Human Body Chemistry and Macromolecules: Key Concepts and Structures
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
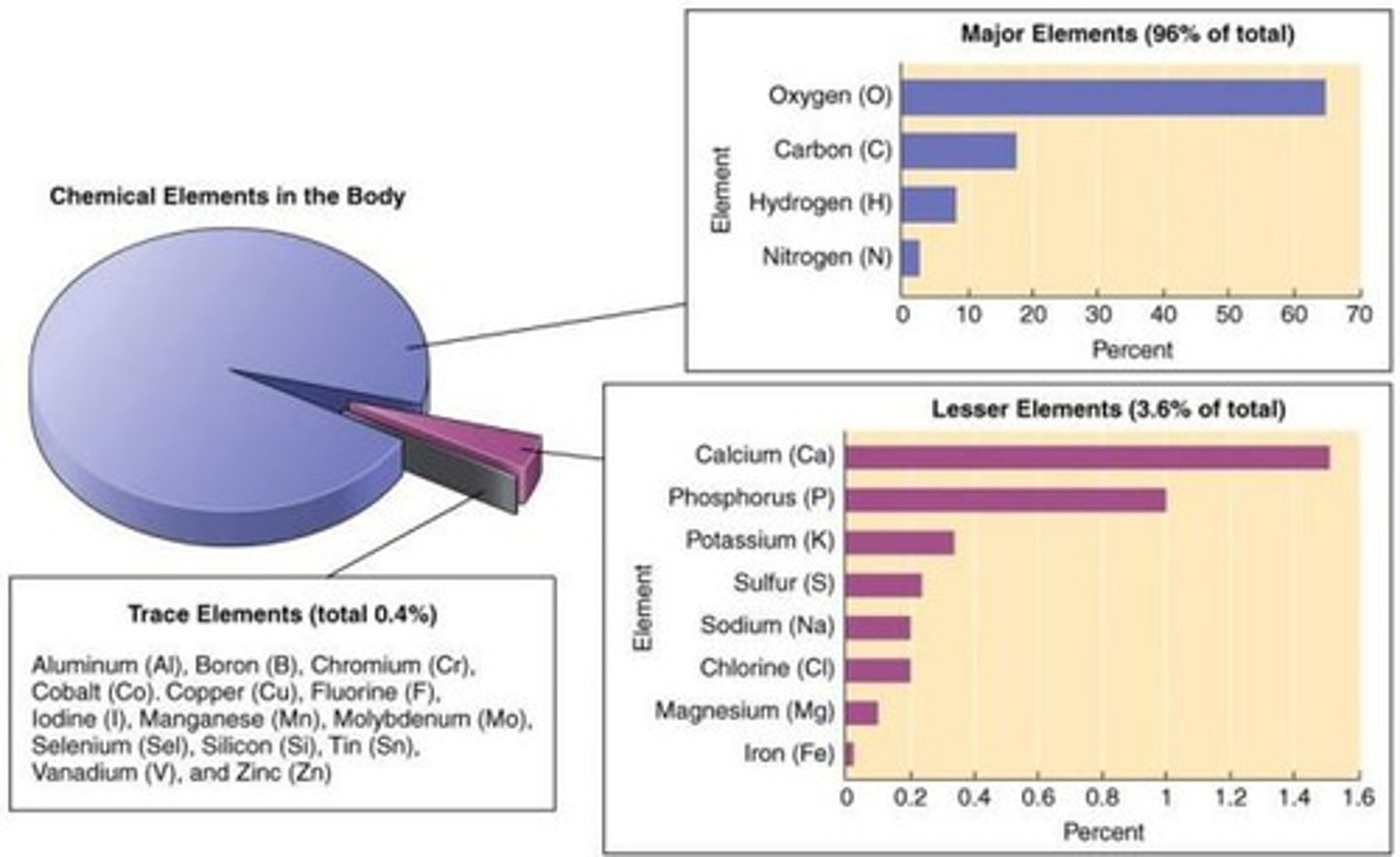
Chemical elements of the human body
Main elements include Carbon (C), Oxygen (O), and Hydrogen (H).
Sodium chloride (NaCl)
A molecule formed by the ionic bond between Sodium (Na) and Chloride (Cl) ions.
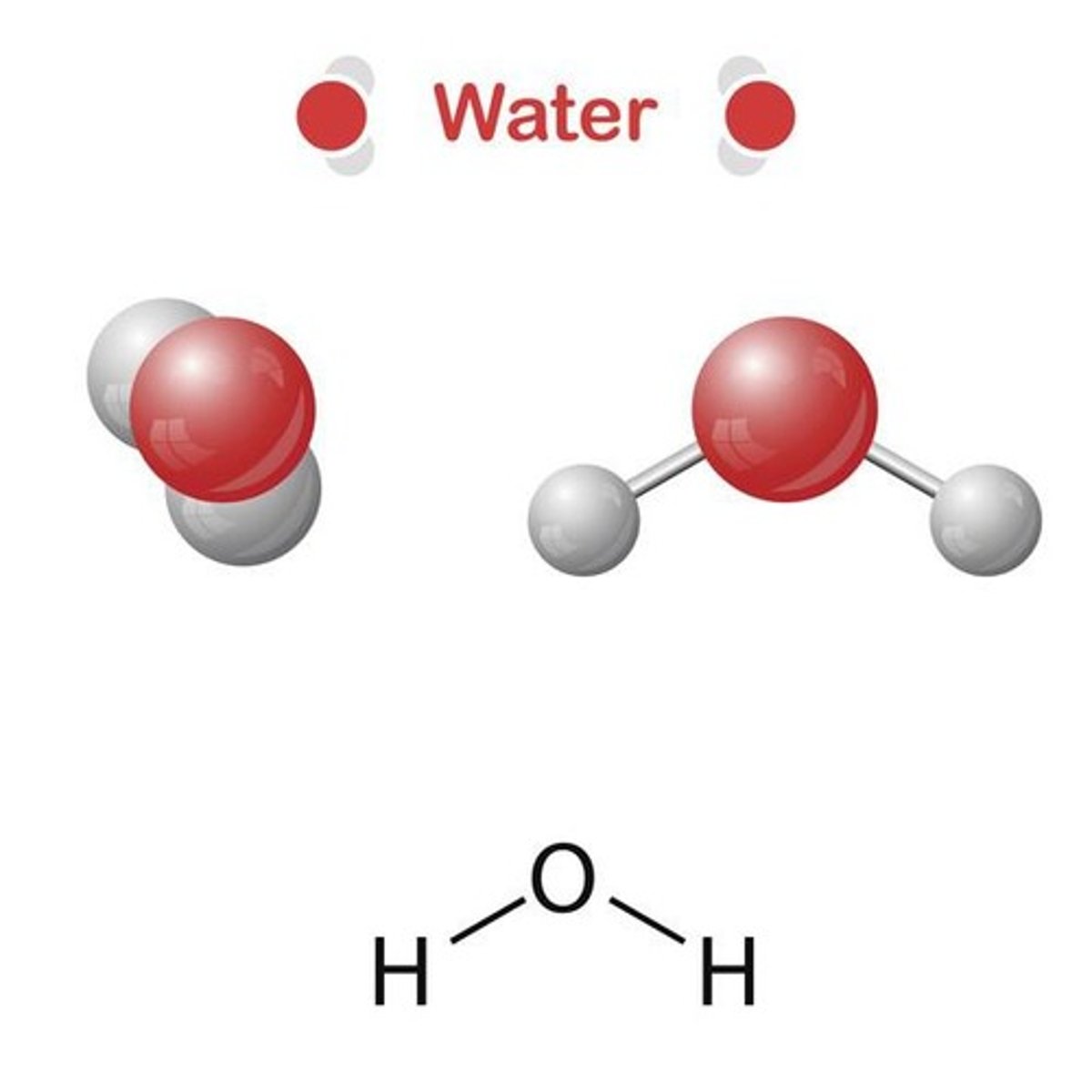
Water (H2O)
A molecule consisting of two Hydrogen (H) atoms and one Oxygen (O) atom, connected by covalent bonds.
Ionic bond
A bond formed through the attraction between oppositely charged ions.
Cation
An ion with a positive charge, such as Sodium (Na+).
Anion
An ion with a negative charge, such as Chloride (Cl-).
Electrolytes
Ions in solution that conduct electricity.
Covalent bond
A bond formed when two or more atoms share electrons.
Polar covalent bond
A type of covalent bond where electrons are shared unequally, resulting in partial charges.
Hydrogen bond
A weak bond formed between molecules due to the attraction of oppositely charged parts.
Hydrophilic
Substances that dissolve easily in water, such as NaCl.
Hydrophobic
Substances that do not dissolve easily in water, such as fats and oils.
Metabolism
The sum of all chemical reactions occurring in the body.
Chemical reaction
A process where new bonds are formed and old bonds are broken, involving changes in energy.
pH
A measure of the acidity or basicity of a solution.
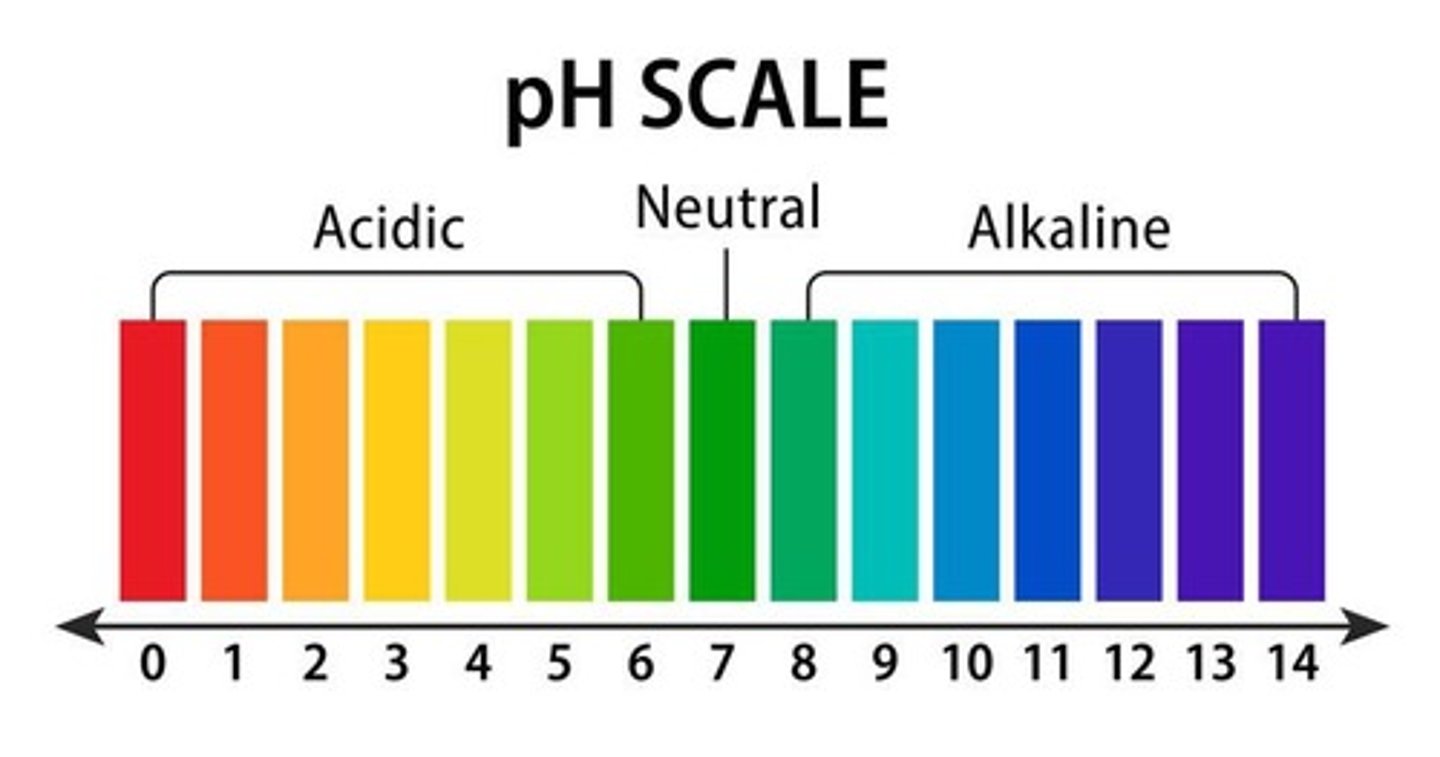
Buffer systems
Systems that help maintain pH homeostasis in the body.
Macromolecules
Large molecules essential for life, including carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids.
Carbohydrates
Organic compounds made of monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides.
Proteins
Macromolecules that perform various functions and have complex structures, which can denature.
Lipids
A group of macromolecules that include triglycerides, phospholipids, and steroids.
Nucleic Acids
Biomolecules that include DNA and RNA, essential for genetic information.
ATP
A molecule that carries energy within cells, playing a critical role in metabolism.
Endergonic reaction
Anabolic reactions where energy is absorbed when chemical bonds are formed.
Exergonic reaction
Catabolic reactions where energy is released when chemical bonds are broken.
Chemical Reactions
Occur slowly; the rate of reaction can be increased with a catalyst.
Catalyst
Lowers the activation energy and brings substrates together.
Acid
Increases the concentration of H+ ions in solution.
Base
Removes H+ from solution (accepts H+ ions).
Bicarbonate (HCO3-)
An important buffer in the human body that binds excess H+ ions in solution.
Normal pH of arterial blood
7.35-7.45; 7.4 is the midpoint.
Organic Compounds
Contain carbon atoms and include macromolecules such as carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids.
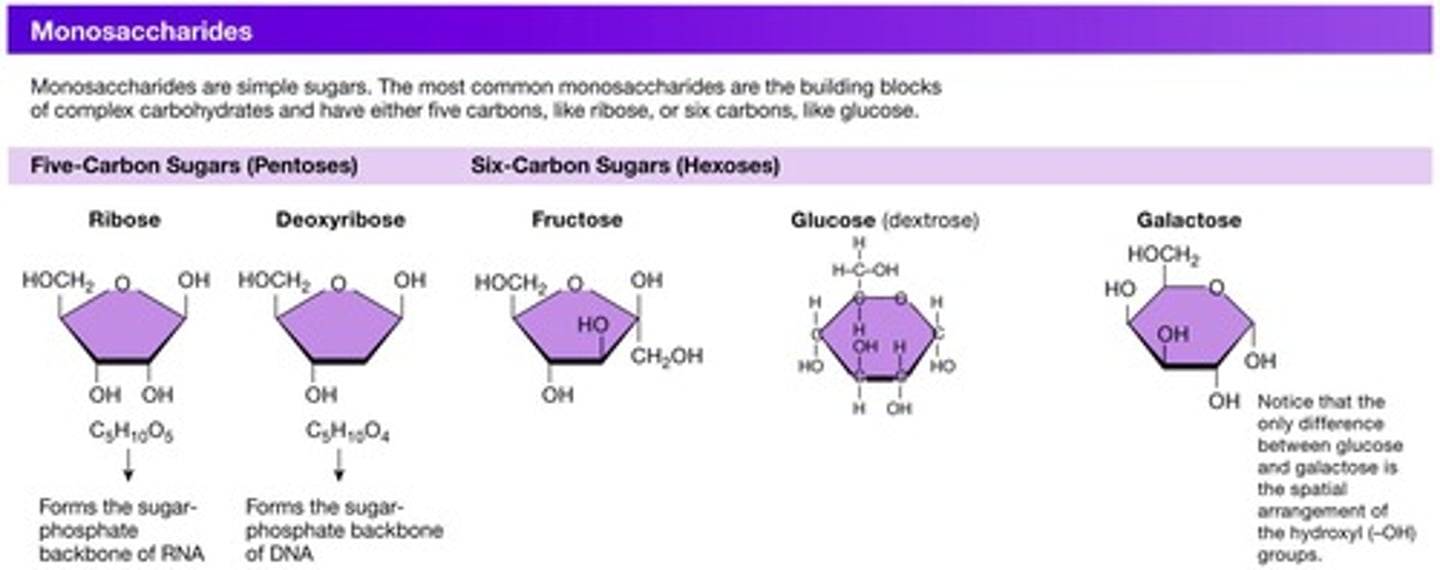
Monosaccharides
Simple sugars such as glucose.
Disaccharide
Two monosaccharides, examples include sucrose and lactose.
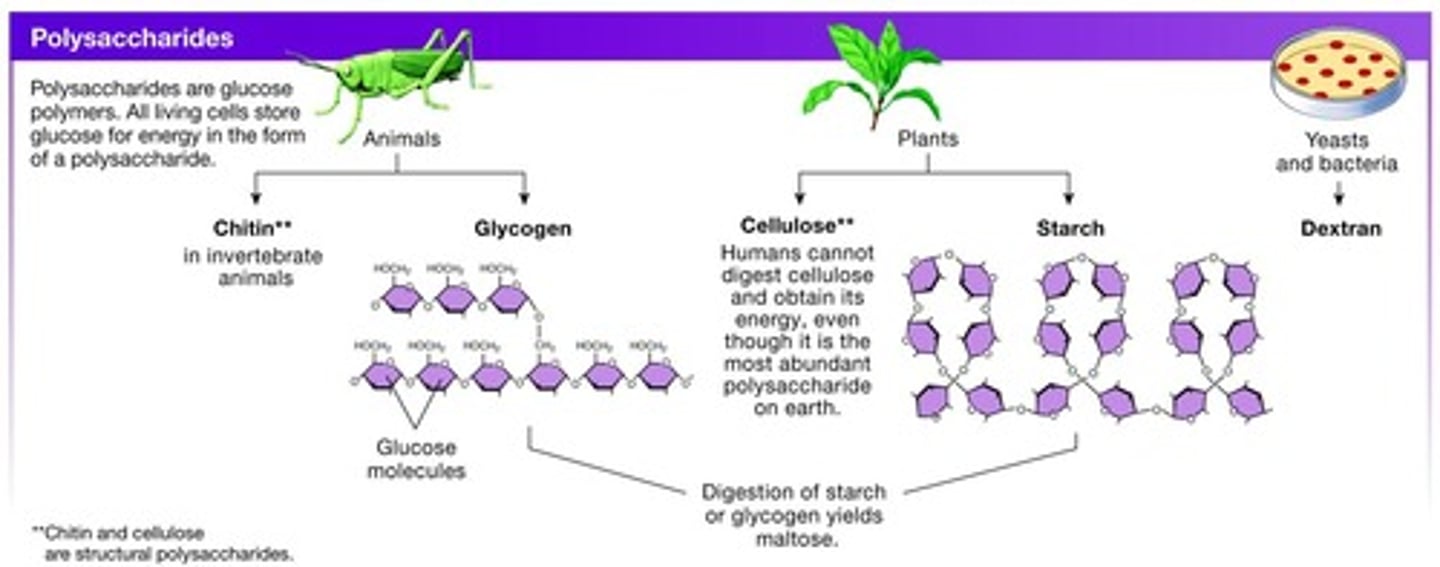
Polysaccharides
Multiple monosaccharides, such as glycogen which is the storage form of glucose.
Protein Functions
Determined by proteins produced by a cell; includes enzymes, motor proteins, antibodies, hormones, and cell surface receptors.
Amino Acids
20 individual building blocks of proteins.
Peptide Bonds
Bonds that form between amino acids to create polypeptides.
Primary structure
Unique sequence of amino acids in a protein.
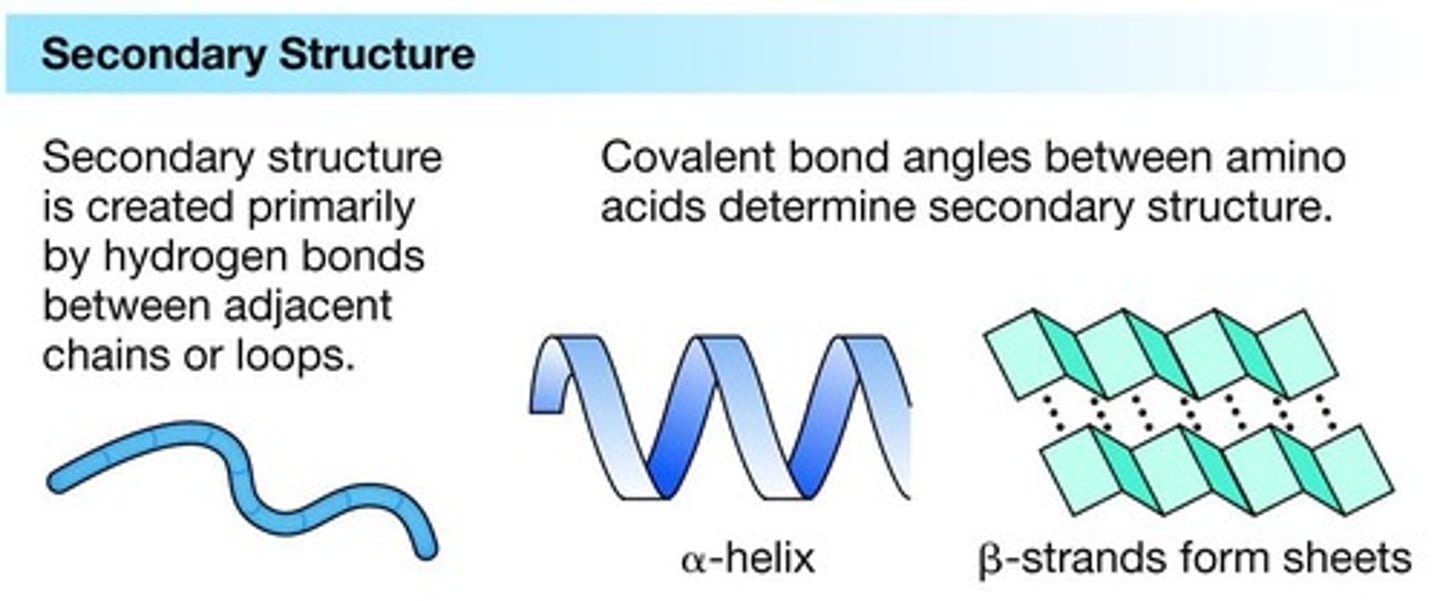
Secondary structure
Folding/twisting of neighboring amino acids in a protein.
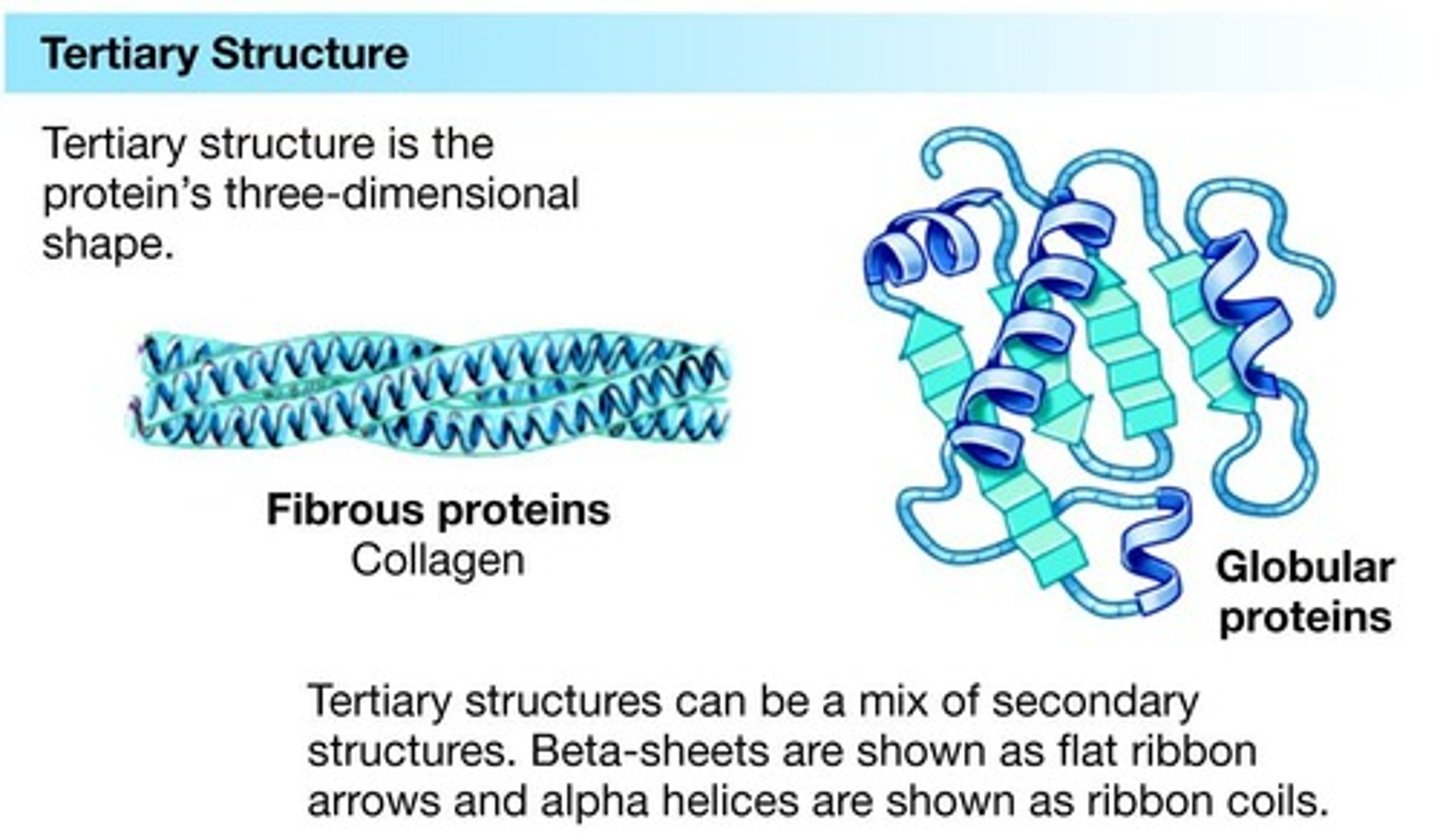
Tertiary structure
3-dimensional shape of a polypeptide, allowing it to carry out a specific function.
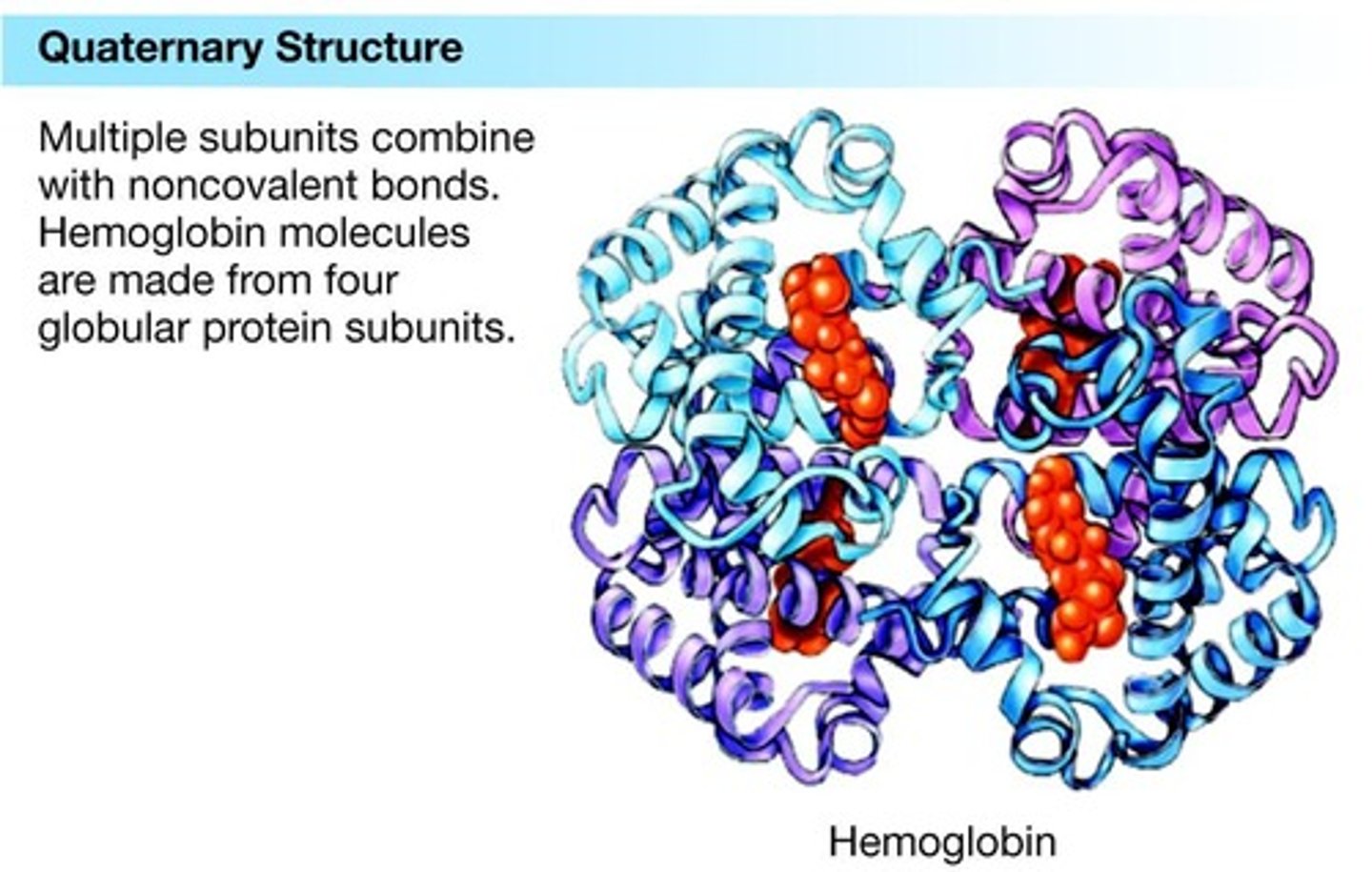
Quaternary structure
Arrangement of multiple polypeptide chains.
Denaturation
Loss of protein tertiary structure due to high temperatures and low pH, leading to loss of function.
Triglycerides
Three fatty acid chains bonded to a glycerol molecule, a highly concentrated form of chemical energy.
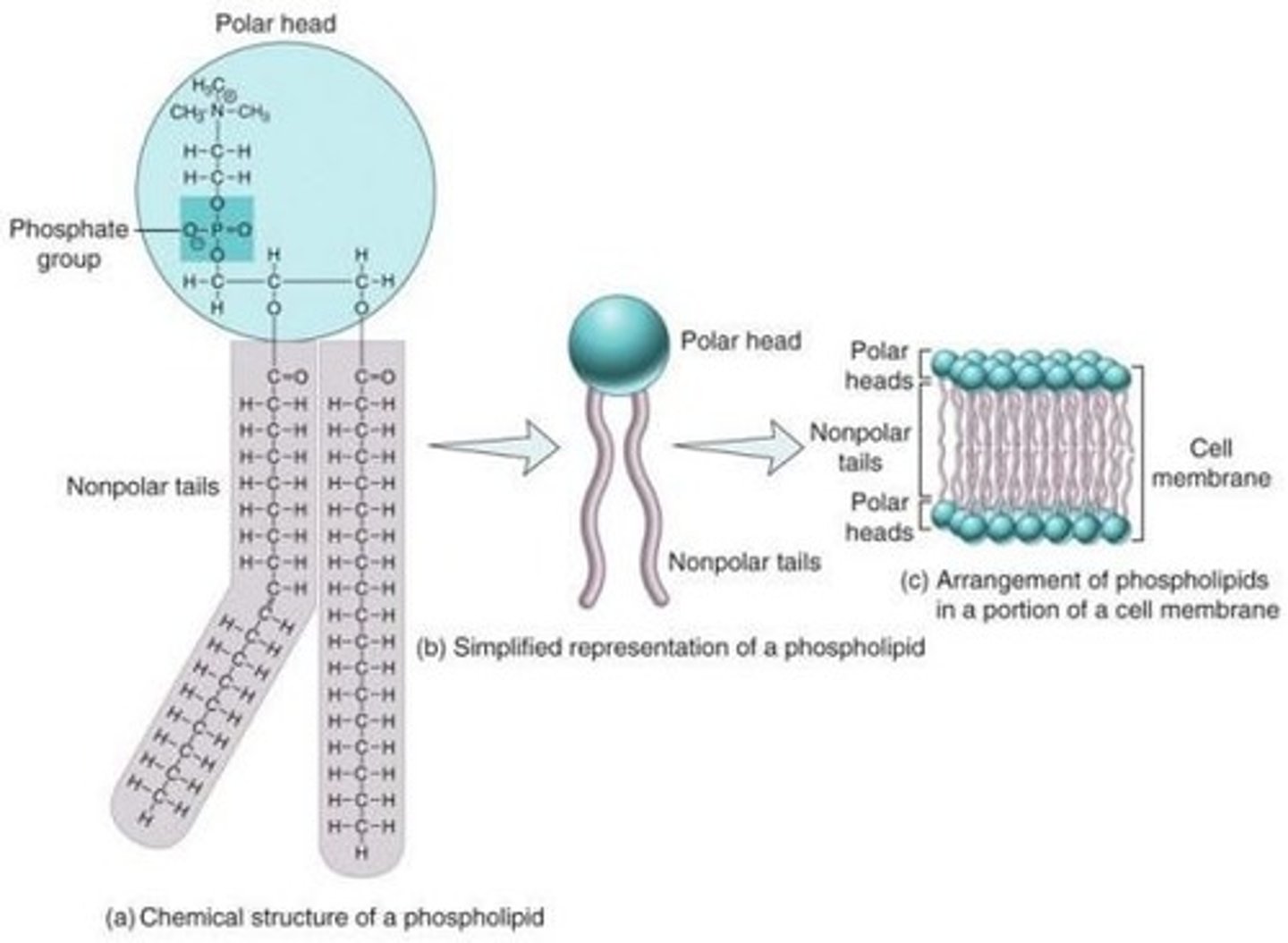
Phospholipids
Two fatty acid chains bonded to a phosphate group, key components of cell membranes.
Steroids
Synthesized from cholesterol, involved in cell membrane structure and include steroid hormones like estrogen and testosterone.
Gene
Segment of DNA.
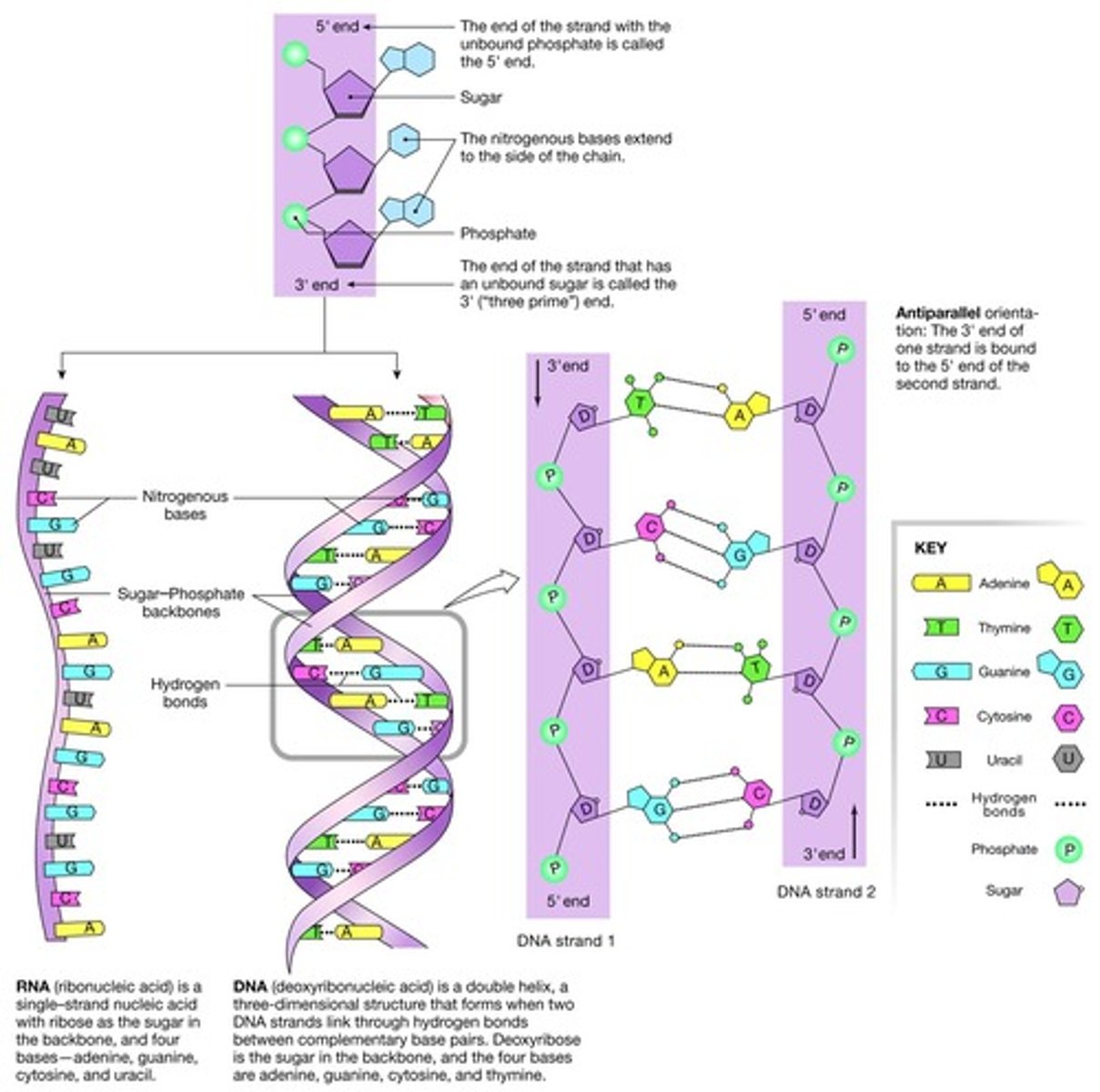
RNA (Ribonucleic Acid)
Single stranded nucleic acid.
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid)
Double stranded nucleic acid that stores genetic information.
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP)
Energy stored in the bonds of ATP; energy is released when the third phosphate group is removed.