to which the alcohol functional group is bonded
Give the half equation for the oxidation of methanol to methanal
CH3OH → HCHO + 2e- + 2H+
Give the full redox equation for the reaction between methanol and acidified dichromate (IV) ions
Cr2O72- + 8H+ + 3CH3OH → 2Cr3+ 7H2O + 3HCHO
Write a half-equation for the oxidation of ethanol to ethanoic acid
H2O + CH3CH2OH → CH3COOH + 4H+ + 4e-
Write the full redox equation for the reaction between ethanol and acidified dichromate (VI) ions
2Cr2O72- + 16H+ + 3CH3CH2OH → 4Cr3+ + 11H2O + 3CH3COOH
What is used to test for the alcohol functional group
Phosphorous (V) chloride
What is formed/observed for the positive test for an alcohol functional group
Steamy fumes of HCl gas, as well as a chloroalkane and POCl3
What are the two substances used to test for aldehydes
Tollen’s Reagent (ammonium silver nitrate, [Ag(NH3)2]+)
Fehling’s solution (containing Cu2+ ions)
Describe and explain the positive result for the test for Aldehydes using Tollens’ Reagent
The aldehyde is oxidised to a carboxylic acid, and the silver ions are reduced to silver (REDOX reaction)
Colourless solution goes to form a silver mirror
Describe and explain the positive result for the test for aldehydes using Fehling’s solution
Aldehydes reduce Cu2+ to Cu+ giving a red precipitate of copper (I) oxide
Blue solution forming red precipitate (Cu2O)
What are the conditions used for the hydration of ethene
300˚C
Phosphoric acid (H3PO4) catalyst
60-70 atm
What are the advantages of hydration
no other products are formed leaving already pure ethanol
Continuous process so fast
What are the disadvantages of hydration
requires expensive equipment
Conditions required need a lot of energy which is costly
Uses non-renewable ethene
Outline the mechanism for the electrophilic addition of H+/H2O to ethene
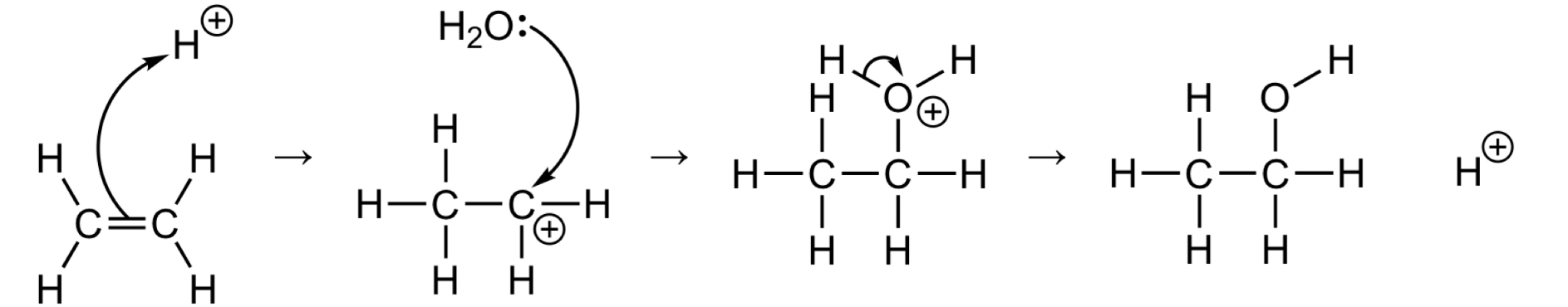
What are the conditions used in the fermentation of glucose
38-40˚C
Zymase from the yeast acts as a catalyst
Anoxic/anaerobic conditions
Give the equation for the fermentation of glucose
C6H12O6 → 2CO2 + 2C2H5OH
What are the advantages of fermentation
Cheaper equipment
Less energy, cheaper
Glucose/sugar used is a renewable resource
What are the disadvantages of fermentation
Non-continuous/batch process
Long process
Product formed (ethanol) is not pure so needs to be purified
Crops used for growing the sugar can take up a lot of space
Why is the use of ethanol as a fuel considered “carbon-neutral”
The amount of carbon dioxide produced in combustion and fermentation is equal to that taken in during photosynthesis (everything cancels out)
Why is the use of ethanol as a fuel not considered “carbon-neutral”
Transportation and purification of fermentation produced ethanol produced additional emissions of carbon dioxide