Pathophysiology 2, blood cells
1/174
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
175 Terms
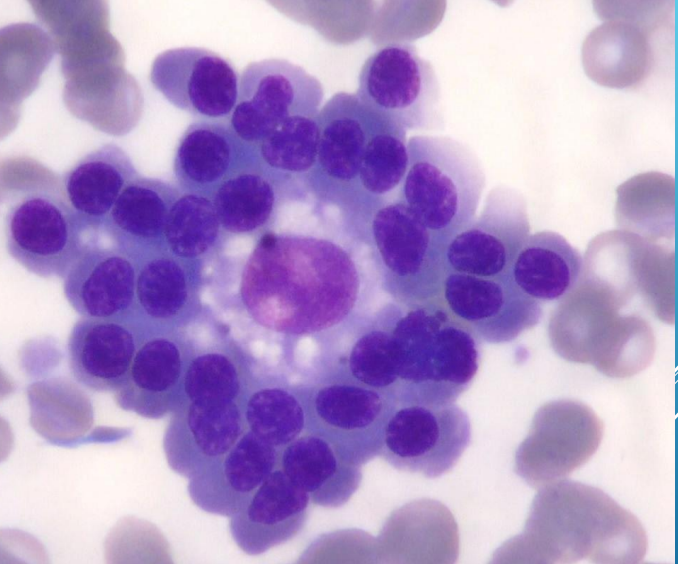
Bone marrow
in the center - macrophage, around - different forms of RBC
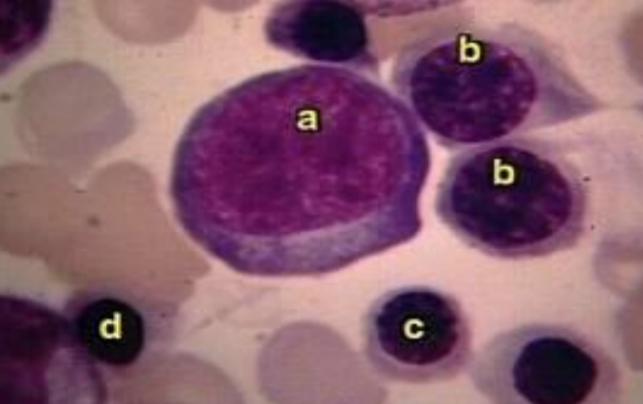
Bone marrow
a - proerythroblast (?), b - basophilic erytroblast, c - polychromatic erytroblast, d - acidophilic erytroblast
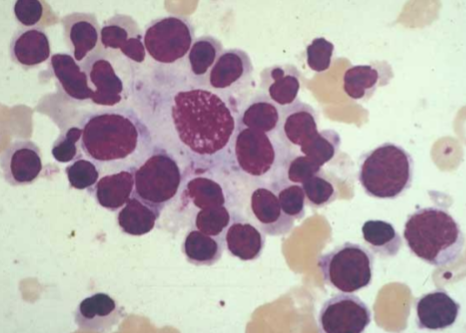
Bone marrow
erytroblastic island

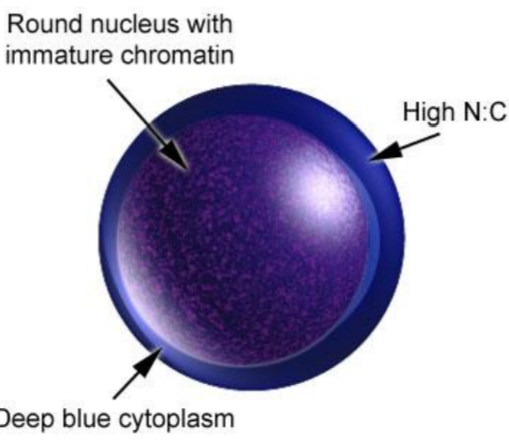
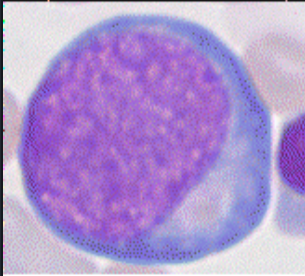
proerythroblast
15-20 μm
round or oval, dark blue cytoplasm, perinuclear
hallo
large nucleus, fine network structure,
chromatin becomes dense with haemoglobin synthesis progression
5 visible nucleoli
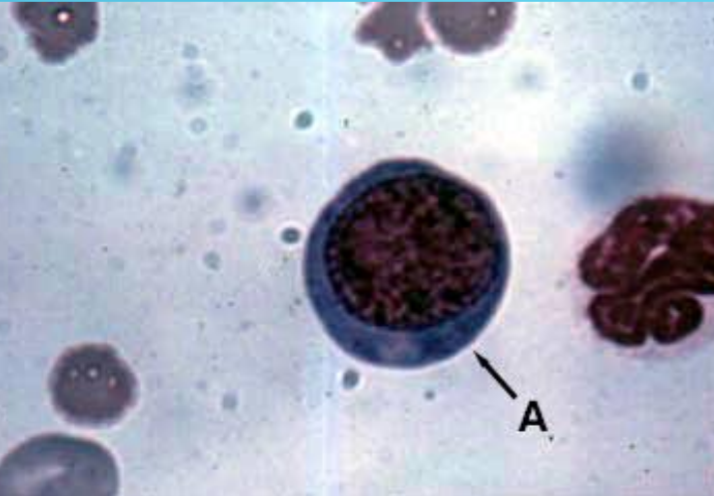
Bone marrow
proerythroblast
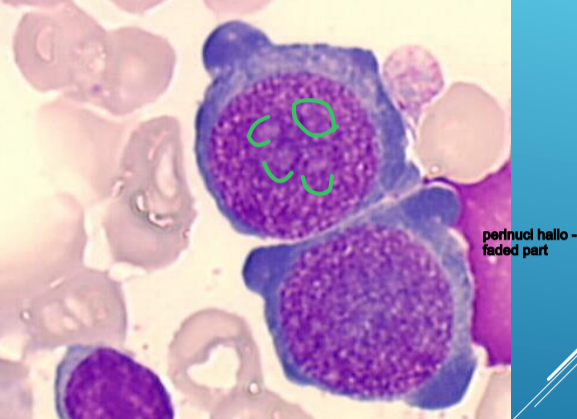
Bone marrow
proerytroblast
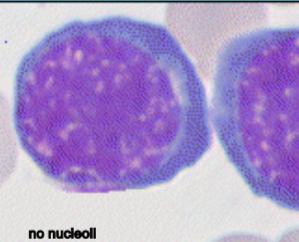
basophilic normoblast (erythroblast)
8-16 μm
round to oval, grey-bluish cytoplasm
hemoglobin synthesis – cytoplasm blue
round nucleus, denser chromatine
no visible nucleoli
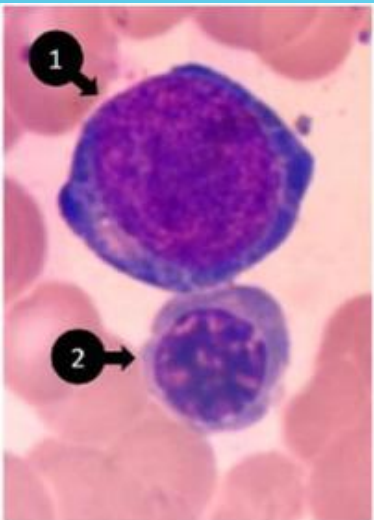
Bone marrow
1 - basophilic normoblast, 2 - polychromatic normoblast
Bone marrow
basophilic normoblast (erytroblast)

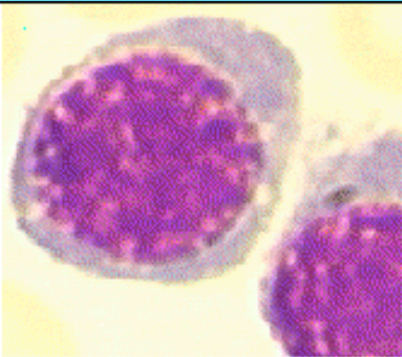
Polychromatic erythroblast (normoblast)
8-12 μm
round to oval, polychromatic greyish blue cytoplasm
round nucleus, granular, central or eccentric with dark patches of chromatin, without nucleoli
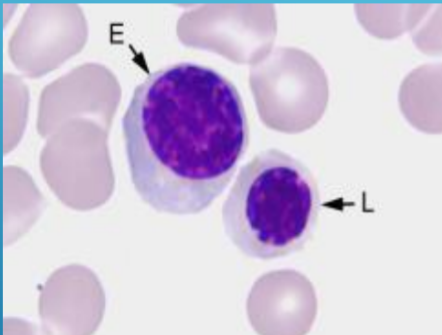
Bone marrow
E - polychromatic normoblast, L - acidophilic normoblast
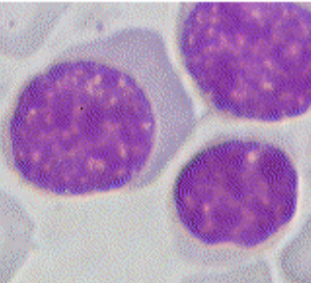
Acidophilic erythroblast (orthocromatic normoblast)
8-12 μm
round to oval, pink cytoplasm, round or oval nucleus
denser, homogenous, dark blue chromatine
picnotic and excentric nucleus, smaller
changed nucleus is expelled from the cell

cell and description
reticulocyte (polychromatophils)
blue pink cytoplasm, no nucleus (remnants)
briliant cresil blue - reticular structure
number increases during bleeding, hemolysis
and succesfull therapies of anemias
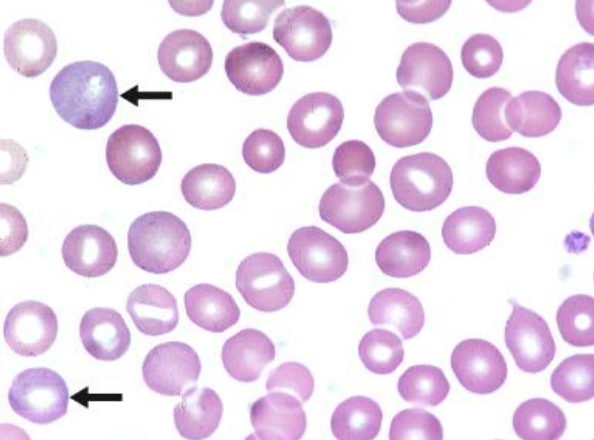
reiculocytes
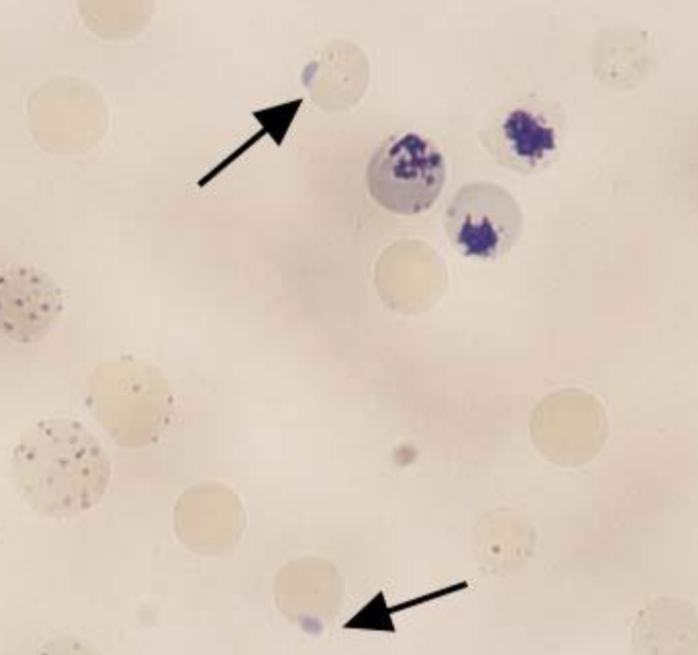
reticulocytes

cell, description
erythrocyte
flexibile, biconcave, discoid cell with
peripherially located hemoglobine and central pale area
red cytoplasm
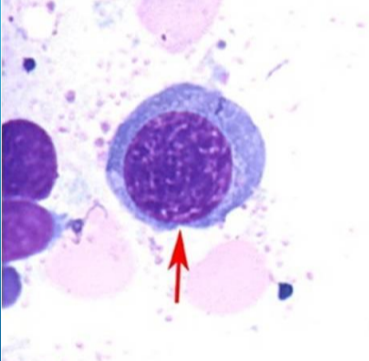
Bone marrow
proerythroblast
Bone marrow
basophilic normoblast
Bone marrow
polychromatic normoblast
Bone marrow
Orthochromatic normoblast
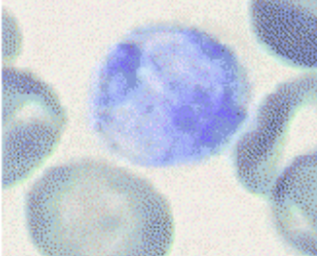
reticulocyte
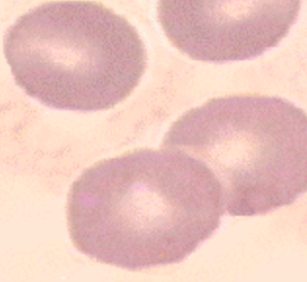
erythrocyte
Bone marrow
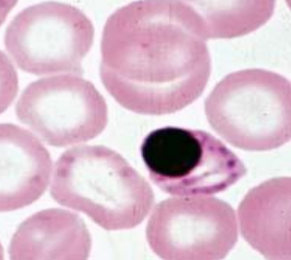
acidophilic erythroblast
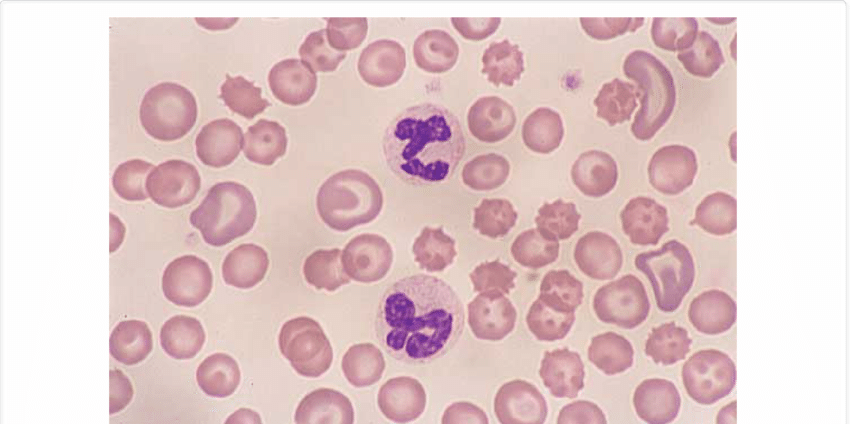
blood;
cell, sp
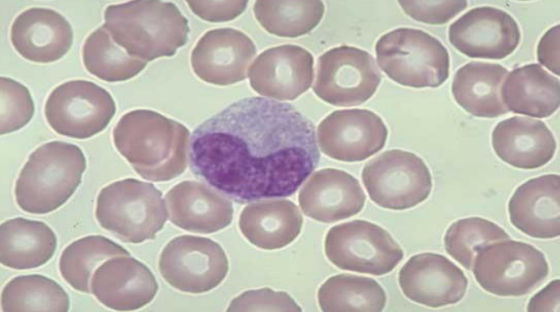
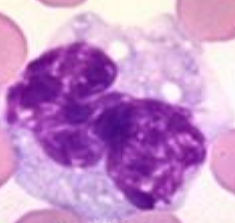
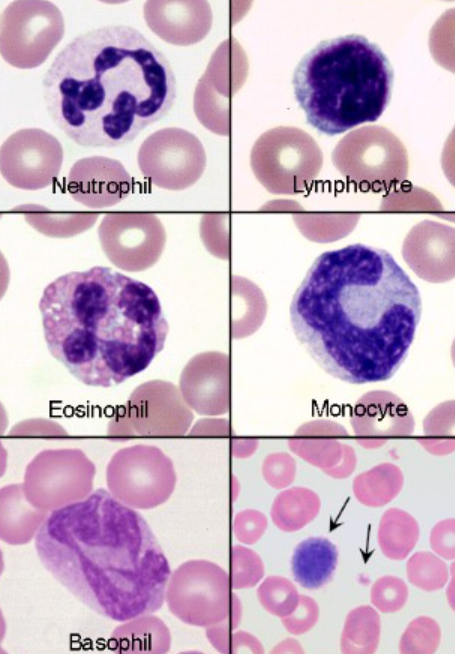
neutrophils (sgmented)
produced in BM, destroyed by macrophages
1st type of Le recruited in inflammation exudate
can’t divide
role: kill microbes. eliminate foreign material, phagocyte, secrete content of granules into exudate
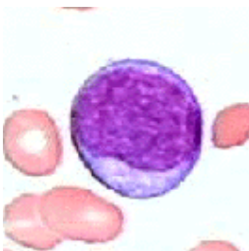
myeloblast
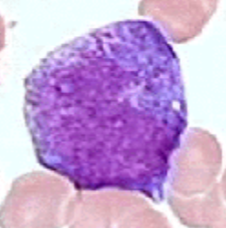
promyelocyte
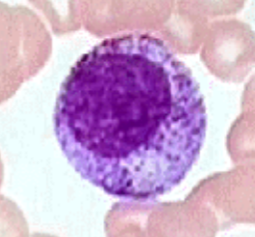
myelocyte
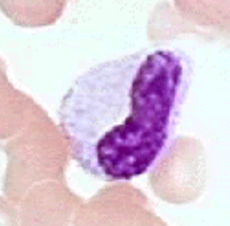
metamyelocyte
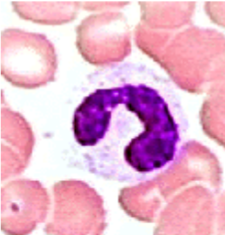
band cell
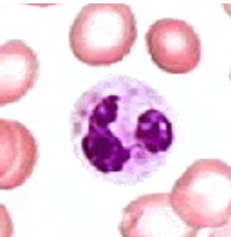
segmented neutrophil

eosinophils (equine)
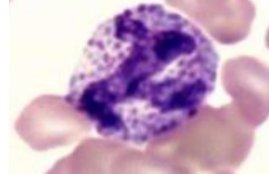
cell, sp
basophils (feline)
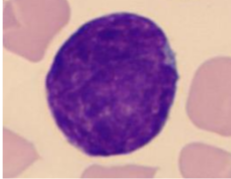
lymphoblast
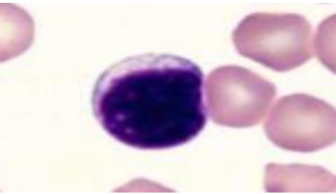
Lymphocyte (feline)
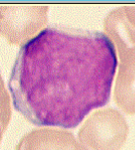
myeloblast
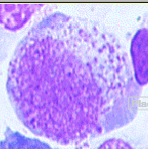
promyelocyte
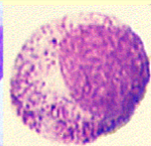
myelocyte
metamyelocyte
band
segmented
cell and desciption
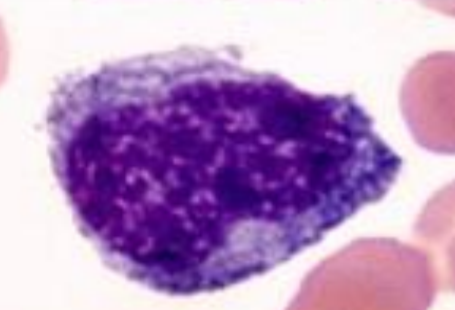
myeloblast
12-20 μm
round to oval
basophilic cytoplasm, darker at corner
big nucleus with reticular chromatine and visible
nucleoli (2-5)
cell, description
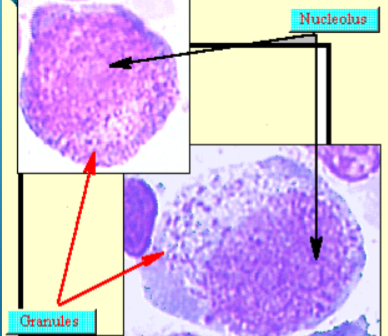
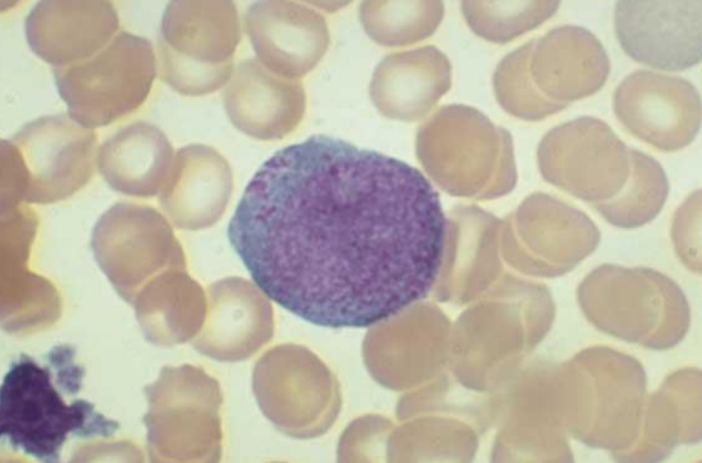
promyelocyte
20-25 microm
round to oval
Cytoplasm blue, darker around corners with
primary azurophil (red) and secondary brownish granules
round to oval nucleus sub centrally, indented
promyelocyte
cell, description
myelocyte
11-20 μm
Round to oval, cytoplasm is pale, basophilic in younger,
acidophilic in mature cells
Secondary, specific granules - neutrophilic, eosinophilic, basophilic myelocyte
Round nucleus, excentric
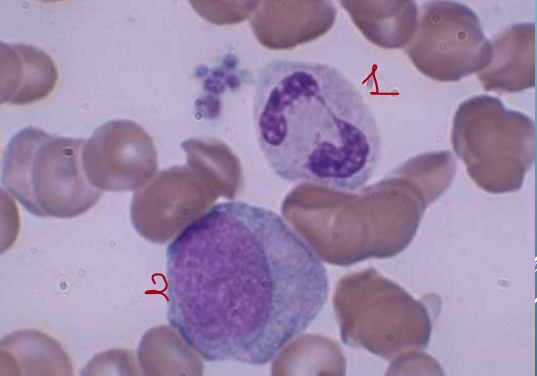
1 - metamyelocyte, 2 - myeloblast
cell, desctiprion
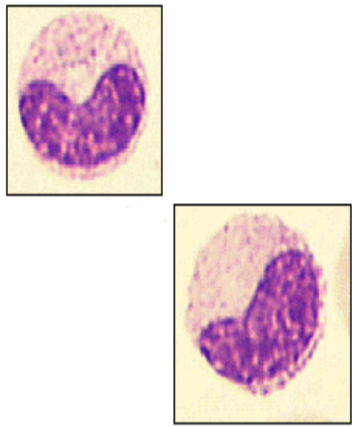
metamyelocyte
12-18 μm
Round to oval, divisions stop
Pink cytoplasm with granules
Kidney shaped nucleus, excentric, no visible
nucleoli
metamyelocyte
cell, description
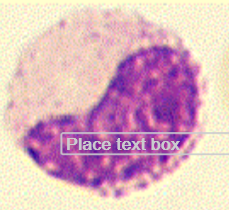
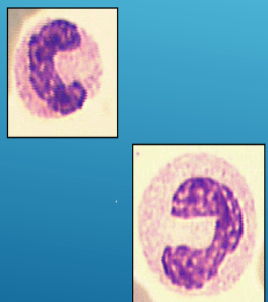
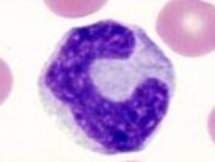
band cells
similar to mature, nucleus in form of C or S letter
chromatin has “leopard-skin” appearance
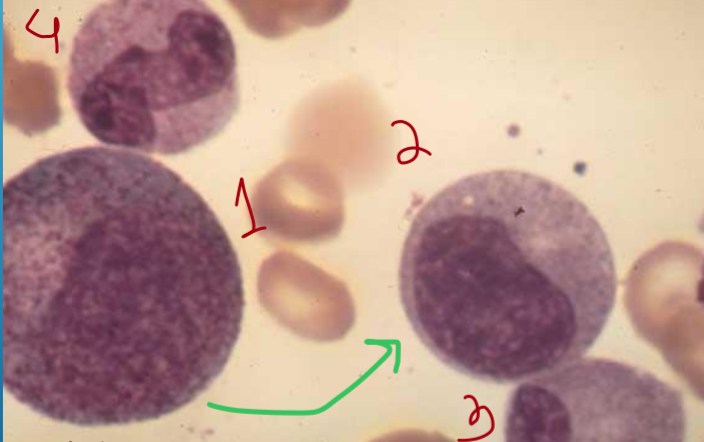
1 - promyelocyte
2 - neutrophilic myelocyte
3 - metamyelocyte
4 - band cell
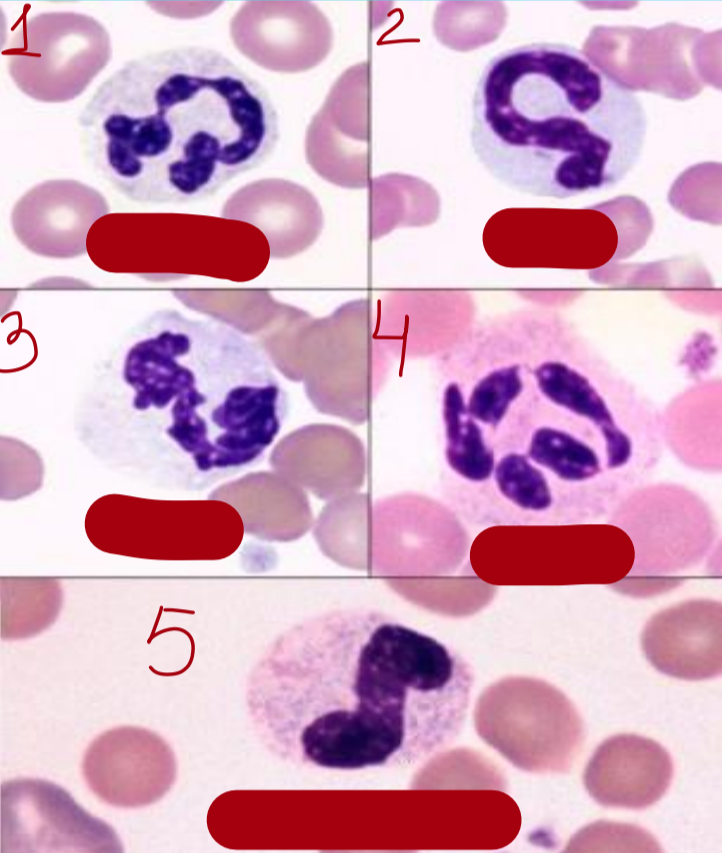
cell, sp
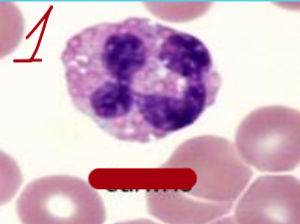
neutrophils
1 - canine, 2 - feline, 3 - equine, 4 - bovine, 5 - band neutrophil
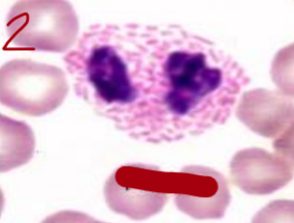
canine eosinophil
cell, sp
feline eosinophils

equine eosinophil
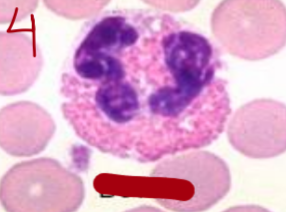
bovine eosinophils
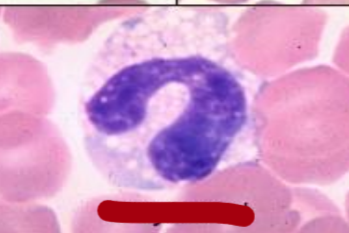
Greyhound eosinophil
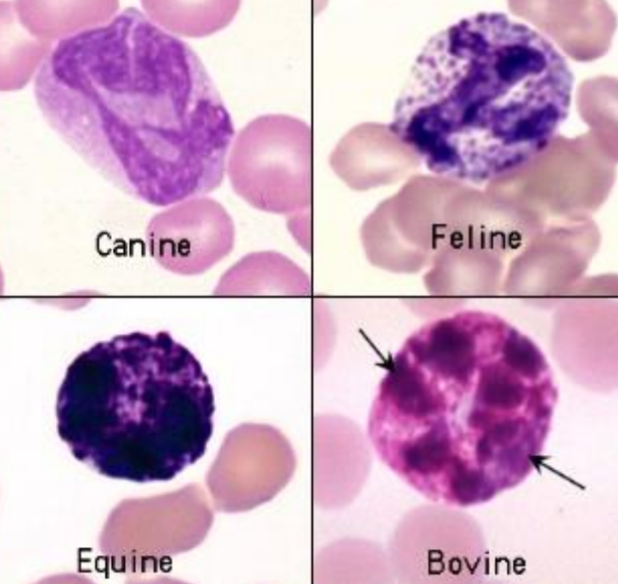
basophils (no specifity between species)
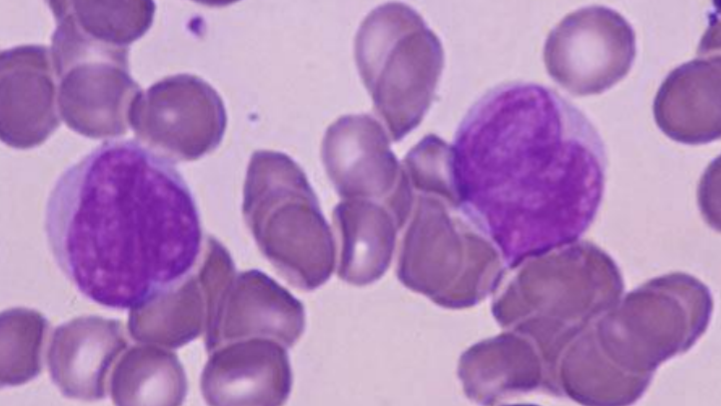
cell, description
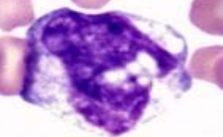
Monoblast
Round to oval, blue or grey cytoplasm,
big indented nucleus with 1-2 nucleoli, heart-shaped
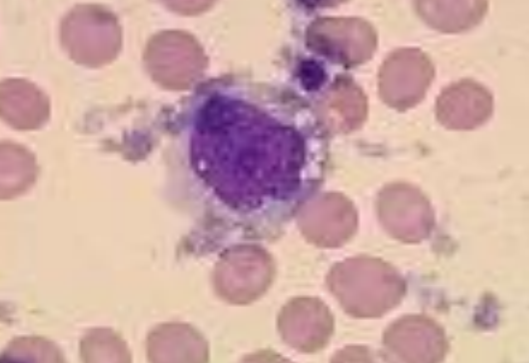
cell, description
Promonocyte
Round to oval, light blue cytoplasm with big
indented or serrated nucleus and nucleolus
promonocyte, canine
promonocyte, feline
cell, specie
promonocyte, equine
promonocyte, bovine
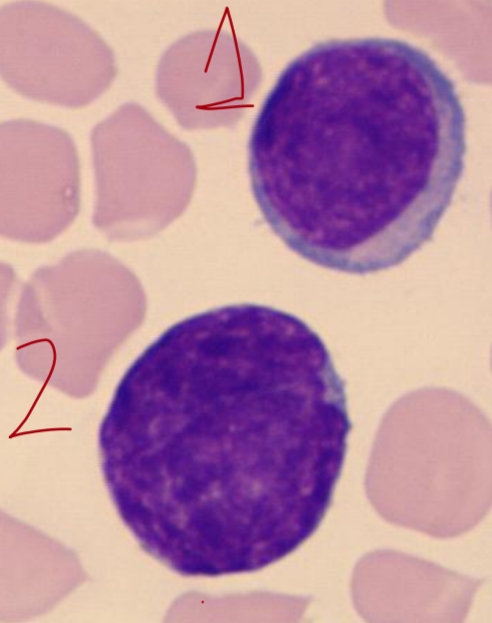
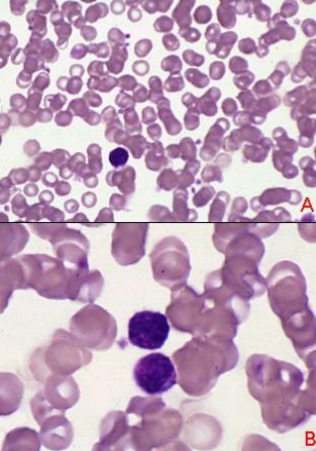
1 - prolymphocyte
2 - lymphoblast
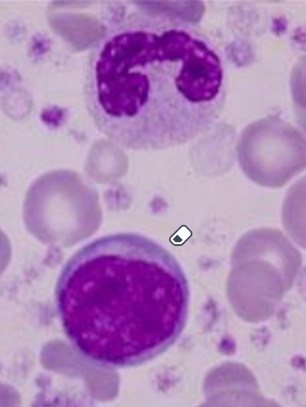
up - could be band cell
down - lymphocyte
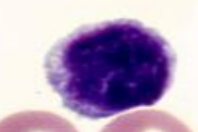
cell, sp
canine lymphocyte
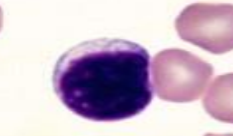
feline lymphocyte
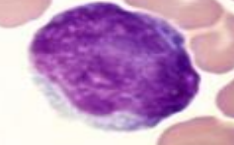
equine lymphocyte
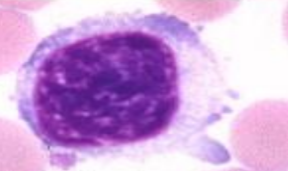
bovine lymphocyte
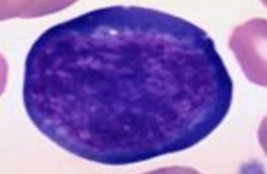
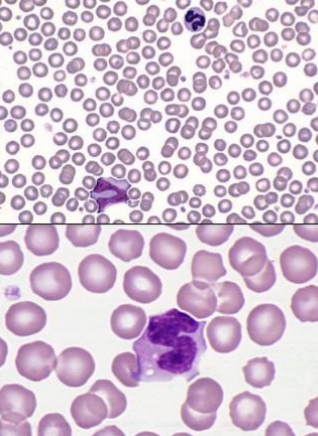
reactive lymphocyte
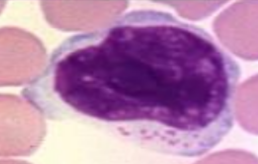
granular lymphocyte
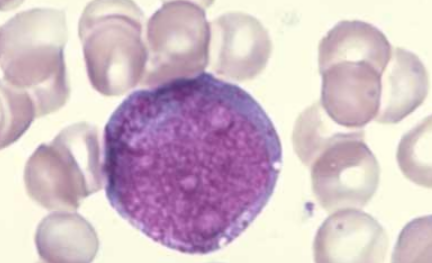
promyelocyte (due to granules)
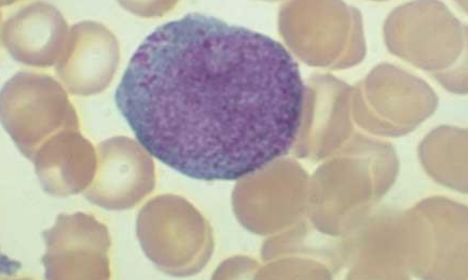
promyelocyte
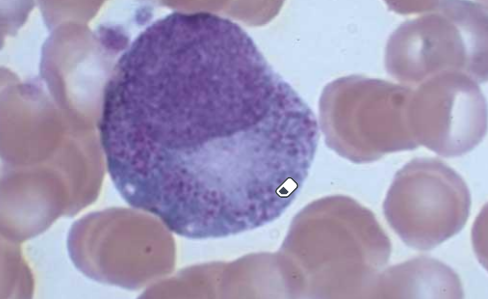
myelocyte
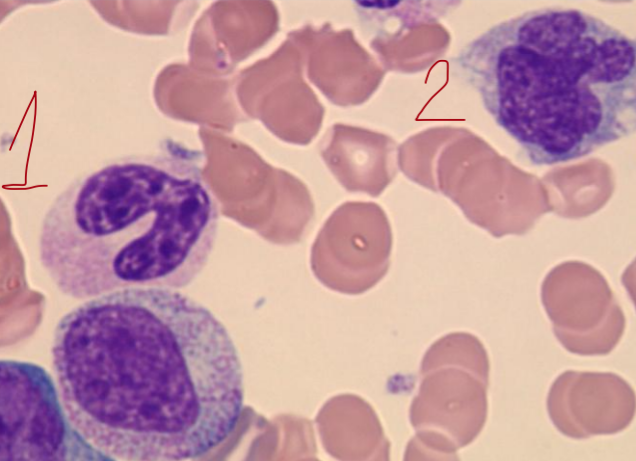
1 - band cell or metamyelocyte (immature)
2 - mature monocyte
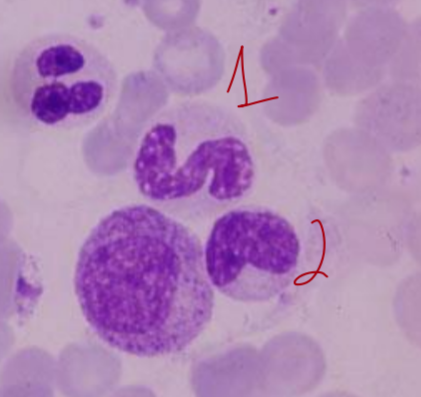
1 - band cell, 2 - metamyelocyte
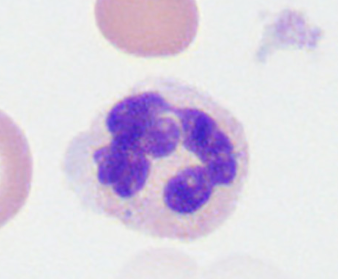
mature neutrophil
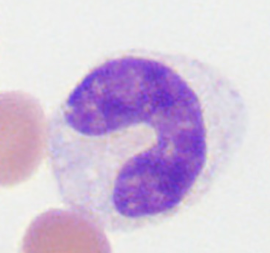
band cell
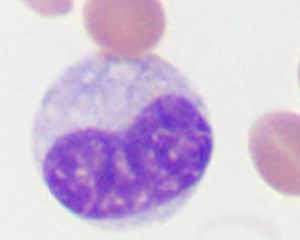
metamyelocyte
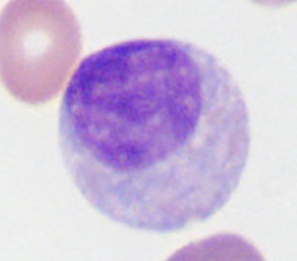
myelocyte
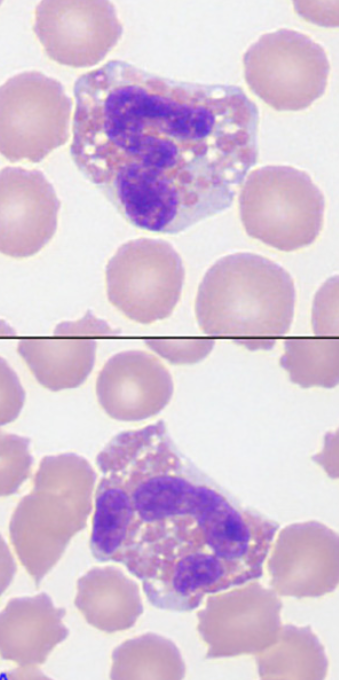
eosinophils (dog)
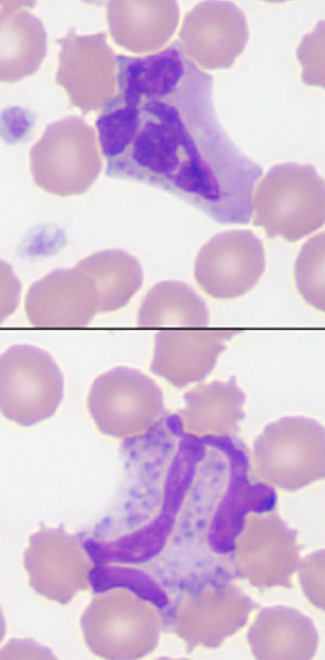
basophils (dog)
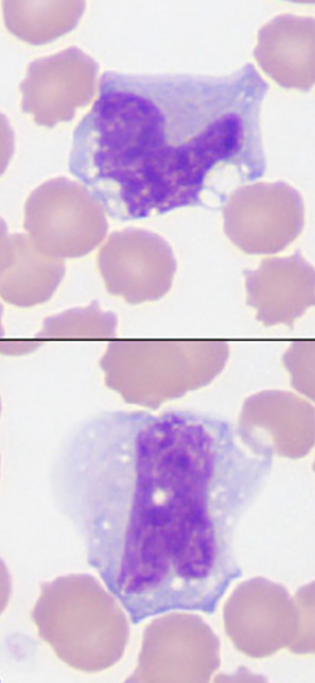
monocyte
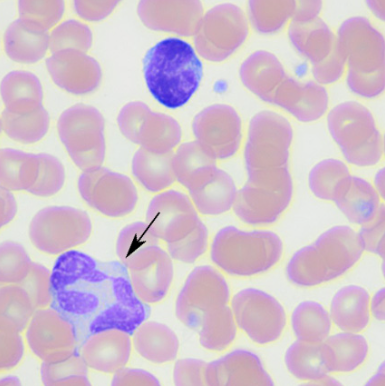
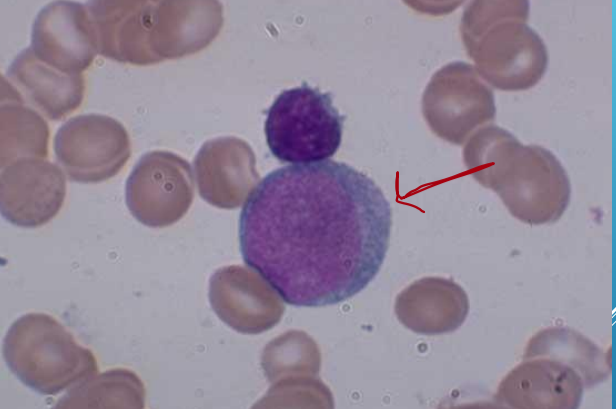
top cell - intermediate reactive lymphocyte, arrow - monocyte (dog)
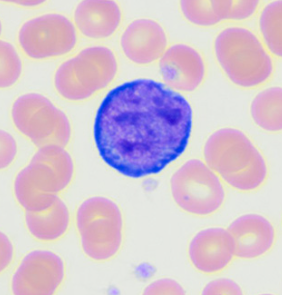
lymphocyte (dog)
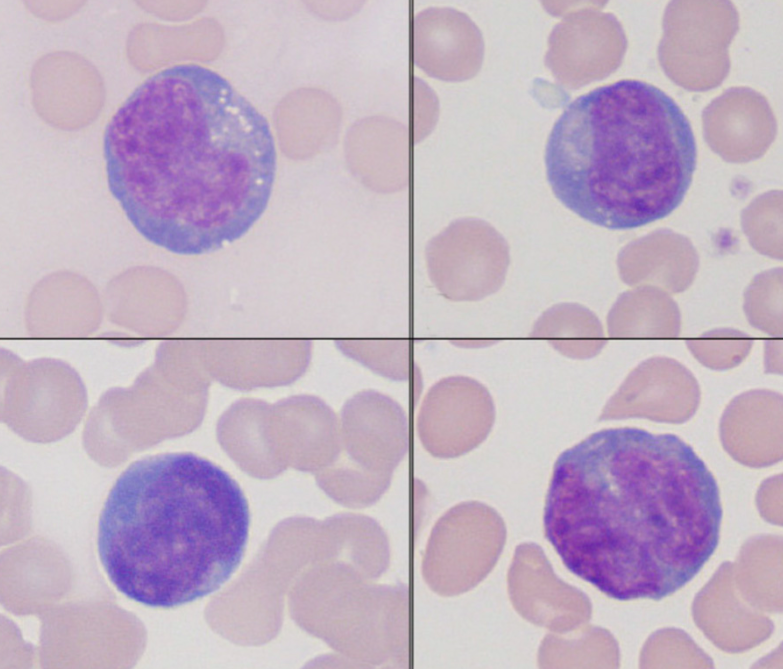
lymphocytes (dog, reactive)
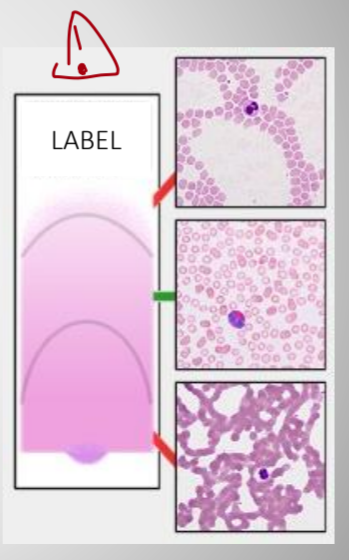
describe
feathered area - cells are flattened and distorted, red cell lose central parlor
monolayer are - cells are in one layer (erythrocytes close to each other but do not overlap),
suitable for differential counting and morphology
body area - Too thick part of blood smear for morphology assessment and differential counting
name the area
body area
name the area
monolayer
name the area
feathered area
name the spiece
dog
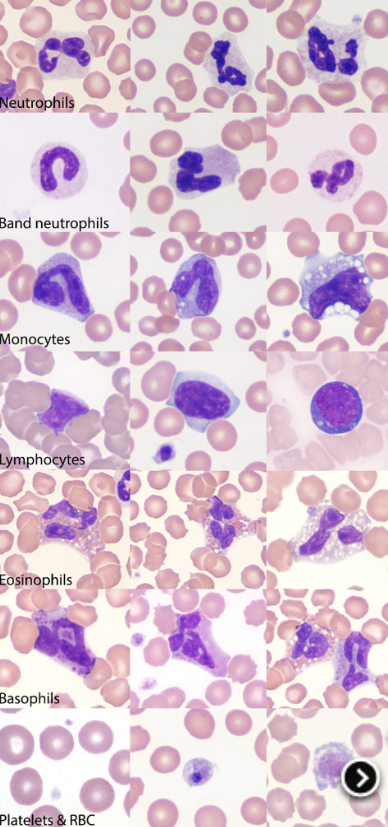
name the spiece
dog
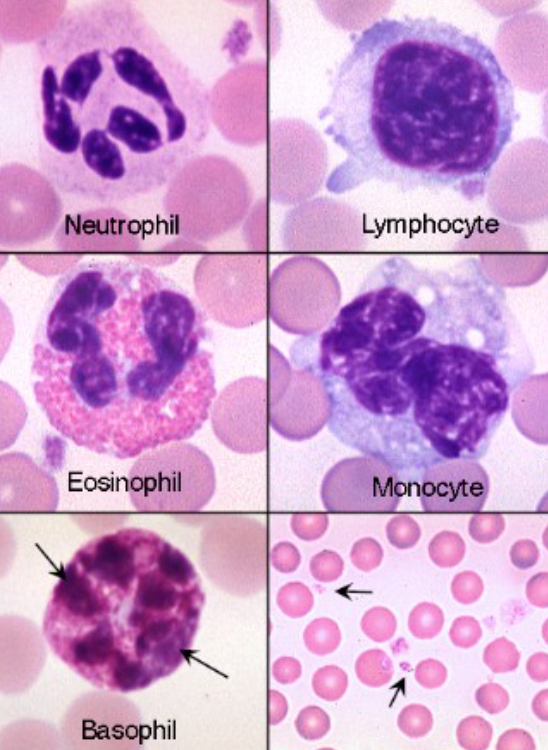
name the spiece
bovine
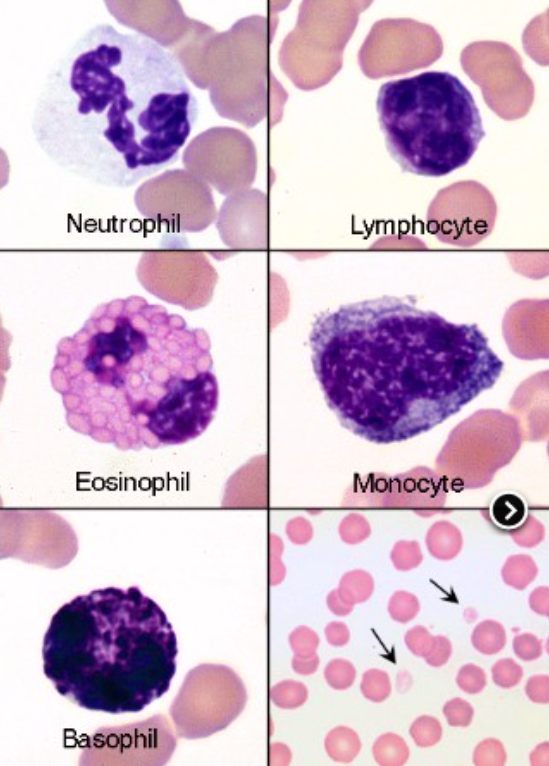
name the spiece
equine
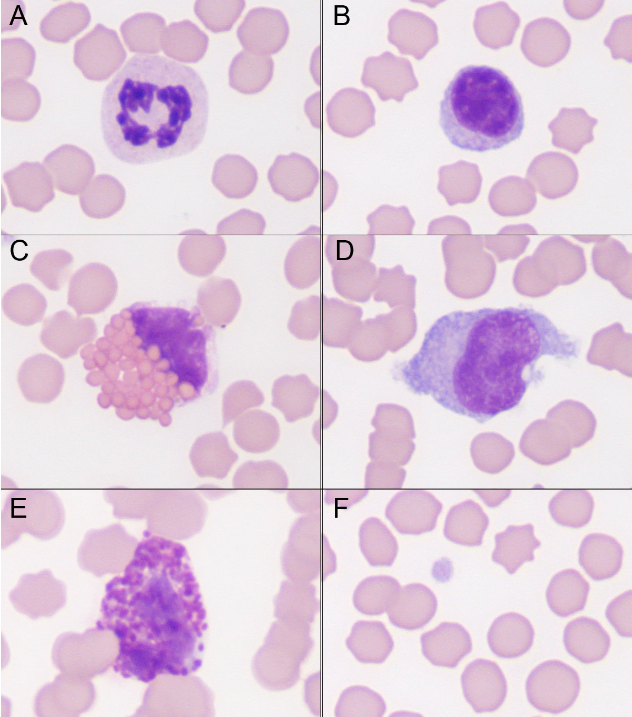
name the spiece and type of cells
equine
A: Neutrophil; B: Small lymphocyte (mildly reactive - bluer cytoplasm than normal), C: Eosinophil; D: Monocyte; E: Basophil; F: Platelets and red blood cells.
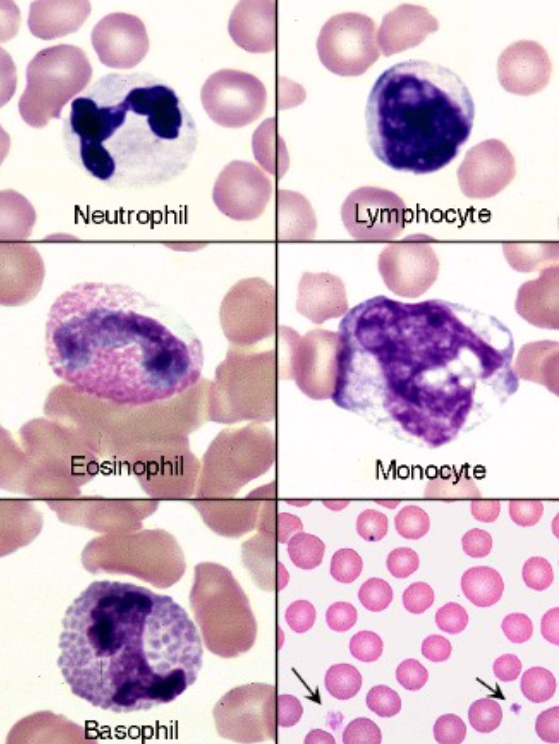
name the spiece
feline
regenerative left shift
Total number of leukocytes is increased, mature cells are
dominant
degenerative left shift
Total number of leukocytes is normal or decreased, Immature cells are dominant
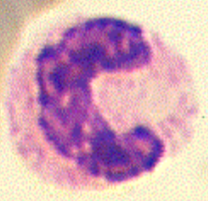
right shift (nuclear hypersegmentation)
5 or more segments
aging, EDTA exposition, glucocorticoids therapy, hyperadrenocorticism, chornic inflam
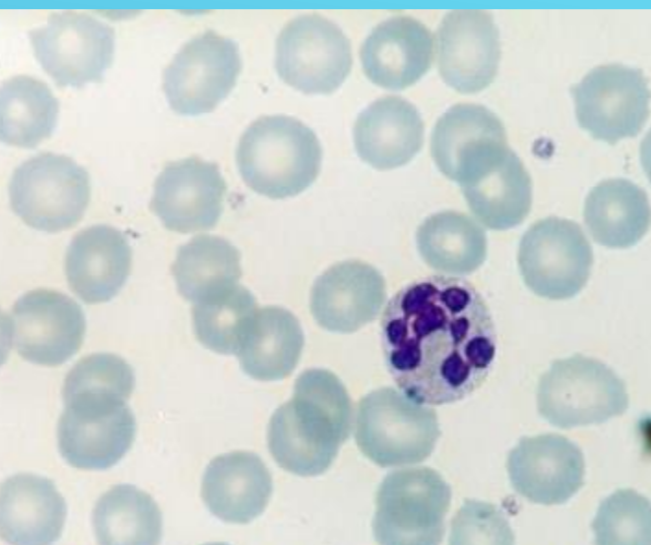
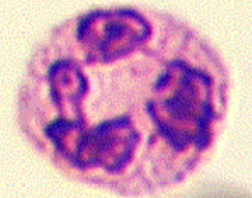
hypersegmentation
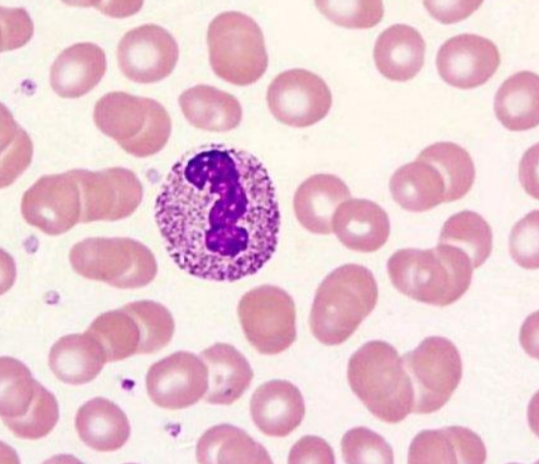
toxic nph
severe inflam, toxemia, c/p basophilia, foamy vacuoals, Dohle’s bodies (1/>more, bs, irregular)