Osteology and Arthrology of the Upper Extremities
1/202
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
203 Terms
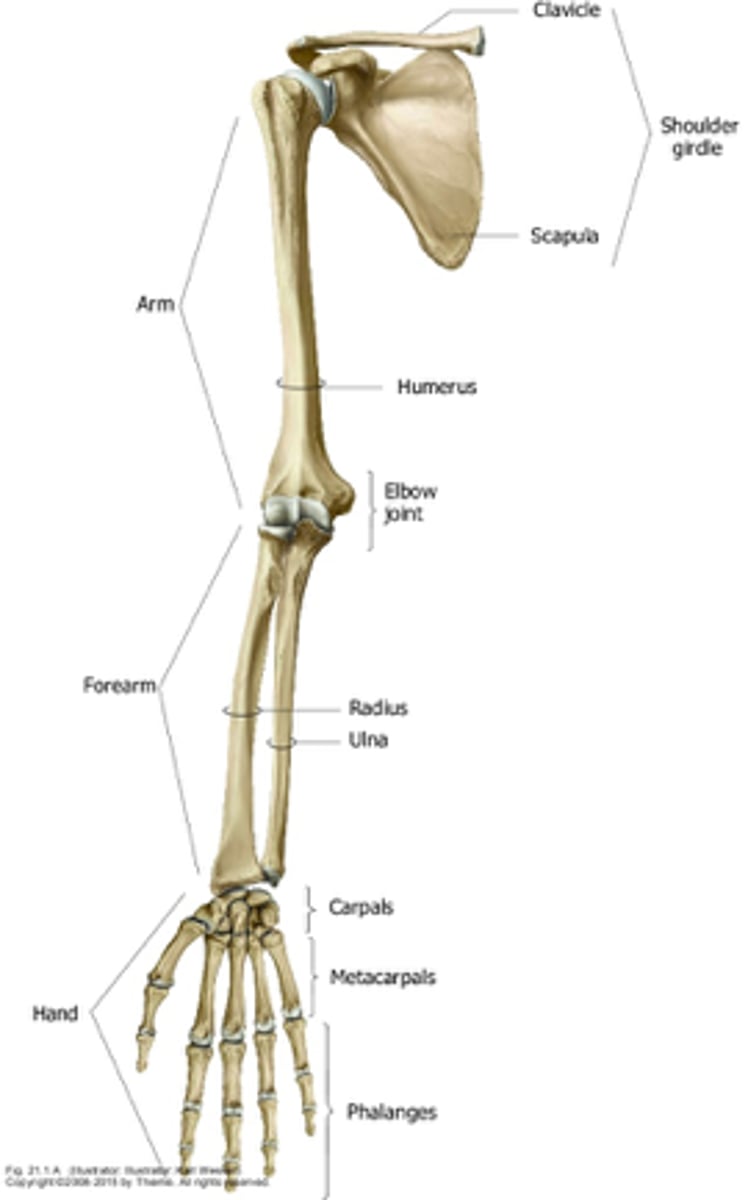
What are the anatomical divisions of the upper extremities?
- shoulder
- arm
- forearm
- hand
Overview of the shoulder:
- not part of the free upper limbs
- proximal segment
- most proximal part of upper limb
- overlapping the trunk and neck
overlies half of the pectoral girdle
What consists of the pectoral girdle?
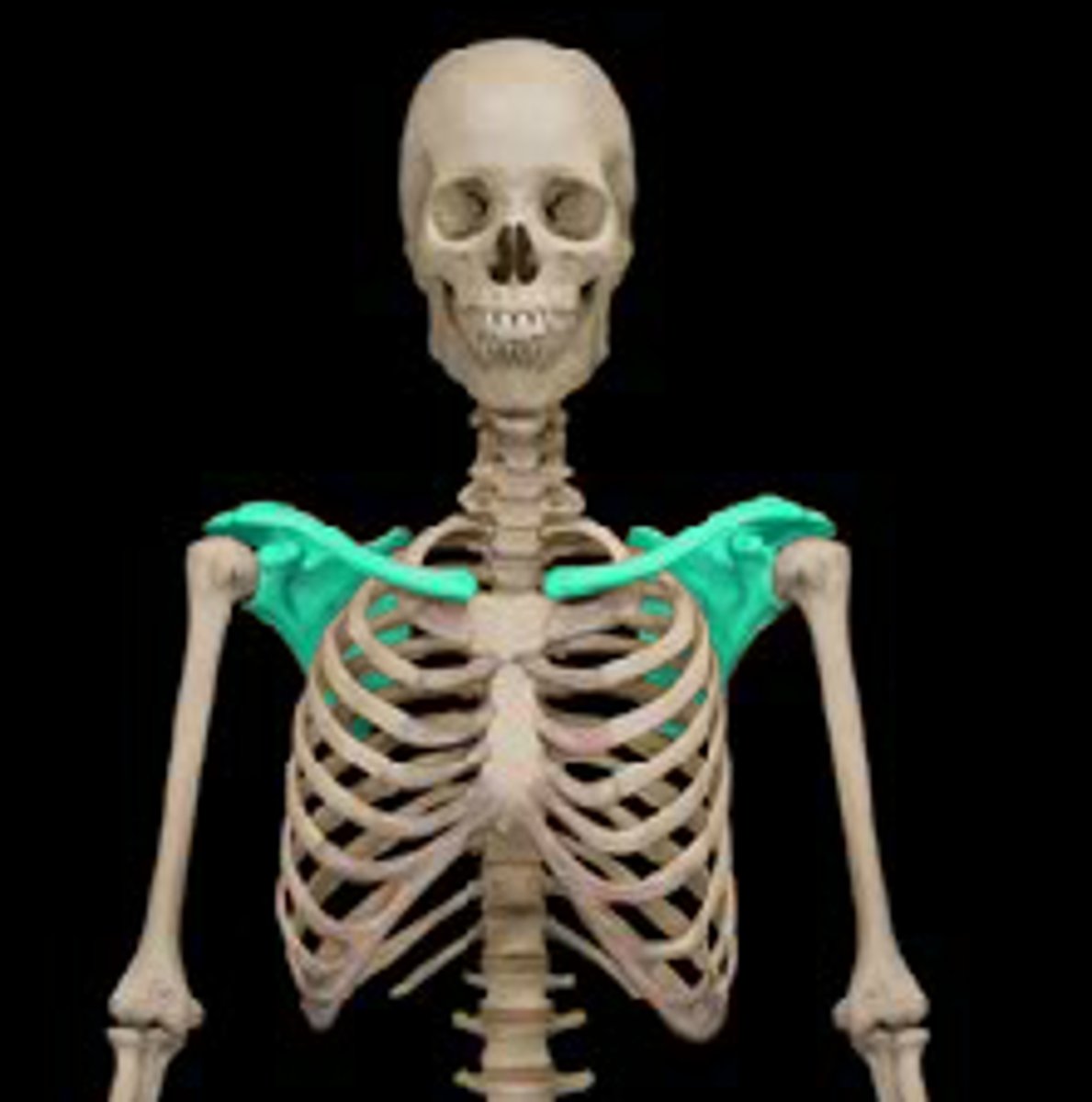
bony ring formed by the scapula, clavicle, and manubrium
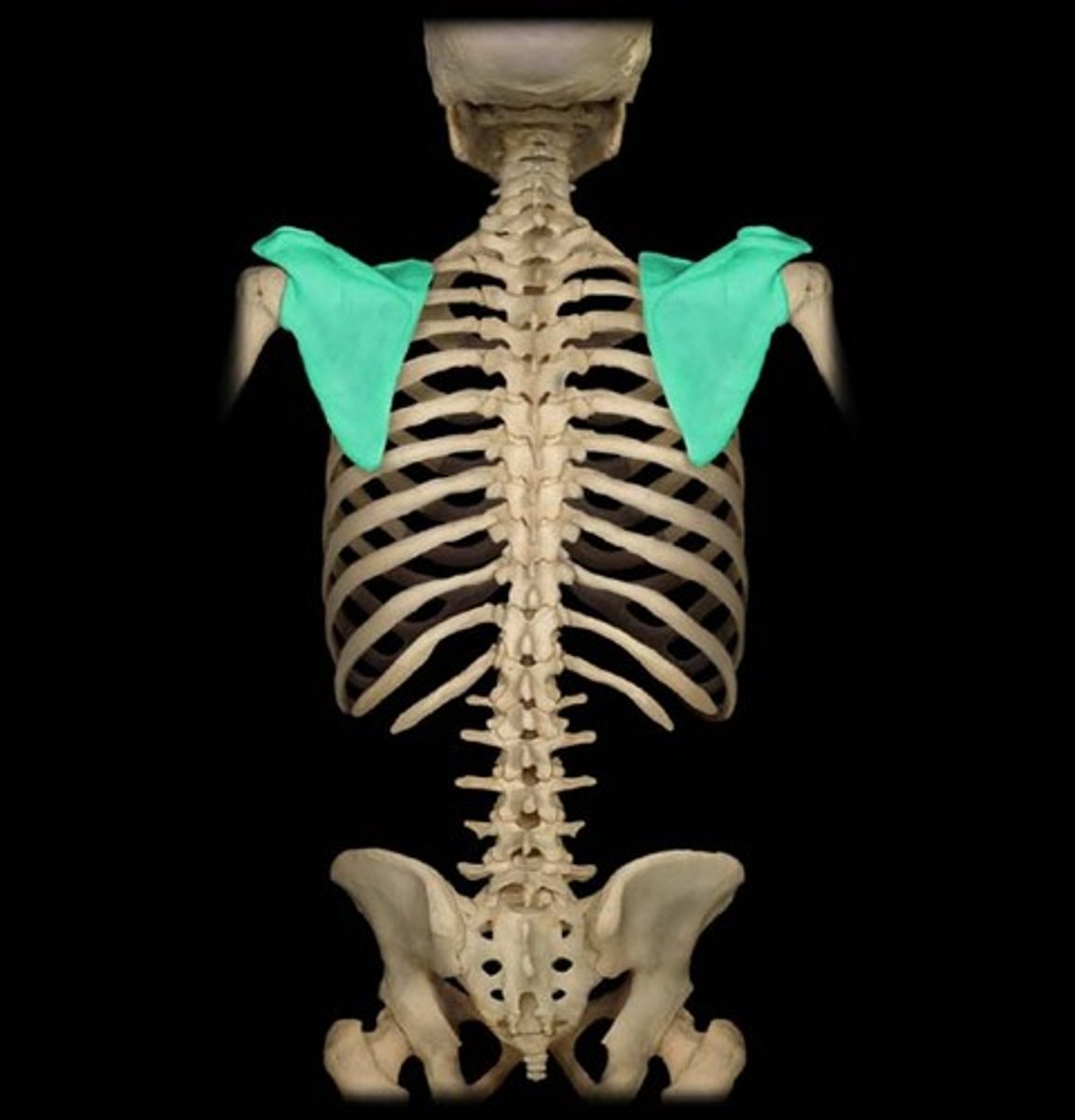
What are parts of the upper limb that are included in the shoulder?
- pectoral
- scapular
- deltoid
Overview of the Arm:
- 1st segment and longest part of the free upper limb
- extends between and connects the shoulder and elbow
Describe parts of the arm:
- anterior region of the arm
- posterior region of the arm
Overview of the forearm:
- 2nd segment and second lomgest portion of the UL
- extends between and connects the elbow and the wrist
What are parts of the forearm?
- anterior region of the forearm
- posterior region of the forearm
Overview of the hand:
- most distal
What parts consist of the hand?
- wrist
- palm
- dorsum of hand
- digits
The clavicle connects the _____ to the ____
connect UE to trunk
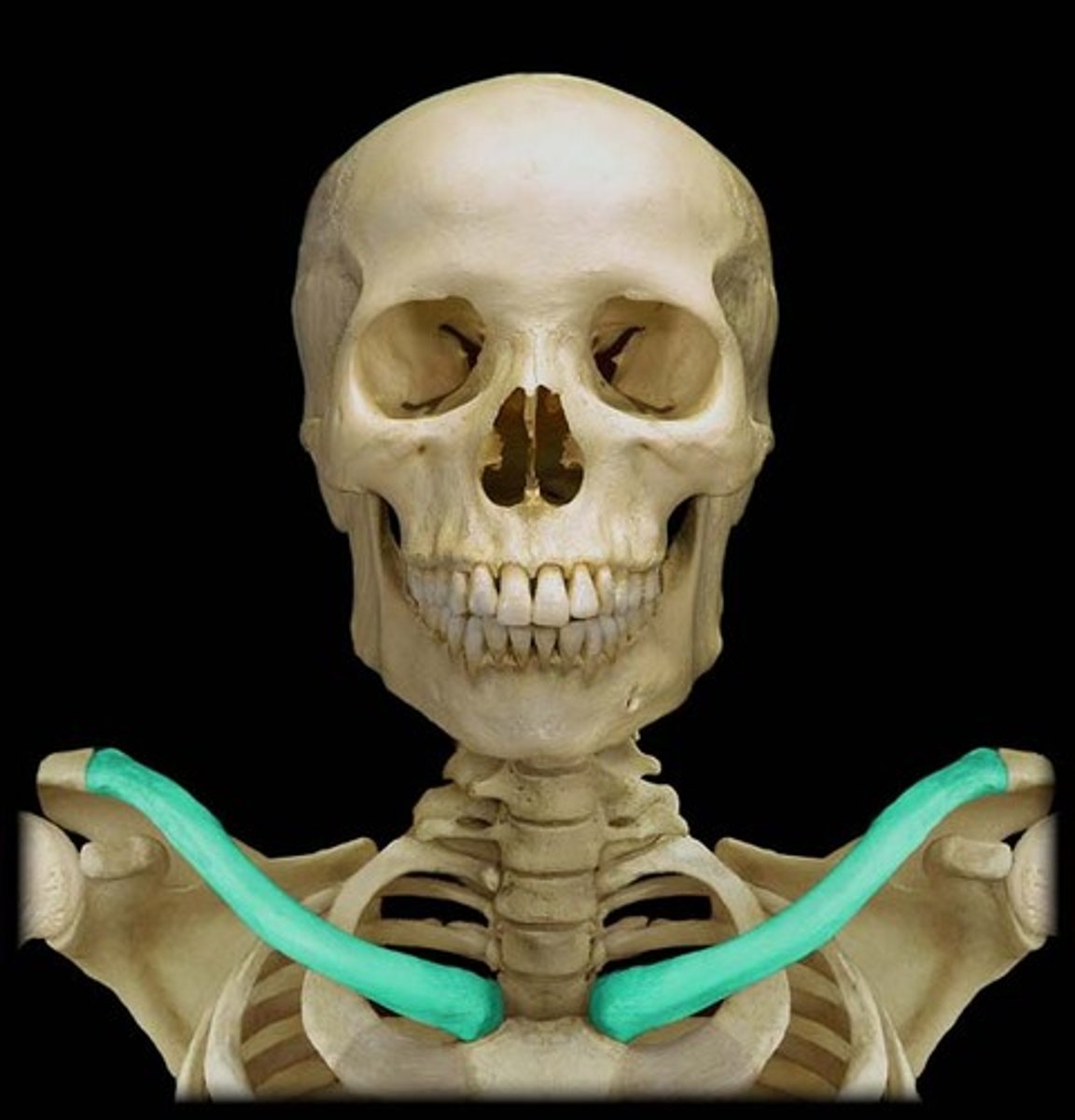
The clavicle suspends____________________
the scapula and free limb from the trunk
The clavicle forms________________________
one of the boundaries of the cervico-axillary canal together with the scapula and 1st rib
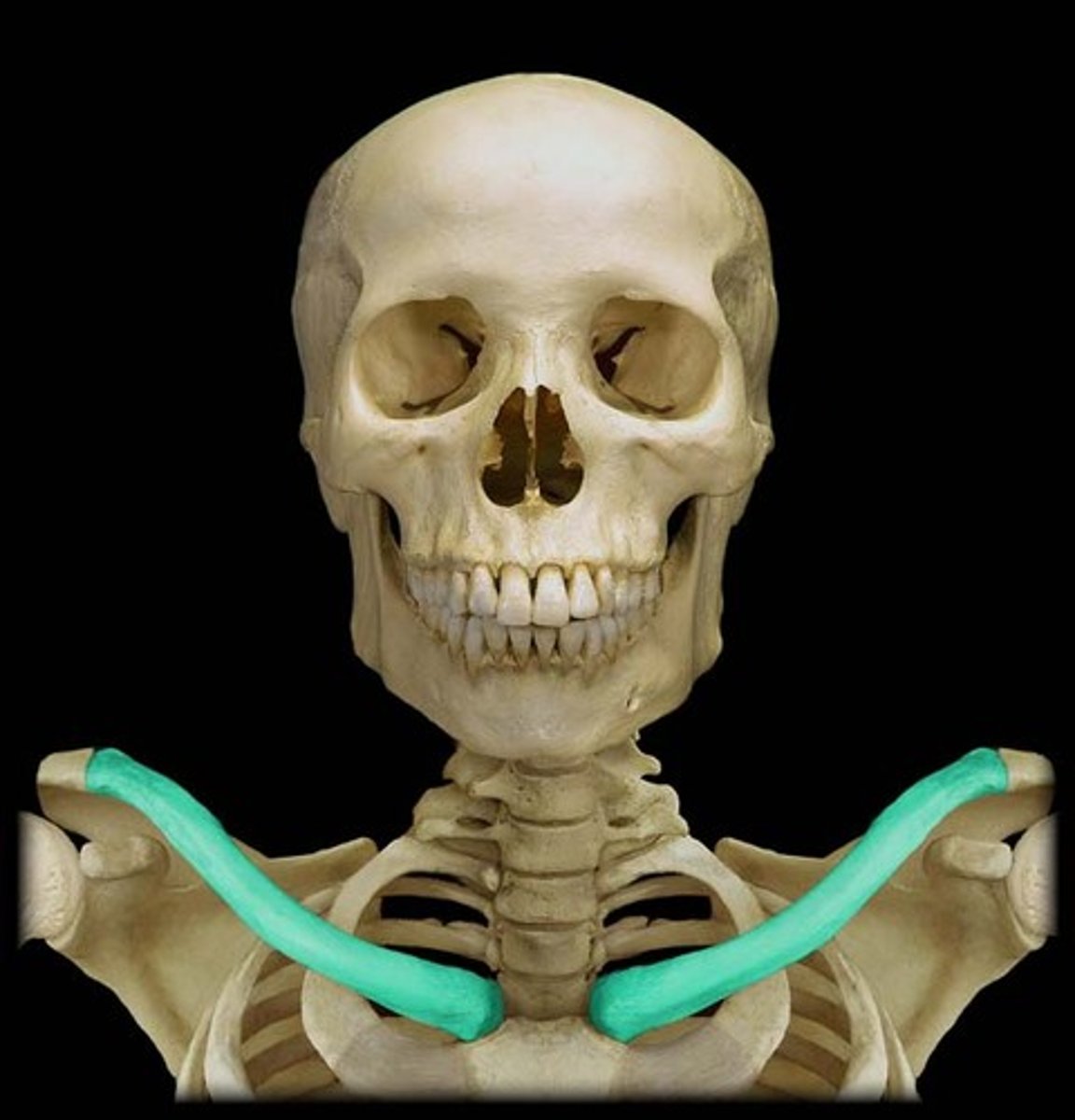
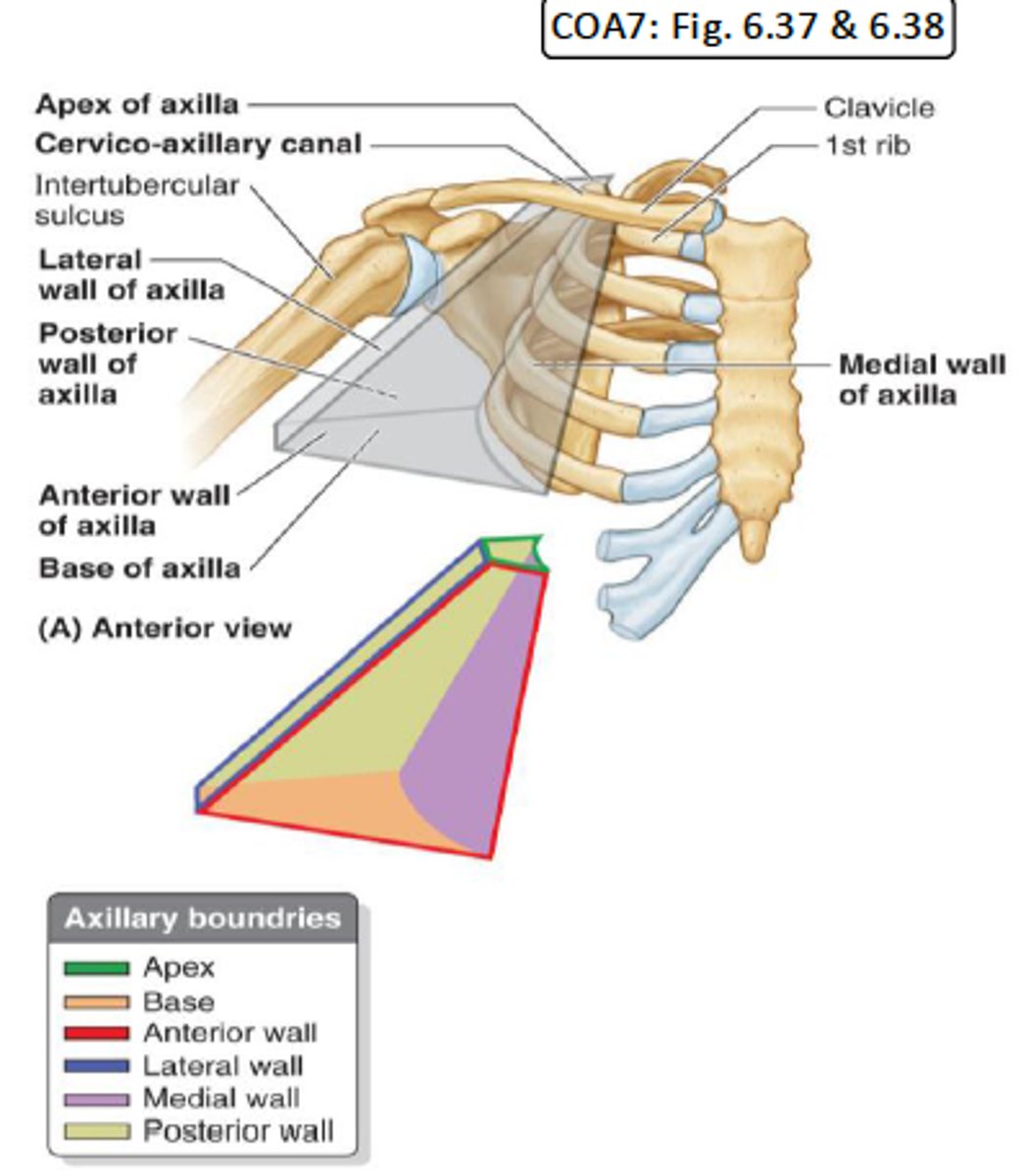
What is the cervico-axillary canal?
passage between neck and arm
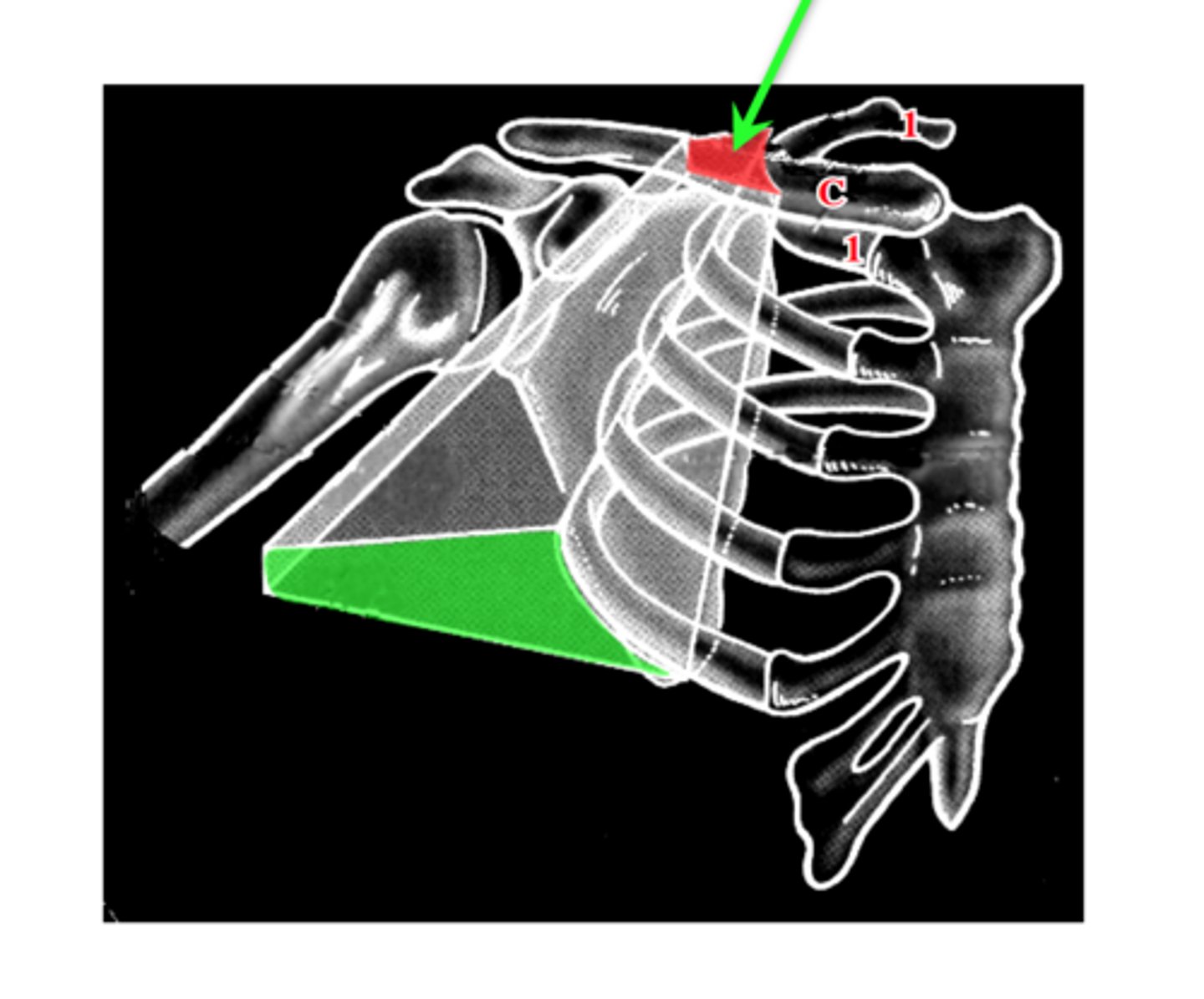
What does the cervico-axillary canal do?
protects the neurovascular bundle supplying the arm
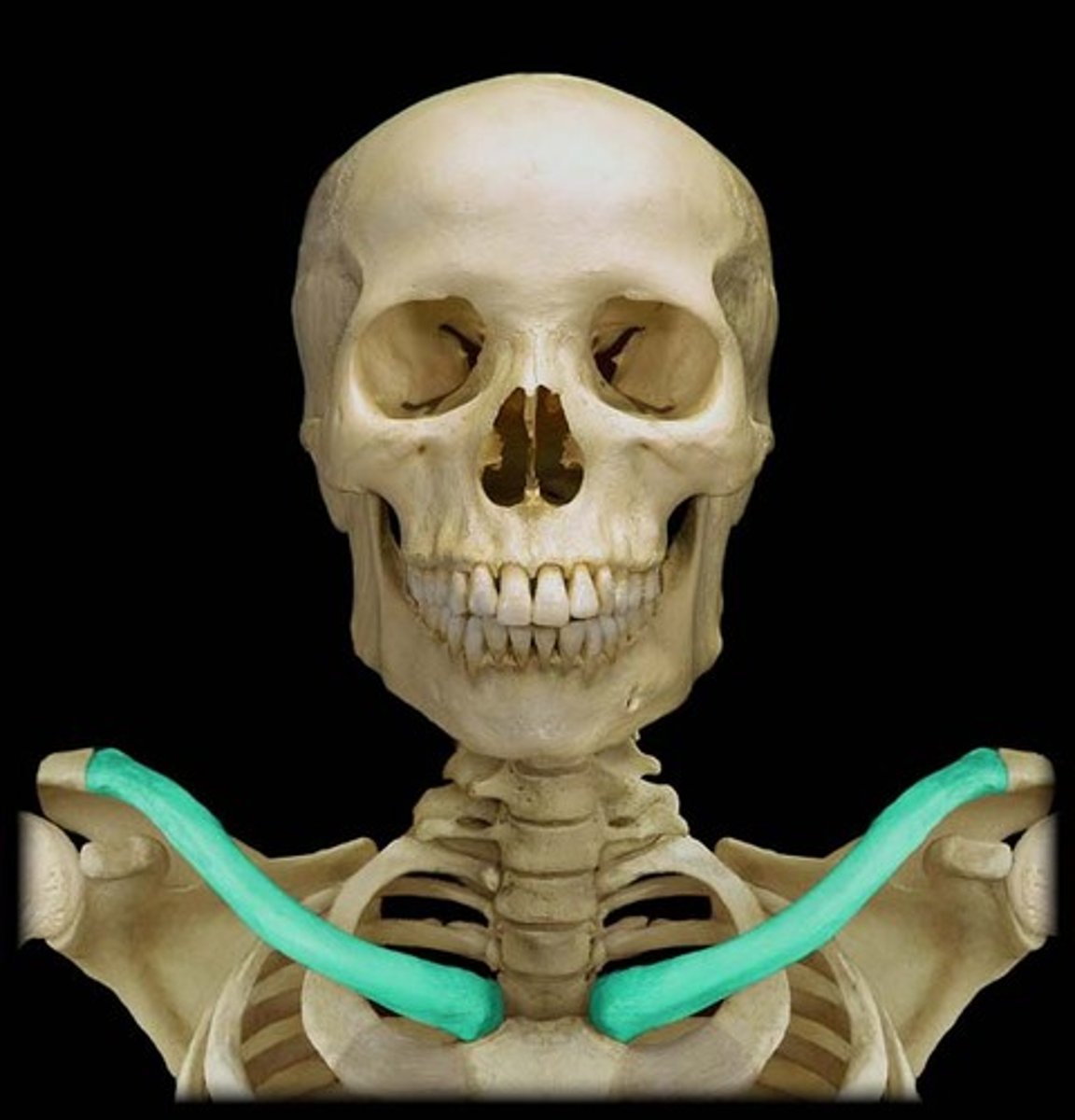
The clavicle transmits___________
shocks from the UE to the axial skeleton
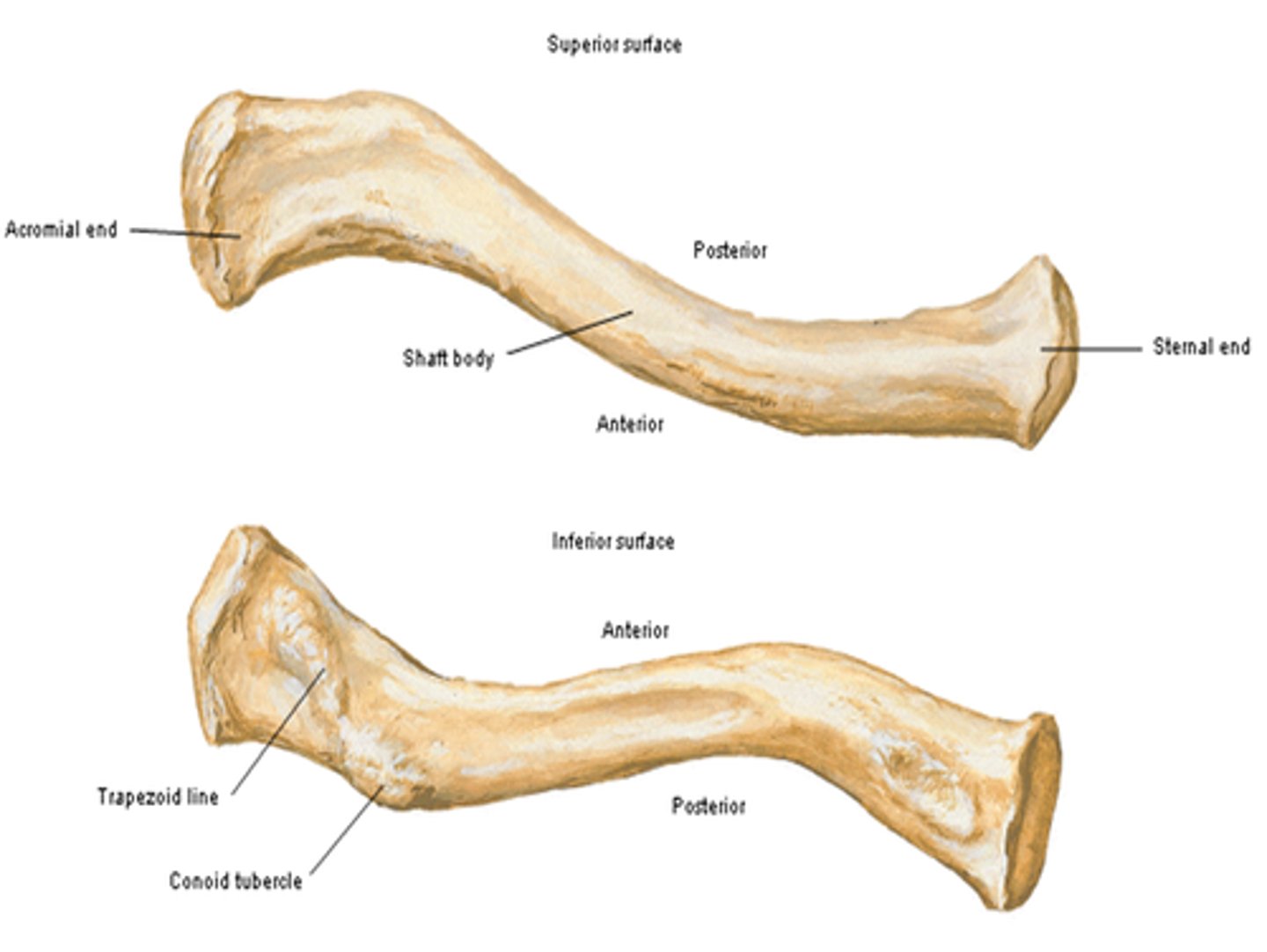
Parts of the clavicle:
- shaft
- superior surface
- inferior surface
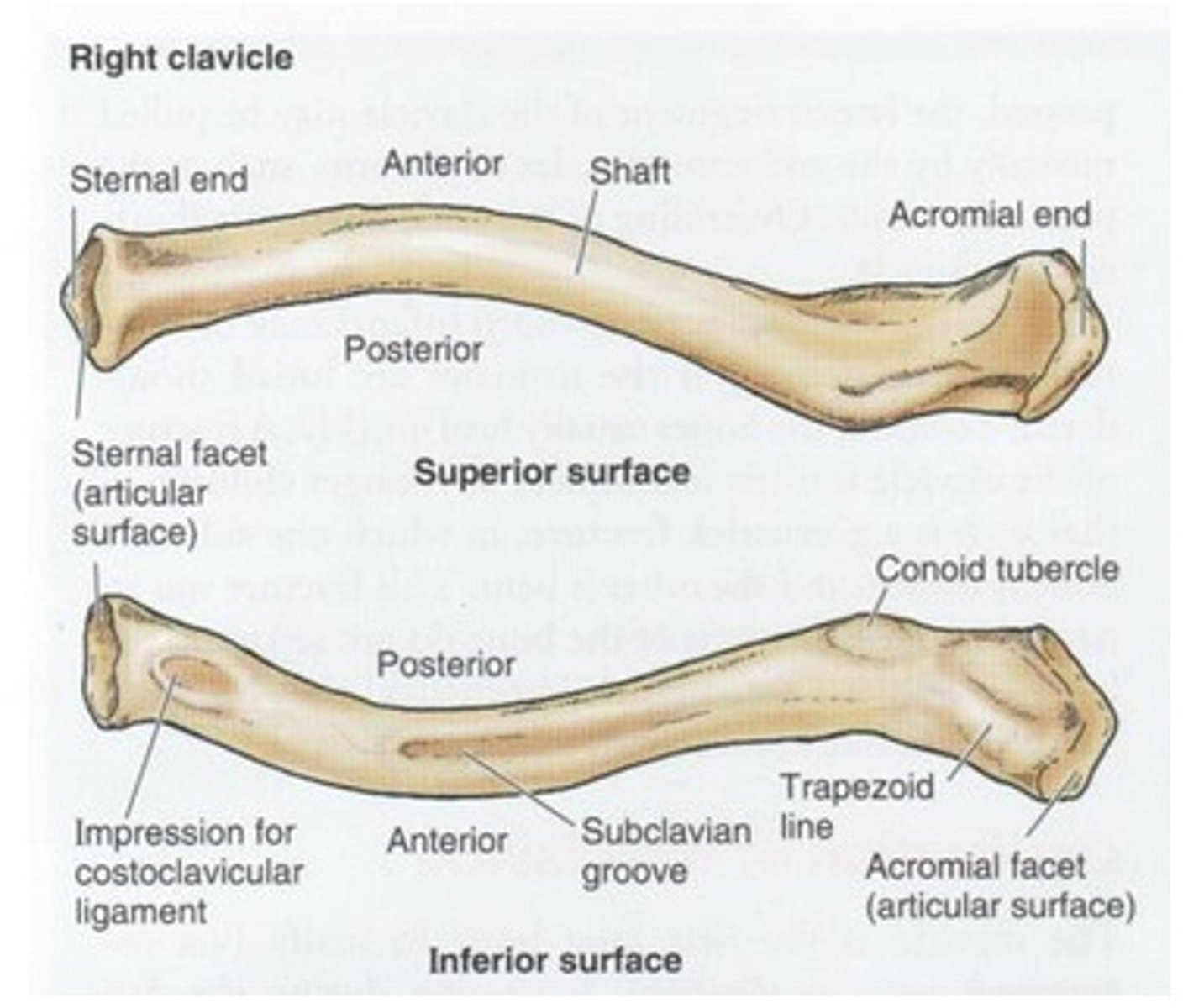
Shaft of the clavicle:
double curved in the horizontal plane, which increases resilience
Middle half of the shaft of the clavicle:
convex anteriorly, and lateral half concave anteriorly
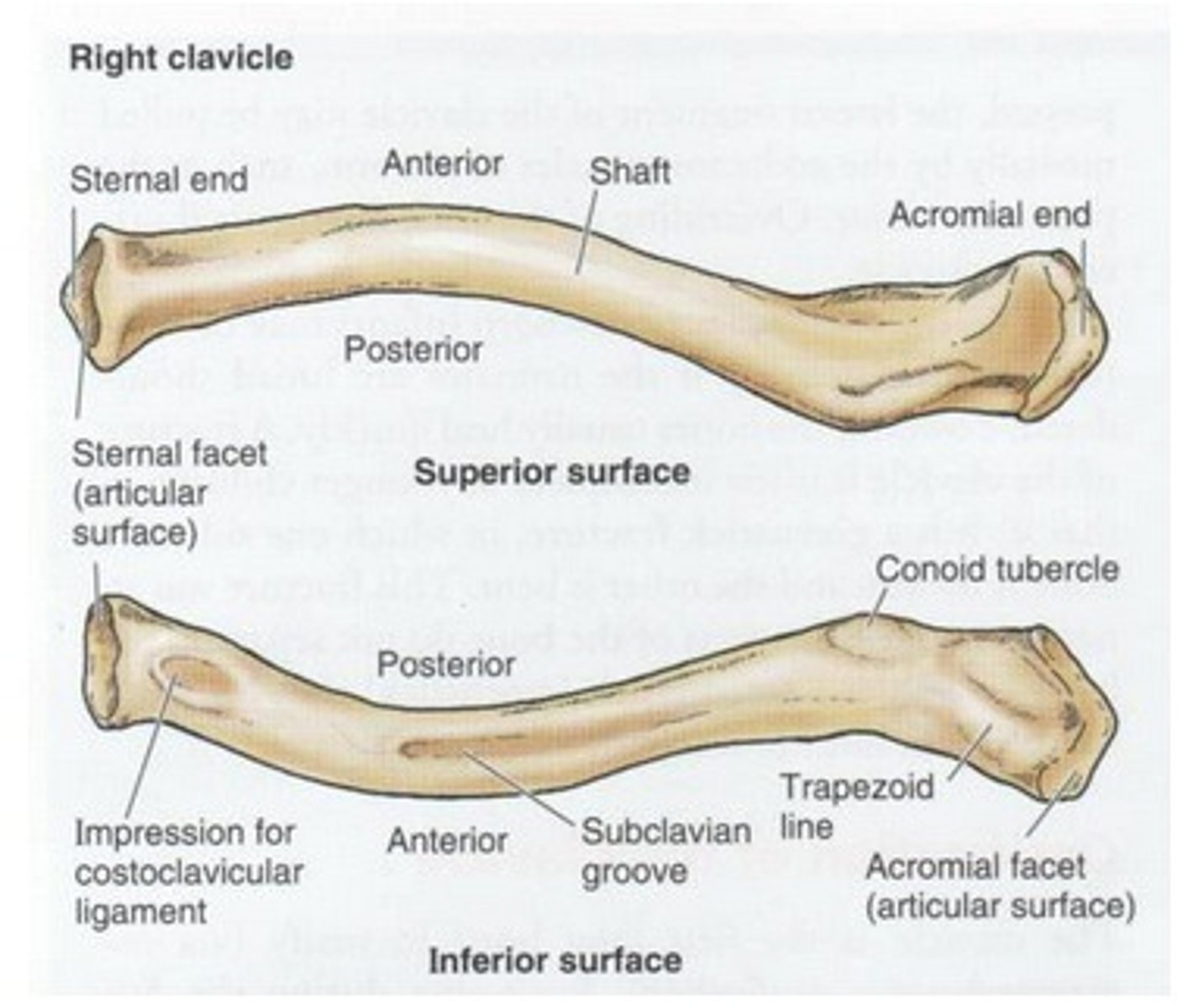
Sternal end of the shaft of the clavicle articulates:
articulates with manubrium via the sternoclavicular joint
Acromial end of the shaft of the clavicle articulates:
articulates with acromion via acromioclavicular joint
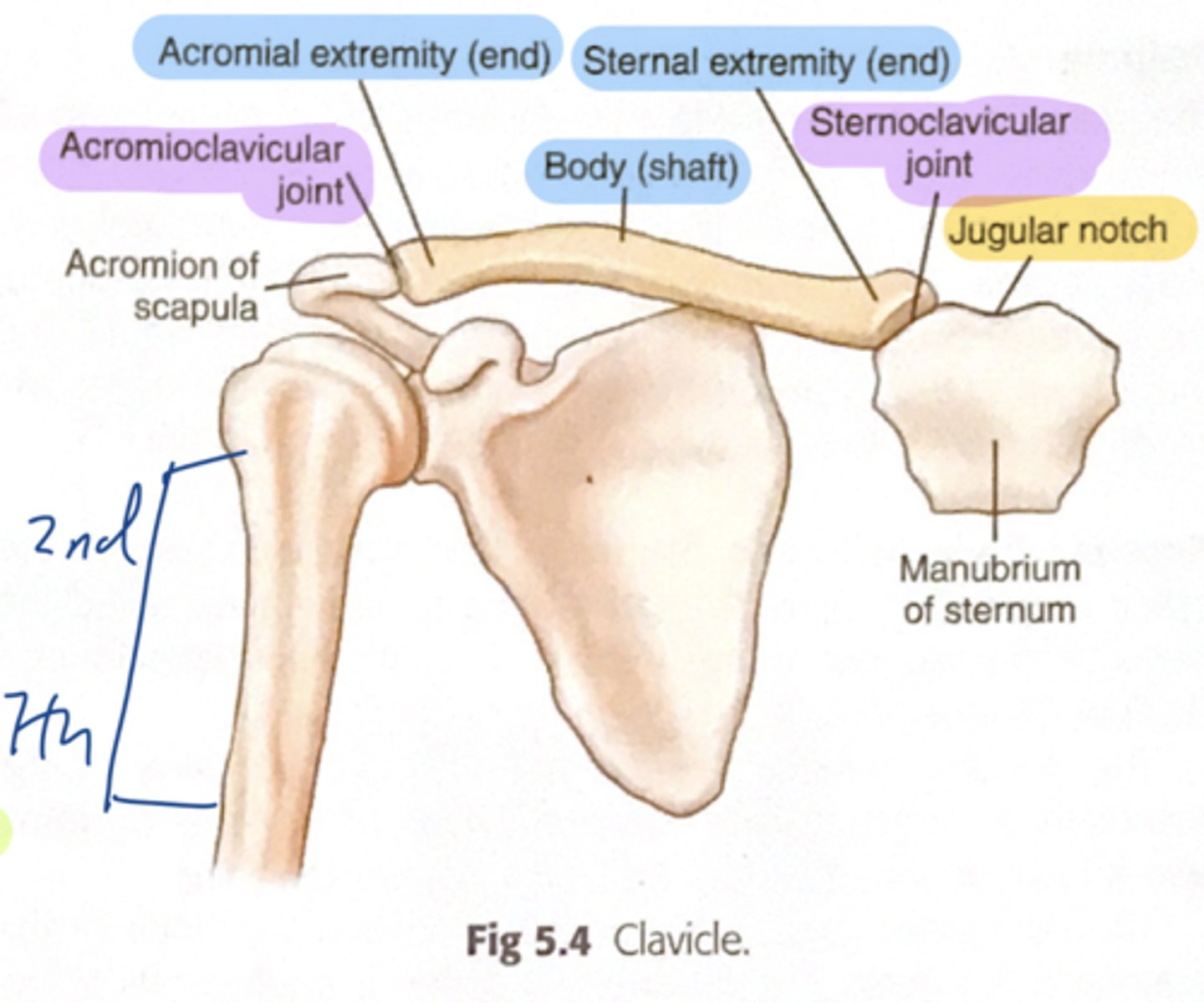
Location of superior surface of the clavicle:
lies deep to the platysma muscle and skin and it is smooth
Inferior surface of the clavicle:
rough surface with ligaments binding to it
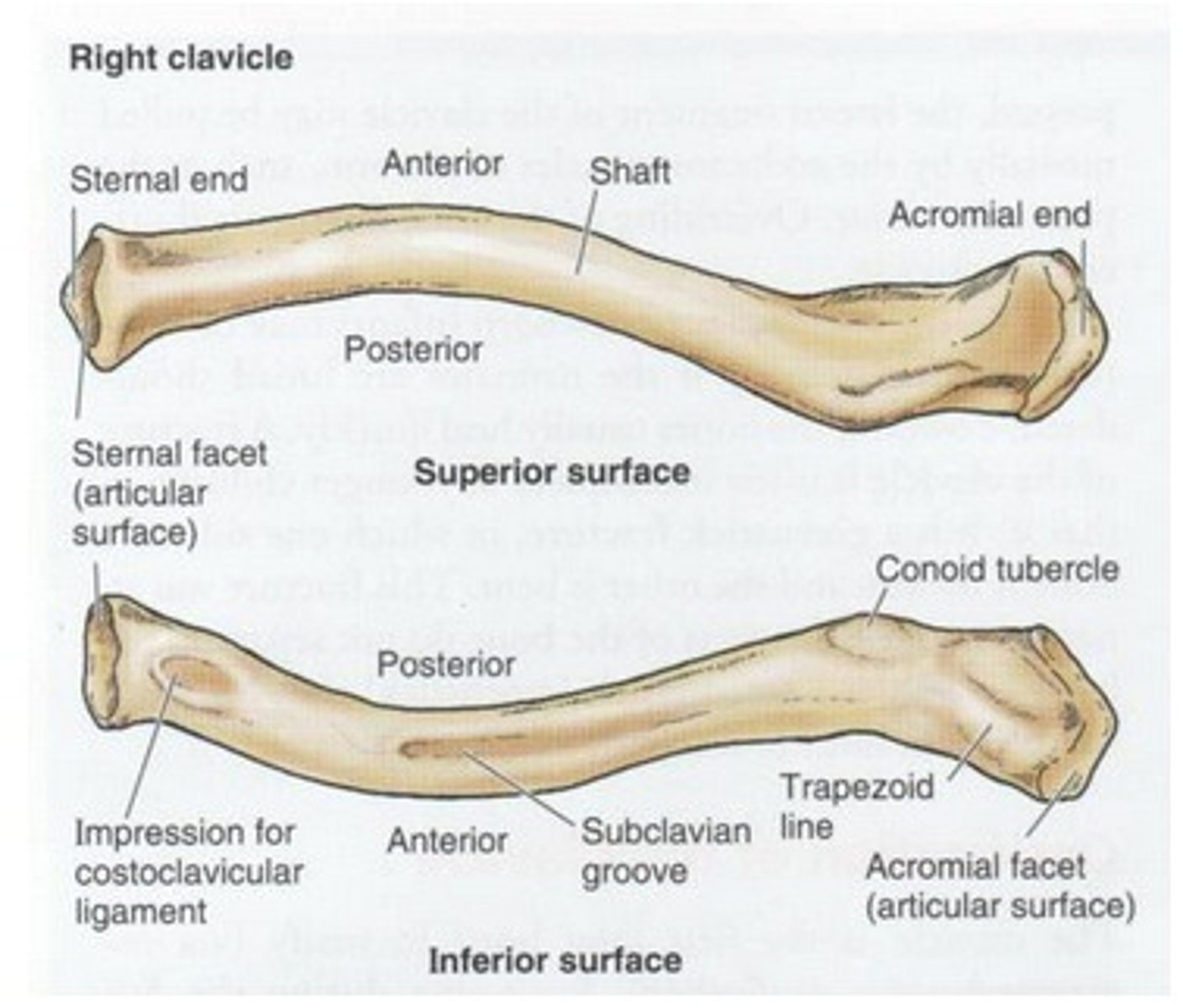
Location of conoid tubercle of the inferior surface of the clavicle:
near acromial end of clavicle
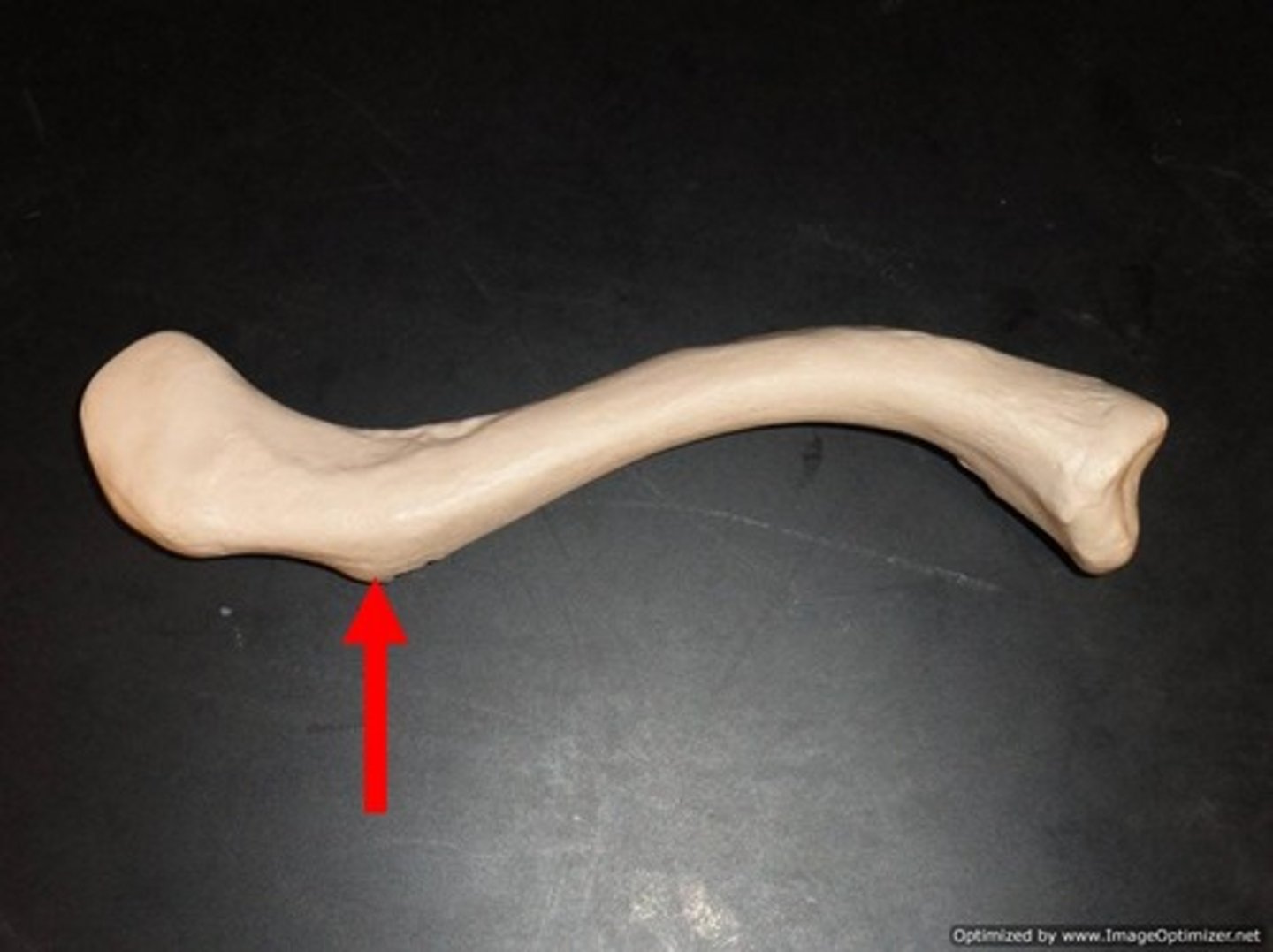
Function of conoid tubercle on the inferior surface of the clavicle:
support for the medial part of the coracoclavicular ligament
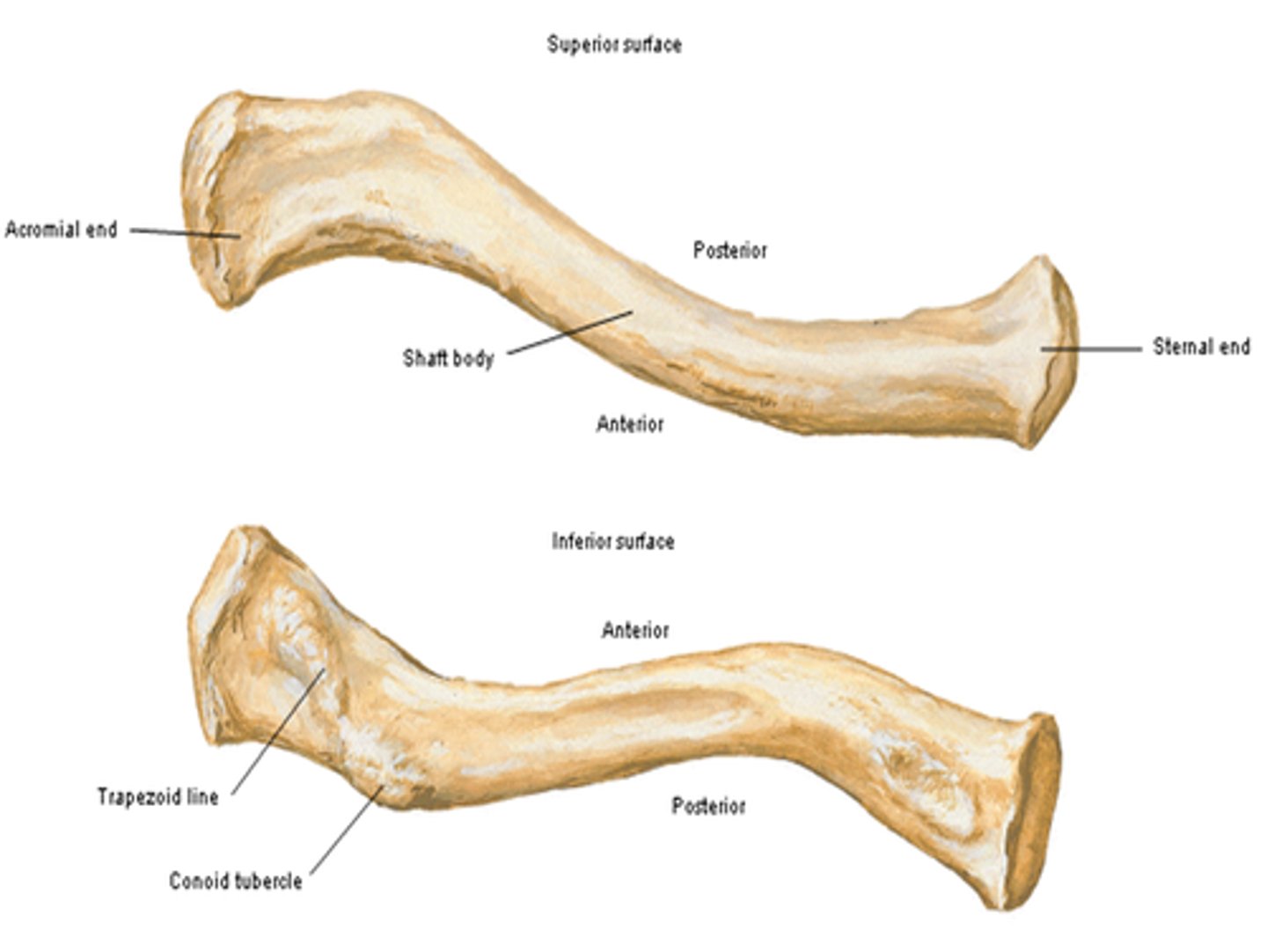
Location of the trapezoid line of the inferior surface of the clavicle:
nearer to the acromial end than the conoid tubercle
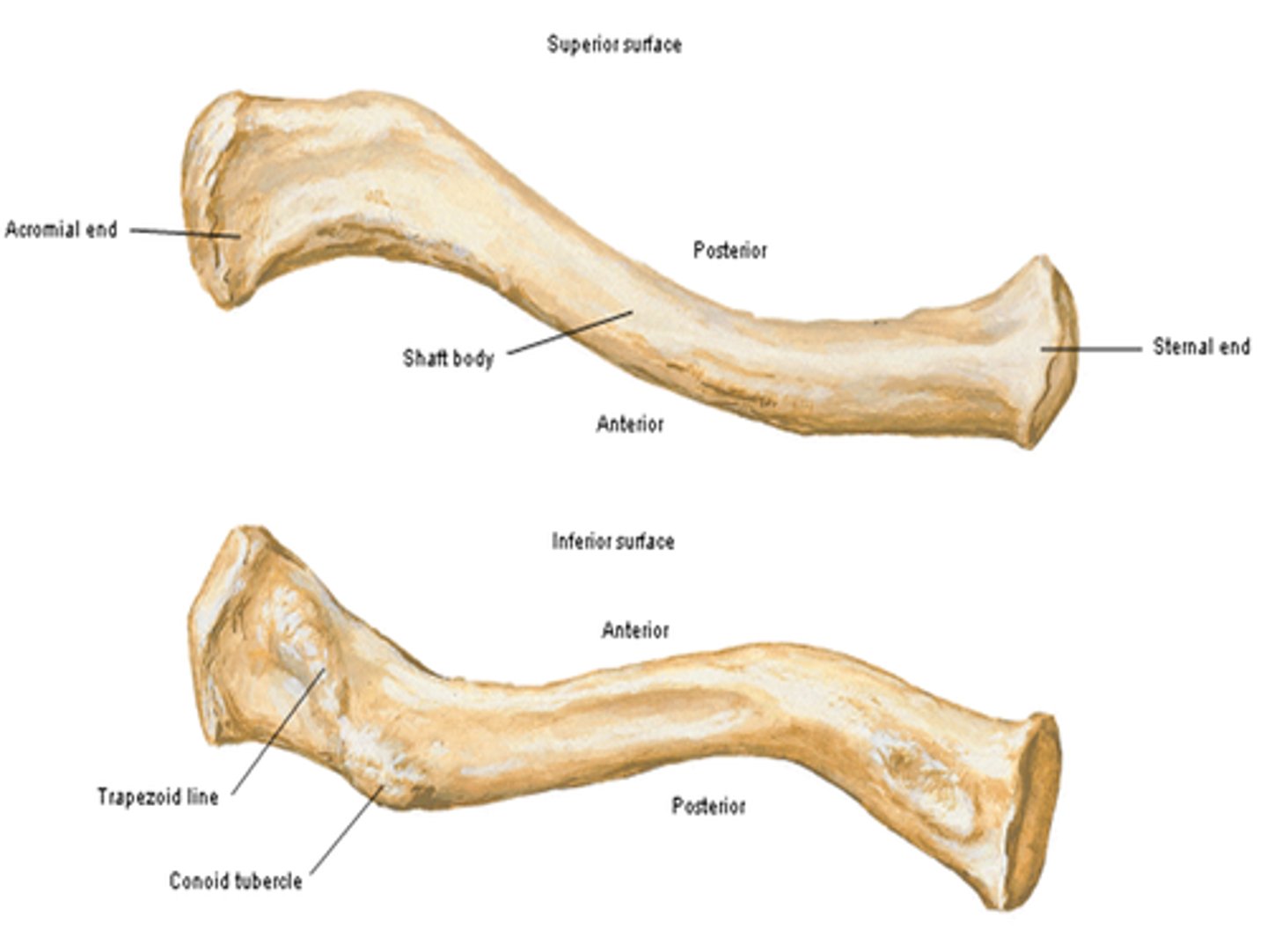
Function of the trapezoid line of the inferior surface of the clavicle:
support for the lateral part of the coracoclavicular joint
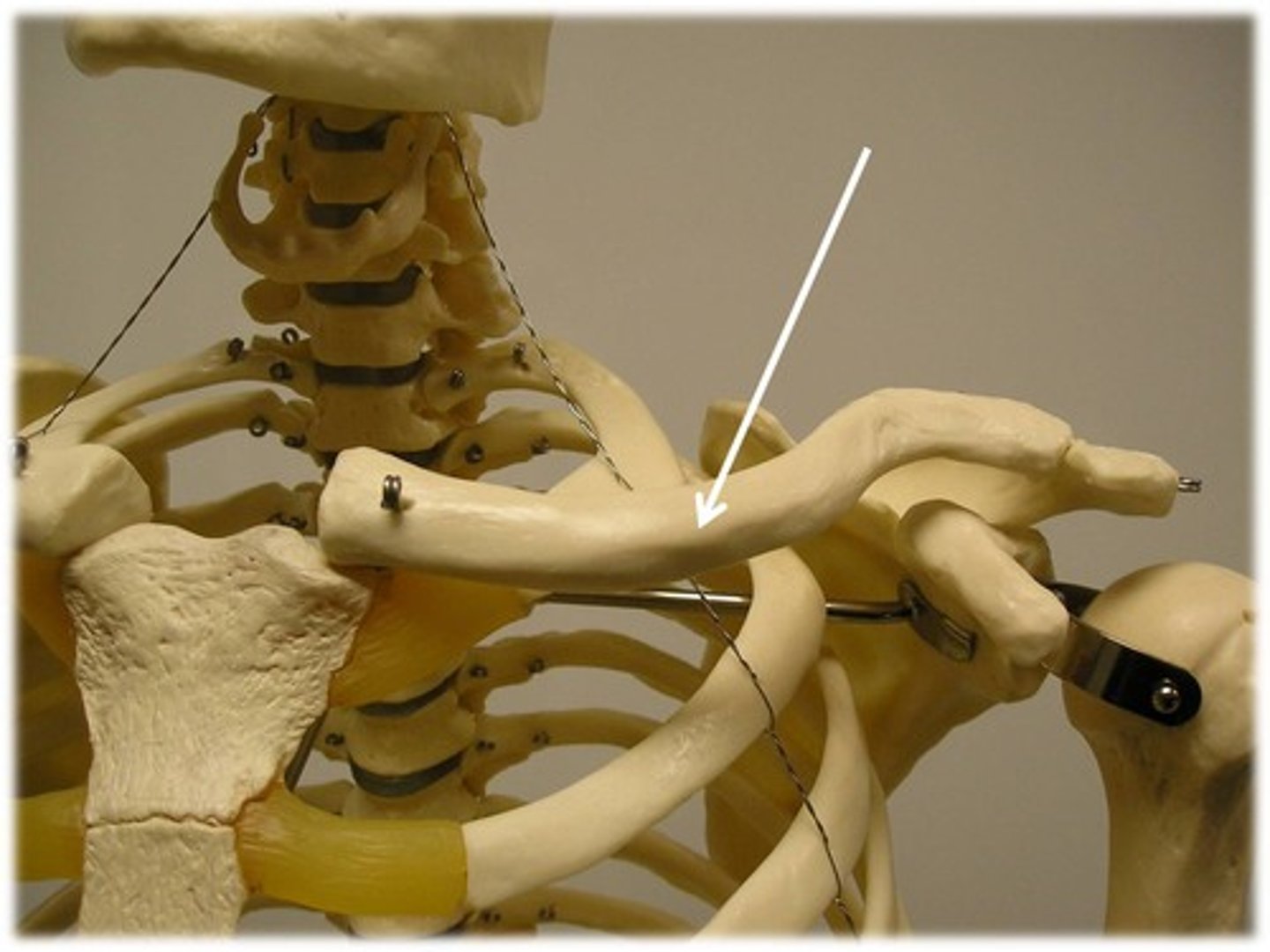
Clinical relevance: fracture of the clavicle
Inflection point: The junction between the medial 2/3rd and lateral 1/3rd. The inflection point is the weakest point of the clavicle, more prone to fractures. The medial 2/3rd is going to be displaced superiorly by the action of the SCM (sternocleidomastoid) muscle
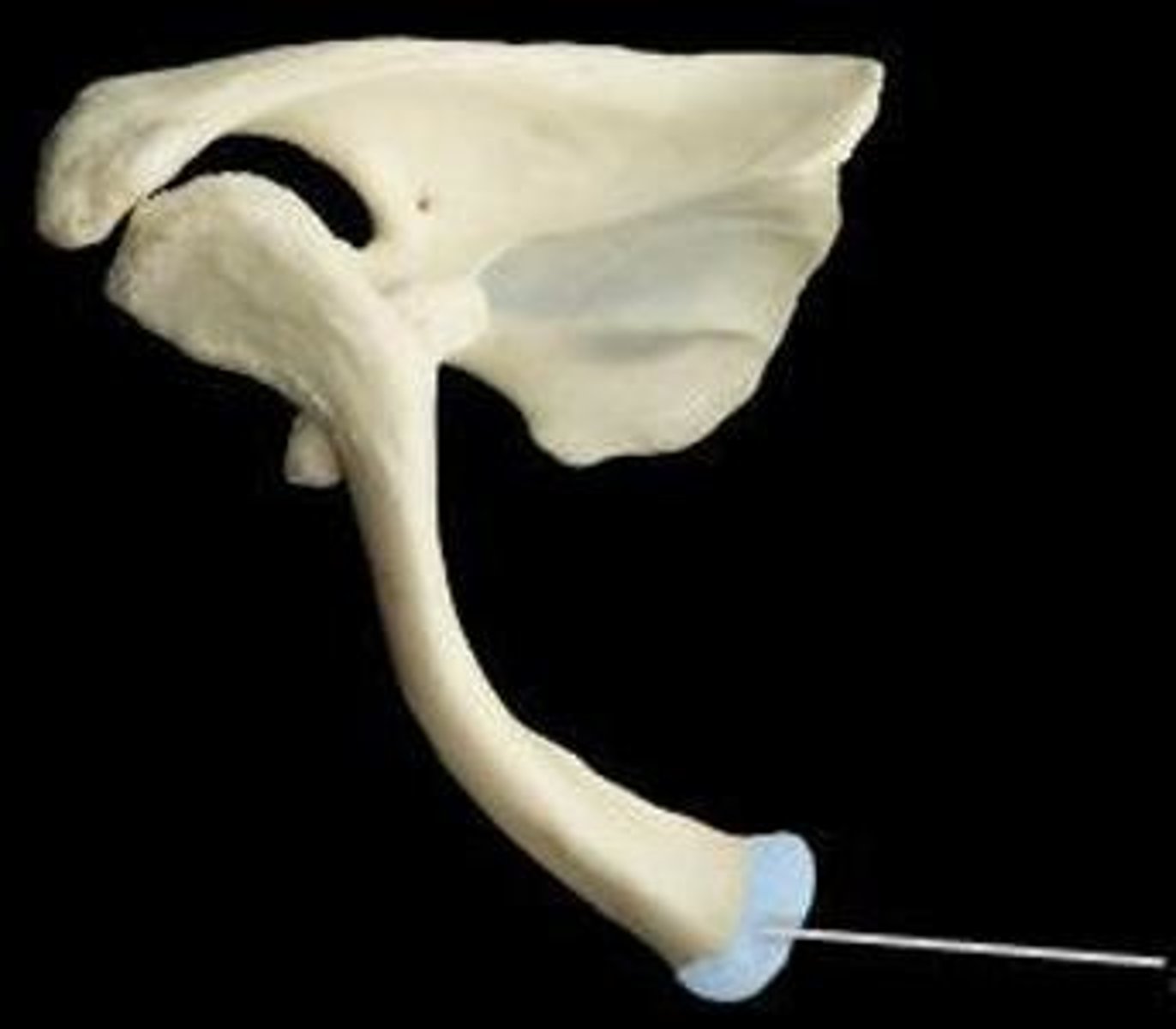
Describe the scapula:
triangular bone
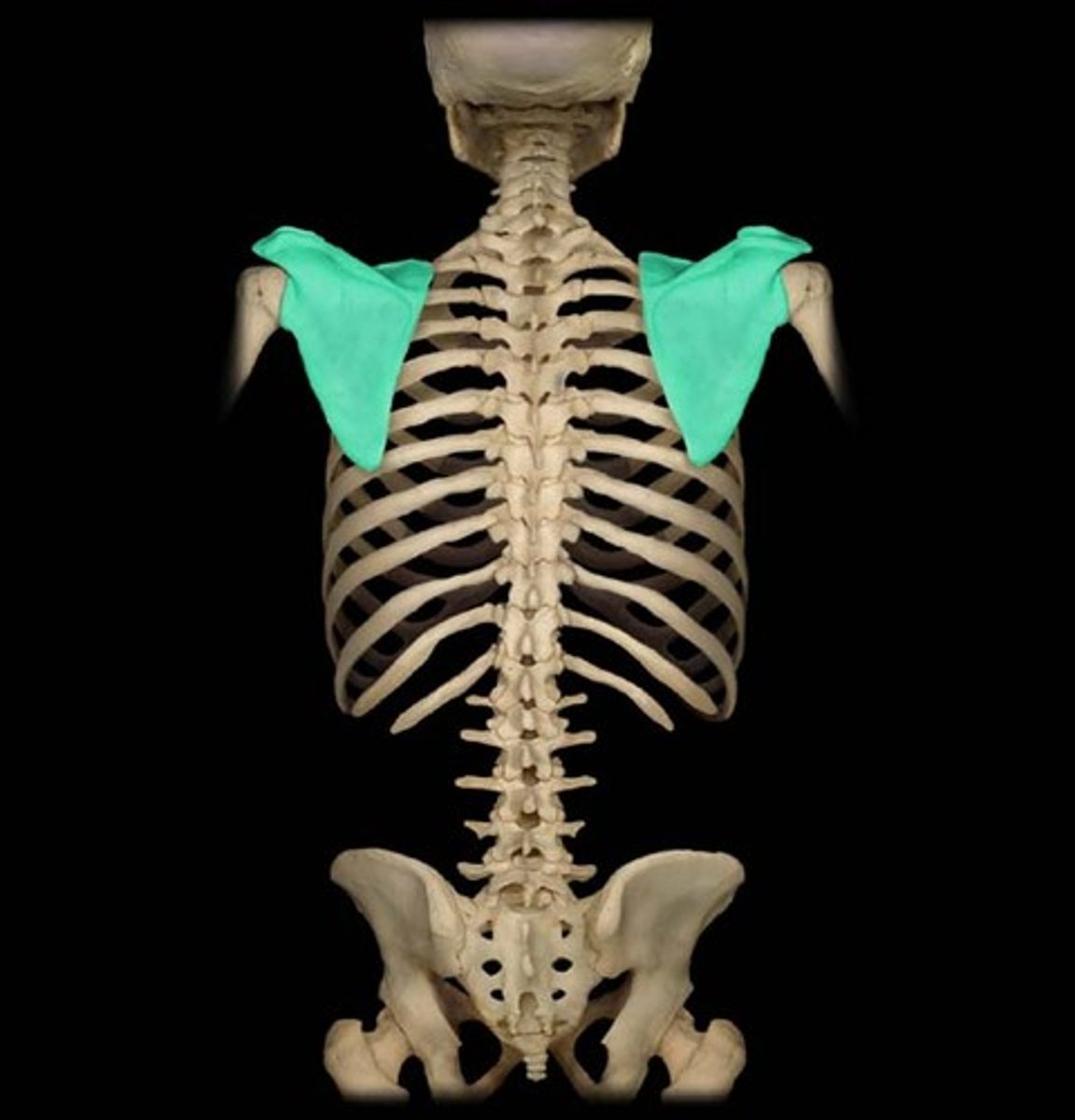
Location of the scapula:
posterior part of the thorax, overlying the 2nd-7th ribs
Scapula articulates with:
humerus (joint) and thoracic wall (physiological scapula-thoracic joint)
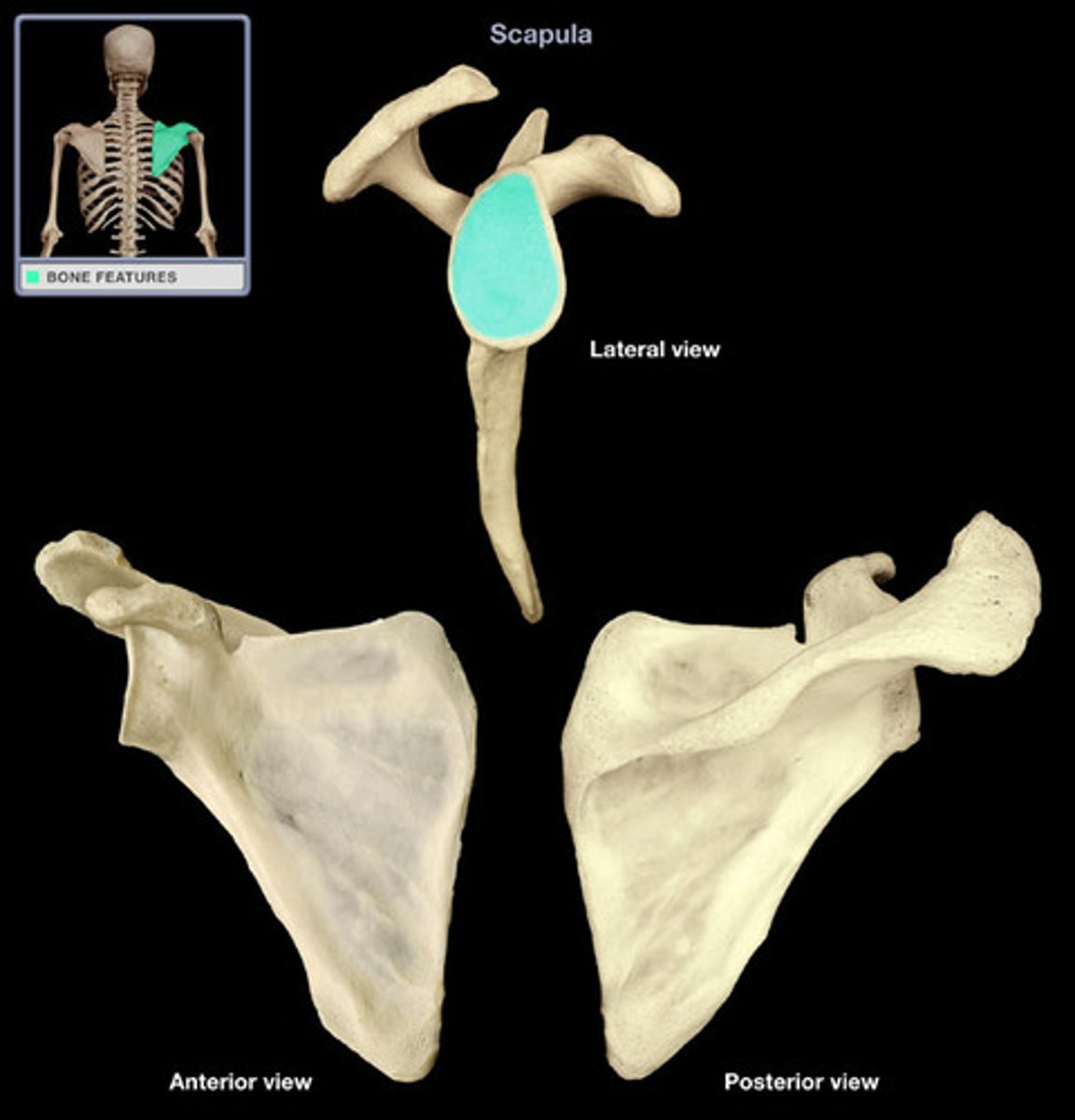
Surfaces of the scapula:
- posterior (convex)
- costal (concave)
- lateral
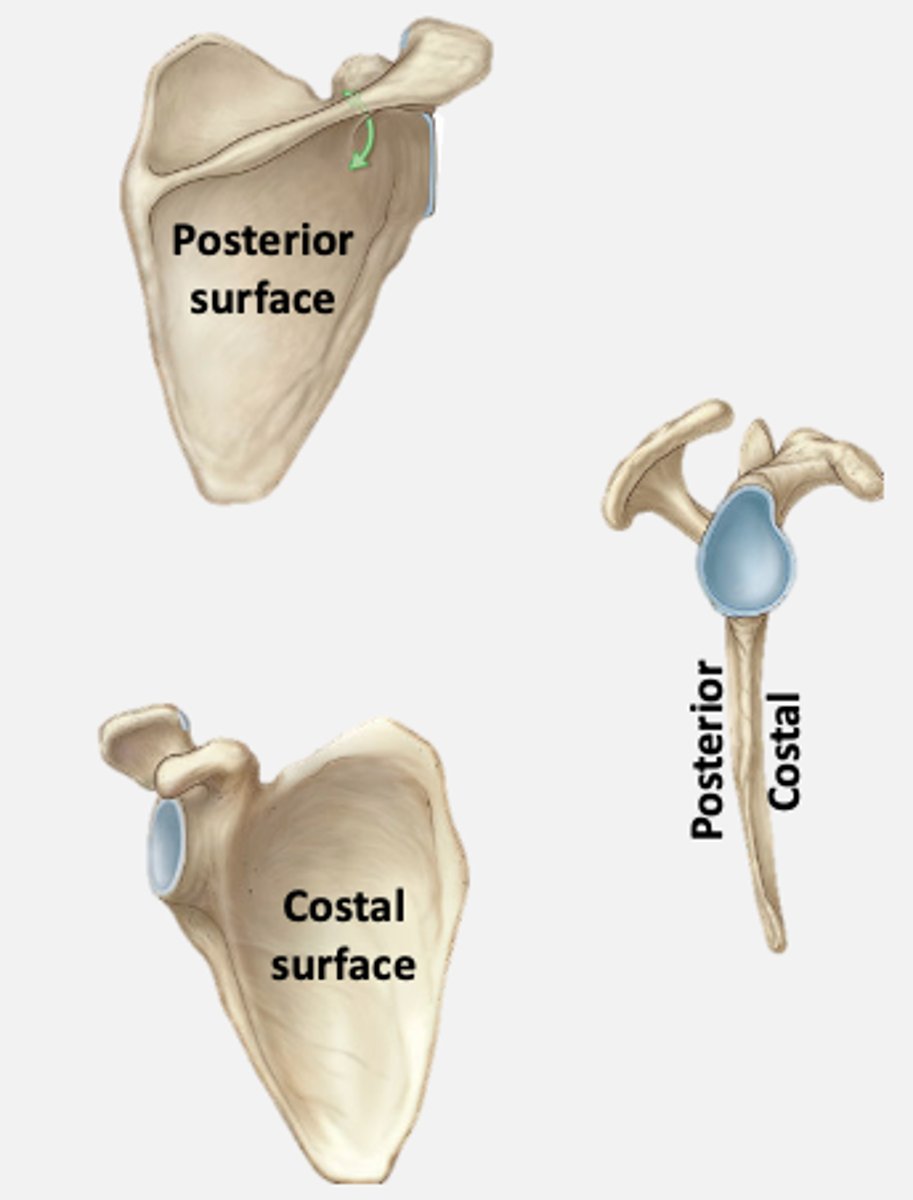
What structures are on the posterior surface of the scapula?
- spine of scapula
- acromion
- supraspinous fossa
- infraspinous fossa
What structure is on the costal surface of the scapula?
subscapular fossa
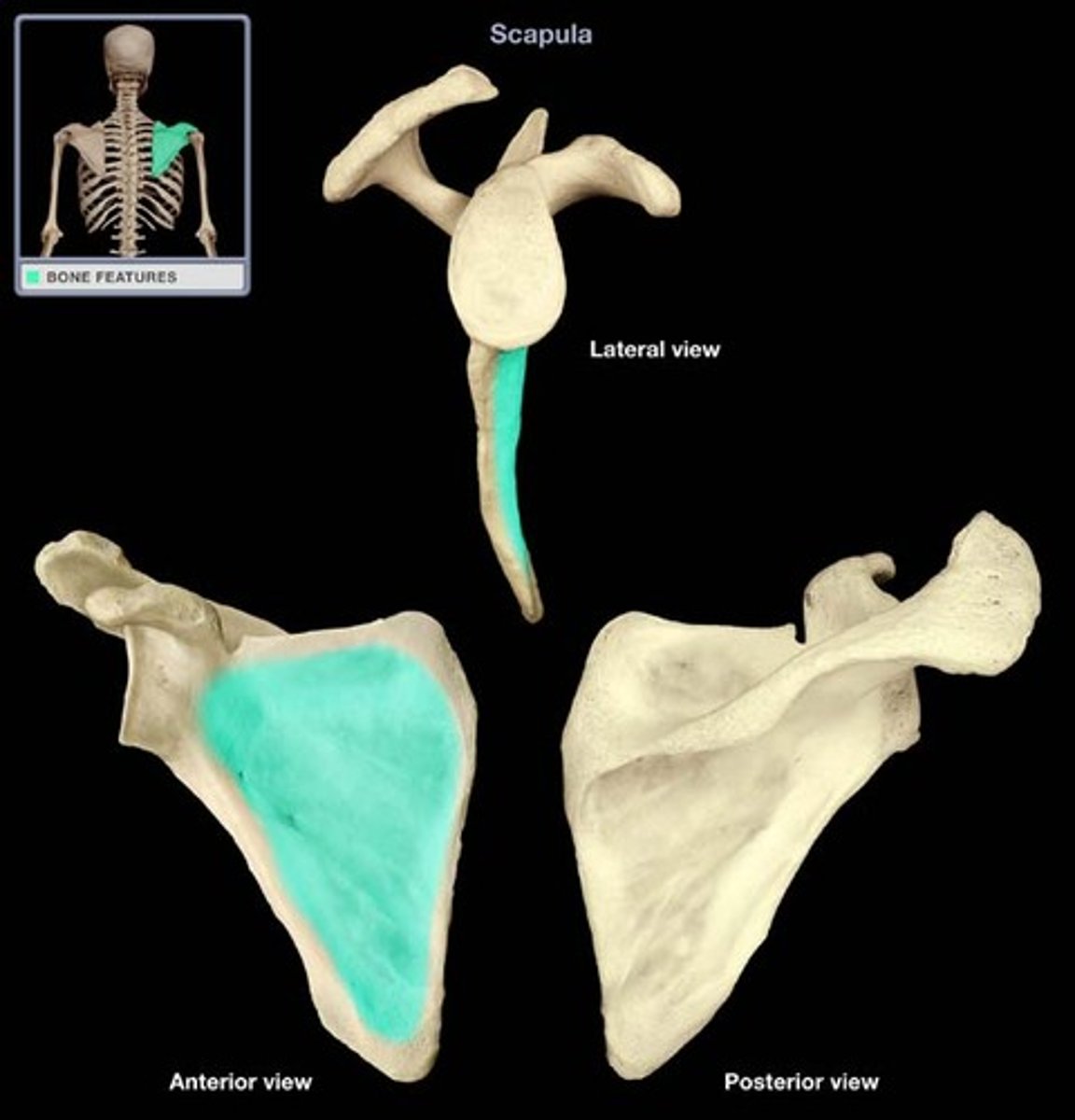
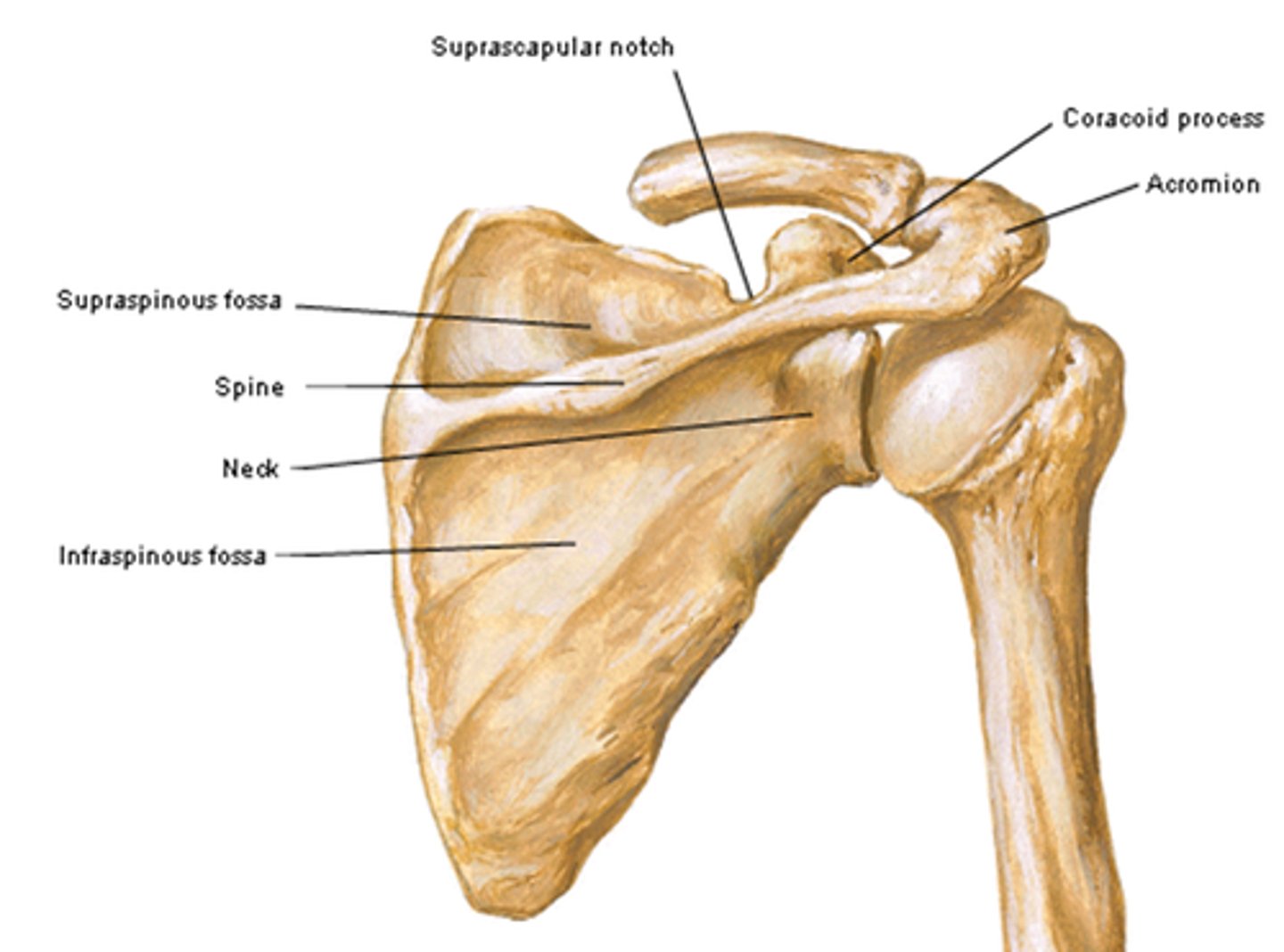
What structures are on the lateral surface of the scapula?
- glenoid cavity
- coracoid process
- head of scapula
- neck of scapula
- suprascapular notch
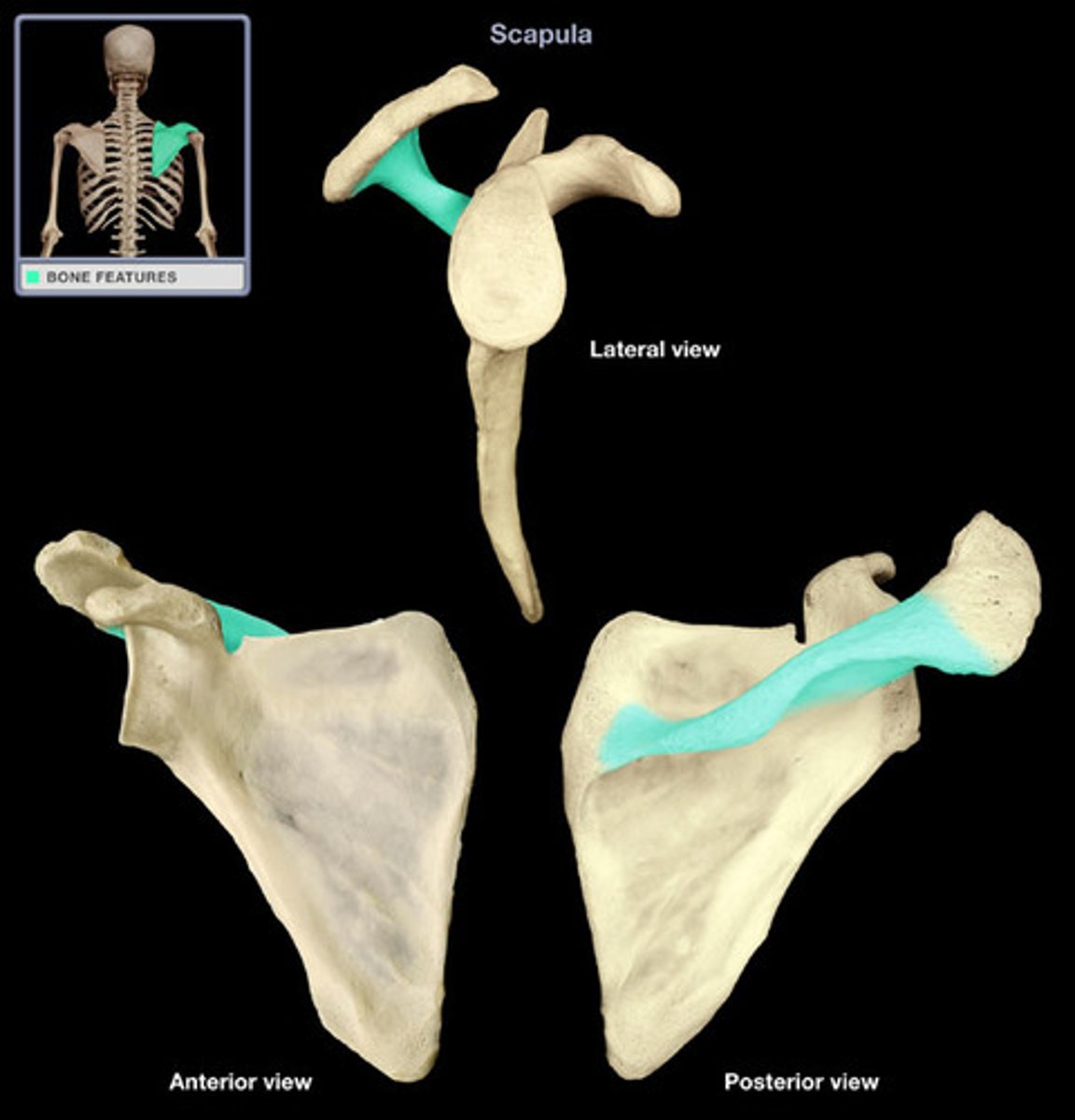
Spine of scapula:
- on posterior surface of scapula
- ridge of bone that divides posterior surface into two fossae
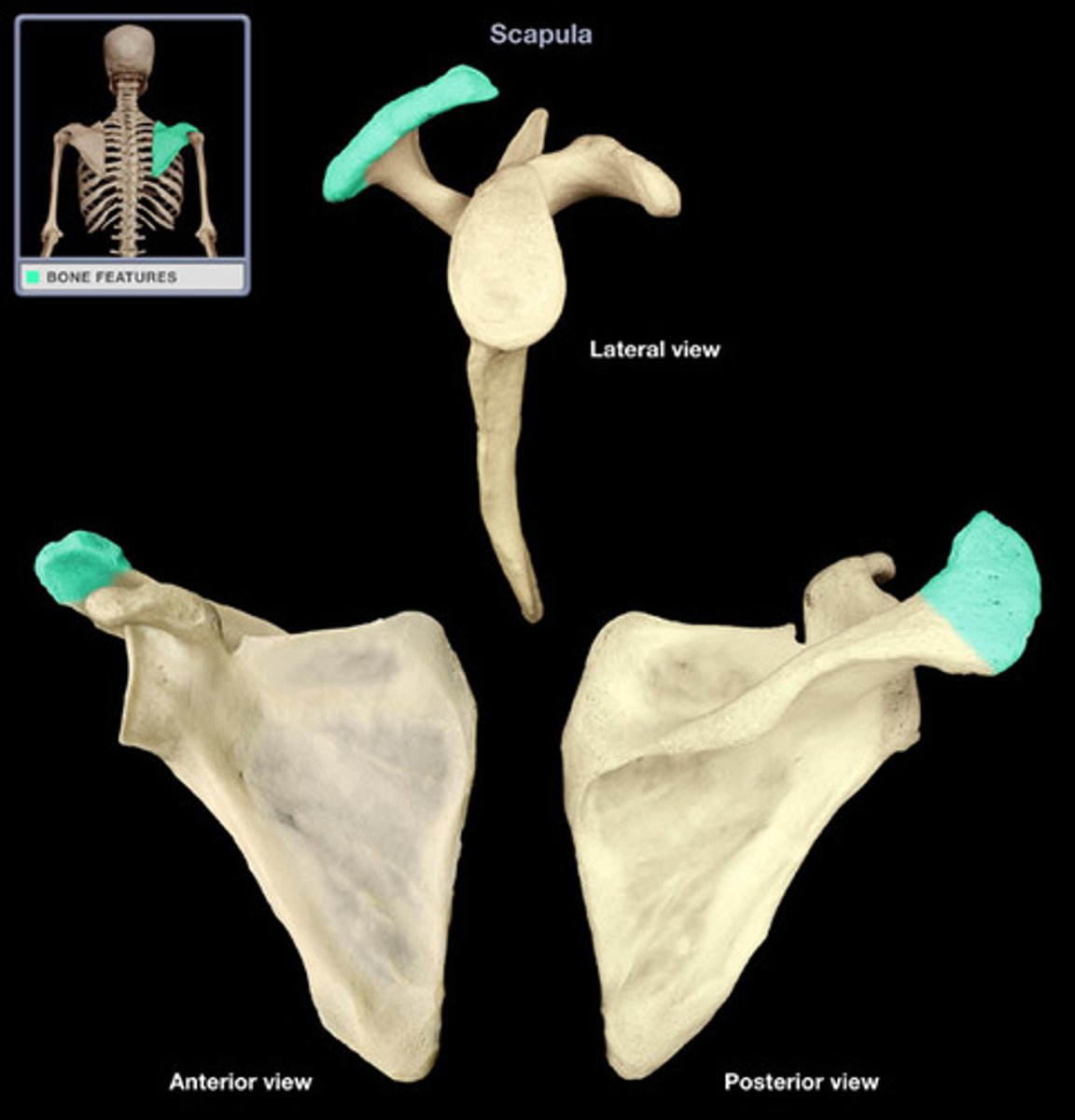
Acromion of scapula:
- on posterior surface of scapula
- lateral contribution of the spine
Supraspinous process of scapula:
- on posterior surface of the scapula
- above the spine of the scapula
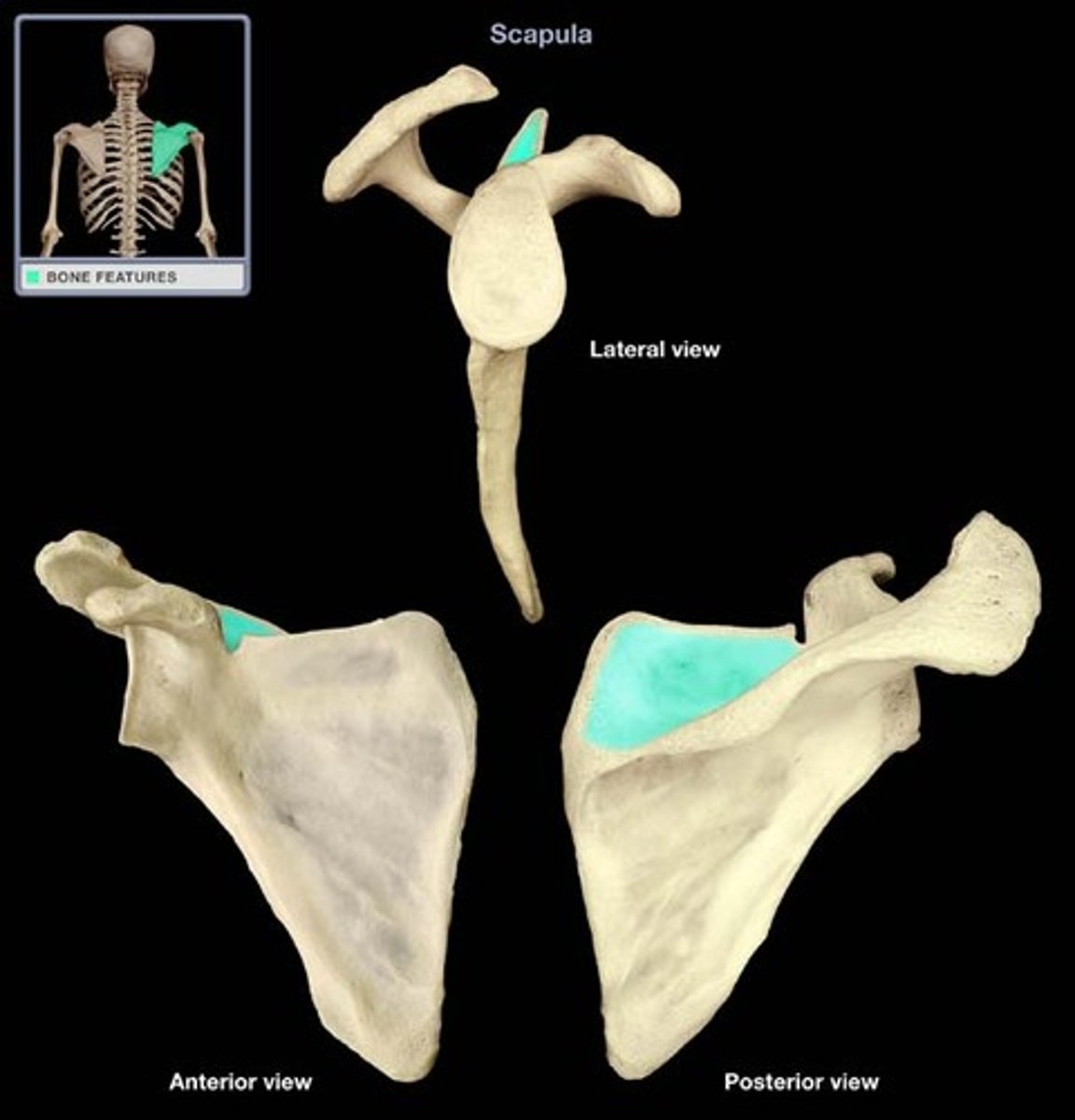
Infraspinous process of scapula:
- on posterior surface of the scapula
- inferior to the spine of the scapula
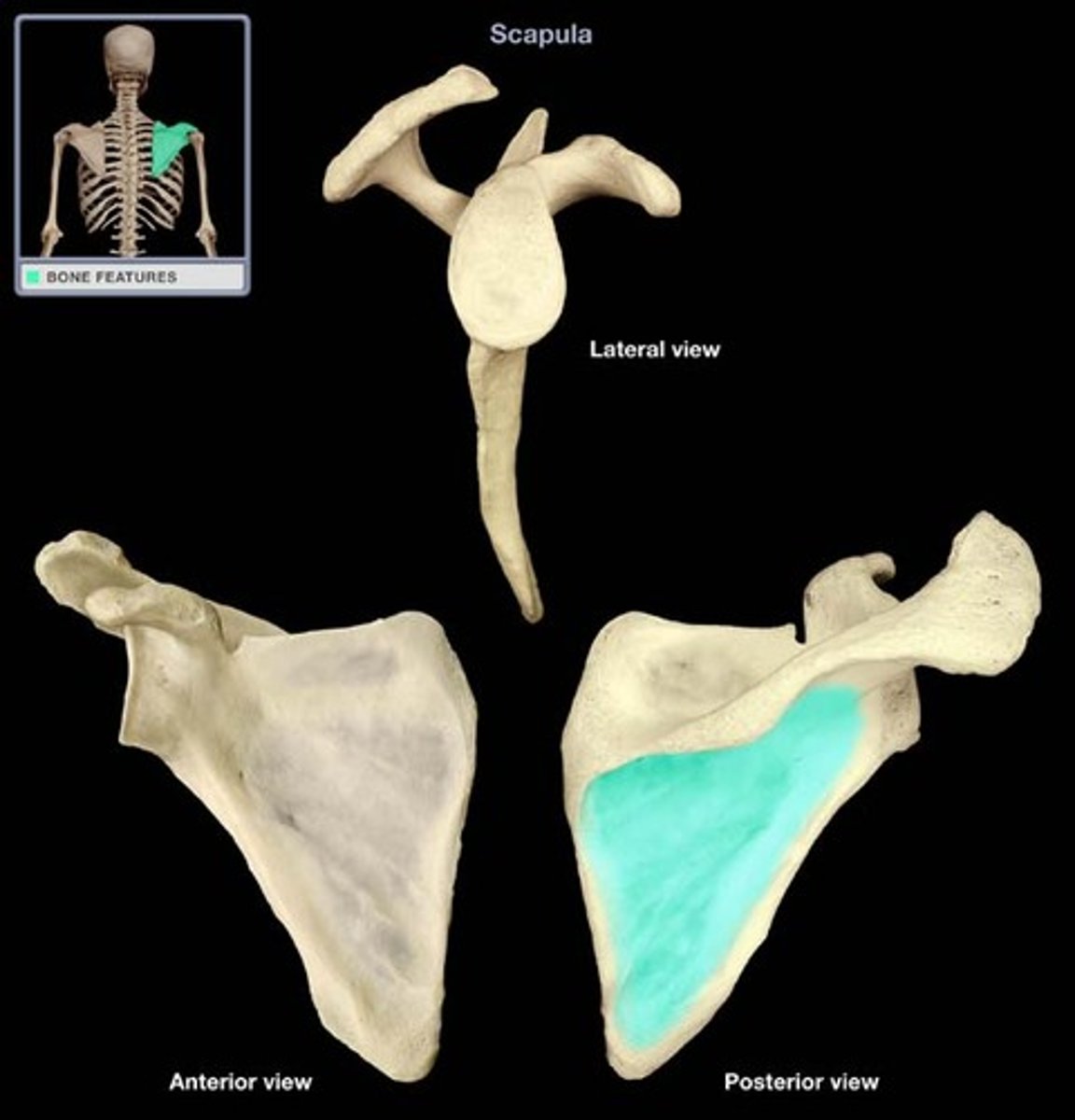
Subscapular fossa of scapula:
- on costal surface of scapula
- occupies most of the costal surface
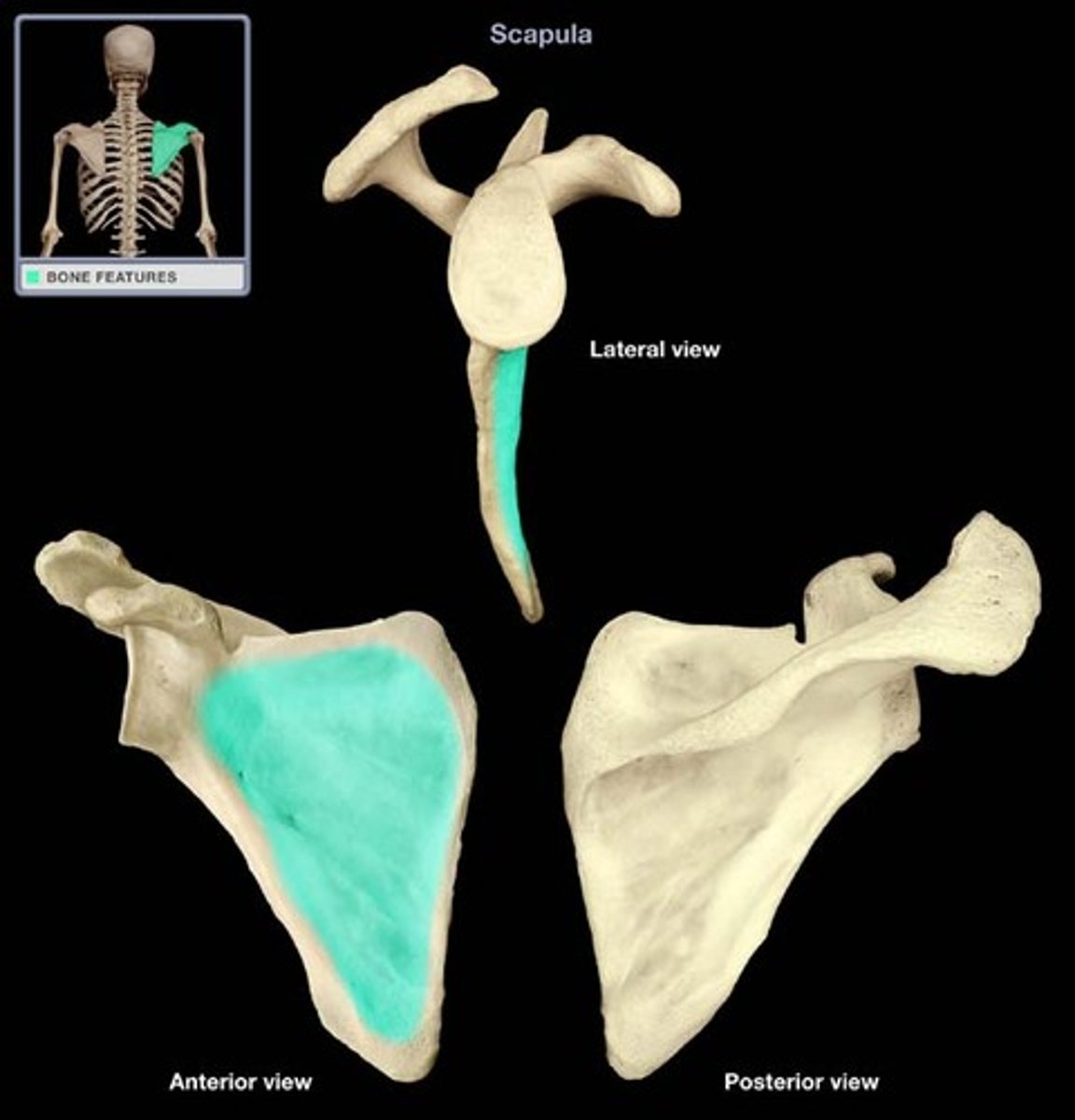
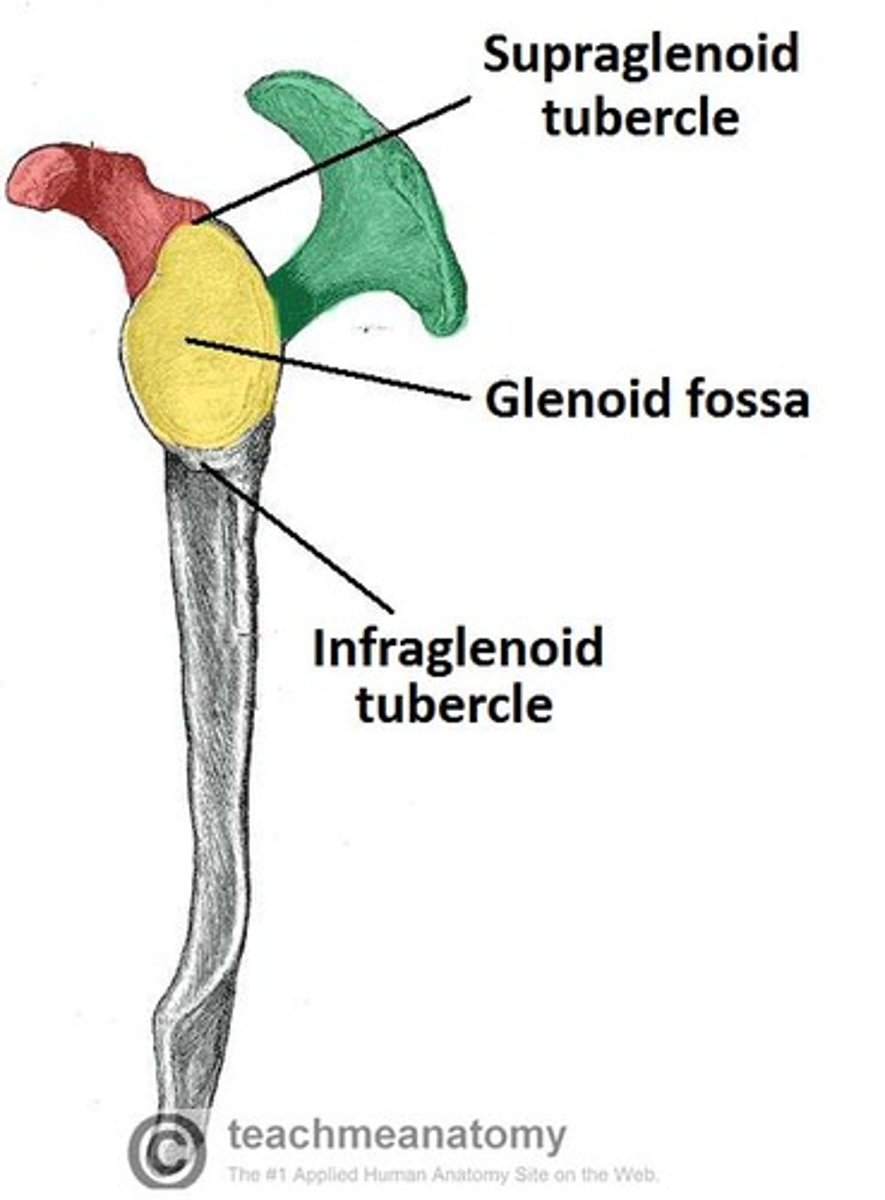
Glenoid cavity of the scapula:
- on the lateral surface of the scapula
- located superolaterally receives and articulates with the head of the humerus (glenohumeral joint)
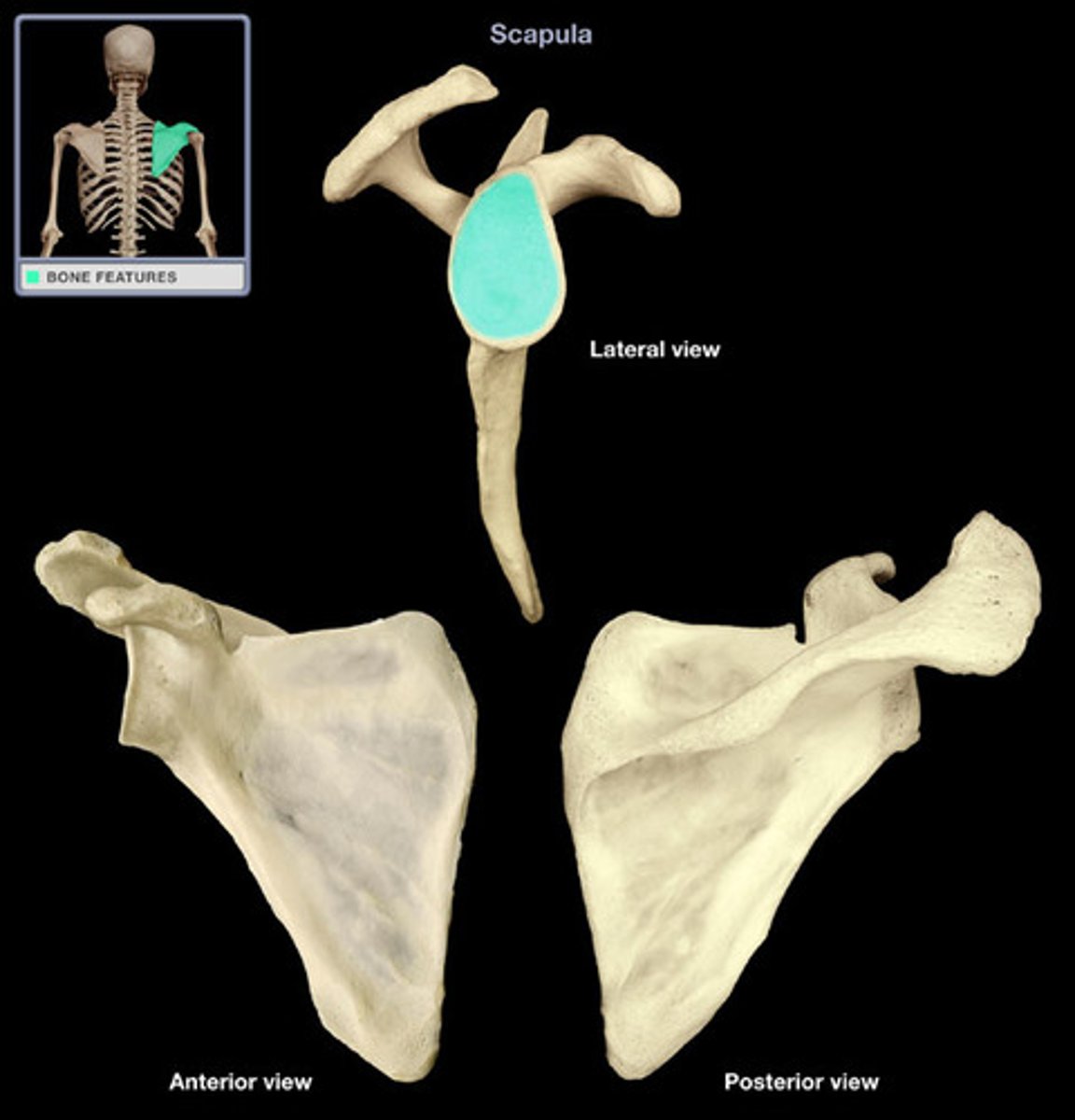
What is the name of the joint between the glenoid cavity and the head of the humerus?
the glenohumeral joint
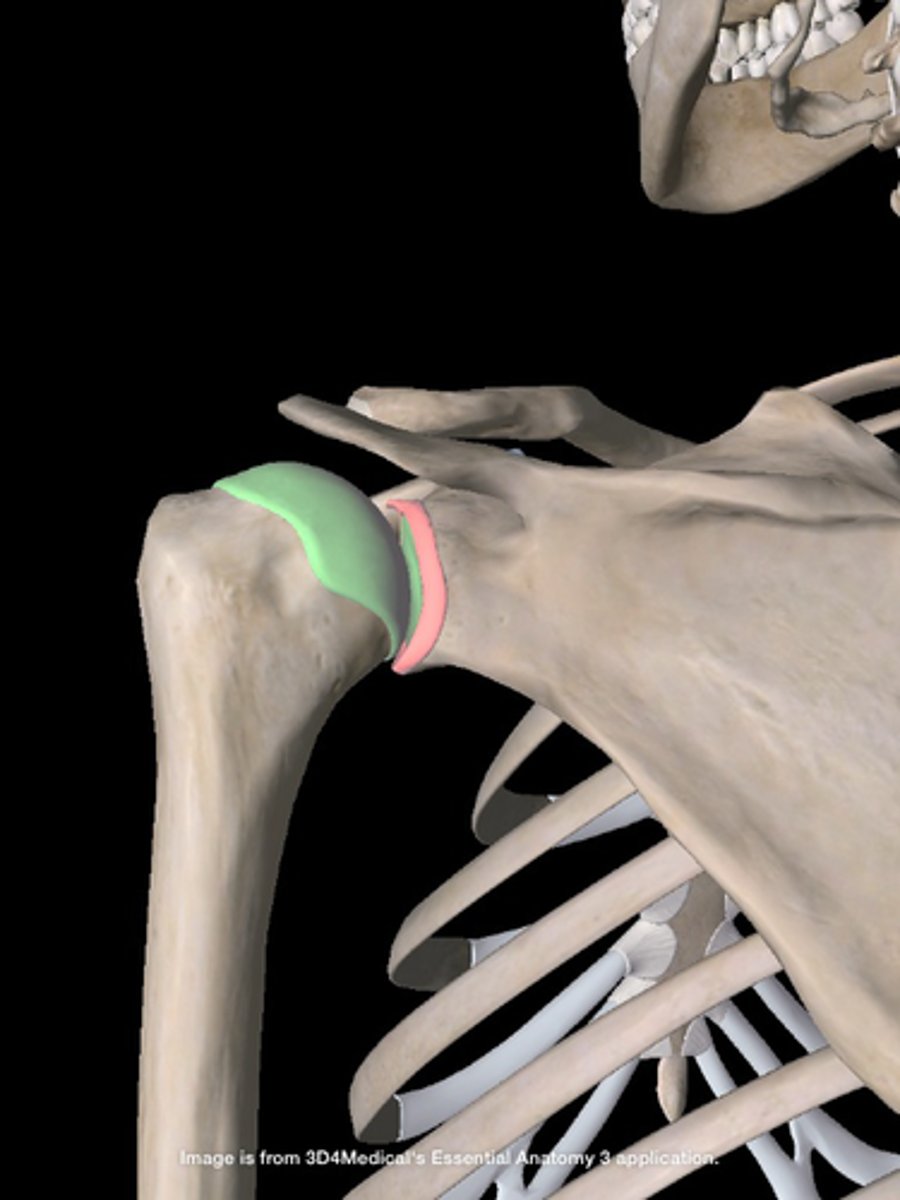
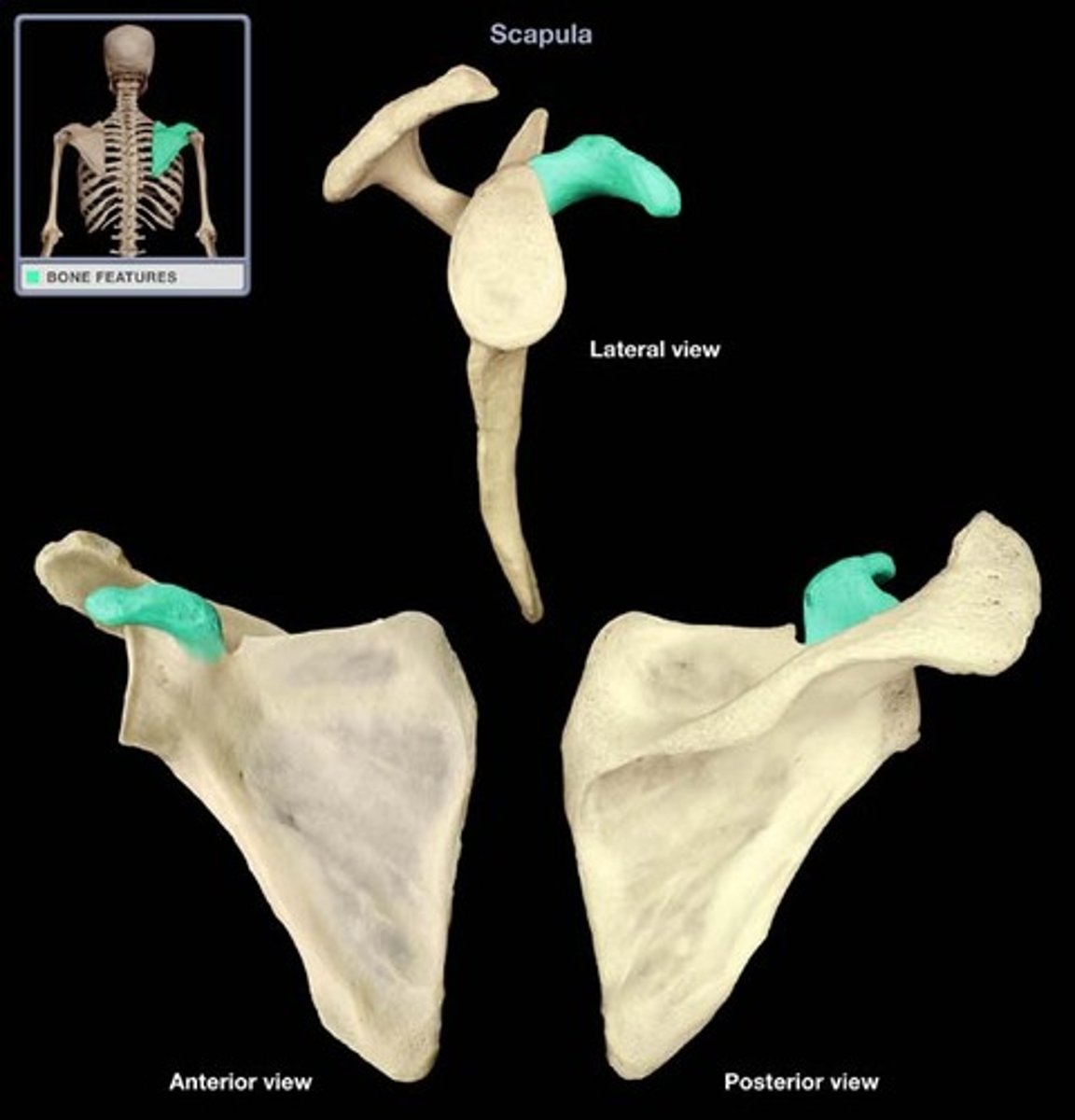
Coracoid process of scapula:
- on lateral surface of the scapula
- superior to the glenoid cavity, projects anterolaterally
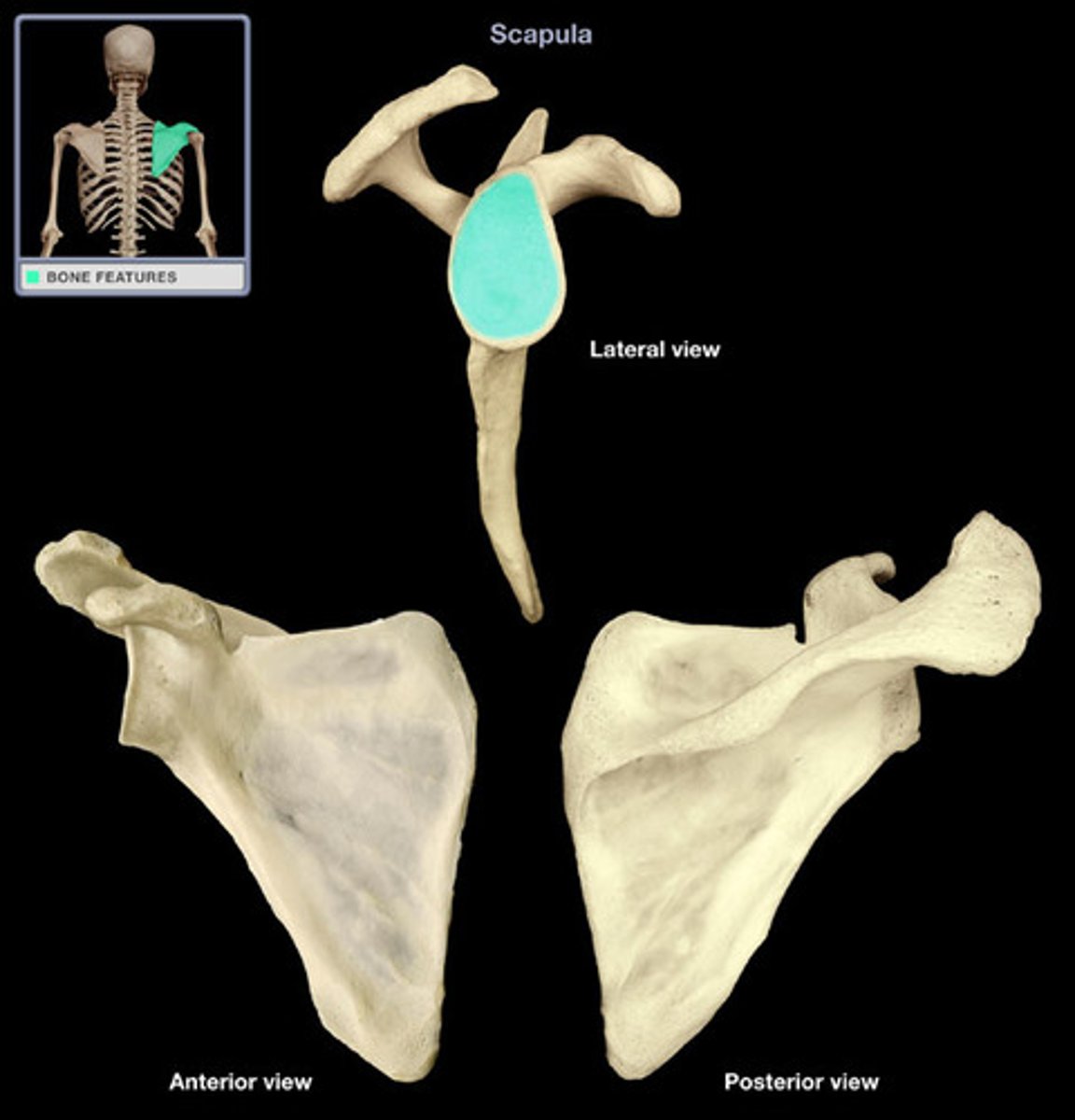
Head of scapula of scapula:
- on the lateral surface of the scapula
- contains the glenoid cavity
Neck of scapula of scapula:
- on the lateral surface of the scapula
- between the head and body of scapula
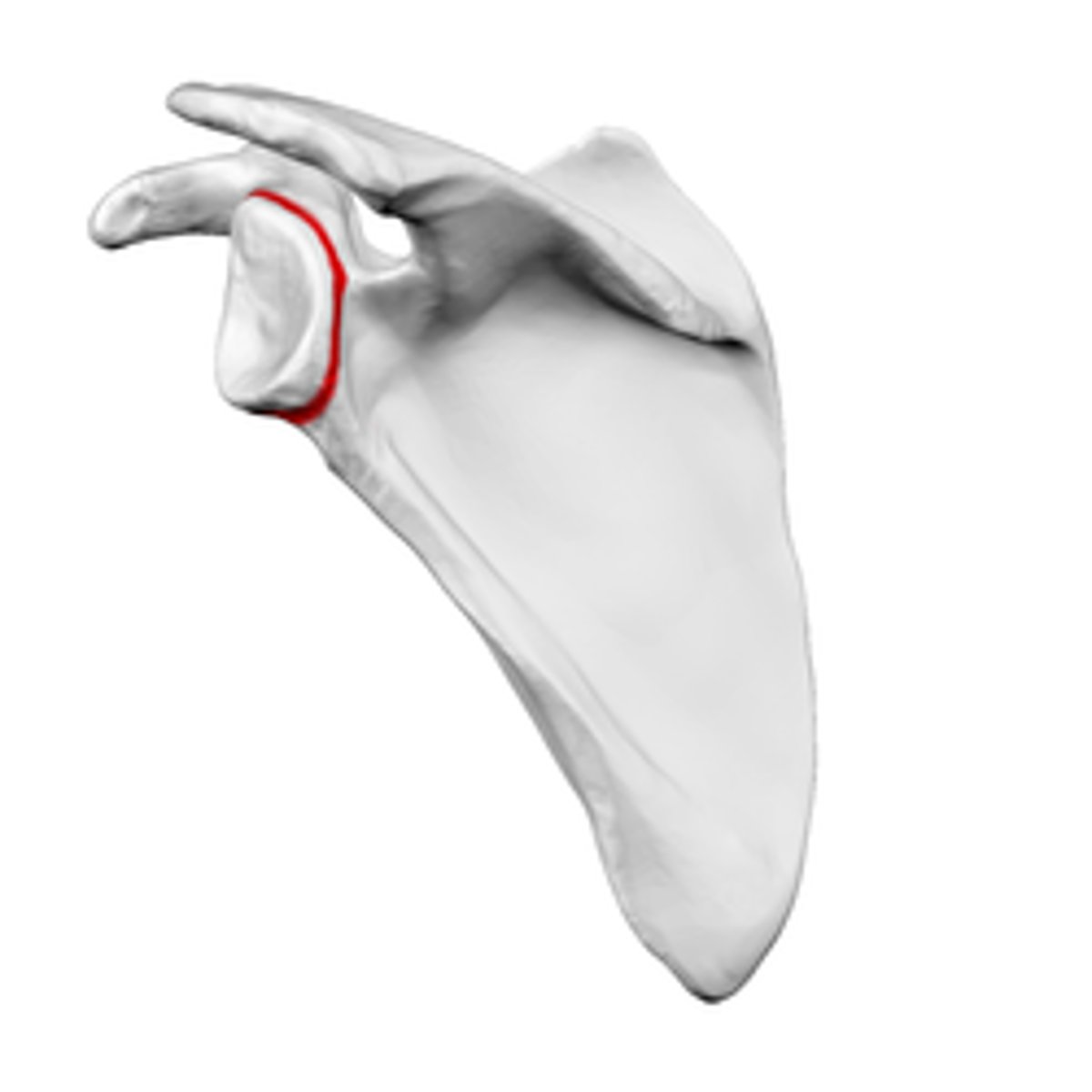
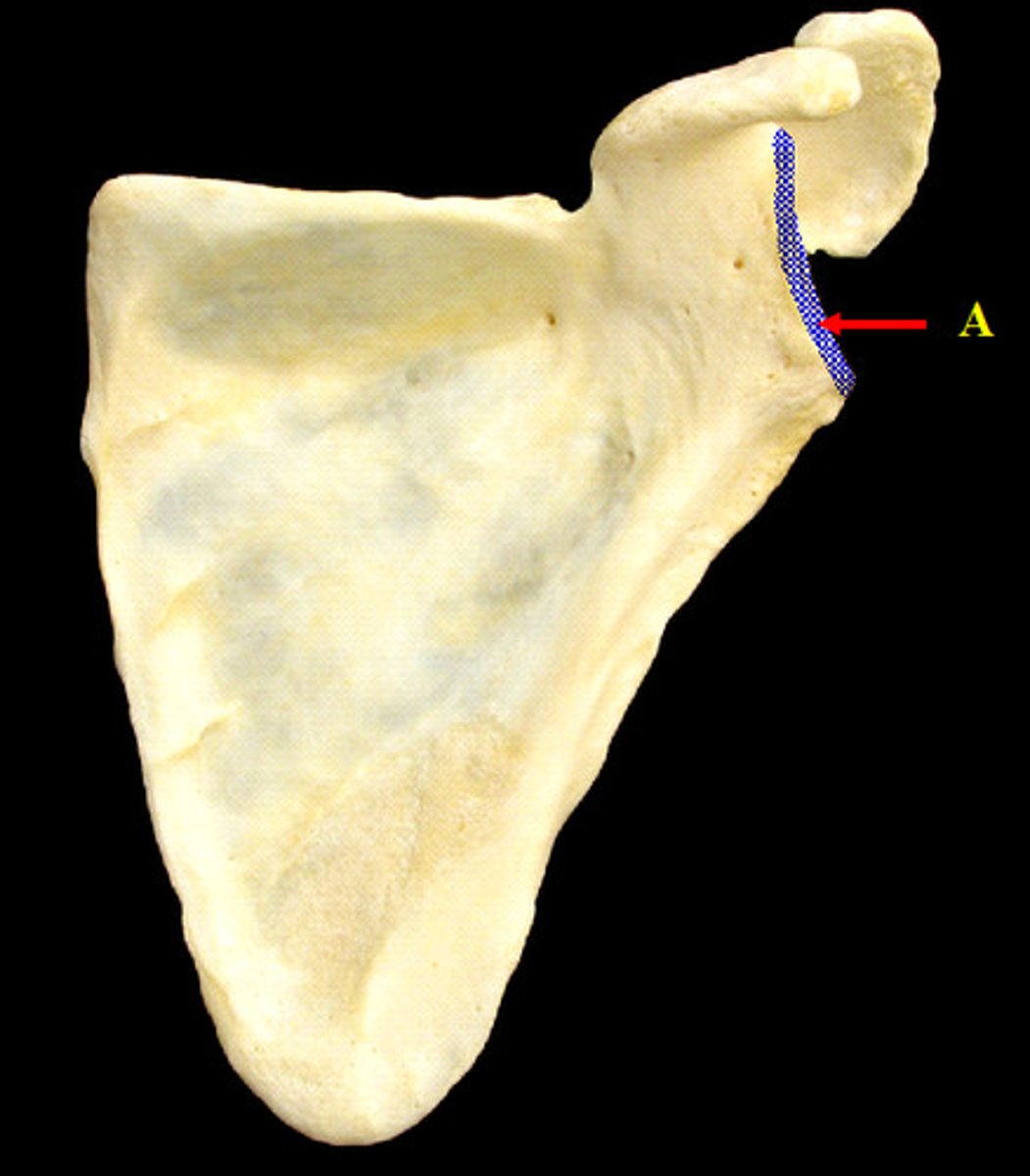
Suprascapular notch of scapula:
- on lateral surface of scapula
- junction of the superior border with the base of the coracoid process
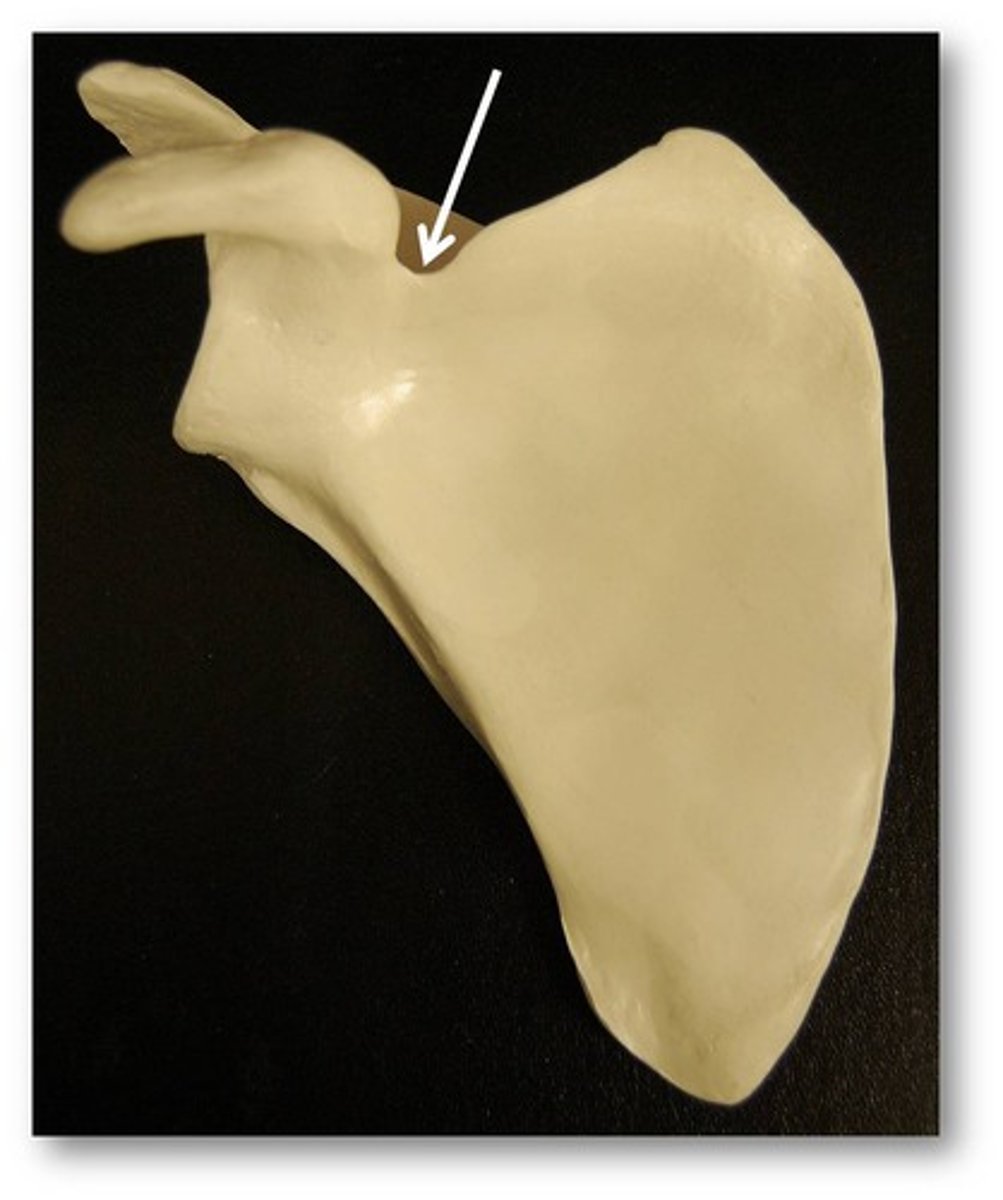
What is the relationship between the suprascapular notch, superior transverse ligament, and the suprascapular nerve?
the suprascapular notch is converted into a foramen by the superior transverse ligament and serves as a passage for the suprascapular nerve
Borders of the scapula:
- superior
- lateral
- medial
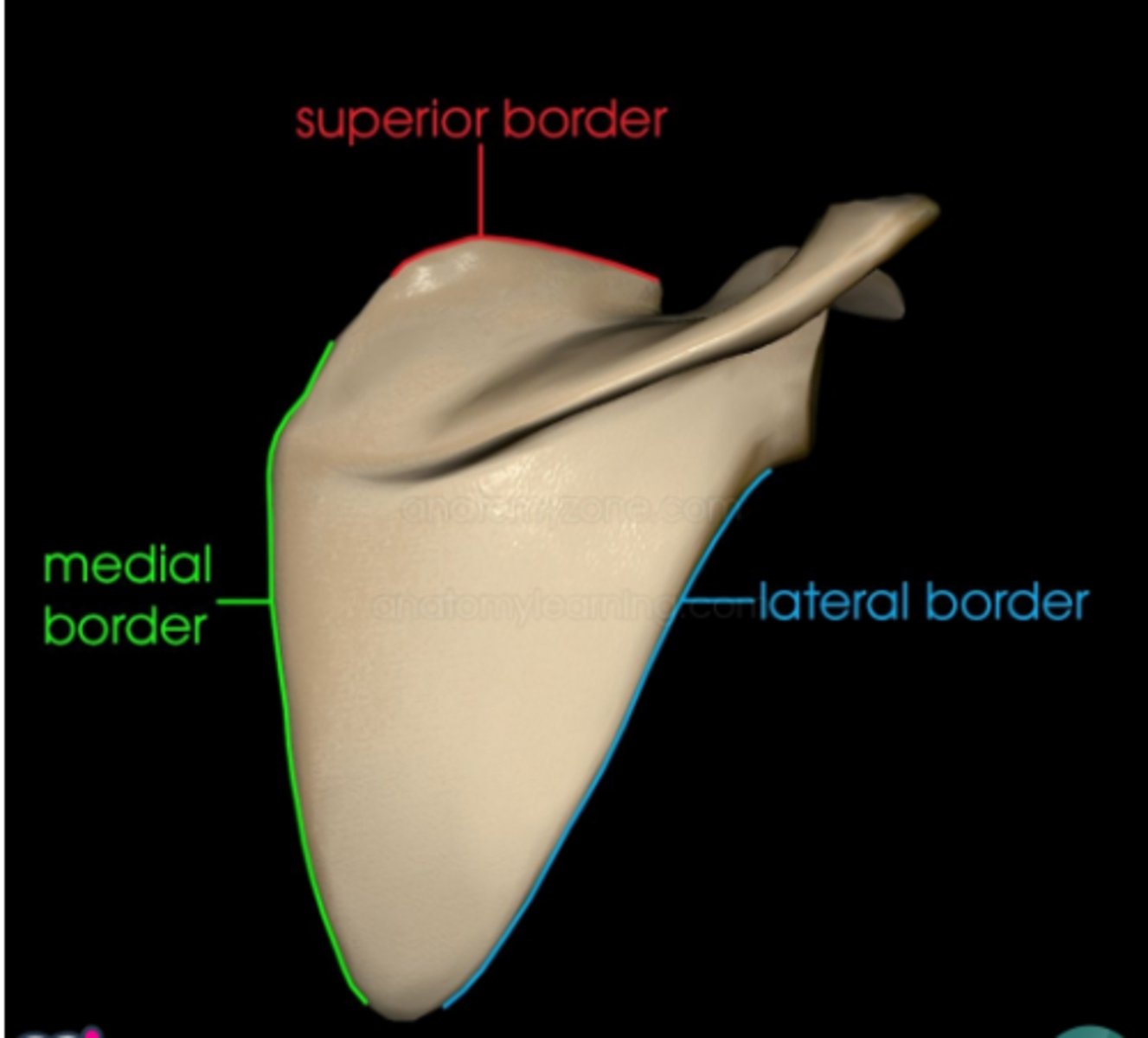
Where is the superior border of the scapula?
border near the suprascapular notch
Where is the lateral border of the scapula?
border near the humerus
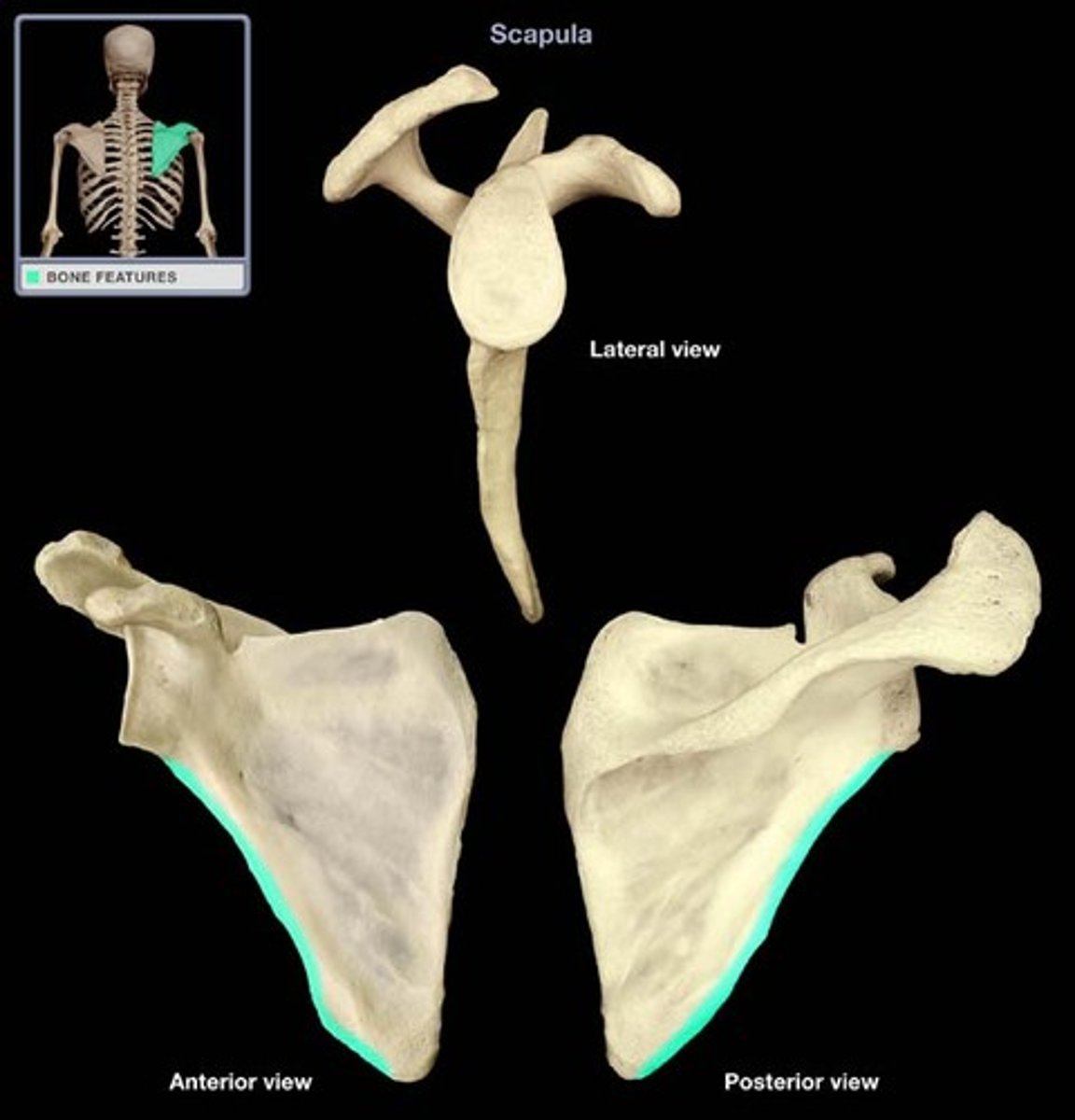
Where is the medial border of the scapula?
border runs parallel to spinous processes of the vertebrae
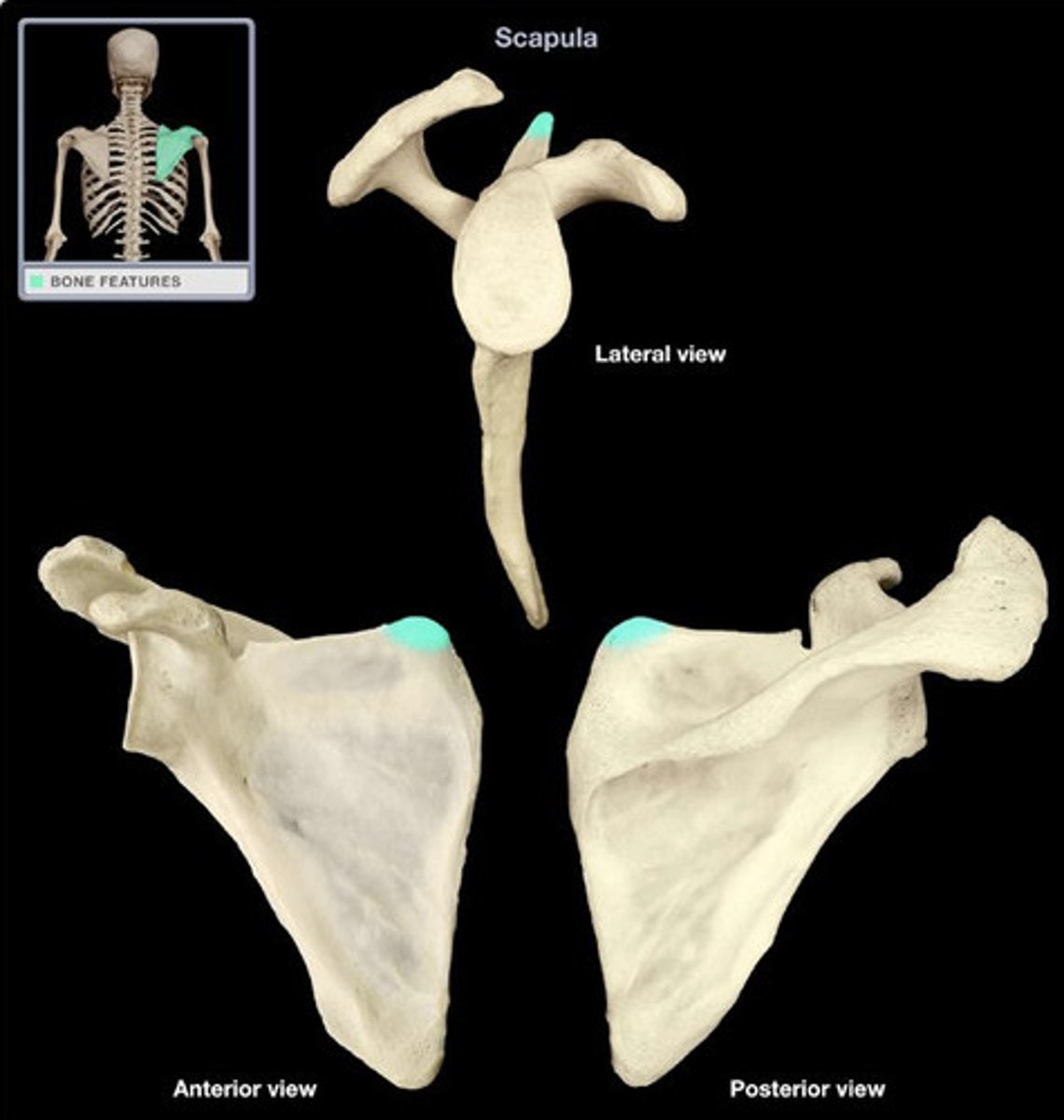
What are the angles of the scapula?
- superior
- inferior
- lateral
Where is the superior angle of the scapula?
angle at the union of superior and medial borders
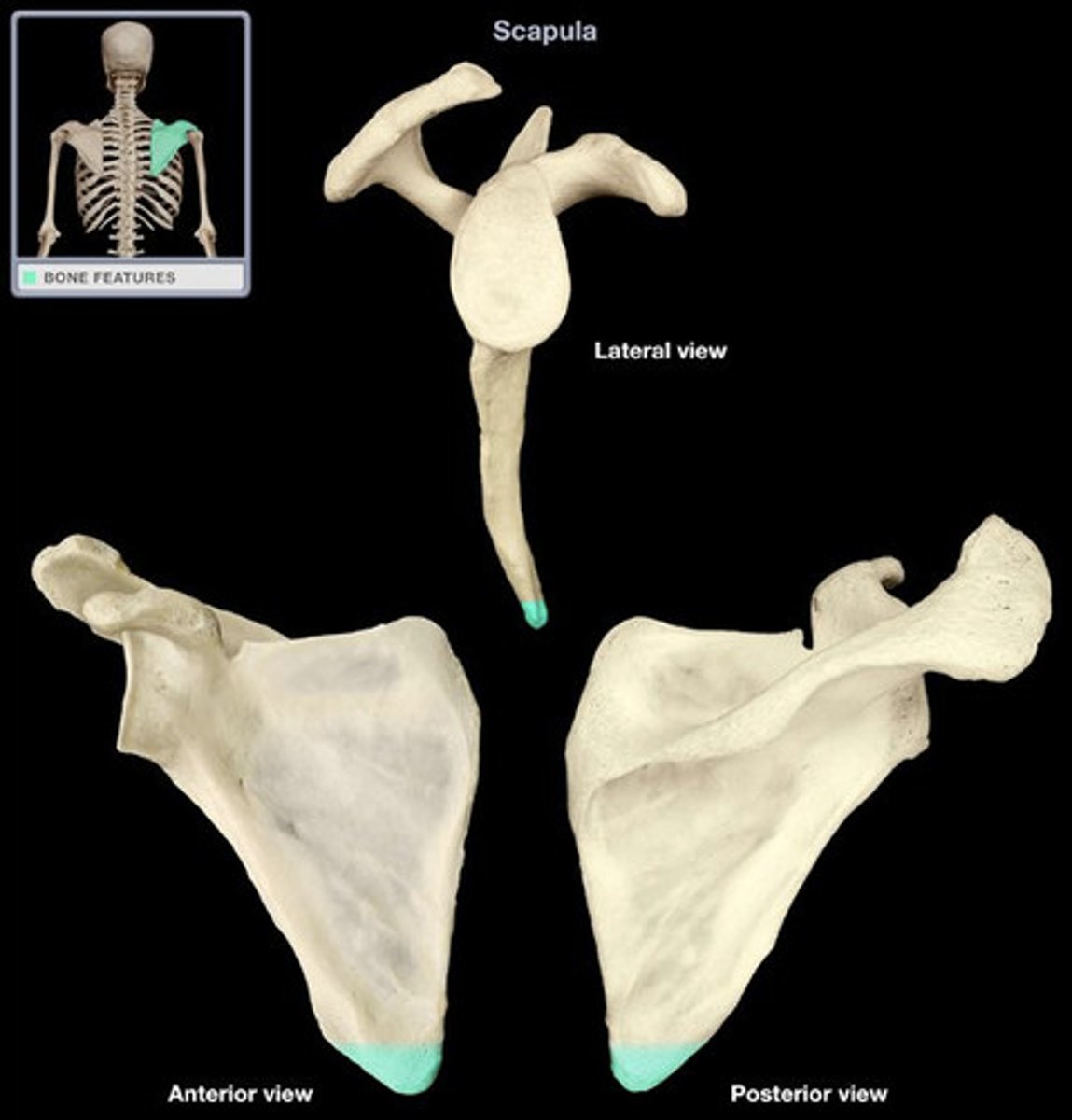
Where is the inferior angle of the scapula?
angle at the union of medial and lateral borders
Where is the lateral angle of the scapula?
angle contains the head of the scapula
The humerus is the ______ bone in the UE
largest
What bones do the humerus articulate with?
- scapula via glenohumeral joint
- radius & ulna via elbow joint
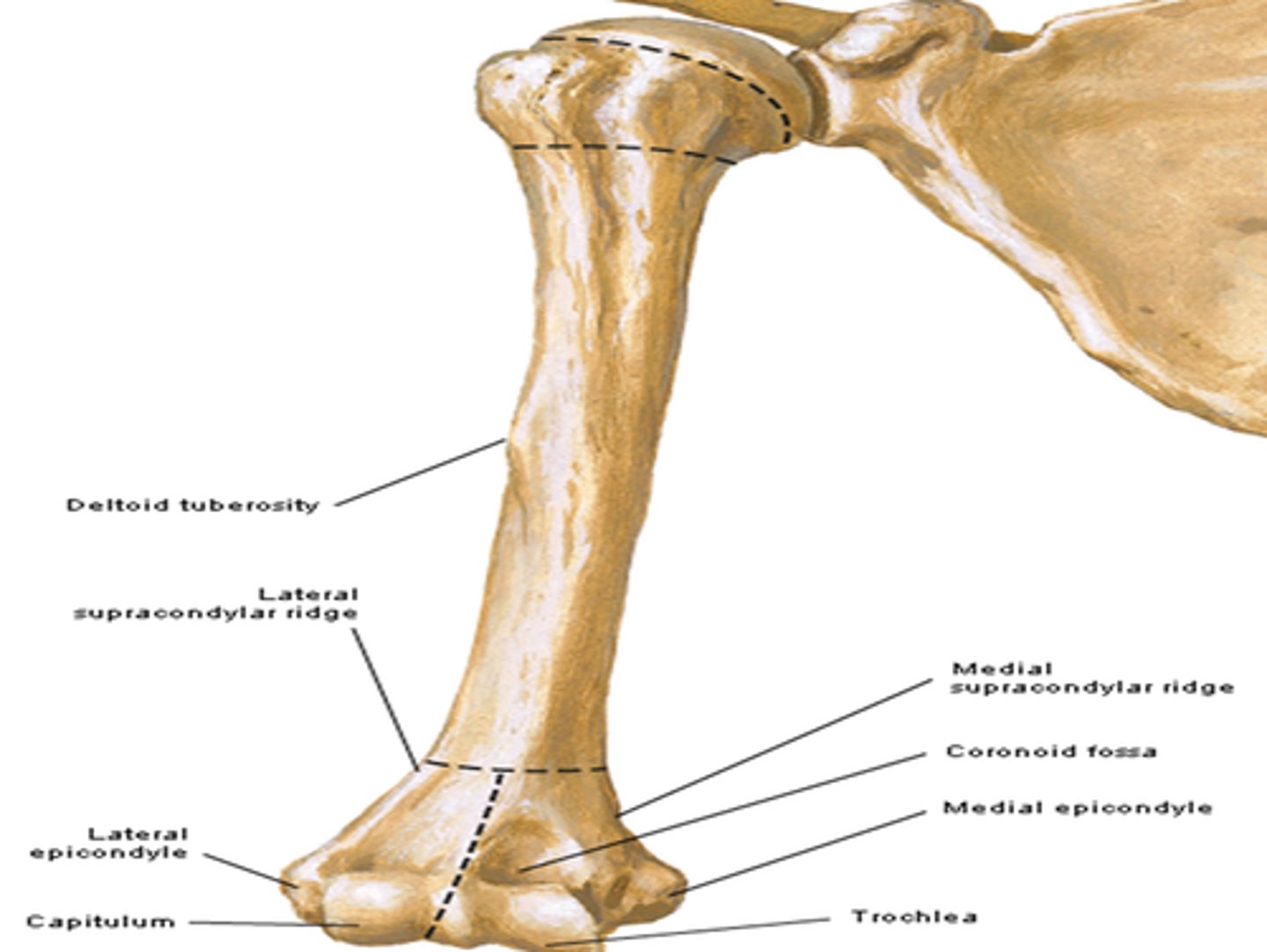
Features of the humerus:
- head
- anatomical nech
- surgical neck
- greater tubercle
- lesser tubercle
- intertubercular groove
- shaft
- deltoid tuberosity
- radial groove
- medial and lateral supra-epicondylar ridges
- condyle
- capitulum
- trochlea
- coronoid fossa
- olecranon fossa
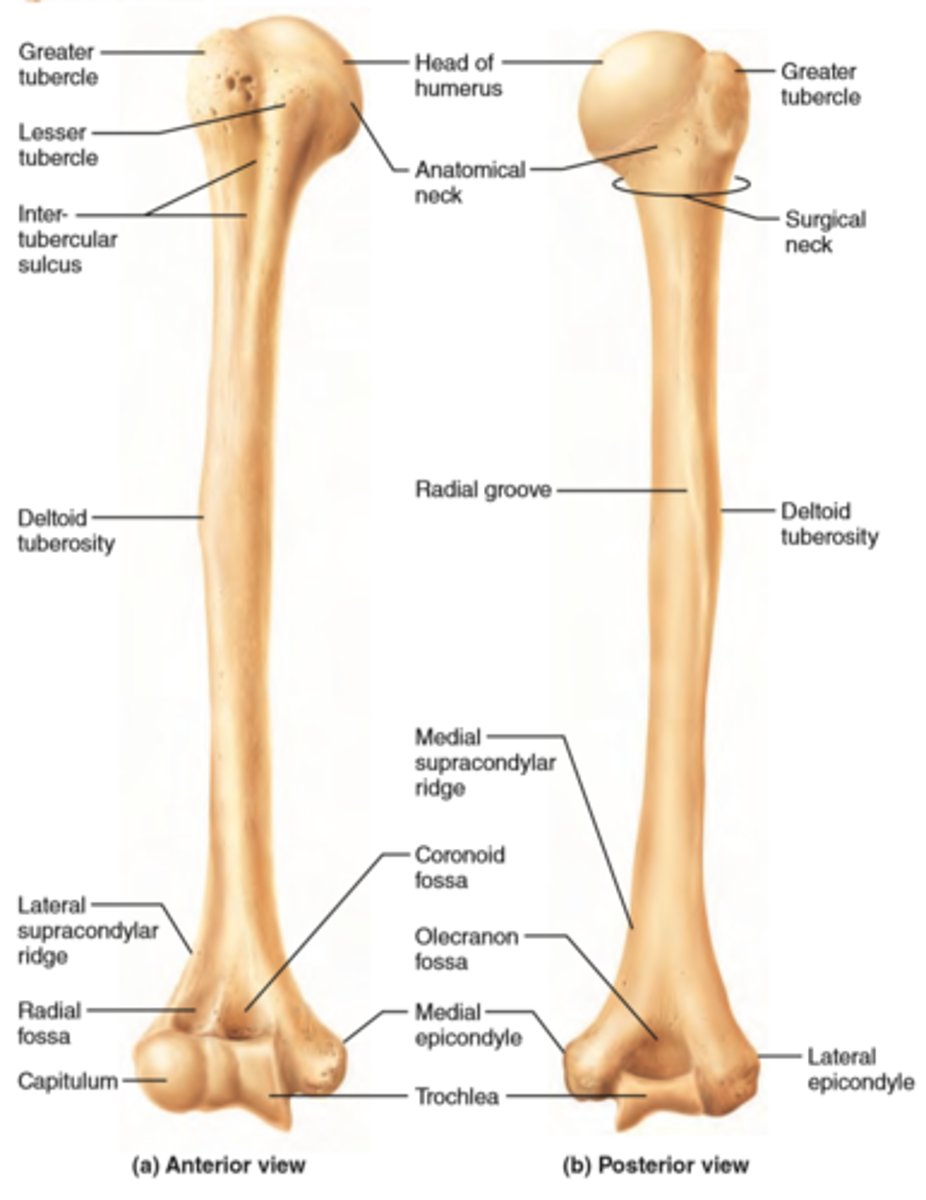
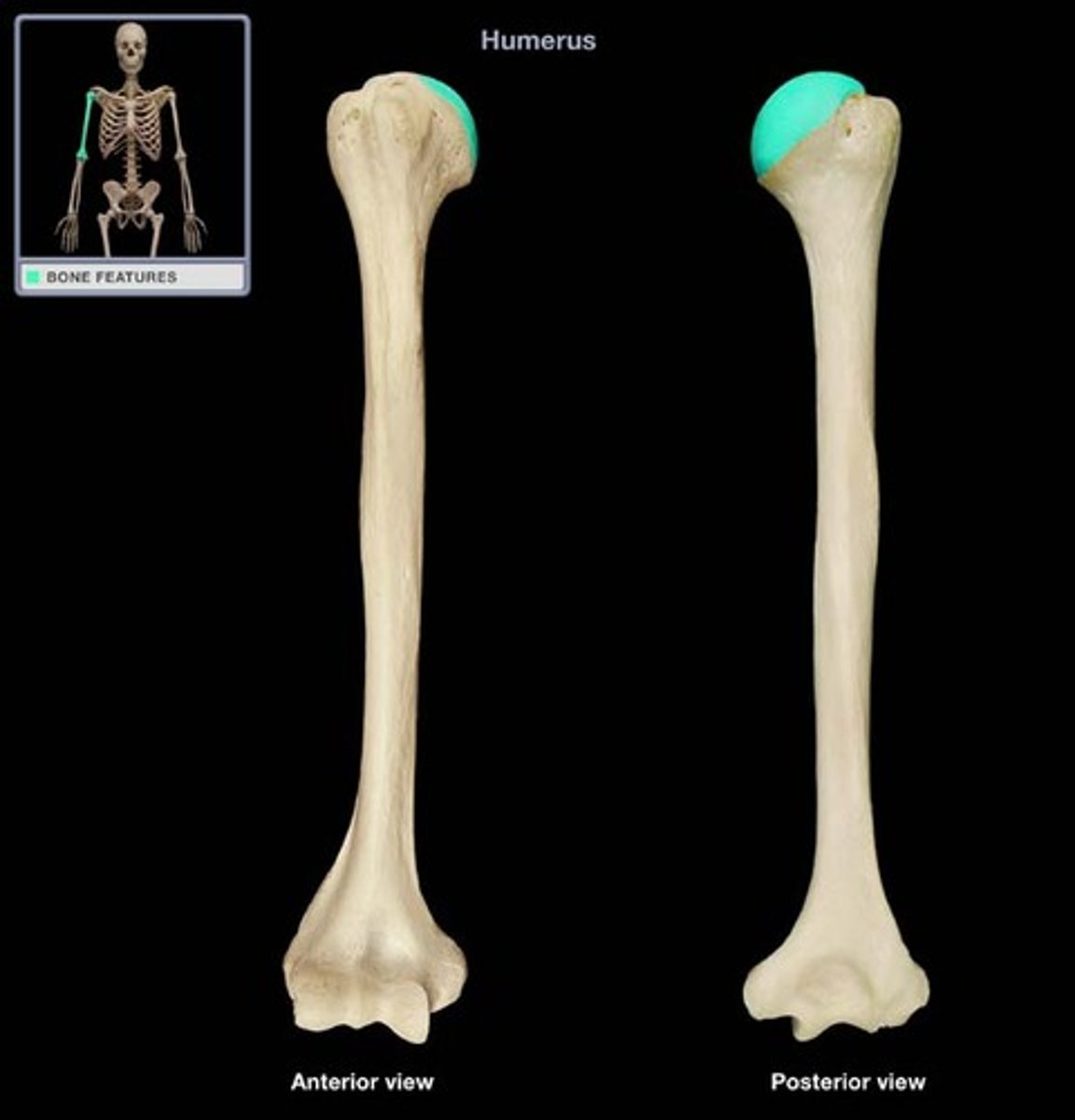
Head of the humerus:
articulates with glenoid cavity of scapula
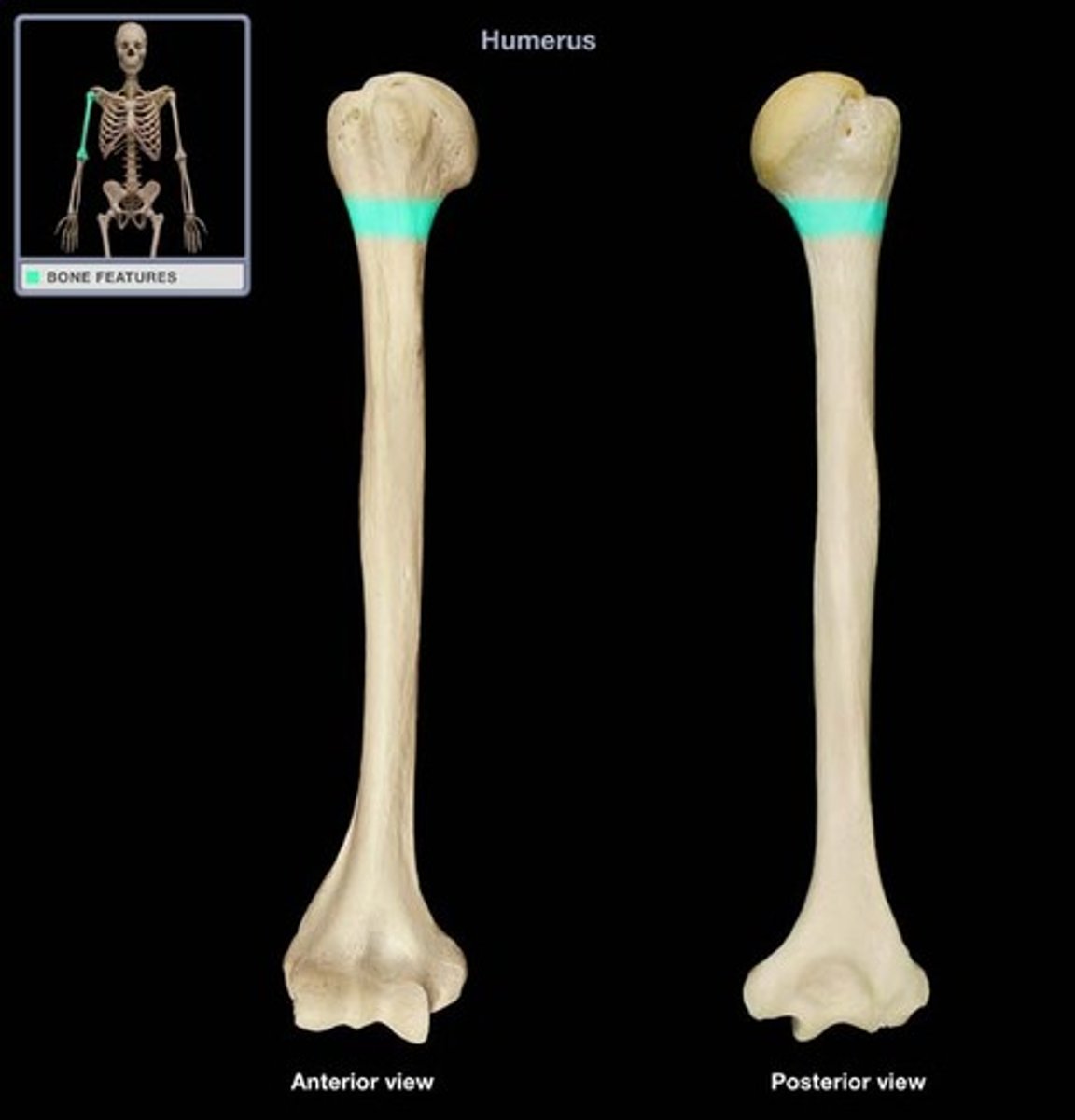
Anatomical neck of the humerus & its function:
- groove
- separates the head from the greater and lesser tubercles
- indicates the place of attachment of the glenohumeral joing capsule
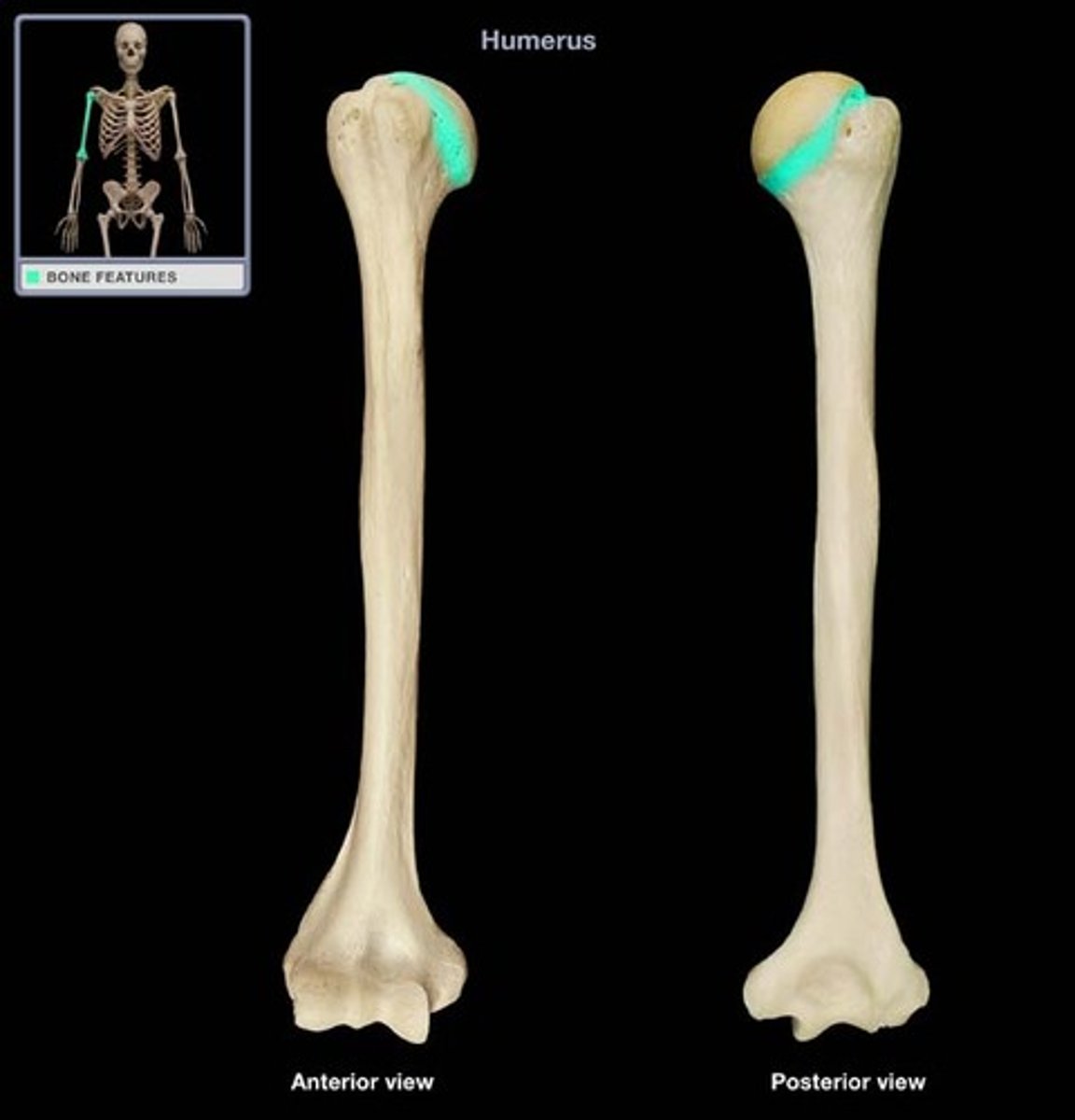
Surgical neck of humerus:
- narrow part distal to head and tubercles
- common site of fracture!!!
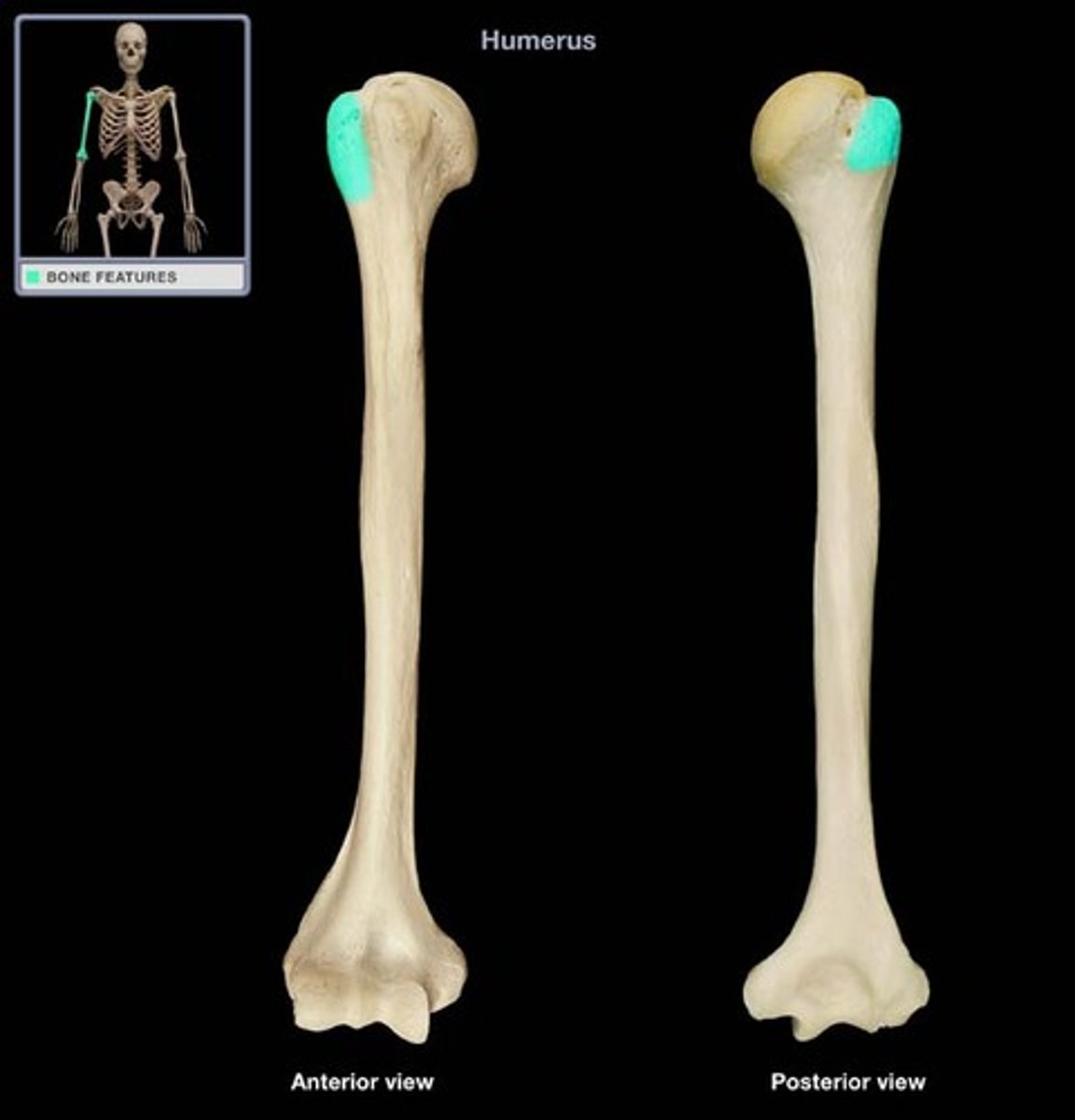
Greater tubercle of humerus:
lateral position from head
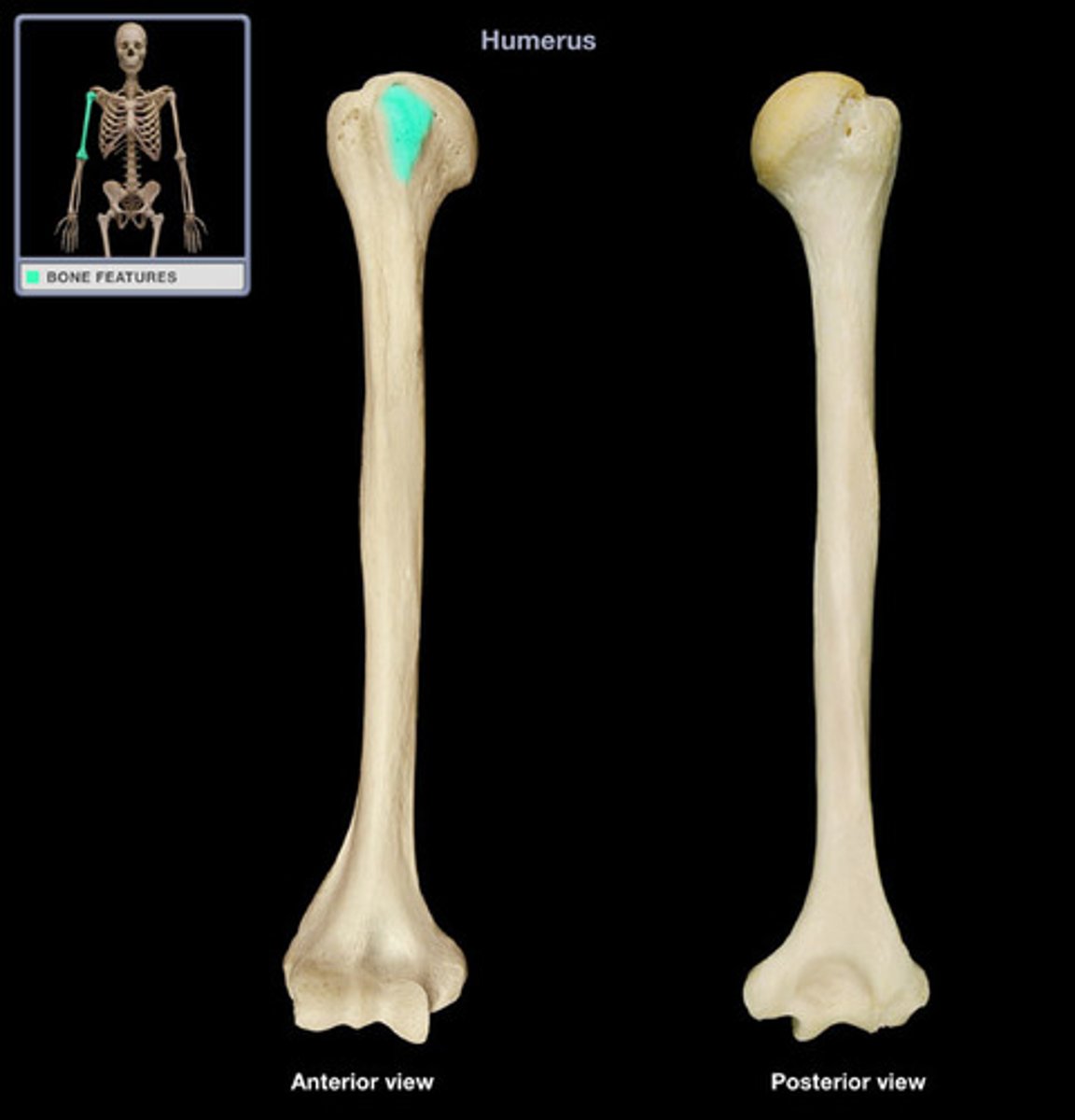
Lesser tubercle of humerus:
anterior position from the head
Intertubercular groove of humerus:
- located between tubercles
- provides passage for the tendon of the long head of the biceps muscle
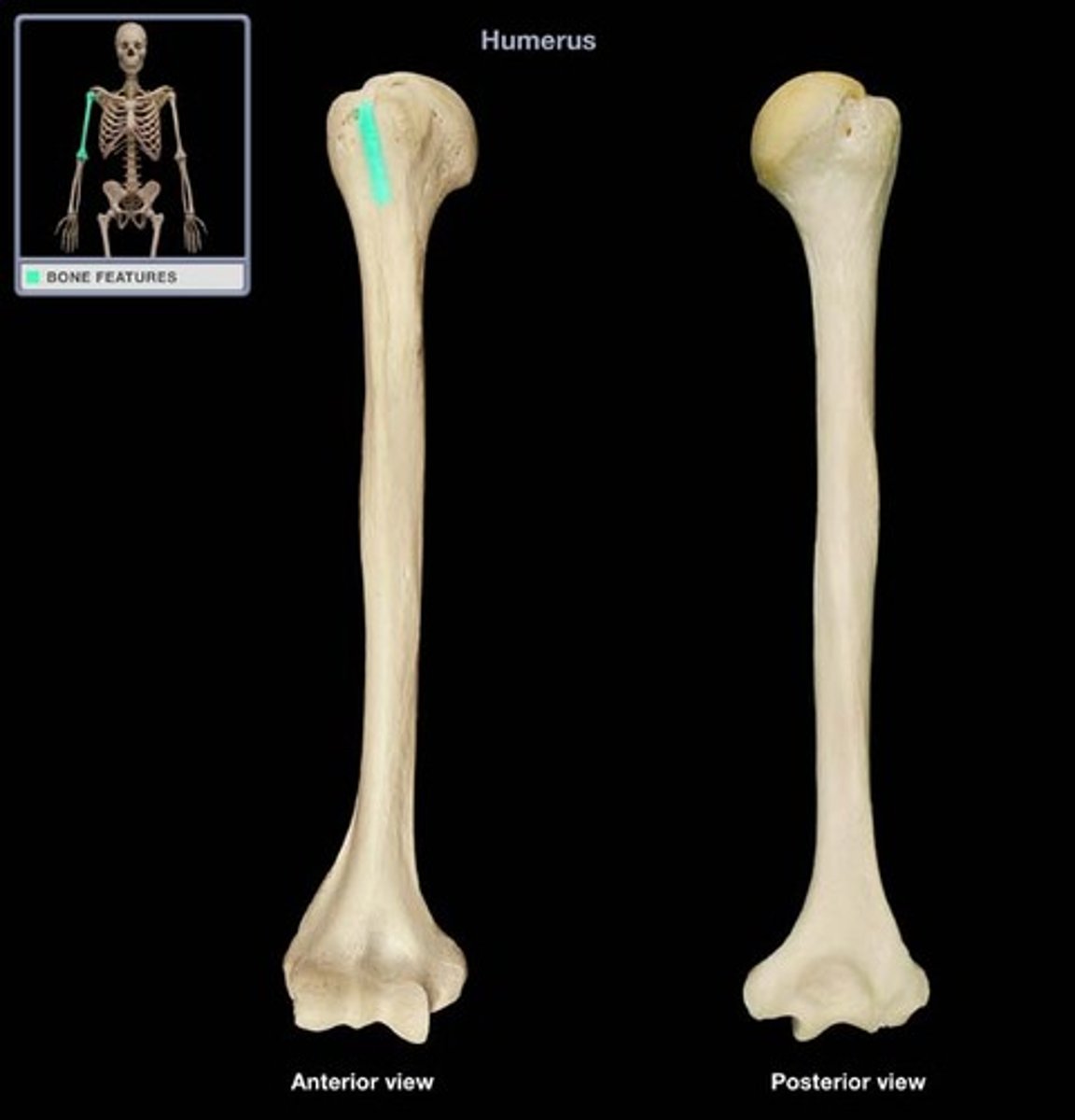
Clinical relevance of humerus:
axillary nerve wraps around the surgical neck. fracture of the surgical neck may damage the axillary nerve. Integrity of this nerve is tested by touching the deltoid, since the nerve provides sensory innervation to this area of the shoulder region
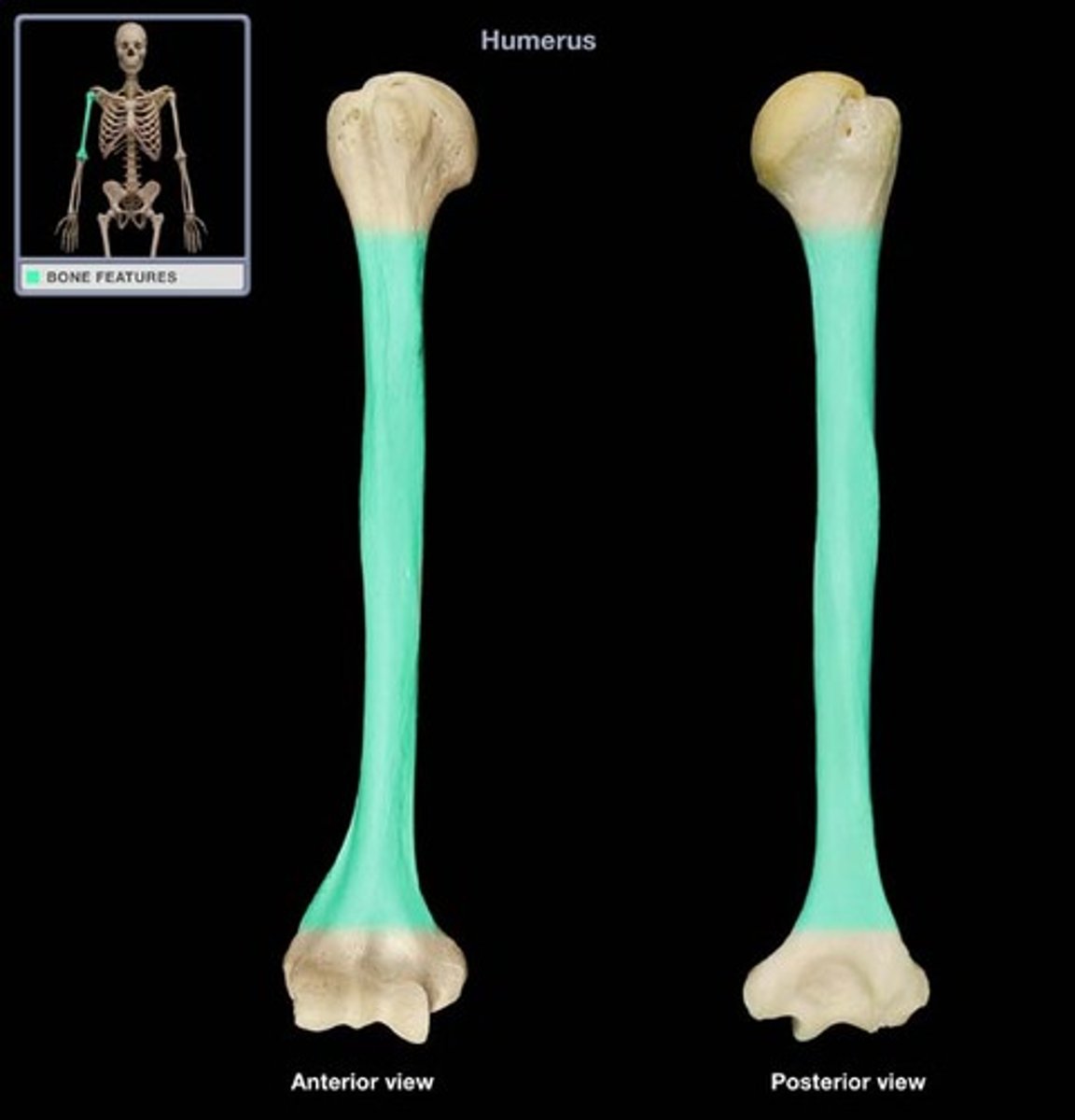
Shaft of the humerus:
long portion of the humerus with a tuberosity and a groove, engrossing distally
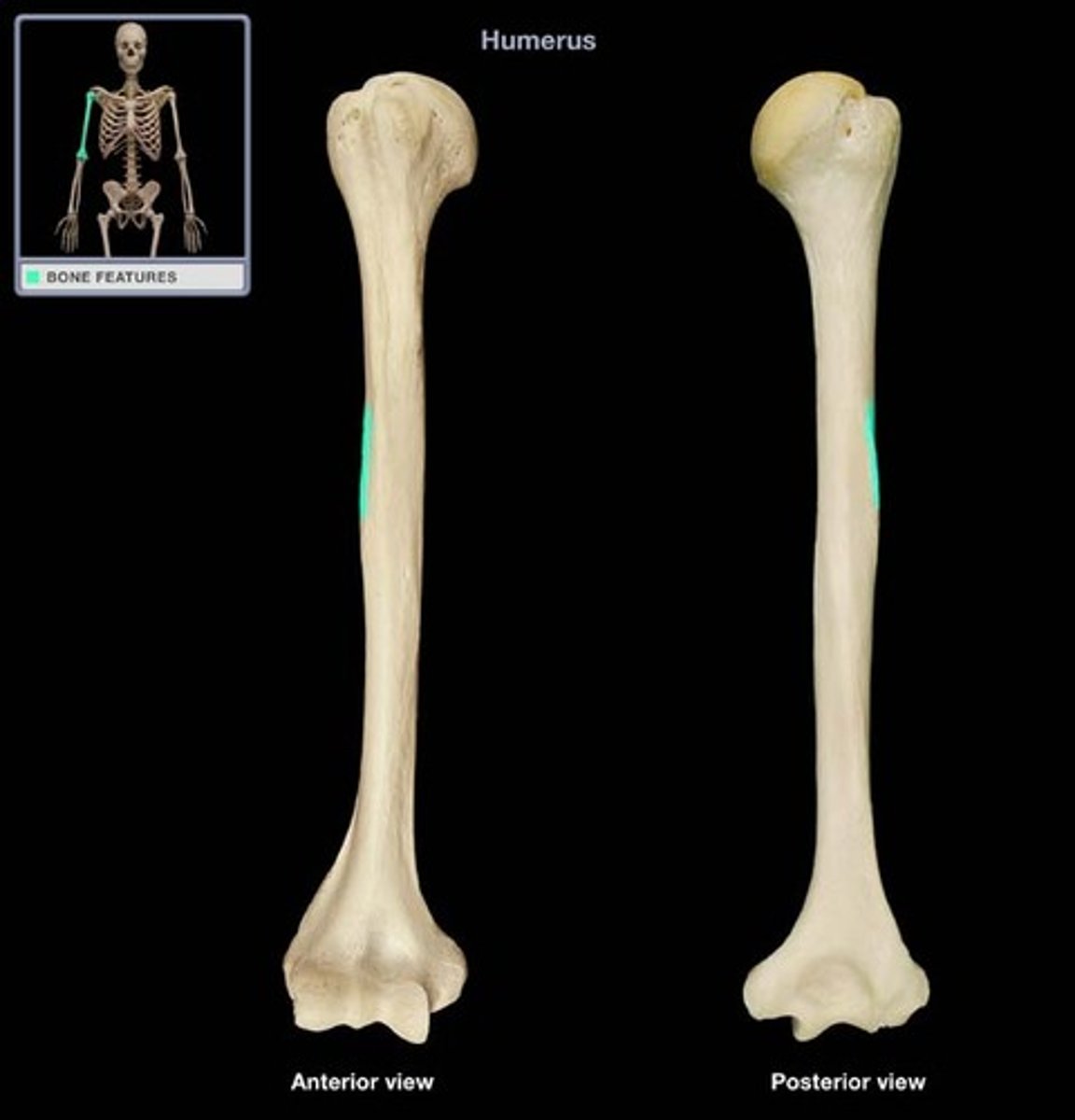
Deltoid tuberosity of humerus:
attachment for deltoid muscle
Radial groove of the humerus:
oblique demarcation on posterior side. Contains the radial nerve and deep artery of arm (named after the nerve)
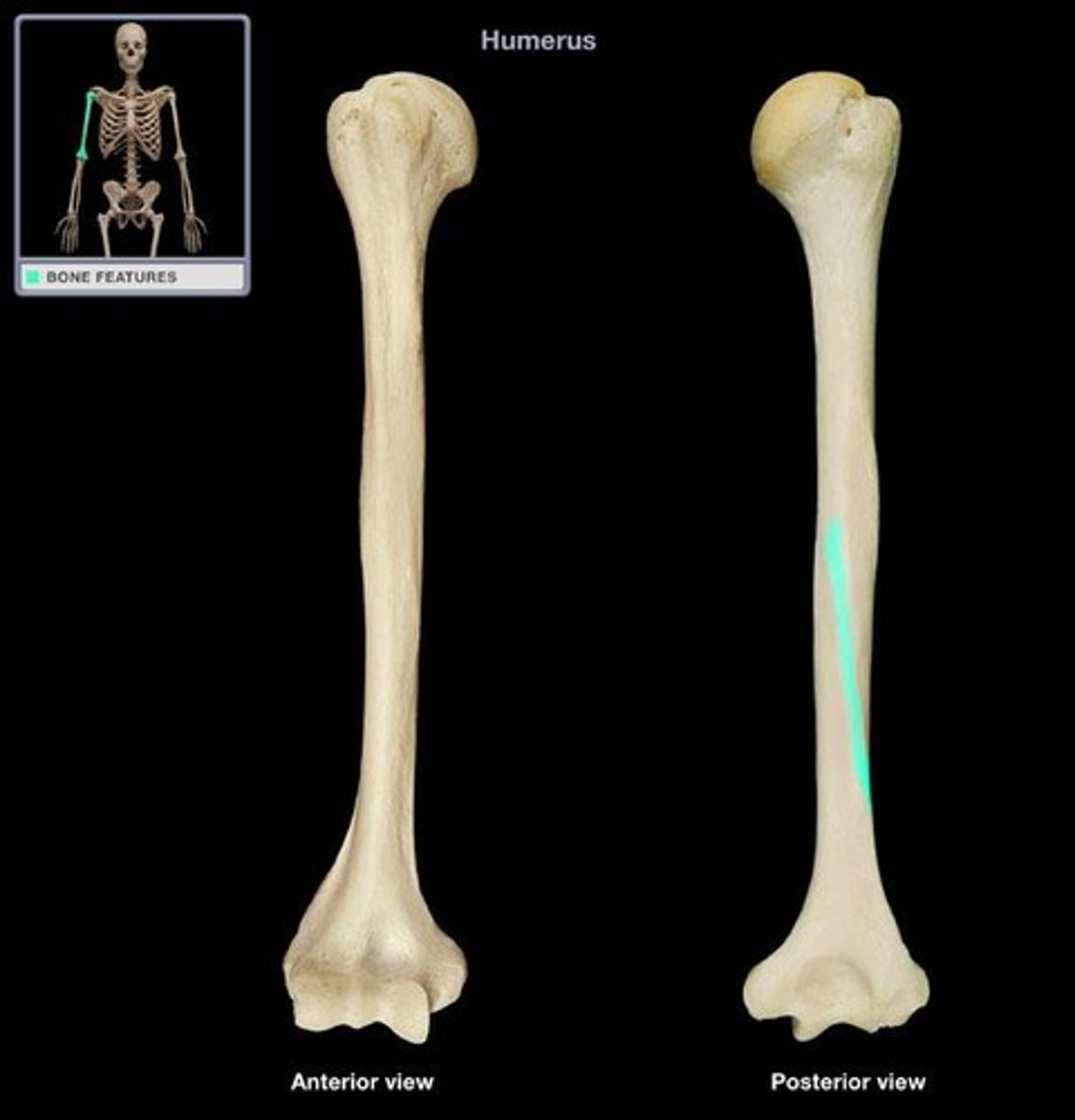
Medial and lateral supra-epicondylar ridges of the humerus:
End distally as the medial and lateral epicondyles, involved in muscle attachment
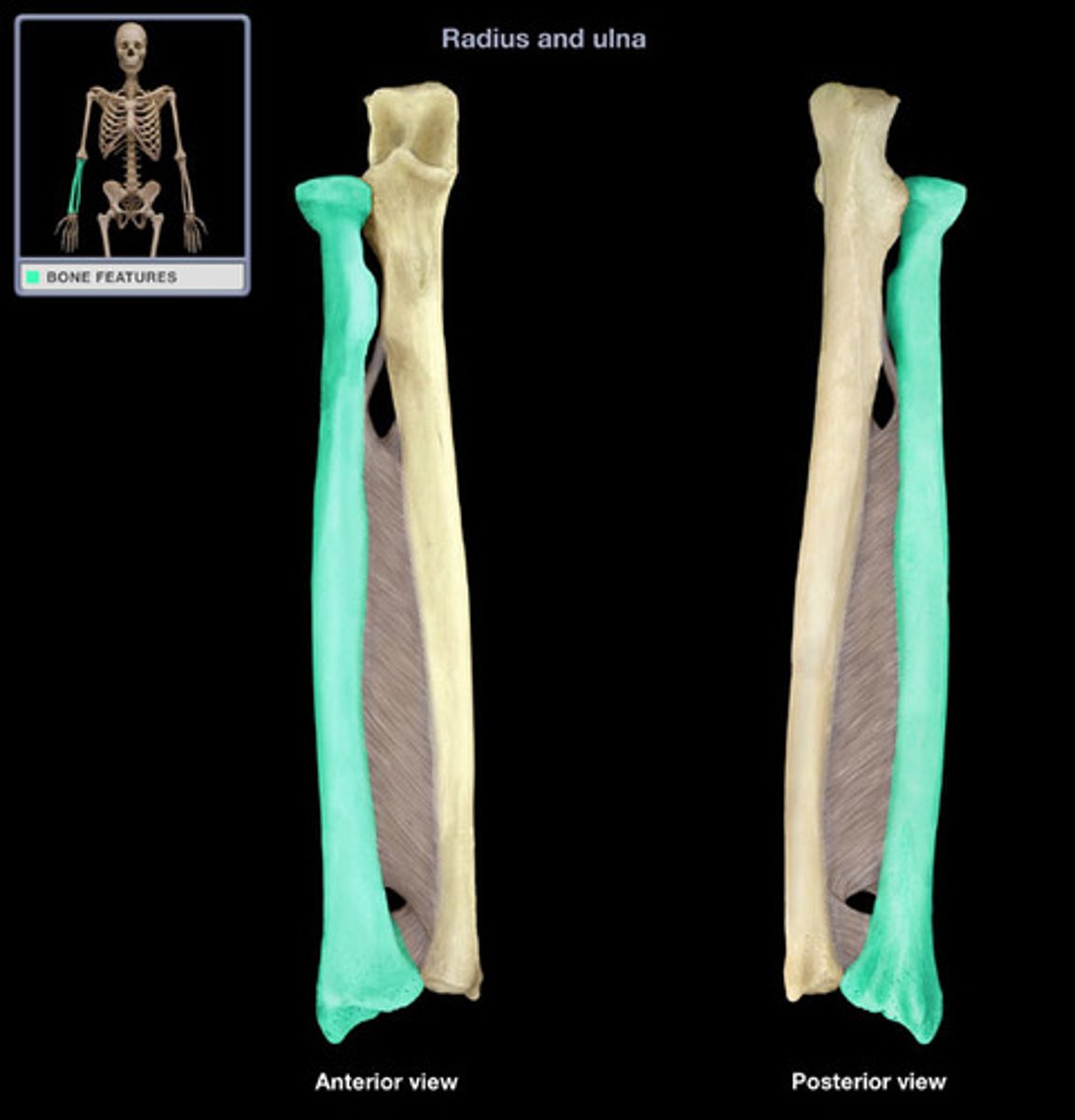
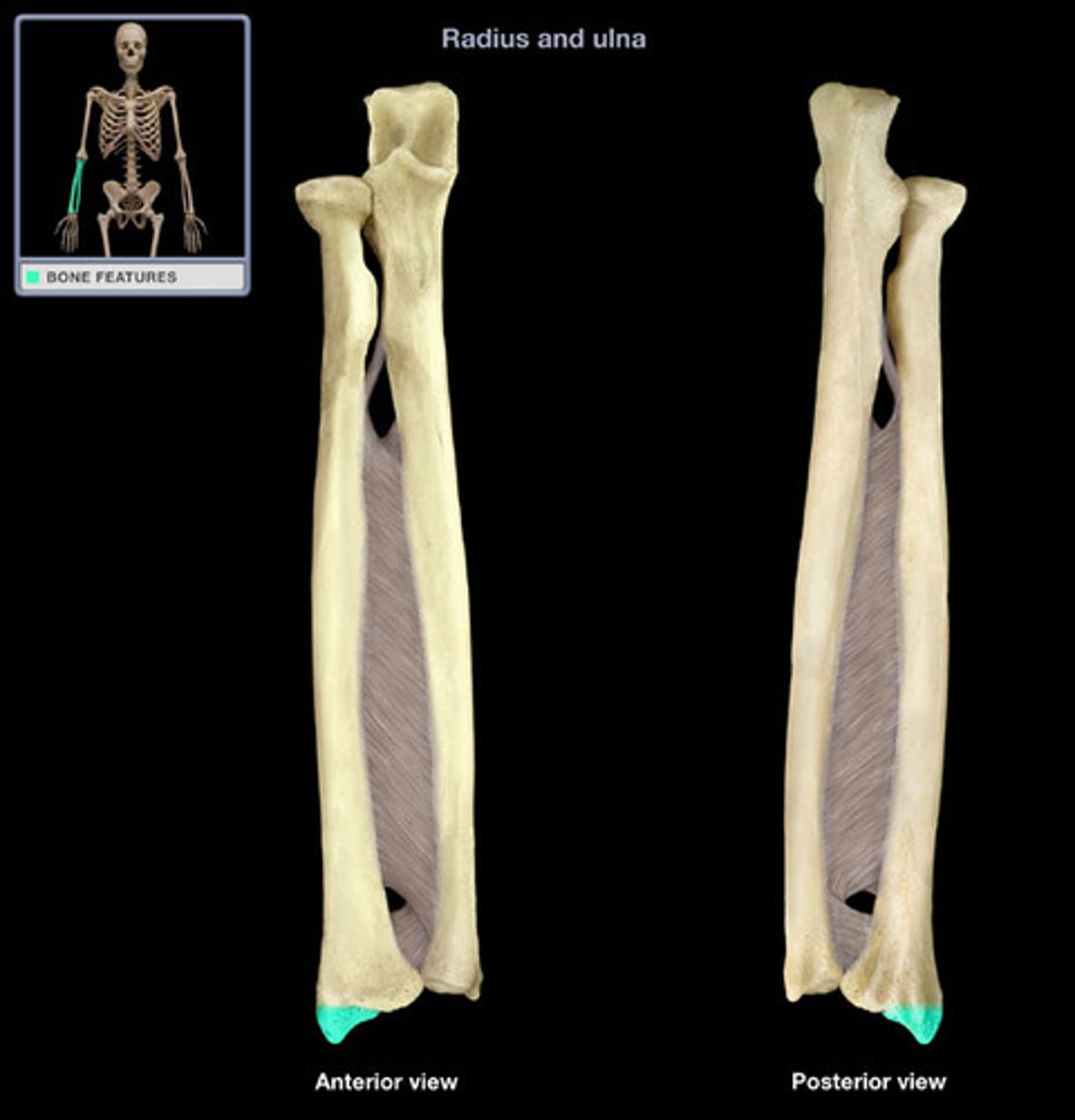
Bones of the forearm:
radius and ulna
Characteristics of the forearm:
- contains 2 bones
- radius can pivot on the ulna (supination and pronation) due to their parallel position

The ulna is the ___________ bone of the forearm
Stabilizing bone
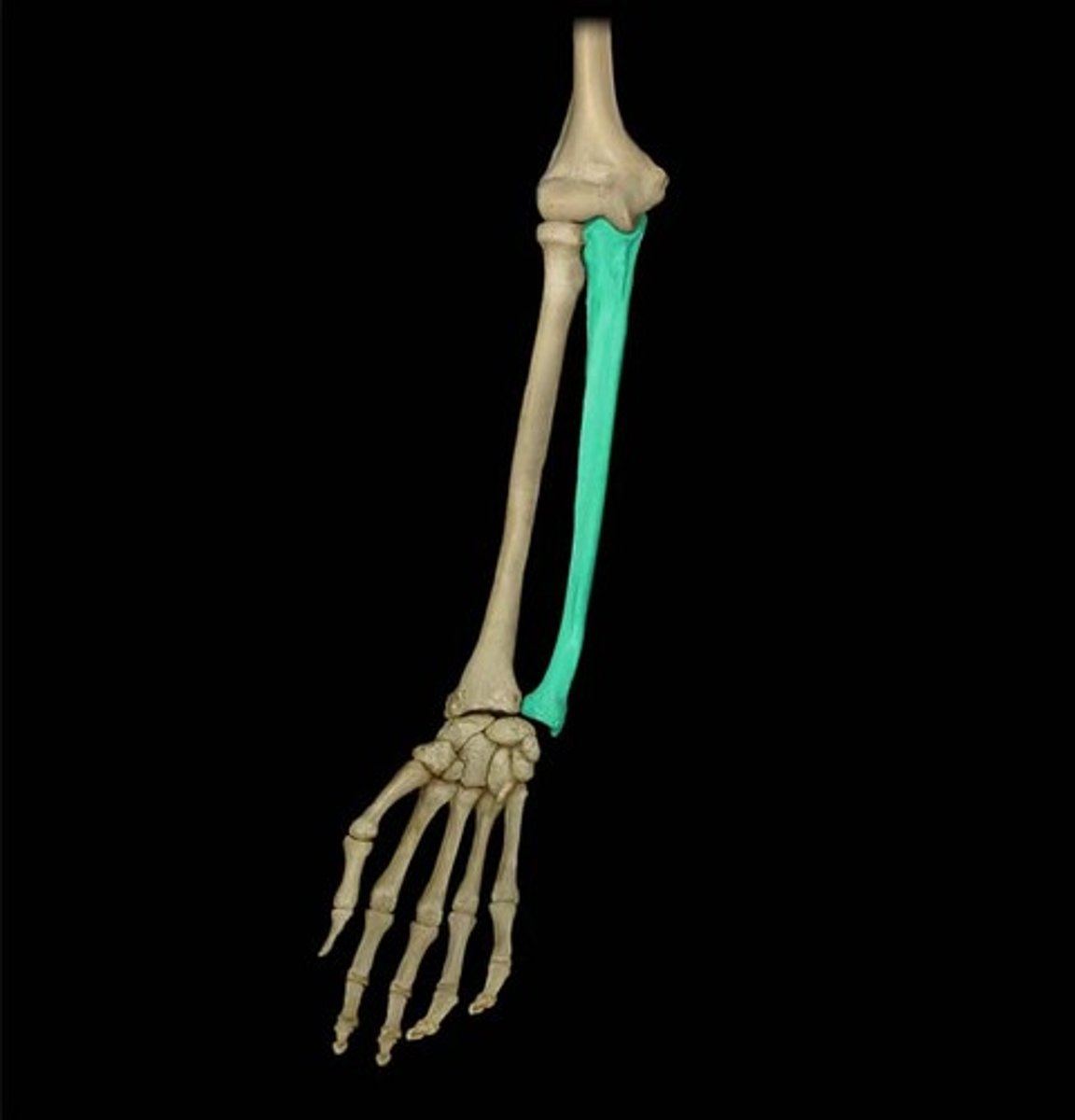
Location of the ulna:
Medial and longer of the two forearm bones
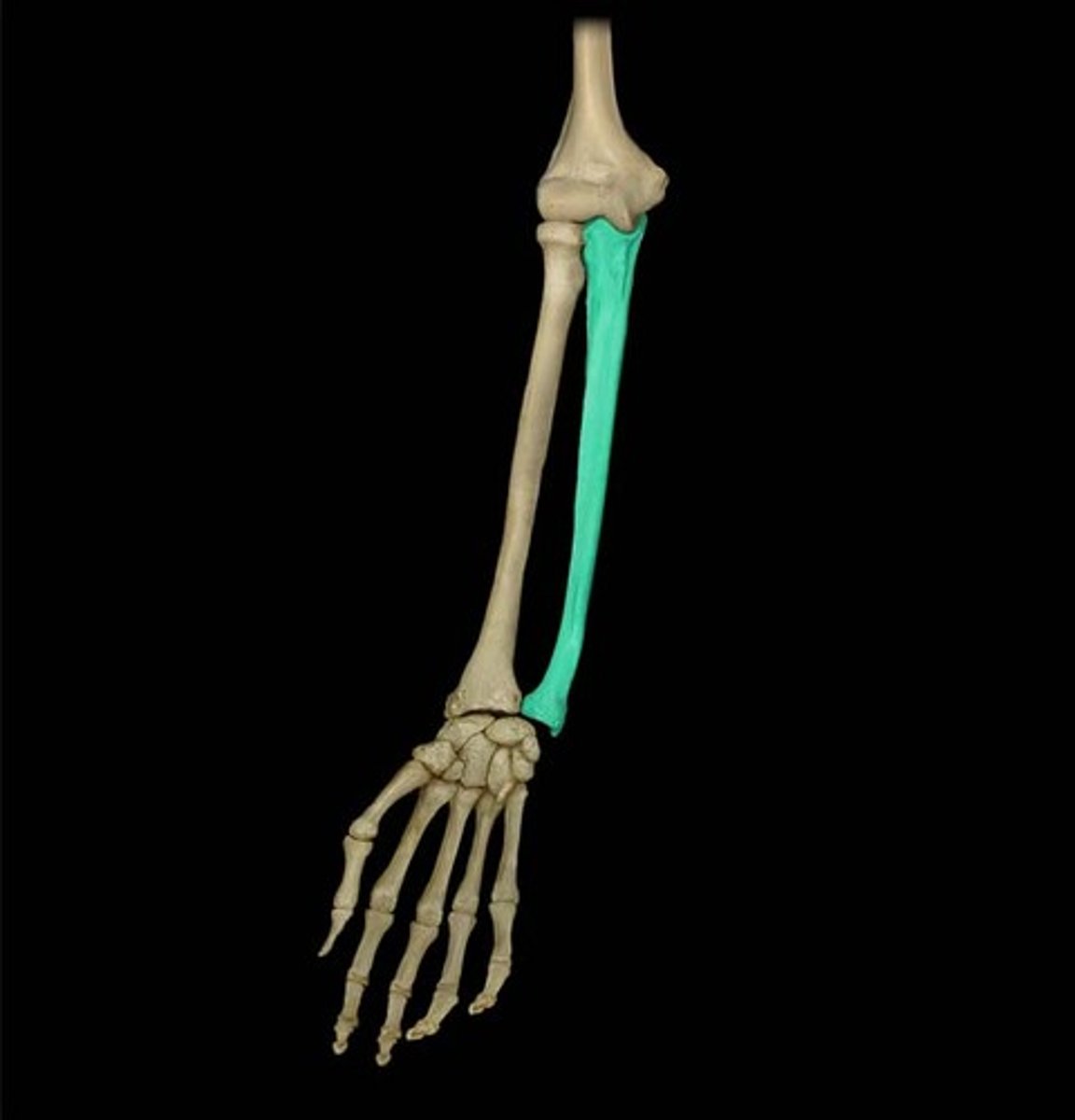
Ulna articulation:
- Proximal end (more bulky) with humerus & head of radius
- does not form wrist distally
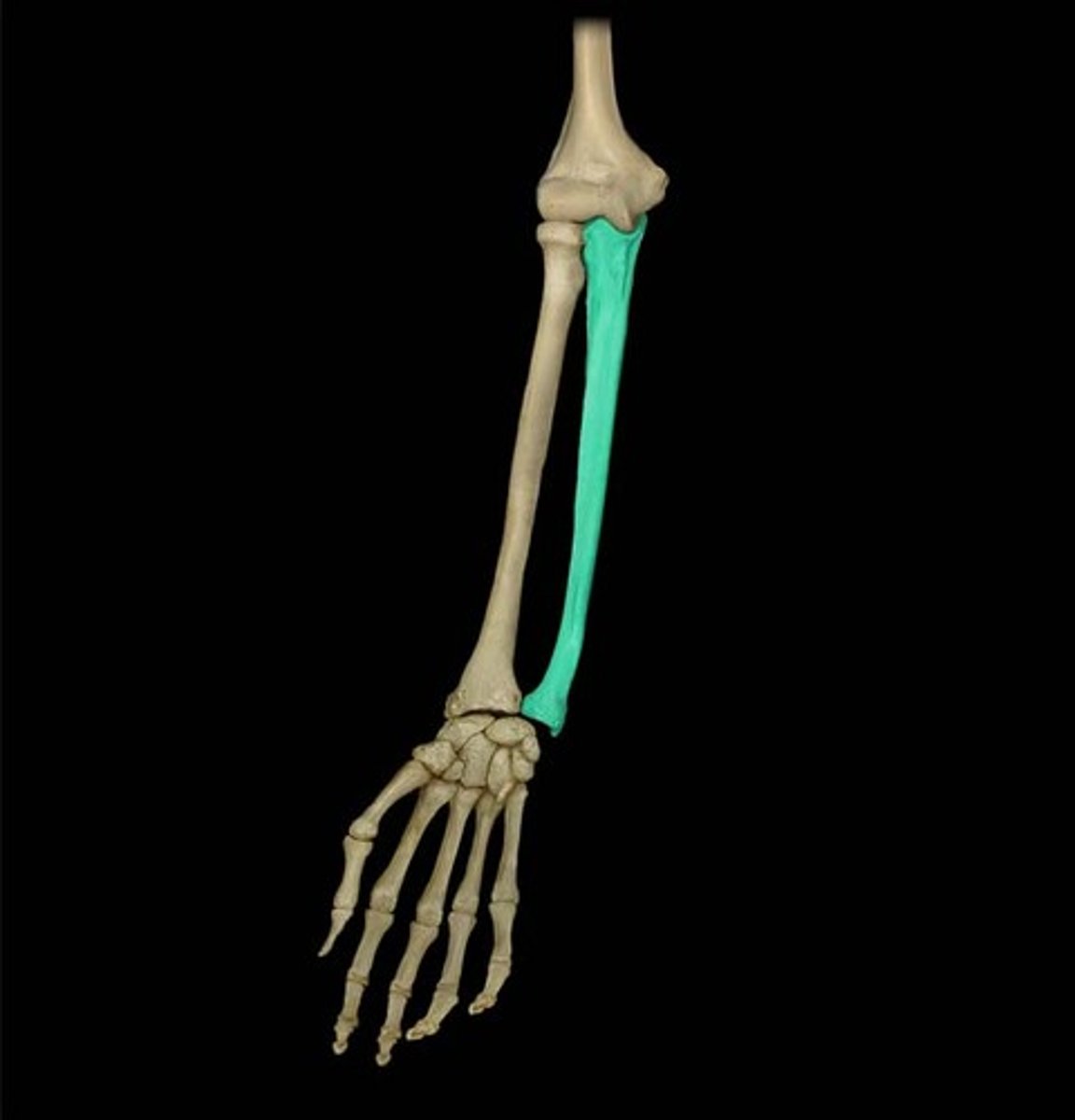
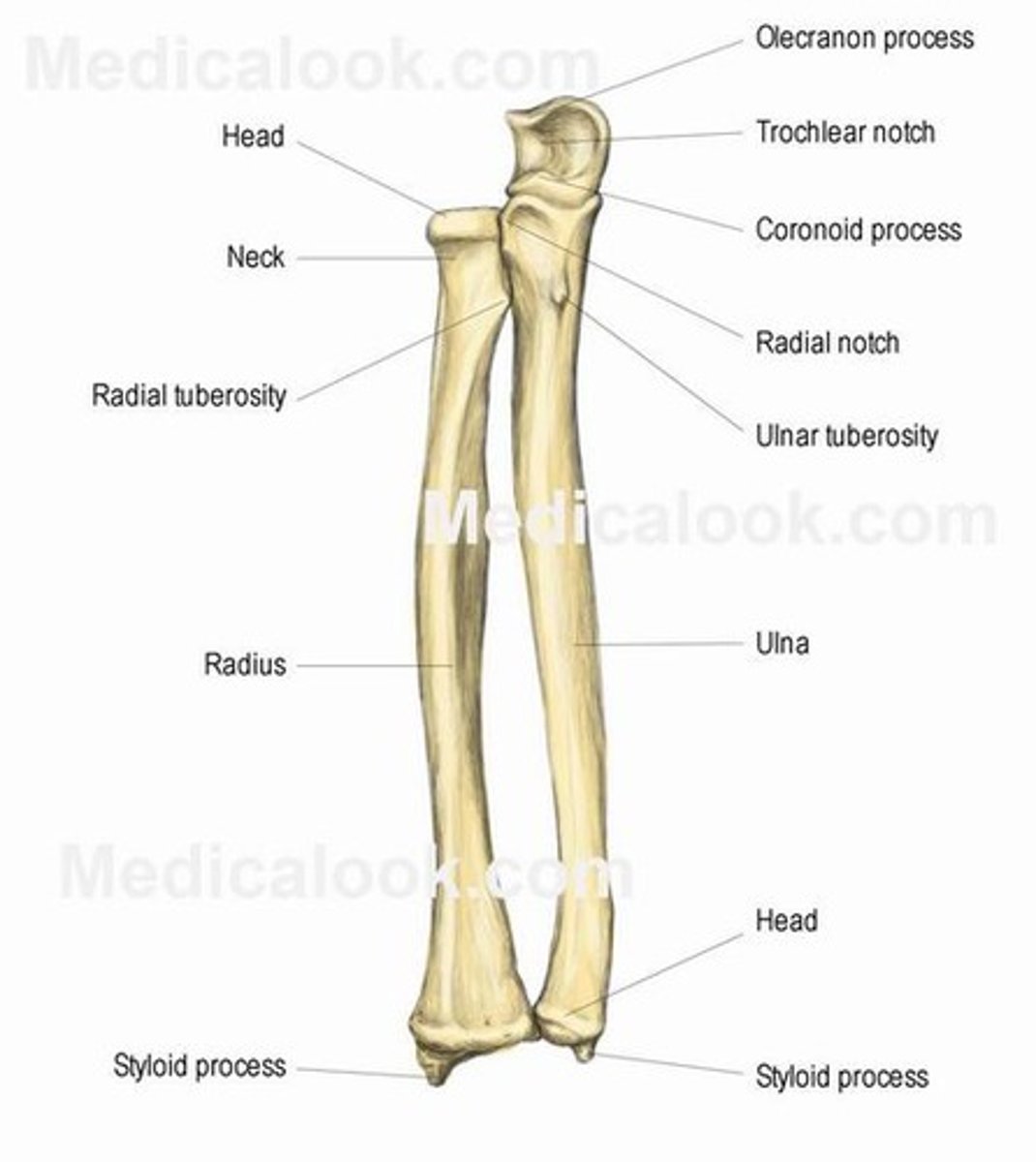
Features of the ulna:
- olecranon
- coronoid process
- ulnar tuberosity
- radial notch
- shaft
- head of ulna
- ulnar styloid process
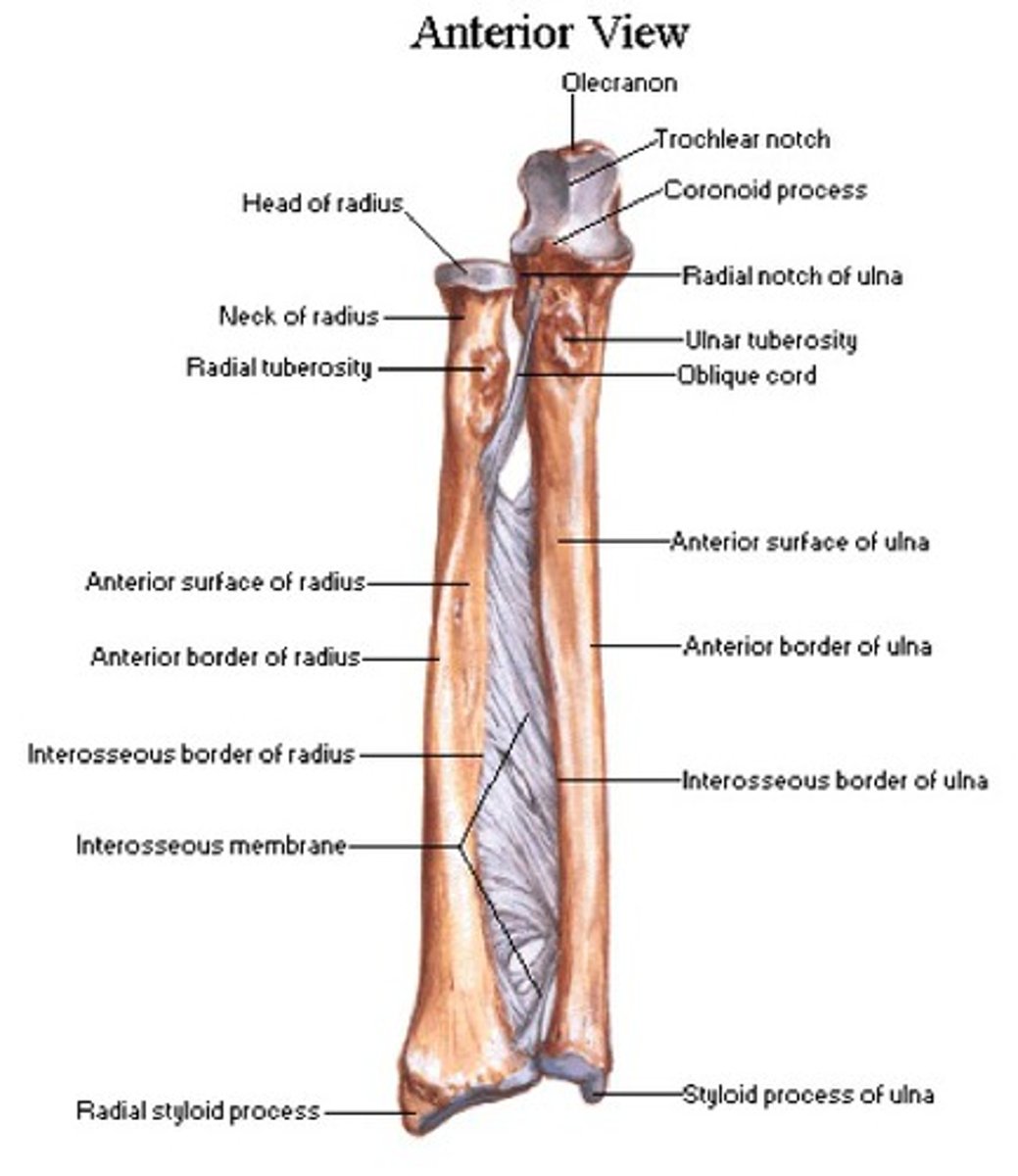
Olecranon of the ulna:
Superior, most proximal portion.
What does the olecranon of the ulna articulate with?
Articulate with olecranon fossa of the humerus on its
anterior side
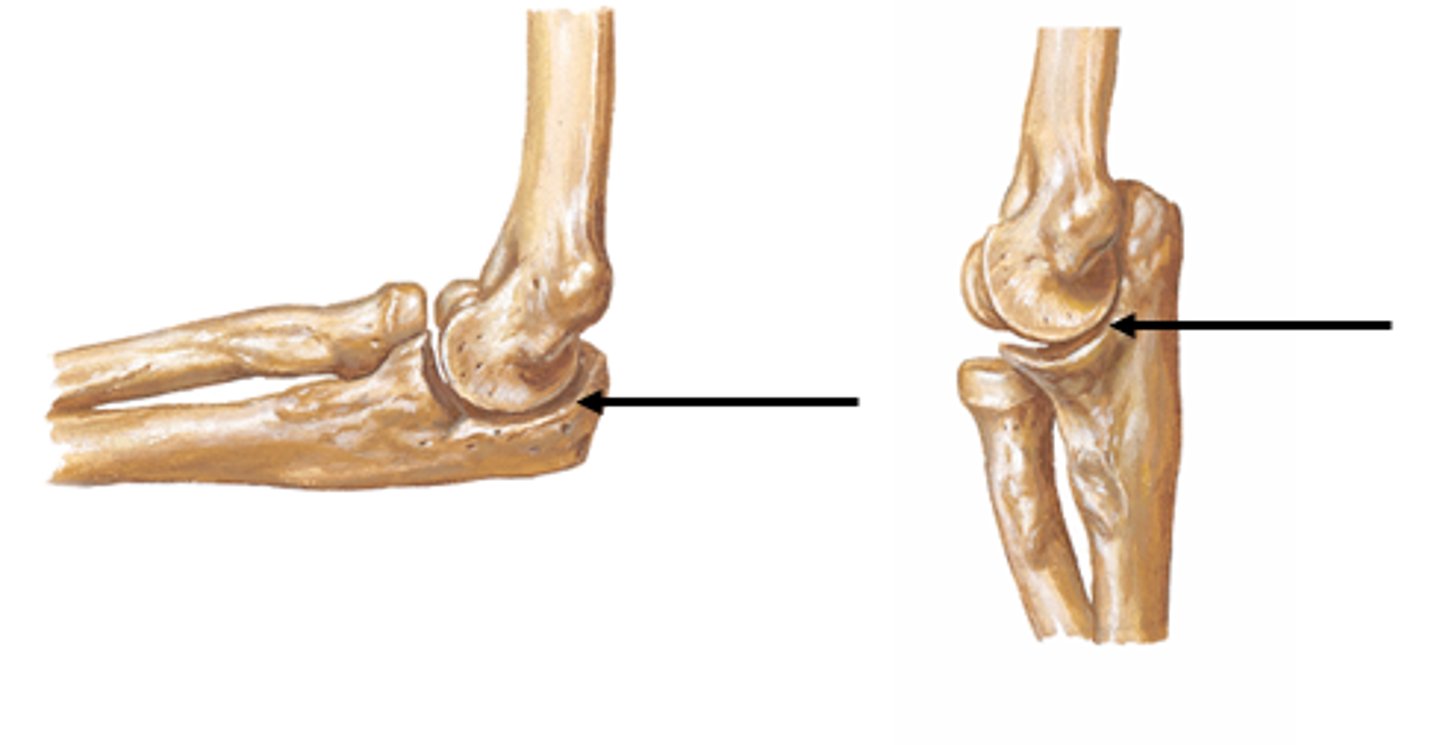
What is the function of the olecranon of the ulna?
Serve as a short lever for extension of the elbow
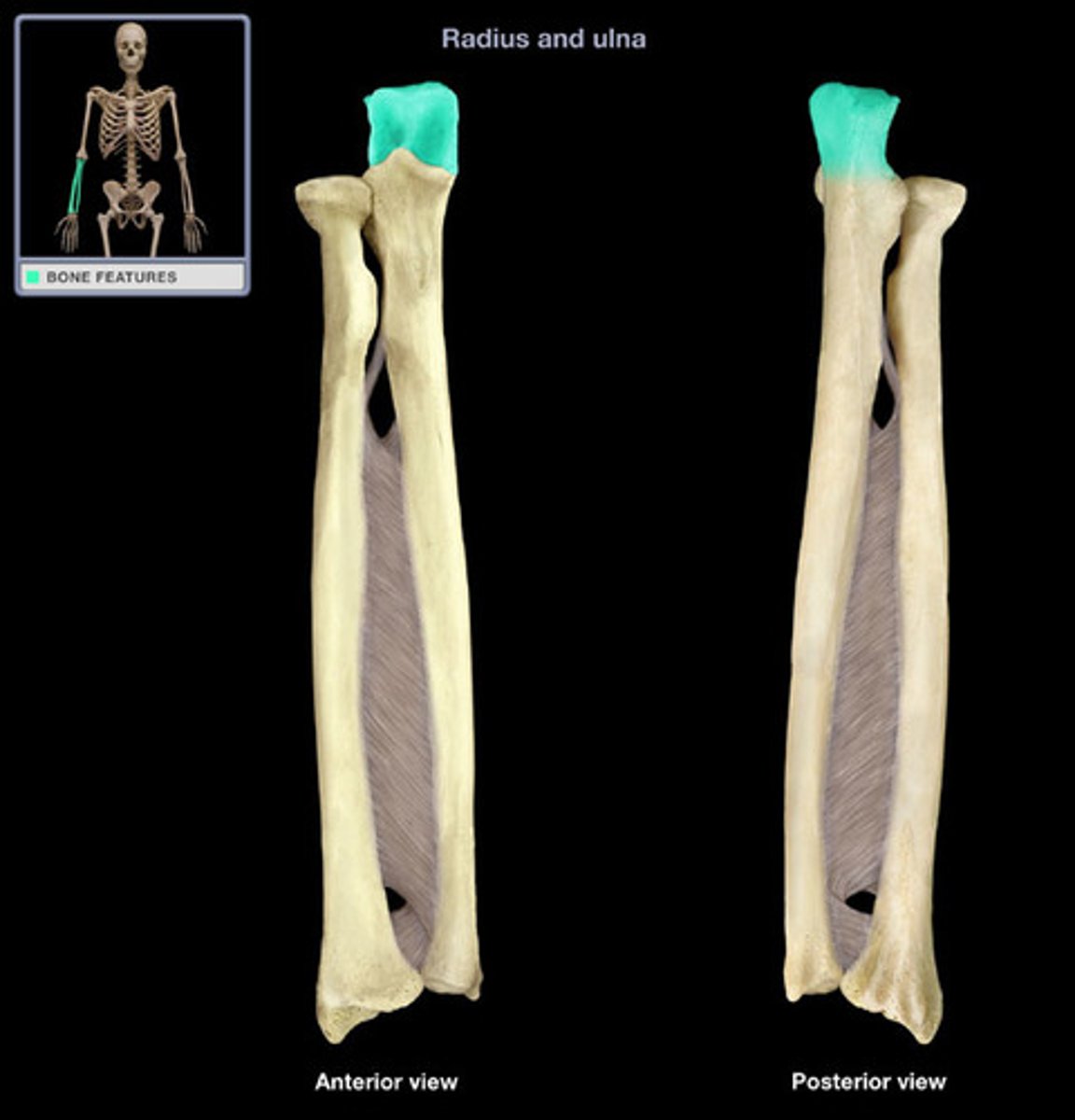
Coronoid process of ulna:
Inferior to the olecranon process
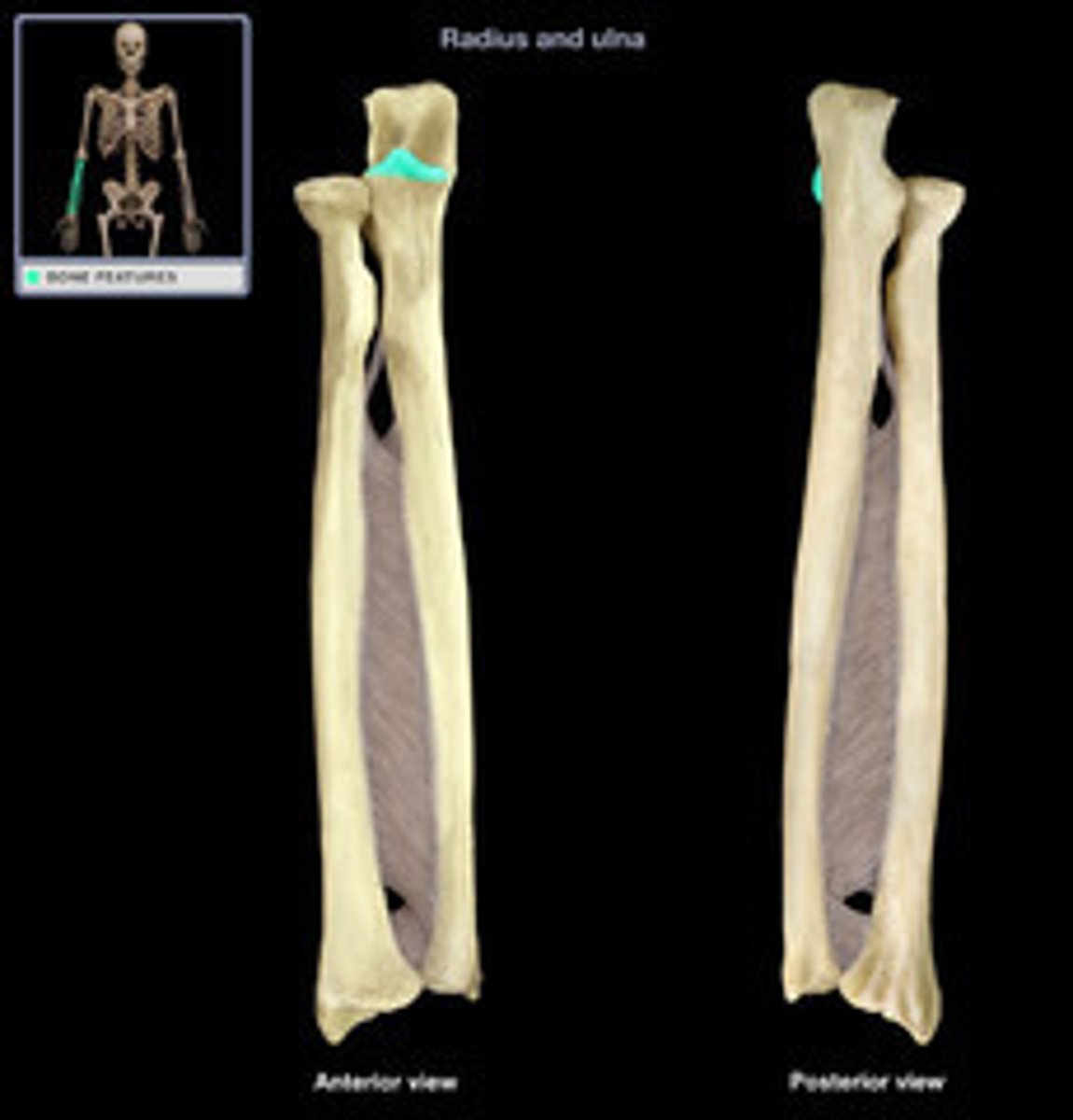
What does the coronoid process of the ulna articulate with?
Articulate with coronoid fossa of humerus on its anterior side
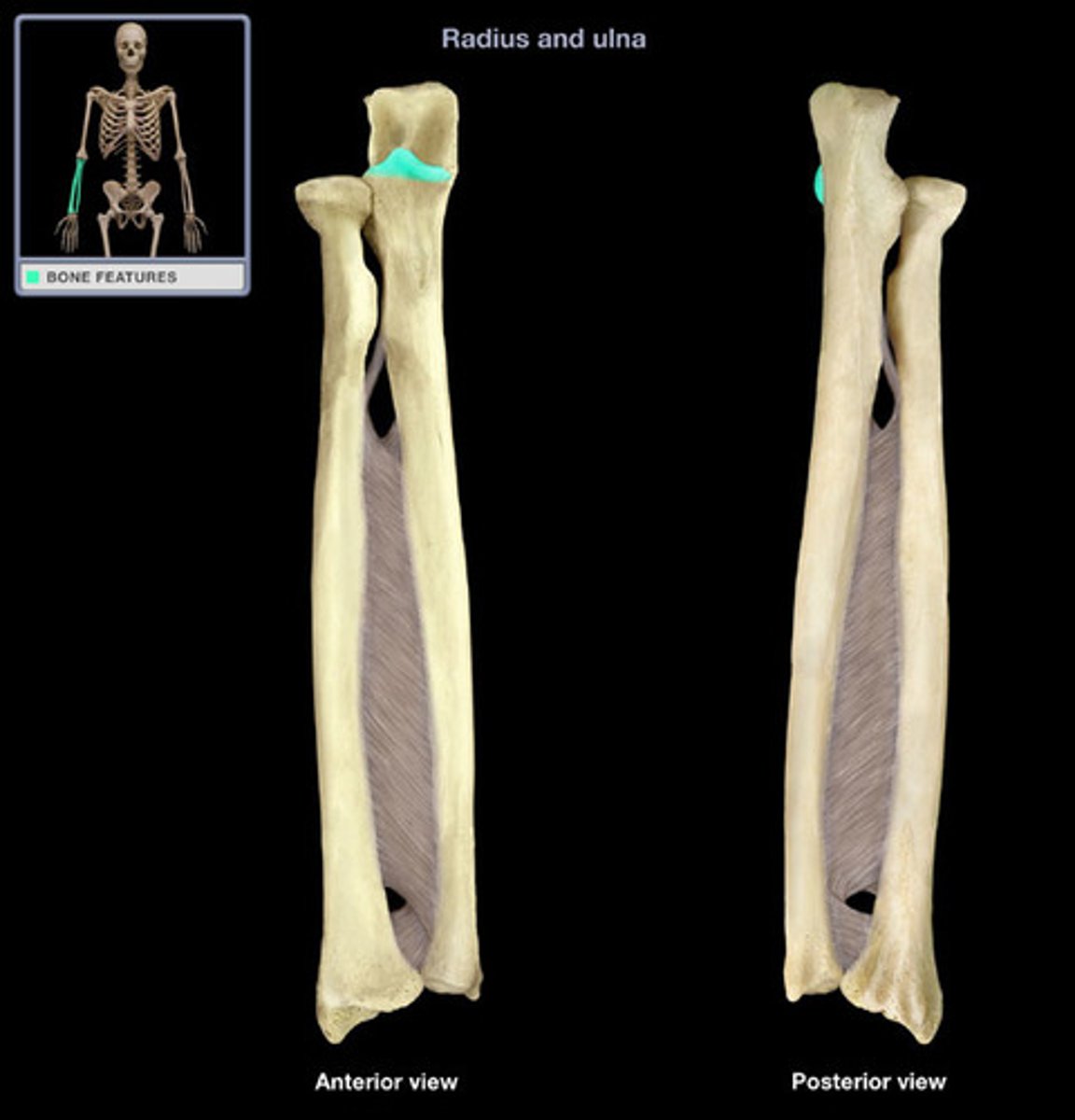
Ulnar tuberosity of the ulna:
Attachment for the brachialis muscle
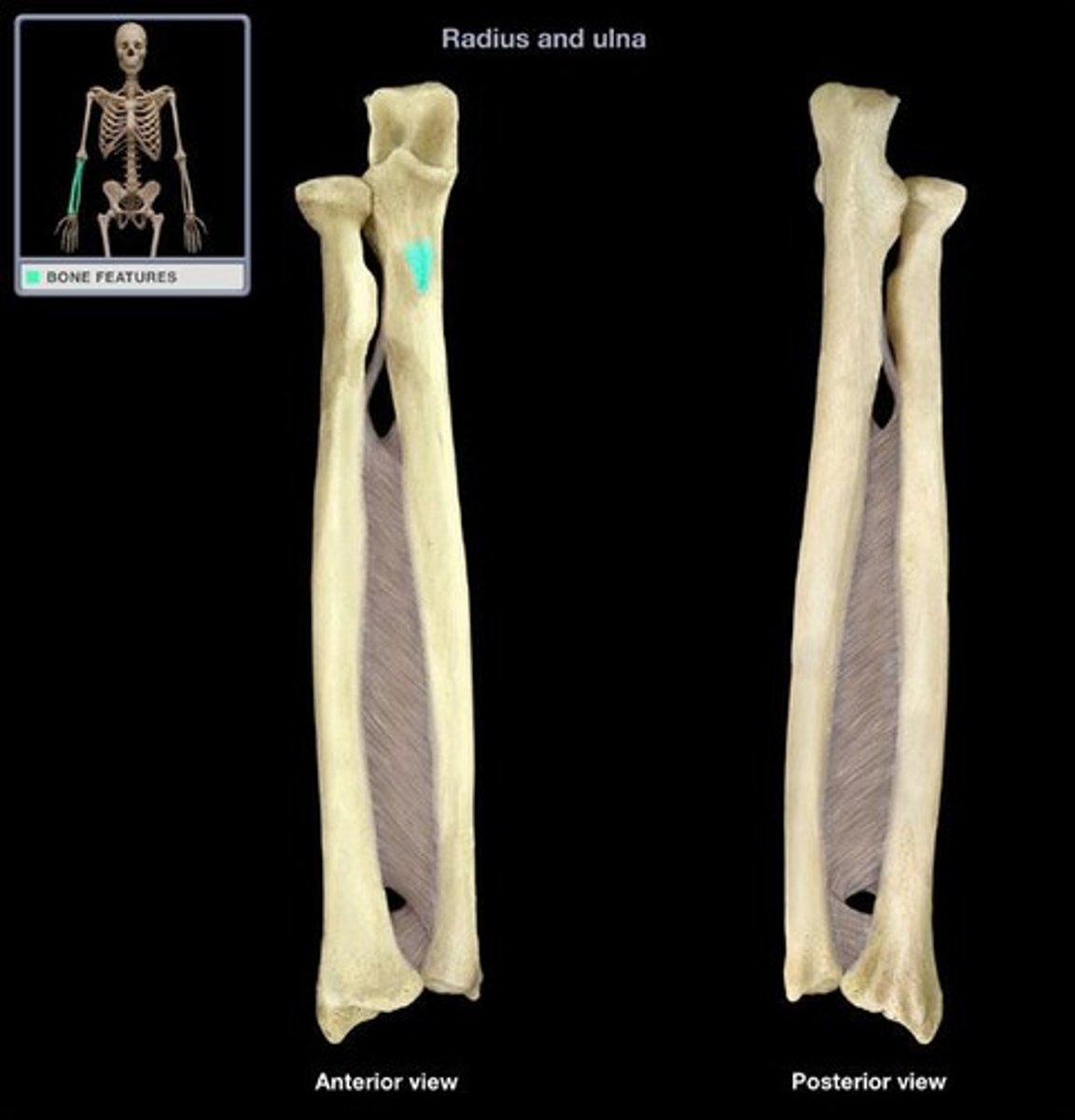
Radial notch of the ulna:
Inferolateral to the coronoid process, receives the head of the radius
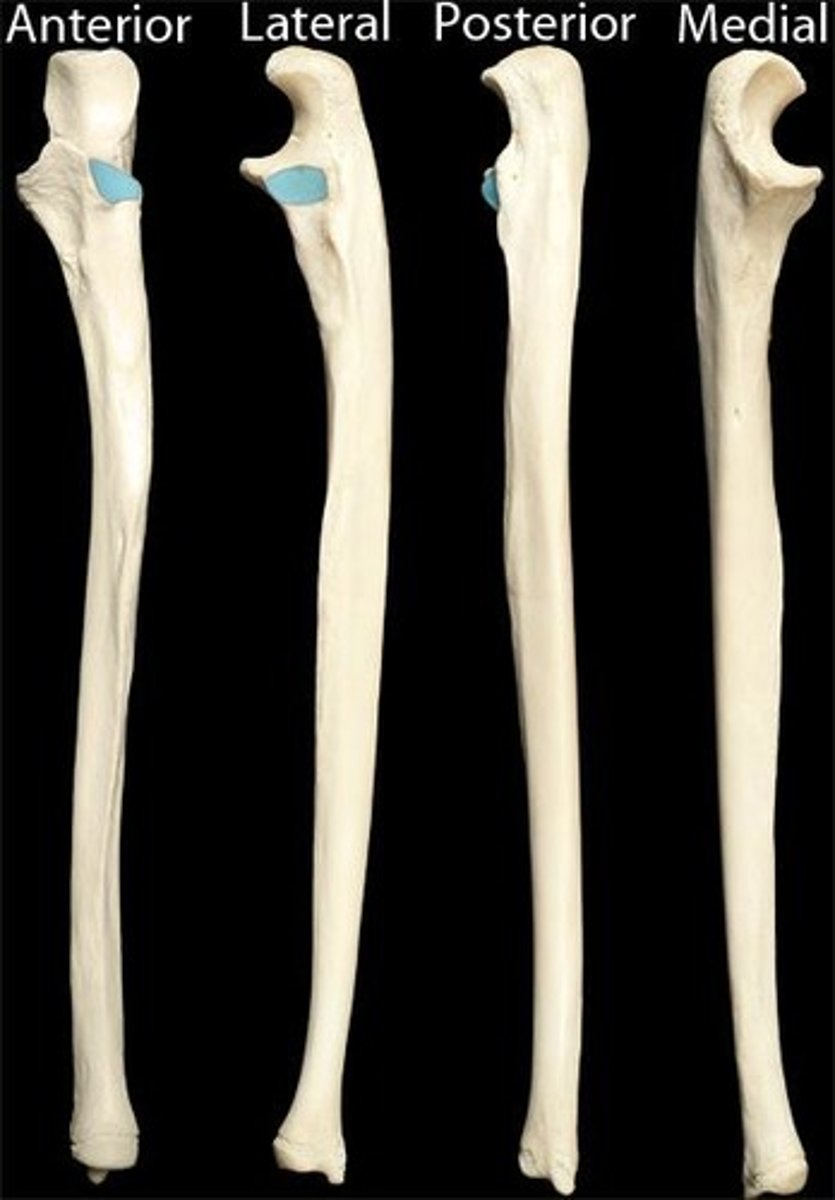
Shaft of the ulna:
Gets thinner distally
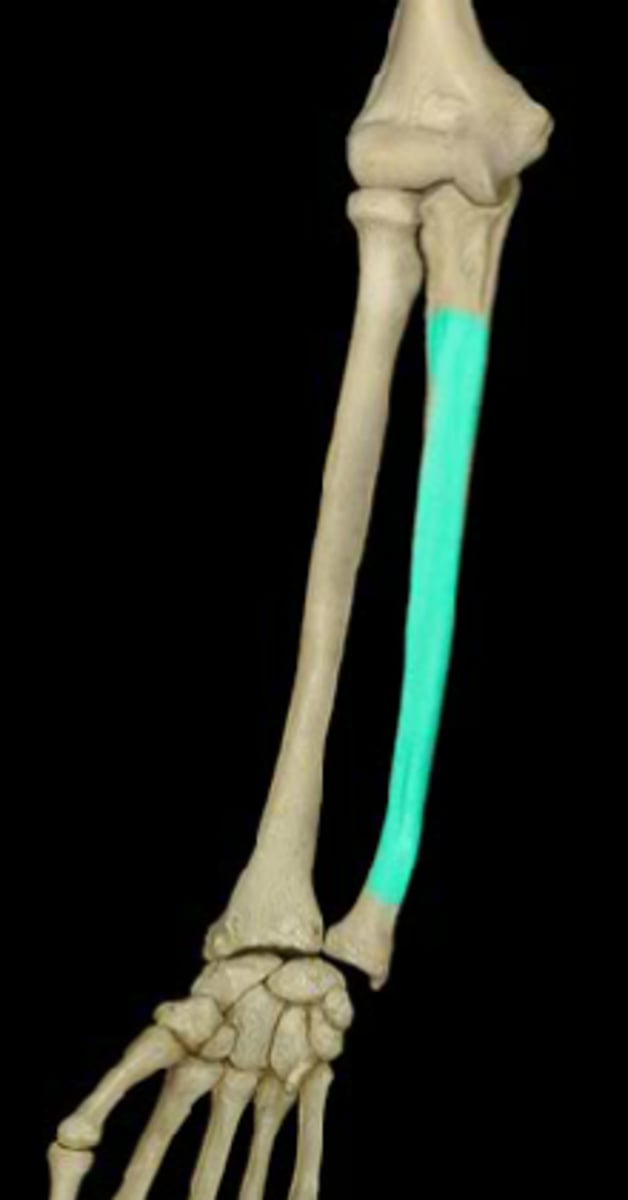
Head of the ulna:
Enlargement on distal part of the shaft
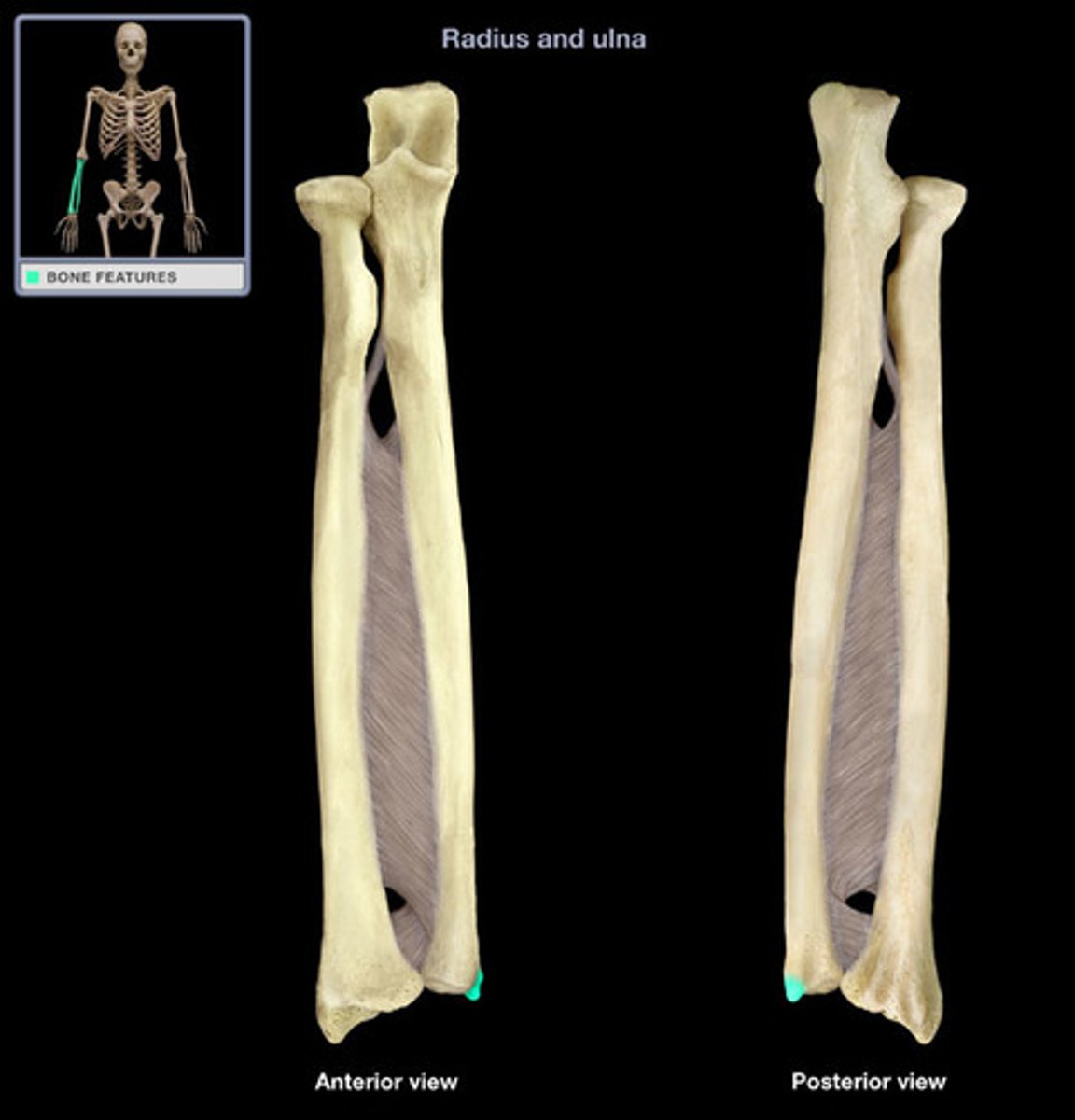
Ulnar styloid process:
Distal ending of the head of the ulna
What is the radius capable of doing?
Can pivot on the ulna (supination and pronation) due to their parallel position
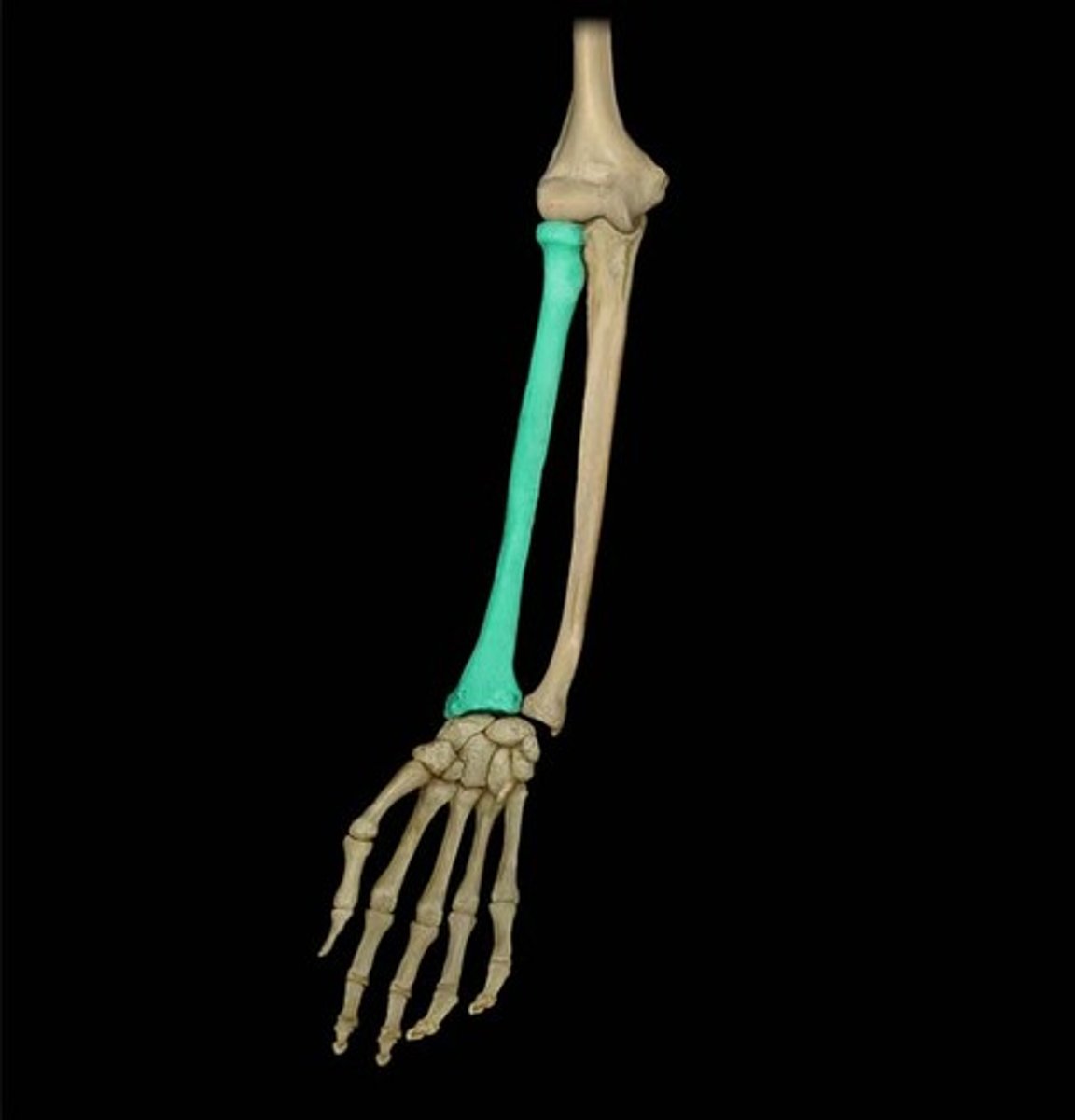
Location of the radius:
Lateral & shorter of the forearm
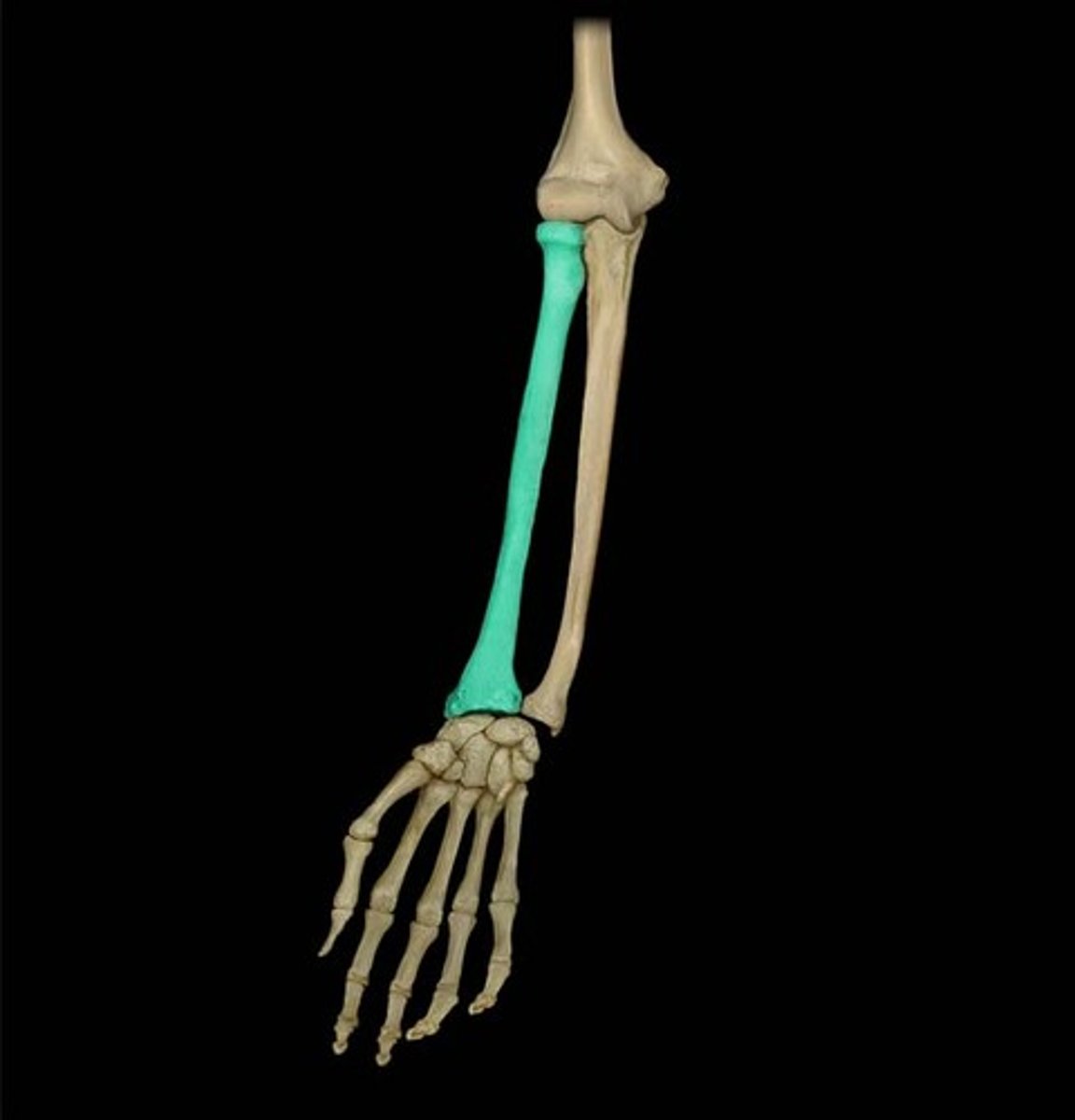
What does the radius articulate with?
- Articulate with the ulna (proximally and distally)
- articulate with carpal bones on the distal side of radius
What structure of the upper extremities does the radius form?
Forms the wrist joint
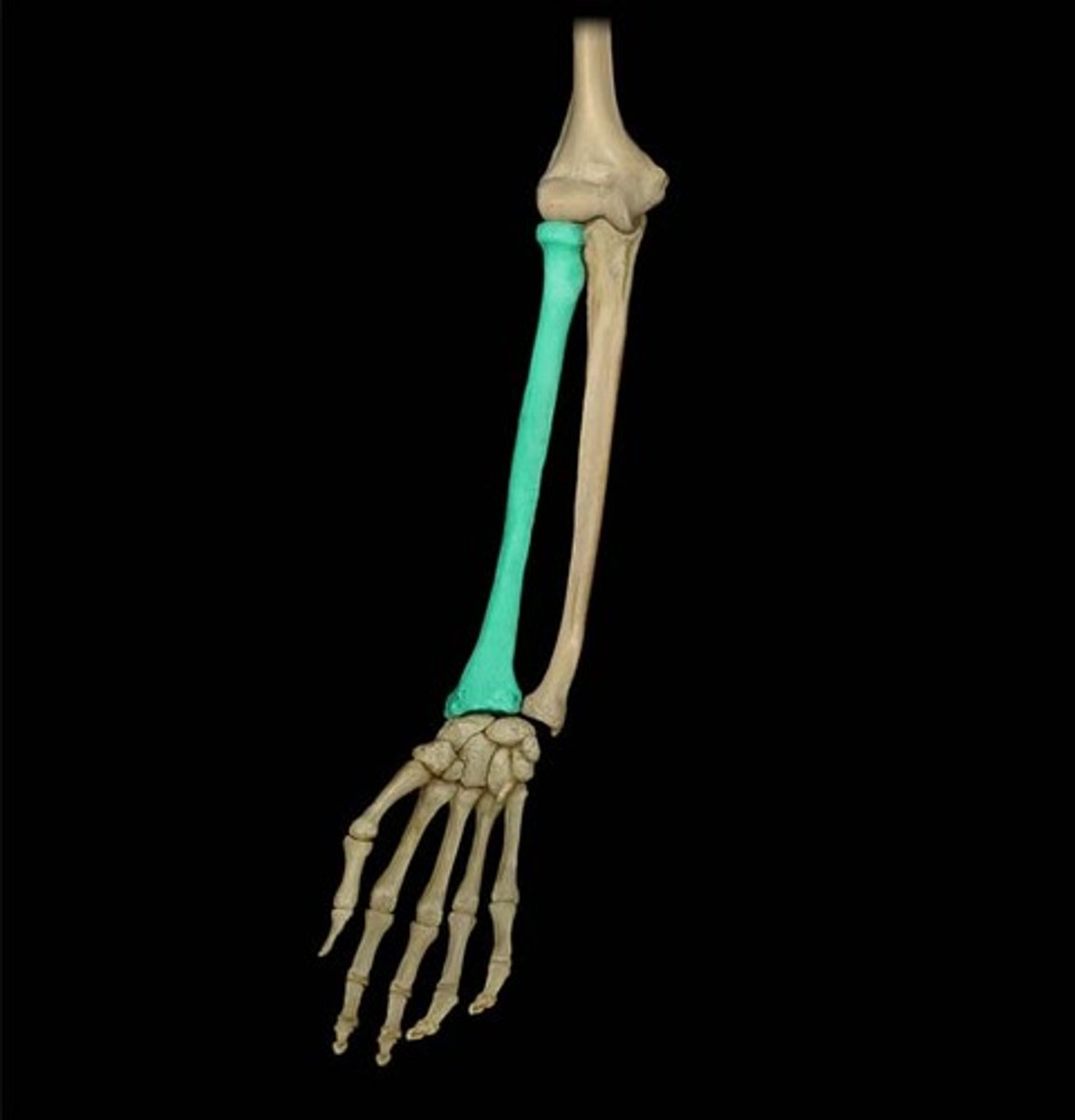
What does the radius control in the forearm?
Controls supination and pronation
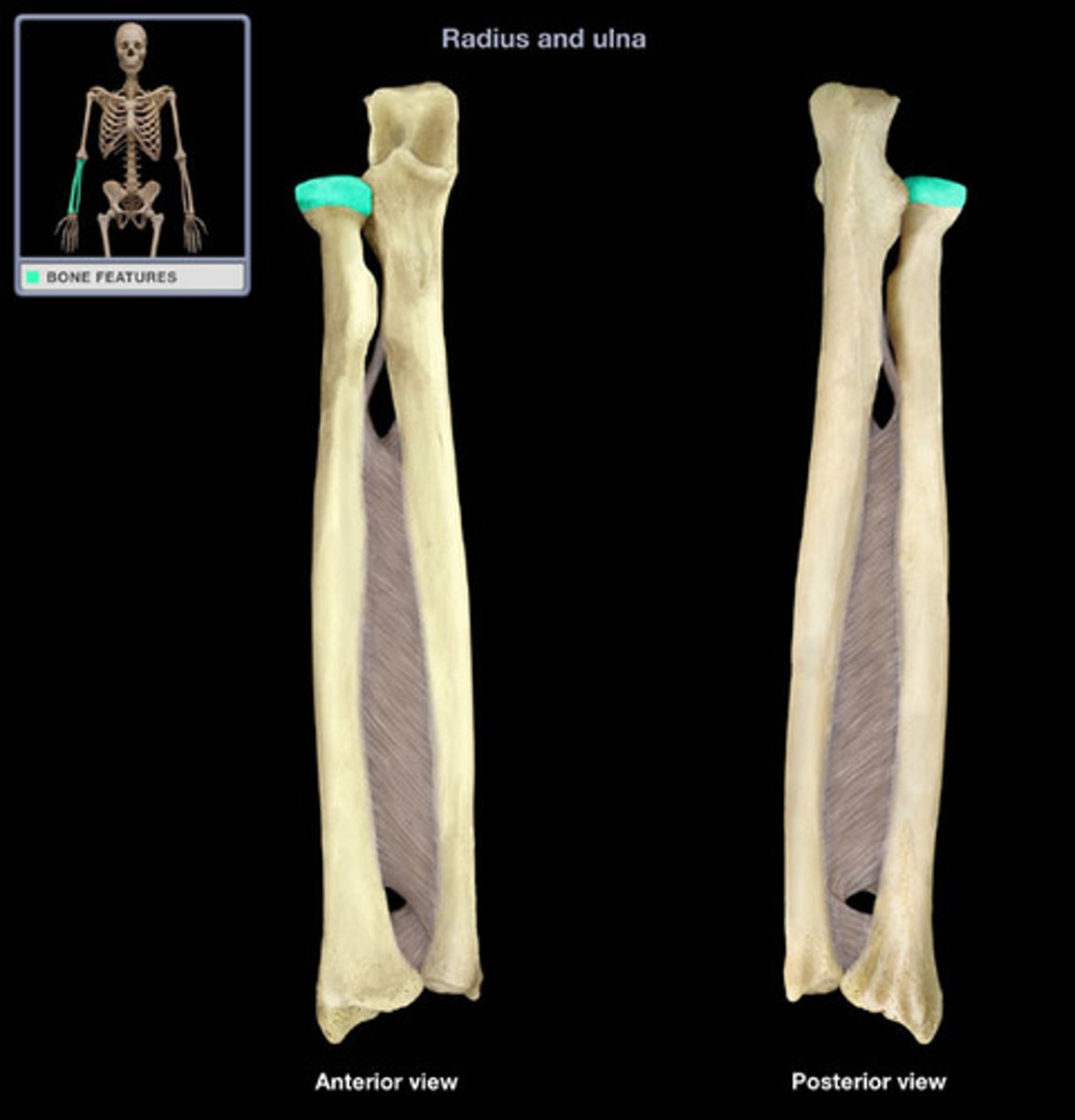
Head of the radius:
Articulates with the capitulum of humerus and with the radial notch of the ulna
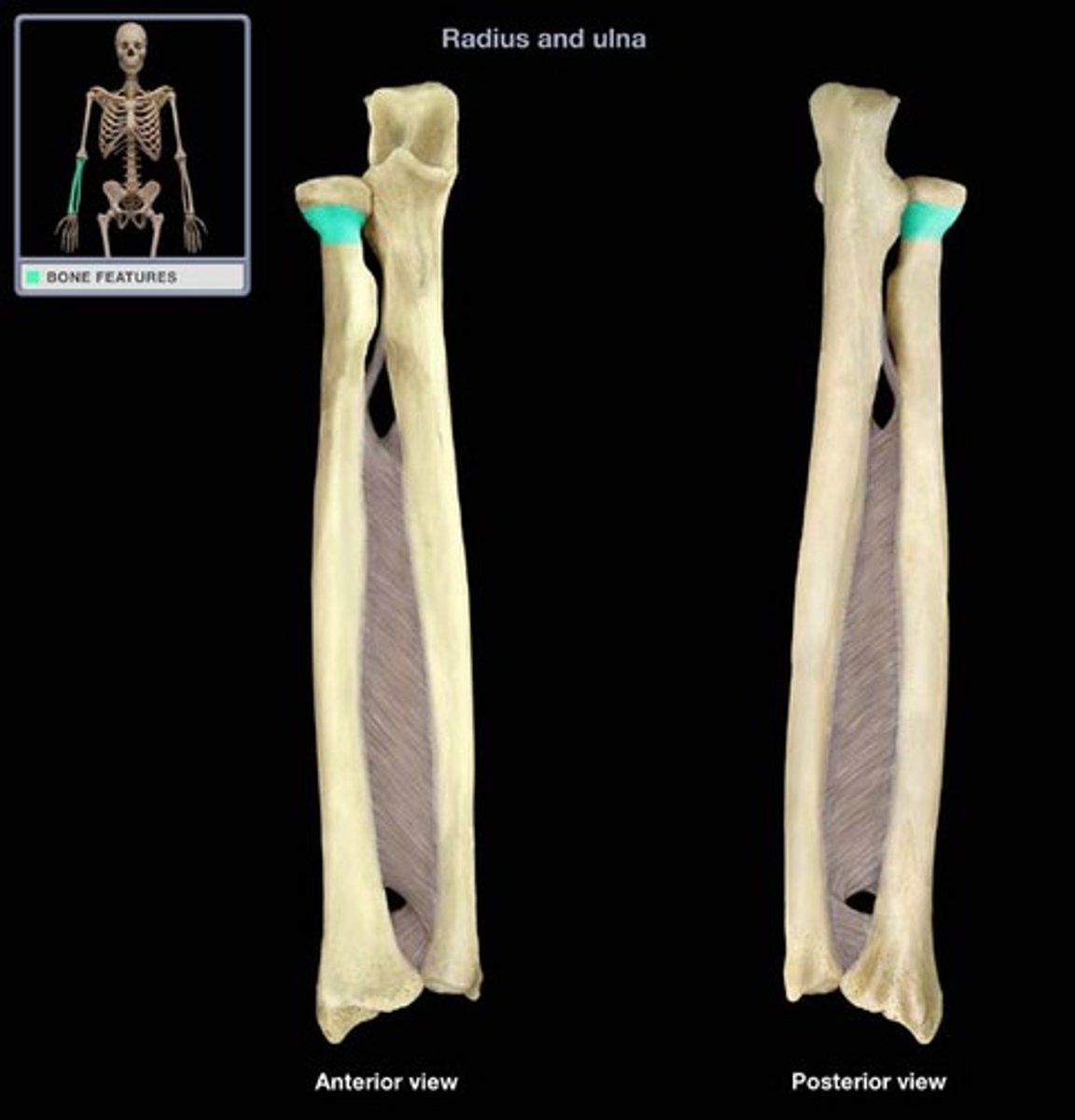
Neck of the radius:
Inferior to the head
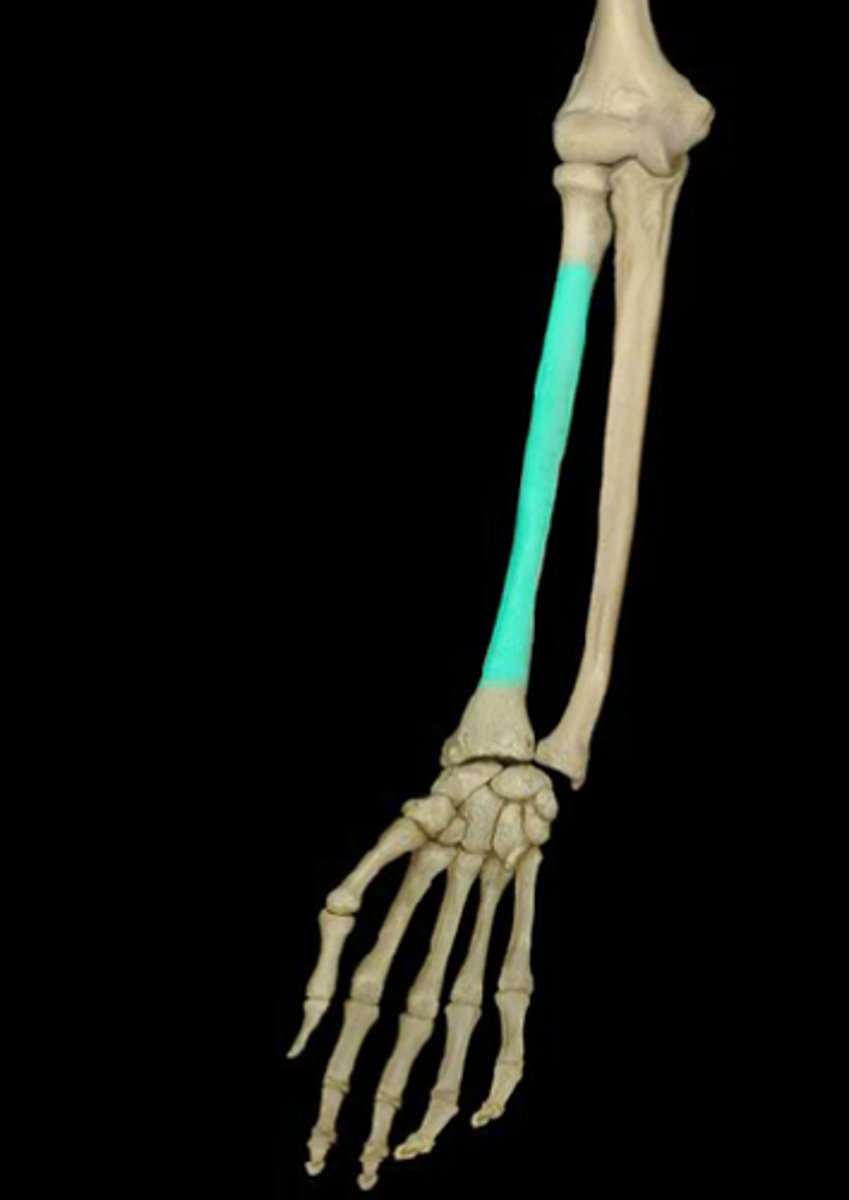
Shaft of the radius:
Gets thicker distally opposite to the ulna
Ulnar notch of the radius:
Articulates with the head of the ulna
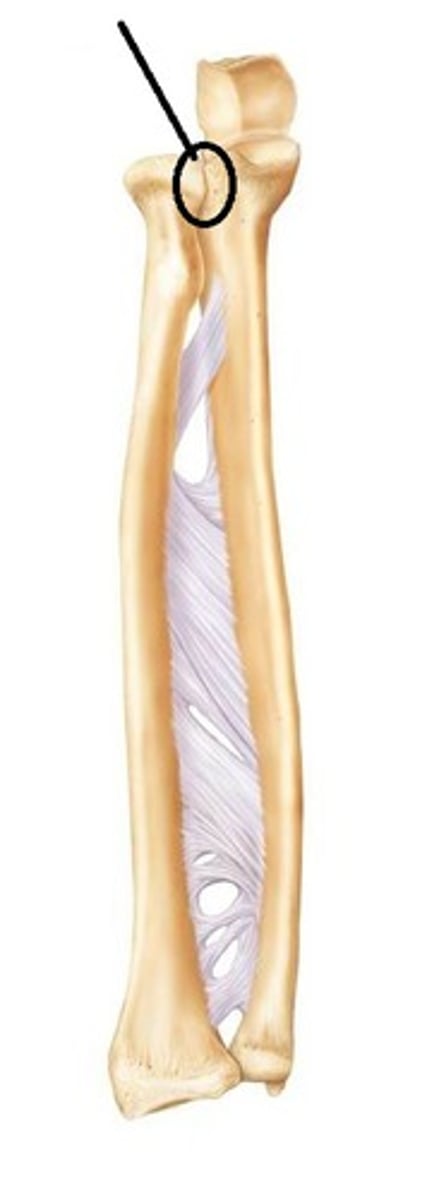

Radial styloid process of radius:
Distal ending on lateral side of the shaft of the radius
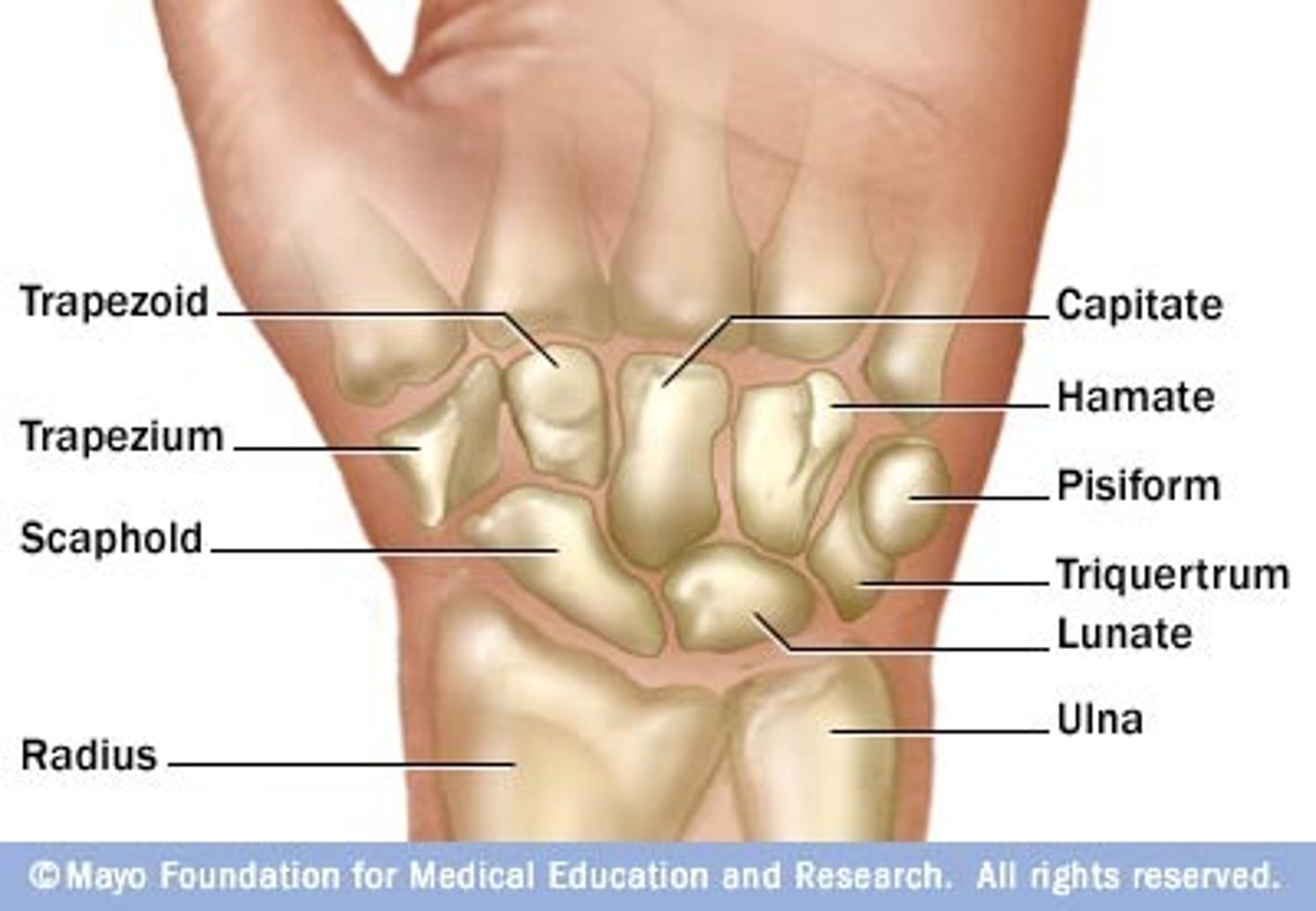
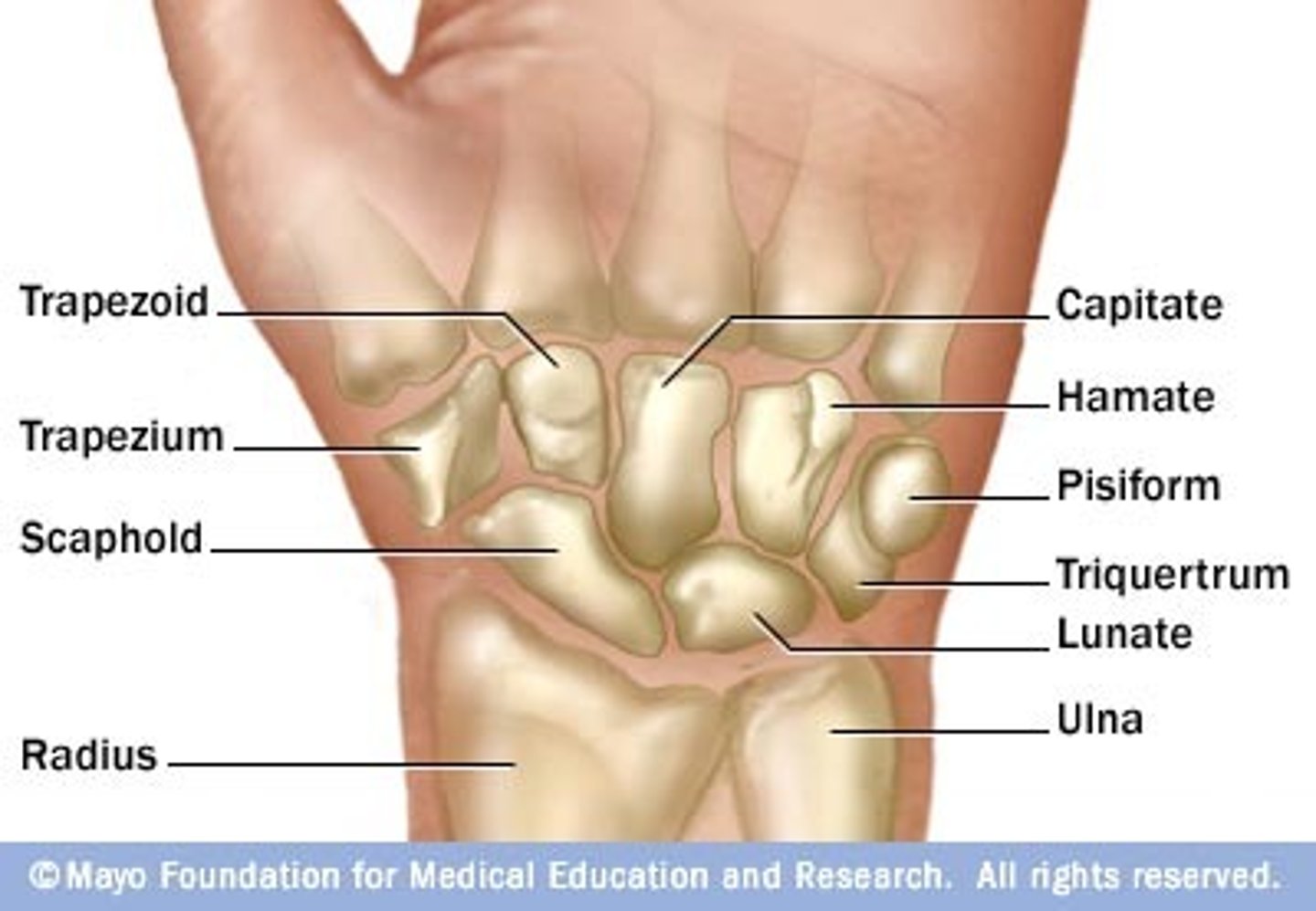
Characteristics of the wrist (or carpus):
- composed of 8 carpal bones arranged in proximal and distal rows of 4
- give flexibility to the wrest, each bone glide on the adjacent to it
- convex posteriorly and concave anteriorly (from side to side)
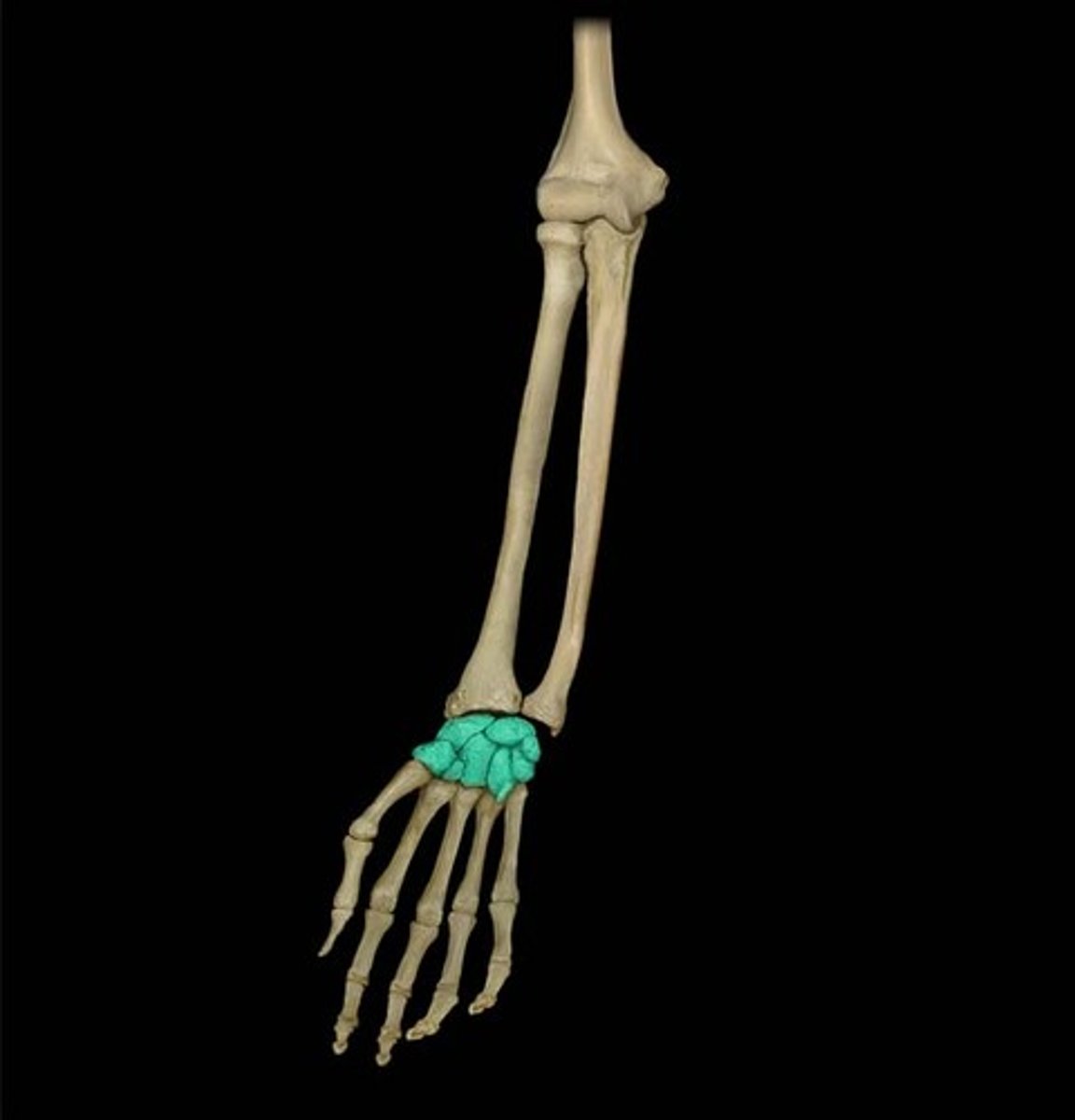
Proximal row of wrist bones (lateral to medial):
- scaphoid,
- lunate
- triquetrum
- pisiform
Scaphoid of the proximal row of the wrist:
- Largest bone in the proximal now
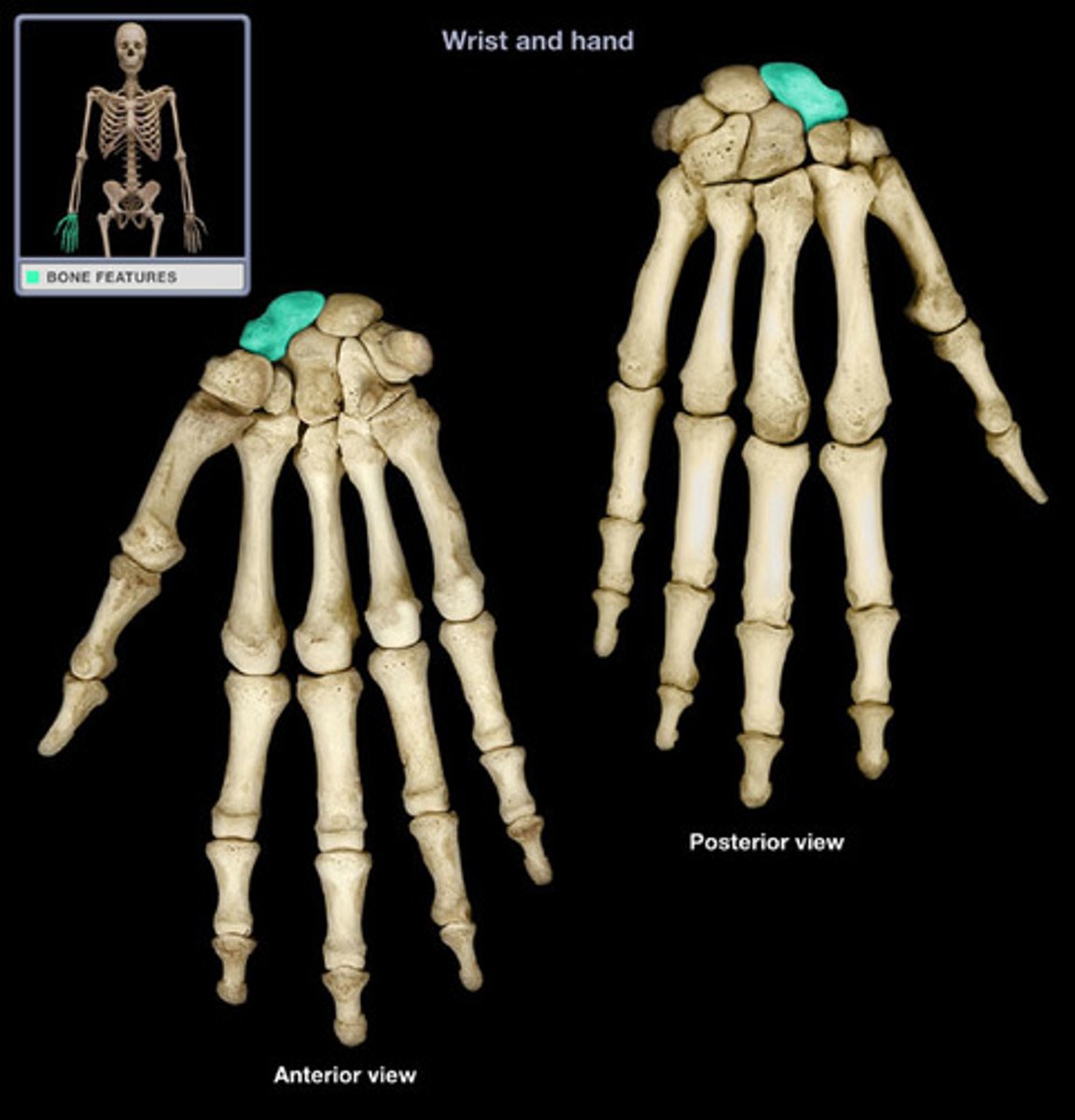
What does the scaphoid of the proximal row of the wrist articulate with?
Articulates with the radius
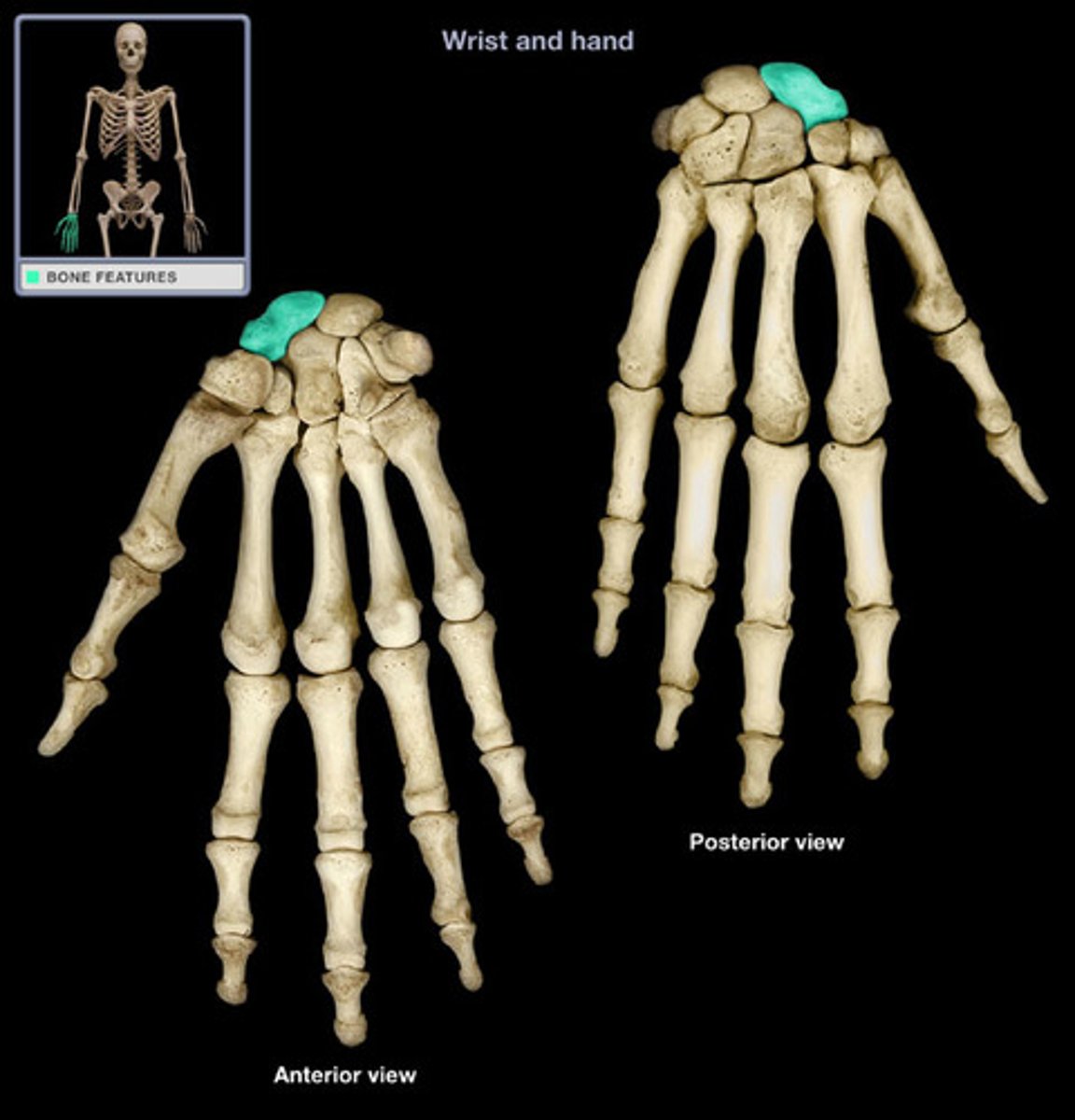
Lunate of the proximal row of the wrist:
Moon shaped