CIE IGCSE Biology Unit 19: Organisms and their Environment
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
The Sun
principal source of energy input to biological systems

energy transfer
Occurs when animals feed on plants and animals feed on other animals. Transferred to environment as heat
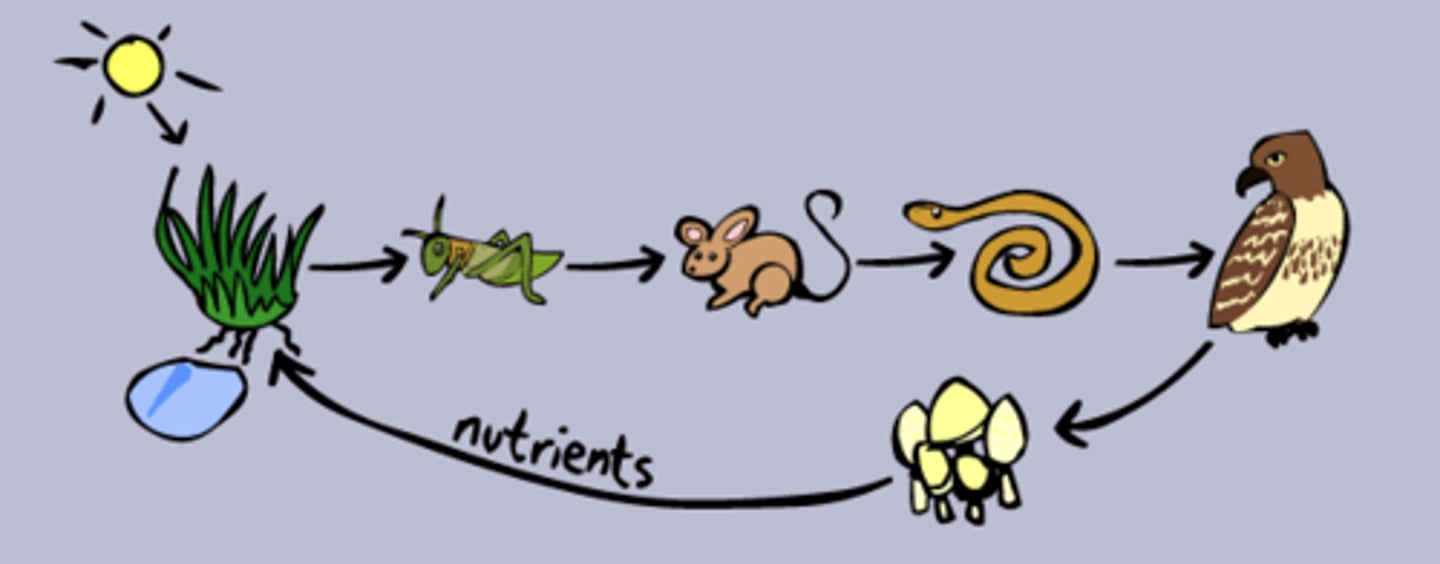
food chain
shows the transfer of energy from one organism to the next beginning with a producer
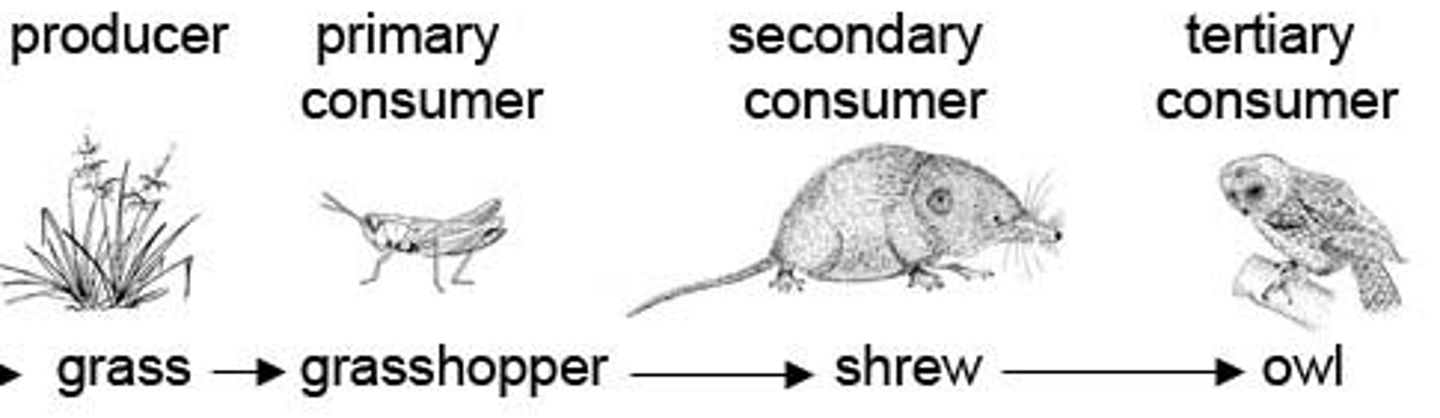
trophic level
the position of an organism in a food chain, food web, pyramid of numbers or pyramid of biomass
why the transfer of energy from one
trophic level to another is inefficient?
energy loss due to activity of organism
-digestion
-respiration
-reproduction
-egestion
why food chains usually have fewer
than five trophic levels?
Energy too little from last trophic level to sustain next trophic level
why there is a greater efficiency in
supplying plants as human food?
Producers are the first trophic level and acquire food from photosynthesis thus contain higher energy content
Energy losses in an ecosystem
-movement causes energy loss by heat
-egestion
-respiration
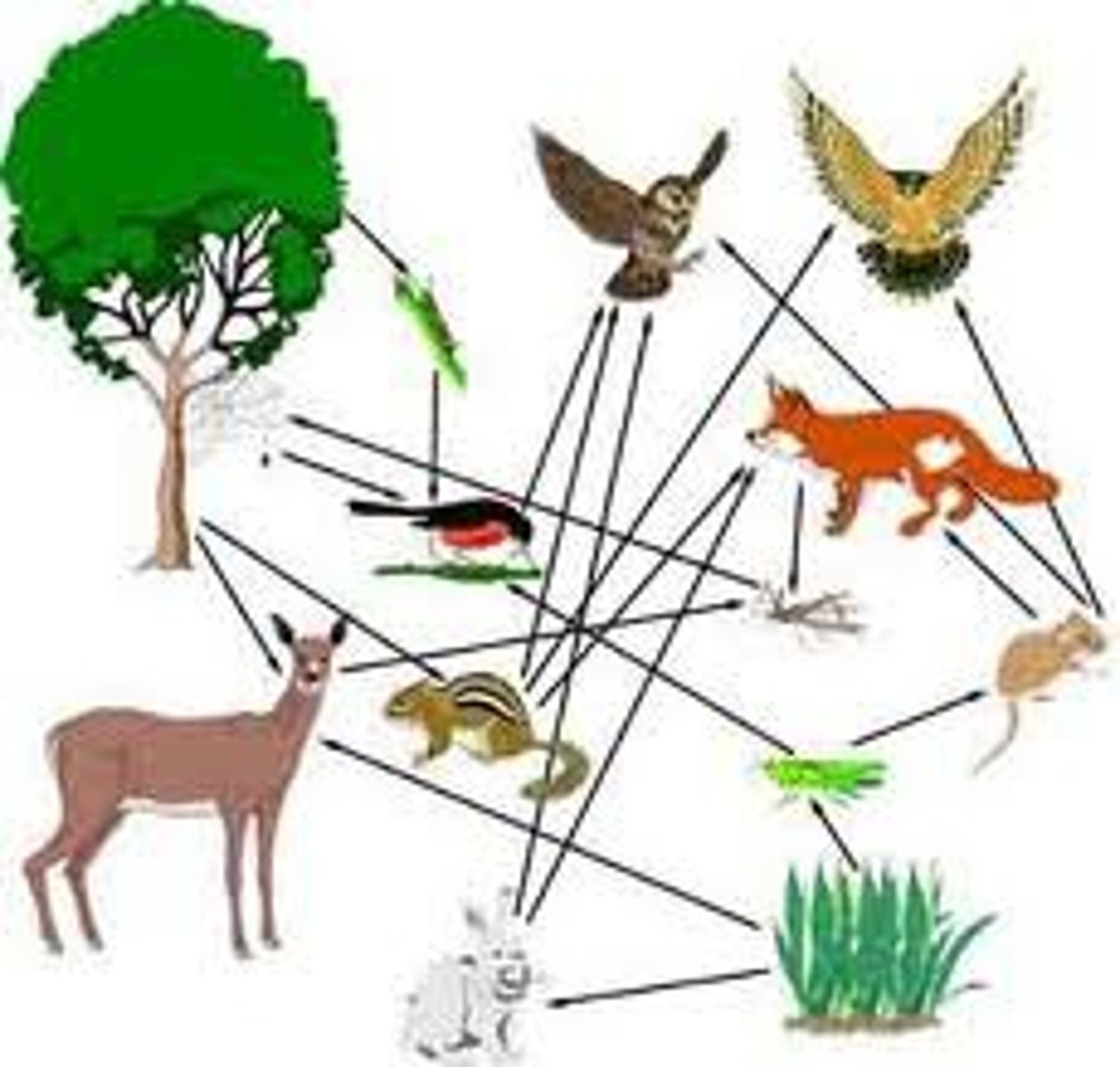
food web
a network of interconnected food chains
producer
an organism that makes its own organic nutrients, usually using energy from sunlight, through photosynthesis

consumer
an organism that gets its energy by feeding on other organisms
herbivore
an animal that gets its energy by eating plants

carnivore
an animal that gets its energy by eating other animals
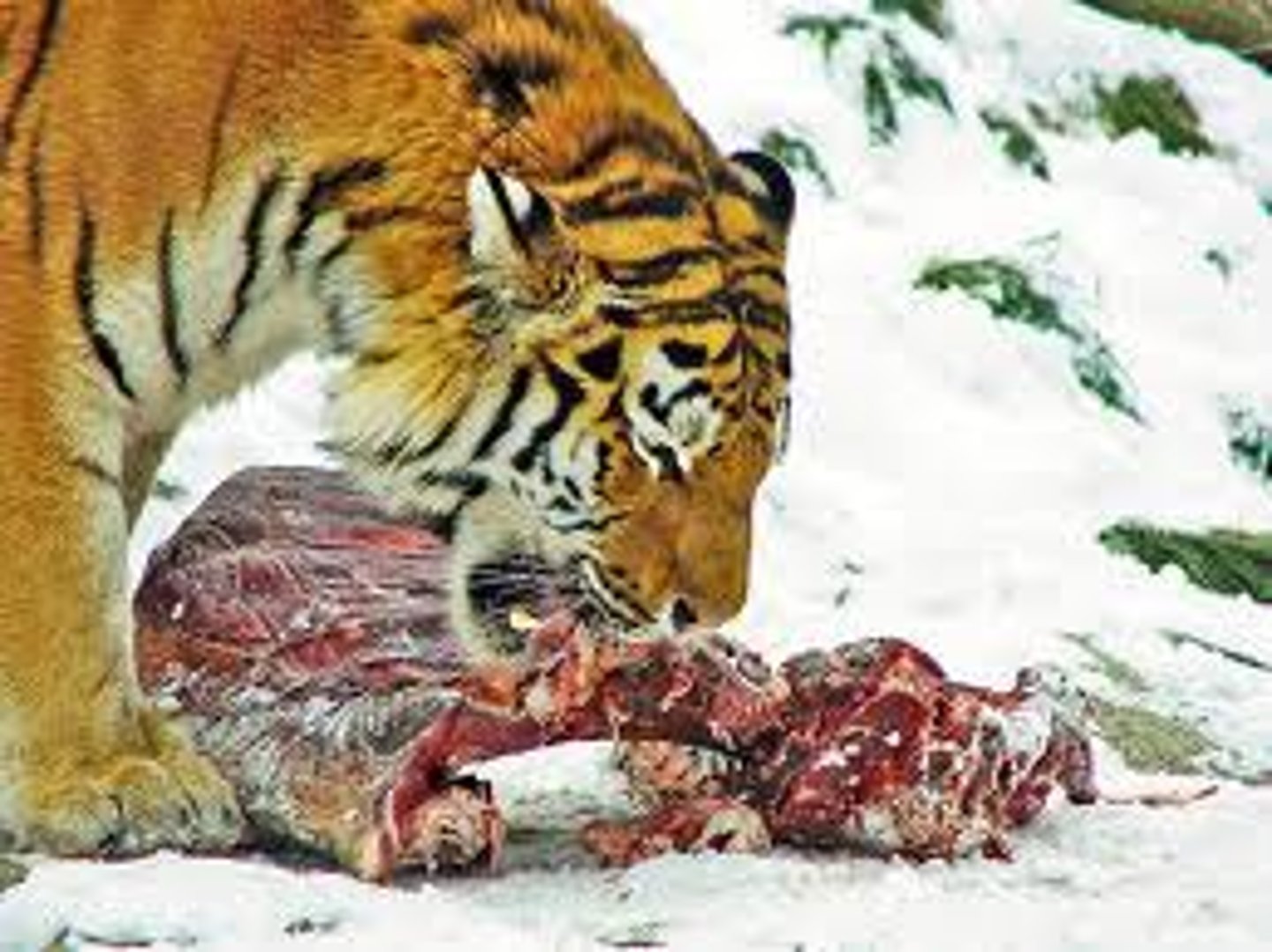

decomposer
an organism that gets its energy from dead or waste organic materials
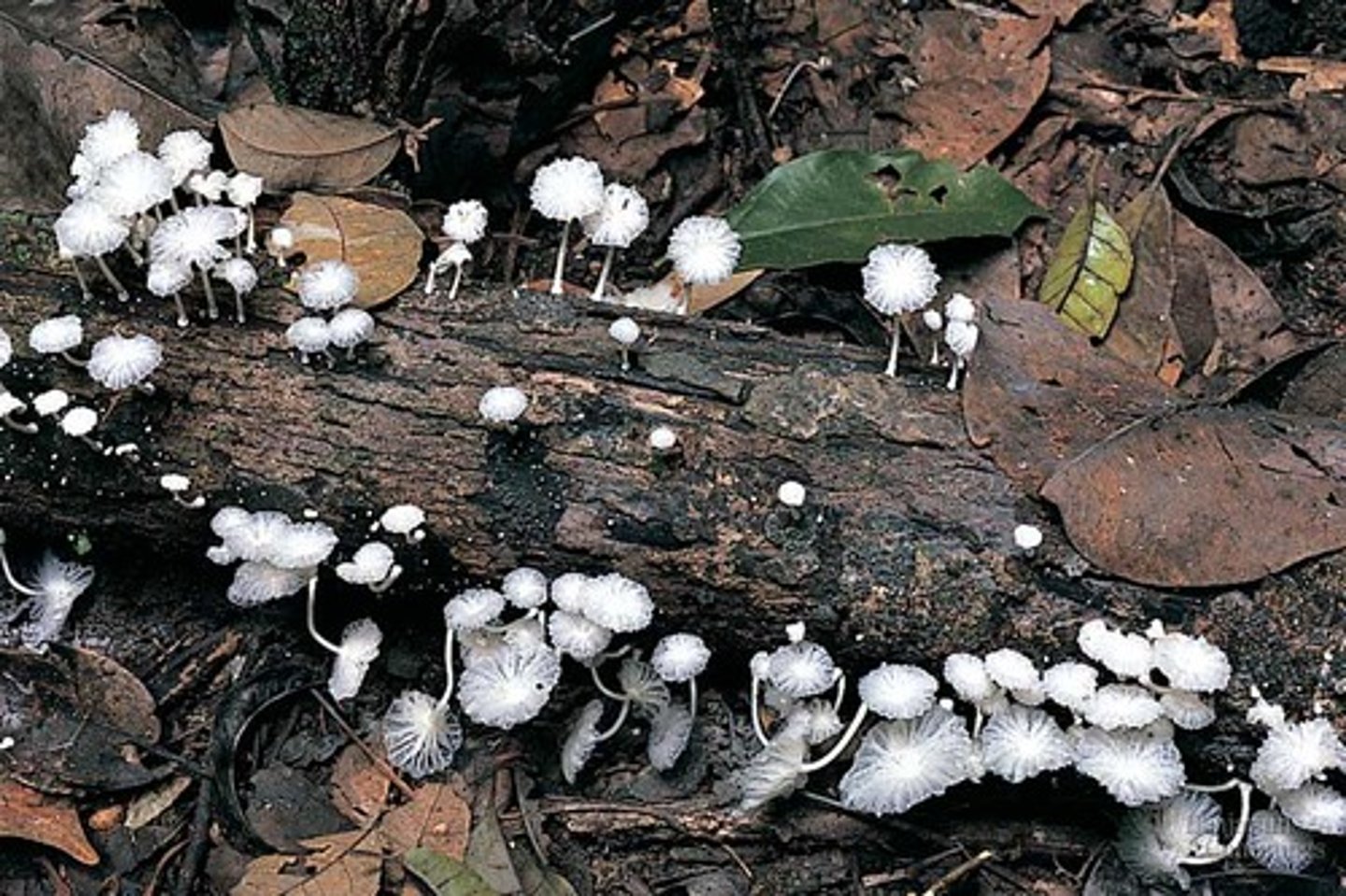

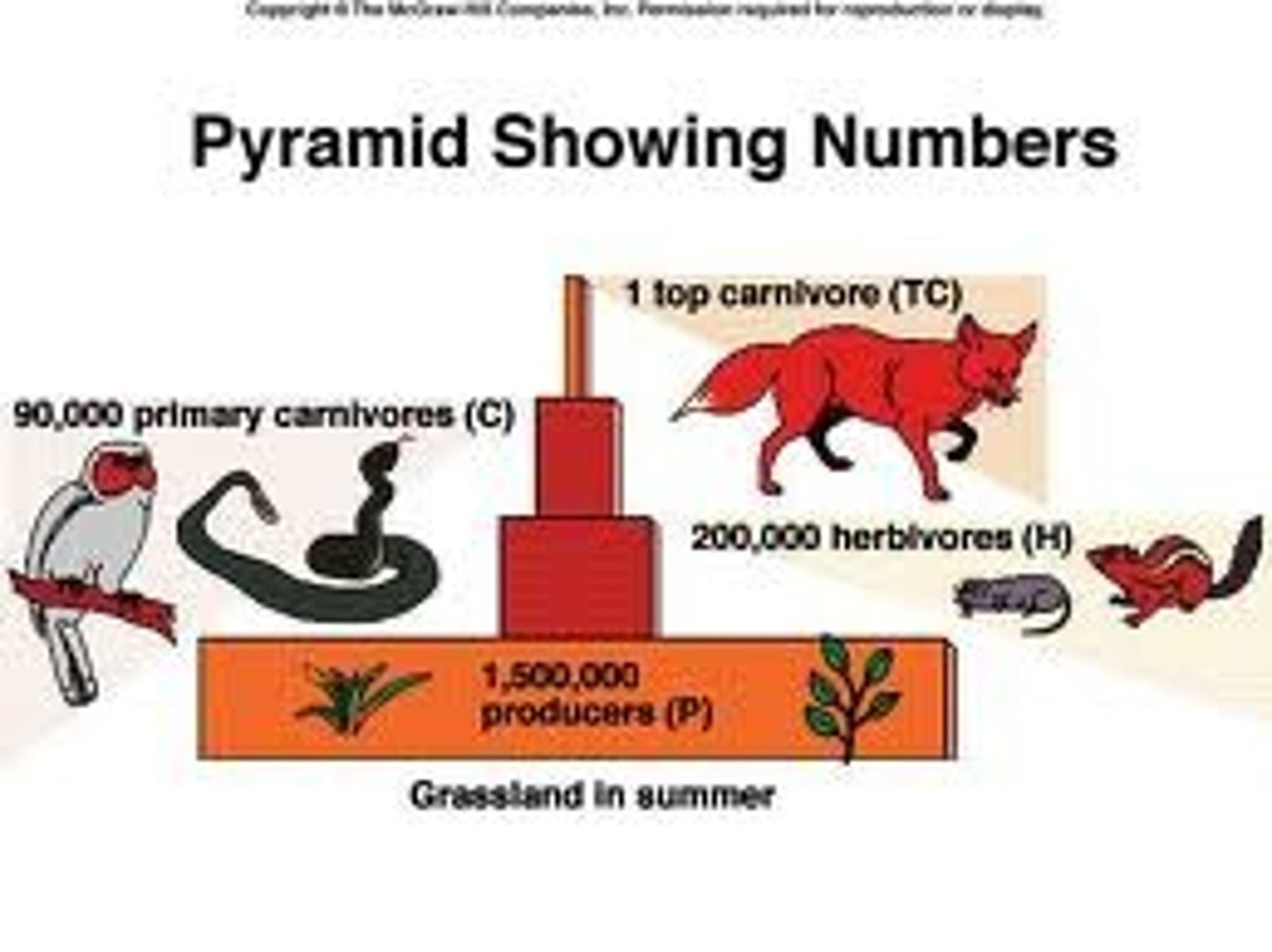
pyramids of numbers
Number of organisms at each trophic level but no indication of size
pyramids of biomass
The mass of living material at each trophic level but no indication of the rate of growth
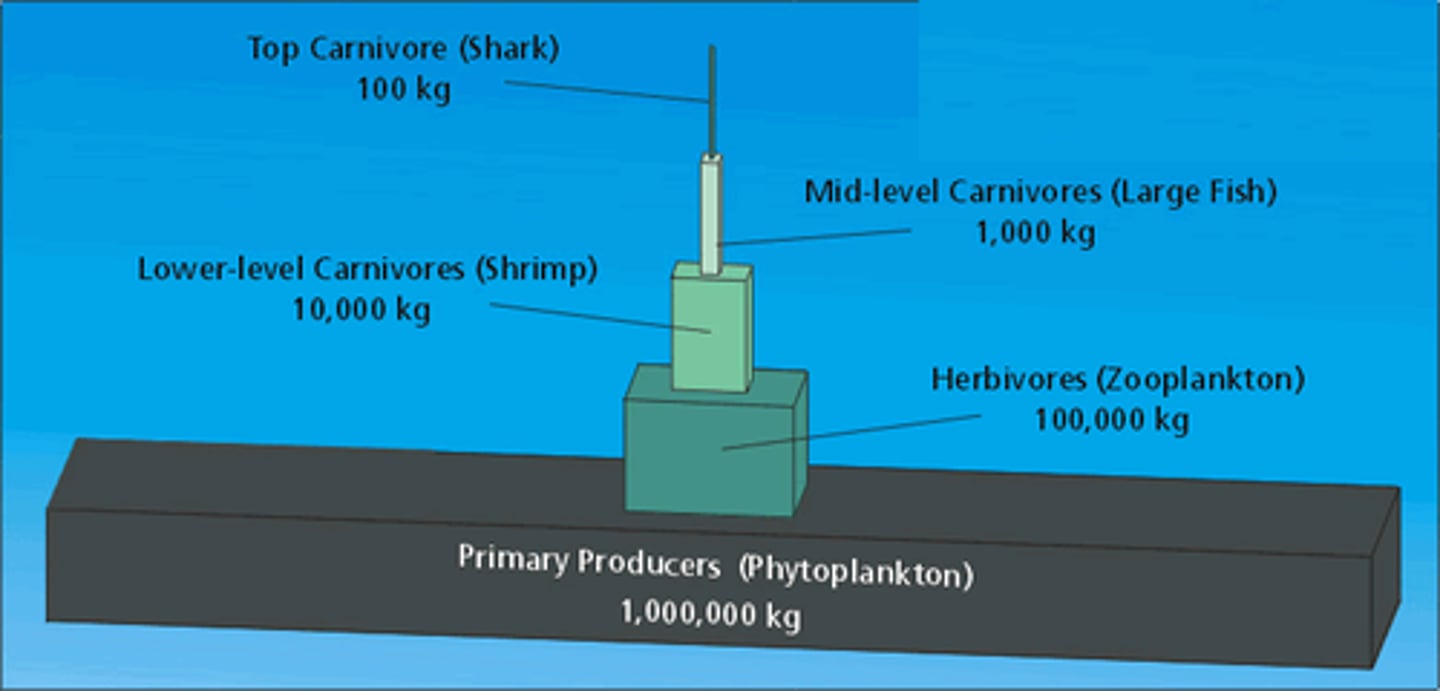
advantages of using a pyramid of biomass
more accurate indication of passing of energy from each trophic level
impacts humans have through over-harvesting
of food species
-Decrease in biodiversity
-Risk of extinction of a species
-Disrupts natural food chain of the habitat
impacts of introducing foreign species to a habitat
-Disrupts natural food chain
-Loss of habitat as foreign species take over
-No natural predators to control population of species
carbon cycle
The organic circulation of carbon from the atmosphere into organisms and back again
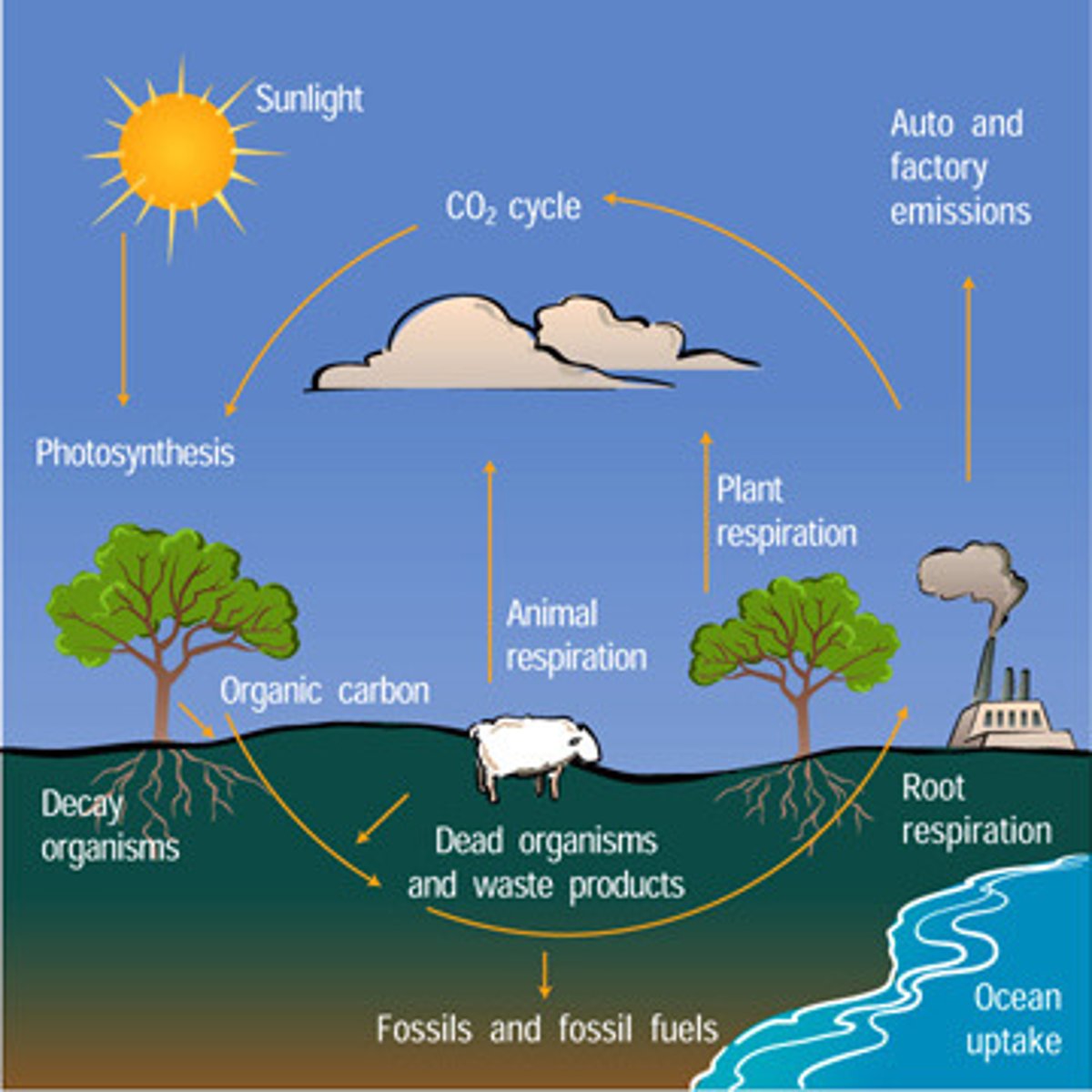
effects of the combustion of
fossil fuels on the carbon dioxide concentrations
-Causes greenhouse effect
-Traps heat
water cycle
The continuous movement of water from the ocean to the atmosphere to the land and back to the ocean
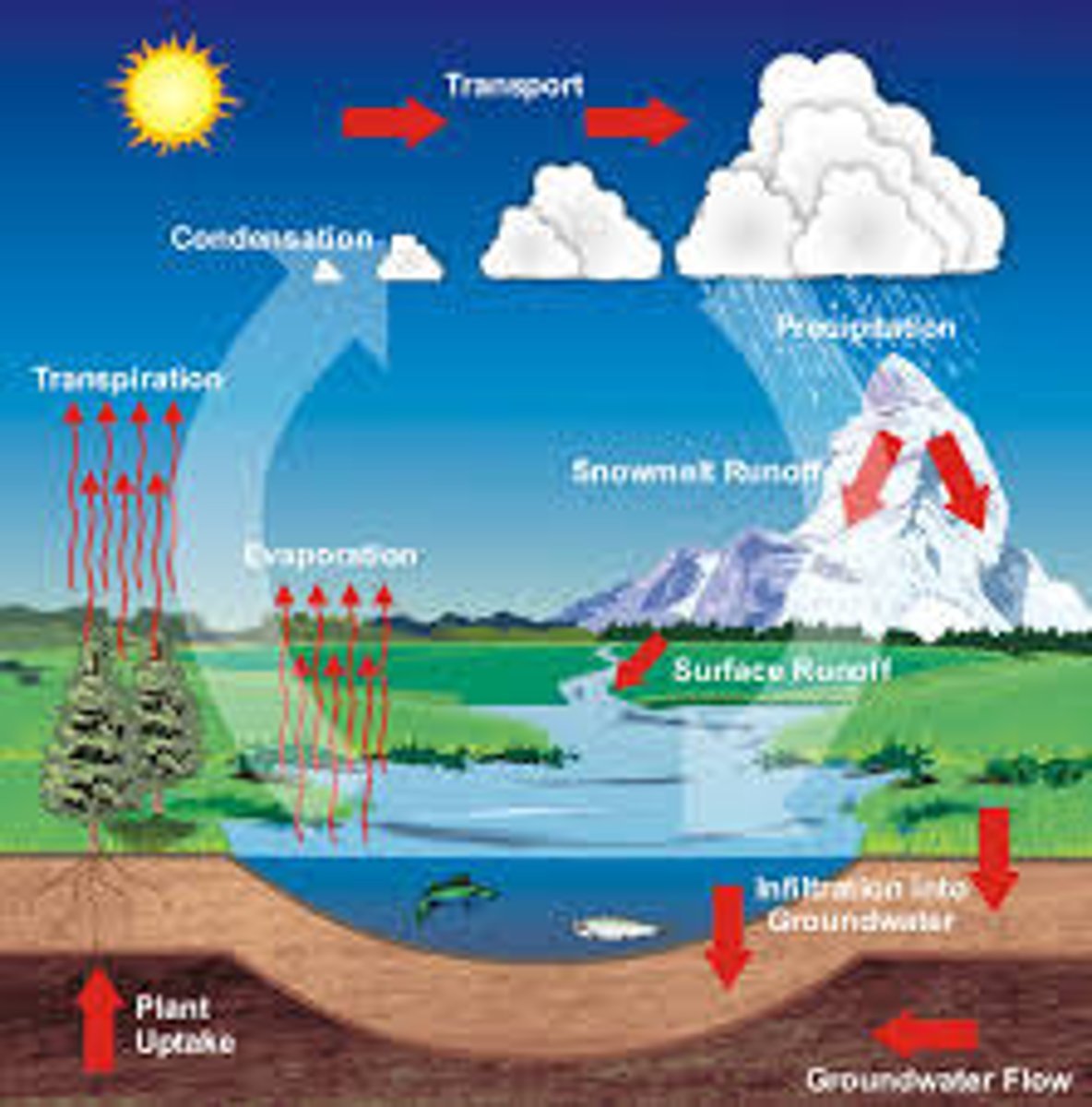
nitrogen cycle
- decomposition of plant and animal protein
to ammonium ions
- nitrification
- nitrogen fixation by lightning and bacteria
- absorption of nitrate ions by plants
- production of amino acids and proteins
- feeding and digestion of proteins
- deamination
- denitrification
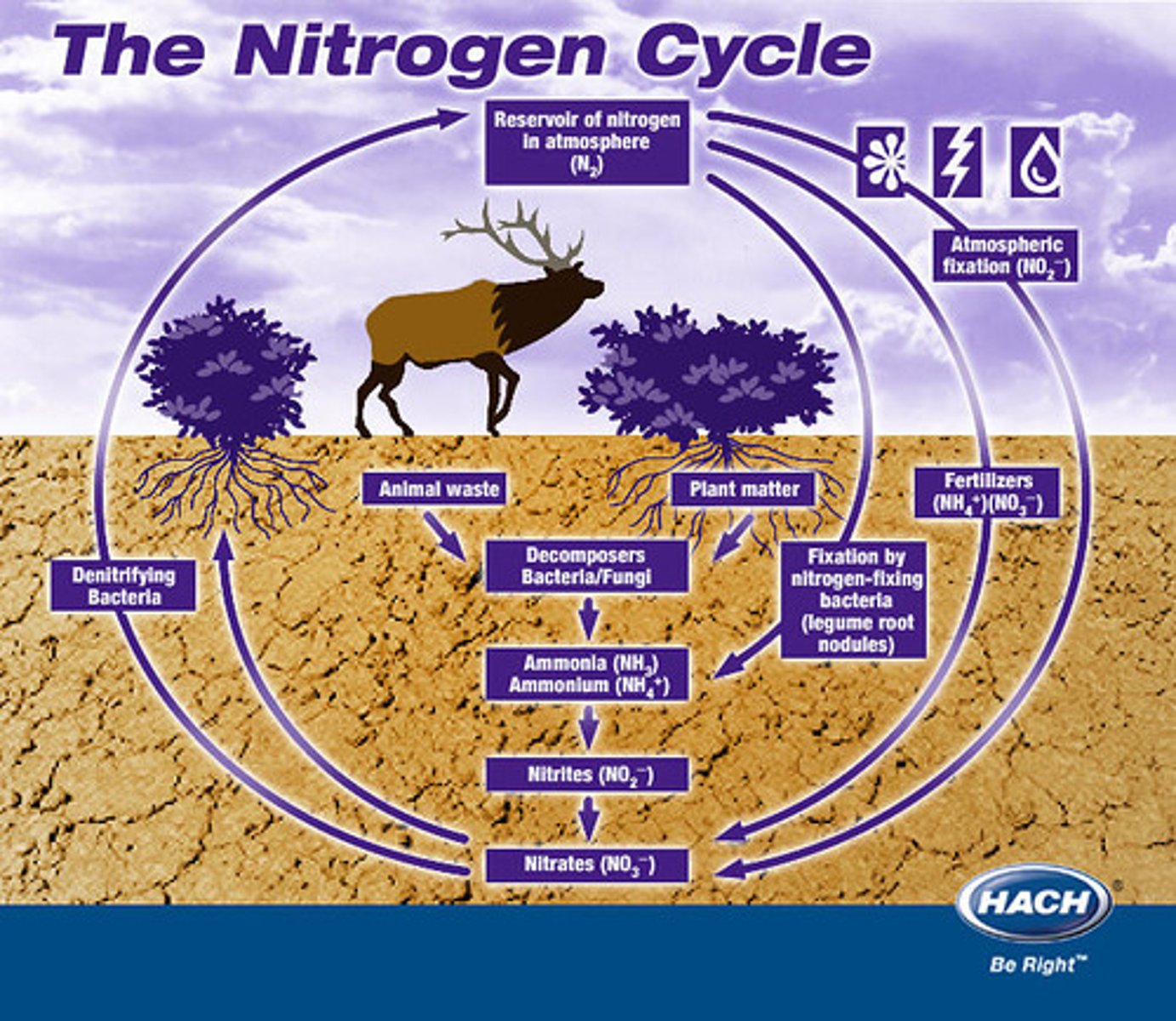
roles of microorganisms in the nitrogen cycle
- decomposition
- nitrification
- nitrogen fixation
- denitrification
denitrification
process by which bacteria convert nitrates into nitrogen gas
population
a group of organisms of one species, living in the same area, at the same time

factors affecting the rate of population growth
- food supply
- predation
- disease
community
all of the populations of different species in an ecosystem

ecosystem
a unit containing the community of organisms and their environment, interacting together,
e.g. a decomposing log, or a lake
sigmoid growth curve
lag - period where the individual bacteria are maturing and not yet able to divide
exponential (log) - period characterized by cell doubling
stationary -reproduction of cell is equal to death rate of cells
death phase -accumulated toxins and nutrients used up
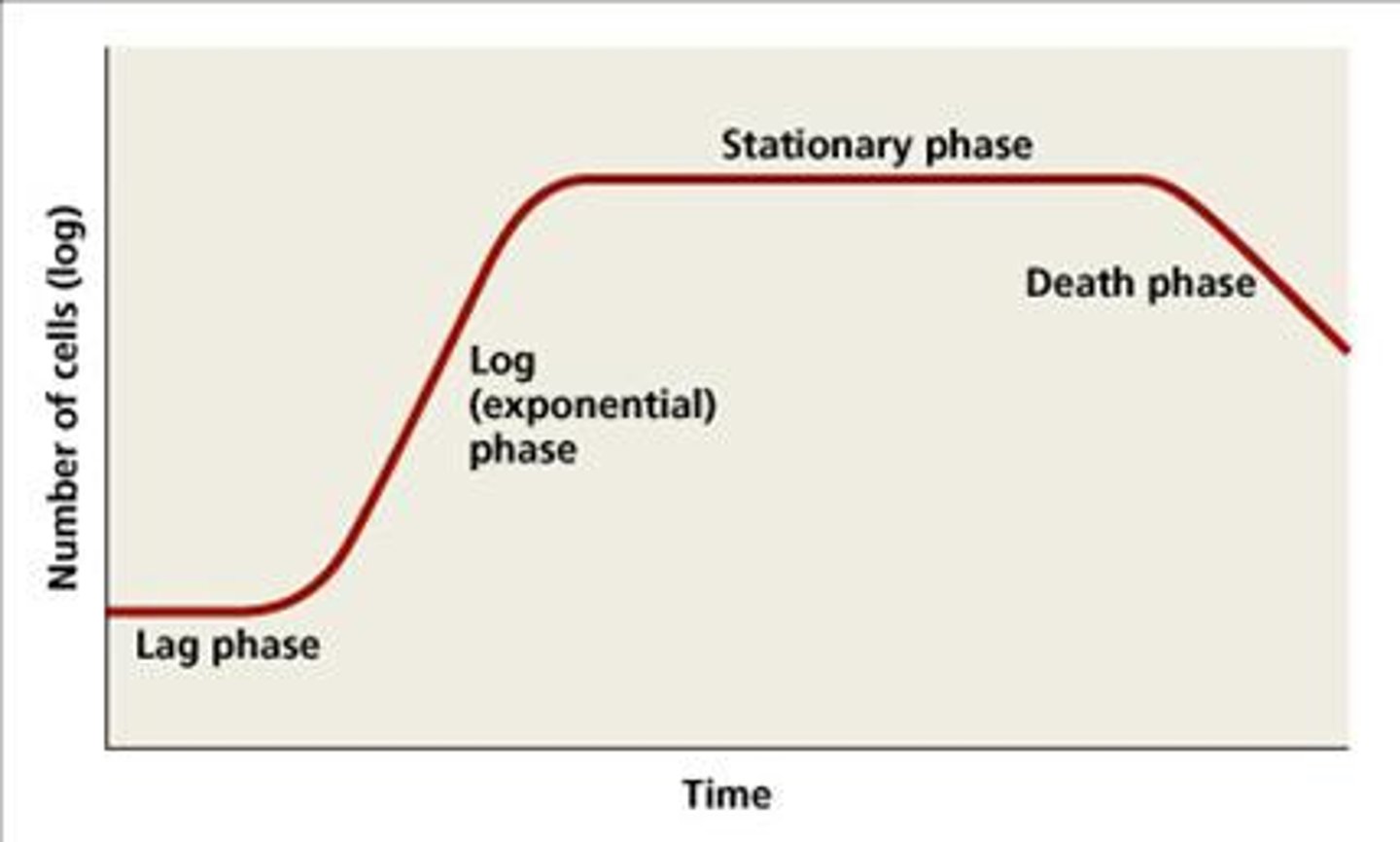
factors that lead to each phase in the sigmoid curve
*temperature- enzymes in bacteria need optimum temperature to function
*pH level- enzymes need optimum pH to function
*oxygen- bacteria need oxygen to under go respiration and reproduce
*nutrients- required for growth and reproduction of bacteria
increase in human population and its social implications
-Overpopulation causes increase in resources to sustain
- Lack of money for services due to strain on government
-Services like healthcare and education can't cope with the rapid increase
increase in human population and its environmental implications
-fossil fuels such as coal, oil and natural gas are being used up rapidly
-raw materials such as metal ores and other minerals are being used up
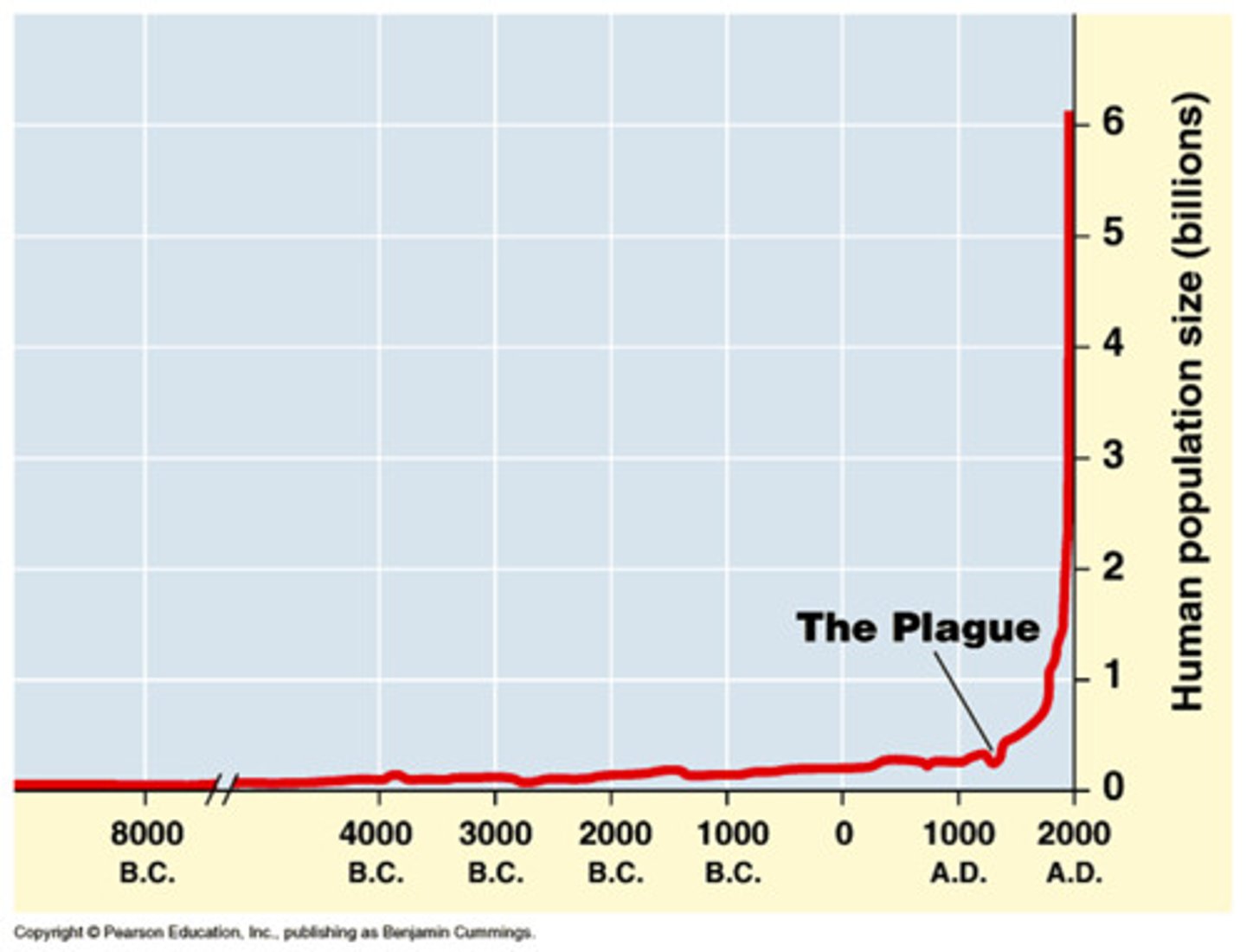
human population growth graph
Has high log phase due to:
-Improved agriculture, better nutrition increase defense against disease
-Improved public health
-Increase healthcare
Thus causes:
-Decrease in infant and child mortality rate
-Decrease in death from malnutrition
-Increase in life expectancy