353 Joint Replacement and Fractures
1/120
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
121 Terms
Who is at risk for fractures?
very young, very old, teenagers, athletes, those with poor vitamin D and calcium intake, women, those genetically predisposed, those who experienced trauma, and those with comorbidities like bone cancer, osteoporosis, HIV, and thyroid problems
Segmental Fracture
large fragments separate from main bone
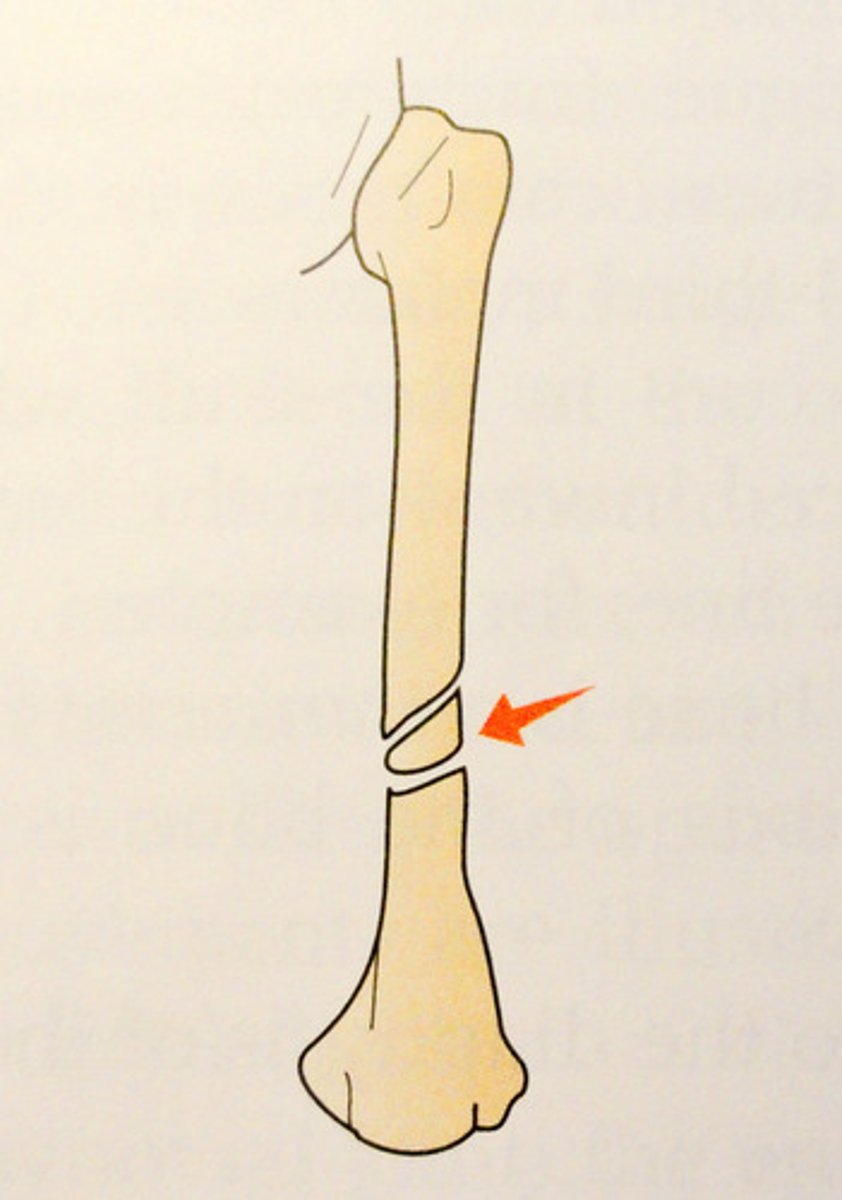
Displaced Fracture
separate, not aligned, two pieces not meeting anymore
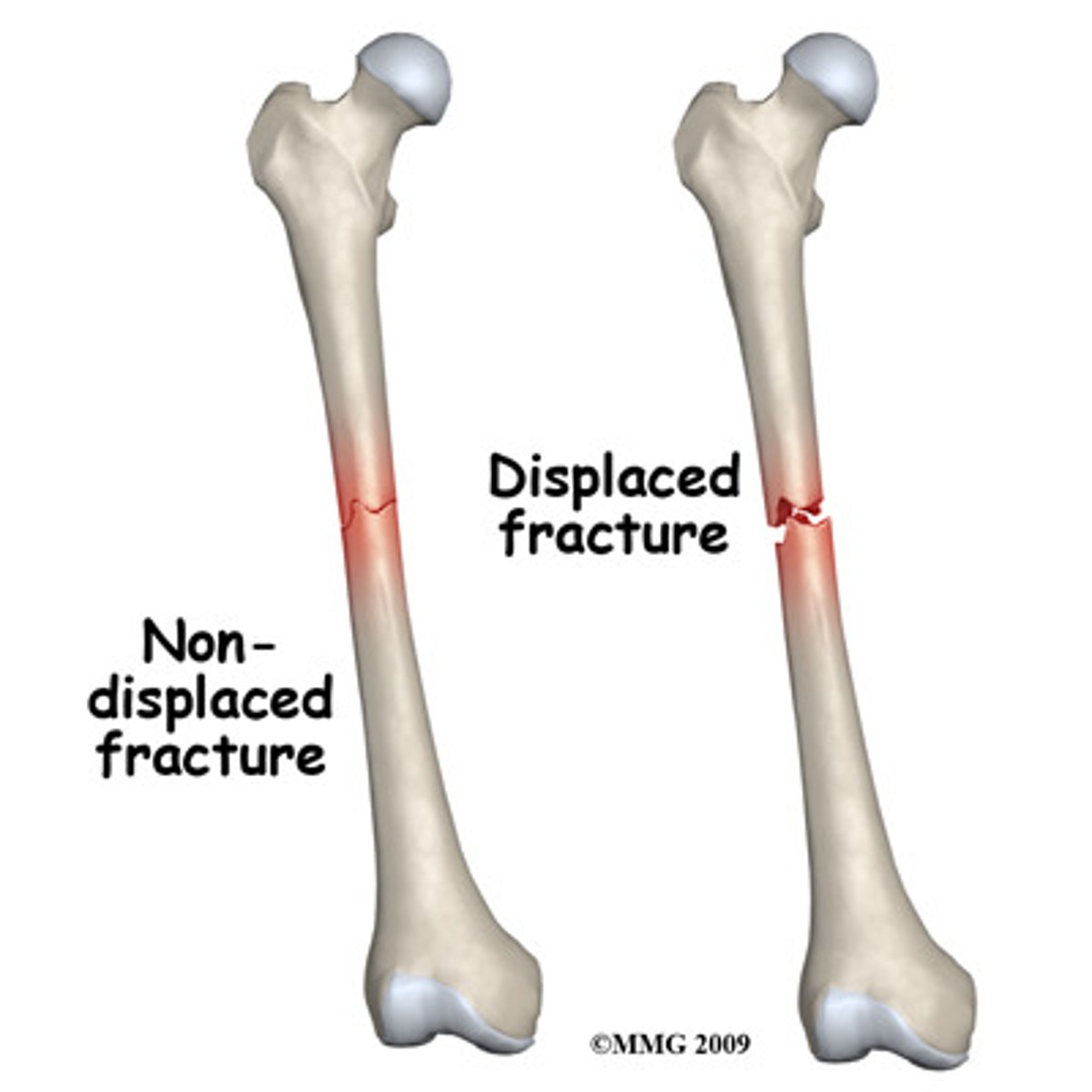
Non-Displaced Fracture
separate but aligned, pieces are right together, just separate and must be healed
Pathological Fracture
result of non-traumatic forces (frequently underlying illness), often missed, often as a result of another condition ie osteoporosis
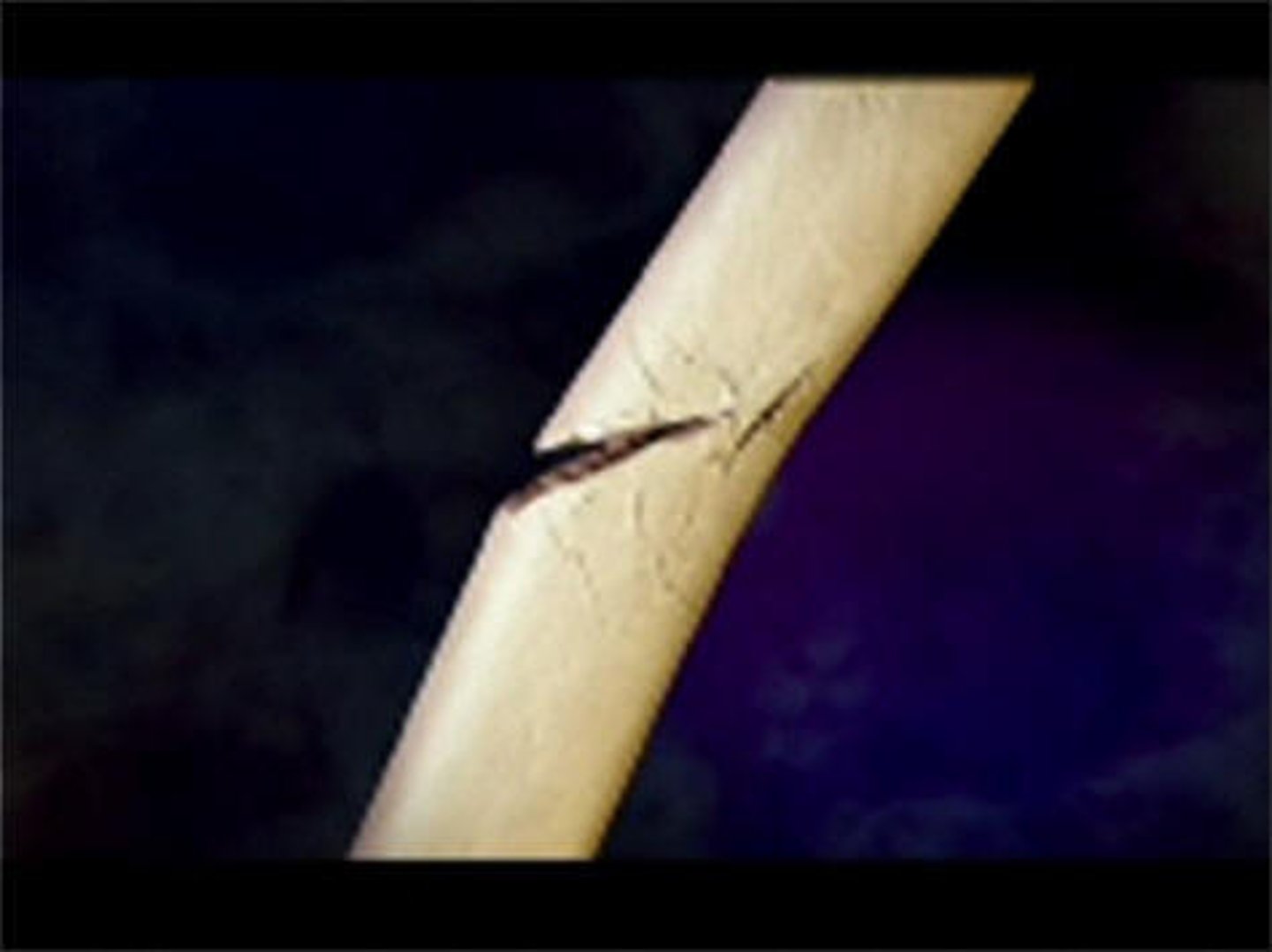
Incomplete Bone Fracture
goes through part of the bone (ie a crack)

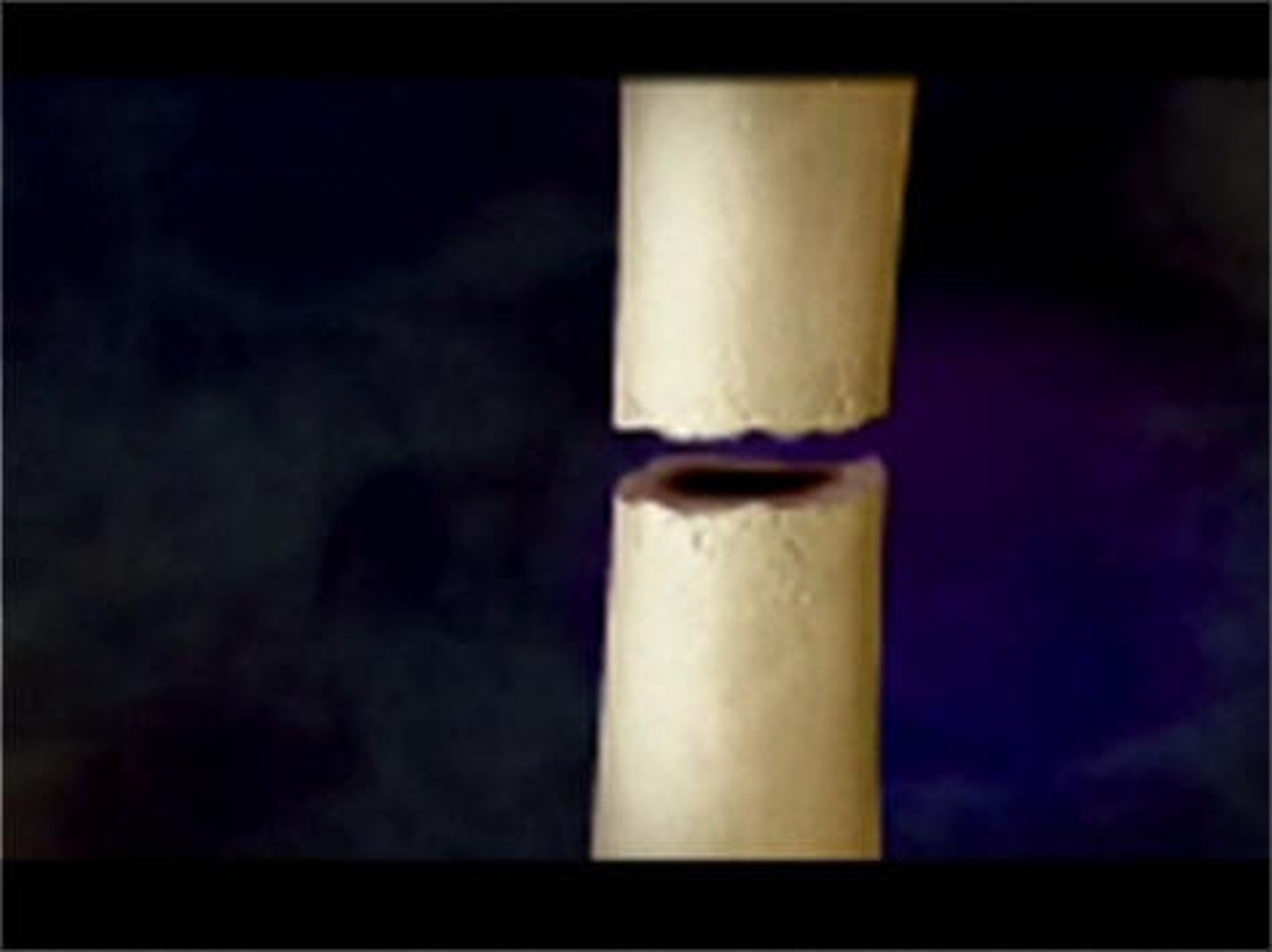
Complete Bone Fracture
goes through the entire bone, makes 2 separate pieces

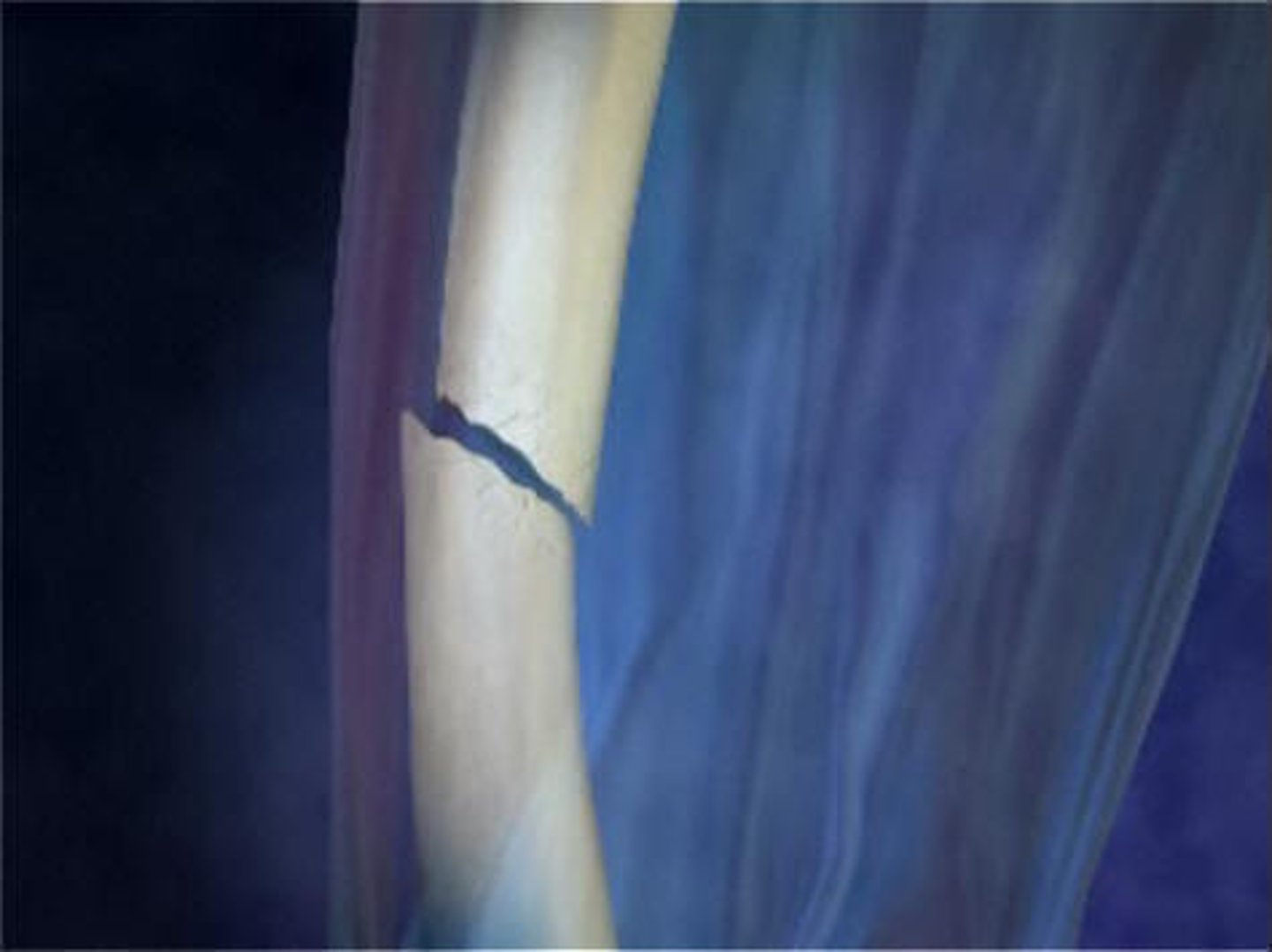
Closed/Simple Skin Fracture
skin remains closed or intact

Open/Compound Fracture
skin is open, greater infection risk
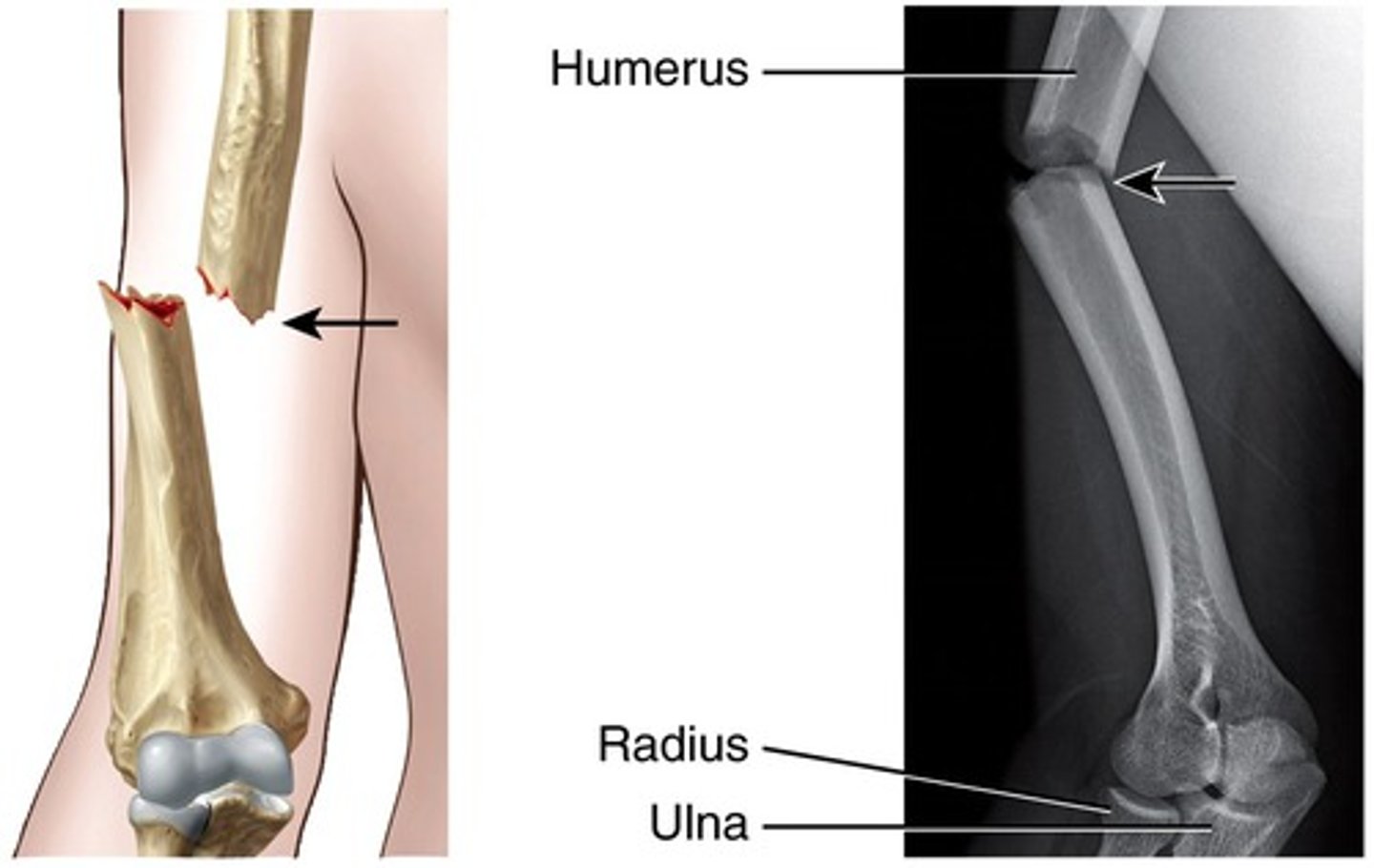
Comminuted Fracture
multiple tiny pieces (can be displaced or nondisplaced)
Avulsed Fracture
pulled away, ie caught in machine and breaks off
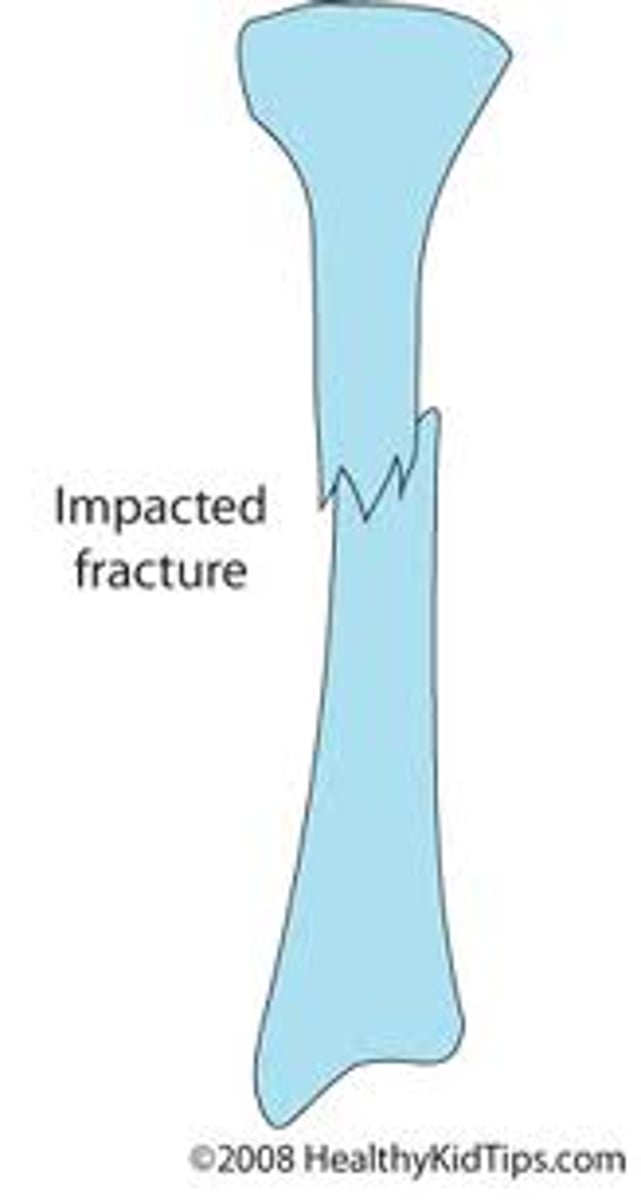
Impacted Fracture
instead of being pulled away, it is pushed down into rest of bone (ie land on something)
Transverse Fracture
transverse break across the bone
Oblique Fracture
oblique break across the bone
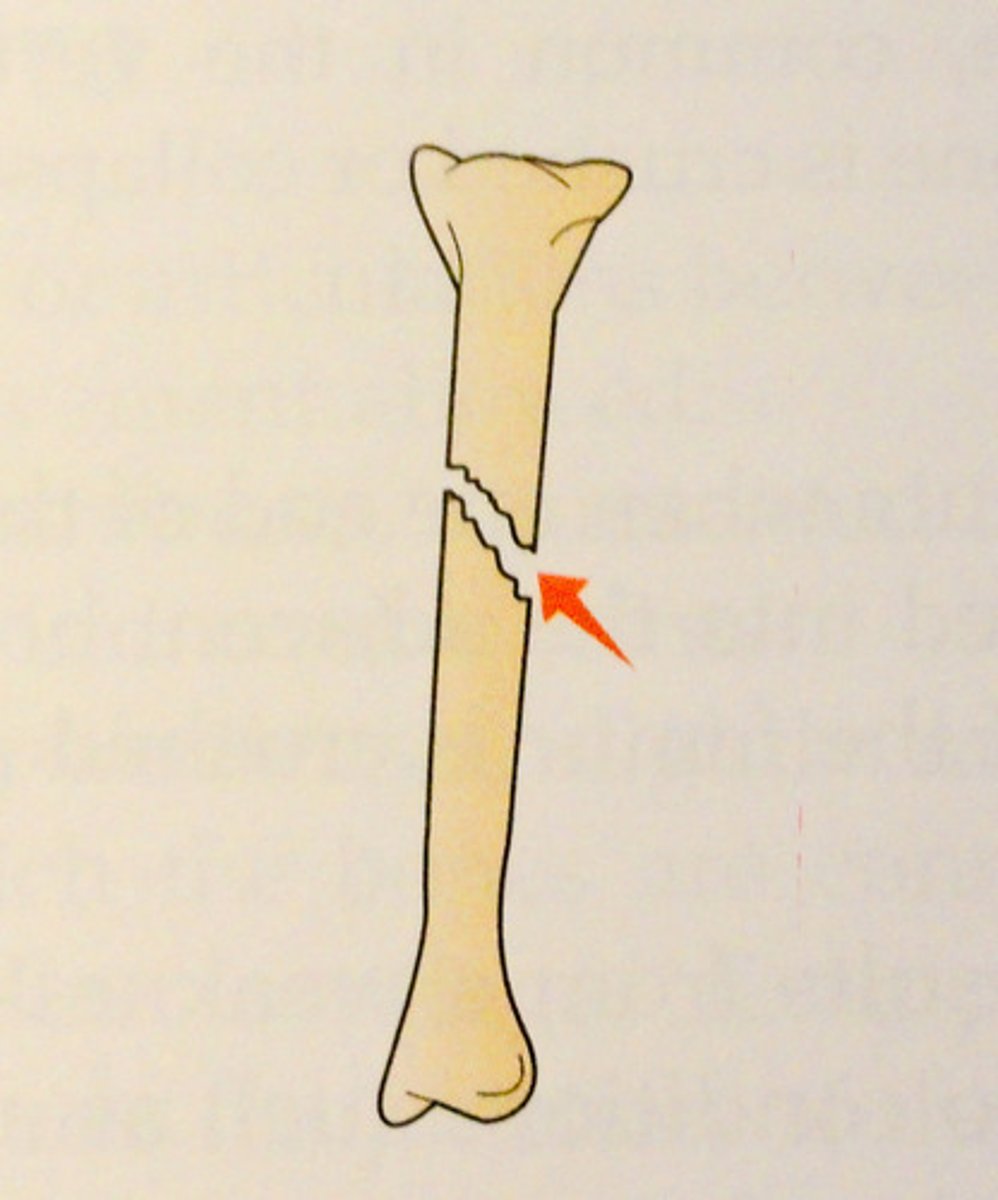
Spiral Fracture
like an oblique break but spirals around the bone
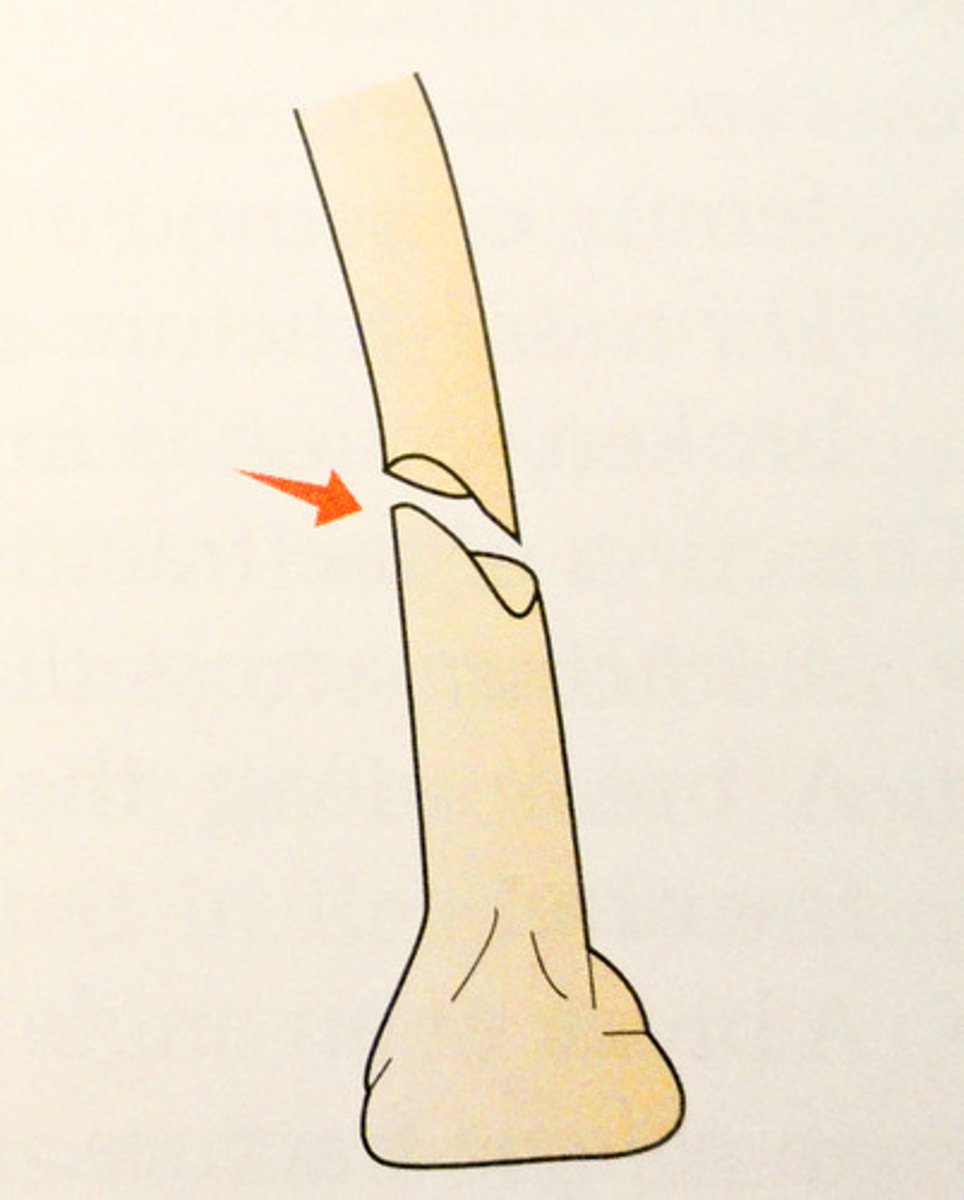
Greenstick Fracture
special case, usually only in kids, happens when your bones are softer, incomplete break like bending a green twig and it breaks on one side
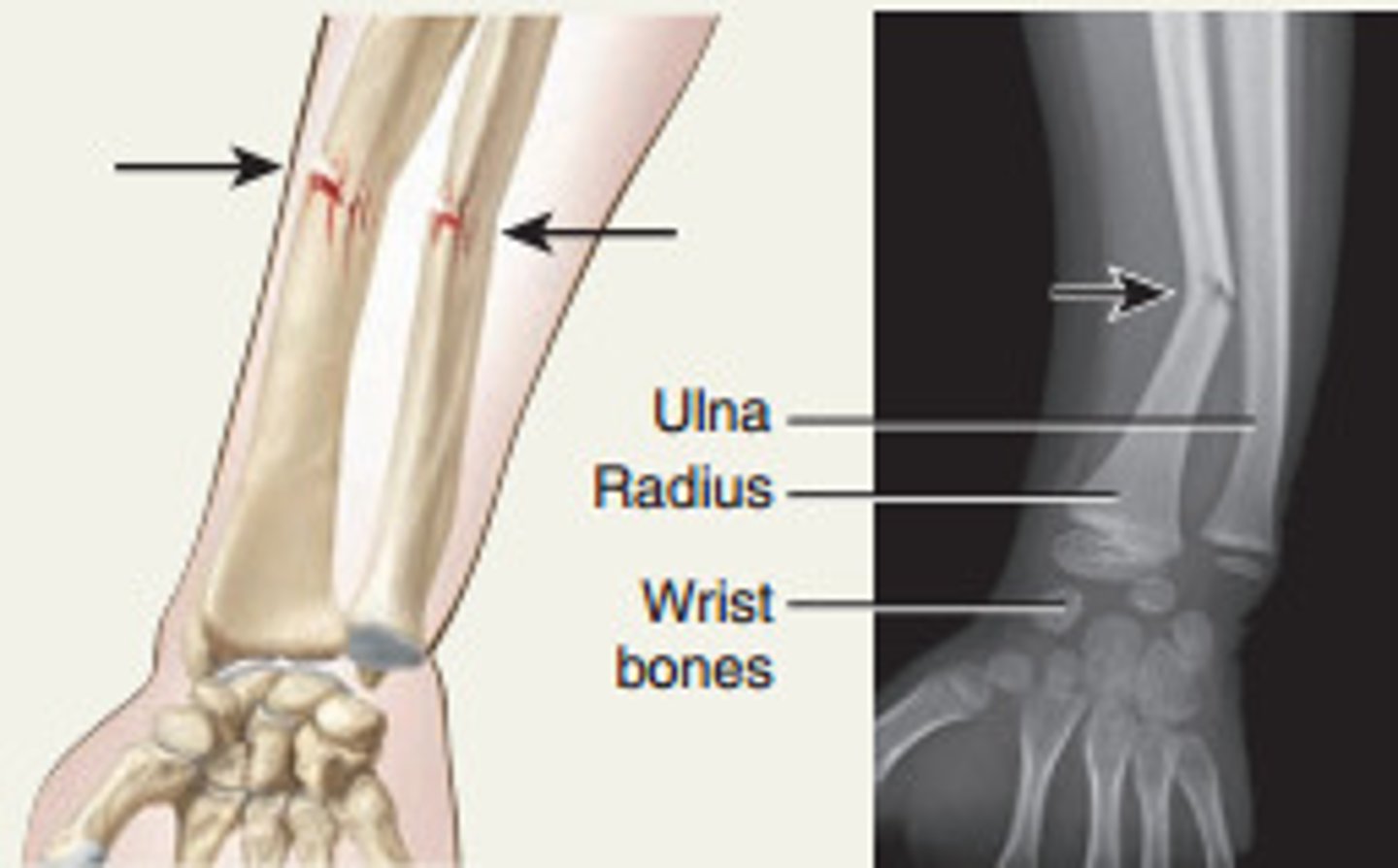
Torus/Buckle Fracture
special case, usually only in kids, happens when your bones are softer, bulge out in middle ie from being pushed down at both ends and it buckles/bulges in the middle
Diagnostic Tests for Fractures
XRAY (most common), CT Scan/MRI if xray not able to diagnose (ie small fracture), bone scane to determine fracture complications (ie if not healing properly)
General Assessment of Fractures
deformity, edema, pain, crepitus, spasms, ecchymosis, loss of function, abnormal ROM, circulatory compromise
What are the early 3 P's? CATCH EARLY
Pain (unrelieved with medication or elevation), paresthesia (numbness, tingling) and pallor (cap refill > 3 seconds, very pale, bluish fingers and toes
What are the late 3 P's?
polar (cool fingers/toes), paralysis (unable to move fingers/toes at all), pules (doppler only pulse, no pulse)
How do you treat more stable fractures?
external immobilization (casts, splints, traction)
How do you treat less stable fractures?
internal immobilixation (surgical procedures, skeletal traction, external fixator, internal fixation (ORIF), bone grafting)
Casts
rigid, external immobilizing device, usually for 6 weeks: immobilizies a reduced fracture, correct a deformity, apply uniform pressure to soft tissues, support to stabilize a joint
What is included in a cast?
the affected bone, as well as the joints proximal and distal
What are cast material options?
fiberglass: lightweight, durable, waterproof or plaster: cheaper, heavier, break apart when wet, require time to dry
Cast: Patient Assessment
check skin (intact, redness, rubbing causing an open area), neurovascular (check fingers for warmth, swelling), edema/swelling (if cast is too tight, swelling underneath, elevate to reduce swelling, expected initially but monitor for worsening)
Cast: Cast Assessment
dry, intact, low rough edges (that can rub and cause openings in the skin)
Cast Education
purpose/goals of cast, expectations during casting process, do not scratch or stick anything under cast, cushion rough edges, activity and mobility options, assistive devices
Cast Education After
control of edema and pain, exercises, safe use of assistive devices, signs and symptoms to report like persistent pain and swelling, changes in sensation, movement, skin color or temp, signs of infection, and burning or itching at pressure areas
Important Pressure Point in Leg Cast
pressure of the peroneal nerve from knee to outside of calf can cause foot drop, which leads to issues with walking and nerve damage can be permanent
What is a body cast?
encases the whole body
What is a spica cast?
encases the trunk and portions of 1 or 2 extremities
Considerations for Body and Spica Casts
requires multiple people to position patient, perineal opening must be large enough for hygiene
Watching for Cast Syndrome
mostly seen on casts that surround trunk, hard to take deep breaths, can be from compression of mesenteric nerve, claustrophobia, anxiety
What is traction (pull) immobilization?
pull of bones to keep things perfectly aligned, purpose is to: reduce muscle spasms, reduce, align, and immobilize fractures, reduce deformity, increase space between opposing forces
Skin/Manual Traction
short term intervention, increases comfort and reduces spasms, used before surgery, can be intermittent, weight limit maximums,
Skeletal Traction
long term intervention, more of a treatment, continuous (you don't take the pins out), pins are screwed through bones to maintain positions for healing
Advanced Skeletal Traction
not used often, particularly used if someone has multiple fractures, moved away from bc person is at risk for pressure ulcers, immobility
External Fixators
put pins in, attach metal cages that go around to keep things in place, external but fixated with pins, concern about infection due to wide opening where organisms can enter
Traction Nursing Responsibilities
skin: hydration, nutrition, reposition, avoid pressure ulcers, minimizing pressure on peroneal nerve, monitoring circulation, pulses and sensation, proper body alignment, inversion, eversion, preventing infection and performing pin care
Pin Care
goal is to prevent infection, initially sites are covered by sterile non-stick dressing to allow membrane to form, later use betadine, water/saline solution per policy/order to clean inner to outer around the pins, crusting may occur and it should be left
What is Open Reduction and Internal Fixation (ORIF)
surgical procedure that repairs bone using internal hardware, open skin and reduce fracture and put an internal fix ie hip replacement surgery
ORIF Nursing Responsibilities
routine post-op care, administer IV antibiotics as ordered, wound care as ordered, elevate extremity, assess neurovascular status frequently, monitor for signs of infection, assess for safety
What are all of the complications of a fracture?
compartment syndrome, FES, DVT, osteomyelitis, avascular necrosis/non-union, localized infection at pin site
Arthro-
a prefix meaning joint
Arthroscopy
the repair of joint problems through the operating arthroscope or through open joint surgery
Arthroplasty
forming a 'new joint'
Hemiarthroplasty
the replacement of one of the articular surfaces
Osteotomy
surgical cutting of the bone (bone spurs)
Prosthesis
artificial substitute for a missing part of the body or as a replacement (remove hip and put a new one in)
-plasty
to build or make
Hemi-
half
THA
Total hip arthroplasty = total hip replacement or THR
TKA
Total knee arthroplasty = total knee replacement or TKR
Component Materials
Plastic (polyethylene)
Metal: Cobalt-chrome or titanium (used for joint stem)
Ceramic: Actually a metal oxide (ball of joint)
Cement
Cementless Hip Prosthesis
(preferred method)
Have a porous coding (like english muffin) for bone to grow into to make a very stable joint over time (must be healthy bone)
Prosthesis is hammered into more precisely bored hole in the femur
Cemented Hip Prosthesis
The prosthesis is placed into a bored opening in the femur and surrounded by the bone cement
Bored opening does not have to be precise
Long term Complications of joint replacement
- Heterotopic ossification
- Avascular necrosis
- Loosening of the joint (not right away a bit down the line)
Heterotopic ossification
extensive bone growth in odd places
Avascular necrosis
lack of blood supply to an area
Respiratory toilet
(addresses cleansing)
C-DB and Incentive spirometer
Early ~ 3 Ps
Pain: Unrelieved with medication or repositioning/elevation
Paresthesia: Numbness, tingling, pins/needle sensation
Pallor: Cap refill time > 3 sec, bluish fingers, toes
Late ~ 3 Ps
Polar: Skin temperature - cool/cold fingers/toes
Paralysis: Unable to move fingers/ toes
Pulses: Palpable pulses, Doppler pulse, or no pulse
Preventing dislocation
avoid flexing hip >90 and no internal or external rotations
Compartment syndrome
Reperfusion swelling, initial injury has happened, WBCs and all things go to area of injury, all fluid and bleeding leads to→ increased pressure within muscle compartment(s) → (possible permanent damage)
- EXTREMELY PAINFUL
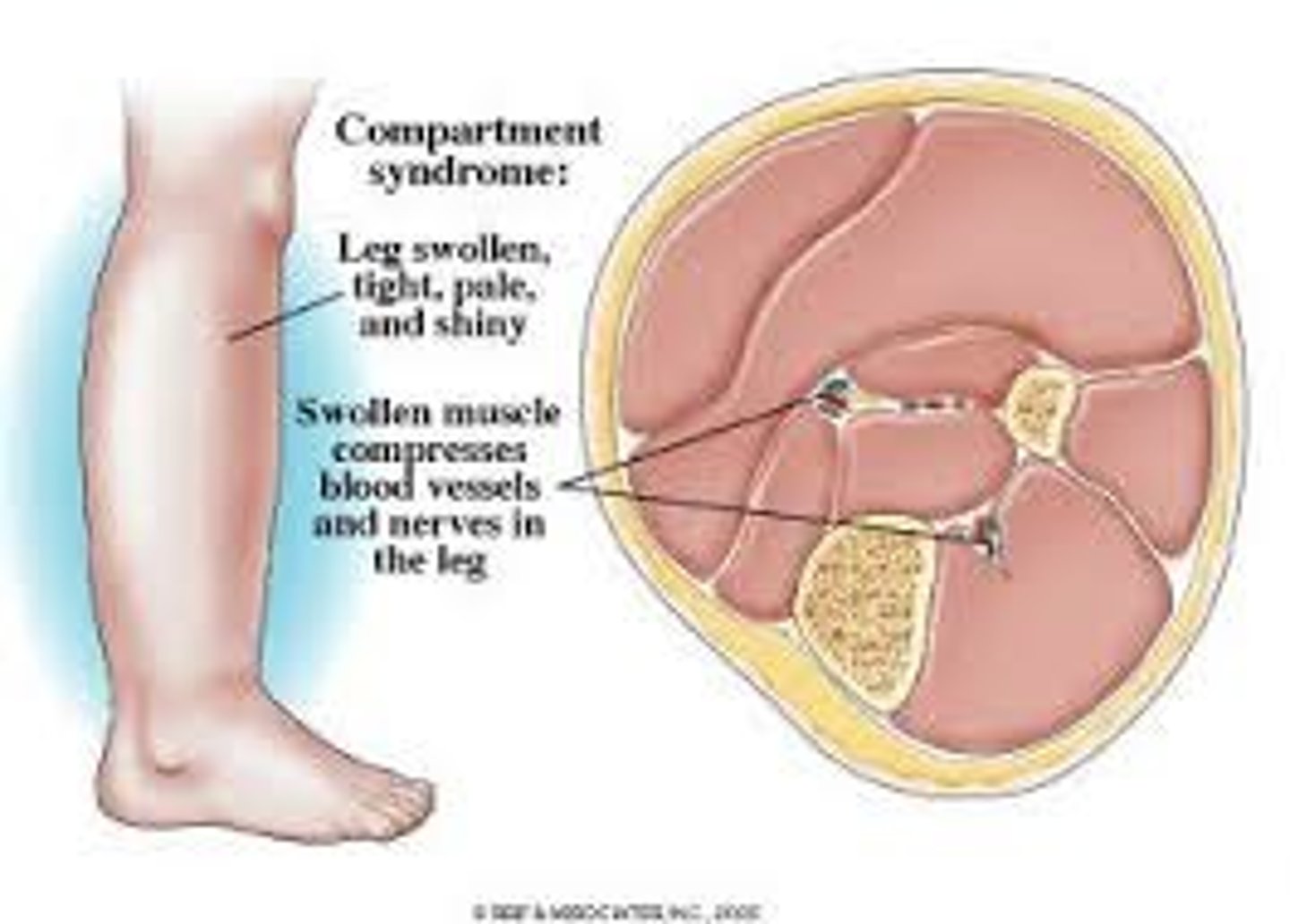
Compartment syndrome: Within 4-6 hours if nothing is done
Necrosis (tissue death)
Neuromuscular damage
Death (severe)
Fasciotomy
a surgical incision through the fascia to relieve tension or pressure
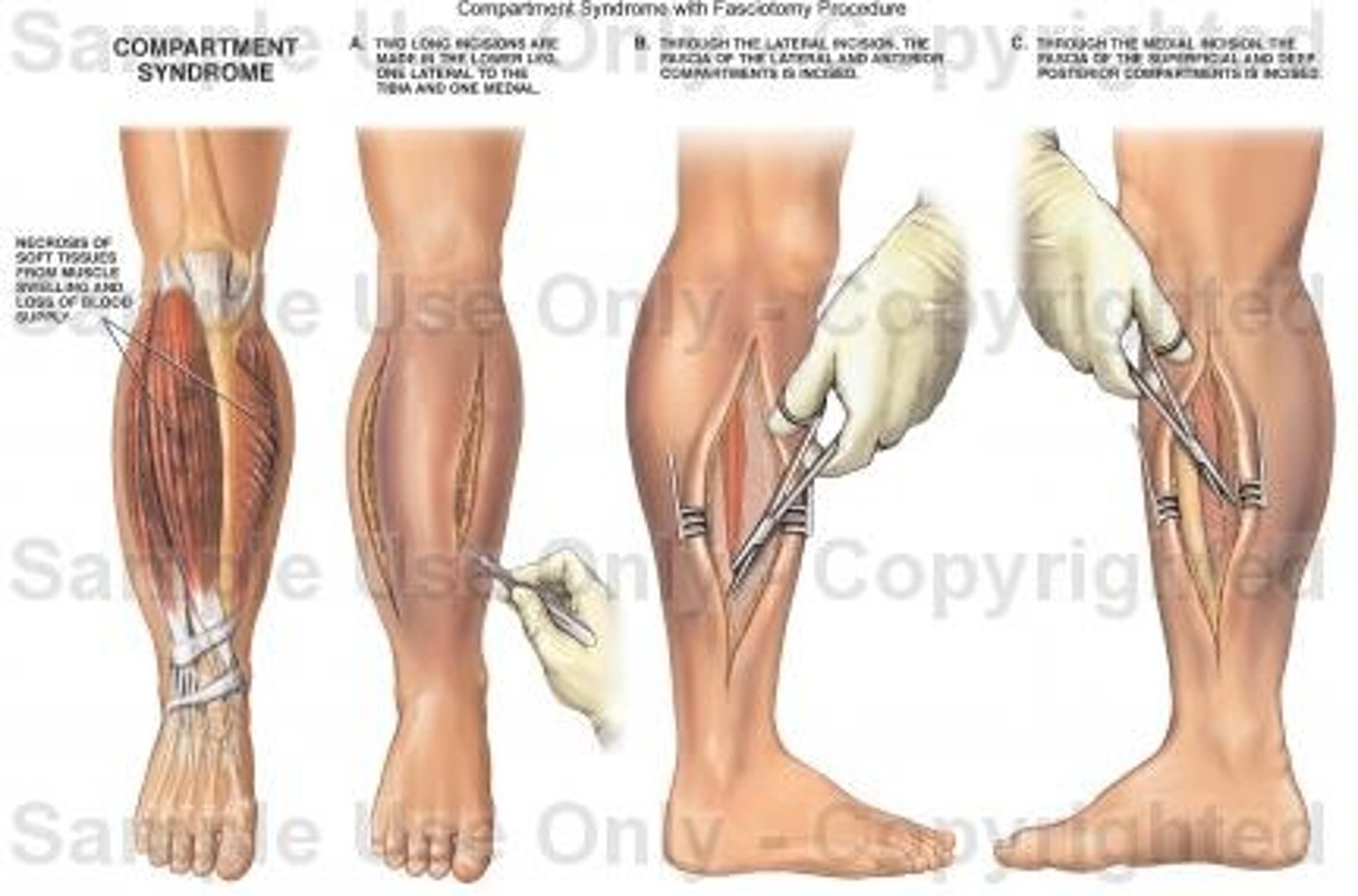
How does compartment syndrome present
(leg can feel "tight")
Pain
Edema (may or may not be seen bc most of the pressure is inside)
Anxiety
Compartment syndrome interventions
1. Analgesics as ordered (if they don't work worry ab something else being wrong)
2. Elevate extremity (help decrease fluid)
3. Educate/answer questions
Fat Emboli Syndrome (FES)
Long bone/hip fracture (femur fracture)
- No treatment (supportive, maintain O2 and circulation) - prevention!
FES: Clinical Presentation
(unique trio)
- Respiratory compromise (seen first, Hypoxemia may be detected hours before the onset of respiratory complaints (IMPORTANT)
Check O2 saturation)
- Cerebral dysfunction (acute confusion)
- Petechiae (pinpoint purple areas, upper torso)
FES: Diagnosis
Hypoxia, with a paO2 < 60 mmHg and
Hypocapnia withrespiratory alkalosis
DVT
Most common complication following trauma, surgery or disability
- Can still feel pulses
- Swelling → Decrease pedal pulse
Osteomyelitis
Inflammation or infection of the bone because of penetrating organisms - Staphylococcus aureus most common
- At risk: patients with diabetes, had orthopedic surgery, previous history
- Approximately 20% to 30% will experience recurrence within 2 years, even with appropriate medical and surgical treatment
Risk reduction of Osteomyelitis
Open fractures who receive antibiotics within 6 hours of injury and prompt surgical treatment
Avoid health care-associated osteomyelitis
Osteomyletis: Diagnosis
biopsy and culture
Osteomyelitis Treatment
Long term antibiotic therapy (3 months)
Surgery/ Debridement to clean out area
Nurse Prevention of Osteomyelitis
Maintain "separation" from potential infectious agents (treated for open fracture or hip replacement will be in different areas)
Non-Union
(bone edges do not heal together)
What is compartment syndrome?
reperfusion and accumulation of fluid and WBCs that increases pressure within muscle compartments and compresses nerves and blood vessels
How do you diagnose compartment syndrome?
use a device and stick into the compartment to measure the pressure
What happens in 4-6 hours of compartment syndrome if nothing is done?
tissue necrosis, neuromuscular damage, death
What are compartment syndrome human responses?
pain, edema, anxiety, leg is tight
Compartment syndrome nursing interventions
analgesics as ordered, elevate extremity, educate and answer questions
Compartment Syndrome medical treatment
control/reduce swelling, elevate, release restrictive dressings if too tight, fasciotomy and leave open to relieve pressure butt cover with moist, sterile dressing
Nursing Responsibilities for Fasciotomy
analgesics as ordered, elevate extremity, maintain moist, sterile dressing, monitor incision, labs, VS, antibiotics as ordered, diet for healing, routine post-op care
What is FES (fat emboli syndrome)?
fat gets into blood stream and causes embolus/globuli
What is the profile of someone who gets FES?
youth, cast (instead of ORIF), closed fracture, long bone, necrosis of bone marrow, trauma
FES Treatment
there is none, only prevention
FES Preventative Care
recognize profile and increased risk, maintain adequate oxygenation and ventilation, stable hemodynamics (BP), hydration and nutrition, early ambulation, monitor labs, VS, ABGs
What is the FES triad?
respiratory, cerebral, petechiae
When does FES occur?
24-72 hours after fracture/trauma
What are the manifestations of FES?
respiratory compromise: tachypnea, dyspnea, cyanosis, elevated temp, low Hct, hypoxemia, cerebral dysfunction: confusion, drowsiness, convlusions, coma, petechiae: pinpoint, purplish areas where fat blocks small blood vessels and causes bleeding, usually in upper torso but can be in neck and eye
What is the diagnosis for FES
clinical picture and risk factors, rule out alternative pathologies, blood gasses, chest xray
FES Nursing Interventions
telemetry, ventilation via face mask or mechanical ventilator, nutrition, adequate hydration, foley catheter, SCDs, air mattress, good eye care, ongoing diagnostics
DVT/VTE
blood clot that originates in a deep vein in the body ie lower extremity, can still feel pulse since clot is in vein but see swelling since you can't get blood back to the heart, MOST COMMON POST OP COMP
DVT Human Responses
pain, swelling, decreased pedal pulse
DVT Nursing Prevention
OOB, leg/ankle exercises, adequate hydration
DVT Nursing Responsibilities
analgesia, assess pulses/pain/swelling, report to PCP