AP Euro: The Western Heritage: Chapter 2: Renaissance and Discovery (1300s-1500s)
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
96 Terms
new secular and scientific values and a rational approach to their world
What were the effects of the revival of ancient learning in Italy according to the Historian Jacob Burkhardt?
fragmented feudal society with culture dominated by the Church; national consciousness and centralization with culture controlled by lay people
What was the differences in society between the middle ages and the renaissance?
Italy; because it's trade with the East improved their knowledge and economy
Where was the birth of the Renaissance and why?
retention of city-states
How was Italy different than the rest of Europe at the end of the Middle Ages?
merchant oligarchy
Most of the city-states of Italy had despotic rulers, except Venice. What type of government did they have?
Renaissance
rebirth; revival of classical learning; changes in art, architecture, science, technology, politics, and religion
Grandi, Popolo grosso, Burghers, and Popolo minuto
the four groups of society in Florence are...?
grandi
the conservative "old rich" class that ruled Florence
popolo grosso
the newly rich merchant class in florence, the capitalists & bankers; means the fat people
burghers
a member of the middle class in Florence who lived in a city or town who sided with the popolo grosso
popolo minuto
lower class, poor people of Florence
Ciompi Revolt
in 1387 the popolo minuto (poor) rebelled in Florence. They ruled for next 4 years until Cosimo de' Medici
the feuding between old and new wealth, social anarchy caused by the population being halved by the Black Death, and the collapse of the banking houses Bardi and Peruzzi
What were the 3 main causes of the Ciompi Revolt?
Signoria
the council that governed Florence consisting of 8 men representing the major guilds
Cosimo de Medici
A wealthy Florentine and an astute statesman, who brought power back to Florence in 1434 when he ascended to power; controlled the city behind the scenes, He skillfully manipulated the constitution and influencing elections; through his informal, cordial relations with the electoral committee, and was able to keep councilors loyal to him in the Signoria; as head of the Office of Public Debt
Podestà
a strongman hired by the most powerful groups in a city-state who was given full power to maintain law and order
humanism
a Renaissance intellectual movement in which thinkers studied classical texts and focused on human potential and achievements
philosophy that stressed dignity, individualism, and secular values; a religious philosophy that stressed dignity and values of the Church; or a neutral stressing on scholarship
People debate about the true meaning of humanism. What are some of the possible meanings?
Francesco Petrarch
father of humanism; author of books on Ancient Rome and love; pretty secular
Dante Alighieri
an Italian poet famous for writing the Divine Comedy that describes a journey through hell and purgatory and paradise (basically means he's a lot more religious than Petrarch)
Giovanni Boccaccio
student of Petrarch who wrote the Decameron and an encyclopedia of Greek and Roman myths
becoming better people through knowledge that improves the whole self
What was the goal of humanism?
Christine de Pisan
a very well educated woman who supported herself by writing poetry, including "the Treasure of the City of Ladies"
Greek studies in Florence
What was one of the most important studies revived during the Renaissance?
Florentine Academy
an informal gathering of humanists devoted to the revival and teachings of Plato, founded in 1462 under the leadership of Marsilio Ficino and the patronage of Cosimo de Medici
Plato and his favorable view of humanity
What Greek teachings were very popular during the Renaissance?
Lorenzo Valla
his writings were critical of the Catholic but he didn't intend them to be so critical that protestants would use his writing
civic humanism
the idea that humanists were being educated well and therefore would be great citizens; however by the end of the Renaissance, most humanists became more interested in modern time's social and power "history"
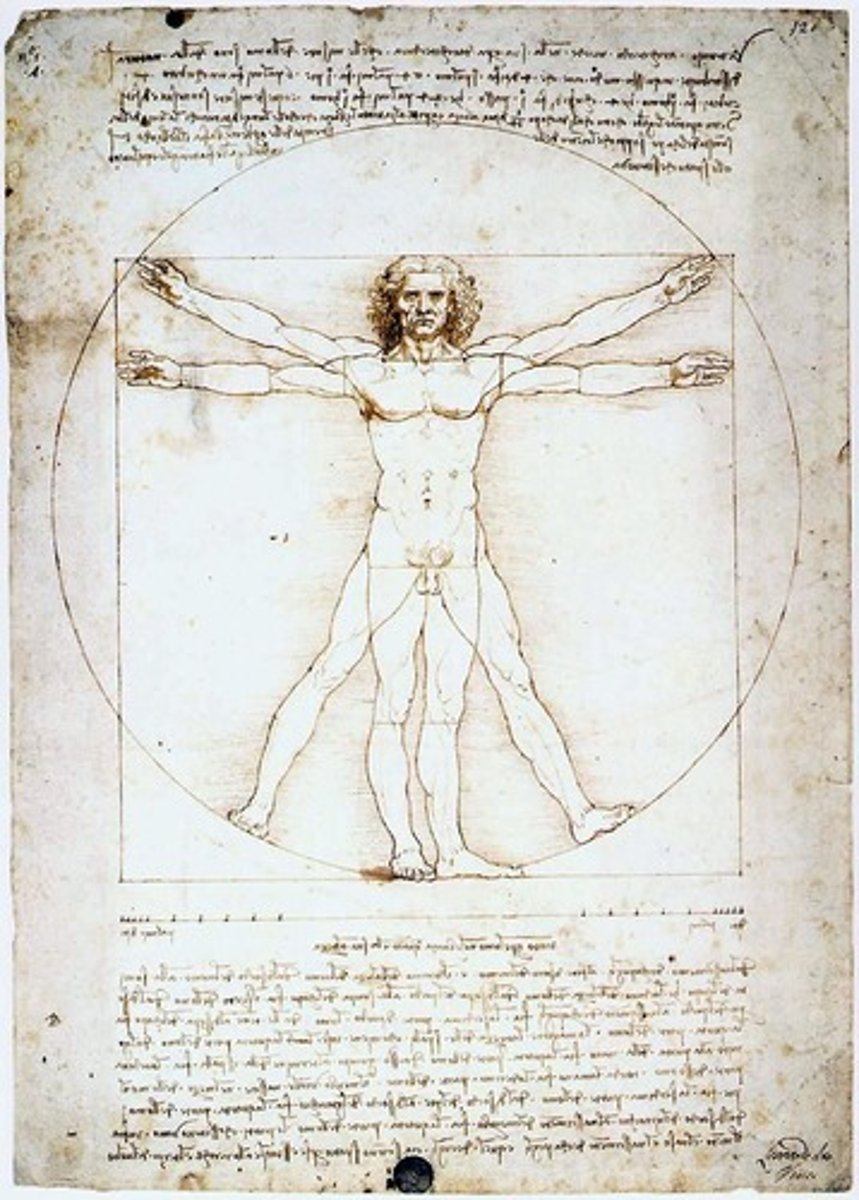
Virtruvian Man
drawing created by Leonardo da Vinci, shows human proportions and movement
Giorgio Vasari
an Italian painter, architect, writer, and historian, most famous today for his Lives of the Most Excellent Painters, Sculptors, and Architects, considered the ideological foundation of art-historical writing
Chain of Being
there is an organization to the universe; Hell is the lowest, then Earth (some humans -kings/men/etc- are above others), then stars, the angels, and God is above all
Scholasticism
This sought to synthesize the beliefs and values of Christianity with the logical rigor of Greek philosophy. Often associated with St. Thomas Aquinas
lay people
Who had more power over culture and values, lay people or religious leaders?
Giotto
the father of Renaissance painting
Leonardo
artist, scientist, and inventor best known for the Mona Lisa and The Last Supper and sketches of inventions such as flying machines (pictured in blue)
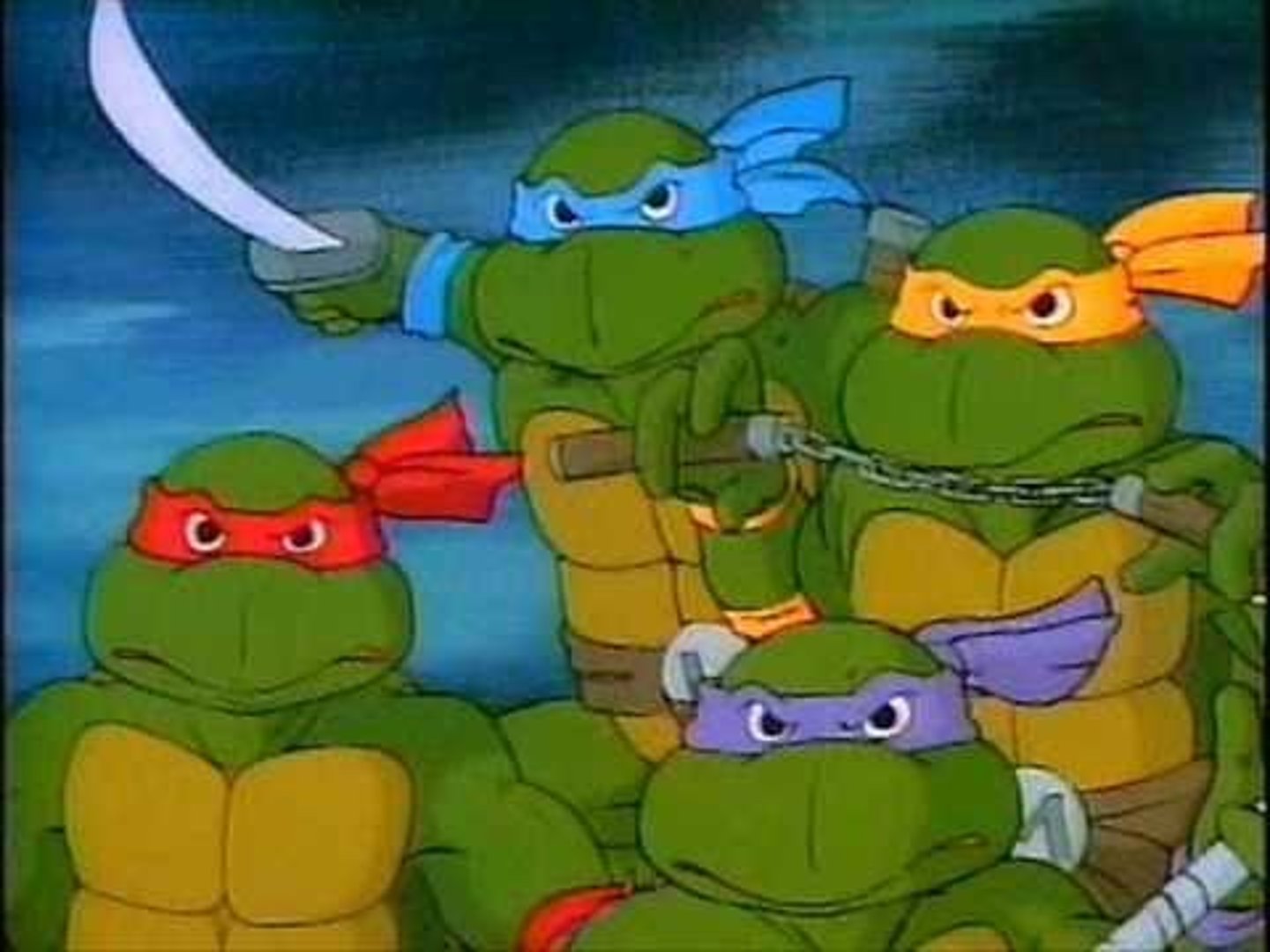

Raphael
Italian Renaissance painter; he painted frescos, his most famous being The School of Athens (pictured in red)
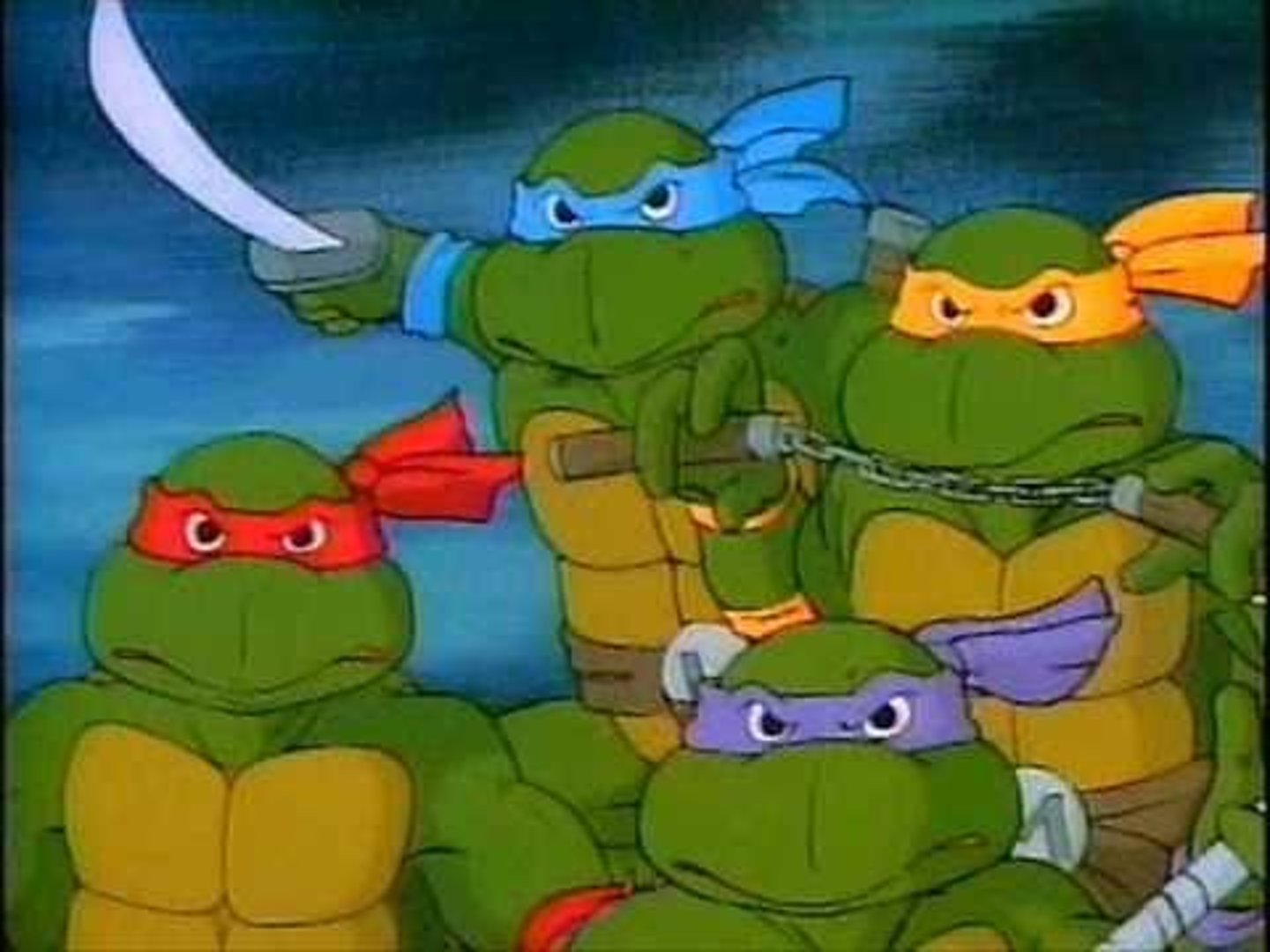

Donatello
Florentine sculptor famous for his lifelike sculptures (pictured in purple)
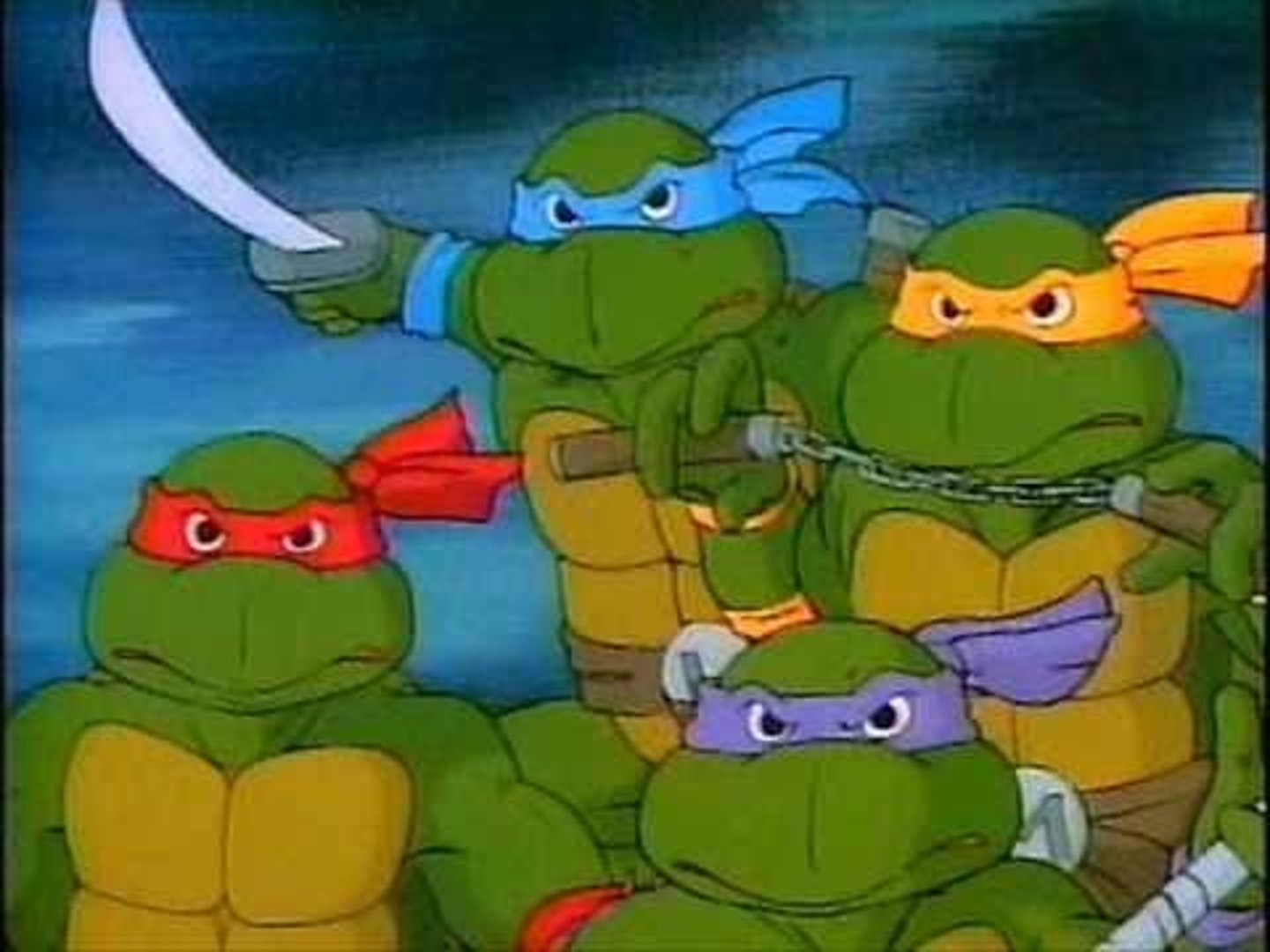

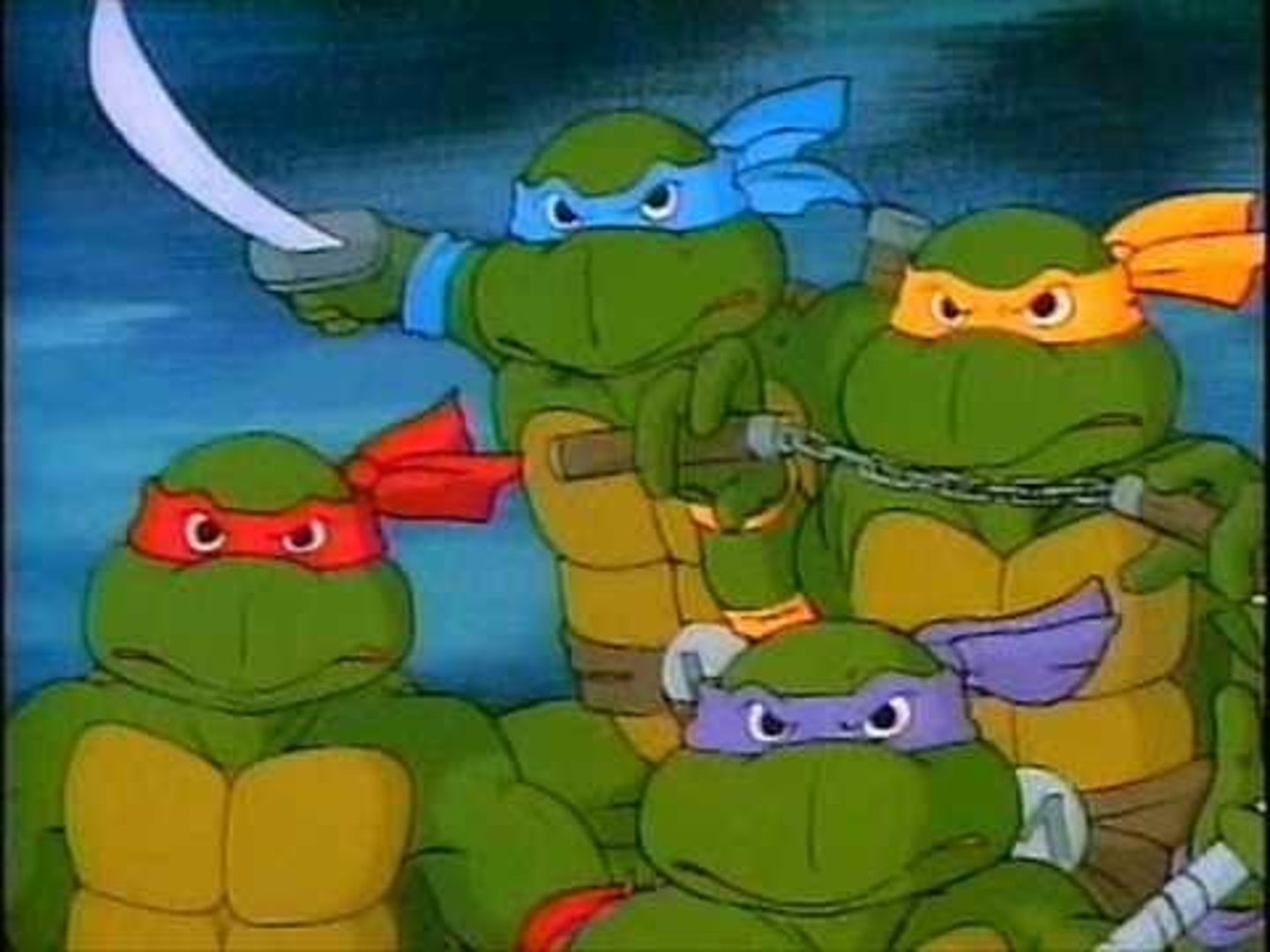
Michelangelo
(1475-1564) An Italian sculptor, painter, poet, engineer, and architect. Famous works include the mural on the ceiling of the Sistine Chapel, and the sculpture of the biblical character David (pictured in orange)

Africa, Eastern Europe, the Middle East, and Asia
Where did the slaves of Italian city-states come from?
Treaty of Lodi
1454-55, political alliance which brought Milan, Naples, and Florence together vs. Venice and Papal States. Helped create international/intercity state balance of power. If invaded from outside they would present a united front. Worked until Milanese despot brought outsiders in against other allies.
Charles VIII
was the king in power when the French "defeated" the English in the 100 years war; French King who responded to Ludovico's call for help and invaded Italy. Conquered Florence, Papal States, and Naples
Girolamo Savonarola
took control of Florence from the Medici family
League of Venice
A league formed by Ferdinand of Aragon as a response to French invasion of Italy. Brought together Venice, Papal States, and emperor Maximillian I against France. Eventually failed after Pope Alex VI abandoned it
Alexander VI
(1492-1503) a very corrupt pope who worked with Louis XII of France to gain control over Italy
Louis XII
French king who invaded Italy with the help of Pope Alexander VI
Pope Julius II
The "Warrior-Pope" who was most involved in war and politics and who helped drive the French out of Italy for the second time
Niccolo Machiavelli
a statesman of Florence who advocated a strong central government (1469-1527)
less nobility and clergy with less power to block strong monarchies and the increasing power of towns and their alliances with monarchs
What allowed strong central monarchies to take over feudal systems?
Burgundy
prosperous duchy that made up a large part of the land of France that hoped to be bigger than France and the Holy Roman Empire; was divided into France and Habsburg after the ruler Charles the Bold died
Isabella of Castile and Ferdinand of Aragon
Rulers who launched Spain's rise as a major European power in control of a vast empire by marrying each other and their kingdoms of Castile and Aragon
Granada (home of the Moors), Naples, and Navarre
What land did Isabella and Ferdinand acquire for Spain?
Inquisition
a national agency of Isabella and Ferdinand's Spain that monitored the activity of converted Jewish people and Muslims
War of the Roses
struggle for the English throne (1455-1485) between the house of York (white rose) and the house of Lancaster (red rose) ending with the accession of the Tudor monarch Henry VII
Tudor Dynasty
dynasty that began with Henry VII (ruled 1485-1509) that ruled England as a result of the War of the Roses
Court of Star Chamber
a judicial innovation of Henry VII of England, designed to curb the independence of the nobility, whereby criminal charges brought against the nobility were judged by a court of the king's own councilors
300
How many different autonomous political entities existed in Germany at the end of the 1400s?
Emperor
elected by a seven member elector college created by the Golden Bull; who did not have much power over the Germanic kingdoms
Reichstag
the national assembly of the Germanic kingdoms made up of the seven electors from the Golden Bull, other princes, and representatives from 65 imperial cities that was a poor substitute for true national unity
Brothers of the Common Life
an influential lay religious movement that began in the Netherlands and permitted men and women to live a shared religious life without making formal vows of poverty, chastity, and obedience. This group helped stimulate humanism in northern Europe
Johann Gutenberg
lived in the German city of Mainz who created printing with movable type
religion, calendars, almanacs, and how to books
What were the first books printed on the printing press about?
increased literacy, more knowledgeable common people who weren't as easy to dupe, and more ways for clergy and monarchs to spread propaganda
What were some of the effects of the printing press?
Erasmus
the most famous northern humanist who gained fame through his books on educational and religious reform; laid the egg of reform that Martin Luther hatched
Colloquies
Dialogues written (beginning in 1519) by the most important and influential of the northern humanists, Desiderius Erasmus, for the purpose of teaching his students both the Latin language and how to live a good life
Adages
a book of 5000 proverbs and sayings collected by Erasmus
Ulrich von Hutten
a fiery knight of German humanism who harshly criticized the church
Reuchlin Affair
A man who had converted from Judaism to Christianity attached Johann Reuchlin's writings; Many humanists marched to Reuchlin's defense; "Letters of Obscure Men" was born from it
Thomas More
best-known English humanist; wrote Utopia, a criticism of society; executed by Henry VIII when he refused to recognize the king's marriage to Anne Boleyn
it helped the Catholic Church in Spain, while it helped lead to the Protestant Reformation in many other kingdoms
How did humanism differ between Spain and other kingdoms?
Prince Henry the Navigator
Portuguese prince who captured the African Muslim city of Ceuta and started Portuguese colonialism
a direct market of spices instead of having to go through middlemen
Why did the Portuguese sail around Africa?
Vasco de Gama
A Portuguese sailor who was the first European to sail around southern Africa to the Indian Ocean
Japan
Where did Columbus think he landed?
Christopher Columbus
he mistakenly "discovered" the Americas in 1492 while searching for a faster route to India
Amerigo Vespucci
A mapmaker and explorer who said that America was a new continent, so America was named after him
Ferdinand Magellan
Portuguese navigator who led the Spanish expedition of 1519-1522 that was the first to sail around the world
more trade; increased revenue for Spanish wars; trade of food and diseases; subduing of Natives; lasting Spanish culture in the Americas
What were some of the consequences of Spanish colonialism?
Aztec Empire
Central American empire expanded greatly during the fifteenth century who were very harsh on their conquered subjects with a capital at Tenochtitlan; ended in 1521 by Hernan Cortes
Hernan Cortes
Spanish conquistador who defeated the Aztecs and conquered Mexico (1485-1547)
Inca Empire
The vast and sophisticated Peruvian empire centered at the capital city of Cuzco that was at its peak from 1438 until 1532; defeated by the Spanish Francisco Pizarro
Francisco Pizarro
Spanish explorer who conquered the Incas in what is now Peru and founded the city of Lima (1475-1541)
Atahualpa
Last ruling Inca emperor of Peru. He was executed by the Spanish
Bartolome de Las Casas
First bishop of Chiapas, in southern Mexico. He devoted most of his life to protecting Amerindian peoples from exploitation. His major achievement was the New Laws of 1542, which limited the ability of Spanish settlers to compel Amerindians to labor
individual priests and clergy
Who did more to protect Native people, individual priests and clergy or the Church?
mining, agriculture, and shipping
The three major components of the colonial economy in Latin America were...?
gold; silver
What were the Spanish looking for when mining, and what ended up being profitable?
hacienda
Large estates built by wealthy Spanish ranchers in North America
food, leather, and sugar
What were the haciendas growing/making?
encomienda
a grant by the Spanish Crown to a colonist in America conferring the right to demand tribute and forced labor from the Native inhabitants of an area
repartimiento
system that required Native adult men to devote a certain amount of days to Spanish economic enterprises
debt peonage
system that bound laborers to work off a debt to the employer, basically slavery
8%
What percent of Native people remained in what is now Mexico, a generation after the Spanish came to the New World
decrease in trust of ancient knowledge, new possibilities in communication and globalization, increase of spices and metals in Europe, increased wealth
What were some of the effects of colonialism?
Marco Polo
(1254-1324) Italian explorer and author. He made numerous trips to China and returned to Europe to write of his journeys; He is responsible for much of the knowledge exchanged between Europe and China during this time period
caravel
a small, fast Spanish or Portuguese sailing ship of the 15th-17th centuries
Colombian Exchange
the transfer of plants, animals, and diseases between the Americas and Europe, Asia, and Africa