Muscle Tissue (lecture)
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
What are the 4 characteristics of muscle tissue?
Excitability (responds to stimulus)
Contractibility
Distendability (stretch to limits without damage)
Elasticity (stretch + recoil) - titin
Is skeletal tissue voluntary or involuntary?
Voluntary (can be controlled)
What are the 6 functions of skeletal muscle tissue?
Produce skeletal movement (only pull, NOT push)(Please)
Maintain posture and body position (muscles contract to hold body in place)(Make)
Support soft tissues (Snacks)
Guard entrances and exits(Gremlins)
Maintain body temperature (energy not converted=heat, shivering=rapid contraction)(Might)
Store nutrient reserves(Starve)
What are the 4 components of skeletal muscle?
Muscle tissue (cells or fibers)
Connective tissues
Nerves
Blood vessels
Myo-, Mys-, and Sacro- refer to what?
Muscle
Hypo- means is what?
Below
Hyper- means what?
Above
Epimysium is made up of what, connected to what, and surrounds what?
Collagen layer
Deep fascia
Muscles (to separate from surrounding tissue)
Perimysium surrounds what and contains what?
Muscle fiber bundles (fascicles)
Blood vessel and nerve supply to fascicles
A bundle of muscle fibers is what?
A fascicle
Endomysium surrounds what and contains what?
Individual muscle cells (muscle fibers) - may fuse together
Capillaries and nerve fibers (contacting muscles cells)
Myosatellite cells (stem cells) repair damage
Endomysium, perimysium, and epimysium come together to form what?
Tendons or aponeurosis (sheets, flat)
Connective tissue attachment to bone matrix
Skeletal muscle cells develop through fusion of what cells?
Myoblasts
The cell membrane is known as what?
Sarcolemma
The cytoplasm is known as what?
Sarcoplasm
Transverse tubules (T tubules) are similar to what and perform what?
Sarcolemma properties
Transmit surface action potential (electrical charges) through deep cell
Myofibrils can be compared to cigarettes in what way?
Box holding cigarettes=muscle cell
Cigarettes=myofibrils, specialized organelle running through muscle fiber
Tobacco=myofilaments, bundles of protein filaments that make up myofibrils
Thin filaments are made up of what?
Actin
Thick filaments are made up of what?
Myosin
The Sarcoplasmic Reticulum (SR) surrounds what, what is its structure, and what is it attached to?
Myofibrils
Web-like
Chambers (terminal cisterna) attached to T tubules
A triad is a part of what and formed by what?
Sarcoplasmic Reticulum (SR)
Formed by T tubule (in middle) and two terminal cisternae (on sides)
What is cisternae apart of and what does it do?
Triad
Store/concentrate calcium via ion pumps
Release calcium into sarcomeres for muscle contraction
What are the dark, thick of myofibrils?
A bands
What are the light, thin filaments of myofibrils?
I bands
Sarcomeres do what in myofibrils?
Contract (structural)
Z line to Z line
The A band is the darker or lighter filament?
Darker
What line is found in the center of the A band and midline of sarcomere?
M line
What is the area of no overlap around the M line with thick filaments no thin filaments?
H band
What is the densest, darkest area on a light micrograph where thin and thick filaments come together? This allows for what and what happens to the sarcomere?
Zone of overlap
Allows for muscle contraction
Shortens sarcomere
Z lines are in the center of what bands and where are they in relation to sarcomeres?
I bands
AT the ends
Titin are made up of what, function to do what, and are found where?
Strands of protein
Between tips of thick filaments and Z line (horizontal)
Stabilize filaments and provide elasticity to muscle tissue
F-actin is like a pearl necklace in what way?
G-actin is twisted into two rows as the pearls of the necklace, F-actin
The active sites on G-actin bind to what?
Myosin
F-actin is a thick or thin filament?
Thin (needs all the help to stabilize)
What structure holds F-actin together (runs down the middle horizontally)?
Nebulin
Tropomyosin looks like what and prevents what?
Double twisted strand
Prevents actin-myosin interactions by covering active/binding sites
Troponin is made up of what kind of protein and binds what to what?
Globular protein
Binds tropomyosin to G-actin
Troponin is made up of what 3 structures?
TnI
TnT
TnC
TnI is what?
Inhibitory (last in line)
TnT attached to what?
Attaches troponin to tropomyosin (first in line)
TnC is where what binds?
Calcium (in the middle of line)
How does troponin change shape and allow for muscle contraction?
1. Calcium comes from SR and binds to TnC (changing troponin shape)
Causes tropomyosin to pull off from active site and allow for contraction
Thick filaments contain what kind of subunits?
Myosin
What does the tail of myosin do?
Bind to other myosin molecules
The head of a myosin molecules is made up of what?
Two globular protein subunits, actin binding site, ATP binding site, and ATPase (breakdown ATP for energy)
What is the function of dystrophin?
Links actin in outermost myofilament to transmembrane proteins and eventually to fibrous endomysium (surrounding entire muscle cell)
Transfers force of muscle contraction to connective tissue around muscle cell
Genetic defects produce diseases, muscular dystrophy
In the sliding filament theory, what zone stays the same, decreases, and what line moves closer?
A zone stays the same
I band and H zone decrease
Z lines move closer together
What is the synapse?
Point where nerve fiber meets its target cell (sometimes a muscle fiber, neuromuscular junction)
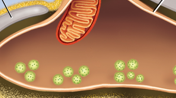
The swollen end of nerve fiber containing synaptic vesicles filled with acetylcholine (ACh)
Synaptic knob

Tiny gab between synaptic knob and sarcolemma
Synaptic cleft
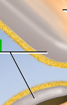
This cell envelops and isolates NMJ from surrounding tissue fluid
Schwann

They undergo exocytosis releasing ACh into synaptic cleft
Synaptic vesicles
A lack of ACh receptors in the muscle cell plasma membrane leads to what?
Paralysis in disease myasthenia gravis