MD311 - T6 RBC disorder
1/197
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
198 Terms
Macrocytic anemia - lab test
increase MCV, normal MCHC
Microcytic hypochromatic anemia - lab test
decrease MCV, MCH, MCHC
Normocytic anemia - lab test
normal mcv, mch, mchc
Mechanistic Classification of Anemia - Type
Production defect, Maturation disorders, RBC survival defects
Anemia - Definition
the decrease in the competence of blood to carry oxygen causing hypoxia
Cause of Anemia - Type
Hemorrhage, Hemolysis, Decrease in Production
Adaptation to Anemia - how is the severity defined - criteria
rate of onset, severity of blood loss, ability for body to adapt
20% blood loss (1000ml) - results in
can have no symptoms, no clinical signs
30-40% blood loss (1500ml to 2000ml) - results in
circulatory collapse and shock
50% blood loss (2500ml) - results in
death
how does body adapt to anemia - mech
increase in oxygenated blood flow, increase in oxygen utilization by tissue
body adapt to anemia by increase oxygen utilization, how? - mech
increase in 2,3-BPG in erythrocyte, decrease in oxygen affinity
Anemia - diagnosis
dietary habits medication, exposure to chemical, symtomps related (fatigue, muscle loss, headache, vertigo, syncope, dypsnea), previous record of abnormal blood examination, family history
Anemia (won’t state the obvious one la) - symptoms
koilonychia, glosstitis, hepatospleenomegaly, jaundice, hypotension, mongolian face, bone deformities in congenital anemia
koilonychia - definition
thin concave nails
Male normal Hb and Ht - value
13, 39
FeMale normal Hb and Ht - value
12, 36
Pregnant normal Hb and Ht - value
11, 33
Newborn normal Hb and Ht - value
15, 45
Child normal Hb and Ht, 3m to 4 yrs - value
11, 33
Reticulocyte count - definition
measure of BM productivity
Reticulocyte - site
2-3 days in BM, 1 day in blood
Reticulocyte count (%) - equation
reticulocyte*100 / 1000rbc
Corrected reticulocyte count - definition
mean to adjust the reticulocyte count proportion to the severity of anemia → reticulocyte % is falsely high in anemia because it's relative to fewer total RBCs
Corrected reticulocyte count - equation
patient Ht * %reticulocyte / normal Ht(45%)
Reticulocyte production index - definition
adjust the reticulocyte count based on maturation time
Reticulocyte production index - equation
(patient’s Ht/ 45%normal Ht) x. (reticulocyte count%/ reticulocyte maturation time(days))
hypoproliferative anemia reticulocyte count - value
<75000/miu liter
maturation anemia reticulocyte count - value
<75000/miu liter
hemolytic anemia reticulocyte count - value
>100000/ miu liter
abnormal blood loss or nutritional supplementation reticulocyte count - value
>100000/ miu liter
Anemia classified on 3 levels - type
morphologic, etiologic, mechanistic
morphologic classification of anemia - type
macro, micro hypochromatic , normocytic normochromatic anemia
etiologic classification of anemia - type
blood loss, excessive destruction, impare rbc production
mechanistic classification of anemia - production defect - example
BM failure, defective erythropoietin in kidney, Aplastic Anemia, Red cell aplaosa, PNH
mechanistic classification of anemia - maturation disorder on erythrocyte - 2 types
nuclear and cytoplasmic
mechanistic classification of anemia - maturation disorder on erythrocyte, nuclear - example
impaired DNA synthesis and mitosis, deficiency of vit 12 or folate, chemo agent
mechanistic classification of anemia - maturation disorder on erythrocyte, cytoplasmic - example
defect in hb production, iron deficiency, globin chain production disorders i.e. thalassemia, heme biosynthesis disorder i.e. sideroblastic anemia
mechanistic classification of anemia - erythrocyte survival defect, intrinsic defects in erythrocyte - example
heriditary spherocytosis, sickle cell anemia, g6pd deficiency (membrane, hb and enzyme defect accordingly), pyrvate kinase deficiency
mechanistic classification of anemia - erythrocyte survival defect, extrinsic factor - example
turbulent blood flow, microangiopathies, diverse immune mediated hemolytic anemia
mechanistic classification of anemia - erythrocyte survival defect - 2 types
intrinsic defect in erythrocyte and extrinsic defect
MCV - normal value
80 - 95 fl
MCH - normal value
27 - 32 fl
MCHC - normal value
30 - 35 g/dl
MCV < 80 - morphologic classification - type
microcytic hypochromatic anemia
MCV 80 -100 - morphologic classification - type
normocytic anemia
MCV > 100 - morphologic classification - type
macrocytic anemia
MCV < 80 problems with - further lab test
iron profile
MCV 80 - 100 problems with - further lab test
reticulocyte count
MCV > 100 problems with - further lab test
macrocyte and hypersegmented neutrophil on blood smear
etiological classification - blood loss acute - example
accident, GI bleeding
etiological classification - blood loss chronic - example
hypermenorrhea, parasitic (malaria) infection
etiologic classification - membrane defect - example
heriditary spherocytosis, hereditary elliptocytosis
etiological classification - enzymatic defect - example
pyruvate kinase deficiency, G6PD deficiency
etiological classification - hemoglobin defect - example
thalassemia, hematoglobinopathies
etiological classification - classification
intracorpuscular defect and extracorpuscular defect
etiological classification - immune hemolytic anemia - example
autoimmune hemolytic anemia, alloimmune hemolytic anemia (ABO incompatible)
etiological classification - non-immune hemolytic anemia - example
Mechanical → microangiopathic hemolytic anemia, chemical → March hemoglobinuria, infection → clostridium tetani (tetanus), hyperspleenism
etiologic classification - extracorpuscuplar defect - type
immune hemolytic anemia and non immune hemolytic anemia
hemolytic anemia - etiology
increase rbc destruction or decrease rbc life span
extravascular hemolysis - definition
lysis in reticuloendothelial system by macrophage in secondary organ (spleen, liver, bm, lymph node)
intravascular hemolysis - definition
lysis in circulation, free hb seen in circulation, urine (hemoglobinemia, hemoglobinuria), iron in urine → hemosiderin
extravascular hemolysis normal - value
80%-90% of aged rbc is lysis by this method
aged rbc - characteristic
decrease ATP synthesis, defective selective permeability, defect in surface volume ratio, rigid membrane, unable to passs through splenic sinus (trapped by macrophages)
Intravascular hemolysis normal - value
10% of aged rbc is lysis by this method
Intravascular hemolysis presentation - lab test
hemogloninemia, hemoglobinuria, hemosiderin
hemolytic anemia - symptoms
anemia, increase bilirubin, gallstone, bm hyperplasia, hepatospleenomegaly
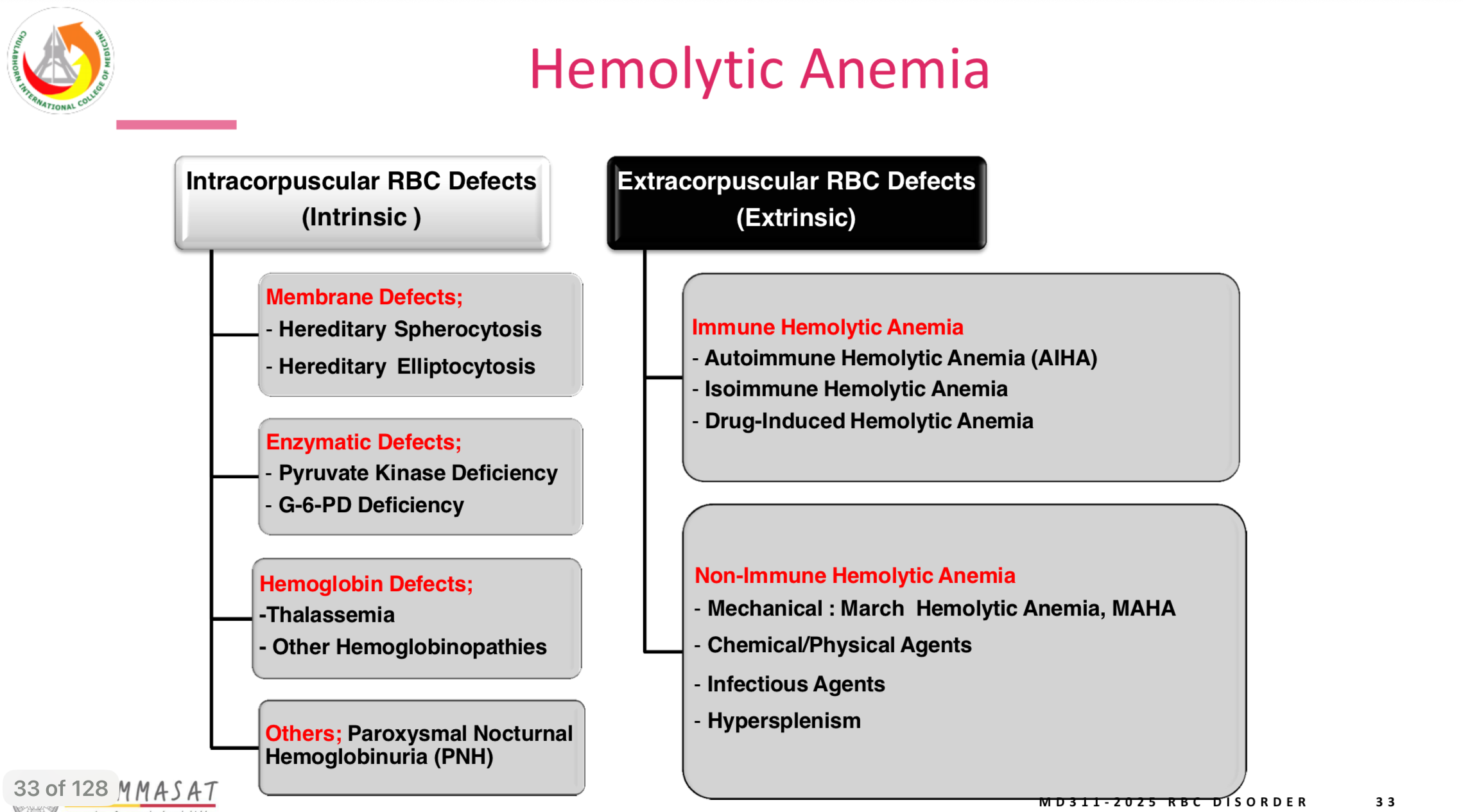
picture for summary
hemolytic anemia
hereditary spherocytosis - which type of anemia
membrane defect, intracorpuscular rbc defect
hereditary spherocytosis - genetic
75% case → autosomal dominance (ankyrin gene and beta spectin gene), autosomal recessive (alpha spectin gene), 25% - non-inheritted → spontaneous mutation.
hereditary spherocytosis - pathophysiology
Defects in the membrane skeleton protein (spectin ankyrin) → unstable membrane→ influx of Na+ → Osmosis → spherocyte → less deformable → trapped and lysis in spleen
hereditary spherocytosis - severity
homozygous (recessive>dominant) → severe, heterozygous → mild to moderate
hereditary spherocytosis - presentation
anemia, jaundice, splenomegaly
Heriditary spherocytosis - Key Mech
Na+ influx → osmosis
Heriditary Spherocytosis - laboratory finding
Smear - spherocyte + microspherocyte + polychromasia, MCHC >36%, Increase RDW, Increase Osmotic fragility
Hereditary Elliptocytosis - description
Presence of ovalocyte or elliptocyte in blood
Hereditary Elliptocytosis - genetic
Most commonly Autosomal Dominance
Hereditary Elliptocytosis - pathophysiology
defect in a/b spectin protein, protein 4.1 → loss horizontal linkage integrety = horizontal defect
Hereditary Elliptocytosis - Key
horizontal defect
Hereditary Elliptocytosis - types
Southeast Asian Ovalocytosis, Common Hereditary elliptocytosis, hereditary pyropoikilocytosism spherocytic hereditary epplitocytosis
Hereditary pyropoikilocytosis - pathophysio
spectin dimer dimer association defect, ankyrin 3 interaction - horizontal defect
Hereditary pyropokilocytosis - presentation
severe form, variable poikilocyte
Southeast Asian Ovalocytosis - most commonly found in
melanesian and malaysian population
Southeast Asian Ovalocytosis Smear - Key
Stomatocyte + Theta cell
Southeast Asian Ovalocytosis - Genetic
protein band 3 SLC4A1 defect
Acantocytosis - cause
Severe Liver Disease, result of altered plasma lipids
Abetalipoproteinemia - cause
Rare Autosomal recessice disorder → caused by MTP gene mutation
G6PD deficiency - prevalance
High prevalence in malaria endemic zone → Mediterranean population
G6PD deficiency - genetic
X-linked recessive → male
G6PD deficiency - clinical
Male - all symptomatic, Female - Homozygous - symptomatic
G6PD deficiency - variants
>127 variants
G6PD deficiency - clinical complication
3: acute hemolytic anemia, neonatal jaundice, congenital non-spherocytic hemolytic anemia
G6PD deficiency - congetinal non-spherocytic hemolytic anemia - key
we won’t see spherocyte in smear
G6PD deficiency - acute hemolytic anemia - key
3 triggers: Certain drug (primaquine for malaria), infection (ticket), fava beans
G6PD deficiency - acute hemolytic anemia - mech
increase oxidative stress from triggers (drug, infection, fava beans) → hemolysis
G6PD deficiency - neonatal jaundice - key
Infant - hyperbilirubinemia = kernicterus
G6PD deficiency - congentital non-spherocytosis hemolytic anemia - presentation
chrononic hyperbilirubinemia, decrease haptoglobin, increase LDH level.
G6PD deficiency - presentation
Asymptomatic hemolytic crisis, intracerebral hemolysis, Hemoglobinuria
Hemolytic crisis - lab finding
defect spherocyte, bite cell, blister cell, Heinz bodies
G6PD deficiency - screening test
Fluorescent spot test → from NADPH (Dark = deficiency)