psych Neuro unit1-1.4
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
neurotransmitters, drugs, brain parts, and brain scans
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Acetylcholine (ACh)
enables muscle action, learning and memory, involved in anger and aggression.
Dopamine
influences movement, learning, attention, emotion, and reward
Serotonin
affects mood, hunger, sleep, arousal and body temperature.
Norepinephrine
influences alertness, arousal, rewards, and stress response.
GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid)
involved in movement and regulation of anxiety, moderates neuron firing, is a major inhibitory neurotransmitter.
Glutamate
involved in memory and learning, a major excitation neurotransmitter.
Endorphins
neurotransmitters that influence the perception of pain or pleasure.
Substance P
involved in pain perception and immune response.
Alcohol
Depressant. favorable effects: initial high followed by relaxation and disinhibition. negative effects: depression, memory loss, organ damage, impaired reactions.
Heroin
Depressant. Favorable effects: rush of euphoria, relief from pain. Negative effects: depressed physiology, loss of natural endorphin function.
Caffeine
Stimulant. Favorable effects: increased alertness and wakefulness. Negative effects: anxiety, restlessness and insomnia in high doses.
Nicotine
Stimulant. Favorable effects: Arousal and relaxation, sense of well-being. Negative effects: heart disease, cancer.
Cocaine
Stimulant. Favorable effects: rush of euphoria, confidence, energy. Negative effects: Cardiovascular stress, suspiciousness, depressive crash.
Methamphetamine
Stimulant. Favorable effects: euphoria, alertness, energy. Negative effects: irritability, insomnia, hypertension, seizures.
Ecstasy (methylenedioxymethamphetamine, MDMA)
Stimulant; Mild Hallucinogen. Favorable effects: emotional elevation, disinhibition. Negative effects: dehydration, overheating, depressed mood, impaired cognitive and immune functioning.
LSD (lysergic acid diethylamide)
Hallucinogen; Favorable effects: Visual “trip” Negative effects: Risk of panic.
Marijuana (delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol, THC)
Mild hallucinogen; Favorable effects: enhanced sensation, relief of pain, distortion of time, relaxation. Negative effects: impaired learning and memory, increased risk of psychological disorders.
Hindbrain
consists of the medulla, pons, and cerebellum; directs essential survival functions, such as breathing, sleeping, and wakefulness, as well as coordination and balance.
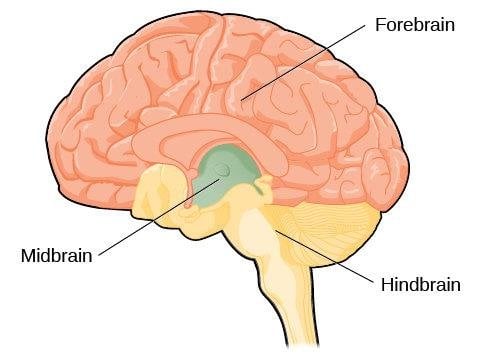
Midbrain
found atop the brain stem; connects the hindbrain with the forebrain, controls some motor movements, and transmits auditory and visual information.

Forebrain
consists of the cerebral cortex, thalamus, and hypothalamus; manages complex cognitive activities, sensory and associative functions, and voluntary motor activities.

Brainstem
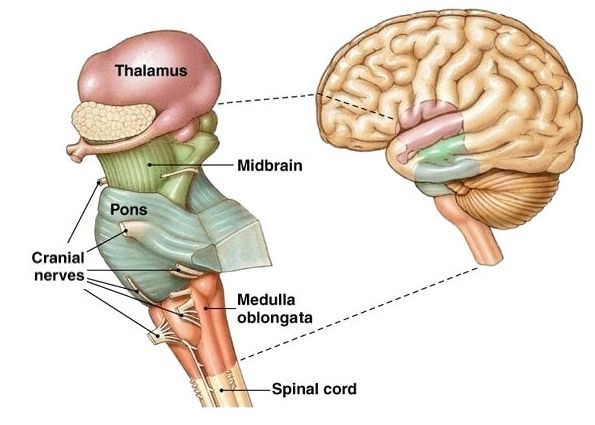
the central core of the brain, beginning where the spinal cord swells as it enters the skull; responsible for automatic survival functions.
medulla

controls heartbeat and breathing. the hindbrain structure that is the brainstem’s base.
thalamus
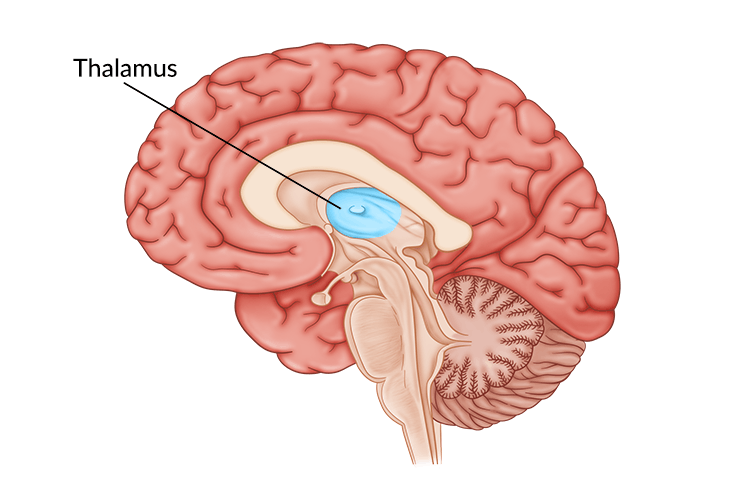
directs messages to the sensory receiving areas in the cortex and transmits replies to the cerebellum and medulla. the forebrain’s sensory control center, located on top of the brainstem.
reticular formation
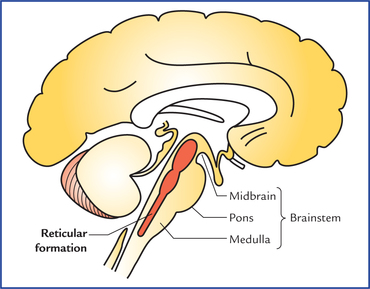
it filters information and plays an important role in controlling arousal. a nerve network that travels though the brainstem into the thalamus.
cerebellum
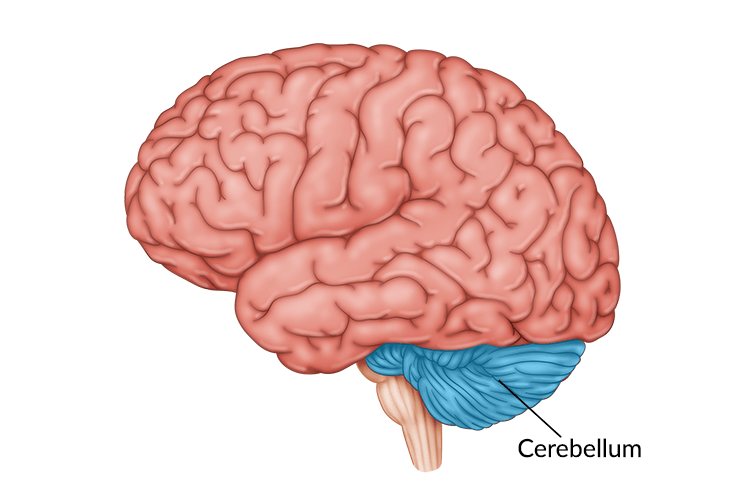
functions include processing sensory input, coordinating movement output and balance, and enabling nonverbal learning and memory. the hindbrain’s “little brain” at the rear of the brainstem.
limbic system

includes the amygdala, hypothalamus, hippocampus, thalamus, and pituitary gland; associated with emotions and drives. neural system located mostly in the forebrain — below the cerebral hemispheres
amygdala

linked to emotions: fear, anger aggression, apprehension, anxiety. two clusters in the limbic system;
hypothalamus

directs several maintenance activities (eating, drinking, body temperature, helps govern endocrine system, and linked to emotions/reward. a limbic system neural structure lying below the thalamus.
hippocampus

process explicit (conscious) memories for facts and events for storage. a neural center in the limbic system.
cerebral cortex

body’s ultimate control and information processing center. intricate fabric of interconnected neural cells covering the forebrain’s cerebral hemispheres.
frontal lobes
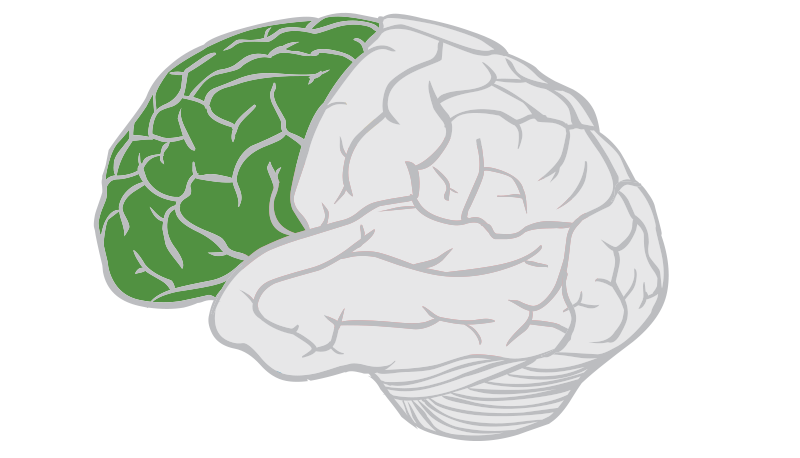
enable linguistic processing, muscle movements, higher-order thinking, executive functioning (making plans and judgments) the portion of the cerebral cortex lying just behind the forehead.
parietal lobes

receives sensory input for touch and body position. the portion of the cerebral cortex lying at the top of the head and towards the rear.
occipital lobes

includes areas that receive information from the visual fields. the portion of the cerebral cortex lying at the back of the head.
temporal lobes
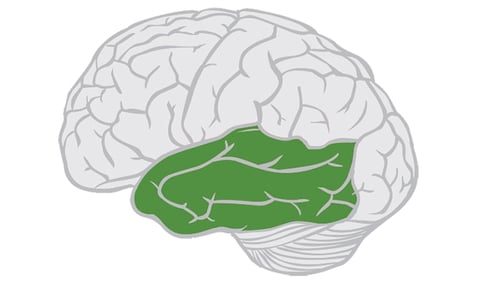
includes auditory areas which receive information primarily from the opposite ear; enables language processing. the portion of the cerebral cortex lying roughly above the ears.
motor cortex

controls voluntary movements; a cerebral cortex area at the back of the frontal lobes.
somatosensory cortex
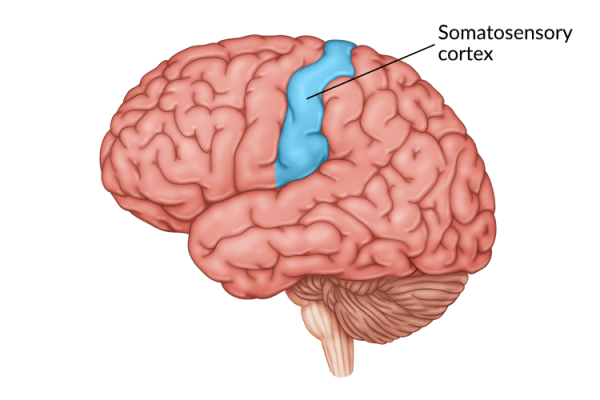
registers and processes body touch and movement sensations. a cerebral cortex area at the front of the parietal lobes
association areas

areas of the cerebral cortex that are not involved in primary motor or sensory functions, but rather are involved in higher mental functions such as learning, remembering, thinking, and speaking.
corpus callosum
the large band of neural fibers connecting the two brain hemispheres and carrying messages between them.
EEG
electrodes placed on head that measures electrical activity on surface. can’t identify specific locations of electrical activity.
MEG
head coil that records magnetic fields from the brain’s natural electrical currents.
CT
x-ray images of brain that locate brain damage.
PET
tracks where the brain temporarily radioactive form of glucose goes while a person does a task.
MRI
uses magnetic fields and radio waves to provide a map of brain.
fMRI
measurs blood flow to brain regions by comparing continuous MRI scans.