Unit 2 (Pelvis/Hip)
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
ischial tuberosity
Bears most of body weight when sitting
ASIS; Superior aspect of iliac Crest; Greater Trochanter
What are all topographic landmarks for hip and pelvis in your textbook
Fractures; lesions; degenerative disease
Pathological Indications for AP Pelvis (Bilateral Hip)
Fractures; bone lesions, dislocations
Pathological indications for AP/Lateral Femur
Orthopedic placement; Exam of acetabulum femoral head/neck; & greater trochanter
Pathological indications for AP Unilateral Hip(& Proximal Femur)
Anterior
Hip bones
Anterior
Sacrum
Anterior
Coccyx
Anterior
Pubis
Anterior
Pubis
Anterior
Acetabulum
Anterior
Ischium
Anterior
ASIS
Anterior
Anterior inferior iliac spine
Anterior
Ilium
Posterior
PSIS
Posterior
Ala (wing)
Posterior
Posterior inferior iliac spine
Thin & flared part of ilium
Ala ( wing )
Crest of ilium
Superior margin of ilium; Goes from ASIS to PSIS
ASIS; iliac crest
Bony prominence used as landmark for hip
Greater Trochanter
Bony prominence use as landmark for femoral head
Greater Sciatic Notch
Deep notch on ischial spine
Ramus Body of each ischium; Pubis
what forms the obturator foramen
Osteopetrosis
Abnormally dense bone; Result of fracture, leads to obliteration of marrow space
Paget's Disease
Bone destruction followed by overproduction of dense yet soft bones
Osteoporosis
Reduction in quantity of bone ar atrophy of skeletal tissue
Congenital hip dysplasia
Hip dislocations due to conditions @birth
Danelius - Miller Method
Axiolateral (Inferosuperior) Projection: Trauma Hip
Unilateral Frog-Leg
Mediolateral Projection-Hip + Proximal Femur
Bilateral Frog-Leg
Bilateral Projection-Hips (Modified Cleaves Methad)
Flex & elevate unaffected leg so thigh is near vertical support w/pad
Place IR in crease above iliac crest o adjust it parallel to femoral neck
how to perform and position for a trauma lateral hip
CR - 2 in ( 5 cm ) below ASIS
CR for: AP Pelvis (Bilateral Hips)
CR- 3 in (8 cm) below ASIS
CR for: AP Bilateral (Hips)
CR: 3-4 in (8-10 cm) below ASIS & 2 in (5cm) medial
CR for: AP Unilateral (Hip)
CR- Midfemoral neck
CR for: Unilateral Frog-Leg
Perpendicular to femoral neck
Danelius-Miller Method (Trauma)
CR @ midline point @ lvl of ASIS; CR: 40° caudad
CR for: AP Axial Inlet Projection
CR @ midline 1-2 in (2.5-5cm) distal to superior border of greater trochanter; & Angled 20-35° cephalad for males; 30°-45° for females
CR for: AP Axial Outlet Method
Suspend breathing
breathing instructions for pelvis/hip exams
Pt supine; Both feet internally rotated 15°-20°
Pt position & degree of pt rotation: AP Pelvis (Bilateral Hips)
Affected side Knee flexed; Abduct leg 45° from vertical
Pt position & degree of pt rotation: Unilateral Frog
Pt supine, Rotate affected leg 15°-20° internally
Pt position & degree of pt rotation: AP Unilateral Hip
Pt supine; Flex both Knees 90%; abduct both legs 45° from vertical
Pt position & degree of pt rotation: AP Bilateral Pelvis
Pt supine; Non-injured leg elevated; no rotation
Pt position & degree of pt rotation: Danelius-Miller Method (Trauma)
• ASIS are both parallel with each other
• Femoral epicondyles parallel with each other
When performing an AP Pelvis , or any other exam involving the pelvis , how do we check for rotation and ensure patient is in true AP position when positioning
Femoral epicondyles parallel
When looking at a radiograph of an AP pelvis how can one determine if the legs where properly positioned
Both legs rotated internally 15°-20°; If there is any foreshortening or elongation of pelvis
AP pelvis how should appear if positioned properly and how should the legs be positioned to be correct ? Also , how can a technologist examine an image for rotation of the pelvis ?
Level of S1 (1st sacral vertebra)
Which level of the spine is the ASIS located
Level of L4-L5
What vertebral level is the Iliac Crest located
Posterior Oblique Projection: Pelvis-Acetabulum (Judet Method)
What method and projection will best visualize the anterior AND posterior rim of the acetabulum
• Axiolateral (Inferosuperior) Projection (Danelius-Miller Method)
• Could result in significant displacement of fracture Fragments
For a Trauma patient with hip pain , what exam is performed first and why
Axiolateral (Inferosuperior) Projection (Danelius-Miller Method)
would a be Trauma done patient with lateral hip hip pain and obvious signs of deformity which projection
Mediolateral Projection: Hip & Proximal femur
What t i is the proper name for a unilateral frog - leg projection
Perpendicular (Horizontal)
When performing the Axiolateral inferosuperior projection the CR should be how in relation to the IR and femoral neck
• ASIS; Iliac Crest
• Greater Trochanter
What are the 2 bony landmarks palpated for localization of the hip? Femoral head?
AP Bilateral Projection (Hips) ; AP Pelvis
When checking a pediatric patient for developmental dysplasia and congenital abnormalities like dislocation of the hip what 2 basic projections are performed
Greater Trochanter
When displaying an axiolateral inferosuperior ( Danelius - Miller method ) image of the hip on the monitor what landmark is useful for correctly hanging the image for viewing
15°-20° anterior angle in relation to body of femur
How is the femoral head and neck located ?
2 in (5 cm) below ASIS
What is the CR location for an AP pelvis
Midfemoral neck
What is the CR location for unilateral frog leg hip
Pt rotated 45° posterior oblique (pelvis & thorax 45° from tabletop)
How much is the patient rotated for the Judet method
CR : 2 in (5 cm) distal & 2 in (5 cm) medial to downside ASIS (Affected down)
CR: 2 in (5cm) directly distal to upside ASIS (affected side up)
What is the CR for Judet Method
IR: Table bucky; KVp: 80-90
How is IR placed for the Judet method? What is the kVp?
Overall shape; Angle of pubic arch; Ischial spines
Criteria to identify female pelvis & male pelvis
male pelvis
Narrower, deeper, less flared pelvic inlet & more oval or heart shaped
male pelvis
Narrower angle (50°-60 °)
male pelvis
More protrusion (inlet)
female pelvis
Wider, more shallow & flared Pelvic inlet = rounder
female pelvis
Wider angle (80°-85°)
female pelvis
Less protrusion (inlet)
45 °
For an AP bilateral frog leg projection how much are the femurs abducted
Parallel
How is the IR placed in relation to the femoral neck in the axiolateral projection
ASIS ; Iliac Crest
What are the two radiographic landmarks found on the ilium
The pt is rotated twd the left
What positioning error has occurred if the left iliac wing is elongated on an AP pelvis radiograph
Sacroiliac joints
located between the sacrum and each ilium
Symphysis pubis
connects the right and left pubic bones
Union of acetabulum
a temporary growth joint that solidifies during the teenage years
Hip joints
connect the head of the femur to the acetabulum of the pelvis
Sacroiliac joint
Synovial; Limited movement; Irregular gliding
Symphysis pubis
Cartilaginous; Amphiarthrodial; Limited
Union of acetabulum
Cartilaginous; Synarthrodial (for adults); Nonmovable
Hip joint
Synovial; Diarthrodial; Ball and socket (spheroidal)
Femoroacetabular impingement (FAI)
Hip joint defects causing pain , with types like pincer (extra acetabulum bone), cam (mis-shaped femur head), or both
Metastatic carcinoma
Cancer that spreads to bones, often to areas with red marrow like the spine and pelvis .
Osteoarthritis
Joint cartilage wears down, common in aging, leading to pain and stiffness, especially in hips
Chondrosarcoma
A cancerous tumor in cartilage, mostly in men over 45, usually in the pelvis or long bones, which may be removed if it doesn't respond to treatment
Developmental dysplasia of the hip ( DDH ) :
Hip dislocations present from birth, often needing frequent X - rays
Pelvic ring fractures
Severe trauma to one side of the pelvis can cause fractures on the opposite side, known as contrecoup injury .
Proximal femur ( hip ) fractures
Common in older adults with weakened bones, often from minimal trauma due to osteoporosis or blood loss .
Ankylosing spondylitis
disease first fuses the sacroiliac joints and then causes the spine to calcify, creating a "bamboo spine" look on X-rays; It mostly affects men
Avulsion fractures of the pelvis
Painful fractures often in young athletes from forceful muscle contractions, usually affecting sites like the iliac spine and iliac crest .
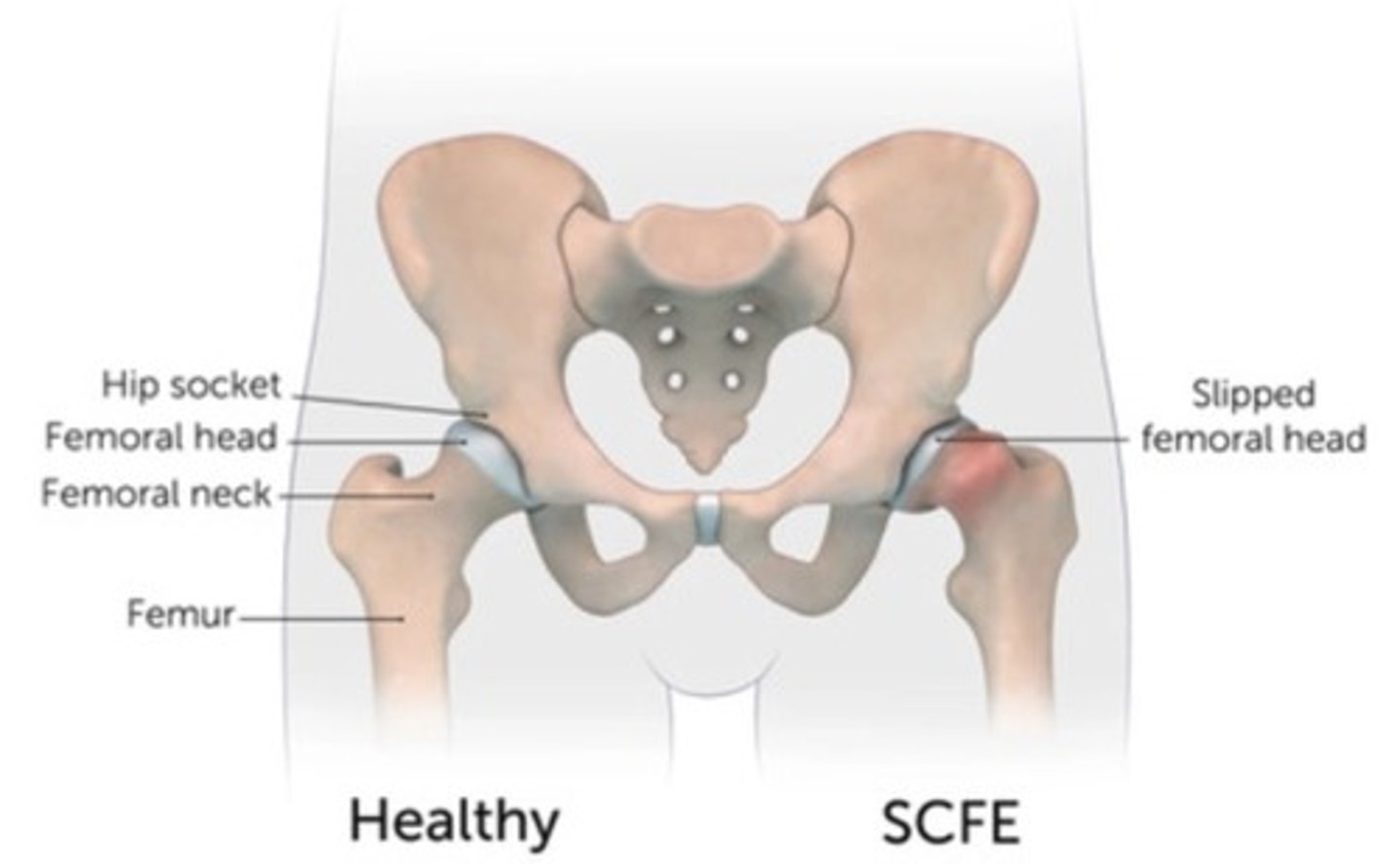
Slipped capital femoral epiphysis (SCFE) :
Occurs in teenagers during growth spurts, causing hip issues due to a slipping femur head
ASIS to PSIS
Iliac crest goes from
ankylosing spondylitis
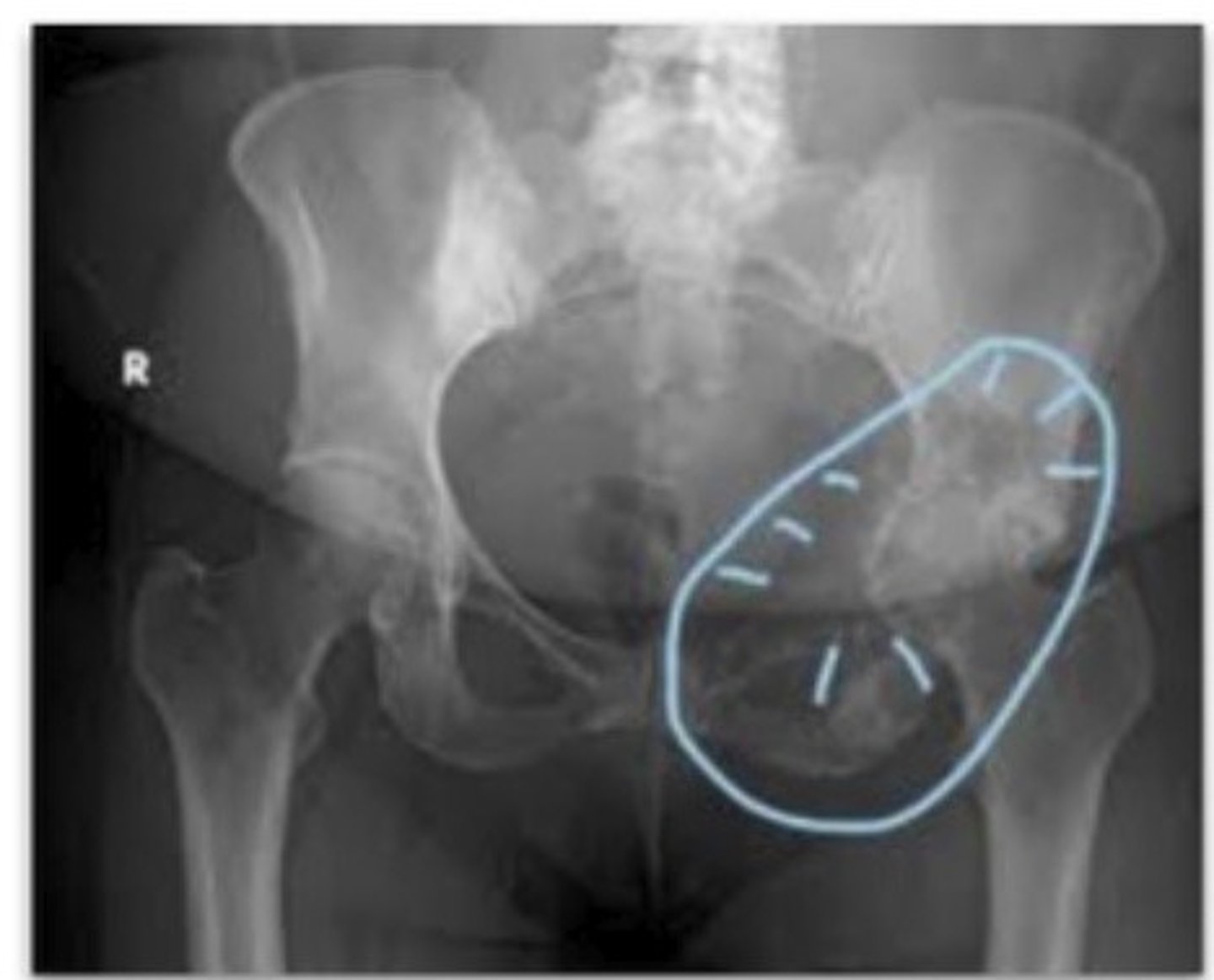
Identify:
Avulsion fractures of pelvis
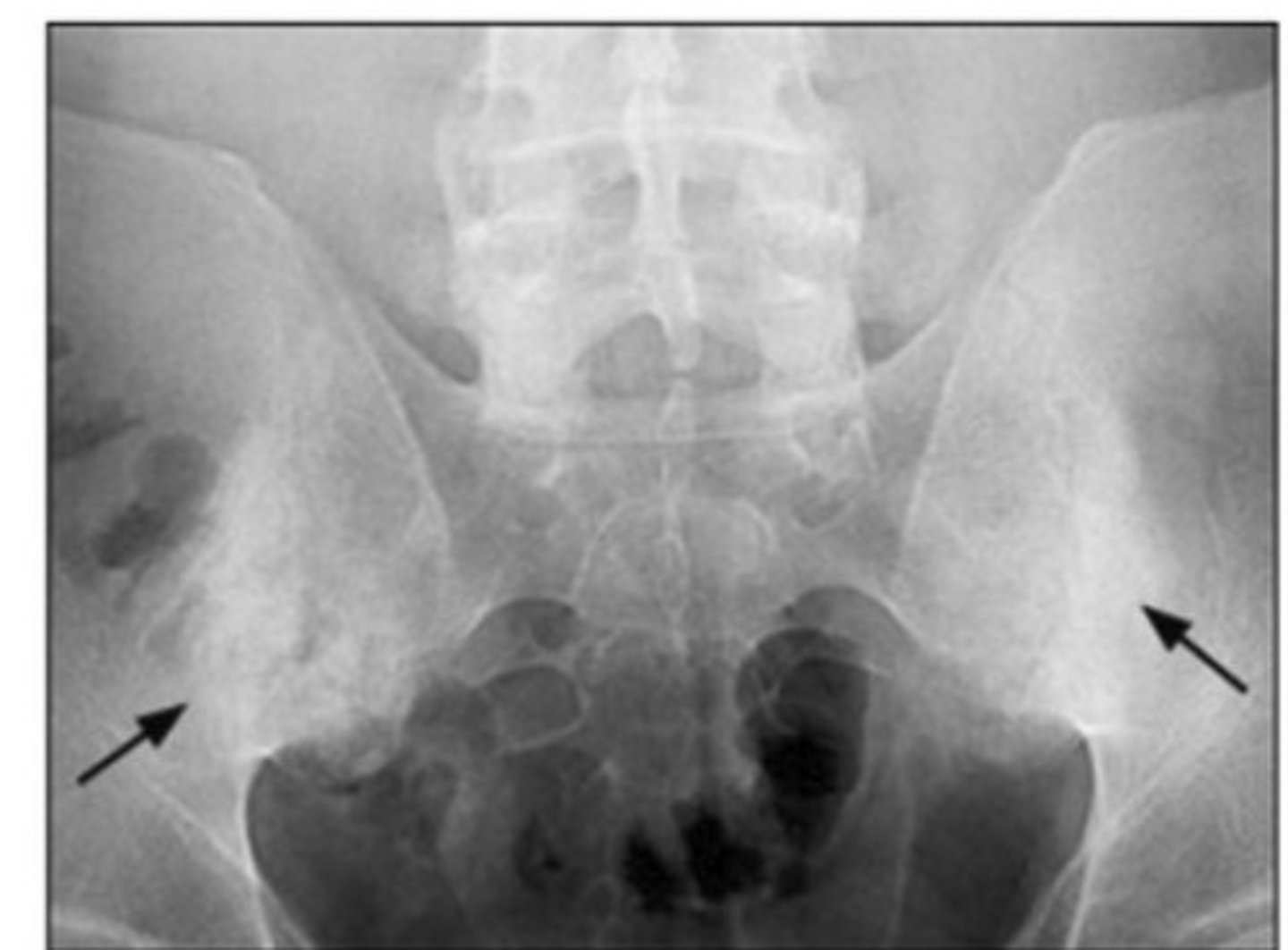
Identify:
Chondrosarcoma
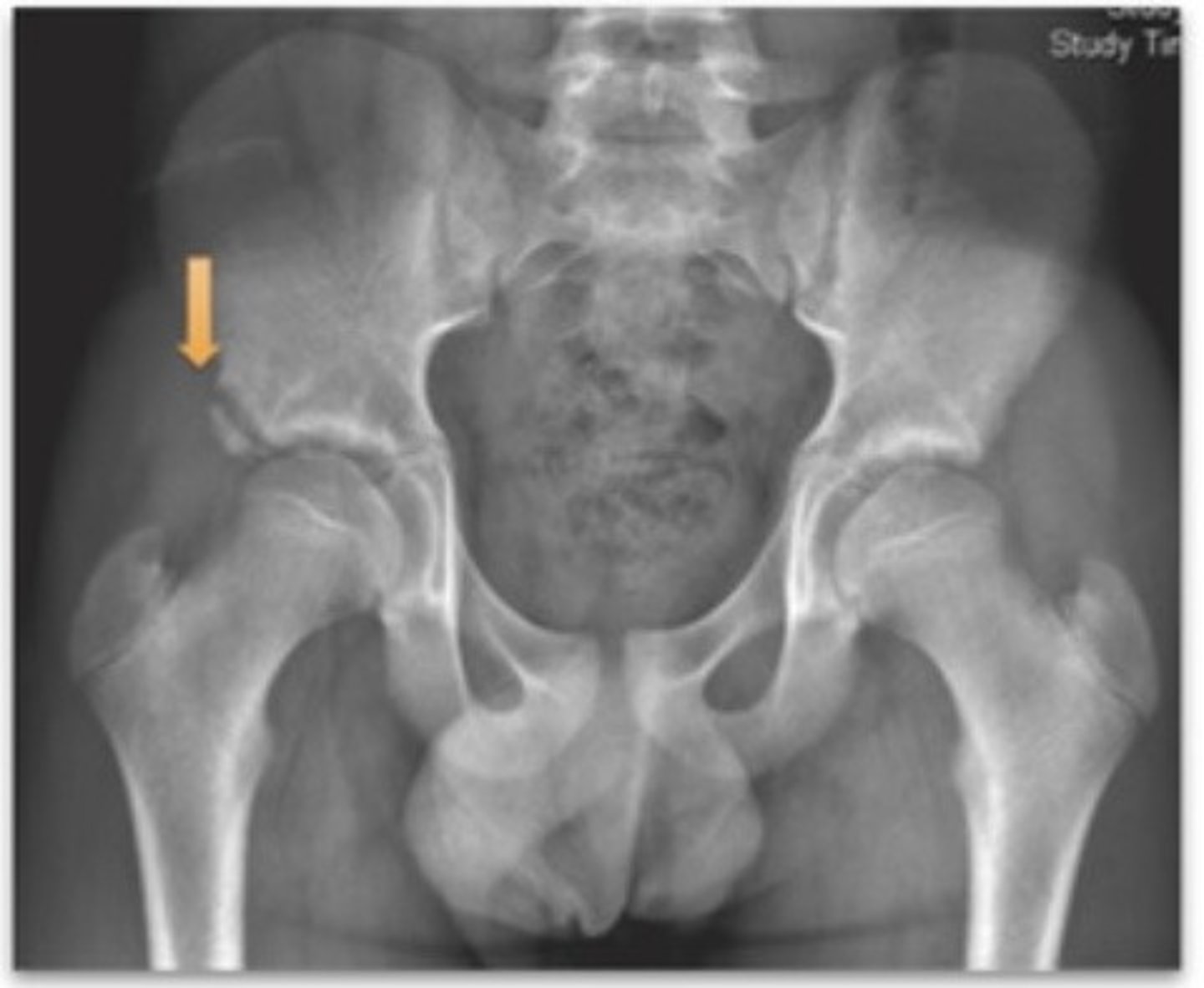
Identify:
Developmental dysplasia of hip (DDH)
Identify:
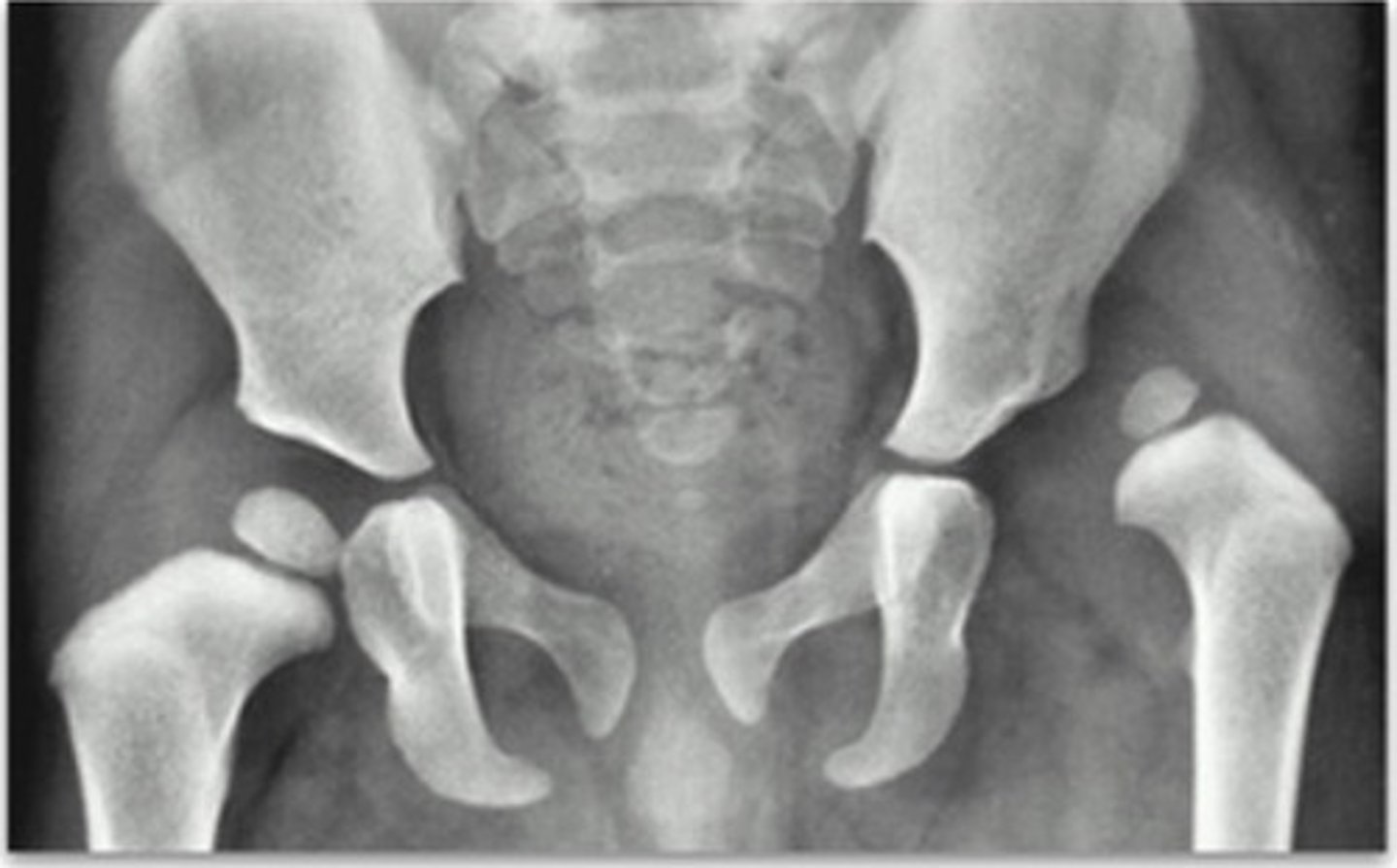
Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis (SCFE)
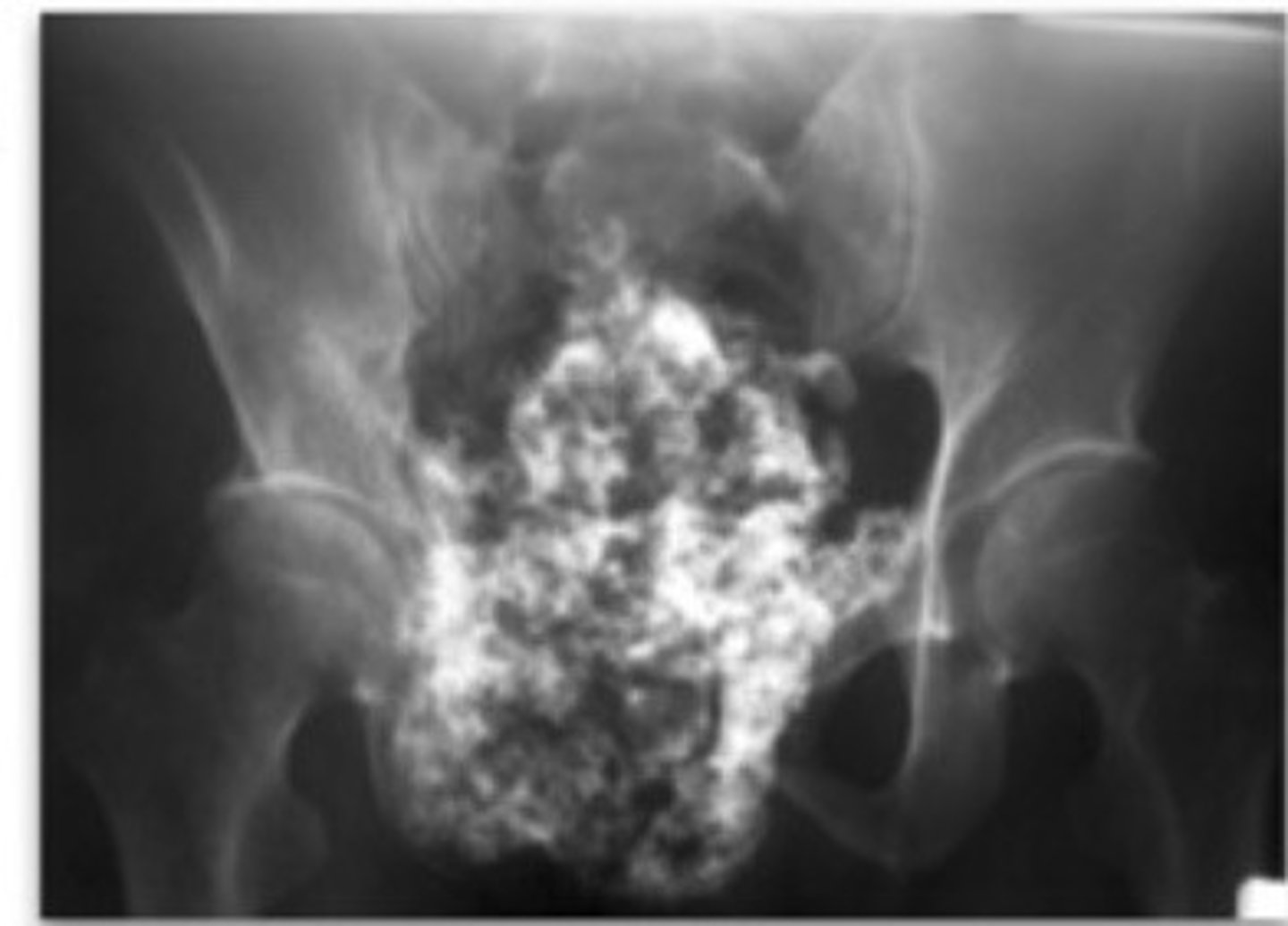
Identify:
Metastatic carcinoma
Identify: