Chapter 2 Genetics | Oxford Science 10 Australian Curriculum
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
gene
basic unit of genetic material passed on from parents to offspring
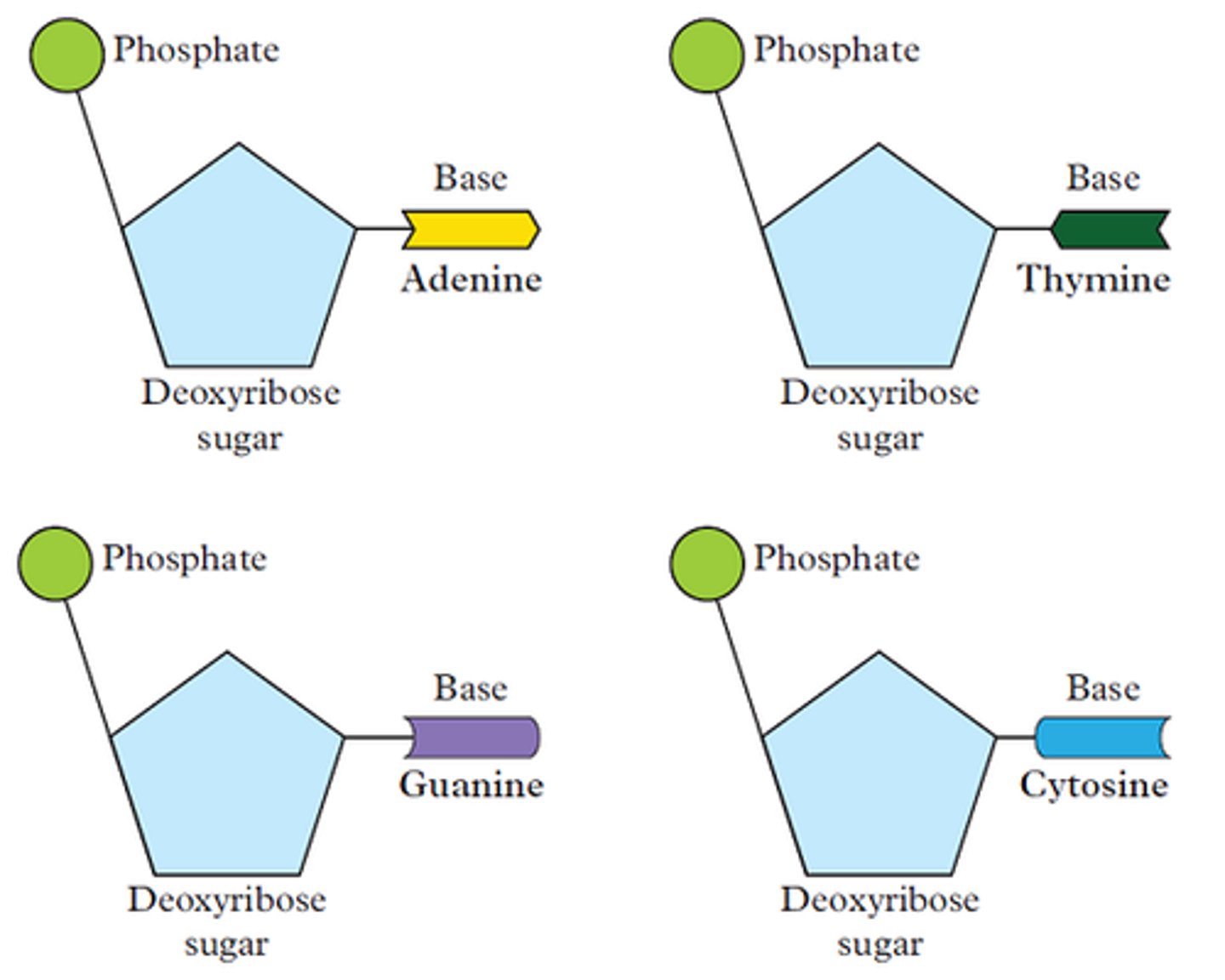
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)
a molecule that contains all the instructions for every job performed by the cell; this information can be passed from one generation to the next
hydrogen bond
a type of weak chemical bond between two groups of atoms; the bond between two nitrogen bases in the DNA helix
complementary base
a nucleotide base that pairs with its partner nucleotide on the alternative DNA strand; adenine pairs with thymine, cytosine pairs with guanine
chromosome
the form of DNA that is tightly wound around proteins before replication
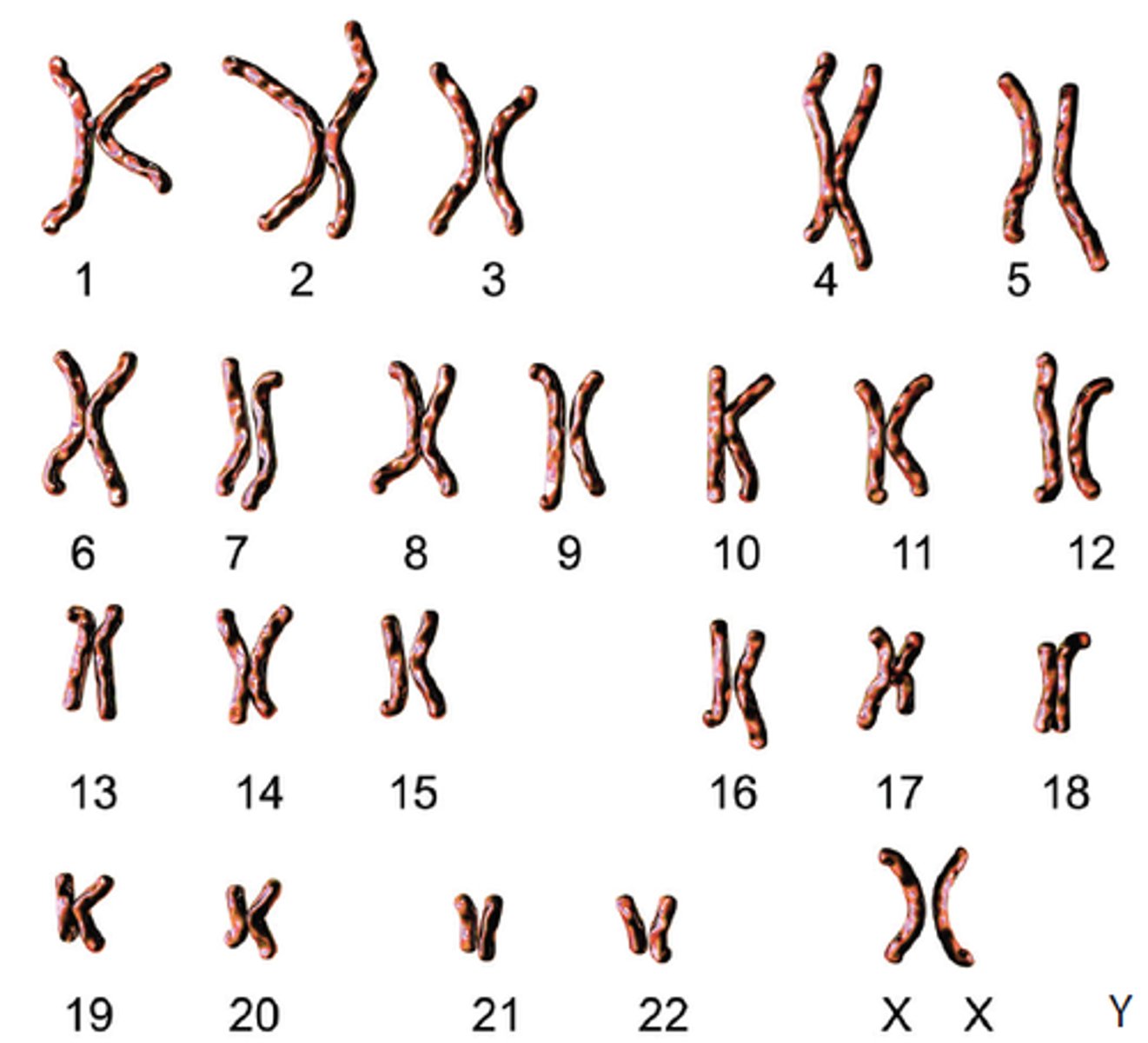
karyotype
a way of representing a complete set of chromosomes, arranged in pairs, in order of decreasing size
chromatid
one side of the X-shaped chromosome that contains a double helix of DNA
genetic code
the sequence of nucleotides in DNA, inherited from parent organisms
transcription
the process of copying the DNA that makes up a gene to messenger RNA
somatic cells
the body cells except gametes (egg and sperm)
interphase
a phase of cell life where normal functioning occurs
dominant trait
a characteristic that needs only one copy of an allele to appear in the physical appearance of an organism
recessive trait
a characteristic that is only expressed in the phenotype when two identical alleles are inherited
co-dominant
two different alleles that can both appear in the phenotype at the same time; both can appear with a single allele
achondroplasia
a genetic (inherited) disorder of bone growth resulting in abnormally short stature and short limbs
substitution mutation
a form of mutation where one nucleotide is substituted for another; may or may not result in a deformed protein
stem cell
a cell that can produce different types of cells; adult stem cells can produce a limited number of cell types (e.g. skin stem cells), whereas embyronic stem cells can produce many types of cells
nucleotide
a subunit of a nucleic acid
translation
the formation of a protein from RNA; occurs on a ribosome
codon
a group of three nucleotides on mRNA
mitosis
the process of cell division that results in genetically identical daughter cells; allows growth and repair
cytokinesis
the splitting of a replicating cell into two cells
diploid
containing two complete sets of chromosomes
apoptosis
programmed cell death
meiosis
the process that results in the formation of gametes with half the genetic material of the parent cell
haploid
containing one complete set of chromosomes in each cell; an example is gametes
allele
a version of a gene; a person inherits two alleles from each gene, one coming from each parent
homozygous
having two identical alleles for a particular trait
heterozygous
having two different alleles for a particular trait; a carrier for a recessive trait
carrier
a person who has the allele for a recessive trait that does not show in their phenotype
genotype
the combination of alleles for a particular trait
phenotype
the physical characteristics that result from an interaction between the genotype and the environment
Punnett square
a diagram used to predict the outcome of breeding organisms
autosome
a chromosome that does not determine the sex of an organism
sex chromosome
a chromosome that determines the sex of an organism
pedigree
a chart showing the phenotypes for an individual and their ancestors, usually over several generations; also known as a family tree diagram
mutation
a permanent change in the sequence or amount of DNA
mutagen
a chemical or physical agent that causes a change in genetic material such as DNA
frameshift mutation
a type of mutation in which a nucleotide is added or deleted, causing a shift in the reading frame of codons; usually results in a deformed protein
non-disjunction
the failure of one or more chromosomes to separate during meiosis; can result in an abnormal number of chromosomes in the daughter cells
maternal serum screening (MSS)
the genetic testing of fetal DNA found in the mother's blood
newborn screening
the testing of chromosomes in a baby's white blood cells for the presence of a genetic disease
early detection and predictive testing for adults
the testing of chromosomes for the presence of alleles that increase the probability of cancers forming
genetically modified organism (GMO)
an organism that has had its DNA changed in a laboratory
transgenic organism
an organism that has a gene from another organism inserted into its own chromosomes
genetic engineering
the deliberate engineering of change in the DNA of an organism
gene cloning
the production of identical copies of a gene
gene therapy
inserting a new healthy allele into an organism to treat a genetic disease