5. caries progression + removal (DONE)
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
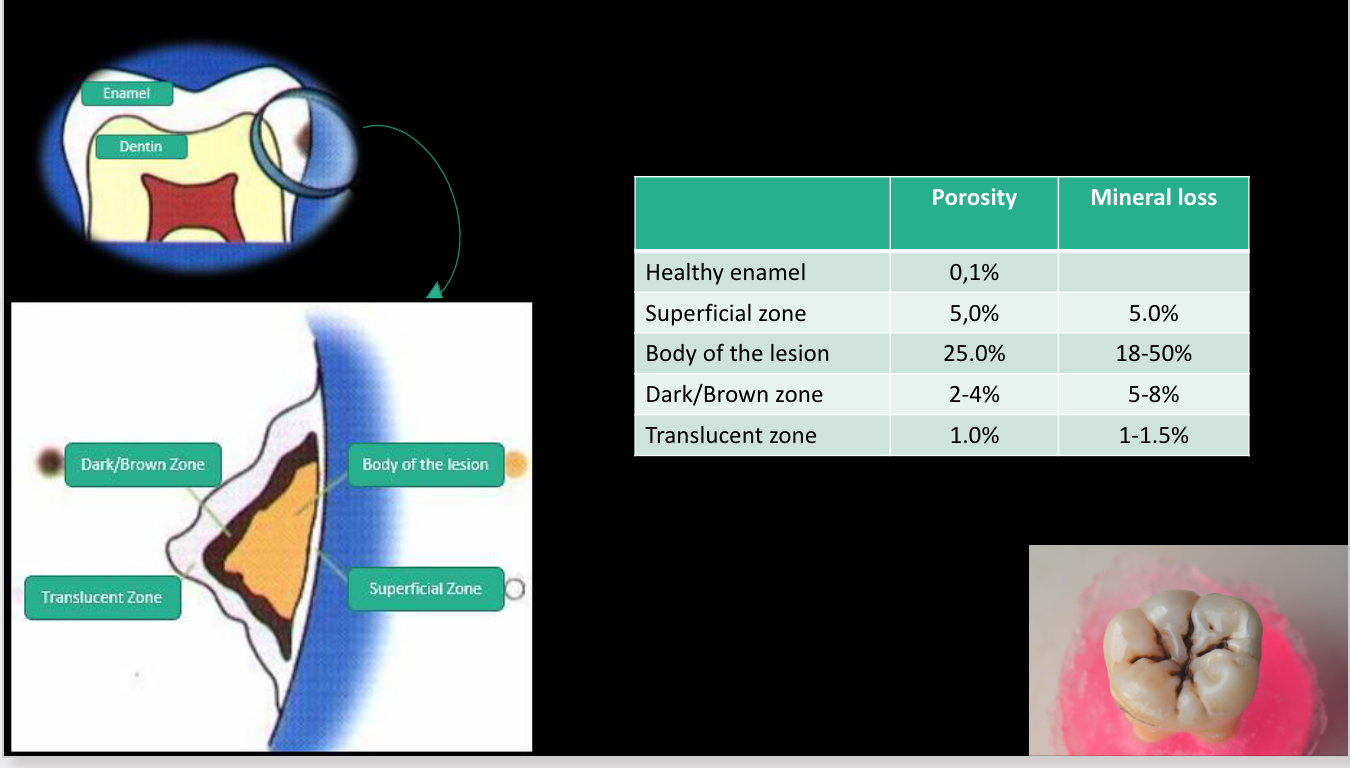
parts of the cavity
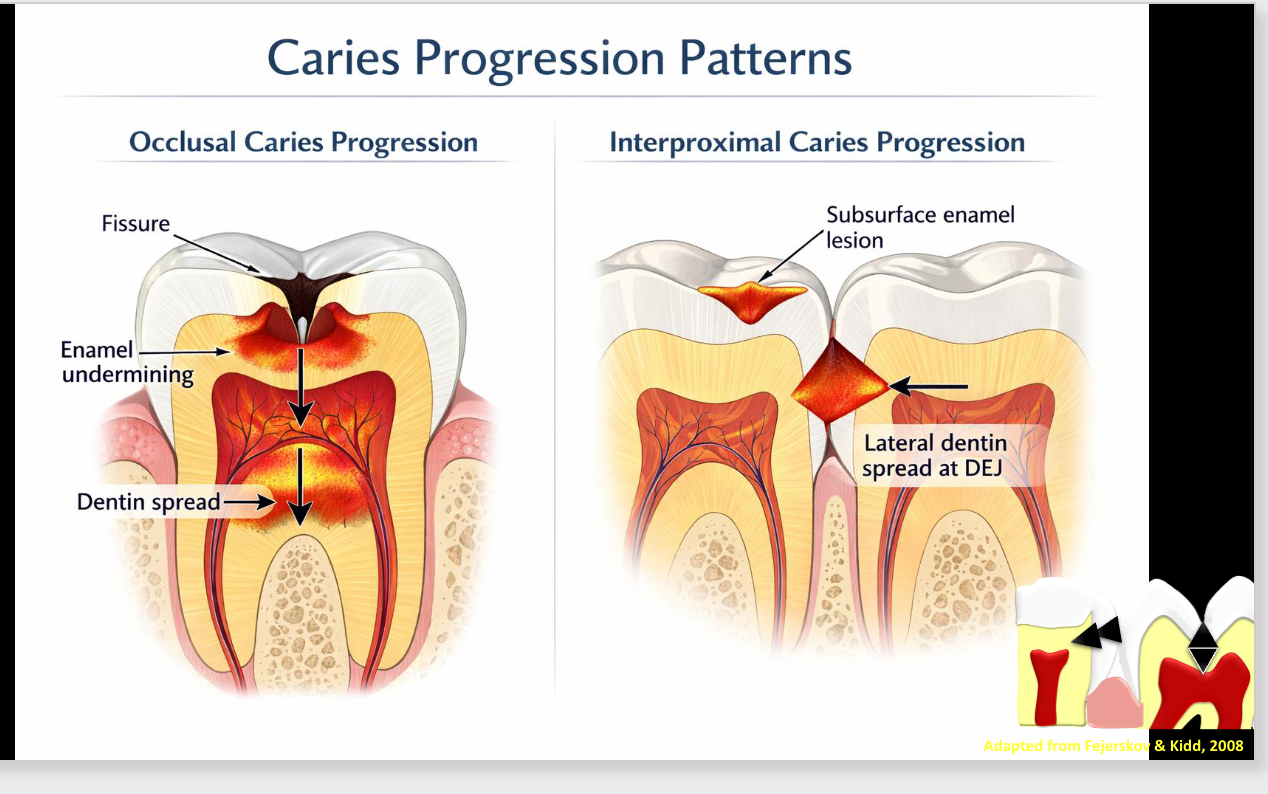
caries progression patterns
INFILTRATION
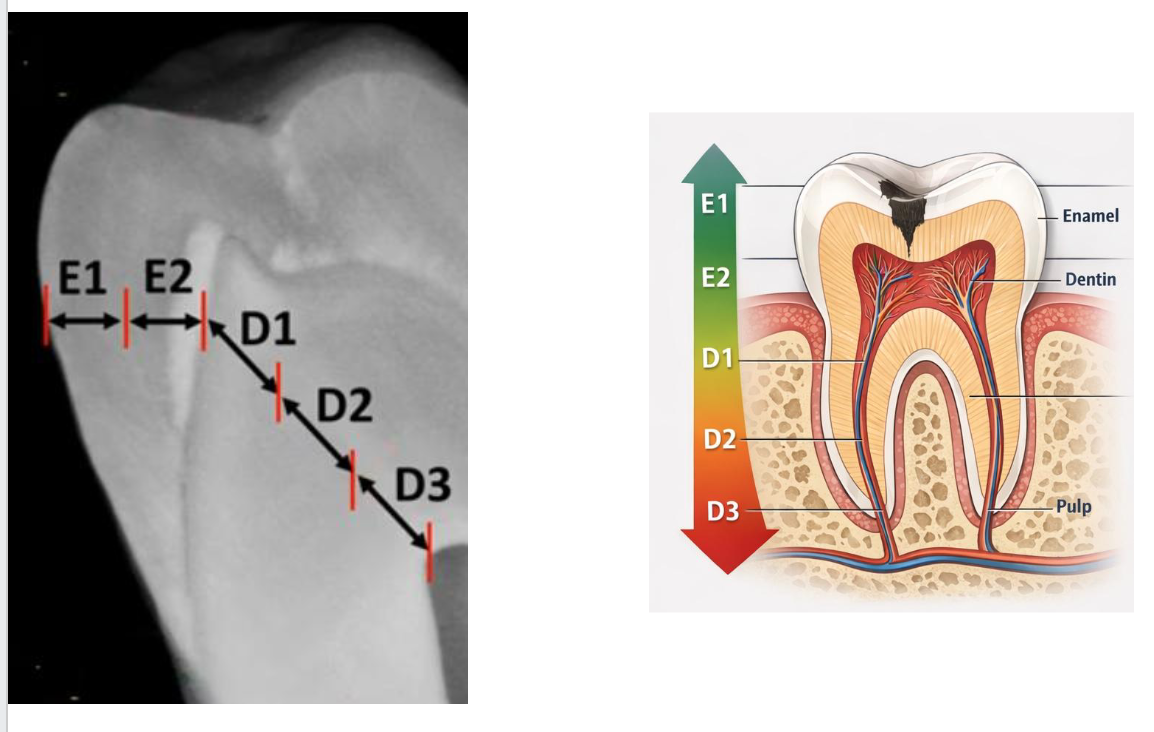
caries progression **KNOW THIS CHART WELL
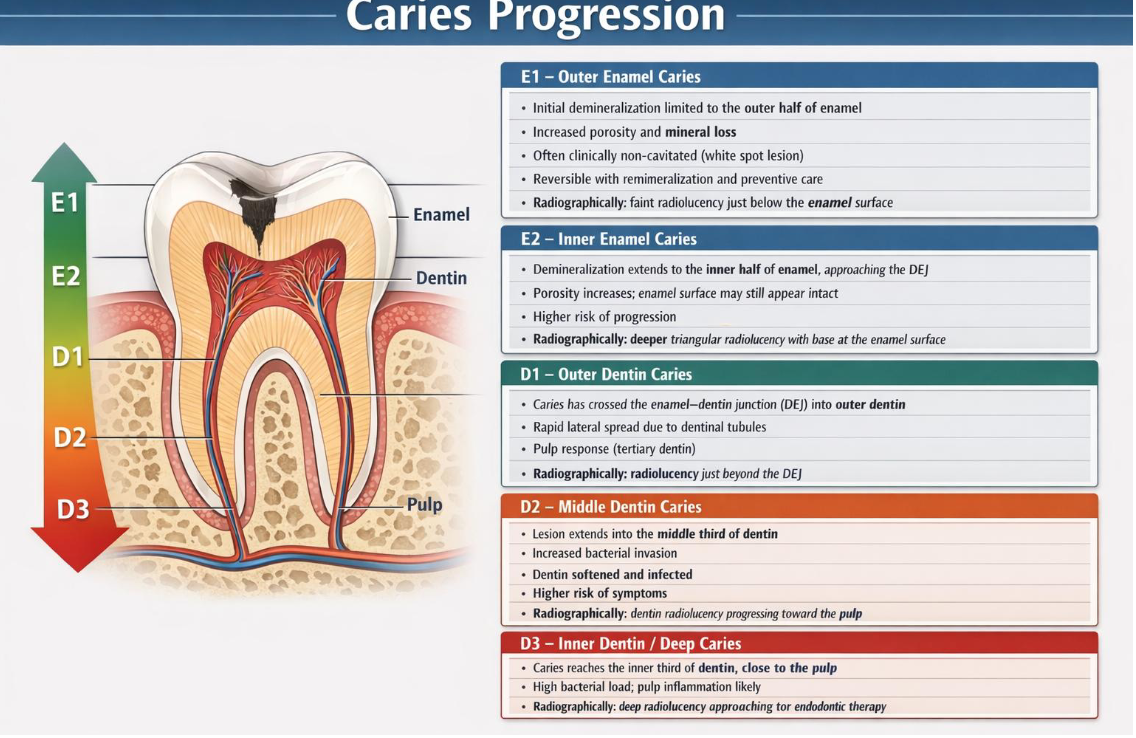
for D2 and D3 combine with liners and bases
Selective caries removal
Extensive caries
Remove infected dentin; Leave affected dentin
What instruments to use? CARBIDE BUR IN LOW SPEED / DENTIN SPOON
Infected Dentin
Necrotic dentin zone
Superficial demineralized dentin zone

Affected Dentin
Deep demineralized dentin zone
Hypermineralized dentin zone
✓ Dentinal sclerosis
✓ Reactionary dentin
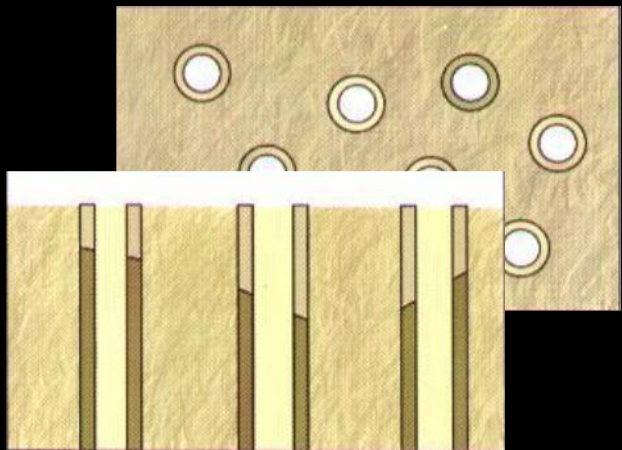
Clinical Caries Detection and Activity Assessment: tactile
Conventional explorer
Rounded-tip explorer
Clinical Caries Detection and Activity Assessment: visual
1. radiographs
Conventional radiography
Digital radiography
fluorescence
QLF-D (Quantitative Light-Induced Fluorescence, Inspector Research Systems BV, Amsterdam, Netherlands)
DIAGNOdent (KaVo Dental, Lake Zurich, IL)
transillumination
FOTI (Fiber-optic transillumination)
DIFOTI (Digital imaging fiber-optic transillumination)
Dental Transillumination
When a high-intensity light is applied to the tooth structure, it passes through the structure and illuminates it.
When affected by a carious lesion, the refractive indexes of the decayed enamel and dentin are modified, causing the light to be scattered instead of transmitted, creating a darker appearance in the affected area.
Fiber-Optic Transillumination Using a Camera (DIFOTI)
Uses a harmless white light to transilluminate each tooth and
instantaneously generate a high-resolution digital image on the computer monitor, allowing the clinician to capture the desired image using simple software and a foot pedal activation.
Clinical Caries Detection and Activity Assessment: visual-tactile
ICDAS International Caries Detection and Assessment System
clinical examination of free surfaces
Visual clinical examination
Do not use the explorer with pressure
Generally does not require other diagnostic methods
clinical examination of Interproximal surfaces
Clinical examination (visual + dental floss)
Tooth separation
Interproximal radiography
Transillumination
clinical examination of occlusal surface
Visual
Tactile (no pressure/blunt tip)
X-ray
Dye or Fluorescence
caries detector dyes
Dyes are capable of increasing the contrast between normal and decay-altered tissues, thus increasing the accuracy in diagnosing carious lesions.
However, dyes do not differentiate infected from affected dentin, leading to unnecessary removal of dental tissue.
have also been linked to toxicity reactions and the creation of stains in dental tissues.
ICON resin infiltration
a minimally invasive technique used to treat early enamel caries (white spot lesions) without drilling
A low-viscosity resin infiltrates the porous, demineralized enamel, blocking acid diffusion and arresting lesion progression.
indicated for non-cavitated enamel lesions and supports a preventive, tooth-preserving approach to caries management
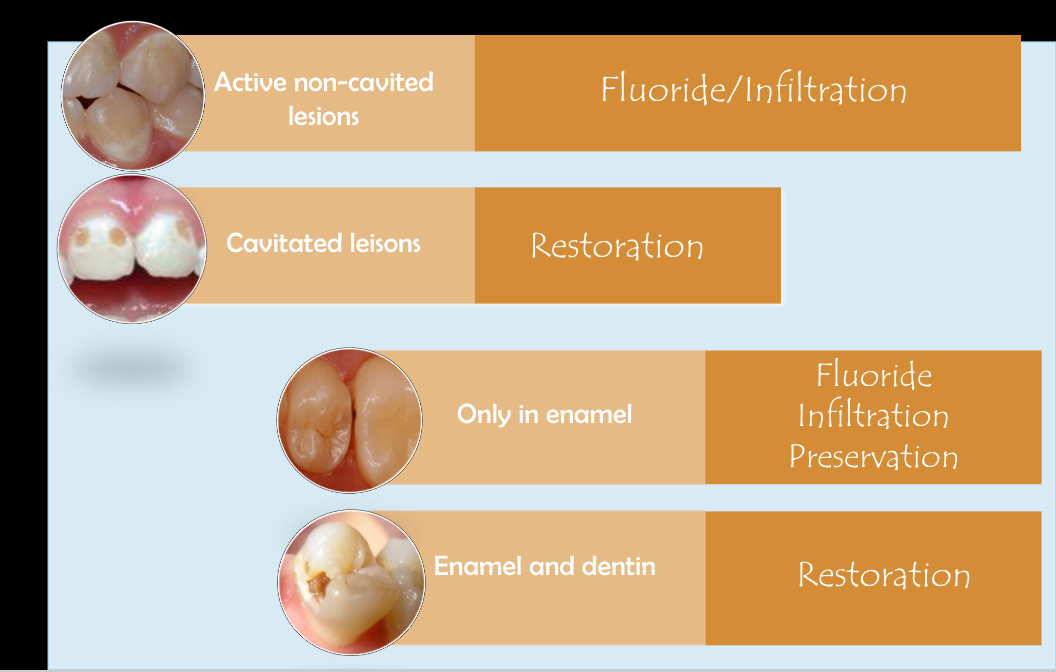
dental tx based on caries