Introduction: Drug Action/dosage Regimen (Cram)
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Why might some exotics need less sedative than expected?
Many exotics are nocturnal, they often don't need that much sedative to become sedate during the day
What are the six factors that modify drug action and dosage regimen?
Remember: STRIP Down
Speceis variation
Timing of administration
Route of administration
Individual variation
Pathological conditions
Drug augmentation
What requires a lower dose of medication to have a greater response: IV or SQ route?
IV, because a larger amount of the drug will be in the plasma at one time
Fill in the blank: Lidocaine if administered SQ acts as a ______ anesthetic, while administering it IV it affects the ______ [organ].
local, heart (it can be used to treat ventricular tachycardia)
Fill in the blank: ____ depressant drugs are more potent at night while ______ produce greater effects during the day.
CNS, stimulants
What two factors vary greatly with the season of the year, or with the animal's intrinsic biological clock?
- Hormone levels
- Metabolic activity
What are some examples of individual varition?
Weight, age, sex, temperament, and biochemical individuality (inherited), idiosyncrasy, drug hypersensitivity, hyperreactive, hyporeactive, tolerance (resistance)
Fill in the blank: Difference in response to a drug may be ______ (degree of) or ______ (nature of).
quantitative, qualitative
What are the three mechanisms that may result in tolerance
- Cells may increase biotransformation of drug
- Cells may adapt
- Increased excretion or decreased absorption of drug
Why might a cat with kidney disease need a different dose of a drug than a healthy cat?
If the kidney disease is effecting excretion, the drug dosage will need to change to reflect this
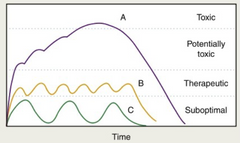
Explain this graft
This represents drug augmentation, due to cumulative dosing. In A, the first dose of the medication is not totally cleared from the plasma before the next dose is introduced. If this continues, it can lead to a toxic dose. B is what we want
Name some of the possible methods of drug interactions
Increasing absorption of each other, receptor interference, increase or reduce biotransformation of another, interfere with excretion, chemical reaction in body, and bind with one another (making inactive)
The movement of drugs in the body after they are absorbed into the blood stream
Drug distribution
Fill in the blank: Drugs move across ______ and in and out of tissues and cells in response to a _______ _______.
membranes, concentration gradient
What are the three things that the distibution of a drug from plasma into different tissues depends upon?
- Lipid solubility (the greater the lipid solubility, the greater the tendency to move into tissues)
- Non–ionized drugs move into the tissues more readily
- Affinity of the tissues for the drug
What are the three storage areas for drugs in the body?
- Plasma proteins (usually albumin)
- Other (fat, liver, kidney, bone, muscle, etc.)
- Cell storage (bound to proteins in the cell)
What is the "active drug", the amount bound to plasma proteins, or the amount that is not bound and can enter tissues?
The active drug is the amount that is not bound and can enter tissues
What is the most important factor affecting drug distribution?
Binding of the drug to plasma proteins
Fill in the blank: There is usually a _______ _______ between bound and free drug in the plasma. This means that when free drug leaves the plasma, some bound drug is released to restore the balance in the blood.
dynamic equilibrium
A patient has hypoproteinemia, should it be given a larger or smaller dose of a drug (especially a drug that tends to bind to plasma well)?
Smaller dose. The binding of all the protein availible in their blood will mean dynamic equilibrium is impossible to maintain. An overdose is very possible
Give two example of specialized barriers in the body
- Blood–brain barrier
- Placental barrier
What type of cells form the blood–brain barrier? They surround the capillaries of the brain
Glial cells
Fill in the blank: The glial cells typically only allow _____- soluble, very small non-______ molecules. And very small ______, _______-soluble molecules to pass through.
lipid, ionized, ionized, water
Which dog breed is known to have a more permeable blood brain barrier?
Border collie
True or false: Drugs tend to pass more readily into the brain of neonates
True. The barrier is more permeable in neonates, making the toxic effects greater
Do highly ionized or non–ionized compounds generally penetrate the blood brain barrier more readily?
Non–ionized compounds penetrate more readily
True or false: Traumatic injury, inflammation, and allergic reactions all increase the permeability of the CNS membranes
True
A patient under anesthesia is experiencing respiratory depression, some hypoxia, and a severe drop in blood pressure. How will this affect the blood brain barrier?
It will make it more permeable, which will further depress the respiratory centre, initiating a life–threatening vicious cycle
Fill in the blank: ____-_______, highly _______-soluble compounds move very rapidly into fetal circulation from the mother's blood. These compounds should NOT be used on a pregnant female without considering fetal harm.
Non, ionized, lipid
True or false: Fetal blood concentrion of a drug will never reach the same concentration as maternal blood concentration
False. Fetal blood concentration can become even HIGHER than maternal blood concentration
The phenomenon of the final distribution of drugs in the body not being the same as the initial distribution
Redistribution
Example: The effects of barbiturates are short acting because they are redistributed from the brain to the fat tissues
Any chemical alteration of the drug molecule by the cells of the animal
Biotransformation
Note: Also called drug metabolism
Drugs must be lipid–soluble and non–ionized in order to move across membranes to reach the sites where they'll be active. Can they be excreted in this form?
No. The kidneys will just reabsorb them back into the bloodstream. They need to be converted into a different form
End products of biotransformation
Metabolites
Note: These are more water–soluble and ionized than the drug, they can be excreted in urine and bile
What are the four qualities of metabolites that make them easier to excrete?
- More ionized
- Less able to bind to plasma protein or cellular protein
- Less likely to store in tissues such as fat, muscle, and kidney
- Less able to pass through membranes
Are metabolites usually more or less active than the original drug?
Usually they are less active, but sometimes they are more active
Principle site of biotransformation in the body
Liver
Which organelle in heptaocytes is responsible for metabolizing drugs?
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Name some other tissues that are biotransformation sites in the body
Nervous system, kidney, small intestine, and plasma
If a drug is administered PO or IP and is absorbed first by the intestine, does it still go to the liver?
Yes, it will travel through the circulation directly to the liver and may be metabolized and/or inactivated before even entering sysmic circulation (ie. first pass metabolism)
What are the four types of reactions involved in drug metabolism? Star which 3 types of reaction may increase OR decrease a drug's activity
- Oxidation *
- Reduction *
- Hydrolysis *
- Conjugation
Note: Conjugation almost always decreases a drug's activity
Splitting a molecule and adding H2O to each part
Hydrolysis
Addition of O2 and/or loss of H+ ion
Oxidation
Gaining an H+ ion
Reduction
Reaction in which the drug is combined with an already existing substance
Conjugation
True or false: Most drugs undergo 100% biotransformation
False. Very few drugs undergo 100% biotransformation. The small unchanged quantities are what can be detected on drug tests
True or false: Newborns and older animals are generally faster at biotransforming drugs
False. Newborns are deficient in the drug metabolizing liver enzymes, and older animals have a decreased ability to synthesize these enzymes. Biotrasformation will be delayed in these animals
True or false: Different species have different levels of enzymes, including those used to metabolize drugs
True. This means that some drugs that are metabolized rapidly by some species can be toxic in others, for whom it takes too long because of a lack of enzymes
Is estrogen or testosterone known to depress some types of metabolism?
Estrogen. Because of this, some drugs can be more dangerous for female animals
Organ that excretes more drugs than any other organ. Proper function of this organ is very important when considering use of some drugs
Kidney
Fill in the blank: In the kidney most drugs are filtered from the blood in the _______ (structure in the kidneys).
glomerulus
Note: Filtration is slowed by the binding of drug to plasma proteins
Fill in the blank: If the urine is acidic, drugs that are weakly _____ are more readily excreted (and vice versa).
basic
Cells that actively secrete some drugs from the blood into the urine. Involves active transport
Tubule cells
A drug is metabolized by the liver, the resulting metabolites can then go to one of two places, what are they?
- Be excreted into the bile
- Returned to the bloodstream and excreted by the kidney
Note: Some drugs (not just metabolites) can be secreted into the bile unchanged
Drugs that are reabsorbed from the intenstine and returned to the liver via the portal vein then returned to systemic circulation have undergone what type of circulation?
Entero–hepatic circulation
Note: Also called recirculation
True or false: Just because a drug appears in the bile, does not mean it is on its way out of the body
True
Name some minor routes of excretion
Lungs, salivary glands, sweat glands, mammary glands, male genital fluid, and eggs
Removal of drug in an unaltered form
Clearance. It is different from excretion in that it does not refer to removal of drugs from the body, only removal from the bloodstream